Targeting Liver X Receptors in Cancer Drug Discovery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Discovery of LXRs and LXR Ligands
3. Molecular Mechanisms of LXRs and Ligands
4. LXR in Normal Physiology and Diseases
5. LXR and LXR Ligands in Cancers
5.1. LXR-Modulated Cell Cycle Mechanisms and Signaling Pathways
5.2. LXR-Associated Metabolic Genes in Cancers
5.3. LXRs and Hormone Signaling
6. LXRs, Tumor Immunity, and Tumor Microenvironment
7. Targeting LXRs with Inverse Agonists
8. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gashaw, I.; Ellinghaus, P.; Sommer, A.; Asadullah, K. What Makes a Good Drug Target? Drug Discov. Today 2012, 17, S24–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, J.; Rees, S.; Kalindjian, S.; Philpott, K. Principles of Early Drug Discovery. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 162, 1239–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Gustafsson, J.-Å. Targeting Liver X Receptors in Cancer Therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Vedin, L.-L.; Steffensen, K.R. The Emerging Roles of Liver X Receptors and Their Ligands in Cancer. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2016, 20, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.; Coombes, R.C. Estrogen Receptor Alpha in Human Breast Cancer: Occurrence and Significance. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 2000, 5, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, V.C. Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulation: Concept and Consequences in Cancer. Cancer Cell 2004, 5, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culig, Z.; Bartsch, G.; Bartsch, A. Antiandrogens in Prostate Cancer Endocrine Therapy. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2004, 4, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, J.R.; Tu, H.; Luk, A.; Repa, J.J.; Medina, J.C.; Li, L.; Schwendner, S.; Wang, S.; Thoolen, M.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; et al. Role of LXRs in Control of Lipogenesis. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 2831–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, A.; Udata, C.; Ott, E.; Hickey, L.; Burczynski, M.E.; Burghart, P.; Vesterqvist, O.; Meng, X. Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of Single Doses of LXR-623, a Novel Liver X-Receptor Agonist, in Healthy Participants. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2009, 49, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weikum, E.R.; Liu, X.; Ortlund, E.A. The Nuclear Receptor Superfamily: A Structural Perspective. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 1876–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinar, D.M.; Endo, N.; Rutledge, S.J.; Vogel, R.; Rodan, G.A.; Schmidt, A. NER, a New Member of the Gene Family Encoding the Human Steroid Hormone Nuclear Receptor. Gene 1994, 147, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Kokontis, J.M.; Hiipakka, R.A.; Liao, S. Ubiquitous Receptor: A Receptor That Modulates Gene Activation by Retinoic Acid and Thyroid Hormone Receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 10809–10813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teboul, M.; Enmark, E.; Li, Q.; Wikström, A.C.; Pelto-Huikko, M.; Gustafsson, J.A. OR-1, a Member of the Nuclear Receptor Superfamily That Interacts with the 9-Cis-Retinoic Acid Receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 2096–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuclear Receptors Nomenclature Committee. A unified nomenclature system for the nuclear receptor superfamily. Cell 1999, 97, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seol, W.; Choi, H.S.; Moore, D.D. Isolation of Proteins That Interact Specifically with the Retinoid X Receptor: Two Novel Orphan Receptors. Mol. Endocrinol. 1995, 9, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apfel, R.; Benbrook, D.; Salbert, G.; Pfahl, A.M. A Novel Orphan Receptor Specific for a Subset of Thyroid Hormone-Responsive Elements and Its Interaction with the Retinoid/Thyroid Hormone Receptor Subfamily. Mol. Cell Biol. 1994, 14, 7025–7035. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Willy, P.J.; Umesono, K.; Ong, E.S.; Evans, R.M.; Heyman, R.A.; Mangelsdorf, D.J. LXR, a Nuclear Receptor That Defines a Distinct Retinoid Response Pathway. Genes Dev. 1995, 9, 1033–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svensson, S.; Östberg, T.; Jacobsson, M.; Norström, C.; Stefansson, K.; Hallén, D.; Climent Johansson, I.; Zachrisson, K.; Ogg, D.; Jendeberg, L. Crystal Structure of the Heterodimeric Complex of LXRα and RXRβ Ligand-Binding Domains in a Fully Agonistic Conformation. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 4625–4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Färnegårdh, M.; Bonn, T.; Sun, S.; Ljunggren, J.; Ahola, H.; Wilhelmsson, A.; Gustafsson, J.-A.; Carlquist, M. The Three-Dimensional Structure of the Liver X Receptor Beta Reveals a Flexible Ligand-Binding Pocket That Can Accommodate Fundamentally Different Ligands. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 38821–38828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janowski, B.A.; Willy, P.J.; Devi, T.R.; Falckt, J.R.; Mangelsdorf, D.J. An Oxysterol Signalling Pathway Mediated by the Nuclear Receptor LXRα. Nature 1996, 383, 728–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janowski, B.A.; Grogan, M.J.; Jones, S.A.; Wisely, G.B.; Kliewer, S.A.; Corey, E.J.; Mangelsdorf, D.J. Structural requirements of ligands for the oxysterol liver X receptors LXRα and LXRβ. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plat, J.; Nichols, J.A.; Mensink, R.P. Plant Sterols and Stanols: Effects on Mixed Micellar Composition and LXR (Target Gene) Activation. J. Lipid Res. 2005, 46, 2468–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houck, K.A.; Borchert, K.M.; Hepler, C.D.; Thomas, J.S.; Bramlett, K.S.; Michael, L.F.; Burris, T.P. T0901317 Is a Dual LXR/FXR Agonist. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2004, 83, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitro, N.; Vargas, L.; Romeo, R.; Koder, A.; Saez, E. T0901317 Is a Potent PXR Ligand: Implications for the Biology Ascribed to LXR. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 1721–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, J.L.; Fivush, A.M.; Watson, M.A.; Galardi, C.M.; Lewis, M.C.; Moore, L.B.; Parks, D.J.; Wilson, J.G.; Tippin, T.K.; Binz, J.G.; et al. Identification of a Nonsteroidal Liver X Receptor Agonist through Parallel Array Synthesis of Tertiary Amines. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 1963–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, S.B.; McKilligin, E.; Pei, L.; Watson, M.A.; Collins, A.R.; Laffitte, B.A.; Chen, M.; Noh, G.; Goodman, J.; Hagger, G.N.; et al. Synthetic LXR Ligand Inhibits the Development of Atherosclerosis in Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 7604–7609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, E.; Matsuda, M.; Yamada, Y.; Tachibana, Y.; Shimomura, I.; Makishima, M. Induction of Intestinal ATP-Binding Cassette Transporters by a Phytosterol-Derived Liver X Receptor Agonist. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 36091–36098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinet, E.M.; Savio, D.A.; Halpern, A.R.; Chen, L.; Miller, C.P.; Nambi, P. Gene-Selective Modulation by a Synthetic Oxysterol Ligand of the Liver X Receptor. J. Lipid Res. 2004, 45, 1929–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaveny, C.A.; Griffett, K.; El-Gendy, B.E.-D.M.; Kazantzis, M.; Sengupta, M.; Amelio, A.L.; Chatterjee, A.; Walker, J.; Solt, L.A.; Kamenecka, T.M.; et al. Broad Anti-Tumor Activity of a Small Molecule That Selectively Targets the Warburg Effect and Lipogenesis. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffett, K.; Welch, R.D.; Flaveny, C.A.; Kolar, G.R.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Burris, T.P. The LXR Inverse Agonist SR9238 Suppresses Fibrosis in a Model of Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Mol. Metab. 2015, 4, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffett, K.; Solt, L.A.; El-Gendy, B.E.-D.M.; Kamenecka, T.M.; Burris, T.P. A Liver-Selective LXR Inverse Agonist That Suppresses Hepatic Steatosis. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaboga, H.; Huang, W.; Srivastava, S.; Widmann, S.; Addanki, S.; Gamage, K.T.; Mazhar, Z.; Ebalunode, J.O.; Briggs, J.M.; Gustafsson, J.-Å.; et al. Screening of Focused Compound Library Targeting Liver X Receptors in Pancreatic Cancer Identified Ligands with Inverse Agonist and Degrader Activity. ACS Chem. Biol. 2020, 15, 2916–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viennois, E.; Mouzat, K.; Dufour, J.; Morel, L.; Lobaccaro, J.-M.; Baron, S. Selective Liver X Receptor Modulators (SLiMs): What Use in Human Health? Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2012, 351, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calkin, A.C.; Tontonoz, P. Transcriptional Integration of Metabolism by the Nuclear Sterol-Activated Receptors LXR and FXR. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buñay, J.; Fouache, A.; Trousson, A.; de Joussineau, C.; Bouchareb, E.; Zhu, Z.; Kocer, A.; Morel, L.; Baron, S.; Lobaccaro, J.-M.A. Screening for Liver X Receptor Modulators: Where Are We and for What Use? Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 3277–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.K.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, Y.C.; Cheong, J.; Lee, J.W. Silencing Mediator of Retinoic Acid and Thyroid Hormone Receptors, as a Novel Transcriptional Corepressor Molecule of Activating Protein-1, Nuclear Factor-kappaB, and Serum Response Factor. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 12470–12474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Li, S.; Wu, J.; Xia, C.; Lala, D.S. Liver X Receptors Interact with Corepressors to Regulate Gene Expression. Mol. Endocrinol. Baltim. Md 2003, 17, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabbi, C.; Warner, M.; Gustafsson, J.-Å. Action Mechanisms of Liver X Receptors. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 446, 647–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakobsson, T.; Treuter, E.; Gustafsson, J.-Å.; Steffensen, K.R. Liver X Receptor Biology and Pharmacology: New Pathways, Challenges and Opportunities. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 33, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boergesen, M.; Pedersen, T.Å.; Gross, B.; Van Heeringen, S.J.; Hagenbeek, D.; Bindesbøll, C.; Caron, S.; Lalloyer, F.; Steffensen, K.R.; Nebb, H.I.; et al. Genome-Wide Profiling of Liver X Receptor, Retinoid X Receptor, and Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor α in Mouse Liver Reveals Extensive Sharing of Binding Sites. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 32, 852–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelcer, N.; Tontonoz, P. Liver X Receptors as Integrators of Metabolic and Inflammatory Signaling. J. Clin. Invest. 2006, 116, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derangère, V.; Chevriaux, A.; Courtaut, F.; Bruchard, M.; Berger, H.; Chalmin, F.; Causse, S.Z.; Limagne, E.; Végran, F.; Ladoire, S.; et al. Liver X Receptor β Activation Induces Pyroptosis of Human and Murine Colon Cancer Cells. Cell Death Differ. 