Skeletal Muscle Ultrasonography and Muscle Fitness Relationships: Effects of Scanning Plane and Echogenicity Correction
Abstract
1. Introduction
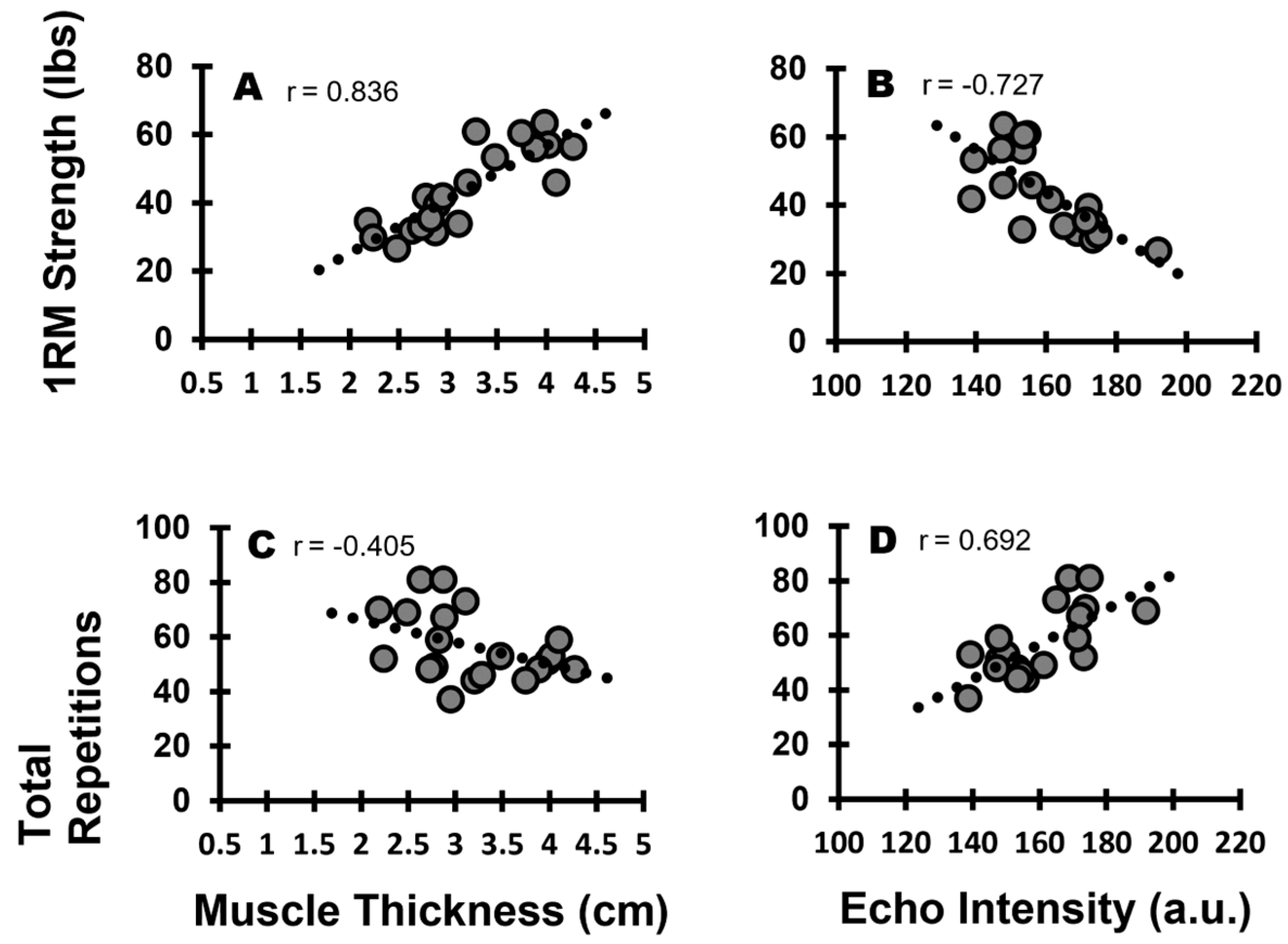
2. Results
2.1. Correlations
2.2. Stepwise Multiple Linear Regression
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Design
4.2. Participants
4.3. Experimental Procedures
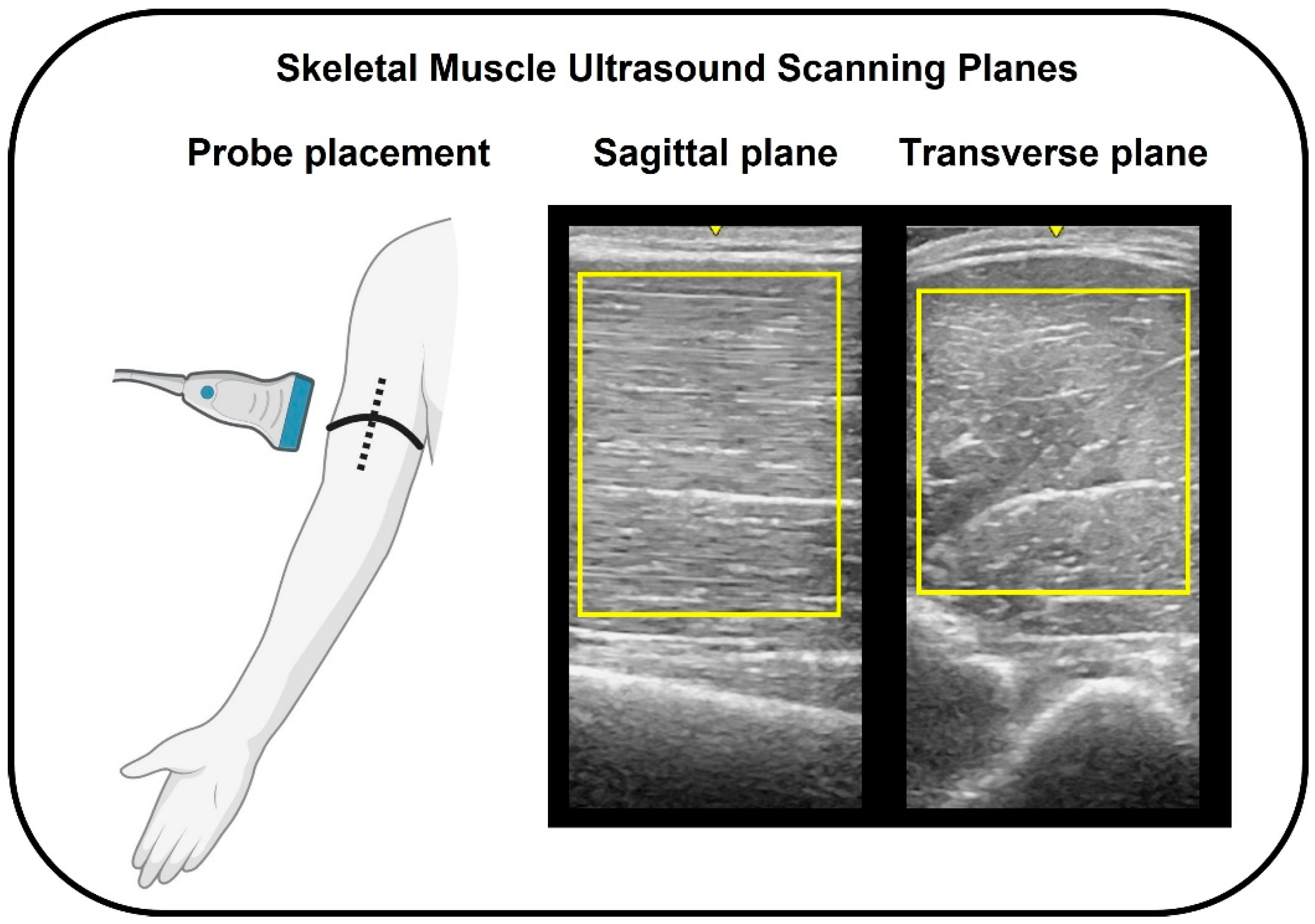
4.3.1. Ultrasonography
4.3.2. Dynamic Strength Testing
4.3.3. Resistance Exercise Protocol
4.3.4. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fujiwara, K.; Asai, H.; Toyama, H.; Kunita, K.; Yaguchi, C.; Kiyota, N.; Tomita, H.; Jacobs, J.V. Changes in muscle thickness of gastrocnemius and soleus associated with age and sex. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2010, 22, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muraki, S.; Fukumoto, K.; Fukuda, O. Prediction of the Muscle Strength by the Muscle Thickness and Hardness Using Ultrasound Muscle Hardness Meter. SpringerPlus 2013, 2, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stock, M.S.; Thompson, B.J. Echo intensity as an indicator of skeletal muscle quality: Applications, methodology, and future directions. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2020, 121, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, N.D.M.; Miller, J.M.; Buckner, S.L.; Cochrane, K.C.; Bergstrom, H.C.; Hill, E.C.; Smith, C.M.; Housh, T.J.; Cramer, J.T. Test-Retest Reliability of Single Transverse versus Panoramic Ultrasound Imaging for Muscle Size and Echo Intensity of the Biceps Brachii. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2015, 41, 1584–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijholt, W.; Scafoglieri, A.; Jager-Wittenaar, H.; Hobbelen, J.S.M.; van der Schans, C.P. The Reliability and Validity of Ultrasound to Quantify Muscles in Older Adults: A Systematic Review. J. Cachex-Sarcopenia Muscle 2017, 8, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, H.-J.; Jenkins, N.T.; Zhao, Q.; Mccully, K.K. Measurement of Intramuscular Fat by Muscle Echo Intensity: Muscle Echo Intensity and Fat. Muscle Nerve 2015, 52, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahtiainen, J.P.; Hoffren, M.; Hulmi, J.J.; Pietikäinen, M.; Mero, A.A.; Avela, J.; Häkkinen, K. Panoramic Ultrasonography Is a Valid Method to Measure Changes in Skeletal Muscle Cross-Sectional Area. