Synthesis and Antimalarial Evaluation of New 1,3,5-tris[(4-(Substituted-aminomethyl)phenyl)methyl]benzene Derivatives: A Novel Alternative Antiparasitic Scaffold
Abstract
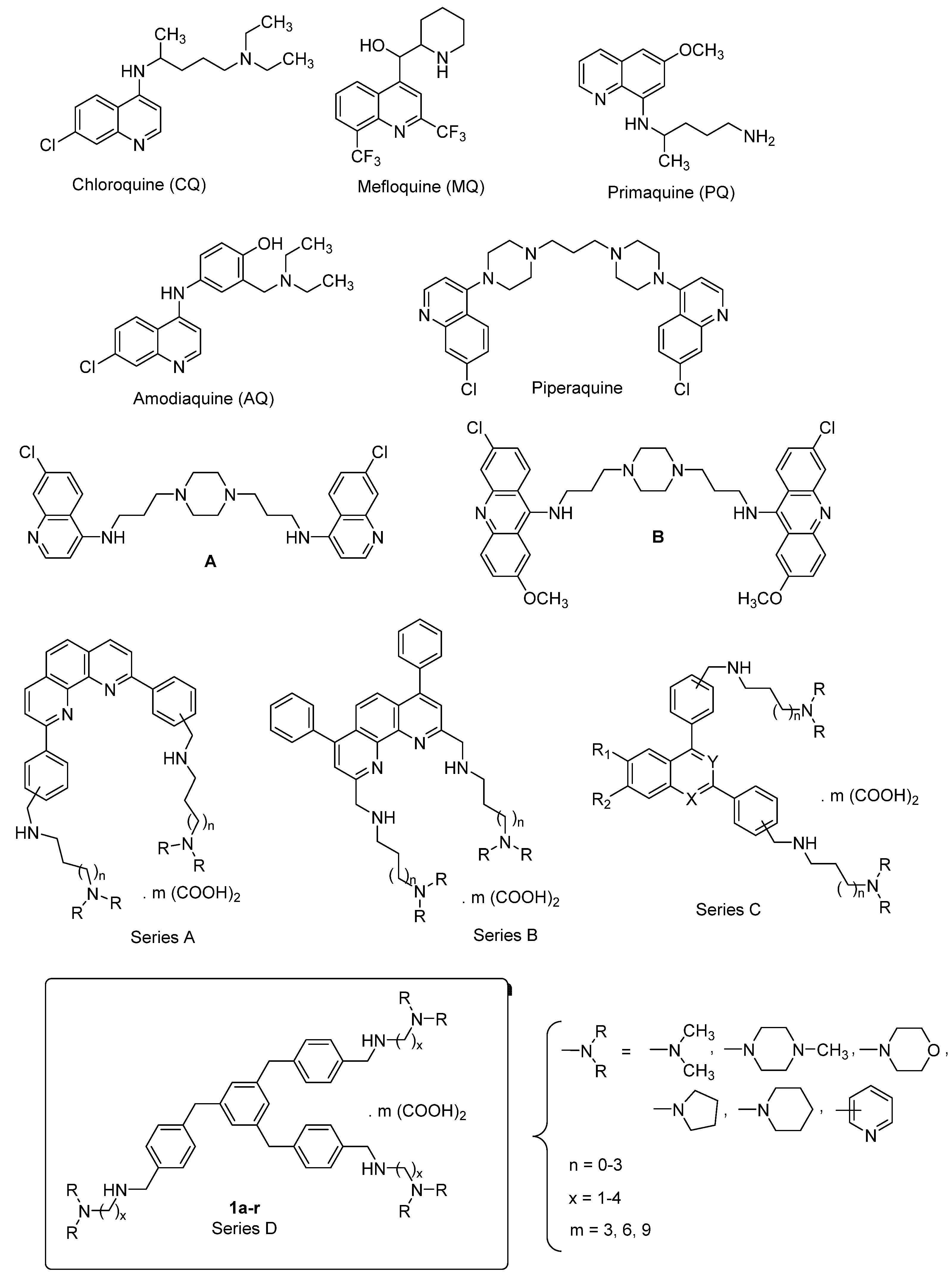
1. Introduction
2. Results
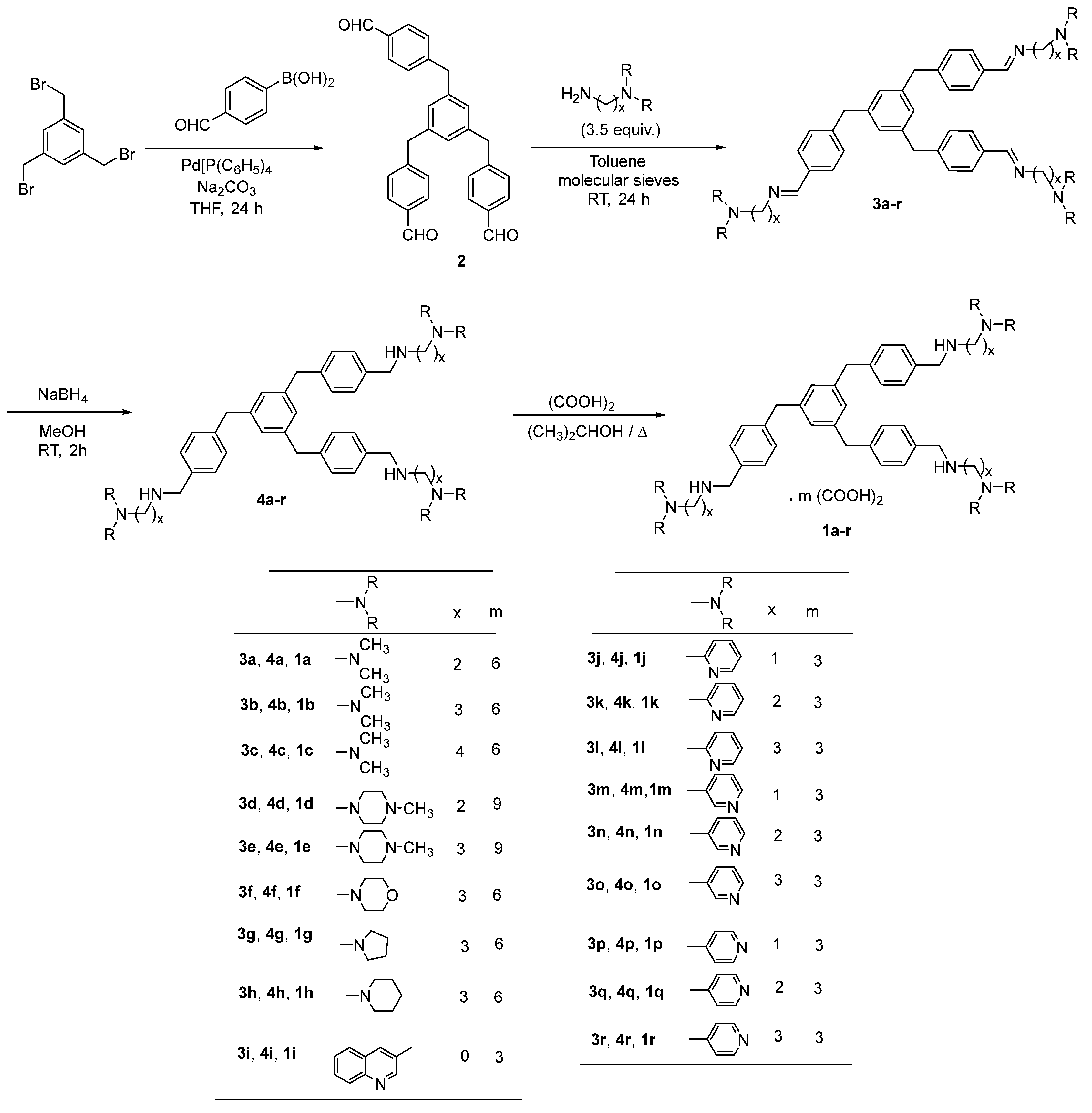
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Biological Evaluation
2.2.1. In Vitro Antimalarial Activity
2.2.2. In Vitro Antileishmanial Activity against Promastigote Forms