2014, 21, 1914–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peet, D.J.; Turley, S.D.; Ma, W.; Janowski, B.A.; Lobaccaro, J.-M.A.; Hammer, R.E.; Mangelsdorf, D.J. Cholesterol and bile acid metabolism are impaired in mice lacking the nuclear oxysterol receptor LXR alpha. Cell 1998, 93, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, C.; Walczak, R.; Dhamko, H.; Bradley, M.N.; Marathe, C.; Boyadjian, R.; Salazar, J.V.; Tontonoz, P. Constitutive Activation of LXR in Macrophages Regulates Metabolic and Inflammatory Gene Expression: Identification of ARL7 as a Direct Target. J. Lipid Res. 2011, 52, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerin, I.; Dolinsky, V.W.; Shackman, J.G.; Kennedy, R.T.; Chiang, S.-H.; Burant, C.F.; Steffensen, K.R.; Gustafsson, J.-Å.; MacDougald, O.A. LXRβ Is Required for Adipocyte Growth, Glucose Homeostasis, and β Cell Function. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 23024–23031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korach-André, M.; Parini, P.; Larsson, L.; Arner, A.; Steffensen, K.R.; Gustafsson, J.-Å. Separate and Overlapping Metabolic Functions of LXRα and LXRβ in C57Bl/6 Female Mice. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 298, E167–E178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korach-André, M.; Archer, A.; Barros, R.P.; Parini, P.; Gustafsson, J.-Å. Both Liver-X Receptor (LXR) Isoforms Control Energy Expenditure by Regulating Brown Adipose Tissue Activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabbi, C.; Kim, H.-J.; Hultenby, K.; Bouton, D.; Toresson, G.; Warner, M.; Gustafsson, J.-Å. Pancreatic Exocrine Insufficiency in LXRβ−/− Mice Is Associated with a Reduction in Aquaporin-1 Expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 15052–15057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-J.; Fan, X.; Gabbi, C.; Yakimchuk, K.; Parini, P.; Warner, M.; Gustafsson, J.-Å. Liver X Receptor β (LXRβ): A Link between β-Sitosterol and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis–Parkinson’s Dementia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2094–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Schuster, G.U.; Hultenby, K.; Zhang, Q.; Andersson, S.; Gustafsson, J.-Å. Liver X Receptors in the Central Nervous System: From Lipid Homeostasis to Neuronal Degeneration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 13878–13883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solt, L.A.; Kamenecka, T.M.; Burris, T.P. LXR-Mediated Inhibition of CD4+ T Helper Cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindinger, C.; Hinton, D.R.; Kirwin, S.J.; Atkinson, R.D.; Burnett, M.E.; Bergmann, C.C.; Stohlman, S.A. Liver X Receptor Activation Decreases the Severity of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. J. Neurosci. Res. 2006, 84, 1225–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, S.B.; Bradley, M.N.; Castrillo, A.; Bruhn, K.W.; Mak, P.A.; Pei, L.; Hogenesch, J.; O’Connell, R.M.; Cheng, G.; Saez, E.; et al. LXR-Dependent Gene Expression Is Important for Macrophage Survival and the Innate Immune Response. Cell 2004, 119, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valledor, A.F.; Hsu, L.-C.; Ogawa, S.; Sawka-Verhelle, D.; Karin, M.; Glass, C.K. Activation of Liver X Receptors and Retinoid X Receptors Prevents Bacterial-Induced Macrophage Apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 17813–17818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birrell, M.A.; Catley, M.C.; Hardaker, E.; Wong, S.; Willson, T.M.; McCluskie, K.; Leonard, T.; Farrow, S.N.; Collins, J.L.; Haj-Yahia, S.; et al. Novel Role for the Liver X Nuclear Receptor in the Suppression of Lung Inflammatory Responses. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 31882–31890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smoak, K.; Madenspacher, J.; Jeyaseelan, S.; Williams, B.; Dixon, D.; Poch, K.R.; Nick, J.A.; Worthen, G.S.; Fessler, M.B. Effects of Liver X Receptor Agonist Treatment on Pulmonary Inflammation and Host Defense. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 3305–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swyer, G.I.M. The Cholesterol Content of Normal and Enlarged Prostates. Cancer Res. 1942, 2, 372–375. [Google Scholar]
- Sporer, A.; Brill, D.R.; Schaffner, C.P. Epoxycholesterols in Secretions and Tissues of Normal, Benign, and Cancerous Human Prostate Glands. Urology 1982, 20, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettinger, S.L.; Sobel, R.; Whitmore, T.G.; Akbari, M.; Bradley, D.R.; Gleave, M.E.; Nelson, C.C. Dysregulation of Sterol Response Element-Binding Proteins and Downstream Effectors in Prostate Cancer during Progression to Androgen Independence. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 2212–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuchi, J.; Kokontis, J.M.; Hiipakka, R.A.; Chuu, C.; Liao, S. Antiproliferative Effect of Liver X Receptor Agonists on LNCaP Human Prostate Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 7686–7689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Sun, L.; Yang, X.; Ma, X.; Li, Q.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Li, X.; Xiang, R.; et al. Activation of Liver X Receptor Inhibits the Development of Pulmonary Carcinomas Induced by 3-Methylcholanthrene and Butylated Hydroxytoluene in BALB/c Mice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Miao, Y.; Wu, W.; Li, Y.; D’Errico, F.; Su, W.; Burns, A.R.; Huang, B.; Maneix, L.; Warner, M.; et al. Ablation of Liver X Receptors α and β Leads to Spontaneous Peripheral Squamous Cell Lung Cancer in Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 7614–7619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geyeregger, R.; Shehata, M.; Zeyda, M.; Kiefer, F.W.; Stuhlmeier, K.M.; Porpaczy, E.; Zlabinger, G.J.; Jäger, U.; Stulnig, T.M. Liver X Receptors Interfere with Cytokine-Induced Proliferation and Cell Survival in Normal and Leukemic Lymphocytes. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2009, 86, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, J.R.; Wang, Q.; Tanno, T.; Rasheed, Z.; Merchant, A.; Ghosh, N.; Borrello, I.; Huff, C.A.; Parhami, F.; Matsui, W. Activation of Liver X Receptors Inhibits of Hedgehog Signaling, Clonogenic Growth, and Self-Renewal in Multiple Myeloma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 1873–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, P.V.; Glantz, S.T.; Scotland, S.; Kasner, M.T.; Carroll, M. Induced Differentiation of Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells by Activation of Retinoid X and Liver X Receptors. Leukemia 2014, 28, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wu, B. LXR Agonist Regulates the Proliferation and Apoptosis of Human T-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Cells via the SOCS3 Pathway. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 78, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, D.; Reinitz, F.; Youssef, M.; Hong, C.; Nathanson, D.; Akhavan, D.; Kuga, D.; Amzajerdi, A.N.; Soto, H.; Zhu, S.; et al. An LXR Agonist Promotes Glioblastoma Cell Death through Inhibition of an EGFR/AKT/SREBP-1/LDLR-Dependent Pathway. Cancer Discov. 2011, 1, 442–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa, G.R.; Hulce, J.J.; Zanca, C.; Bi, J.; Ikegami, S.; Cahill, G.L.; Gu, Y.; Lum, K.M.; Masui, K.; Yang, H.; et al. An LXR-Cholesterol Axis Creates a Metabolic Co-Dependency for Brain Cancers. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, F.; Wei, J.; Ding, P.; Zhou, H.; Gu, Q.; et al. Discovery of New LXRβ Agonists as Glioblastoma Inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 194, 112240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.; Ahmad, F.; Kambach, D.M.; Sun, Q.; Halim, A.S.; Kramp, T.; Camphausen, K.A.; Stommel, J.M. LXRβ Controls Glioblastoma Cell Growth, Lipid Balance, and Immune Modulation Independently of ABCA1. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuchi, J.; Hiipakka, R.A.; Kokontis, J.M.; Hsu, S.; Ko, A.L.; Fitzgerald, M.L.; Liao, S. Androgenic Suppression of ATP-Binding Cassette Transporter A1 Expression in LNCaP Human Prostate Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 7682–7685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vedin, L.-L.; Lewandowski, S.A.; Parini, P.; Gustafsson, J.-Å.; Steffensen, K.R. The Oxysterol Receptor LXR Inhibits Proliferation of Human Breast Cancer Cells. Carcinogenesis 2009, 30, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen-Vu, T.; Vedin, L.-L.; Liu, K.; Jonsson, P.; Lin, J.Z.; Candelaria, N.R.; Candelaria, L.P.; Addanki, S.; Williams, C.; Gustafsson, J.-Å.; et al. Liver × Receptor Ligands Disrupt Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation through an E2F-Mediated Mechanism. Breast Cancer Res. 2013, 15, R51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roz, A.E.; Bard, J.-M.; Huvelin, J.-M.; Nazih, H. LXR Agonists and ABCG1-Dependent Cholesterol Efflux in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells: Relation to Proliferation and Apoptosis. Anticancer Res. 2012, 32, 3007–3013. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gong, H.; Guo, P.; Zhai, Y.; Zhou, J.; Uppal, H.; Jarzynka, M.J.; Song, W.-C.; Cheng, S.-Y.; Xie, W. Estrogen Deprivation and Inhibition of Breast Cancer Growth in Vivo through Activation of the Orphan Nuclear Receptor Liver X Receptor. Mol. Endocrinol. 2007, 21, 1781–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premaratne, A.; Ho, C.; Basu, S.; Khan, A.F.; Bawa-Khalfe, T.; Lin, C.-Y. Liver X Receptor Inverse Agonist GAC0001E5 Impedes Glutaminolysis and Disrupts Redox Homeostasis in Breast Cancer Cells. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haugen, M.H.; Von Der Lippe Gythfeldt, H.; Egeland, E.V.; Svartdal Normann, L.; Pandya, A.D.; Vedin, L.; Juell, S.; Tenstad, E.; Øy, G.F.; Kristian, A.; et al. Liver X Receptors Induce Antiproliferative Effects in Basal-like Breast Cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2023, 17, 2041–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, K.J.; Valfort, A.-C.; Steinauer, N.; Chatterjee, A.; Abuirqeba, S.; Majidi, S.; Sengupta, M.; Di Paolo, R.J.; Shornick, L.P.; Zhang, J.; et al. LXR-Inverse Agonism Stimulates Immune-Mediated Tumor Destruction by Enhancing CD8 T-Cell Activity in Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Hou, Y.; Wang, K.; Cheng, Y.; Pu, X.; Ye, X. The LXR-623-Induced Long Non-Coding RNA LINC01125 Suppresses the Proliferation of Breast Cancer Cells via PTEN/AKT/P53 Signaling Pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, M.T.; Ponce, C.; Santos, J.M.; Sufian, H.B.; Al-Harrasi, A.; Gollahon, L.S.; Hussain, F.; Rahman, S.M. VD3 and LXR Agonist (T0901317) Combination Demonstrated Greater Potency in Inhibiting Cholesterol Accumulation and Inducing Apoptosis via ABCA1-CHOP-BCL-2 Cascade in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 7771–7782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Sasso, G.; Bovenga, F.; Murzilli, S.; Salvatore, L.; Di Tullio, G.; Martelli, N.; D’Orazio, A.; Rainaldi, S.; Vacca, M.; Mangia, A.; et al. Liver X Receptors Inhibit Proliferation of Human Colorectal Cancer Cells and Growth of Intestinal Tumors in Mice. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 1497–1507.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savic, D.; Ramaker, R.C.; Roberts, B.S.; Dean, E.C.; Burwell, T.C.; Meadows, S.K.; Cooper, S.J.; Garabedian, M.J.; Gertz, J.; Myers, R.M. Distinct Gene Regulatory Programs Define the Inhibitory Effects of Liver X Receptors and PPARG on Cancer Cell Proliferation. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Ren, M.; Feng, F.; Chen, K.; Ju, X. Treatment of Colon Cancer with Liver X Receptor Agonists Induces Immunogenic Cell Death. Mol. Carcinog. 2018, 57, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Wang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Qi, G.; Xia, Q. Targeting the Transcription Factor Receptor LXR to Treat Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: Agonist or Inverse Agonist? Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Ni, Z.; He, J.; Li, X.; Li, B.; Zhao, K.; Yang, F.; Zeng, Y.; et al. Induction of SOCS3 by Liver X Receptor Suppresses the Proliferation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 64083–64094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, W.; Zhu, W.; Lin, J.; Luo, M.; Lin, Z.; Lu, L.; Jia, H.; Qin, L.; Lu, M.; Chen, J. Liver X Receptor Agonism Sensitizes a Subset of Hepatocellular Carcinoma to Sorafenib by Dual-Inhibiting MET and EGFR. Neoplasia 2019, 22, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Zhu, M.; Zheng, J.; Wang, C.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, S.; Yang, X.; Duan, Y.; et al. Liver X Receptor Agonists Exert Antitumor Effects against Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Inducing REPS2 Expression. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2023, 44, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Xia, S.; Liang, Y.; Ji, L.; Pan, Y.; Jiang, S.; Wan, Z.; Tao, L.; Chen, J.; Lin, C.; et al. LXR Activation Potentiates Sorafenib Sensitivity in HCC by Activating microRNA-378a Transcription. Theranostics 2020, 10, 8834–8850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Yang, T.; He, W.; Jiang, S.; Zhong, D.; Xu, Z.; Wei, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, C. Liver X Receptor Inhibits the Growth of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells via Regulating HULC/miR-134-5p/FOXM1 Axis. Cell. Signal. 2020, 74, 109720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morén, A.; Bellomo, C.; Tsubakihara, Y.; Kardassis, D.; Mikulits, W.; Heldin, C.-H.; Moustakas, A. LXRα Limits TGFβ-Dependent Hepatocellular Carcinoma Associated Fibroblast Differentiation. Oncogenesis 2019, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, T.; Li, Z.; Huang, X.; Lu, K.; Xie, W.; Zhou, Z.; Tu, J. TO901317 Inhibits the Development of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by LXRα/Glut1 Decreasing Glycometabolism. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2019, 316, G598–G607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Ma, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, M.; Li, X.; Xiang, R.; Miao, R.; Hajjar, D.P.; Duan, Y.; et al. Identification of Interferon-γ as a New Molecular Target of Liver X Receptor. Biochem. J. 2014, 459, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, R.; Cao, H.; Dong, S.; Shi, C.; Xu, X.; Ma, R.; Wu, J.; Feng, J. Liver X Receptor Agonist T0901317 Inhibits the Migration and Invasion of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells In Vivo and In Vitro. Anticancer. Drugs 2019, 30, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashiwagi, K.; Sato-Yazawa, H.; Ishii, J.; Kohno, K.; Tatsuta, I.; Miyazawa, T.; Takagi, M.; Chiba, H.; Yazawa, T. LXRβ Activation Inhibits the Proliferation of Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells by Depleting Cellular Cholesterol. Anticancer Res. 2022, 42, 2923–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.-J.; Shi, Y.; Shi, J.-F.; Yuan, Z.-H.; Ma, J.-Y.; Fang, S.-R.; Gu, W. Liver X Receptors Agonist T0901317 Downregulates Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Expression in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer by Repressing Nuclear Factor-κB. Anticancer. Drugs 2017, 28, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rough, J.J.; Monroy, M.A.; Yerrum, S.; Daly, J.M. Anti-Proliferative Effect of LXR Agonist T0901317 in Ovarian Carcinoma Cells. J. Ovarian Res. 2010, 3, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candelaria, N.R.; Addanki, S.; Zheng, J.; Nguyen-Vu, T.; Karaboga, H.; Dey, P.; Gabbi, C.; Vedin, L.-L.; Liu, K.; Wu, W.; et al. Antiproliferative Effects and Mechanisms of Liver X Receptor Ligands in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Widmann, S.; Ho, C.; Nguyen, D.; Nguyen, A.; Premaratne, A.; Gustafsson, J.-Å.; Lin, C.-Y. Novel Liver X Receptor Ligand GAC0001E5 Disrupts Glutamine Metabolism and Induces Oxidative Stress in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widmann, S.; Srivastava, S.; Lin, C.-Y. A Novel Liver X Receptor Inverse Agonist Impairs Cholesterol and Phospholipid Metabolism and Induces Apoptosis and Necroptosis in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Cells. Receptors 2023, 2, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Lai, X.; Ding, H.; Zhang, A.; Sun, Y.; Ling, J.; Chiao, P.J.; Chen, Z.; Xia, X. ATF4/TXNIP/REDD1/mTOR Signaling Mediates the Antitumor Activities of Liver X Receptor in Pancreatic Cancers. Cancer Innov. 2022, 1, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuu, C.; Chen, R.-Y.; Hiipakka, R.A.; Kokontis, J.M.; Warner, K.V.; Xiang, J.; Liao, S. The Liver X Receptor Agonist T0901317 Acts as Androgen Receptor Antagonist in Human Prostate Cancer Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 357, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youlin, K.; Li, Z.; Weiyang, H.; Jian, K.; Siming, L.; Xin, G. Liver X Receptor Activation Inhibits PC-3 Prostate Cancer Cells via the Beta-Catenin Pathway. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2017, 213, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Xu, J.; Fu, W. EGFR/FOXO3A/LXR-α Axis Promotes Prostate Cancer Proliferation and Metastasis and Dual-Targeting LXR-α/EGFR Shows Synthetic Lethality. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Feng, F.; Wang, J.; Ren, M.; Shi, Z.; Mao, X.; Zhang, H.; Ju, X. Liver X Receptor Activation Reduces Gastric Cancer Cell Proliferation by Suppressing Wnt Signalling via LXRβ Relocalization. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Qi, Y.-B. Activation of LXRβ Inhibits Proliferation, Promotes Apoptosis, and Increases Chemosensitivity of Gastric Cancer Cells by Upregulating the Expression of ATF4. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 14336–14347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, A.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, X.; Lin, Z.; Yuan, X. Liver X Receptor Activation Induces Apoptosis of Melanoma Cell through Caspase Pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2014, 14, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pencheva, N.; Buss, C.G.; Posada, J.; Merghoub, T.; Tavazoie, S.F. Broad-Spectrum Therapeutic Suppression of Metastatic Melanoma through Nuclear Hormone Receptor Activation. Cell 2014, 156, 986–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, W.; Yao, J.; Huang, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, W.; Chen, Z.; He, F.; Zhou, Z.; Yan, J. LXR Agonist Regulates the Carcinogenesis of PCa via the SOCS3 Pathway. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 33, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kneitz, B.; Krebs, M.; Kalogirou, C.; Schubert, M.; Joniau, S.; van Poppel, H.; Lerut, E.; Kneitz, S.; Scholz, C.J.; Ströbel, P.; et al. Survival in Patients with High-Risk Prostate Cancer Is Predicted by miR-221, Which Regulates Proliferation, Apoptosis, and Invasion of Prostate Cancer Cells by Inhibiting IRF2 and SOCS3. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 2591–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedin, L.; Gustafsson, J.; Steffensen, K.R. The Oxysterol Receptors Lxrα and Lxrβ Suppress Proliferation in the Colon. Mol. Carcinog. 2013, 52, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonnelle, D.; Luu, T.H.; Chaillou, C.; Huvelin, J.-M.; Bard, J.-M.; Nazih, H. LXR Activation Down-Regulates Lipid Raft Markers FLOT2 and DHHC5 in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 4067–4073. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ji, L.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, G. Liver X Receptor α (LXRα) Promoted Invasion and EMT of Gastric Cancer Cells by Regulation of NF-κB Activity. Hum. Cell 2017, 30, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.T.T.; Ishida, C.T.; Shang, E.; Shu, C.; Torrini, C.; Zhang, Y.; Bianchetti, E.; Sanchez-Quintero, M.J.; Kleiner, G.; Quinzii, C.M.; et al. Activation of LXRβ Inhibits Tumor Respiration and Is Synthetically Lethal with Bcl-xL Inhibition. EMBO Mol. Med. 2019, 11, e10769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pommier, A.J.C.; Alves, G.; Viennois, E.; Bernard, S.; Communal, Y.; Sion, B.; Marceau, G.; Damon, C.; Mouzat, K.; Caira, F.; et al. Liver X Receptor Activation Downregulates AKT Survival Signaling in Lipid Rafts and Induces Apoptosis of Prostate Cancer Cells. Oncogene 2010, 29, 2712–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Suárez, M.E.; Daimiel, L.; Villa-Turégano, G.; Pavón, M.V.; Busto, R.; Escolà-Gil, J.C.; Platt, F.M.; Lasunción, M.A.; Martínez-Botas, J.; Gómez-Coronado, D. Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs) Affect Cholesterol Homeostasis through the Master Regulators SREBP and LXR. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 141, 111871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.H.; Lee, G.Y.; Kim, J.I.; Ham, M.; Won Lee, J.; Kim, J.B. Inhibitory Effect of LXR Activation on Cell Proliferation and Cell Cycle Progression through Lipogenic Activity. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 3425–3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Zhang, B.; Cao, Z.; Xu, X.; Huo, Z.; Zhang, P.; Xiang, S.; Zhao, Z.; Lv, C.; Meng, M.; et al. The Lipogenic LXR-SREBF1 Signaling Pathway Controls Cancer Cell DNA Repair and Apoptosis and Is a Vulnerable Point of Malignant Tumors for Cancer Therapy. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 2433–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pencheva, N.; Tran, H.; Buss, C.; Huh, D.; Drobnjak, M.; Busam, K.; Tavazoie, S.F. Convergent Multi-miRNA Targeting of ApoE Drives LRP1/LRP8-Dependent Melanoma Metastasis and Angiogenesis. Cell 2012, 151, 1068–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, M.; Rashid, A.; Wang, Y.; Jain, A.; Li, D.; Behari, A.; Kapoor, V.K.; Koay, E.J.; Chang, P.; Vauthey, J.N.; et al. RNA Sequencing-Based Analysis of Gallbladder Cancer Reveals the Importance of the Liver X Receptor and Lipid Metabolism in Gallbladder Cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 35302–35312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, P.E.; Cirrito, J.R.; Wesson, D.W.; Daniel Lee, C.Y.; Karlo, J.C.; Zinn, A.E.; Casali, B.T.; Restivo, J.L.; Goebel, W.D.; James, M.J.; et al. ApoE-Directed Therapeutics Rapidly Clear β-Amyloid and Reverse Deficits in AD Mouse Models. Science 2012, 335, 1503–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragnev, K.H.; Petty, W.J.; Shah, S.J.; Lewis, L.D.; Black, C.C.; Memoli, V.; Nugent, W.C.; Hermann, T.; Negro-Vilar, A.; Rigas, J.R.; et al. A Proof-of-Principle Clinical Trial of Bexarotene in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 1794–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteva, F.J.; Glaspy, J.; Baidas, S.; Laufman, L.; Hutchins, L.; Dickler, M.; Tripathy, D.; Cohen, R.; DeMichele, A.; Yocum, R.C.; et al. Multicenter Phase II Study of Oral Bexarotene for Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.