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 108, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radaelli, R.; Botton, C.E.; Wilhelm, E.N.; Bottaro, M.; Lacerda, F.; Gaya, A.; Moraes, K.; Peruzzolo, A.; Brown, L.E.; Pinto, R.S. Low- and High-Volume Strength Training Induces Similar Neuromuscular Improvements in Muscle Quality in Elderly Women. Exp. Gerontol. 2013, 48, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, J.G.; Ryan, E.D.; Sobolewski, E.J.; Scharville, M.J.; Thompson, B.J.; King, G.E. Reliability of Panoramic Ultrasound Imaging to Simultaneously Examine Muscle Size and Quality of the Medial Gastrocnemius. Muscle Nerve 2014, 49, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.M.; Martin, D.S.; Ploutz-Snyder, R.; Caine, T.; Matz, T.; Arzeno, N.M.; Buxton, R.; Ploutz-Snyder, L. Reliability and Validity of Panoramic Ultrasound for Muscle Quantification. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2012, 38, 1656–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, J.C.; Gerstner, G.R.; Voskuil, C.C.; Harden, J.E.; Dunnick, D.; Badillo, K.M.; Pagan, J.I.; Harmon, K.K.; Girts, R.M.; Beausejour, J.P.; et al. The Influence of Sonographer Experience on Skeletal Muscle Image Acquisition and Analysis. JFMK 2021, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, J.C.; Millán, I.S. Validation of Musculoskeletal Ultrasound to Assess and Quantify Muscle Glycogen Content. A Novel Approach. Physician Sportsmed. 2014, 42, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, N.D.M. Are Resistance Training-Mediated Decreases in Ultrasound Echo Intensity Caused by Changes in Muscle Composition, or Is There an Alternative Explanation? Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2016, 42, 3050–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieman, D.C.; Shanely, R.A.; Zwetsloot, K.A.; Meaney, M.P.; Farris, G.E. Ultrasonic Assessment of Exercise-Induced Change in Skeletal Muscle Glycogen Content. BMC Sport. Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2015, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarvazyan, A.; Tatarinov, A.; Sarvazyan, N. Ultrasonic Assessment of Tissue Hydration Status. Ultrasonics 2005, 43, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akazawa, N.; Okawa, N.; Tamura, K.; Moriyama, H. Relationships between Intramuscular Fat, Muscle Strength and Gait Independence in Older Women: A Cross-Sectional Study. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2017, 17, 1683–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaka, M.; Sugimoto, K.; Yasunobe, Y.; Akasaka, H.; Fujimoto, T.; Kurinami, H.; Takeya, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Rakugi, H. The Usefulness of an Alternative Diagnostic Method for Sarcopenia Using Thickness and Echo Intensity of Lower Leg Muscles in Older Males. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2019, 20, 1185.e1–1185.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, H.; Kera, T.; Hirayama, R.; Hirano, H.; Fujiwara, Y.; Ihara, K.; Kojima, M.; Obuchi, S. Morphological and Qualitative Characteristics of the Quadriceps Muscle of Community-Dwelling Older Adults Based on Ultrasound Imaging: Classification Using Latent Class Analysis. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2018, 30, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirón Mombiela, R.; Facal de Castro, F.; Moreno, P.; Borras, C. Ultrasonic Echo Intensity as a New Noninvasive In Vivo Biomarker of Frailty. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2017, 65, 2685–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Kimura, Y.; Ishiyama, D.; Nishio, N.; Abe, Y.; Kakehi, T.; Fujimoto, J.; Tanaka, T.; Ohji, S.; Otobe, Y.; et al. Differential Characteristics of Skeletal Muscle in Community-Dwelling Older Adults. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2017, 18, 807.e9–807.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bali, A.U.; Harmon, K.K.; Burton, A.M.; Phan, D.C.; Mercer, N.E.; Lawless, N.W.; Stock, M.S. Muscle Strength, Not Age, Explains Unique Variance in Echo Intensity. Exp. Gerontol. 2020, 139, 111047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadore, E.; Izquierdo, M.; Conceição, M.; Radaelli, R.; Pinto, R.; Baroni, B.; Vaz, M.; Alberton, C.; Pinto, S.; Cunha, G.; et al. Echo Intensity Is Associated with Skeletal Muscle Power and Cardiovascular Performance in Elderly Men. Exp. Gerontol. 2012, 47, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, J.A.; Stock, M.S. Rectus Femoris Echo Intensity Correlates with Muscle Strength, but Not Endurance, in Younger and Older Men. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2017, 43, 1651–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, M.S.; Mota, J.A.; DeFranco, R.N.; Grue, K.A.; Jacobo, A.U.; Chung, E.; Moon, J.R.; DeFreitas, J.M.; Beck, T.W. The Time Course of Short-Term Hypertrophy in the Absence of Eccentric Muscle Damage. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2017, 117, 989–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dankel, S.J.; Abe, T.; Bell, Z.W.; Jessee, M.B.; Buckner, S.L.; Mattocks, K.T.; Mouser, J.G.; Loenneke, J.P. The Impact of Ultrasound Probe Tilt on Muscle Thickness and Echo-Intensity: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Clin. Densitom. 2020, 23, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maughan, R.J.; Watson, J.S.; Weir, J. Strength and Cross-Sectional Area of Human Skeletal Muscle. J. Physiol. 1983, 338, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balshaw, T.G.; Massey, G.J.; Maden-Wilkinson, T.M.; Lanza, M.B.; Folland, J.P. Neural Adaptations after 4 Years vs 12 Weeks of Resistance Training vs Untrained. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sport. 2019, 29, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, M.S.; Mota, J.A.; Hernandez, J.M.; Thompson, B.J. Echo Intensity and Muscle Thickness as Predictors Of Athleticism and Isometric Strength in Middle-School Boys. Muscle Nerve 2017, 55, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, M.S.; Whitson, M.; Burton, A.M.; Dawson, N.T.; Sobolewski, E.J.; Thompson, B.J. Echo Intensity Versus Muscle Function Correlations in Older Adults Are Influenced by Subcutaneous Fat Thickness. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2018, 44, 1597–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinberg, C.R.; Ryan, E.D.; Tweedell, A.J.; Barnette, T.J.; Wagoner, C.W. Influence of Lower Extremity Muscle Size and Quality on Stair-Climb Performance in Career Firefighters. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2016, 30, 1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangine, G.T.; Hoffman, J.R.; Wang, R.; Gonzalez, A.M.; Townsend, J.R.; Wells, A.J.; Jajtner, A.R.; Beyer, K.S.; Boone, C.H.; Miramonti, A.A.; et al. Resistance Training Intensity and Volume Affect Changes in Rate of Force Development in Resistance-Trained Men. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2016, 116, 2367–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schober, P.; Boer, C.; Schwarte, L.A. Correlation Coefficients: Appropriate Use and Interpretation. Anesth. Analg. 2018, 126, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.S.; Abe, T.; Bell, Z.W.; Wong, V.; Spitz, R.W.; Yamada, Y.; Loenneke, J.P. The Relationship Between Muscle Size and Strength Does Not Depend on Echo Intensity in Healthy Young Adults. J. Clin. Densitom. 