Abstract
Neuroinflammation is considered to be a significant component in a range of neuropathologies. Unfortunately, whilst its role is well recognised, the options for therapeutic intervention are limited. As such, there is a need to identify novel targets in order to increase treatment options. Given its role as both a neurotransmitter and an immune modulator, substance P (SP) and its NK1 receptor (NK1R) have been widely studied as a potential therapeutic target. There is evidence that NK1R antagonists may exert beneficial effects in a range of conditions, including traumatic brain injury and stroke. Blocking the NK1R has been shown to reduce blood–brain barrier dysfunction, reduce cerebral oedema, and reduce the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines. These actions are associated with improved survival and functional outcomes. The NK1R has also been shown to be involved in the inflammatory reaction to CNS infection, and hence antagonists may have some benefit in reducing infection-driven inflammation. However, the NK1R may also play a role in the host immune response to infection, and so here, the potential beneficial and detrimental effects need to be carefully balanced. The purpose of this review is to provide a summary of evidence for the involvement of the NK1R in acute CNS inflammation, particularly in the context of traumatic brain injury and stroke.
1. Introduction
A major advance in our understanding of central nervous system disorders has been the recognition that inflammation plays a significant role in many acute and chronic conditions. The role of inflammation is clearly seen in relation to acute traumatic and ischaemic insults, as well as infection. However, it is also an important factor in the development of many chronic and neurodegenerative conditions, including multiple sclerosis, epilepsy, Alzheimer’s, and Parkinson’s disease [1]. Collectively, neuroinflammatory conditions represent a major healthcare challenge, both in terms of their social and economic impact. Unfortunately, the common anti-inflammatory agents, namely steroids and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), as well as the newer immunosuppressive therapies, may have limited efficacy in managing this inflammation, or potentially significant side effects, or both [2,3,4,5]. Hence, there is a need to develop novel, targeted, and more effective anti-inflammatory or immune-modulatory therapies that may help manage these significant and prevalent conditions [6,7]. Given the role that substance P (SP) and the NK1 receptor (NK1R) appear to play in neurogenic inflammation in peripheral tissues, there has been an interest in seeing whether the NK1R may represent a novel target to manage acute neuroinflammatory responses in the CNS [8,9].
The neuropeptide SP, a member of the tachykinin family of peptides, and its preferred receptor, the NK1R, are widely distributed throughout the body and exhibit a wide range of biological activities [10]. The NK1R is a seven-transmembrane domain G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR). Depending on the cell location, the effects of NK1R stimulation range from causing smooth muscle contraction, and increasing vascular permeability, to influencing learning, memory, and mood [10]. That wide range of biological responses associated with NK1R activation reflects the tissue-specific differences in the signal transduction pathways through which receptor signals. The NK1R may activate the phospholipase C (PLC) pathway, increasing the concentration of intracellular free Ca2+ ions and activating protein kinase C (PKC). The NK1R may also activate adenylyl cyclase (AC), leading to the formation of cAMP, and activation of protein kinase A (PKA). In addition, the receptor may activate phospholipase A2, liberating arachidonic acid, and leading to the production of prostaglandins, leukotrienes, and thromboxane. In terms of inflammation, activation of the PLC pathway leads to phosphorylation of PKC. Phosphorylated PKC in turn can activate members of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade, including the extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 and p38 MAPK, thereby activating the transcription factor, nuclear factor-κB (NFκB), leading to the production of key pro-inflammatory cytokines [10,11].
GPCRs, like the NK1R, primarily function as cell surface receptors, responding to extracellular signals. However, following activation, they combine with β-arrestins, which terminates cell surface signaling and helps convey the ligand-receptor complex to endosomes. This receptor internalisation was once merely considered a mechanism for GPCR trafficking, but it is now recognised that endosomes are also a vital site of cell signaling [12]. The β-arrestins can act as signaling scaffolds for many pathways, including the MAPK pathway [10]. There is evidence that SP-NK1R signaling from endosomes can induce sustained excitation of spinal neurons, potentiating pain transmission [13].
In relation to NK1R signaling, it is also recognised that there are two naturally occurring isoforms of the NK1R, a full-length isoform consisting of 407 amino acid (AA) residues, and a truncated one comprising only 311 AA residues. Critically, those 96 AAs form the normal C-terminus of the receptor [14]. Given the role of the C-terminus in GPCR coupling to effector mechanisms, the two isoforms are functionally distinct. Although the SP binding site is identical in both isoforms, the full-length form has a higher affinity binding for SP [15]. In terms of effector coupling, cells expressing the full-length NK1R will activate NF-κB and increase IL-8 expression, while cells expressing the truncated isoform do not activate NF-κB, and decreased IL-8 expression is seen [14]. The truncated NK1R also lacks the phosphorylation sites that are necessary for high-affinity β-arrestin binding, impacting receptor internalisation and endosomal signaling. These differences may have implications for NK1R signaling in pathological situations where upregulation of the truncated receptor has been observed [16].
2. Inflammation in the Central Nervous System
Both naturally, and clinically, there is a need to maintain the beneficial aspects of inflammation (e.g., defense against pathogens, tissue healing, etc.) while at the same time, limiting the detrimental aspects (i.e., tissue injury, chronic inflammation) [17,18,19]. Balancing these opposing effects of inflammation within the CNS is even more critical than in the periphery. As in the periphery, uncontrolled activation of CNS inflammatory responses can progress to detrimental, chronic inflammation. With traumatic brain injury, stroke, and infection, excessive acute inflammatory responses are known to contribute to secondary injury processes such as cerebral oedema and raised intracranial pressure [3,20]. In addition, there is growing evidence to suggest that excessive neuroinflammation associated with these acute events can play an active role in the progression of neurodegenerative conditions, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. Hence, there may be clinical value in being able to ameliorate acute CNS inflammation [21,22,23,24].
In terms of immune and inflammatory responses, the CNS was historically viewed as being immunoprivileged, with the notion that it was shielded from the peripheral immune system by the blood–brain barrier (BBB) [21]. Allied to that, within the CNS glial cells were known to provide dedicated immune function, engaging in inflammatory responses that serve to defend the CNS against pathogens, as well as aid in its recovery from insult and injury. However, by nature, the immune response provided by the resident glial cells is an innate response. In contrast to the periphery, in the healthy state, there is no dendritic cell-like activity to prime T cells and mount an adaptive response [25].
In terms of glial immune function, microglia are a key component in the capacity of the CNS to mount an acute immune response [26,27]. As the most motile cells in the CNS, they are active in immune surveillance and, along with perivascular macrophages, represent the phagocytic cells of the CNS [27,28,29]. Glial cells express a broad range of pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), including Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and receptors for advanced glycation end-products (RAGE). These receptors enable the detection of both infection (pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs)) and tissue trauma (damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs)) [25,28,30]. Astrocytes, the most numerous cell type in the CNS, play a key role in maintaining homeostatic balance in the brain, including BBB function [31]. However, they also express TLRs, and when activated, express a range of pro-inflammatory mediators through the activation of NFκB [25,32]. Crosstalk between astrocytes and microglia may also be an important aspect of regulating inflammatory responses [33]. The initial innate immune response mediated by the glial cells contributes to the acute inflammatory response [27] and, as in the periphery, that acute inflammatory response is primarily protective. Following activation, microglia may exhibit pro-inflammatory characteristics, but can then subsequently revert to an anti-inflammatory state, enabling repair and resolution [26,34,35]. However, severe insults, as may occur with strokes or TBI, can result in a neuroinflammatory response that is chronic and progressive [26]. In such situations, the microglia, rather than reverting to an anti-inflammatory phenotype after activation, may maintain pro-inflammatory characteristics, being designated as disease-associated microglia [34].
However, glial-mediated responses represent only part of the picture in terms of CNS inflammation. Instead of the BBB representing a physical barrier separating peripheral and glial immune responses, it is a dynamic, functional barrier that serves as an interface between the two [36]. It is this inflammatory response within the CNS, orchestrated by both glial cells and peripheral immune cells, that is referred to as neuroinflammation [26].
3. The Blood–Brain Barrier
The BBB, rather than being a physical barrier between the periphery and the CNS, is a functional and selective barrier, helping to maintain an optimal microenvironment for normal CNS function [36,37,38]. Under physiologic conditions, the BBB ensures constant supply of nutrients (oxygen, glucose, and other substances) for brain cells, while also shielding those cells from potentially toxic substances. The integrity of the BBB is a critical factor in maintaining brain homeostasis. Part of that homeostatic role is the regulation of immune and inflammatory responses. The BBB can guide inflammatory cells to respond to changes in a local environment, while exaggerated inflammatory responses may correlate with increased BBB permeability [38].
The BBB is composed of, and regulated by, complex interactions between a variety cell types. At its core are the vascular endothelial cells (VECs) with their specialised tight junctions which limit paracellular flow, enabling selective transcellular movement that is dependent on specific transporters and receptors [31,39]. Surrounding the VECs is a basement membrane along with astrocyte end-feet processes and pericytes. The astrocytic end-feet, which are closely associated with the VECs, also express specific, polarised transport molecules, including the water channel, aquaporin 4 (AQP4), which again play a role in the regulation solute and fluid movement that is characteristic of the BBB [40]. The astrocytes, through these end-foot processes, also provide a mechanism of communication between neurons and VECs [38,41]. The pericytes, which are embedded in the basement membrane of the cerebral vessels, have extensive contacts with the VECs, astrocyte end-feet, as well as perivascular microglia, macrophages, and neurons [42,43]. They are uniquely positioned, enabling them to integrate and coordinate signals from the neighboring cells in order to regulate blood–brain barrier permeability, promote angiogenesis, and promote inflammatory responses. Together, all these elements represent the functional neurovascular unit (NVU), a concept developed to encompass the anatomical and functional relationships between brain cells, both neurons and glial cells, and the cerebrovasculature. The precise relationship between these cells that constitute the NVU has been clearly detailed by a number of authors [39,44].
