Analysis of Cell–Cell Communication by Single-Nuclei RNA Sequencing Identifies AHR-Mediated Induction of NRG-ERBB Signaling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dose-Response Single-Nuclei RNAseq Dataset
2.2. Cell–Cell Interaction and Functional Enrichment Analyses
2.3. ChIP-seq, pDRE, and Spatial Transcriptomic Data
3. Results
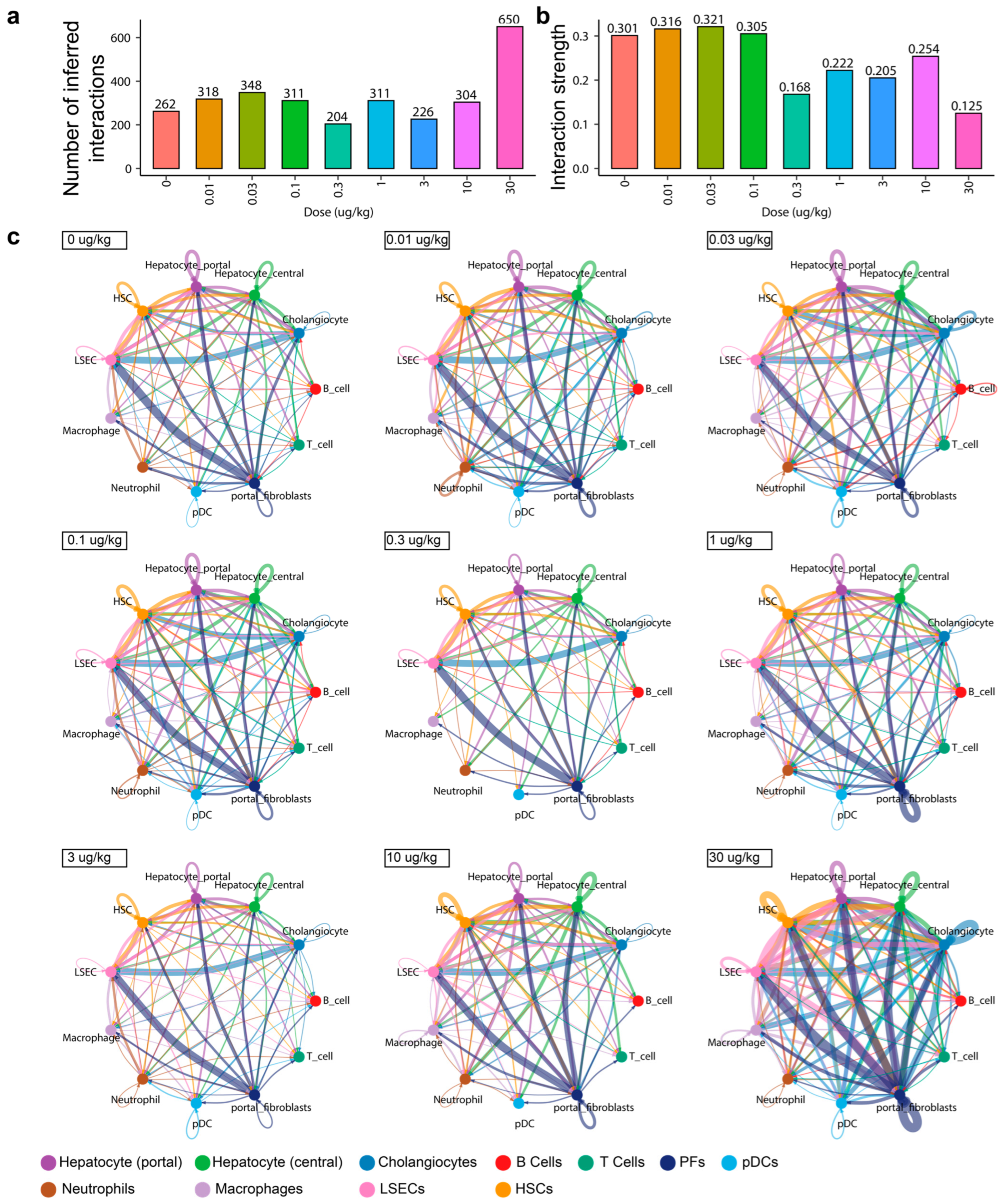
3.1. AHR Activation by TCDD Increases the Number of Cell–Cell Interaction
3.2. AHR Dysregulation of Cell–Cell Interactions Increases Weak Signaling
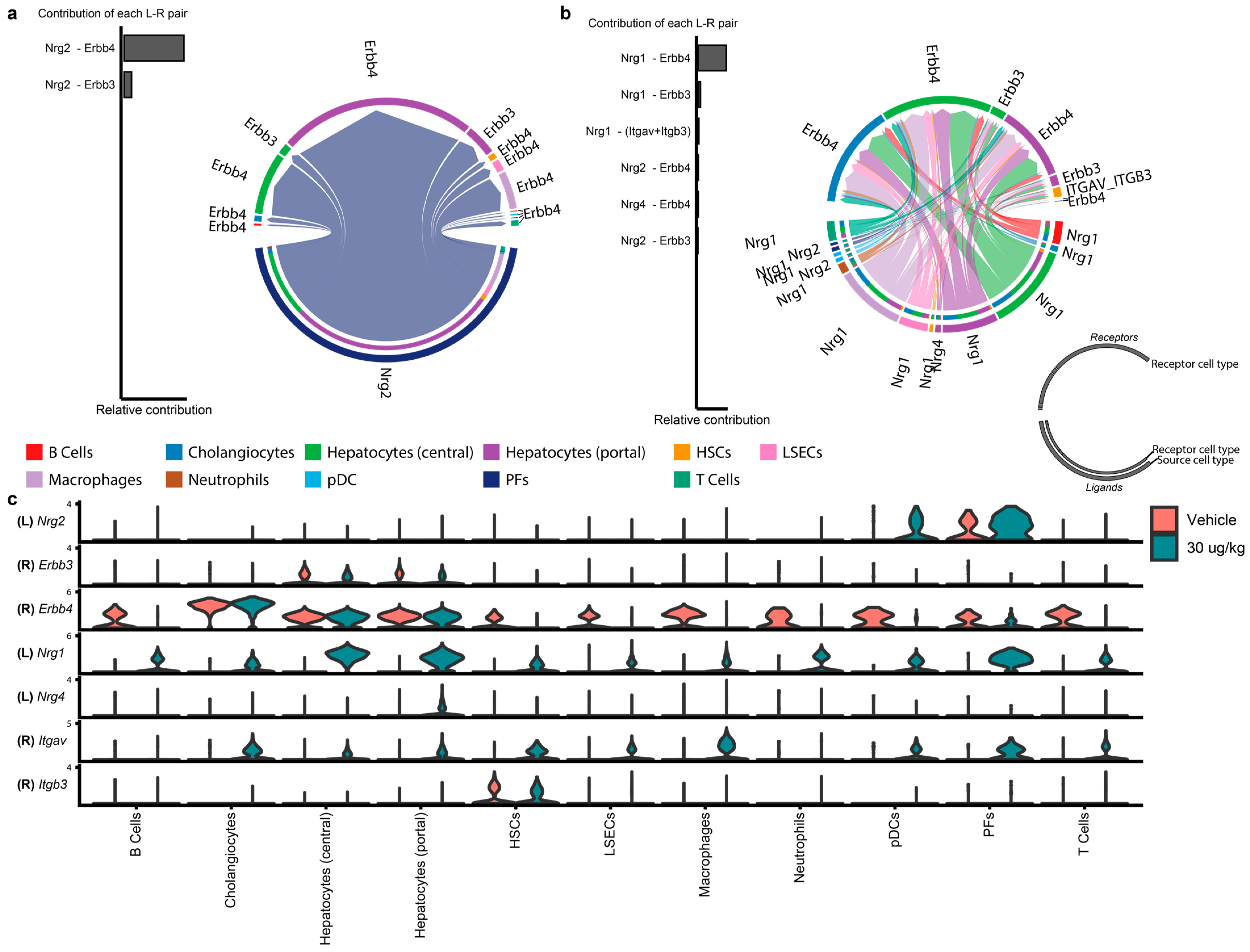
3.3. Neuregulin-Erb-B2 Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Signaling by AHR Activation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, J.; Lind, L.; Salihovic, S.; van Bavel, B.; Ingelsson, E.; Lind, P.M. Persistent organic pollutants and liver dysfunction biomarkers in a population-based human sample of men and women. Environ. Res. 2014, 134, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, K.W.; Novak, R.F.; Anderson, H.A.; Birnbaum, L.S.; Blystone, C.; Devito, M.; Jacobs, D.; Kohrle, J.; Lee, D.H.; Rylander, L.; et al. Evaluation of the association between persistent organic pollutants (POPs) and diabetes in epidemiological studies: A national toxicology program workshop review. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 774–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nault, R.; Fader, K.A.; Ammendolia, D.A.; Dornbos, P.; Potter, D.; Sharratt, B.; Kumagai, K.; Harkema, J.R.; Lunt, S.Y.; Matthews, J.; et al. Dose-Dependent Metabolic Reprogramming and Differential Gene Expression in TCDD-Elicited Hepatic Fibrosis. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 154, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nault, R.; Colbry, D.; Brandenberger, C.; Harkema, J.R.; Zacharewski, T.R. Development of a computational high-throughput tool for the quantitative examination of dose-dependent histological features. Toxicol. Pathol. 2015, 43, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fader, K.A.; Nault, R.; Zhang, C.; Kumagai, K.; Harkema, J.R.; Zacharewski, T.R. 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD)-elicited effects on bile acid homeostasis: Alterations in biosynthesis, enterohepatic circulation, and microbial metabolism. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierre, S.; Chevallier, A.; Teixeira-Clerc, F.; Ambolet-Camoit, A.; Bui, L.C.; Bats, A.S.; Fournet, J.C.; Fernandez-Salguero, P.; Aggerbeck, M.; Lotersztajn, S.; et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-dependent induction of liver fibrosis by dioxin. Toxicol. Sci. 2014, 137, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riazi, K.; Azhari, H.; Charette, J.H.; Underwood, F.E.; King, J.A.; Afshar, E.E.; Swain, M.G.; Congly, S.E.; Kaplan, G.G.; Shaheen, A.A. The prevalence and incidence of NAFLD worldwide: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.J.; Aguilar, M.; Cheung, R.; Perumpail, R.B.; Harrison, S.A.; Younossi, Z.M.; Ahmed, A. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is the second leading etiology of liver disease among adults awaiting liver transplantation in the United States. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casals-Casas, C.; Desvergne, B. Endocrine disruptors: From endocrine to metabolic disruption. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2011, 73, 135–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grun, F.; Blumberg, B. Endocrine disrupters as obesogens. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2009, 304, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neel, B.A.; Sargis, R.M. The paradox of progress: Environmental disruption of metabolism and the diabetes epidemic. Diabetes 2011, 60, 1838–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, Z.D.; Reed, K.R.; Phesse, T.J.; Sansom, O.J.; Clarke, A.R.; Tosh, D. Liver zonation occurs through a beta-catenin-dependent, c-Myc-independent mechanism. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 2316–2324.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, R.P.; Porat-Shliom, N. Liver Zonation—Revisiting Old Questions with New Technologies. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 732929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.I.; Mars, W.M.; Michalopoulos, G.K. Signals and cells involved in regulating liver regeneration. Cells 2012, 1, 1261–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, D.A.; Summerfield, J.A. Hemostasis in liver disease. Semin. Liver Dis. 1987, 7, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, A.; Kopec, A.K.; Luyendyk, J.P. Role of the blood coagulation cascade in hepatic fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2018, 315, G171–G176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Guerrero-Juarez, C.F.; Zhang, L.; Chang, I.; Ramos, R.; Kuan, C.H.; Myung, P.; Plikus, M.V.; Nie, Q. Inference and analysis of cell-cell communication using CellChat. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fader, K.A.; Nault, R.; Doskey, C.M.; Fling, R.R.; Zacharewski, T.R. 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin abolishes circadian regulation of hepatic metabolic activity in mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nault, R.; Saha, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Sinha, S.; Maiti, T.; Zacharewski, T. Single-cell transcriptomics shows dose-dependent disruption of hepatic zonation by TCDD in mice. Toxicol. Sci. 2023, 191, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Hao, S.; Andersen-Nissen, E.; Mauck, W.M., 3rd; Zheng, S.; Butler, A.; Lee, M.J.; Wilk, A.J.; Darby, C.; Zager, M.; et al. Integrated analysis of multimodal single-cell data. Cell 2021, 184, 3573–3587.e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nault, R.; Fader, K.A.; Bhattacharya, S.; Zacharewski, T.R. Single-Nuclei RNA Sequencing Assessment of the Hepatic Effects of 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 11, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nault, R.; Saha, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Dodson, J.; Sinha, S.; Maiti, T.; Zacharewski, T. Benchmarking of a Bayesian single cell RNAseq differential gene expression test for dose-response study designs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, e48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Liu, X.; Peltz, G. GSEApy: A comprehensive package for