2021, 24, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Fukumoto, Y.; Ishihara, T.; Yokoyama, K.; Yoshida, T.; Miyake, M.; Yamagata, E.; Kimura, M. Echo Intensity Obtained from Ultrasonography Images Reflecting Muscle Strength in Elderly Men. Clin. Interv. Aging 2013, 8, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckner, S.L.; Yitzchaki, N.; Kataoka, R.; Vasenina, E.; Zhu, W.G.; Kuehne, T.E.; Loenneke, J.P. Do Exercise-Induced Increases in Muscle Size Contribute to Strength in Resistance-Trained Individuals? Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2021, 41, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagle, J.P.; Carroll, K.M.; Cunanan, A.J.; Taber, C.B.; Wetmore, A.; Bingham, G.E.; DeWeese, B.H.; Sato, K.; Stuart, C.A.; Stone, M.H. Comparison of the Relationship between Lying and Standing Ultrasonography Measures of Muscle Morphology with Isometric and Dynamic Force Production Capabilities. Sports 2017, 5, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, E.N.; Rech, A.; Minozzo, F.; Botton, C.E.; Radaelli, R.; Teixeira, B.C.; Reischak-Oliveira, A.; Pinto, R.S. Concurrent Strength and Endurance Training Exercise Sequence Does Not Affect Neuromuscular Adaptations in Older Men. Exp. Gerontol. 2014, 60, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, T.; Kearns, C.; Fukunaga, T. Sex Differences in Whole Body Skeletal Muscle Mass Measured by Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Its Distribution in Young Japanese Adults—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14514537/ (accessed on 22 December 2022).
- Avin, K.; Naughton, M.; Ford, B.; Moore, H.; Monitto-Webber, M.; Stark, A.; Gentile, A.; Frey Law, L. Sex Differences in Fatigue Resistance Are Muscle Group Dependent—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20195184/ (accessed on 22 December 2022).
- Hicks, A.; Kent-Braun, J.; Ditor, D. Sex Differences in Human Skeletal Muscle Fatigue—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11474957/ (accessed on 22 December 2022).
- Shephard, R.; Bouhlel, E.; Vandewalle, H.; Monod, H. Muscle Mass as a Factor Limiting Physical Work.—PMC. Available online: https://www-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.ezproxy.tcu.edu/pmc/articles/PMC1197179/ (accessed on 22 December 2022).