The NVU is considered to exert control over such functions as cerebral blood flow and immune responses [45]. The NVU is involved in neurovascular coupling, with the glial cells and neurons regulating cerebral vessel calibre in response to metabolic activity, enabling the matching of cerebral blood flow to neuronal activity [41,45]. Positioned at the interface between the systemic circulation and brain parenchyma, the NVU can monitor and respond to immune and inflammatory signals in both the systemic circulation and the CNS [42]. The concept of the NVU serving as a functional immune interface emphasises the range of cell types that may contribute to immune/inflammatory function in the CNS. In terms of responding to systemic influences, neuroinflammation may occur in response to systemic stimuli, such as sepsis [27]. Similarly, CNS pathologies may impact on BBB function [31]. Specifically, the VECs of the cerebrovasculature mediate changes in vascular permeability, as well as the expression and function of adhesion molecules, allowing for leukocyte transmigration [46,47,48]. The pericytes, lying in close contact with capillary endothelial cells, also have immunoregulatory functions which may enable the integration of CNS and peripheral immune and inflammatory responses [43,49]. They play an important role in maintaining BBB integrity, as well as controlling a number of aspects of CNS immune responses, including leukocyte extravasation [42,49]. Other vessel-associated immune cells include perivascular macrophages and vessel-associated microglia [29]. The numerous microglia that perform immune surveillance within the environment of the NVU are capable of producing a wide range of pro-inflammatory mediators that influence NVU function, and with that, BBB integrity [50]. Similarly, astrocytes have the capacity to detect pathogenic signals and respond by expressing pro-inflammatory mediators [27].
In terms of CNS inflammation, there appears to be a two-way relationship between BBB dysfunction and neuroinflammation. Altered BBB function may serve as a precursor for neuroinflammation, while neuroinflammation and altered NVU function, will impact BBB permeability and function [42]. BBB dysfunction is implicated in some of the most prevalent and significant neurological conditions, ranging from acute insults, such as trauma, ischaemia, and infection, through to chronic and neurodegenerative conditions, such as epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease [51]. Studies of systemic circulation indicate that perivascular nerves may play a role in mediating vascular inflammatory responses [52,53]. As a result, there was an interest in whether similar mechanisms may be involved in regulating BBB integrity and central inflammation [54,55,56].
4. Perivascular Innervation and Neurogenic Inflammation
The systemic vasculature is innervated by the peripheral nervous system, encompassing both autonomic and sensory nerves. The perivascular sensory nerves include the neuropeptide-containing nociceptive nerves, which release a range of neurotransmitters, including the amino acid transmitter, glutamate, and the neuropeptides, SP and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) [52]. They are also characterised by the expression of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) ion channels [57]. The peptide neurotransmitters are synthesised in the cell bodies of these neurons located in the dorsal root ganglia of the spinal cord, from where they are transported both centrally, and peripherally to the free nerve endings [58]. Activation of nociceptive nerves leads to peptide release from both the central and peripheral nerve terminals, conferring these nerves with a sensory-motor function involving local axon reflexes. The peripheral peptide release can provoke a potent vasodilator effect mediated by CGRP, as well as SP-mediated plasma extravasation [59]. This motor response may underlie the cutaneous “flare” reaction seen following injury, as well as hyperaemia and oedema in other tissues. It has been postulated that the sensory-motor function of these nerves could represent a mechanism to respond to tissue ischaemia, but it may also have a broader role in initiating immune and inflammatory responses following the detection of a noxious event [53,59].
Role of the NK1R in Neurogenic Inflammation
The term neurogenic inflammation is used to denote the role of sensory nerves in inflammatory responses [52,53]. There is considerable evidence to support SP and the NK1R playing a key role in mediating the vascular changes associated with neurogenic inflammation [60,61,62], as well as playing a broader role in the innate immune response [63,64,65]. SP increases vascular permeability and promotes oedema as a result of endothelial cell retraction and the formation of gaps between cells [64,66,67]. The NK1-mediated effects of SP on vascular endothelium appear to occur at the level of venules and capillaries [68]. SP also enhances leukocyte migration, through its effects on vascular and intracellular adhesion molecules, as well as matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) secretion [69,70,71]. In addition to its direct vascular effects, SP can also activate mast cells, leading to the release of other vasoactive mediators [72]. Mast cells have been shown to exist in close proximity to SP-containing nerve terminals [73]. Indeed, the literature also supports a broader role for SP in inflammation, such that SP is one of the earliest activators of NF κB in response to injury, and can increase the secretion of other pro-inflammatory mediators, including interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), elaborating the inflammatory response [63]. Beyond its neuronal expression, SP and the NK1R are expressed in a range of immune cells, including T lymphocytes, macrophages, and eosinophils, suggesting the potential for cross-talk between the immune and nervous systems [69,73,74]. For example, both in vitro and in vivo studies suggest a role for SP in neutrophil migration and activation at the site of inflammation [74].
The wealth of data supporting the role of perivascular sensory nerves, and in particular SP, in modulating immune and iκlammatory responses in the periphery, subsequently drove interest as to whether the same neuropeptides may be exerting a similar pro-iκlammatory action within the CNS [55].
5. Distribution of SP and the NK1R in the CNS
The initial characterisation of SP’s biological activity focused on its actions in peripheral tissues. However, it was soon recognised that SP and the NK1R were also both abundant and widespread within the CNS [11,75,76,77]. While some of that localisation, for example, the dorsal horn of the spinal cord is consistent with SP being associated with primary sensory nerve signaling, there is both anatomical and functional evidence that SP is involved in other CNS pathways [78]. While the presence of SP has been demonstrated in structures such as the cerebral cortex and cerebellum, more intense immunostaining has been observed in regions such as the amygdala, locus ceruleus, and hypothalamus [79]. There is also a reasonable correlation between the distribution of SP and the neuronal expression of the NK1R, with some of the highest levels of constitutive NK1R expression being associated with the putamen and caudate nuclei, and the limbic system. There is, to some extent, an anatomical mismatch in relation to the co-localisation of SP and NK1Rs in the CNS, raising the suggestion that SP may be involved in non-synaptic signaling, relying on local diffusion in the manner of an autocrine signal [80]. The high levels of expression of SP and the NK1R in the limbic and reticular activating systems led to the notion that SP may be involved in stress and emotional responses [81], which has been validated in preclinical studies demonstrating that NK1R antagonists may exert anxiolytic and antidepressant activity [82,83]. The potential for SP and the NK1R to play a role in depression is of interest, given the recognition that inflammation is associated with the development of depression [84]. However, the best clinical evidence to support the central activity of SP is the effective antiemetic action of the NK1R antagonists [85,86], which appears to correlate with the brainstem distribution of SP and the NK1R [87].
Within the CNS, there is a significant and widespread distribution of the NK1R. While some initial studies suggested that expression of the NK1R in the CNS was almost exclusively neuronal, with distinct labeling of neuronal dendrites and soma [80], there is strong evidence to suggest that it is also associated with non-neuronal cells, including endothelial cells, astrocytes and microglia [88].
As mentioned previously, there are two main, naturally occurring isoforms of the NK1R, the full-length and the truncated receptor [89]. In the study performed by Liu and colleagues [80], the antibody used was directed against the carboxyl terminal of the NK1 receptor, which would selectively label the full-length receptor isoform. This study demonstrated the association of the full-length isoform with neurons [90]. Glial cells have also been shown to express the full-length isoform [88]. However, there is evidence that the truncated isoform of the receptor is also expressed in the CNS [91]. However, in terms of constitutive expression, the long isoform appears to predominate in neurons and glial cells. Nonetheless, it is worth being aware that pro-inflammatory states, or pathologies, could influence the nature of NK1R expression [11,92]. In the periphery, the truncated NK1R isoform has been shown to be associated with immune cells, such as macrophages and lymphocytes. Importantly, in relation to this, this isoform requires higher SP concentrations in order to generate responses [53,55], whilst, unlike the full-length receptor, stimulation does not result in NFκB activation [14].
In terms of the neural regulation of vascular function, while there are similarities between the innervation of the cerebrovascular and systemic circulations, there are also clear distinctions. The superficial, or extracerebral vessels of the brain, are extrinsically innervated, including those receiving sensory innervation by the trigeminal nerve [93]. Indeed, there is good evidence to support the involvement of these nerves in migraine, with a particular focus on the role of CGRP [94]. However, the cerebrovasculature itself is “intrinsically” innervated by the central neurons that contribute to the function of the NVU [93]. Hence, for SP to be influencing the function of the cerebrovasculature and BBB, it would either have to be of central origin, and influence the function of the NVU, or else be in the circulation. The latter would rely on SP having a luminal influence on BBB integrity, for which there is little supporting evidence [56,95,96,97].
While SP and the NK1R have not been explicitly documented as being associated with the NVU, the expression of both the NK1R and SP in the cells that constitute the NVU has been clearly demonstrated (Figure 1). In addition to the neuronal expression of the NK1R, there is also constitutive and induced expression of NK1Rs associated with non-neuronal cells linked to CNS immune function.
