Drugs of the Kallikrein–Kinin System: An Overview
Abstract
1. Kallikrein–Kinin Systems: The Formation and Clearance of Kinins
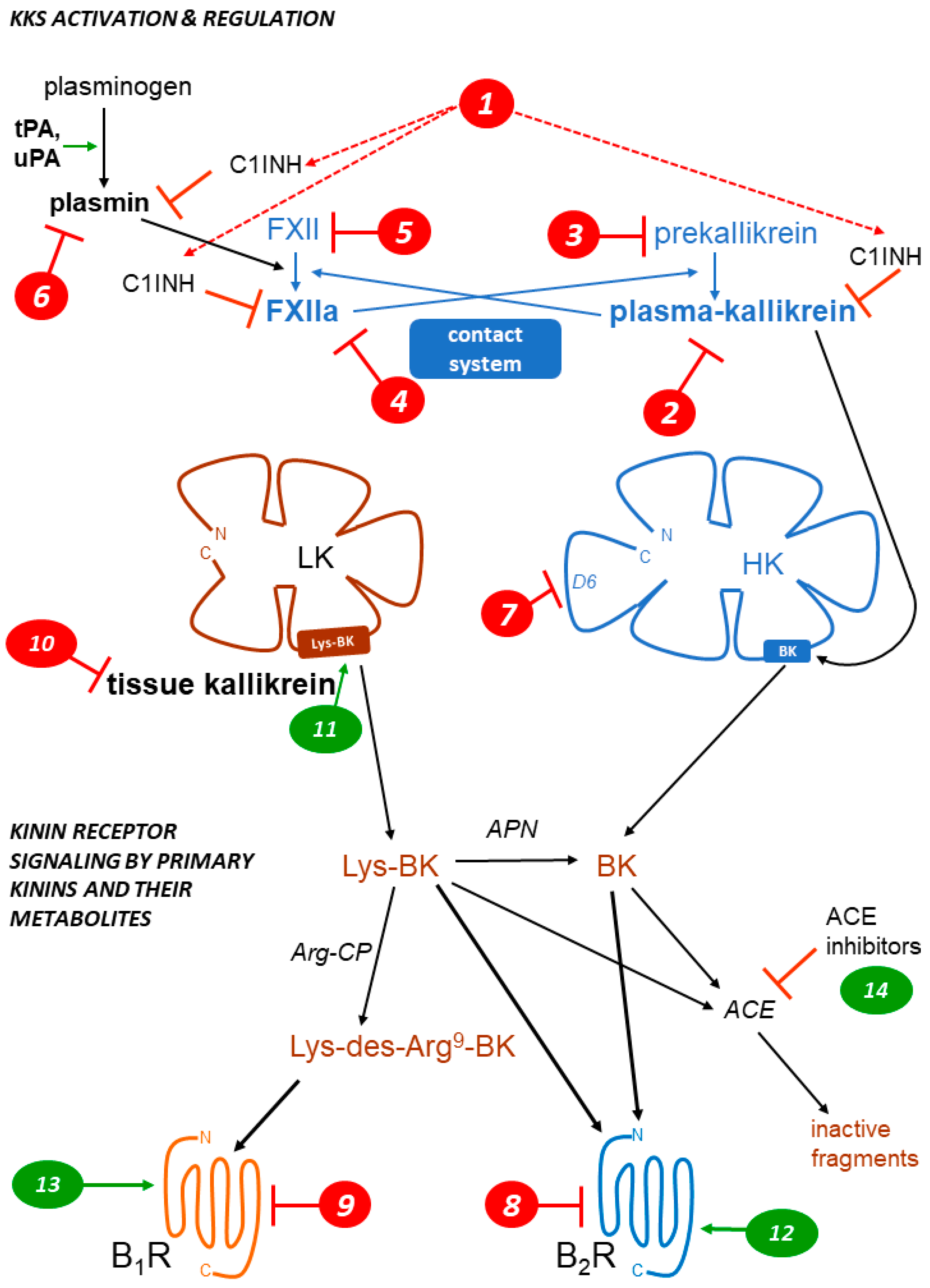
2. Kinin Receptors
3. Pharmacological Inhibition of the KKS: Hereditary Angioedema (HAE)
| Type of Agent Mode of Action Marker in Figure 1 | Drug or Intervention | Development Status | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parenteral replacement of C1INH 1 | various C1INH concentrates, natural or recombinant | approved, widely used | [37] |
| Gene therapy to increase the endogenous synthesis of C1INH 1 | BMN 311 HAE | clinical trials | [38] |
| OTL-105 HAE | preclinical | [39] | |
| Kunitz-domain-based peptide inhibitor of plasma kallikrein 2 | ecallantide | approved | [40] |
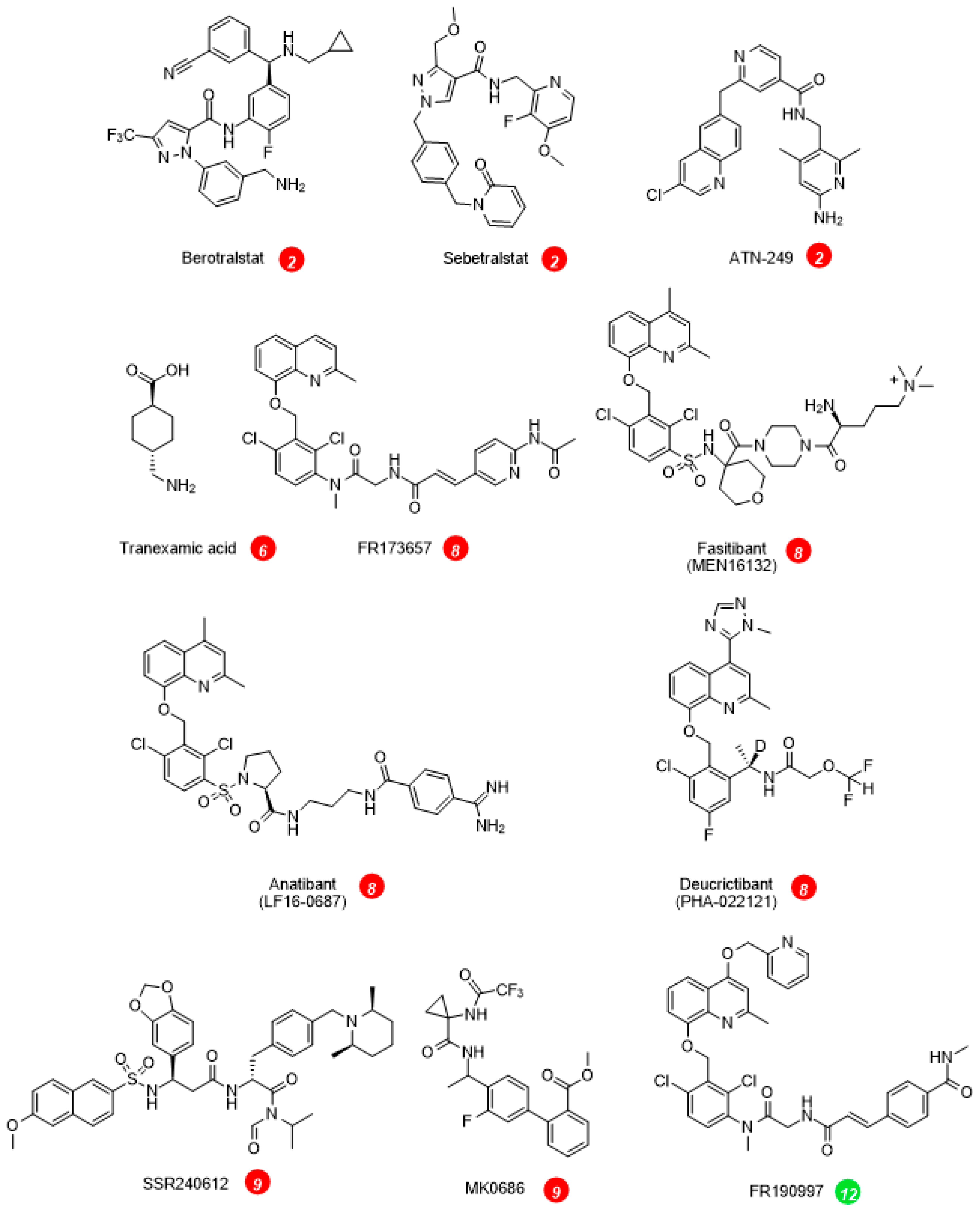
| Small molecule inhibitors of plasma kallikrein 2 | berotralstat (BCX7353) | approved | [41] |
| sebetralstat (KVD-900) | clinical trials | [42] | |
| ATN-249, ATN-111 | clinical trials | [43] | |
| Anti-plasma kallikrein mAb 2 | lanadelumab | approved | [44] |
| STAR-0215 | clinical trials | [45] | |
| Transfer of a gene encoding an anti-plasma kallikrein mAb 2 | RegenxBio undisclosed | preclinical | [46] |
| Antisense suppressor of hepatic plasma prekallikrein production 3 | donidalorsen (PKK-L Rx) | clinical trials | [47] |
| Gene therapy to disrupt hepatic plasma prekallikrein production 3 | NTLA-2002 | clinical trials | [48] |
| Small molecule inhibitor of factor XIIa 4 | KV998086 | preclinical | [49] |
| Anti-factor XII mAb 4 | garadacimab (CSL312) | clinical trials | [50] |
| Small interfering RNA targeting factor XII mRNA 5 | ALN-F12 | preclinical, halted? | [51] |
| ARC-F12 | preclinical, halted? | [52] | |
| Plasmin/tPA inhibitor 6 | tranexamic acid | approved, 2nd line prophylactic agent | [53] |
| Bradykinin B2R antagonists 8 | peptide icatibant | approved | [54] |
| NPA deucrictibant (PHA-022121, PHA-121) | clinical trials | [24,55] |
4. Other Application of KKS Inhibitors
| Indication | Drug Mode of Action Marker in Figure 1 | Status | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACE-inhibitor-induced acquired angioedema | C1INH concentrate 1 | ineffective in a small clinical trial | [68] |
| Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, interstitial lung disease | mAb garadacimab (CSL312) 4 | clinical trials | [69] |
| Thrombosis prevention | ALN-F12 5 | preclinical | [70] |
| Intradyalytic hypotension | peptide B2R antagonist icatibant 8 | effective in a small clinical trial | [71] |
| COVID-19 pneumonia | icatibant 8 | ineffective in a clinical trial | [72] |
| Cerebral edema/head trauma | B2R NPA anatibant (LF16-0687) 8 | ineffective in an interrupted clinical trial | [73] |
| Osteoarthritis pain | B2R NPA fasitibant (MEN16132) 8 | largely ineffective in a clinical trial | [63] |
| Diabetic macula edema | B1R NPA BI1026706 9 | ineffective in a clinical trial | [74] |
| Glioma | intracerebroventricular icatibant 8 | preclinical | [67] |
| ACE-inhibitor-induced acquired angioedema | icatibant 8 | ineffective in a clinical trial | [75] |
| Diarrheal states induced by dextran sulfate | oral icatibant, oral FR173657 8 | preclinical | [76,77] |
| Pancreatitis | icatibant, FR173657 8 | preclinical | [78,79] |
| Circulatory complications of burns | icatibant 8 | preclinical | [80,81] |
| Inflammatory edema of various causes | FR173657, icatibant 8 | preclinical | [82,83] |
| Chagas disease myocarditis | B1R antagonist R-954 9 | preclinical | [29] |
| Breast cancer | B1R NPA SSR240612, etc. 9 | preclinical, in vitro | [84] |
| Inflammatory pain | B1R NPA MK-0686, SS240612 9 | ineffective in clinical trials | [62] |
| Inflammatory bowel disease | B1R NPA SSR240612 9 | preclinical | [85] |
| Airway disease | mAb DX-2300 10 | preclinical | [86] |
| Aortic aneurysm expansion | mAb DX-2300, etc. 10 | preclinical | [87] |
5. Therapeutic Value of KKS Stimulation
6. Conclusions
| Type of Agent Mode of Action Marker in Figure 1 | Drug | Status | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Activated tissue kallikrein injection for cerebrovascular or renal indications 11 | purified from human urine: Kailikang | approved in China, stroke | [97] |
| recombinant: DM199 | clinical trials | [98,99] | |
| B2R agonist to open the blood–brain barrier: adjuvant to brain tumor chemotherapy 12 | labradimil, other peptides | clinical trials of labradimil failed | [105,106] |
| Combined B1R and B2R agonists to open the blood–brain barrier: adjuvant to brain tumor chemotherapy 12, 13 | co-administered peptide agonists or kinin heterodimer | preclinical | [107] |