- Goodpaster, B.H.; He, J.; Watkins, S.; Kelley, D.E. Skeletal Muscle Lipid Content and Insulin Resistance: Evidence for a Paradox in Endurance-Trained Athletes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 5755–5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Loon, L.J.C.; Goodpaster, B.H. Increased Intramuscular Lipid Storage in the Insulin-Resistant and Endurance-Trained State. Pflug. Arch-Eur. J. Physiol. 2006, 451, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillen, S.; Tak, R.O.; Zwarts, M.J.; Lammens, M.M.Y.; Verrijp, K.N.; Arts, I.M.P.; van der Laak, J.A.; Hoogerbrugge, P.M.; van Engelen, B.G.M.; Verrips, A. Skeletal Muscle Ultrasound: Correlation Between Fibrous Tissue and Echo Intensity. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2009, 35, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimers, K.; Reimers, C.D.; Wagner, S.; Paetzke, I.; Pongratz, D.E. Skeletal Muscle Sonography: A Correlative Study of Echogenicity and Morphology. J. Ultrasound Med. 1993, 12, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsiaras, A.; Newman, A.B.; Kriska, A.; Brach, J.; Krishnaswami, S.; Feingold, E.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Li, R.; Harris, T.B.; Schwartz, A.; et al. Skeletal Muscle Fatigue, Strength, and Quality in the Elderly: The Health ABC Study. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005, 99, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melvin, M.N.; Smith-Ryan, A.E.; Wingfield, H.L.; Fultz, S.N.; Roelofs, E.J. Evaluation of Muscle Quality Reliability and Racial Differences in Body Composition of Overweight Individuals. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2014, 40, 1973–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miljkovic, I.; Cauley, J.A.; Petit, M.A.; Ensrud, K.E.; Strotmeyer, E.; Sheu, Y.; Gordon, C.L.; Goodpaster, B.H.; Bunker, C.H.; Patrick, A.L.; et al. Greater Adipose Tissue Infiltration in Skeletal Muscle among Older Men of African Ancestry. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 2735–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, M.S.; Oranchuk, D.J.; Burton, A.M.; Phan, D.C. Age-, Sex-, and Region-Specific Differences in Skeletal Muscle Size and Quality. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2020, 45, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liguori, G.; Feito, Y.; Fountaine, C.; Roy, B. ACSM’s Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription, 11th ed.; Wolters Kluwer: Alphen aan den Rijn, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar]
| 1 Repetition Maximum | Total Repetitions | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ultrasonography Measure | Pearson Correlation | p-Value | Pearson Correlation | p-Value |
| Sagittal View | ||||
| Muscle Thickness | 0.836 | <0.001 * | −0.405 | 0.038 * |
| Echo Intensity | −0.350 | 0.065 | 0.308 | 0.093 |
| Corrected EI | −0.727 | <0.001 * | 0.692 | <0.001 * |
| Transverse View | ||||
| Muscle Thickness | 0.813 | <0.001 * | −0.435 | 0.028 * |
| Echo Intensity | −0.230 | 0.165 | 0.111 | 0.321 |
| Corrected EI | −0.618 | 0.002 * | 0.515 | 0.010 * |
| Extended Field of View | ||||
| Cross-Sectional Area | 0.802 | <0.001 * | −0.433 | 0.028 * |
| Echo Intensity | −0.108 | 0.325 | 0.196 | 0.204 |
| Corrected EI | −0.519 | 0.01 * | 0.556 | 0.005 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Voskuil, C.; Dudar, M.; Zhang, Y.; Carr, J. Skeletal Muscle Ultrasonography and Muscle Fitness Relationships: Effects of Scanning Plane and Echogenicity Correction. Muscles 2023, 2, 109-118. https://doi.org/10.3390/muscles2020010
Voskuil C, Dudar M, Zhang Y, Carr J. Skeletal Muscle Ultrasonography and Muscle Fitness Relationships: Effects of Scanning Plane and Echogenicity Correction. Muscles. 2023; 2(2):109-118. https://doi.org/10.3390/muscles2020010
Chicago/Turabian StyleVoskuil, Caleb, Monique Dudar, Yan Zhang, and Joshua Carr. 2023. "Skeletal Muscle Ultrasonography and Muscle Fitness Relationships: Effects of Scanning Plane and Echogenicity Correction" Muscles 2, no. 2: 109-118. https://doi.org/10.3390/muscles2020010
APA StyleVoskuil, C., Dudar, M., Zhang, Y., & Carr, J. (2023). Skeletal Muscle Ultrasonography and Muscle Fitness Relationships: Effects of Scanning Plane and Echogenicity Correction. Muscles, 2(2), 109-118. https://doi.org/10.3390/muscles2020010