2.2.3. Cytotoxicity and Selectivity Index
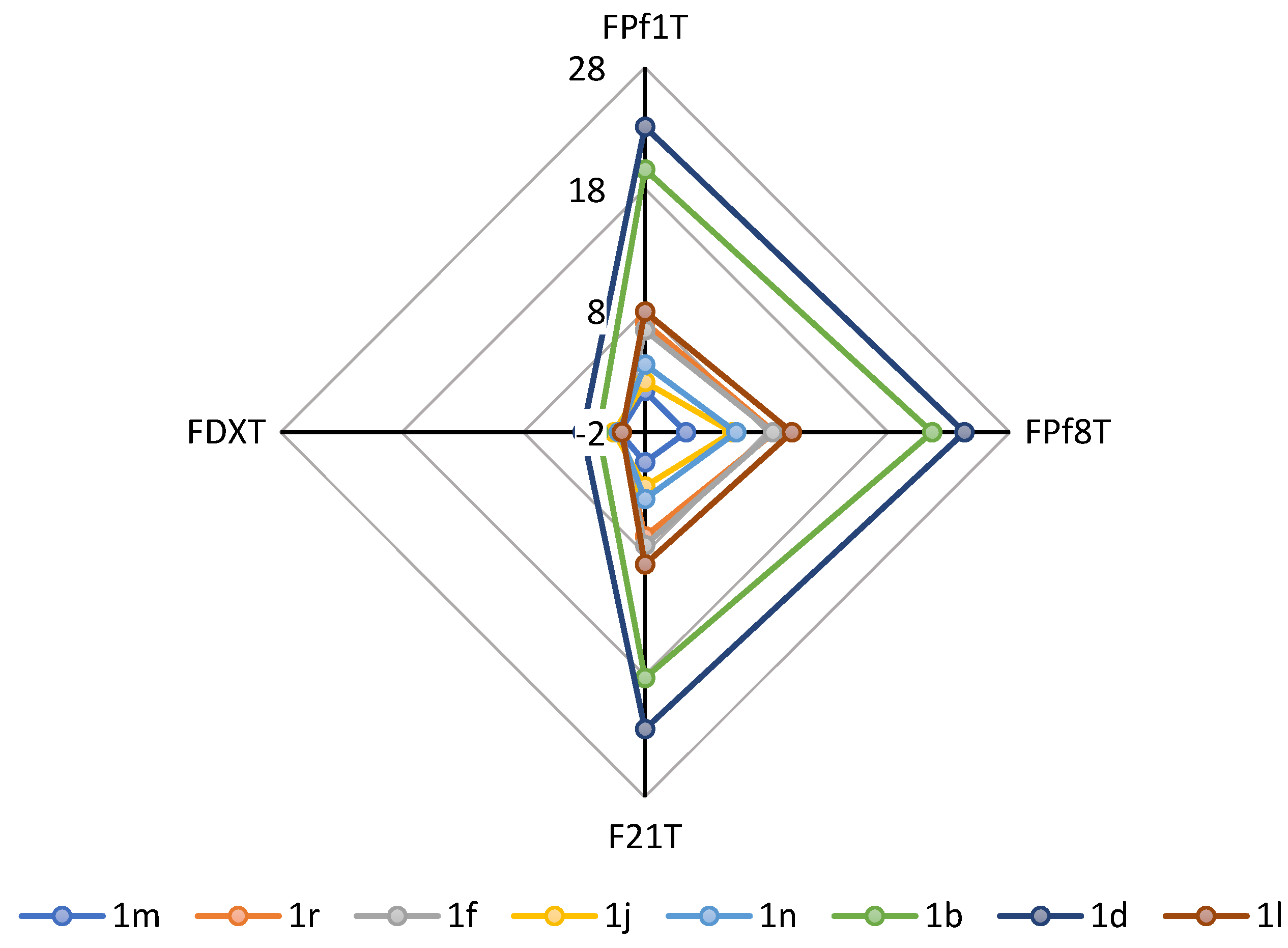
2.3. FRET Melting Experiments
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. General
3.1.2. Synthesis of the 1,3,5-tris[(4-formylphenyl)methyl]benzene 2
3.1.3. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 1,3,5-tris[(4-(substituted-iminomethyl)phenyl)methyl]benzenes 3a-r
3.1.4. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 1,3,5-tris[(4-(substituted-aminomethyl)phenyl)methyl]benzenes 4a-r
3.2. Biological Evaluation
3.2.1. In Vitro Antiplasmodial Activity
3.2.2. In Vitro Antileishmanial Activity
3.2.3. Cytotoxicity Evaluation
3.3. FRET Melting Experiments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO Guidelines for Malaria, Geneva: World Health Organization; 2022 (WHO/UCN/GMP/2022.01 Rev.2). License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/354781 (accessed on 6 March 2023).