| Peptide pro-drugs that release bradykinin via the action of peptidases 12 | bradykinin-Arg, D-Arg-bradykinin-Arg-Arg, others | preclinical | [100,101,102] |
| B2R agonist for breast cancer 12 | FR-190997 and analogs | preclinical, in vitro | [108] |
| Attenuation of Alzheimer’s disease development, B2R agonist 12 | [Hyp3,Thi5,NChg7,Thi8]–BK | preclinical, animal model | [103] |
| ACE inhibition 14 | enalapril, ramipril, many others | a fraction of therapeutic effects mediated by kinins | [88] |
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leeb-Lundberg, L.M.; Marceau, F.; Müller-Esterl, W.; Pettibone, D.J.; Zuraw, B.L. International union of pharmacology. XLV. Classification of the kinin receptor family: From molecular mechanisms to pathophysiological consequences. Pharmacol. Rev. 2005, 57, 27–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, A.P.; Joseph, K.; Ghebrehiwet, B. The complex role of kininogens in hereditary angioedema. Front. Allergy 2022, 3, 952753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, A.P. Enzymatic pathways in the pathogenesis of hereditary angioedema: The role of C1 inhibitor therapy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauberti, M.; Potzeha, F.; Vivien, D.; Martinez de Lizarrondo, S. Impact of Bradykinin Generation During Thrombolysis in Ischemic Stroke. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobó, J.; Major, B.; Kékesi, K.A.; Szabó, I.; Megyeri, M.; Hajela, K.; Juhász, G.; Závodszky, P.; Gál, P. Cleavage of kininogen and subsequent bradykinin release by the complement component: Mannose-binding lectin-associated serine protease (MASP)-1. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charest-Morin, X.; Hébert, J.; Rivard, G.É.; Bonnefoy, A.; Wagner, E.; Marceau, F. Comparing Pathways of Bradykinin Formation in Whole Blood From Healthy Volunteers and Patients With Hereditary Angioedema Due to C1 Inhibitor Deficiency. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoef, J.J.F.; Barendrecht, A.D.; Nickel, K.F.; Dijkxhoorn, K.; Kenne, E.; Labberton, L.; McCarty, O.W.T.; Schiffelers, R.; Heijnen, H.; Hendricks, A.P.; et al. Polyphosphate nanoparticles on the platelet surface trigger contact system activation. Blood 2017, 129, 1707–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousef, G.M.; Chang, A.; Scorilas, A.; Diamandis, E.P. Genomic organization of the human kallikrein gene family on chromosome 19q13.3-q13.4. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 276, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deperthes, D.; Marceau, F.; Frenette, G.; Lazure, C.; Tremblay, R.R.; Dubé, J.Y. Human kallikrein hK2 has low kininogenase activity while prostate-specific antigen (hK3) has none. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1997, 1343, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charest-Morin, X.; Raghavan, A.; Charles, M.L.; Kolodka, T.; Bouthillier, J.; Jean, M.; Robbins, M.S.; Marceau, F. Pharmacological effects of recombinant human tissue kallikrein on bradykinin B2 receptors. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2015, 3, e00119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marceau, F.; Rivard, G.E.; Gauthier, J.M.; Binkley, K.E.; Bonnefoy, A.; Boccon-Gibod, I.; Bouillet, L.; Picard, M.; Levesque, G.; Elfassy, H.L.; et al. Measurement of Bradykinin Formation and Degradation in Blood Plasma: Relevance for Acquired Angioedema Associated With Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibition and for Hereditary Angioedema Due to Factor XII or Plasminogen Gene Variants. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marceau, F.; Bachelard, H.; Charest-Morin, X.; Hébert, J.; Rivard, G.E. In vitro modeling of bradykinin-mediated angioedema states. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fryer, R.M.; Segreti, J.; Banfor, P.N.; Widomski, D.L.; Backes, B.J.; Lin, C.W.; Ballaron, S.J.; Cox, B.F.; Trevillyan, J.M.; Reinhart, G.A.; et al. Effect of bradykinin metabolism inhibitors on evoked hypotension in rats: Rank efficacy of enzymes associated with bradykinin-mediated angioedema. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, H.; Scicli, A.G.; Carretero, O.A. Contributions of various rat plasma peptidases to kinin hydrolysis. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1989, 251, 817–820. [Google Scholar]