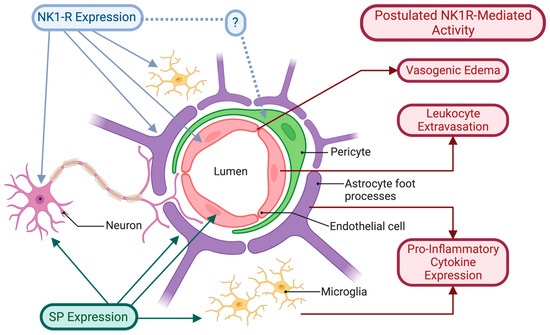
Figure 1.
NK1R and SP expression in the cells associated with the NVU. NK1Rs have been shown to be expressed in neurons, endothelial cells, astrocytes, and microglia. While NK1Rs have not been explicitly shown to be associated with pericytes, their embryological origin makes this a possibility. Similarly, SP expression is associated with neurons involved in neurovascular coupling, as well as with the vascular endothelium and glial cells, including astrocytes and microglia. The potential role of NK1R-mediated activity in acute CNS inflammation is summarised.
6. Non-Neuronal NK1 Receptor Activity in the CNS
As in the periphery, NK1Rs have been shown to be associated with the VECs of the cerebrovasculature, and in particular with post-capillary venules [46,92,98]. Through the use of selective NK1R antagonists, SP has been shown to mediate the increased endothelial permeability induced by pro-inflammatory mediators, such as TNF-α, as well as viral proteins [46,99]. In the same manner, NK1R antagonism can reduce the expression of endothelial adhesion molecules, thereby reducing the recruitment of inflammatory cells and their transmigration into the brain [71]. In addition, an autocrine feedback mechanism may be associated with these SP-mediated changes in endothelial function. Pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α and IL-1β, can stimulate the expression and release of SP from endothelial cells, which can in turn activate endothelial NK1Rs [46,100]. In addition, the expression of endothelial NK1Rs may also be influenced by an inflammatory state [92] which could establish a pro-inflammatory positive feedback mechanism.
In terms of glial cells, NK1Rs have been shown to be constitutively expressed by astrocytes, including human astrocytes [88,101]. Whilst more contentious following early studies, there is now a growing body of evidence to support the involvement of the NK1R in the activation of microglia as well [88,92,102]. Stimulation of the NK1R results in the activation of NFκB and an elaboration of inflammatory mediators [103,104]. Importantly, since we are considering immune and inflammatory responses, it is the full-length isoform of the receptor that is expressed in these cells [88,89]. In terms of cytokine production by astrocytes, the selective NK1R antagonist, SR 140333, has been shown to inhibit SP-induced cytokine production in cultured human astrocytes (U373MG cell line) [105]. However, a maximal pro-inflammatory response may rely on co-stimulation involving SP/NK1R activation together with the activity of other pro-inflammatory factors [102].
Although we are primarily concerned with the potential role of SP and the NK1R in promoting neuroinflammation, there is evidence that SP-containing interneurons can play a role in normal neurovascular coupling [106,107]. This would suggest that SP and the NK1R can contribute to the NVU function. However, it is the association of the NK1R with the cells that maintain and control BBB function that is of interest in terms of the potential to ameliorate both vasogenic oedema and neuroinflammatory responses [46]. While the intravenous administration of capsaicin and activation of TRPV1 were shown to affect vascular permeability in meningeal, but not cerebral vessels [95], activation of TRPV1 associated with the cerebral microvasculature does increase vessel permeability via SP [56]. TRPV1 has also been shown to play a role in BBB disruption following ischaemia-reperfusion injury [56]. The NK1R also has the potential to generate a significant positive feedback cycle in relation to neuroinflammation. The NK1R has been shown to not only activate resident glial cells but also stimulate infiltrating leukocytes, recruited through BBB disruption, in the same manner. SP-mediated activation of NF-κB will lead to the elaboration of inflammatory mediators, such as IL-1β [103,104]. In turn, this can lead to the upregulation of SP and NK1R expression [108,109], initiating a positive feedback cycle. Based on these observations, the NK1R appears to represent an important novel target for managing acute neuroinflammatory responses in the CNS. Indeed, there is a growing list of neuropathologies where there is evidence of a beneficial action of NK-1R antagonists (Table 1).
It is also worth noting that a substantial number of in vivo studies examining the role of SP and the NK1R have used N-acetyl-L-tryptophan (NAT) as an agent with assumed NK1R antagonist activity, primarily based on the reported activities of analogues of L-tryptophan [110]. Specific NK1R binding of NAT has not been characterised, and a recent publication has demonstrated a lack of NK1R binding by NAT [111]. However, an in silico screening assay for NK1R antagonist activity predicted that NAT would have favourable binding characteristics [112]. In line with the concerns raised by Matalinska and Lipinski [111], it is appropriate that further studies investigating the role of NK1R in neuropathologies should utilise selective NK1R antagonists. That said, there have also been in vivo studies where positive neuroprotective outcomes assigned to the supposed NK1-mediated action of NAT have subsequently been fully replicated with highly selective NK1 antagonists [113,114,115,116,117].

Table 1.
In vivo and cellular models where selective NK1R antagonists or NAT have been shown to ameliorate neuroinflammation and its associated consequences.
Table 1.
In vivo and cellular models where selective NK1R antagonists or NAT have been shown to ameliorate neuroinflammation and its associated consequences.
| CNS Pathology | Model | Drug | Mechanism of Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ischaemic Stroke | Rat—internal carotid A | SR140333 | Selective NK1 antagonist | Yu et al. [118] |
| Rat—transient middle cerebral (tMC) | NAT | ? NK1 antagonist? * | Turner et al. [116] | |
| Rat—tMC + tPA | NAT | ? NK1 antagonist? * | Turner et al. [119] | |
| Sheep—tMC | EU-C-001 | Selective NK1 antagonist | Sorby-Adams et al. [115] | |
| Rat—bilateral common carotid | Aprepitant | Selective NK1 antagonist | Kaur et al. [120] | |
| Traumatic Brain Injury | Rat—diffuse axonal injury | Capsaicin | TRPV1 agonist | Nimmo et al. [54] |
| Rat—diffuse axonal injury | NAT | ? NK1 antagonist? * | Donkin et al. [113] | |
| Rat—diffuse axonal injury | EU-C-001 | Selective NK1 antagonist | Hoffmann et al. [114] | |
| Rat—Blast injury and CTE | EU-C-001 | Selective NK1 antagonist | Corrigan et al. [121] | |
| Mouse—Cortical impact | L-733,060 | Selective NK1 antagonist | Li et al. [122] | |
| Sheep—Diffuse axonal injury | NAT | ? NK1 antagonist? * | Vink et al. [123,124] | |
| Hematoma | Mouse—intracerebral hemorrhage | Aprepitant | Selective NK1 antagonist | Jin et al. [125] |
| Spinal Cord Injury | Rat—contusion/compression SCI | EU-C-001 | Selective NK1 antagonist | Zheng et al. [126] |
| Rat—Autonomic dysreflexia SCI | GR205171 | Selective NK1 antagonist | Rupniak et al. [127] | |
| Bacterial Infection | Mouse—N. meningitidis and B. burgdorferi | L 703,606 | Selective NK1 antagonist | Chauhan et al. [102] |
| Mouse—S. pneumoniae | L 703,606 | Selective NK1 antagonist | Chauhan et al. [128] | |
| Primary mouse microglia—B. burgdorferi | L 703,606 | Selective NK1 antagonist | Rasley et al. [129] | |
| Viral Infection | Human mononuclear phagocytes—HIV | CP-96,345 | Selective NK1 antagonist | Lai et al. [130] |
| Microglia/macrophages—HIV | Aprepitant | Selective NK1 antagonist | Wang et al. [131] | |
| Peripheral blood monocytes—HIV | Aprepitant | Selective NK1 antagonist | Manak et al. [132] | |
| Mouse—WNV neuroinvasive disease | Ro 67,5930 | Selective NK1 antagonist | Ronca et al. [133] | |
| Parasitic Infection | Mouse—Trypanosoma brucei brucei | RP 67,580 | Selective NK1 antagonist | Kennedy et al. [134] |
* As discussed, the precise mechanism of action of NAT remains to be determined.
7. NK1R and SP Activity in Models of Acute CNS Inflammation
Acute CNS inflammation is associated with infection (bacterial, viral & parasitic), as well as autoimmune reactions, trauma, and ischaemia [11,21]. Although there are significant differences in relation to the primary insult, there is a broad evidence base to support the role of the NK1R in the associated inflammatory response, as well as the potential benefit of antagonising the receptor [8]. Another common factor across these diverse conditions is, following the insult, there is a common pattern of increased expression of SP and the NK1R, which could fuel that cycle of inflammation [118,133,135]. Interestingly, in a murine model of West Nile neuroinvasive disease, there was a positive correlation between SP levels and mortality [133].