performing gene set enrichment analysis in Python. Bioinformatics 2022, 39, btac757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fader, K.A.; Nault, R.; Kirby, M.P.; Markous, G.; Matthews, J.; Zacharewski, T.R. Convergence of hepcidin deficiency, systemic iron overloading, heme accumulation, and REV-ERBalpha/beta activation in aryl hydrocarbon receptor-elicited hepatotoxicity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2017, 321, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nault, R.; Fader, K.A.; Kirby, M.P.; Ahmed, S.; Matthews, J.; Jones, A.D.; Lunt, S.Y.; Zacharewski, T.R. Pyruvate Kinase Isoform Switching and Hepatic Metabolic Reprogramming by the Environmental Contaminant 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-Dioxin. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 149, 358–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.; Mizuno, S. The discovery of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and its significance for cell biology, life sciences and clinical medicine. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2010, 86, 588–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nault, R.; Fader, K.A.; Harkema, J.R.; Zacharewski, T. Loss of liver-specific and sexually dimorphic gene expression by aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation in C57BL/6 mice. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaelson, J.J.; Trump, S.; Rudzok, S.; Gräbsch, C.; Madureira, D.J.; Dautel, F.; Mai, J.; Attinger, S.; Schirmer, K.; von Bergen, M.; et al. Transcriptional signatures of regulatory and toxic responses to benzo-[a]-pyrene exposure. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, N.; Saito, N.; Zhao, S.; Terai, K.; Hiruta, N.; Park, Y.; Bujo, H.; Nemoto, K.; Kanno, Y. Heregulin-induced cell migration is promoted by aryl hydrocarbon receptor in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells. Exp. Cell. Res. 2018, 366, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Kuang, H.; He, Y.; Idiga, S.O.; Li, S.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Z.; Cai, X.; Zhang, K.; Potthoff, M.J.; et al. NRG1-Fc improves metabolic health via dual hepatic and central action. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e98522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellat, A.; Vaquero, J.; Fouassier, L. Role of ErbB/HER family of receptor tyrosine kinases in cholangiocyte biology. Hepatology 2018, 67, 762–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, N.J.; Wyde, M.E.; Fischer, L.J.; Nyska, A.; Bucher, J.R. Comparison of chronic toxicity and carcinogenicity of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) in 2-year bioassays in female Sprague-Dawley rats. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2006, 50, 934–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Tao, Y.; Lv, C.; Xia, Y.; Wei, Z.; Dai, Y. Tetrandrine enhances the ubiquitination and degradation of Syk through an AhR-c-src-c-Cbl pathway and consequently inhibits osteoclastogenesis and bone destruction in arthritis. Cell. Death Dis. 2019, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, K.; Kennedy, L.; Liangpunsakul, S.; Kusumanchi, P.; Yang, Z.; Meng, F.; Glaser, S.; Francis, H.; Alpini, G. Intercellular Communication between Hepatic Cells in Liver Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kana, O.; Nault, R.; Filipovic, D.; Marri, D.; Zacharewski, T.; Bhattacharya, S. Generative Modeling of Single Cell Gene Expression for Dose-Dependent Chemical Perturbations. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, K.K.; Simon-Santamaria, J.; McCuskey, R.S.; Smedsrod, B. Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells. Compr. Physiol. 2015, 5, 1751–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, E.; Nour, A.S.; Harris, E.N. Prominent Receptors of Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells in Liver Homeostasis and Disease. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuji, H.; Miller, G.; Nishio, T.; Koyama, Y.; Lam, K.; Zhang, V.; Loomba, R.; Brenner, D.; Kisseleva, T. The role of Mesothelin signaling in Portal Fibroblasts in the pathogenesis of cholestatic liver fibrosis. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 790032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, R.G. The portal fibroblast: Not just a poor man’s stellate cell. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nault, R.; Fader, K.A.; Kopec, A.K.; Harkema, J.R.; Zacharewski, T.R.; Luyendyk, J.P. From the Cover: Coagulation-Driven Hepatic Fibrosis Requires Protease Activated Receptor-1 (PAR-1) in a Mouse Model of TCDD-Elicited Steatohepatitis. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 154, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCuskey, R.S.; Bethea, N.W.; Wong, J.; McCuskey, M.K.; Abril, E.R.; Wang, X.; Ito, Y.; DeLeve, L.D. Ethanol binging exacerbates sinusoidal endothelial and parenchymal injury elicited by acetaminophen. J. Hepatol. 2005, 42, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyao, M.; Kotani, H.; Ishida, T.; Kawai, C.; Manabe, S.; Abiru, H.; Tamaki, K. Pivotal role of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in NAFLD/NASH progression. Lab. Investig. A J. Tech. Methods Pathol. 2015, 95, 1130–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szafranska, K.; Kruse, L.D.; Holte, C.F.; McCourt, P.; Zapotoczny, B. The wHole Story About Fenestrations in LSEC. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 735573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abril, N.; Chicano-Galvez, E.; Michan, C.; Pueyo, C.; Lopez-Barea, J. iTRAQ analysis of hepatic proteins in free-living Mus spretus mice to assess the contamination status of areas surrounding Donana National Park (SW Spain). Sci. Total. Environ. 2015, 523, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casagrande, V.; Mauriello, A.; Bischetti, S.; Mavilio, M.; Federici, M.; Menghini, R. Hepatocyte specific TIMP3 expression prevents diet dependent fatty liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, C.; Latorre, J.; Ortega, F.; Arnoriaga-Rodriguez, M.; Lluch, A.; Oliveras-Canellas, N.; Diaz-Saez, F.; Aragones, J.; Camps, M.; Guma, A.; et al. Serum neuregulin 4 is negatively correlated with insulin sensitivity in humans and impairs mitochondrial respiration in HepG2 cells. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 950791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanEtten, S.L.; Bonner, M.R.; Ren, X.; Birnbaum, L.S.; Kostyniak, P.J.; Wang, J.; Olson, J.R. Effect of exposure to 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) on mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) copy number in rats. Toxicology 2021, 454, 152744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanos, R.; Patel, R.D.; Murray, I.A.; Smith, P.B.; Patterson, A.D.; Perdew, G.H. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor regulates the cholesterol biosynthetic pathway in a dioxin response element-independent manner. Hepatology 2012, 55, 1994–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dornbos, P.; Jurgelewicz, A.; Fader, K.A.; Williams, K.; Zacharewski, T.R.; LaPres, J.J. Characterizing the Role of HMG-CoA Reductase in Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor-Mediated Liver Injury in C57BL/6 Mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diani-Moore, S.; Ram, P.; Li, X.; Mondal, P.; Youn, D.Y.; Sauve, A.A.; Rifkind, A.B. Identification of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor target gene TiPARP as a mediator of suppression of hepatic gluconeogenesis by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and of nicotinamide as a corrective agent for this effect. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 38801–38810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, S.; Dalton, T.P.; Sinclair, P.R.; Gorman, N.; Wang, B.; Smith, A.G.; Miller, M.L.; Shertzer, H.G.; Nebert, D.W. Cyp1a1(-/-) male mice: Protection against high-dose TCDD-induced lethality and wasting syndrome, and resistance to intrahepatocyte lipid accumulation and uroporphyria. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2004, 196, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Accession IDs 1 | Data Type | Study Design | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| GSE184506SCP1871 | snRNAseq | Dose response (0.01, 0.03, 0.1, 0.3, 1, 3, 10, and 30 μg/kg) | [17] |
| GSE206294SCP1875 | Spatial | Dose response (0.3, 3, and 30 μg/kg) | [17] |
| GSE97634 | ChIP-seq | 2 h following gavage of 30 μg/kg TCDD | [25] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nault, R.; Cholico, G.N.; Zacharewski, T. Analysis of Cell–Cell Communication by Single-Nuclei RNA Sequencing Identifies AHR-Mediated Induction of NRG-ERBB Signaling. Receptors 2023, 2, 148-159. https://doi.org/10.3390/receptors2020009
Nault R, Cholico GN, Zacharewski T. Analysis of Cell–Cell Communication by Single-Nuclei RNA Sequencing Identifies AHR-Mediated Induction of NRG-ERBB Signaling. Receptors. 2023; 2(2):148-159. https://doi.org/10.3390/receptors2020009
Chicago/Turabian StyleNault, Rance, Giovan N. Cholico, and Tim Zacharewski. 2023. "Analysis of Cell–Cell Communication by Single-Nuclei RNA Sequencing Identifies AHR-Mediated Induction of NRG-ERBB Signaling" Receptors 2, no. 2: 148-159. https://doi.org/10.3390/receptors2020009
APA StyleNault, R., Cholico, G. N., & Zacharewski, T. (2023). Analysis of Cell–Cell Communication by Single-Nuclei RNA Sequencing Identifies AHR-Mediated Induction of NRG-ERBB Signaling. Receptors, 2(2), 148-159. https://doi.org/10.3390/receptors2020009