- WHO Guidelines for Malaria Hosted on the MAGICapp Online Platform. Available online: https://app.magicapp.org/#/guideline/7089 (accessed on 6 March 2023).
- World Malaria Report 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/global-malaria-programme/reports/world-malaria-report-2022 (accessed on 5 March 2023).
- WHO Neglected Tropical Diseases. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/questions-and-answers/item/neglected-tropical-diseases (accessed on 5 March 2023).
- WHO Ending the Neglect to Attain the Sustainable Development Goals: A Rationale for Continued Investment in Tackling Neglected Tropical Diseases 2021–2030. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240052932 (accessed on 5 March 2023).
- Dola, V.R.; Soni, A.; Agarwal, P.; Ahmad, H.; Raju, K.S.R.; Rashid, M.; Wahajuddin, M.; Srivastava, K.; Haq, W.; Dwivedi, A.K.; et al. Synthesis and Evaluation of Chirally Defined Side Chain Variants of 7-Chloro-4-Aminoquinoline to Overcome Drug Resistance in Malaria Chemotherapy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e01152-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manohar, S.; Tripathi, M.; Rawat, D.S. 4-Aminoquinoline based molecular hybrids as antimalarials: An overview. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 1706–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshpande, S.; Kay, B. 4-aminoquinolines: An Overview of Antimalarial Chemotherapy. Med. Chem. 2016, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Singh, R.K.; Patial, B.; Goyal, S.; Bhardwaj, T.R. Recent advances in novel heterocyclic scaffolds for the treatment of drug-resistant malaria. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Walle, T.; Cools, L.; Mangelinckx, S.; D’hooghe, M. Affiliations expand et al. Recent contributions of quinolines to antimalarial and anticancer drug discovery research. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 226, 113865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, A.; Kharkwal, H.; Piplani, M.; Singh, Y.; Murugesan, S.; Aggarwal, A.; Kumar, P.; Chander, S. Spotlight on 4-substituted quinolines as potential anti-infective agents: Journey beyond chloroquine. Arch. Pharm. 2023, 356, e2200361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillon, J.; Grellier, P.; Labaied, M.; Sonnet, P.; Léger, J.-M.; Déprez-Poulain, R.; Forfar-Bares, I.; Dallemagne, P.; Lemaître, N.; Péhourcq, F.; et al. Synthesis, antimalarial activity, and molecular modeling of new pyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoxalines, bispyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoxalines, bispyrido[3,2-e]pyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazines, and bispyrrolo[1,2-a]thieno[3,2-e]pyrazines. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1997–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dassonville-Klimpt, A.; Cézard, C.; Mullié, C.; Agnamey, P.; Jonet, A.; Da Nascimento, S.; Marchivie, M.; Guillon, J.; Sonnet, P. Absolute Configuration and Antimalarial Activity of erythro-Mefloquine Enantiomers. ChemPlusChem 2013, 78, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillon, J.; Cohen, A.; Gueddouda, N.M.; Das, R.N.; Moreau, S.; Ronga, L.; Savrimoutou, S.; Basmaciyan, L.; Monnier, A.; Monget, M.; et al. Design, synthesis and antimalarial activity of novel bis{N-[(pyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoxalin-4-yl)benzyl]-3-aminopropyl}amine derivatives. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2017, 32, 547–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonet, A.; Guillon, J.; Mullie, C.; Cohen, A.; Bentzinger, G.; Schneider, J.; Taudon, N.; Hutter, S.; Azas, N.; Moreau, S.; et al. Synthesis and Antimalarial Activity of New Enantiopure Aminoalcoholpyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoxalines. Med. Chem. 2018, 14, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dassonville-Klimpt, A.; Schneider, J.; Damiani, C.; Tisnerat, C.; Cohen, A.; Azas, N.; Marchivie, M.; Guillon, J.; Mullié, C.; Agnamey, P.; et al. Design, synthesis, and characterization of novel aminoalcohol quinolines with strong in vitro antimalarial activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 228, 113981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillon, J.; Cohen, A.; Nath Das, R.; Boudot, C.; Meriem Gueddouda, N.; Moreau, S.; Ronga, L.; Savrimoutou, S.; Basmaciyan, L.; Tisnerat, C.; et al. Design, synthesis, and antiprotozoal evaluation of new 2,9-bis[(substituted-aminomethyl)phenyl]-1,10-phenanthroline derivatives. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2018, 91, 974–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillon, J.; Cohen, A.; Monic, S.; Boudot, C.; Savrimoutou, S.; Albenque-Rubio, S.; Moreau, S.; Dassonville-Klimpt, A.; Mergny, J.-L.; Ronga, L.; et al. Synthesis and antiprotozoal evaluation of new 2,9-bis[(pyridinylalkylaminomethyl)phenyl]-1,10-phenanthroline derivatives by targeting G-quadruplex, an interesting pharmacophore against drug efflux. Acta Sci. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 7, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillon, J.; Cohen, A.; Boudot, C.; Monic, S.; Savrimoutou, S.; Moreau, S.; Albenque-Rubio, S.; Lafon-Schmaltz, C.; Dassonville-Klimpt, A.; Mergny, J.-L.; et al. Design, synthesis, biophysical and antiprotozoal evaluation of new promising 2,9-bis[(substituted-aminomethyl)]-4,7-phenyl-1,10-phenanthroline derivatives by targeting G-quadruplex, a potential alternative to drug efflux. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillon, J.; Cohen, A.; Boudot, C.; Valle, A.; Milano, V.; Das, R.N.; Guédin, A.; Moreau, S.; Ronga, L.; Savrimoutou, S.; et al. Design, synthesis, and antiprotozoal evaluation of new 2,4-bis[(substituted-aminomethyl)phenyl]quinoline, 1,3-bis[(substituted-aminomethyl)phenyl]isoquinoline and 2,4-bis[(substituted-aminomethyl)phenyl]quinazoline derivatives. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2020, 35, 432–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, E.P.; Wasserman, M. G-Quadruplex ligands: Potent inhibitors of telomerase activity and cell proliferation in Plasmodium falciparum. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2016, 207, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tidwell, R.R.; Boykin, D.W.; Ismail, M.A.; Wilson, W.D.; White, E.W.; Kumar, A.; Nanjunda, R. Dicationic Compounds which Selectively Recognize G-quadruplex DNA. EP 1792613A2, 6 June 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Leeder, W.-M.; Hummel, N.F.C.; Göringer, H.U. Multiple G-quartet structures in pre-edited mRNAs suggest evolutionary driving force for RNA editing in trypanosomes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombrana, R.; Alvarez, A.; Fernandez-Justel, J.M.; Almeida, R.; Poza-Carrion, C.; Gomes, F.; Calzada, A.; Requena, J.M.; Gomez, M. Transcriptionally Driven DNA Replication Program of the Human Parasite Leishmania major. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 1774–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottius, E.; Bakhsis, N.; Scherf, A. Plasmodium falciparum Telomerase: De Novo Telomere Addition to Telomeric and Nontelomeric Sequences and Role in Chromosome Healing. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998, 18, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, D.K.; Das, D.R.; Dash, A.P.; Supakar, P.C. Identification of telomerase activity in gametocytes of Plasmodium falciparum. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 309, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cian, A.; Grellier, P.; Mouray, E.; Depoix, D.; Bertrand, H.; Monchaud, D.; Telade-Fichou, M.-P.; Mergny, J.-L.; Alberti, P. Plasmodium Telomeric Sequences: Structure, Stability and Quadruplex Targeting by Small Compounds. ChemBioChem 2008, 9, 2730–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotha, S.; Mandal, K. Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling and ring-closing metathesis: A strategic combination for the synthesis of cyclophane derivatives. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 23, 5387–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillon, J.; Denevault-Sabourin, C.; Chevret, E.; Brachet-Botineau, M.; Milano, V.; Guédin-Beaurepaire, A.; Moreau, S.; Ronga, L.; Savrimoutou, S.; Rubio, S.; et al. Design, synthesis, and antiproliferative effect of 2,9-bis [4-(pyridinylalkylaminomethyl)phenyl]-1,10-phenanthroline derivatives on human leukemic cells by targeting G-quadruplex. Arch. Pharm. (Weinheim) 2021, 354, e2000450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, T.; Strigun, A.; Verlohner, A.; Huener, H.A.; Peter, E.; Herold, M.; Bordag, N.; Mellert, W.; Walk, T.; Spitzer, M.; et al. Prediction of liver toxicity and mode of action using metabolomics in vitro in HepG2 cells. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 893–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Antona, C.; Donato, M.T.; Boobis, A.; Edwards, R.J.; Watts, P.S.; Castell, J.V.; Gómez-Lechón, M.J. Cytochrome P450 expression in human hepatocytes and hepatoma cell lines: Molecular mechanisms that determine lower expression in cultured cells. Xenobiotica 2002, 32, 505–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desjardins, R.E.; Canfield, C.J.; Haynes, J.D.; Chulay, J.D. Quantitative assessment of antimalarial activity in vitro by a semiautomated microdilution technique. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1979, 16, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, T.N.; Paguio, M.; Gligorijevic, B.; Seudieu, C.; Kosar, A.D.; Davidson, E.; Roepe, P.D. Novel, Rapid, and Inexpensive Cell-Based Quantification of Antimalarial Drug Efficacy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 1807–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacon, D.J.; Latour, C.; Lucas, C.; Colina, O.; Ringwald, P.; Picot, S. Comparison of a SYBR Green I-Based Assay with a Histidine-Rich Protein II Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for In Vitro Antimalarial Drug Efficacy Testing and Application to Clinical Isolates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 1172–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaddouri, H.; Nakache, S.; Houzé, S.; Mentré, F.; Le Bras, J. Assessment of the Drug Susceptibility of Plasmodium falciparum Clinical Isolates from Africa by Using a Plasmodium Lactate Dehydrogenase Immunodetection Assay and an Inhibitory Maximum Effect Model for Precise Measurement of the 50-Percent Inhibitory Concentration. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 3343–3349. [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emami, S.A.; Zamanai Taghizadeh Rabe, S.; Ahi, A.; Mahmoudi, M. Inhibitory Activity of Eleven Artemisia Species from Iran against Leishmania Major Parasites. Iran J. Basic Med. Sci. 2012, 15, 807–811. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Cian, A.; Guittat, L.; Kaiser, M.; Saccà, B.; Amrane, S.; Bourdoncle, A.; Alberti, P.; Teulade-Fichou, M.-P.; Lacroix, L.; Mergny, J.-L. Fluorescence-based melting assays for studying quadruplex ligands. Methods 2007, 42, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Compound | Salt a | mp (°C) b | % Yield c | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1a | Beige crystals | 6 (COOH)2 | 239–241 | 97 |
| 1b | Grey crystals | 6 (COOH)2 | 241–242 | 84 |
| 1c | Beige crystals | 6 (COOH)2 | 177–179 | 68 |
| 1d | White crystals | 9 (COOH)2 | 209–211 | 73 |
| 1e | White crystals | 9 (COOH)2 | 189–191 | 99 |
| 1f | White crystals | 6 (COOH)2 | 175–177 | 57 |
| 1g | Beige crystals | 6 (COOH)2 | 167–169 | 61 |
| 1h | White crystals | 6 (COOH)2 | 189–191 | 70 |
| 1i | Yellow crystals | 3 (COOH)2 | 140–142 | 52 |
| 1j | Yellow crystals | 3 (COOH)2 | 151–153 | 88 |
| 1k | Orange crystals | 3 (COOH)2 | 159–161 | 98 |
| 1l | Yellow crystals | 3 (COOH)2 | 174–176 | 81 |
| 1m | Beige crystals | 3 (COOH)2 | 185–187 | 82 |
| 1n | Orange crystals | 3 (COOH)2 | 159–161 | 98 |
| 1o | Beige crystals | 3 (COOH)2 | 181–183 | 95 |
| 1p | Grey crystals | 3 (COOH)2 | 157–159 | 57 |
| 1q | Beige crystals | 3 (COOH)2 | 171–173 | 73 |
| 1r | White crystals | 3 (COOH)2 | 178–180 | 98 |
| Compound | P. falciparum Strains IC50 Values (μM) a | L. donovani IC50 Values (μM) b | Cytotoxicity to HepG2 Cells CC50 Values (μM) c | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| W2 | 3D7 | |||
| CQ d | 0.40 ± 0.04 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | n.d. g | 30 |
| MQ d | 0.016 ± 0.002 | 0.06 ± 0.003 | n.d. g | n.d. f |
| Pentamidine e | n.d. f | n.d. f | 5.5 ± 0.80 | 2.3 ± 0.50 |
| Amphotericin B e | n.d. f | n.d. f | 0.1 ± 0.04 | 8.8 ± 0.60 |
| 1a | >40 | 3.29 ± 0.81 | >15.6 g | 22.33 ± 0.89 |
| 1b | 15.63 ± 0.32 | 15.01 ± 0.61 | >15.6 g | 72.90 ± 3.66 |
| 1c | >40 | 20.41 ± 0.42 | >15.6 g | 70.38 ± 4.41 |
| 1d | 24.82 ± 0.28 | 11.25 ± 1.25 | >15.6 g | 51.82 ± 2.00 |
| 1e | 15.46 ± 0.64 | 6.71 ± 1.24 | >15.6 g | 32.34 ± 2.52 |
| 1f | 3.27 ± 0.42 | 1.18 ± 0.17 | >15.6 g | 25.35 ± 1.60 |
| 1g | 13.28 ± 0.86 | 8.64 ± 0.79 | >15.6 g | 18.49 ± 0.52 |
| 1h | 14.43 ± 2.55 | 7.22 ± 0.88 | >15.6 g | 18.68 ± 1.72 |
| 1i | >40 | >40 | >15.6 g | >100 |
| 1j | 0.79 ± 0.28 | 0.71 ± 0.25 | >15.6 g | 11.70 ± 0.60 |
| 1k | 1.54 ± 0.64 | 0.66 ± 0.23 | >15.6 g | 2.59 ± 0.14 |
| 1l | 0.63 ± 0.40 | 0.42 ± 0.12 | >15.6 g | 2.44 ± 0.31 |
| 1m | 4.82 ± 0.98 | 0.30 ± 0.05 | >15.6 g | 25.10 ± 2.05 |
| 1n | 0.43 ± 0.10 | 0.26 ± 0.05 | >15.6 g | 2.78 ± 0.18 |
| 1o | 0.63 ± 0.16 | 25.78 ± 2.06 | 14.04 ± 1.1 | 2.12 ± 0.18 |
| 1p | n.d. f | 0.93 ± 0.21 | >15.6 g | 2.36 ± 0.52 |
| 1q | 0.29 ± 0.02 | >40 | 5.96 ± 0.50 | 2.00 ± 0.21 |