7.1. Stroke
In a similar vein, data from stroke patients has shown that there is a significant increase in serum SP levels following cerebral ischaemia [136]. One of the earliest reports of NK1R antagonists having a neuroprotective action was in a rat model of cerebral ischaemia [118]. The selective antagonist, SR140333, was shown to reduce infarct volume and improve functional outcomes. This valuable observation has been replicated by multiple groups using different models. Turner and colleagues, using NAT in a rodent model of transient middle cerebral artery occlusion, demonstrated the potential to restore BBB integrity and reduce cerebral oedema, as well as significantly reduce functional deficits [116]. In a similar study, they also demonstrated that NAT was able to ameliorate tissue plasminogen activator-induced BBB dysfunction, in both naïve and stroke animals [119]. While there are concerns about inferring a selective mode of action to NAT, Turner, and colleagues also demonstrated the ability of a highly selective NK1 antagonist (EU-C-001) to reduce post-stroke cerebral oedema and raised intracranial pressure (ICP) in their ovine model of stroke [115,137]. SP release associated with ischaemia and reperfusion, and the associated neurogenic inflammation, are considered to be involved in the pathogenesis of vascular dementia. Kaur and colleagues, using a rodent model of bilateral common carotid artery occlusion, have demonstrated the ability of the selective antagonist, aprepitant, to reduce the ischaemia-induced cerebrovasculature dysfunction [120].
7.2. Traumatic Brain Injury
In terms of traumatic brain injury (TBI), neuroinflammation is a significant secondary injury mechanism following the primary insult, and it is linked to the development of complications such as cerebral oedema and raised ICP [138,139,140]. Given the clinical need to better control cerebral oedema and raised ICP, there was an interest to see whether inflammatory neuropeptides, particularly the NK1-R, may represent an effective target to manage inflammation and oedema [55]. In an initial study, using capsaicin as a pre-injury treatment to produce neuropeptide depletion in a rodent model of TBI, there was a significant reduction in post-traumatic BBB dysfunction and oedema formation, together with a significant decrease in the motor and cognitive deficits associated with injury [54]. From this initial observation, intravenously administered NAT was used in order to see whether this protective effect could be achieved using a post-injury treatment [113]. Administration of NAT 30 min after trauma significantly attenuated vascular permeability and edema formation, as well as improved both motor and cognitive neurologic outcomes. While a question mark remains around the mechanism of action of NAT, these results were fully replicated when a highly selective NK1 antagonist was administered in the same manner and model [114,117]. Indeed, there is evidence that a selective NK1 antagonist may exert a broader neuroprotectant effect than NAT. Studies on blast injury and chronic traumatic encephalopathy have shown that, in contrast to NAT, an NK1 antagonist can attenuate the injury-induced phosphorylation of tau by modulating the activity of several key kinases including Akt, ERK1/2, and JNK [121]. Li and colleagues have also shown that a selective NK1 antagonist, as well as SP deletion, can exert a neuroprotective effect in a murine model of TBI [122]. The use of a large animal model of severe TBI has demonstrated the ability of an NK1 antagonist to control raised ICP and the associated reduction in brain tissue oxygen levels [123]. A selective NK1R antagonist, EU-C-001, is currently in a multi-national Phase 2 clinical trial for TBI (ACTRN 12619000074190) [114].
7.3. Intracerebral Hemorrhage
Hematoma clearance is an important therapeutic target to improve outcomes following intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH). Jin and colleagues examined the potential value of NK1R antagonism on hematoma clearance in a mouse model of ICH (autologous blood injection) [125]. They observed that the expression of both SP and the NK1R and SP were significantly upregulated after ICH, while an intraperitoneal injection of the selective antagonist, aprepitant, significantly improved functional outcomes and reduced hematoma volume. In terms of neuroinflammation, the antagonist treatment promoted microglia polarisation towards the anti-inflammatory state by decreasing the levels of phosphorylated PKC, p38MAPK, and NFκB [125].
7.4. Spinal Cord Injury
Like TBI, acute inflammation is also associated with traumatic spinal cord injuries [141], and there is evidence for the involvement of SP and NK1R [142]. Although a study using systemic i.v. administration of NAT did not demonstrate any significant benefit [143], a recent study using continuous subdural infusion of a selective NK1 antagonist, did exhibit some reduction in neuroinflammation together with some positive functional outcomes [126]. In addition, it has been shown that the NK1R antagonist, GR205171, is able to alleviate autonomic dysreflexia in a rodent model of severe spinal cord injury [127].
7.5. Bacterial Infections
Acute neuroinflammation is also associated with CNS infections. Infections can lead to inflammation of both the meningeal membranes (meningitis) and parenchyma of the brain (encephalitis) and spinal cord (myelitis) [144]. Bacterial infections of the CNS are of significant clinical concern and are associated with the proliferation of resident glial cells, as well as the recruitment of peripheral leukocytes to the site of infection. Using murine models of bacterial infection, the use of a selective NK1R antagonist (L703,606), as well as using NK1R deficient mice, provided evidence for the role of the NK1R in altered BBB function and promotion of neuroinflammation [102,128]. Antagonism of the NK1R reduced the proliferation of pro-inflammatory cytokines, as well as a decrease in the severity of the disease. These beneficial effects were demonstrated against a range of clinically relevant infectious agents, including Streptococcus pneumoniae and Neisseria meningitidis. These studies also demonstrated that the NK1R was involved in bacterial-induced demyelination [128]. Infection was also associated with increased expression of the NK1R on microglia and astrocytes, while SP was shown to have a broad pro-inflammatory action [102,129].
7.6. Viral Infections
A similar picture of neuroinflammation is associated with viral infections. In terms of CNS inflammation associated with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) infection, perivascular macrophages are potentially the first cells infected in the CNS [135]. Studies of the brains of SIV-infected macaque monkeys have shown that there is an intense expression of SP and NK1R in SIV-infected cells and encephalitic lesions [135]. In addition, HIV infection has been associated with increased serum levels of SP and a similar picture is seen with SIV infection in monkeys [135,145,146]. Positive correlations between SP levels and viral load have suggested that the peptide may play a role in facilitating viral replication [132,147], potentially by increasing the expression of the receptors (e.g., CCR5) required for uptake of the virus. There is evidence that SP, acting via the NK1R, can enhance HIV infection [148], while the NK1 antagonist, aprepitant, may potentially exert anti-HIV activity, and help prevent infection in microglia and macrophages [131]. Aprepitant may also produce synergistically beneficial effects when used in combination with other antiretrovirals [132]. Another virus with neuroinvasive potential is the West Nile virus. Those who develop neuroinvasive disease (WNND) will present with meningitis and encephalitis. In cases of encephalitis, pathology of brain tissue reveals inflammation, which is mostly mononuclear, with formed microglial nodules and perivascular clusters in both white and gray matter. In a mouse model of MNV infection, Ronca and colleagues showed that SP was significantly upregulated in the brain during infection, which correlated with neuroinvasion and BBB dysfunction [133]. Blocking the NK1R with a selective antagonist at disease onset modestly improved survival and prolonged time to death. Unlike HIV infection, the results indicated that SP does not appear to play a role in viral replication, but rather may mediate the immune response to infection.
7.7. Parasitic Infections
Finally, there is also evidence that the NK1R contributes to neuroinflammation in response to parasitic infection. Cysticercosis is a parasitic infection associated with the pork tapeworm, Taenia solium. If larval cysts infect the brain, this is referred to as neurocysticercosis. Dying parasites trigger a granulomatous response, which is associated with the development of seizures. SP-positive cells are observed as in association with these granulomas, both in human biopsies and animal models [149]. There is evidence that SP and the NK1R are associated with seizure activity, granuloma development, and the cytokine response associated with granuloma formation [150,151]. SP and the NK1R have been associated with other parasitic infections that lead to CNS involvement, including the Trypanosoma brucei brucei infection associated with sleeping sickness. Trypanosoma infection is associated with a severe neuroinflammatory reaction and peripheral inflammatory infiltration. In a mouse model of Trypanosoma infection, which exhibited severe meningoencephalitis, the selective NK1R antagonist, RP-67,580, was shown to significantly reduce the inflammatory response and reactive astrogliosis [134].
8. The Dual Role of the NK1R in Inflammation
As discussed, inflammation represents a double-edged sword, with both beneficial and detrimental aspects. The host immune response is central to dealing with infection, and there is significant evidence to support the role of the NK1R in the host response to infection, viral, bacterial, and parasitic [147,152,153]. SP and the NK1R exert an immune-protective role at mucosal barriers, contributing to the host response to a diverse range of infections [154]. In a mouse model of herpes virus infection, increased expression of the NK1R was found to correlate to decreased viral load when compared to mice who were NK1R-deficient [152]. Similarly, in relation to salmonella bacterial infection, it was shown that NK1R antagonism was associated with increased bacterial load in response to infection [155]. This reduced host response is also observed in parasitic infections, with mice treated with an NK1R antagonist showing limited granuloma formation in response to infection with Schistosoma mansoni [154]. However, as we have seen, the NK1R can also contribute to the pathogenesis of infection, particularly the destructive inflammatory response [147], so both aspects need to be considered in relation to the potential application of NK1R antagonists.
While the NK1R plays a role in some of the positive aspects of the acute inflammatory response, there is also growing evidence that it may contribute to the negative aspects of neuroinflammation, particularly when considering the significant inflammatory responses associated with events like TBI and stroke [8,115,121]. As such, NK1R antagonists may have a potential role in ameliorating acute neuroinflammation. Such an action may not only help to manage acute issues, such as cerebral oedema and raised intracranial pressure [115], but, with timely intervention, may also help to prevent the progression to chronic neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration [23,156].