- Defendi, F.; Charignon, D.; Ghannam, A.; Baroso, R.; Csopaki, F.; Allegret-Cadet, M.; Ponard, D.; Favier, B.; Cichon, S.; Nicolie, B.; et al. National Reference Centre for Angioedema CREAK. Enzymatic assays for the diagnosis of bradykinin-dependent angioedema. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marceau, F.; Rivard, G.E.; Hébert, J.; Gauthier, J.; Bachelard, H.; Gangnus, T.; Burckhardt, B.B. Picomolar Sensitivity Analysis of Multiple Bradykinin-Related Peptides in the Blood Plasma of Patients With Hereditary Angioedema in Remission: A Pilot Study. Front. Allergy 2022, 3, 837463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cugno, M.; Salerno, F.; Nussberger, J.; Bottasso, B.; Lorenzano, E.; Agostoni, A. Bradykinin in the ascitic fluid of patients with liver cirrhosis. Clin. Sci. 2001, 101, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofman, Z.L.M.; van den Elzen, M.T.; Kuijpers, J.; de Maat, S.; Hack, C.E.; Knulst, A.C.; Röckmann, H.; Maas, C. Evidence for bradykinin release in chronic spontaneous urticaria. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2020, 50, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostmans, Y.; De Smedt, K.; Richert, B.; Elieh Ali Komi, D.; Maurer, M.; Michel, O. Markers for the involvement of endothelial cells and the coagulation system in chronic urticaria: A systematic review. Allergy 2021, 76, 2998–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barratt-Due, A.; Johansen, H.T.; Sokolov, A.; Thorgersen, E.B.; Hellerud, B.C.; Reubsaet, J.L.; Seip, K.F.; Tønnessen, T.I.; Lindstad, J.K.; Pharo, A.; et al. The role of bradykinin and the effect of the bradykinin receptor antagonist icatibant in porcine sepsis. Shock 2011, 36, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparkenbaugh, E.M.; Kasztan, M.; Henderson, M.W.; Ellsworth, P.; Davis, P.R.; Wilson, K.J.; Reeves, B.; Key, N.S.; Strickland, S.; McCrae, K.; et al. High molecular weight kininogen contributes to early mortality and kidney dysfunction in a mouse model of sickle cell disease. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 2329–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regoli, D.; Barabé, J. Pharmacology of bradykinin and related kinins. Pharmacol. Rev. 1980, 32, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hock, F.J.; Wirth, K.; Albus, U.; Linz, W.; Gerhards, H.J.; Wiemer, G.; Henke, S.; Breipohl, G.; König, W.; Knolle, J.; et al. Hoe 140 a new potent and long acting bradykinin-antagonist: In vitro studies. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1991, 102, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesage, A.; Marceau, F.; Gibson, C.; Loenders, B.; Katzer, W.; Ambrosi, H.D.; Saupe, J.; Faussner, A.; Pardali, E.; Knolle, J. In vitro pharmacological profile of PHA-022121, a small molecule bradykinin B2 receptor antagonist in clinical development. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 105, 108523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marceau, F.; Bachelard., H.; Bouthillier, J.; Fortin, J.P.; Morissette, G.; Bawolak, M.T.; Charest-Morin, X.; Gera, L. Bradykinin receptors: Agonists, antagonists, expression, signaling, and adaptation to sustained stimulation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 82, 106305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larrivée, J.-F.; Bachvarov, D.R.; Houle, F.; Landry, J.; Huot, J.; Marceau, F. Role of the mitogen-activated protein kinases in the expression of the kinin B1 receptors induced by tissue injury. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 1419–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, M.E.; Bawolak, M.T.; Morissette, G.; Adam, A.; Marceau, F. Role of nuclear factor-kappaB and protein kinase C signaling in the expression of the kinin B1 receptor in human vascular smooth muscle cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 71, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koumbadinga, G.A.; Désormeaux, A.; Adam, A.; Marceau, F. Effect of interferon-γ on inflammatory cytokine-induced bradykinin B1 receptor expression in human vascular cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 647, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.C.; Vicentino, A.R.R.; Andrade, D.; Pereira, I.R.; Saboia-Vahia, L.; Moreira, O.D.C.; Carvalho-Pinto, C.E.; Mota, J.B.D.; Maciel, L.; Vilar-Pereira, G.; et al. Genetic Ablation and Pharmacological Blockade of Bradykinin B1 Receptor Unveiled a Detrimental Role for the Kinin System in Chagas Disease Cardiomyopathy. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanueli, C.; Bonaria Salis, M.; Stacca, T.; Pintus, G.; Kirchmair, R.; Isner, J.M.; Pinna, A.; Gaspa, L.; Regoli, D.; Cayla, C.; et al. Targeting kinin B1 receptor for therapeutic neovascularization. Circulation 2002, 105, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marceau, F.; Regoli, D. Bradykinin receptor ligands: Therapeutic perspectives. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, R.S.; Fijen, L.M.; Levi, M.; Cohn, D.M. Hereditary Angioedema: The Clinical Picture of Excessive Contact Activation. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valerieva, A.; Longhurst, H.J. Treatment of hereditary angioedema-single or multiple pathways to the rescue. Front. Allergy 2022, 3, 952233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, M.; Magerl, M.; Betschel, S.; Aberer, W.; Ansotegui, I.J.; Aygören-Pürsün, E.; Banerji, A.; Bara, N.A.; Boccon-Gibod, I.; Bork, K.; et al. The international WAO/EAACI guideline for the management of hereditary angioedema—The 2021 revision and update. World Allergy Organ J. 2022, 15, 100627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bork, K.; Wulff, K.; Witzke, G.; Staubach, P.; Hardt, J.; Meinke, P. Gene Mutations Linked to Hereditary Angioedema in Solitary Angioedema Patients With Normal C1 Inhibitor. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2023; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.L.; Singh, P.K.; Horn, K.; Calvano, M.R.; Kaneki, S.; McCrae, K.R.; Strickland, S.; Norris, E.H. Anti-HK antibody inhibits the plasma contact system by blocking prekallikrein and factor XI activation in vivo. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 1156–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longhurst, H.; Farkas, H. Biological therapy in hereditary angioedema: Transformation of a rare disease. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2020, 20, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biomarin. Available online: https://www.biomarin.com/our-treatments/pipeline/bmn-331-for-hae/ (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Pharming Group N.V. Available online: https://www.pharming.com/pipeline (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Duffey, H.; Firszt, R. Management of acute attacks of hereditary angioedema: Role of ecallantide. J. Blood Med. 2015, 6, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, M.; Dorr, A.; Bode, E.; Boulton, A.P.R.; Buckland, M.; Chee, S.; Dalley, C.; Denman, S.; Ekbote, A.; Elkhalifa, S.; et al. Berotralstat for the prophylaxis of hereditary angioedema-Real-world evidence data from the United Kingdom. Allergy 2023, 78, 1380–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aygören-Pürsün, E.; Zanichelli, A.; Cohn, D.M.; Cancian, M.; Hakl, R.; Kinaciyan, T.; Magerl, M.; Martinez-Saguer, I.; Stobiecki, M.; Farkas, H.; et al. An investigational oral plasma kallikrein inhibitor for on-demand treatment of hereditary angioedema: A two-part, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover phase 2 trial. Lancet 2023, 401, 458–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalfus, I.; Offman, E.; McDonald, A. Pharmacokinetics, safety, and potency of ATN-249, a novel oral plasma kallikrein inhibitor for hereditary angioedema. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2019, 15 (Suppl. S4), 45. [Google Scholar]
- Riedl, M.A.; Maurer, M.; Bernstein, J.A.; Banerji, A.; Longhurst, H.J.; Li, H.H.; Lu, P.; Hao, J.; Juethner, S.; Lumry, W.R.; et al. Lanadelumab demonstrates rapid and sustained prevention of hereditary angioedema attacks. Allergy 2020, 75, 2879–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astria Therapeutics. Available online: https://astriatx.com/our-science/scientific-presentations-and-publications/ (accessed on 26 April 2023).
- REGENXBIO Inc. Available online: https://ir.regenxbio.com/news-releases/news-release-details/regenxbio-reports-continued-progress-across-programs-year-end-0/ (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Ferrone, J.D.; Bhattacharjee, G.; Revenko, A.S.; Zanardi, T.A.; Warren, M.S.; Derosier, F.J.; Viney, N.J.; Pham, N.C.; Kaeser, G.E.; Baker, B.F.; et al. IONIS-PKKRx a Novel Antisense Inhibitor of Prekallikrein and Bradykinin Production. Nucleic Acid. Ther. 2019, 29, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intellia Therapeutics, Inc. Available online: https://www.intelliatx.com/our-science/publications-and-presentations/ (accessed on 26 April 2023).
- KalVista Pharmaceuticals. Available online: https://www.kalvista.com/products-pipeline/factor-xiia (accessed on 26 April 2023).