| 1r | 0.18 ± 0.05 | 0.07 ± 0.03 | 6.44 ± 1.20 | 3.11 ± 0.76 |
| Compound | Selectivity Index a | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| HepG2/W2 | HepG2/3D7 | HepG2/L. donovani | |
| CQ | 75 | 272 | n.d. b |
| Pentamidine | n.d. b | n.d. b | n.d. b |
| Amphotericin B | n.d. b | n.d. b | 88.0 |
| 1a | 0.56> | 6.79 | n.d. b |
| 1b | 4.66 | 4.86 | n.d. b |
| 1c | 1.76> | 3.45 | n.d. b |
| 1d | 2.09 | 4.61 | n.d. b |
| 1e | 2.09 | 4.82 | n.d. b |
| 1f | 7.75 | 21.48 | n.d. b |
| 1g | 1.39 | 2.14 | n.d. b |
| 1h | 1.29 | 2.59 | n.d. b |
| 1i | n.d. b | n.d. b | n.d. b |
| 1j | 14.81 | 16.48 | n.d. b |
| 1k | 1.68 | 3.92 | n.d. b |
| 1l | 3.87 | 5.81 | n.d. b |
| 1m | 5.21 | 83.67 | n.d. b |
| 1n | 6.46 | 10.69 | n.d. b |
| 1o | 3.36 | 0.08 | 0.15 |
| 1p | n.d. b | 2.54 | n.d. b |
| 1q | 6.90 | 0.05> | 0.34 |
| 1r | 17.28 | 44.43 | 0.48 |
| Compound | ΔTm (°C) a | ΔTm (°C) a | ΔTm (°C) a | ΔTm (°C) a | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FPf1T | FPf8T | F21T | FdxT | |||||
| PhenDC3 | 24.6 | ±0.1 | 24.7 | ±0.2 | 26.3 | ±0.1 | 0.1 | ±0.2 |
| CQ | 1.9 | ±0.1 | 2.4 | ±1.2 | 2.4 | ±1.1 | n.d. b | |
| MQ | 3.1 | ±0.5 | 6.6 | ±2.3 | 2.6 | ±0.5 | n.d. b | |
| 1b | 19.6 | ±0.3 | 21.6 | ±0.7 | 18.2 | ±0.6 | 1.8 | ±0.2 |
| 1d | 23.1 | ±0.4 | 24.3 | ±1.5 | 22.4 | ±3.3 | 3.1 | ±0.3 |
| 1f | 6.4 | ±1.4 | 8.5 | ±0.8 | 7.3 | ±0.5 | 0.0 | ±0.1 |
| 1l | 7.9 | ±0.6 | 10.1 | ±1.2 | 8.9 | ±0.5 | −0.1 | ±0.1 |
| 1m | 1.4 | ±0.3 | 1.4 | ±0.3 | 0.5 | ±0.4 | 0.1 | ±0.1 |
| 1n | 3.6 | ±0.6 | 5.5 | ±1.0 | 3.5 | ±1.0 | 0.2 | ±0.0 |
| 1r | 7.0 | ±2.0 | 8.7 | ±1.8 | 6.6 | ±0.6 | −0.1 | ±0.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Albenque-Rubio, S.; Guillon, J.; Cohen, A.; Agnamey, P.; Savrimoutou, S.; Moreau, S.; Mergny, J.-L.; Ronga, L.; Kanavos, I.; Moukha, S.; et al. Synthesis and Antimalarial Evaluation of New 1,3,5-tris[(4-(Substituted-aminomethyl)phenyl)methyl]benzene Derivatives: A Novel Alternative Antiparasitic Scaffold. Drugs Drug Candidates 2023, 2, 653-672. https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc2030033
Albenque-Rubio S, Guillon J, Cohen A, Agnamey P, Savrimoutou S, Moreau S, Mergny J-L, Ronga L, Kanavos I, Moukha S, et al. Synthesis and Antimalarial Evaluation of New 1,3,5-tris[(4-(Substituted-aminomethyl)phenyl)methyl]benzene Derivatives: A Novel Alternative Antiparasitic Scaffold. Drugs and Drug Candidates. 2023; 2(3):653-672. https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc2030033
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlbenque-Rubio, Sandra, Jean Guillon, Anita Cohen, Patrice Agnamey, Solène Savrimoutou, Stéphane Moreau, Jean-Louis Mergny, Luisa Ronga, Ioannis Kanavos, Serge Moukha, and et al. 2023. "Synthesis and Antimalarial Evaluation of New 1,3,5-tris[(4-(Substituted-aminomethyl)phenyl)methyl]benzene Derivatives: A Novel Alternative Antiparasitic Scaffold" Drugs and Drug Candidates 2, no. 3: 653-672. https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc2030033
APA StyleAlbenque-Rubio, S., Guillon, J., Cohen, A., Agnamey, P., Savrimoutou, S., Moreau, S., Mergny, J.-L., Ronga, L., Kanavos, I., Moukha, S., Dozolme, P., & Sonnet, P. (2023). Synthesis and Antimalarial Evaluation of New 1,3,5-tris[(4-(Substituted-aminomethyl)phenyl)methyl]benzene Derivatives: A Novel Alternative Antiparasitic Scaffold. Drugs and Drug Candidates, 2(3), 653-672. https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc2030033