Neuroinflammation involves both the glial-mediated inflammatory response, along with the transmigration of peripheral leukocytes into the CNS, and the NK1R may contribute to both aspects [26]. The glial response involves the elaboration of a range of key pro-inflammatory mediators, including IL-1β, IL-6, and TNFα [157]. The NK1R has been shown to be present in both astrocytes and microglia, and stimulation of the receptor can lead to the expression and release of pro-inflammatory mediators [88,105]. In terms of NK1R signal transduction, proinflammatory action is primarily associated with the MAPK pathway and activation of NFκB [10,63,158]. The NK1R can also activate the phospholipase pathway, leading to the generation of eicosanoids [159]. It has also been shown in a diverse range of CNS pathologies, ranging from infection to stroke and trauma, that the initial stimulus can lead to an upregulation of both NK1R and SP expression, which can further drive a pro-inflammatory cycle [88,92,133].
In addition, the NK1R may also be involved in the transmigration of peripheral leukocytes into the CNS. NK1Rs are associated with the vascular endothelium, and activation can lead to increased vascular permeability [46,99]. Stimulation of the endothelial NK1R, via activation of NFB, may increase the expression of vascular adhesion molecules, including ICAM and VCAM, which then facilitates leukocyte adhesion and infiltration [10,69,71,160]. In relation to this, SP and the NK1R may also be involved in a cytokine-stimulated autocrine feedback mechanism which may impact BBB function in response to inflammation [55,100]. Cytokines may stimulate VECs to increase NK1R expression and SP release, which further drives that vascular-mediated inflammatory response [100].
9. Concluding Remarks
The NK1R has been shown to play a key role in neurogenic inflammation in the periphery, and there is growing evidence to suggest that it may play a similar role in acute neuroinflammatory responses [8]. In terms of neuroinflammation, the NK1R may not only be involved in activating the resident immune cells in the CNS, such as astrocytes and microglia [88] but may also facilitate the entry of peripheral immune cells into the CNS [71]. The NK1R on cerebrovascular endothelium may also be responsible for the development of cerebral oedema and raised intracranial pressure [123]. As such, NK1R antagonists may have a potential role in ameliorating acute neuroinflammation. Severe acute neuroinflammation is associated with significant mortality and morbidity in a range of clinical situations including CNS trauma, ischaemia, and infection. Given the availability of safe, effective antagonists of the NK1R, there is the potential for expedited clinical translation of these agents [86]. There have been multiple in vivo studies to support the potential beneficial effects of NK1R antagonists in TBI and stroke [113,115,116,118]. Whilst some of these studies did utilise NAT as a proposed NK1R antagonist, the results have been fully replicated using highly potent and selective agents. Indeed, these agents may exhibit more benefits than initially exhibited by NAT [121,126].
There is also evidence that NK1R antagonists can help ameliorate severe neuroinflammation associated with CNS infection, be it viral, bacterial, or parasitic [102,133,151], as well as decrease viral load [130]. However, the double-edged sword nature of inflammation is apparent with the NK1R’s role in infection, as it may also contribute to the host immune response against infection [154]. Hence, the application of NK1R antagonists to manage infection needs to be carefully considered. However, in summary, there is significant foundational evidence to support the wider use of NK1R antagonists in the clinic.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to gratefully acknowledge Shannon Stuckey for their assistance with the preparation of Figure 1.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Guzman-Martinez, L.; Maccioni, R.B.; Andrade, V.; Navarrete, L.P.; Pastor, M.G.; Ramos-Escobar, N. Neuroinflammation as a Common Feature of Neurodegenerative Disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beauchamp, K.; Mutlak, H.; Smith, W.R.; Shohami, E.; Stahel, P.F. Pharmacology of traumatic brain injury: Where is the “golden bullet”? Mol. Med. 2008, 14, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, A.M.; Morgan Jones, G.; Hawryluk, G.W.J.; Mailloux, P.; McLaughlin, D.; Papangelou, A.; Samuel, S.; Tokumaru, S.; Venkatasubramanian, C.; Zacko, C.; et al. Guidelines for the Acute Treatment of Cerebral Edema in Neurocritical Care Patients. Neurocritical Care 2020, 32, 647–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ADAPT Research Group. Cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events in the randomized, controlled Alzheimer’s Disease Anti-Inflammatory Prevention Trial (ADAPT). PLoS Clin. Trials 2006, 1, e33. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, J.S.; Ferreira, D.; Paige, E.; Gedye, C.; Boyle, M. Infectious Complications of Biological and Small Molecule Targeted Immunomodulatory Therapies. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vink, R.; Nimmo, A.J. Multifunctional drugs for head injury. Neurotherapeutics 2009, 6, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouras, M.; Asehnoune, K.; Roquilly, A. Immune modulation after traumatic brain injury. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 995044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrigan, F.; Vink, R.; Turner, R.J. Inflammation in acute CNS injury: A focus on the role of substance P. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 703–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A.N.; Philipp, M.T. Substance P and Antagonists of the Neurokinin-1 Receptor in Neuroinflammation Associated with Infectious and Neurodegenerative Diseases of the Central Nervous System. J. Neurol. Neuromed. 2016, 1, 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Steinhoff, M.S.; von Mentzer, B.; Geppetti, P.; Pothoulakis, C.; Bunnett, N.W. Tachykinins and their receptors: Contributions to physiological control and the mechanisms of disease. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 265–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.B.; Young, A.D.; Marriott, I. The Therapeutic Potential of Targeting Substance P/NK-1R Interactions in Inflammatory CNS Disorders. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeWire, S.M.; Ahn, S.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; Shenoy, S.K. Beta-arrestins and cell signaling. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2007, 69, 483–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, D.D.; Lieu, T.; Halls, M.L.; Veldhuis, N.A.; Imlach, W.L.; Mai, Q.N.; Poole, D.P.; Quach, T.; Aurelio, L.; Conner, J.; et al. Neurokinin 1 receptor signaling in endosomes mediates sustained nociception and is a viable therapeutic target for prolonged pain relief. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaal3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.P.; Lai, S.; Tuluc, F.; Tansky, M.F.; Kilpatrick, L.E.; Leeman, S.E.; Douglas, S.D. Differences in the length of the carboxyl terminus mediate functional properties of neurokinin-1 receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 12605–12610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, T.M.; Anderson, S.A.; Yu, H.; Huang, R.R.; Strader, C.D. Differential activation of intracellular effector by two isoforms of human neurokinin-1 receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 1992, 41, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gillespie, E.; Leeman, S.E.; Watts, L.A.; Coukos, J.A.; O’Brien, M.J.; Cerda, S.R.; Farraye, F.A.; Stucchi, A.F.; Becker, J.M. Truncated neurokinin-1 receptor is increased in colonic epithelial cells from patients with colitis-associated cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 17420–17425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, S. Phagocytosis: An Immunobiologic Process. Immunity 2016, 44, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serhan, C.N.; Levy, B.D. Resolvins in inflammation: Emergence of the pro-resolving superfamily of mediators. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 2657–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.H.; Abrams, N.D.; Carrick, D.M.; Chander, P.; Dwyer, J.; Hamlet, M.R.J.; Macchiarini, F.; PrabhuDas, M.; Shen, G.L.; Tandon, P.; et al. Biomarkers of chronic inflammation in disease development and prevention: Challenges and opportunities. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 1175–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, R.M.; Kochanek, P.M.; Simard, J.M. Pathophysiology and treatment of cerebral edema in traumatic brain injury. Neuropharmacology 2019, 145, 230–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, S.M.; Rothwell, N.J.; Gibson, R.M. The role of inflammation in CNS injury and disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 147 (Suppl. S1), S232–S240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arena, G.; Sharma, K.; Agyeah, G.; Kruger, R.; Grunewald, A.; Fitzgerald, J.C. Neurodegeneration and Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s Disease: A Self-Sustained Loop. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2022, 22, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuckey, S.M.; Ong, L.K.; Collins-Praino, L.E.; Turner, R.J. Neuroinflammation as a Key Driver of Secondary Neurodegeneration Following Stroke? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luis, J.P.; Simoes, C.J.V.; Brito, R.M.M. The Therapeutic Prospects of Targeting IL-1R1 for the Modulation of Neuroinflammation in Central Nervous System Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ransohoff, R.M.; Brown, M.A. Innate immunity in the central nervous system. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 1164–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiSabato, D.J.; Quan, N.; Godbout, J.P. Neuroinflammation: The devil is in the details. J. Neurochem. 2016, 139 (Suppl. S2), 136–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millan Solano, M.V.; Salinas Lara, C.; Sanchez-Garibay, C.; Soto-Rojas, L.O.; Escobedo-Avila, I.; Tena-Suck, M.L.; Ortiz-Butron, R.; Choreno-Parra, J.A.; Romero-Lopez, J.P.; Melendez Camargo, M.E. Effect of Systemic Inflammation in the CNS: A Silent History of Neuronal Damage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.Q.; Zhou, J.W. Neuroinflammation in the central nervous system: Symphony of glial cells. Glia 2019, 67, 1017–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koizumi, T.; Kerkhofs, D.; Mizuno, T.; Steinbusch, H.W.M.; Foulquier, S. Vessel-Associated Immune Cells in Cerebrovascular Diseases: From Perivascular Macrophages to Vessel-Associated Microglia. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balança, B.; Desmurs, L.; Grelier, J.; Perret-Liaudet, A.; Lukaszewicz, A.