- Craig, T.J.; Reshef, A.; Li, H.H.; Jacobs, J.S.; Bernstein, J.A.; Farkas, H.; Yang, W.H.; Stroes, E.S.G.; Ohsawa, I.; Tachdjian, R.; et al. Efficacy and safety of garadacimab, a factor XIIa inhibitor for hereditary angioedema prevention (VANGUARD): A global, multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2023, 401, 1079–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Qin, J.; Borodovsky, A.; Racie, T.; Castoreno, A.; Schlegel, M.; Maier, M.A.; Zimmerman, T.; Fitzgerald, K.; Butler, J.; et al. An investigational RNAi therapeutic targeting Factor XII (ALN-F12) for the treatment of hereditary angioedema. RNA 2019, 25, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Available online: http://ir.arrowheadpharma.com/news-releases/news-release-details/arrowhead-pharmaceuticals-presents-new-data-arc-f12-and-arc-lpa (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Wintenberger, C.; Boccon-Gibod, I.; Launay, D.; Fain, O.; Kanny, G.; Jeandel, P.Y.; Martin, L.; Gompel, A.; Bouillet, L. Tranexamic acid as maintenance treatment for non-histaminergic angioedema: Analysis of efficacy and safety in 37 patients. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2014, 178, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, M.; Aberer, W.; Caballero, T.; Bouillet, L.; Grumach, A.S.; Botha, J.; Andresen, I.; Longhurst, H.J.; IOS Study Group. The Icatibant Outcome Survey: 10 years of experience with icatibant for patients with hereditary angioedema. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2022, 52, 1048–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, M.; Anderson, J.; Aygören-Pürsün, E.; Bouillet, L.; Baeza, M.L.; Chapdelaine, H.; Cohn, D.; Du-Thanh, A.; Fain, O.; Farkas, H.; et al. Efficacy And Safety of Bradykinin B2 Receptor Inhibition With Oral PHVS416 In Treating Hereditary Angioedema Attacks: Results Of RAPIDe-1 Phase 2 Trial. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 151, AB134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshef, A.; Zanichelli, A.; Longhurst, H.; Relan, A.; Hack, C.E. Elevated D-dimers in attacks of hereditary angioedema are not associated with increased thrombotic risk. Allergy 2015, 70, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, C. Plasminflammation-An Emerging Pathway to Bradykinin Production. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marceau, F.; Bachelard, H.; Rivard, G.É.; Hébert, J. Increased fibrinolysis-induced bradykinin formation in hereditary angioedema confirmed using stored plasma and biotechnological inhibitors. BMC Res. Notes 2019, 12, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zotter, Z.; Csuka, D.; Szabó, E.; Czaller, I.; Nébenführer, Z.; Temesszentandrási, G.; Fust, G.; Varga, L.; Farkas, H. The influence of trigger factors on hereditary angioedema due to C1-inhibitor deficiency. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2014, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Känel, R. Acute mental stress and hemostasis: When physiology becomes vascular harm. Thromb Res. 2015, 135 (Suppl. S1), S52–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinmetzer, T.; Pilgram, O.; Wenzel, B.M.; Wiedemeyer, S.J.A. Fibrinolysis Inhibitors: Potential Drugs for the Treatment and Prevention of Bleeding. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 1445–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fincham, C.I.; Bressan, A.; Paris, M.; Rossi, C.; Fattori, D. Bradykinin receptor antagonists—A review of the patent literature 2005–2008. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2009, 19, 919–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, C.G.; Pavelka, K.; Nizzardo, A.; Rossi, C.; Scartoni, S.; Contini, M.P.; di Molfetta, S.; Bertolotti, M.; Capriati, A.; Maggi, C.A. A Double-Blind, Randomized, Controlled, Four parallel Arm, Dose-Finding Study to Evaluate the Efficacy, Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of Single Intra-Articular (IA) Injections of Fasitibant in Patients with Symptomatic OA of the Knee. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67 (Suppl. S10), 314. Available online: https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-double-blind-randomized-controlled-four-parallel-arm-dose-finding-study-to-evaluate-the-efficacy-safety-tolerability-and-pharmacokinetics-of-single-intra-articular-ia-injections-of-fas/ (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Brusco, I.; Becker, G.; Palma, T.V.; Pillat, M.M.; Scussel, R.; Steiner, B.T.; Sampaio, T.B.; Ardisson-Araújo, D.M.P.; de Andrade, C.M.; Oliveira, M.S.; et al. Kinin B1 and B2 receptors mediate cancer pain associated with both the tumor and oncology therapy using aromatase inhibitors. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, G.M.M.; Do Nascimento, I.J.B.; Marazzi-Diniz, P.H.; Da Silveira, I.B.; Itaborahy, M.F.; Viana, L.E.; Silva, F.A.; Santana, M.F.; Pinto, R.A.; Dutra, B.G.; et al. The des-Arg9-bradykinin/B1R axis: Hepatic damage in COVID-19. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 1080837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Shi, F.; Shan, A.; Xu, S.; Lv, W. BDKRB2 is a novel EMT-related biomarker and predicts poor survival in glioma. Aging 2021, 13, 7499–7516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletti, N.F.; Sénécal, J.; da Silva, V.D.; Roxo, M.R.; Ferreira, N.P.; de Morais, R.L.T.; Pesquero, J.B.; Campos, M.M.; Couture, R.; Morrone, F.B. Primary Role for Kinin B1 and B2 Receptors in Glioma Proliferation. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 7869–7882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strassen, U.; Bas, M.; Wirth, M.; Wirth, M.; Gröger, M.; Stelter, K.; Volkenstein, S.; Kehl, V.; Kojda, G.; Hoffmann, T.K.; et al. Efficacy of human C1 esterase inhibitor concentrate for treatment of ACE-inhibitor induced angioedema. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2023, 64, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CSL, Limited. Available online: https://www.csl.com/research-and-development/product-pipeline (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Liu, J.; Cooley, B.C.; Akinc, A.; Butler, J.; Borodovsky, A. Knockdown of liver-derived factor XII by GalNAc-siRNA ALN-F12 prevents thrombosis in mice without impacting hemostatic function. Thromb. Res. 2020, 196, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamboa, J.L.; Mambungu, C.A.; Clagett, A.R.; Nian, H.; Yu, C.; Ikizler, T.A.; Brown, N.J. Bradykinin B2 receptor blockade and intradialytic hypotension. BMC Nephrol. 2023, 24, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- I-SPY COVID Consortium. Report of the first seven agents in the I-SPY COVID trial: A phase 2, open label, adaptive platform randomised controlled trial. EClinicalMedicine 2023, 58, 101889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakur, H.; Andrews, P.; Asser, T.; Balica, L.; Boeriu, C.; Quintero, J.D.; Dewan, Y.; Druwé, P.; Fletcher, O.; Frost, C.; et al. The BRAIN TRIAL: A randomised, placebo controlled trial of a Bradykinin B2 receptor antagonist (Anatibant) in patients with traumatic brain injury. Trials 2009, 10, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, G.E.; Tadayoni, R.; Tang, W.; Barth, C.; Weiss-Haljiti, C.; Chong, V. BI 1026706 Study Group. Bradykinin 1 Receptor Antagonist BI1026706 Does Not Reduce Central Retinal Thickness in Center-Involved Diabetic Macular Edema. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straka, B.T.; Ramirez, C.E.; Byrd, J.B.; Stone, E.; Woodard-Grice, A.; Nian, H.; Yu, C.; Banerji, A.; Brown, N.J. Effect of bradykinin receptor antagonism on ACE inhibitor-associated angioedema. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, Y.; Takanashi, H.; Kitagawa, H.; Wirth, K.J.; Okayasu, I. Effect of icatibant, a bradykinin B2 receptor antagonist, on the development of experimental ulcerative colitis in mice. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1999, 44, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamata, K.; Hayashi, I.; Mizuguchi, Y.; Arai, K.; Saeki, T.; Ohno, T.; Saigenji, K.; Majima, M. Suppression of dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in kininogen-deficient rats and non-peptide B2 receptor antagonist-treated rats. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 90, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, M.; Hayashi, I.; Yoshimura, K.; Ishii, K.; Soma, K.; Ohwada, T.; Kakita, A.; Majima, M. Blockade of bradykinin B2 receptor suppresses acute pancreatitis induced by obstruction of the pancreaticobiliary duct in rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 135, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanbe, T.; Naruse, S.; Kitagawa, M.; Nakae, Y.; Hayakawa, T. Effects of a bradykinin receptor antagonist (HOE140) on taurocholate-induced acute pancreatitis in rats. Pancreas 1996, 13, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonkam, C.C.; Enkhbaatar, P.; Nakano, Y.; Boehm, T.; Wang, J.; Nussberger, J.; Esechie, A.; Traber, L.D.; Herndon, D.; Traber, D.L. Effects of the bradykinin B2 receptor antagonist icatibant on microvascular permeability after thermal injury in sheep. Shock 2007, 28, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.M.; O’Halloran, E.B.; Ippolito, J.A.; Choudhry, M.A.; Kovacs, J. Alcohol potentiates postburn remote organ damage through shifts in fluid compartments mediated by bradykinin. Shock 2015, 43, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griesbacher, T.; Legat, F.J. Effects of the non-peptide B2 receptor antagonist FR173657 in models of visceral and cutaneous inflammation. Inflamm. Res. 2000, 49, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirth, K.J.; Alpermann, H.G.; Satoh, R.; Inazu, M. The bradykinin antagonist Hoe 140 inhibits carrageenan- and thermically induced paw oedema in rats. Agents Actions Suppl. 1992, 38, 428–431. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dubuc, C.; Savard, M.; Bovenzi, V.; Lessard, A.; Côté, J.; Neugebauer, W.; Geha, S.; Chemtob, S.; Gobeil, F., Jr. Antitumor activity of cell-penetrant kinin B1 receptor antagonists in human triple-negative breast cancer cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 2851–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, D.B.; Leite, D.F.; Fernandes, E.S.; Passos, G.F.; Guimarães, A.O.; Pesquero, J.B.; Campos, M.M.; Calixto, J.B. The relevance of kinin B1 receptor upregulation in a mouse model of colitis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 154, 1276–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sexton, D.J.; Chen, T.; Martik, D.; Kuzmic, P.; Kuang, G.; Chen, J.; Nixon, A.E.; Zuraw, B.L.; Forteza, R.M.; Abraham, W.M.; et al. Specific inhibition of tissue kallikrein 1 with a human monoclonal antibody reveals a potential role in airway diseases. Biochem. J. 2009, 422, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, C.S.; Biros, E.; Krishna, S.M.; Morton, S.K.; Sexton, D.J.; Golledge, J. Kallikrein-1 Blockade Inhibits Aortic Expansion in a Mouse Model and Reduces Prostaglandin E2 Secretion From Human Aortic Aneurysm Explants. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e019372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainer, J.V.; Morrow, J.D.; Loveland, A.; King, D.J.; Brown, N.J. Effect of bradykinin-receptor blockade on the response to angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitor in normotensive and hypertensive subjects. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 1285–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, T.; Lippmann, M.; Grouzmann, E.; Marceau, F.; Herscu, P. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor induced angio-oedema: A review of the pathophysiology and risk factors. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2010, 40, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubers, S.A.; Kohm, K.; Wei, S.; Yu, C.; Nian, H.; Grabert, R.; Sexton, D.J.; Brown, N.J. Endogenous bradykinin and B1-B5 during angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-associated angioedema. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 142, 1636–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheong, E.; Dodd, L.; Smith, W.; Kleinig, T. Icatibant as a Potential Treatment of Life-Threatening Alteplase-Induced Angioedema. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2018, 27, e36–e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.; Campana, C.; Zimmerman, J.; Brooks, S. Icatibant for the treatment of orolingual angioedema following the administration of tissue plasminogen activator. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 36, e1–e1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, O.A.; Richer, C.; Emanueli, C.; van Weel, V.; Quax, P.H.; Katare, R.; Kraenkel, N.; Campagnolo, P.; Barcelos, L.S.; Siragusa, M.; et al. Critical role of tissue kallikrein in vessel formation and maturation: Implications for therapeutic revascularization. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2009, 29, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.; Spillmann, F.; Dendorfer, A.; Westermann, D.; Altmann, C.; Sahabi, M.; Linthout, S.V.; Bader, M.; Walther, T.; Schultheiss, H.P.; et al. Cardiac function and remodeling is attenuated in transgenic rats expressing the human kallikrein-1 gene after myocardial infarction. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 550, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katori, M.; Majima, M. Renal (tissue) kallikrein-kinin system in the kidney and novel potential drugs for salt-sensitive hypertension. Prog. Drug Res. 2014, 69, 59–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergaya, S.; Meneton, P.; Bloch-Faure, M.; Mathieu, E.; Alhenc-Gelas, F.; Lévy, B.I.; Boulanger, C.M. Decreased flow-dependent dilation in carotid arteries of tissue kallikrein-knockout mice. Circ. Res. 2001, 88, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, J. Urinary Kallidinogenase plus rt-PA Intravenous Thrombolysis for Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2022, 2022, 1500669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander-Curtis, M.; Pauls, R.; Chao, J.; Volpi, J.J.; Bath, P.M.; Verdoorn, T.A. Human tissue kallikrein in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2019, 12, 1756286418821918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shehjar, F.; Maktabi, B.; Rahman, Z.A.; Bahader, G.A.; James, A.W.; Naqvi, A.; Mahajan, R.; Shah, Z.A. Stroke: Molecular mechanisms and therapies: Update on recent developments. Neurochem. Int. 2023, 162, 105458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charest-Morin, X.; Roy, C.; Fortin, E.J.; Bouthillier, J.; Marceau, F. Pharmacological evidence of bradykinin regeneration from extended sequences that behave as peptidase-activated B2 receptor agonists. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean, M.; Gera, L.; Charest-Morin, X.; Marceau, F.; Bachelard, H. In Vivo Effects of Bradykinin B2 Receptor Agonists with Varying Susceptibility to Peptidases. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 6, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachelard, H.; Charest-Morin, X.; Marceau, F. D-Arg0-Bradykinin-Arg-Arg, a Latent Vasoactive Bradykinin B2 Receptor Agonist Metabolically Activated by Carboxypeptidases. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, M.A.; Toricelli, M.; Schöwe, N.M.; Malerba, H.N.; Dong-Creste, K.E.; Farah, D.M.A.T.; De Angelis, K.; Irigoyen, M.C.; Gobeil, F.; Araujo Viel, T.; et al. Kinin B2 Receptor Activation Prevents the Evolution of Alzheimer’s Disease Pathological Characteristics in a Transgenic Mouse Model. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nokkari, A.; Abou-El-Hassan, H.; Mechref, Y.; Mondello, S.; Kindy, M.S.; Jaffa, A.A.; Kobeissy, F. Implication of the Kallikrein-Kinin system in neurological disorders: Quest for potential biomarkers and mechanisms. Prog. Neurobiol. 2018, 165, 26–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prados, M.D.; Schold, S.C.; Fine, H.A.; Jaeckle, K.; Hochberg, F.; Mechtler, L.; Fetell, M.R.; Phuphanich, S.; Feun, L.; Janus, T.J.; et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 study of RMP-7 in combination with carboplatin administered intravenously for the treatment of recurrent malignant glioma. Neuro. Oncol. 2003, 5, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, K.; Jakacki, R.; Widemann, B.; Aikin, A.; Libucha, M.; Packer, R.; Vezina, G.; Reaman, G.; Shaw, D.; Krailo, M.; et al. Phase II trial of intravenous lobradimil and carboplatin in childhood brain tumors: A report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2006, 58, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Côté, J.; Savard, M.; Neugebauer, W.; Fortin, D.; Lepage, M.; Gobeil, F. Dual kinin B1 and B2 receptor activation provides enhanced blood-brain barrier permeability and anticancer drug delivery into brain tumors. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2013, 14, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassias, G.; Leonardi, S.; Rigopoulou, D.; Vachlioti, E.; Afratis, K.; Piperigkou, Z.; Koutsakis, C.; Karamanos, N.K.; Gavras, H.; Papaioannou, D. Potent antiproliferative activity of bradykinin B2 receptor selective agonist FR-190997 and analogue structures thereof: A paradox resolved? Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 210, 112948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Abbreviation | Standing for | Corresponding Gene |
|---|---|---|
| ACE | angiotensin-I-converting enzyme | ACE |
| angiopoietin 1 | ANGPT1 | |
| APN | aminopeptidase N | ANPEP |
| Arg-CP | arginine carboxypeptidase | |
| B1R | bradykinin B1 receptor | BDKRB1 |
| B2R | bradykinin B2 receptor | BDKRB2 |
| BK | bradykinin | |
| C1INH | C1-esterase inhibitor | SERPING1 |
| D6 | domain 6 of HK | |
| FXII | coagulation factor XII | F12 |
| FXIIa | activated factor XII | |
| HAE | hereditary angioedema | |
| HAE-C1INH | HAE caused by C1INH haplodeficiency | |
| heparan sulfate–glucosamine 3-sulfotransferase 6 | HS3ST6 | |
| HK | high-molecular-weight kininogen | KNG1 |
| KKS | Kallikrein–kinin system | |
| KLK-1 | tissue kallikrein | KLK1 |
| LK | low-molecular-weight kininogen | KNG1 |
| Lys-BK | kallidin | |
| mAb | therapeutic monoclonal antibody | |
| MASP-1 | mannan-binding lectin-associated serine protease 1 | MASP1 |
| myoferlin | MYOF | |
| NPA | non-peptide antagonist | |
| plasminogen | PLG | |
| tPA | tissue plasminogen activator | PLAT |
| uPA | urokinase-type plasminogen | PLAU |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marceau, F. Drugs of the Kallikrein–Kinin System: An Overview. Drugs Drug Candidates 2023, 2, 538-553. https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc2030028
Marceau F. Drugs of the Kallikrein–Kinin System: An Overview. Drugs and Drug Candidates. 2023; 2(3):538-553. https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc2030028
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarceau, François. 2023. "Drugs of the Kallikrein–Kinin System: An Overview" Drugs and Drug Candidates 2, no. 3: 538-553. https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc2030028
APA StyleMarceau, F. (2023). Drugs of the Kallikrein–Kinin System: An Overview. Drugs and Drug Candidates, 2(3), 538-553. https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc2030028