-T.; Li, Z.-Y.; Fan, J.; Li, P.-D.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Dai, X.-F. Liver X Receptors Agonist T0901317 Exerts Ferroptosis Sensitization in Cancer. Neoplasma 2022, 69, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Gong, H.; Khadem, S.; Lu, Y.; Gao, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Xie, W. Androgen Deprivation by Activating the Liver X Receptor. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 3778–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bensinger, S.J.; Bradley, M.N.; Joseph, S.B.; Zelcer, N.; Janssen, E.M.; Hausner, M.A.; Shih, R.; Parks, J.S.; Edwards, P.A.; Jamieson, B.D.; et al. LXR Signaling Couples Sterol Metabolism to Proliferation in the Acquired Immune Response. Cell 2008, 134, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waddington, K.E.; Robinson, G.A.; Rubio-Cuesta, B.; Chrifi-Alaoui, E.; Andreone, S.; Poon, K.-S.; Ivanova, I.; Martin-Gutierrez, L.; Owen, D.M.; Jury, E.C.; et al. LXR Directly Regulates Glycosphingolipid Synthesis and Affects Human CD4+ T Cell Function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2017394118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Du, X.; Tao, Z.; Jing, N.; Bao, S.; Gao, W.-Q.; Dong, B.; Fang, Y.-X. Taurine Inhibits Ferroptosis Mediated by the Crosstalk between Tumor Cells and Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Prostate Cancer. Adv. Sci. Weinh. Baden-Wurtt. Ger. 2024, 11, e2303894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbó, J.M.; León, T.E.; Font-Díaz, J.; De la Rosa, J.V.; Castrillo, A.; Picard, F.R.; Staudenraus, D.; Huber, M.; Cedó, L.; Escolà-Gil, J.C.; et al. Pharmacologic Activation of LXR Alters the Expression Profile of Tumor-Associated Macrophages and the Abundance of Regulatory T Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 968–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavazoie, M.F.; Pollack, I.; Tanqueco, R.; Ostendorf, B.N.; Reis, B.S.; Gonsalves, F.C.; Kurth, I.; Andreu-agullo, C.; Derbyshire, M.L.; Posada, J.; et al. LXR/ApoE Activation Restricts Innate Immune Suppression in Cancer. Cell 2018, 172, 825–840.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, G.; Yuan, H.; Jin, L.; Ranjit, S.; Panov, J.; Lu, X.; Levi, M.; Glazer, R.I. Reduction of Fibrosis and Immune Suppressive Cells in ErbB2-Dependent Tumorigenesis by an LXR Agonist. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebergall, S.R.; Angdisen, J.; Chan, S.H.; Chang, Y.; Osborne, T.F.; Koeppel, A.F.; Turner, S.D.; Schulman, I.G. Inflammation Triggers Liver X Receptor-Dependent Lipogenesis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2020, 40, e00364-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo-Umeda, K.; Nakashima, H.; Uno, S.; Toyoshima, S.; Umeda, N.; Komine-Aizawa, S.; Seki, S.; Makishima, M. Liver X Receptors Regulate Natural Killer T Cell Population and Antitumor Activity in the Liver of Mice. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villablanca, E.J.; Raccosta, L.; Zhou, D.; Fontana, R.; Maggioni, D.; Negro, A.; Sanvito, F.; Ponzoni, M.; Valentinis, B.; Bregni, M.; et al. Tumor-Mediated Liver X Receptor-α Activation Inhibits CC Chemokine Receptor-7 Expression on Dendritic Cells and Dampens Antitumor Responses. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noghero, A.; Perino, A.; Seano, G.; Saglio, E.; Lo Sasso, G.; Veglio, F.; Primo, L.; Hirsch, E.; Bussolino, F.; Morello, F. Liver X Receptor Activation Reduces Angiogenesis by Impairing Lipid Raft Localization and Signaling of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor-2. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 2280–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premaratne, A.; Basu, S.; Bagchi, A.; Zhou, T.; Feng, Q.; Lin, C.-Y. Liver X Receptor Ligand GAC0001E5 Downregulates Antioxidant Capacity and ERBB2/HER2 Expression in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Cells. Cancers 2024, 16, 1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Sarhadi, M.; Song, X.; Xue, J.; Dai, Y.; Gustafsson, J.-A. Liver X Receptors and Estrogen Receptor β, Two Players in a Rare Subtype of NSCLC. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 19, 2848–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Wu, W.; Dai, Y.; Warner, M.; Nalvarte, I.; Antonson, P.; Varshney, M.; Gustafsson, J.-Å. Loss of ERβ in Aging LXRαβ Knockout Mice Leads to Colitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuu, C.-P.; Lin, H.-P. Antiproliferative Effect of LXR Agonists T0901317 and 22(R)-Hydroxycholesterol on Multiple Human Cancer Cell Lines. Anticancer Res. 2010, 30, 3643–3648. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Cao, H.; Chen, D.; Yu, S.; Sha, H.; Wu, J.; Ma, R.; Wang, Z.; Jing, C.; Zhang, J.; et al. LXR Ligands Induce Apoptosis of EGFR-TKI-Resistant Human Lung Cancer Cells In Vitro by Inhibiting Akt-NF-κB Activation. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 7168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, T.; Grillot, D.; Billheimer, J.T.; Briand, F.; Delerive, P.; Huet, S.; Rader, D.J. Tissue-Specific Liver X Receptor Activation Promotes Macrophage Reverse Cholesterol Transport In Vivo. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, T.K.; Willems, S.; Arp, C.J.; Morstein, J.; Haake, C.T.; Merk, D.; Trauner, D. Development of Light-Activated LXR Agonists. ChemMedChem 2023, 18, e202200647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lianto, P.; Hutchinson, S.A.; Moore, J.B.; Hughes, T.A.; Thorne, J.L. Characterization and Prognostic Value of LXR Splice Variants in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. iScience 2021, 24, 103212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.; Shen, X. LXR Activation Radiosensitizes Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer by Restricting Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 528, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Yu, S.; Chen, D.; Jing, C.; Wang, Z.; Ma, R.; Liu, S.; Ni, J.; Feng, J.; Wu, J. Liver X Receptor Agonist T0901317 Reverses Resistance of A549 Human Lung Cancer Cells to EGFR-TKI Treatment. FEBS Open Bio 2017, 7, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zang, J.; Cao, H.; Wu, Y.; Yan, D.; Qin, X.; Zhou, L.; Fan, F.; Ni, J.; Xu, X.; et al. Liver X Receptors Agonist GW3965 Re-Sensitizes Gefitinib-Resistant Human Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cell to Gefitinib Treatment by Inhibiting NF-κB In Vitro. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 15802–15814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Zang, J.; Qin, X.; Yan, D.; Cao, H.; Zhou, L.; Ni, J.; Yu, S.; Wu, J.; Feng, J.-F. Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition Correlates with Gefitinib Resistance in NSCLC Cells and the Liver X Receptor Ligand GW3965 Reverses Gefitinib Resistance through Inhibition of Vimentin. OncoTargets Ther. 2017, 10, 2341–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Shen, B.; Qin, X.; Liu, S.; Feng, J. Akt/mTOR and AMPK Signaling Pathways Are Responsible for Liver X Receptor Agonist GW3965-Enhanced Gefitinib Sensitivity in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Lines. Transl. Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Primary Site | Type of Cancer | Expressed LXR | LXR Ligand | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blood | ALL, AML, CLL, Multiple Myeloma | LXRα, LXRβ | GW3965, T0901317 | [63,64,65,66] |
| Brain | Glioblastoma | LXRβ | GW3965, LXR-623 | [67,68,69,70] |
| Breast | Ductal carcinoma, Adenocarcinoma | LXRα, LXRβ | GW3965, T0901317, SR9243, GAC0001E5, LXR-623 | [71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80] |
| Colon | Adenocarcinoma, Carcinoma | LXRα, LXRβ | GW3965, T0901317, SR9243 | [29,81,82,83] |
| Kidney | Carcinoma | LXRα, LXRβ | SR9243, LXR-623 | [84] |
| Liver | Carcinoma | LXRα, LXRβ | GW3965, T0901317 | [85,86,87,88,89,90,91] |
| Lung | Adenocarcinoma | LXRα, LXRβ | T0901317, SR9243 | [29,92,93,94,95] |
| Ovaries | Carcinoma | LXRα, LXRβ | T0901317 | [96] |
| Pancreas | Adenocarcinoma | LXRβ | GW3965, T0901317, SR9243, GAC0001E5, GAC0003A4 | [29,32,97,98,99,100] |
| Prostate | Carcinoma | LXRα, LXRβ | GW3965, T0901317, SR9243 | [29,60,101,102,103] |
| Stomach | Adenocarcinoma | LXRβ | GW3965, T0901317 | [104,105] |
| Skin | Melanoma | LXRβ | GW3965, T0901317 | [106,107] |
| Cancer Hallmark | Activity | Cancer Type | Downstream Genes | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
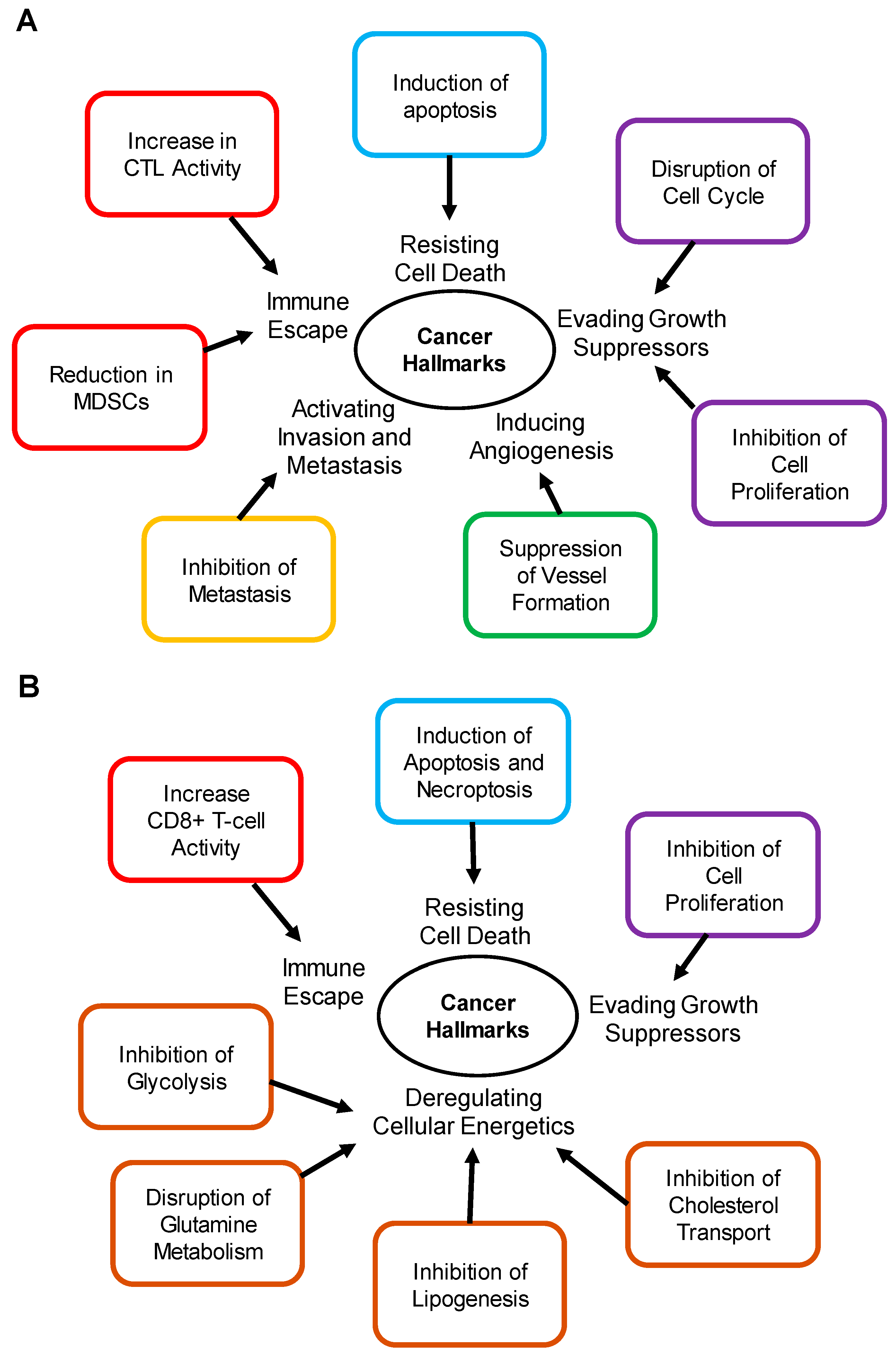
| Activating Invasion and Metastasis | Inhibition of Metastasis | Prostate, Murine melanoma, Murine breast | APOE, LRP1, LRP8, CDKN1B, CDKN1A, CDH1, CDH2 | [61,103,118] |
| Evading Growth Suppressors | Inhibition of Cell Proliferation | Breast, Cervical, Epidermoid carcinoma, Glioblastoma, Hepatoma, Lung, Melanoma, Multiple myeloma, Osteosarcoma, Pancreas, Prostate, Squamous carcinoma | ABCA1, ABCG1, SREBP1-c, IDOL, LDLR | [60,64,67,72,73,101,138] |
| Immune Escape | Increase in CTL Activity | Murine melanoma | Unknown | [129] |
| Reduction in MDSCs | Murine melanoma | APOE, LRP8 | [129] | |
| Inducing Angiogenesis | Suppression of Vessel Formation | Endothelial cells, Murine melanoma | ABCA1, ABCG1, CETP, SREBP1-c, IDOL, LDLR, APOE, LRP8 | [118,134] |
| Resisting Cell Death | Induction of Apoptosis | Breast, Gastric, Lung, Prostate, Murine melanoma | ABCA1, ABCG1, AKT, ATF4, NF-κB, CHOP, BAX, BCL-2 | [74,80,105,106,114,139] |
| Cancer Hallmark | Activity | Cancer Type | Downstream Genes | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deregulating Cellular Energetics | Inhibition of Cholesterol Metabolism | Pancreas | ABCA1, ABCG1 | [99] |
| Inhibition of Lipogenesis | Breast, Lung, Prostate | SREBP1c, FASN, ACC, SCD1 | [14,29] | |
| Disruption of Glutamine Metabolism | Breast, Pancreas | GOT1, GOT2, GLUD1, GLS1, SLC7A11 | [14,76,98] | |
| Inhibition of Glycolysis | Colon, Lung, Prostate | GCK1, PFK1, PFK2 | [29] | |
| Evading Growth Suppressors | Inhibition of Cell Proliferation | Breast, Pancreas | SREBP1c, FASN, ACC, SCD1, ABCA1, ABCG1 | [32,76] |
| Immune Escape | Increase CD8+ T-cell Activity | Triple negative breast cancer (C57BL6J Mouse CD4+ and CD8+ T cells) | Unknown | [78] |
| Resisting Cell Death | Induction of Apoptosis and Necroptosis | Colon, Lung, Pancreas, Prostate | Unknown | [29,99] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Premaratne, A.; Bagchi, A.; Basu, S.; Gustafsson, J.-Å.; Lin, C.-Y. Targeting Liver X Receptors in Cancer Drug Discovery. Receptors 2024, 3, 304-322. https://doi.org/10.3390/receptors3030015
Premaratne A, Bagchi A, Basu S, Gustafsson J-Å, Lin C-Y. Targeting Liver X Receptors in Cancer Drug Discovery. Receptors. 2024; 3(3):304-322. https://doi.org/10.3390/receptors3030015
Chicago/Turabian StylePremaratne, Asitha, Abhinav Bagchi, Shinjini Basu, Jan-Åke Gustafsson, and Chin-Yo Lin. 2024. "Targeting Liver X Receptors in Cancer Drug Discovery" Receptors 3, no. 3: 304-322. https://doi.org/10.3390/receptors3030015
APA StylePremaratne, A., Bagchi, A., Basu, S., Gustafsson, J.-Å., & Lin, C.-Y. (2024). Targeting Liver X Receptors in Cancer Drug Discovery. Receptors, 3(3), 304-322. https://doi.org/10.3390/receptors3030015