-C. DAMPs and RAGE Pathophysiology at the Acute Phase of Brain Injury: An Overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezas, R.; Avila, M.; Gonzalez, J.; El-Bacha, R.S.; Baez, E.; Garcia-Segura, L.M.; Jurado Coronel, J.C.; Capani, F.; Cardona-Gomez, G.P.; Barreto, G.E. Astrocytic modulation of blood brain barrier: Perspectives on Parkinson’s disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellaver, B.; Dos Santos, J.P.; Leffa, D.T.; Bobermin, L.D.; Roppa, P.H.A.; da Silva Torres, I.L.; Goncalves, C.A.; Souza, D.O.; Quincozes-Santos, A. Systemic Inflammation as a Driver of Brain Injury: The Astrocyte as an Emerging Player. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 2685–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, M.K.; Jo, M.; Kim, J.H.; Suk, K. Microglia-Astrocyte Crosstalk: An Intimate Molecular Conversation. Neuroscientist 2019, 25, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyse, E.; Krantic, S.; Djellouli, N.; Roger, S.; Angoulvant, D.; Debacq, C.; Leroy, V.; Fougere, B.; Aidoud, A. Neuroinflammation: A Possible Link Between Chronic Vascular Disorders and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 827263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellwardt, E.; Zipp, F. Molecular mechanisms linking neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration in MS. Exp. Neurol. 2014, 262 Pt A, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodnar, C.N.; Watson, J.B.; Higgins, E.K.; Quan, N.; Bachstetter, A.D. Inflammatory Regulation of CNS Barriers After Traumatic Brain Injury: A Tale Directed by Interleukin-1. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 688254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harilal, S.; Jose, J.; Parambi, D.G.T.; Kumar, R.; Unnikrishnan, M.K.; Uddin, M.S.; Mathew, G.E.; Pratap, R.; Marathakam, A.; Mathew, B. Revisiting the blood-brain barrier: A hard nut to crack in the transportation of drug molecules. Brain Res. Bull. 2020, 160, 121–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uprety, A.; Kang, Y.; Kim, S.Y. Blood-brain barrier dysfunction as a potential therapeutic target for neurodegenerative disorders. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2021, 44, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, M.D.; Sagare, A.P.; Zlokovic, B.V. Blood-brain barrier breakdown in Alzheimer disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, N.J.; Rönnbäck, L.; Hansson, E. Astrocyte–endothelial interactions at the blood–brain barrier. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haydon, P.G.; Carmignoto, G. Astrocyte control of synaptic transmission and neurovascular coupling. Physiol. Rev. 2006, 86, 1009–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustenhoven, J.; Jansson, D.; Smyth, L.C.; Dragunow, M. Brain Pericytes As Mediators of Neuroinflammation. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 38, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, M.D.; Ayyadurai, S.; Zlokovic, B.V. Pericytes of the neurovascular unit: Key functions and signaling pathways. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto-Rojas, L.O.; Pacheco-Herrero, M.; Martinez-Gomez, P.A.; Campa-Cordoba, B.B.; Apatiga-Perez, R.; Villegas-Rojas, M.M.; Harrington, C.R.; de la Cruz, F.; Garces-Ramirez, L.; Luna-Munoz, J. The Neurovascular Unit Dysfunction in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, S.; Iadecola, C. Revisiting the neurovascular unit. Nat. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 1198–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annunziata, P.; Cioni, C.; Santonini, R.; Paccagnini, E. Substance P antagonist blocks leakage and reduces activation of cytokine-stimulated rat brain endothelium. J. Neuroimmunol. 2002, 131, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pober, J.S.; Sessa, W.C. Inflammation and the blood microvascular system. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 7, a016345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, W.F. Leukocyte traffic in the central nervous system: The participants and their roles. Semin. Immunol. 1999, 11, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, D.; Rustenhoven, J.; Feng, S.; Hurley, D.; Oldfield, R.L.; Bergin, P.S.; Mee, E.W.; Faull, R.L.; Dragunow, M. A role for human brain pericytes in neuroinflammation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2014, 11, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Fonseca, A.C.; Matias, D.; Garcia, C.; Amaral, R.; Geraldo, L.H.; Freitas, C.; Lima, F.R. The impact of microglial activation on blood-brain barrier in brain diseases. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuwelt, E.A.; Bauer, B.; Fahlke, C.; Fricker, G.; Iadecola, C.; Janigro, D.; Leybaert, L.; Molnar, Z.; O’Donnell, M.E.; Povlishock, J.T.; et al. Engaging neuroscience to advance translational research in brain barrier biology. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 12, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa-Valente, J.; Brain, S.D. A historical perspective on the role of sensory nerves in neurogenic inflammation. Semin. Immunopathol. 2018, 40, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, I.M.; von Hehn, C.A.; Woolf, C.J. Neurogenic inflammation and the peripheral nervous system in host defense and immunopathology. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 1063–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimmo, A.J.; Cernak, I.; Heath, D.L.; Hu, X.; Bennett, C.J.; Vink, R. Neurogenic inflammation is associated with development of edema and functional deficits following traumatic brain injury in rats. Neuropeptides 2004, 38, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorby-Adams, A.J.; Marcoionni, A.M.; Dempsey, E.R.; Woenig, J.A.; Turner, R.J. The Role of Neurogenic Inflammation in Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption and Development of Cerebral Oedema Following Acute Central Nervous System (CNS) Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.E.; Easton, A.S.; Fraser, P.A. TRPV1 activation results in disruption of the blood-brain barrier in the rat. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 146, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargbo, R.B. TRPV1 Modulators for the Treatment of Pain and Inflammation. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 143–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmar, A.; Keen, P. Synthesis, and central and peripheral axonal transport of substance P in a dorsal root ganglion-nerve preparation in vitro. Brain Res. 1982, 231, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalkjær, C.; Nilsson, H.; De Mey, J.G.R. Sympathetic and Sensory-Motor Nerves in Peripheral Small Arteries. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 495–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garret, C.; Carruette, A.; Fardin, V.; Moussaoui, S.; Peyronel, J.F.; Blanchard, J.C.; Laduron, P.M. Pharmacological properties of a potent and selective nonpeptide substance P antagonist. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 10208–10212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, P.V.; Helme, R.D.; Thomas, K.L. NK-1 receptor mediation of neurogenic plasma extravasation in rat skin. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1989, 97, 1232–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, J.M.; Saria, A.; Brodin, E.; Rosell, S.; Folkers, K. A substance P antagonist inhibits vagally induced increase in vascular permeability and bronchial smooth muscle contraction in the guinea pig. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1983, 80, 1120–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, S.D.; Leeman, S.E. Neurokinin-1 receptor: Functional significance in the immune system in reference to selected infections and inflammation. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1217, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzer, P. Neurogenic vasodilatation and plasma leakage in the skin. Gen. Pharmacol. 1998, 30, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekkemeyer, H.; Oehme, P.; Foreman, J.C. Accidental injection of substance P. J. R. Soc. Med. 1983, 76, 801–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Hinsbergh, V.W.; van Nieuw Amerongen, G.P. Endothelial hyperpermeability in vascular leakage. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2002, 39, 171–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baluk, P.; Hirata, A.; Thurston, G.; Fujiwara, T.; Neal, C.R.; Michel, C.C.; McDonald, D.M. Endothelial gaps: Time course of formation and closure in inflamed venules of rats. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 1997, 272, L155–L170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowden, J.J.; Baluk, P.; Lefevre, P.M.; Vigna, S.R.; McDonald, D.M. Substance P (NK1) receptor immunoreactivity on endothelial cells of the rat tracheal mucosa. Am. J. Physiol. 1996, 270, L404–L414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashaghi, A.; Marmalidou, A.; Tehrani, M.; Grace, P.M.; Pothoulakis, C.; Dana, R. Neuropeptide substance P and the immune response. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 4249–4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroux, A.; Paiva Dos Santos, B.; Leng, J.; Oliveira, H.; Amedee, J. Sensory neurons from dorsal root ganglia regulate endothelial cell function in extracellular matrix remodelling. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nessler, S.; Stadelmann, C.; Bittner, A.; Schlegel, K.; Gronen, F.; Brueck, W.; Hemmer, B.; Sommer, N. Suppression of autoimmune encephalomyelitis by a neurokinin-1 receptor antagonist—A putative role for substance P in CNS inflammation. J. Neuroimmunol. 2006, 179, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foreman, J.C.; Jordan, C.C.; Oehme, P.; Renner, H. Structure-activity relationships for some substance P-related peptides that cause wheal and flare reactions in human skin. J. Physiol. 1983, 335, 449–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsythe, P. Mast Cells in Neuroimmune Interactions. Trends Neurosci. 2019, 42, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suvas, S. Role of Substance P Neuropeptide in Inflammation, Wound Healing, and Tissue Homeostasis. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 1543–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokfelt, T.; Kellerth, J.O.; Nilsson, G.; Pernow, B. Substance p: Localization in the central nervous system and in some primary sensory neurons. Science 1975, 190, 889–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantyh, P.W.; Johnson, D.J.; Boehmer, C.G.; Catton, M.D.; Vinters, H.V.; Maggio, J.E.; Too, H.P.; Vigna, S.R. Substance P receptor binding sites are expressed by glia in vivo after neuronal injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 5193–5197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, J.K.; Stephens, P.H.; Hopf, A.; Cuello, A.C. Substance P in the human brain. Neuroscience 1986, 17, 709–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantyh, P.W. Neurobiology of substance P and the NK1 receptor. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2002, 63 (Suppl. S11), 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Dudas, B.; Merchenthaler, I. Substance P-Immunoreactive Fiber Varicosities Appear to Innervate Galaninergic Perikarya in the Human Hypothalamus. Brain Connect. 2021, 11, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Brown, J.L.; Jasmin, L.; Maggio, J.E.; Vigna, S.R.; Mantyh, P.W.; Basbaum, A.I. Synaptic relationship between substance P and the substance P receptor: Light and electron microscopic characterization of the mismatch between neuropeptides and their receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 1009–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftikhar, K.; Siddiq, A.; Baig, S.G.; Zehra, S. Substance P: A neuropeptide involved in the psychopathology of anxiety disorders. Neuropeptides 2020, 79, 101993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupniak, N.M.J.; Kramer, M.S. NK1 receptor antagonists for depression: Why a validated concept was abandoned. J. Affect. Disord. 2017, 223, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frick, A.; Ahs, F.; Linnman, C.; Jonasson, M.; Appel, L.; Lubberink, M.; Långström, B.; Fredrikson, M.; Furmark, T. Increased neurokinin-1 receptor availability in the amygdala in social anxiety disorder: A positron emission tomography study with [11C]GR205171. Transl. Psychiatry 2015, 5, e597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berk, M.; Williams, L.J.; Jacka, F.N.; O’Neil, A.; Pasco, J.A.; Moylan, S.; Allen, N.B.; Stuart, A.L.; Hayley, A.C.; Byrne, M.L.; et al. So depression is an inflammatory disease, but where does the inflammation come from? BMC Med. 2013, 11, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tattersall, F.D.; Rycroft, W.; Hill, R.G.; Hargreaves, R.J. Enantioselective inhibition of apomorphine-induced emesis in the ferret by the neurokinin1 receptor antagonist CP-99,994. Neuropharmacology 1994, 33, 259–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aapro, M.; Carides, A.; Rapoport, B.L.; Schmoll, H.J.; Zhang, L.; Warr, D. Aprepitant and fosaprepitant: A 10-year review of efficacy and safety. Oncologist 2015, 20, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, R.; Takano, Y.; Kamiya, H.O. Roles of substance P and NK(1) receptor in the brainstem in the development of emesis. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2003, 91, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burmeister, A.R.; Johnson, M.B.; Chauhan, V.S.; Moerdyk-Schauwecker, M.J.; Young, A.D.; Cooley, I.D.; Martinez, A.N.; Ramesh, G.; Philipp, M.T.; Marriott, I. Human microglia and astrocytes constitutively express the neurokinin-1 receptor and functionally respond to substance P. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spitsin, S.; Pappa, V.; Douglas, S.D. Truncation of neurokinin-1 receptor-Negative regulation of substance P signaling. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2018, 103, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuluc, F.; Lai, J.P.; Kilpatrick, L.E.; Evans, D.L.; Douglas, S.D. Neurokinin 1 receptor isoforms and the control of innate immunity. Trends Immunol. 2009, 30, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.P.; Cnaan, A.; Zhao, H.; Douglas, S.D. Detection of full-length and truncated neurokinin-1 receptor mRNA expression in human brain regions. J. Neurosci. Methods 2008, 168, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Stumm, R.; Culmsee, C.; Schafer, M.K.; Krieglstein, J.; Weihe, E. Adaptive plasticity in tachykinin and tachykinin receptor expression after focal cerebral ischemia is differentially linked to gabaergic and glutamatergic cerebrocortical circuits and cerebrovenular endothelium. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 798–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamel, E. Perivascular nerves and the regulation of cerebrovascular tone. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006, 100, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edvinsson, L.; Haanes, K.A.; Warfvinge, K.; Krause, D.N. CGRP as the target of new migraine therapies—Successful translation from bench to clinic. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowitz, S.; Saito, K.; Moskowitz, M.A. Neurogenically mediated leakage of plasma protein occurs from blood vessels in dura mater but not brain. J. Neurosci. 1987, 7, 4129–4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashina, M.; Hansen, J.M.; Do, T.P.; Melo-Carrillo, A.; Burstein, R.; Moskowitz, M.A. Migraine and the trigeminovascular system-40 years and counting. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saria, A.; Lundberg, J.M.; Skofitsch, G.; Lembeck, F. Vascular protein linkage in various tissue induced by substance P, capsaicin, bradykinin, serotonin, histamine and by antigen challenge. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 1983, 324, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyrino, L.A.; Cardoso, R.C.; Hackl, L.P.; Nicolau, M. Effect of quercetin on plasma extravasation in rat CNS and dura mater by ACE and NEP inhibition. Phytother. Res. 2002, 16, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annunziata, P.; Cioni, C.; Toneatto, S.; Paccagnini, E. HIV-1 gp120 increases the permeability of rat brain endothelium cultures by a mechanism involving substance P. AIDS 1998, 12, 2377–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioni, C.; Renzi, D.; Calabro, A.; Annunziata, P. Enhanced secretion of substance P by cytokine-stimulated rat brain endothelium cultures. J. Neuroimmunol. 1998, 84, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marriott, D.R.; Wilkin, G.P. Substance P receptors on O-2A progenitor cells and type-2 astrocytes in vitro. J. Neurochem. 1993, 61, 826–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, V.S.; Sterka, D.G., Jr.; Gray, D.L.; Bost, K.L.; Marriott, I. Neurogenic exacerbation of microglial and astrocyte responses to Neisseria meningitidis and Borrelia burgdorferi. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 8241–8249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieb, K.; Fiebich, B.L.; Berger, M.; Bauer, J.; Schulze-Osthoff, K. The neuropeptide substance P activates transcription factor NF-kappa B and kappa B-dependent gene expression in human astrocytoma cells. J. Immunol. 1997, 159, 4952–4958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasley, A.; Bost, K.L.; Olson, J.K.; Miller, S.D.; Marriott, I. Expression of functional NK-1 receptors in murine microglia. Glia 2002, 37, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derocq, J.M.; Segui, M.; Blazy, C.; Emonds-Alt, X.; Le Fur, G.; Brelire, J.C.; Casellas, P. Effect of substance P on cytokine production by human astrocytic cells and blood mononuclear cells: Characterization of novel tachykinin receptor antagonists. FEBS Lett. 1996, 399, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, T.T.; Im, G.H.; Han, K.; Suh, M.; Drew, P.J.; Kim, S.G. Parvalbumin interneuron activity drives fast inhibition-induced vasoconstriction followed by slow substance P-mediated vasodilation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2220777120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vruwink, M.; Schmidt, H.H.; Weinberg, R.J.; Burette, A. Substance P and nitric oxide signaling in cerebral cortex: Anatomical evidence for reciprocal signaling between two classes of interneurons. J. Comp. Neurol. 2001, 441, 288–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.J.; Douglas, S.D.; Gao, Z.; Wolf, B.A.; Grinspan, J.; Lai, J.P.; Riedel, E.; Ho, W.Z. Interleukin-1beta upregulates functional expression of neurokinin-1 receptor (NK-1R) via NF-kappaB in astrocytes. Glia 2004, 48, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstock, J.V.; Blum, A.; Metwali, A.; Elliott, D.; Arsenescu, R. IL-18 and IL-12 signal through the NF-kappa B pathway to induce NK-1R expression on T cells. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 5003–5007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLeod, A.M.; Merchant, K.J.; Brookfield, F.; Kelleher, F.; Stevenson, G.; Owens, A.P.; Swain, C.J.; Casiceri, M.A.; Sadowski, S.; Ber, E.; et al. Identification of L-tryptophan derivatives with potent and selective antagonist activity at the NK1 receptor. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 1269–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matalinska, J.; Lipinski, P.F.J. Correcting a widespread error: Neuroprotectant N-acetyl-L-tryptophan does not bind to the neurokinin-1 receptor. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 120, 103728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satarker, S.; Maity, S.; Mudgal, J.; Nampoothiri, M. In silico screening of neurokinin receptor antagonists as a therapeutic strategy for neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Divers. 2022, 26, 443–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkin, J.J.; Nimmo, A.J.; Cernak, I.; Blumbergs, P.C.; Vink, R. Substance P is associated with the development of brain edema and functional deficits after traumatic brain injury. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2009, 29, 1388–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, T.; Nimmo, A.; Sleight, A.; Vankan, P.; Vink, R. Method of Treatment and/or Prevention of Brain, Spinal or Nerve Injury. U.S. Patent US20030083345A1, 1 May 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Sorby-Adams, A.J.; Leonard, A.V.; Hoving, J.W.; Yassi, N.; Vink, R.; Wells, A.J.; Turner, R.J. NK1-r Antagonist Treatment Comparable to Decompressive Craniectomy in Reducing Intracranial Pressure Following Stroke. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R.J.; Helps, S.C.; Thornton, E.; Vink, R. A substance P antagonist improves outcome when administered 4 h after onset of ischaemic stroke. Brain Res. 2011, 1393, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimmo, A.J.; Vink, R. Recent patents in CNS drug discovery: The management of inflammation in the central nervous system. Recent Pat. CNS Drug Discov. 2009, 4, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Cheng, G.; Huang, X.; Li, K.; Cao, X. Neurokinin-1 receptor antagonist SR140333: A novel type of drug to treat cerebral ischemia. Neuroreport 1997, 8, 2117–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R.J.; Vink, R. Combined tissue plasminogen activator and an NK1 tachykinin receptor antagonist: An effective treatment for reperfusion injury following acute ischemic stroke in rats. Neuroscience 2012, 220, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, J.; Sharma, S.; Sandhu, M.; Sharma, S. Neurokinin-1 receptor inhibition reverses ischaemic brain injury and dementia in bilateral common carotid artery occluded rats: Possible mechanisms. Inflammopharmacology 2016, 24, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrigan, F.; Cernak, I.; McAteer, K.; Hellewell, S.C.; Rosenfeld, J.V.; Turner, R.J.; Vink, R. NK1 antagonists attenuate tau phosphorylation after blast and repeated concussive injury. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wu, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; He, F.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Tao, L.; Luo, C. Tachykinin NK1 receptor antagonist L-733,060 and substance P deletion exert neuroprotection through inhibiting oxidative stress and cell death after traumatic brain injury in mice. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2019, 107, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vink, R.; Gabrielian, L.; Thornton, E. The Role of Substance P in Secondary Pathophysiology after Traumatic Brain Injury. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabrielian, L.; Helps, S.C.; Thornton, E.; Turner, R.J.; Leonard, A.V.; Vink, R. Substance P antagonists as a novel intervention for brain edema and raised intracranial pressure. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2013, 118, 201–204. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, P.; Deng, S.; Sherchan, P.; Cui, Y.; Huang, L.; Li, G.; Lian, L.; Xie, S.; Lenahan, C.; Travis, Z.D.; et al. Neurokinin Receptor 1 (NK1R) Antagonist Aprepitant Enhances Hematoma Clearance by Regulating Microglial Polarization via PKC/p38MAPK/NFκB Pathway After Experimental Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Mice. Neurotherapeutics 2021, 18, 1922–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, G.; Harms, A.K.; Tail, M.; Zhang, H.; Nimmo, A.; Skutella, T.; Kiening, K.; Unterberg, A.; Zweckberger, K.; Younsi, A. Effects of a neurokinin-1 receptor antagonist in the acute phase after thoracic spinal cord injury in a rat model. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2023, 16, 1128545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupniak, N.M.J.; Fernandes, S.; Hou, S.; Thor, K.B.; Marson, L. Effect of GR205171 on autonomic dysreflexia induced by colorectal distension in spinal cord injured rats. Spinal Cord 2023, 61, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, V.S.; Kluttz, J.M.; Bost, K.L.; Marriott, I. Prophylactic and therapeutic targeting of the neurokinin-1 receptor limits neuroinflammation in a murine model of pneumococcal meningitis. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 7255–7263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasley, A.; Marriott, I.; Halberstadt, C.R.; Bost, K.L.; Anguita, J. Substance P augments Borrelia burgdorferi-induced prostaglandin E2 production by murine microglia. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 5707–5713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.P.; Ho, W.Z.; Zhan, G.X.; Yi, Y.; Collman, R.G.; Douglas, S.D. Substance P antagonist (CP-96,345) inhibits HIV-1 replication in human mononuclear phagocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 3970–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Douglas, S.D.; Song, L.; Wang, Y.J.; Ho, W.Z. Neurokinin-1 receptor antagonist (aprepitant) suppresses HIV-1 infection of microglia/macrophages. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2008, 3, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Manak, M.M.; Moshkoff, D.A.; Nguyen, L.T.; Meshki, J.; Tebas, P.; Tuluc, F.; Douglas, S.D. Anti-HIV-1 activity of the neurokinin-1 receptor antagonist aprepitant and synergistic interactions with other antiretrovirals. AIDS 2010, 24, 2789–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronca, S.E.; Gunter, S.M.; Kairis, R.B.; Lino, A.; Romero, J.; Pautler, R.G.; Nimmo, A.; Murray, K.O. A Potential Role for Substance P in West Nile Virus Neuropathogenesis. Viruses 2022, 14, 1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, P.G.; Rodgers, J.; Jennings, F.W.; Murray, M.; Leeman, S.E.; Burke, J.M. A substance P antagonist, RP-67,580, ameliorates a mouse meningoencephalitic response to Trypanosoma brucei brucei. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 4167–4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinet-Oliphant, H.; Alvarez, X.; Buza, E.; Borda, J.T.; Mohan, M.; Aye, P.P.; Tuluc, F.; Douglas, S.D.; Lackner, A.A. Neurokinin-1 receptor (NK1-R) expression in the brains of SIV-infected rhesus macaques: Implications for substance P in NK1-R immune cell trafficking into the CNS. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 1286–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, G.; Tega, F.; Bruno, A.; Graf, U.; Corelli, F.; Molfetta, R.; Barucco, M. The role of substance P in cerebral ischemia. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2003, 16, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, T.; Bös, M.; Stadler, H.; Schnider, P.; Hunkeler, W.; Godel, T.; Galley, G.; Ballard, T.M.; Higgins, G.A.; Poli, S.M.; et al. Design and synthesis of a novel, achiral class of highly potent and selective, orally active neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 1362–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, K.; Koggel, M.; Blaauw, J.; van der Horn, H.J.; Jacobs, B.; van der Naalt, J. Blood-based biomarkers of inflammation in mild traumatic brain injury: A systematic review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 132, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahuquillo, J.; Dennis, J.A. Decompressive craniectomy for the treatment of high intracranial pressure in closed traumatic brain injury. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 12, Cd003983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrigan, F.; Mander, K.A.; Leonard, A.V.; Vink, R. Neurogenic inflammation after traumatic brain injury and its potentiation of classical inflammation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellenbrand, D.J.; Quinn, C.M.; Piper, Z.J.; Morehouse, C.N.; Fixel, J.A.; Hanna, A.S. Inflammation after spinal cord injury: A review of the critical timeline of signaling cues and cellular infiltration. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, A.V.; Manavis, J.; Blumbergs, P.C.; Vink, R. Changes in substance P and NK1 receptor immunohistochemistry following human spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 2014, 52, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Leonard, A.V.; Thornton, E.; Vink, R. NK1 receptor blockade is ineffective in improving outcome following a balloon compression model of spinal cord injury. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bystritsky, R.J.; Chow, F.C. Infectious Meningitis and Encephalitis. Neurol. Clin. 2022, 40, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, S.D.; Cnaan, A.; Lynch, K.G.; Benton, T.; Zhao, H.; Gettes, D.R.; Evans, D.L. Elevated substance P levels in HIV-infected women in comparison to HIV-negative women. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2008, 24, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, S.D.; Ho, W.Z.; Gettes, D.R.; Cnaan, A.; Zhao, H.; Leserman, J.; Petitto, J.M.; Golden, R.N.; Evans, D.L. Elevated substance P levels in HIV-infected men. AIDS 2001, 15, 2043–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bost, K.L. Tachykinin-modulated anti-viral responses. Front. Biosci. 2004, 9, 1994–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, L.; Spitsin, S.V.; Meshki, J.; Tuluc, F.; Douglas, S.D.; Wolfe, J.H. Substance P enhances HIV-1 infection in human fetal brain cell cultures expressing full-length neurokinin-1 receptor. J. Neurovirol. 2013, 19, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Robinson, P.; White, A.C.; Lewis, D.E.; Thornby, J.; David, E.; Weinstock, J. Sequential expression of the neuropeptides substance P and somatostatin in granulomas associated with murine cysticercosis. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 4534–4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza, A.; Tweardy, D.J.; Weinstock, J.; Viswanathan, B.; Robinson, P. Substance P signaling contributes to granuloma formation in Taenia crassiceps infection, a murine model of cysticercosis. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010, 2010, 597086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza, A.; Weinstock, J.; Robinson, P. Absence of the SP/SP receptor circuitry in the substance P-precursor knockout mice or SP receptor, neurokinin (NK)1 knockout mice leads to an inhibited cytokine response in granulomas associated with murine Taenia crassiceps infection. J. Parasitol. 2008, 94, 1253–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsawa, S.F.; Taylor, W.; Petty, C.C.; Marriott, I.; Weinstock, J.V.; Bost, K.L. Reduced CTL response and increased viral burden in substance P receptor-deficient mice infected with murine gamma-herpesvirus 68. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 2605–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, A.M.; Metwali, A.; Kim-Miller, M.; Li, J.; Qadir, K.; Elliott, D.E.; Lu, B.; Fabry, Z.; Gerard, N.; Weinstock, J.V. The substance P receptor is necessary for a normal granulomatous response in murine schistosomiasis mansoni. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 6080–6085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, A.M.; Elliott, D.E.; Metwali, A.; Li, J.; Qadir, K.; Weinstock, J.V. Substance P regulates somatostatin expression in inflammation. J. Immunol. 1998, 161, 6316–6322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kincy-Cain, T.; Bost, K.L. Increased susceptibility of mice to Salmonella infection following in vivo treatment with the substance P antagonist, spantide II. J. Immunol. 1996, 157, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.M.; Moore, Z.; Minter, M.R.; Crack, P.J. Type-I interferon pathway in neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration: Focus on Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neural Transm. (Vienna) 2018, 125, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltani Khaboushan, A.; Yazdanpanah, N.; Rezaei, N. Neuroinflammation and Proinflammatory Cytokines in Epileptogenesis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 1724–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Recio, S.; Gascón, P. Biological and Pharmacological Aspects of the NK1-Receptor. Biomed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 495704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marriott, D.; Wilkin, G.P.; Coote, P.R.; Wood, J.N. Eicosanoid synthesis by spinal cord astrocytes is evoked by substance P; possible implications for nociception and pain. Adv. Prostaglandin Thromboxane Leukot. Res. 1991, 21B, 739–741. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, N.; Sano, H.; Iwamoto, I. Substance P induces the expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 on vascular endothelial cells and enhances neutrophil transendothelial migration. Peptides 1995, 16, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).