Abstract
Yohimbine hydrochloride (YHM) is an alpha-2-adrenergic receptor antagonist that possesses sympathomimetic properties, but few studies have investigated YHM in the context of exercise. The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of acute YHM ingestion on bench press exercise power, velocity, and strength-endurance levels. In a double-blinded crossover design, resistance-trained males (n = 16) participated in two separate bench press trials, each with a different single-dose treatment: placebo (PL; gluten-free corn starch) or yohimbine hydrochloride (YHM; 2.5 mg). In each trial, the participants consumed their respective treatment 20 min prior to exercise. Following a warm-up, the participants completed 1 set × 2 explosive repetitions while a linear position transducer monitored the barbell velocity. The participants then completed 3 sets × repetitions to failure (RTF) at 75% of 1-repetition maximum (1-RM) separated by 2 min of rest. The motivation to exercise and subjective measures of energy or fatigue were measured post-exercise. The total RTF, mean velocity, mean power, motivation, and subjective energy or fatigue values were compared and analyzed. The mean power (p = 0.472; d = 0.16) and mean velocity (p = 0.297; d = 0.25) values were unchanged by treatment. However, the RTF (p = 0.002; d = 0.82) value was higher with YHM treatment. The motivation to exercise (p = 0.011; d = 0.64) and energy levels (p < 0.001; d = 1.27) were significantly higher with YHM ingestion versus PL. The subjective fatigue was significantly lower with YHM ingestion (p < 0.001; d = 1.65). In conclusion, the current findings show that YHM consumption enhanced muscular strength-endurance while improving feelings of motivation, energy, and fatigue. YHM ingestion may, therefore, be useful for athletes or competitors seeking to improve their performance or combat subjective fatigue.
1. Introduction
Yohimbine is a naturally occurring alkaloid that is highly concentrated in the bark of the Corynanthe johimbe tree native to various parts of Africa [1]. Extracts from the bark have been used in folk medicine for centuries to prevent fatigue and improve virility [2]. Recently, standardized forms, such as yohimbine hydrochloride (YHM), have been used in nutritional practices by athletes and competitors in an effort to optimize performance. Physiologically, YHM exerts pleiotropic effects, which are principally mediated through the antagonism of α2- adrenergic receptors and increased catecholamine release [3,4]. Through sympathomimetic actions, YHM administration has been shown to increase catecholamine release [5], blood pressure [3], and arousal [6] and to alter blow flow [4]. However, the effects of YHM on exercise responses remain largely understudied, especially regarding resistance exercise.
As an α2- adrenergic receptor antagonist, YHM has a rapid onset of action (~10 min) and is typically eliminated by ~60 min post-ingestion [7]. Catecholamine responses (i.e., norepinephrine, epinephrine) have been shown to significantly increase during this time frame, effectively heightening the sympathetic stimulation [2,3,8]. The mechanistic determinants of exercise responses with YHM ingestion remain unknown. However, YHM supplementation has been shown to result in neuromuscular hyperemia (i.e., cerebrum, skeletal muscle) while attenuating fatigue [4,8]. Indeed, Barnes et al. reported lower blood lactate (La) levels post-exercise, which were coupled to lower fatigue [8]. From a performance perspective, increased catecholamines and skeletal muscle blood flow with YHM could plausibly increase muscular force production levels and allow for a greater ability to sustain repeated contractions. Psychophysiologically, YHM has been shown to increase alertness [6], emotional reactivity [9], and “psyching up” or motivation [1,2]. Given that muscular endurance and strength have been shown to be limited by fatigue and motivation [10,11], YHM may serve as an effective strategy to enhance performance, but this remains unknown.
YHM has only recently been studied in the context of exercise, despite being widely available as an ingredient in many commercially available supplements in the United States [12]. While chronic dosing protocols have shown limited efficacy in humans [13], multiple investigations have shown that acute YHM ingestion may improve aspects of performance [8,14]. Hoffman et al. showed hastened reactive ability and feelings of alertness during agility tests with an acute dosing protocol, albeit in a multi-ingredient supplement containing YHM [15]. Al-Kuraishy et al. reported that following a single 5 mg dose of YHM, aerobic cycling performance, and oxygen uptake levels were enhanced [14]. Recently, our lab showed that a single 2.5 mg dose of YHM resulted in improved repeated sprint performance (+5%), lower post-exercise La (−19%), and diminished power output loss (i.e., fatigue index; −16%) levels [8]. However, whether previous reports of sprint performance enhancements with acute YHM ingestion translate to resistance exercise remains unknown. Additionally, a large amount of the available literature on YHM treatment is decades old, leaving a dire need for novel research, especially pertaining to exercise. The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of acute YHM ingestion on bench press exercise power, velocity, and strength-endurance levels, and the psychophysiological responses thereof. We hypothesized that YHM would increase bench press power, velocity, and repetition volume values, and would result in greater feelings of energy or lower feelings of fatigue.
2. Results
2.1. Bench Press Performance
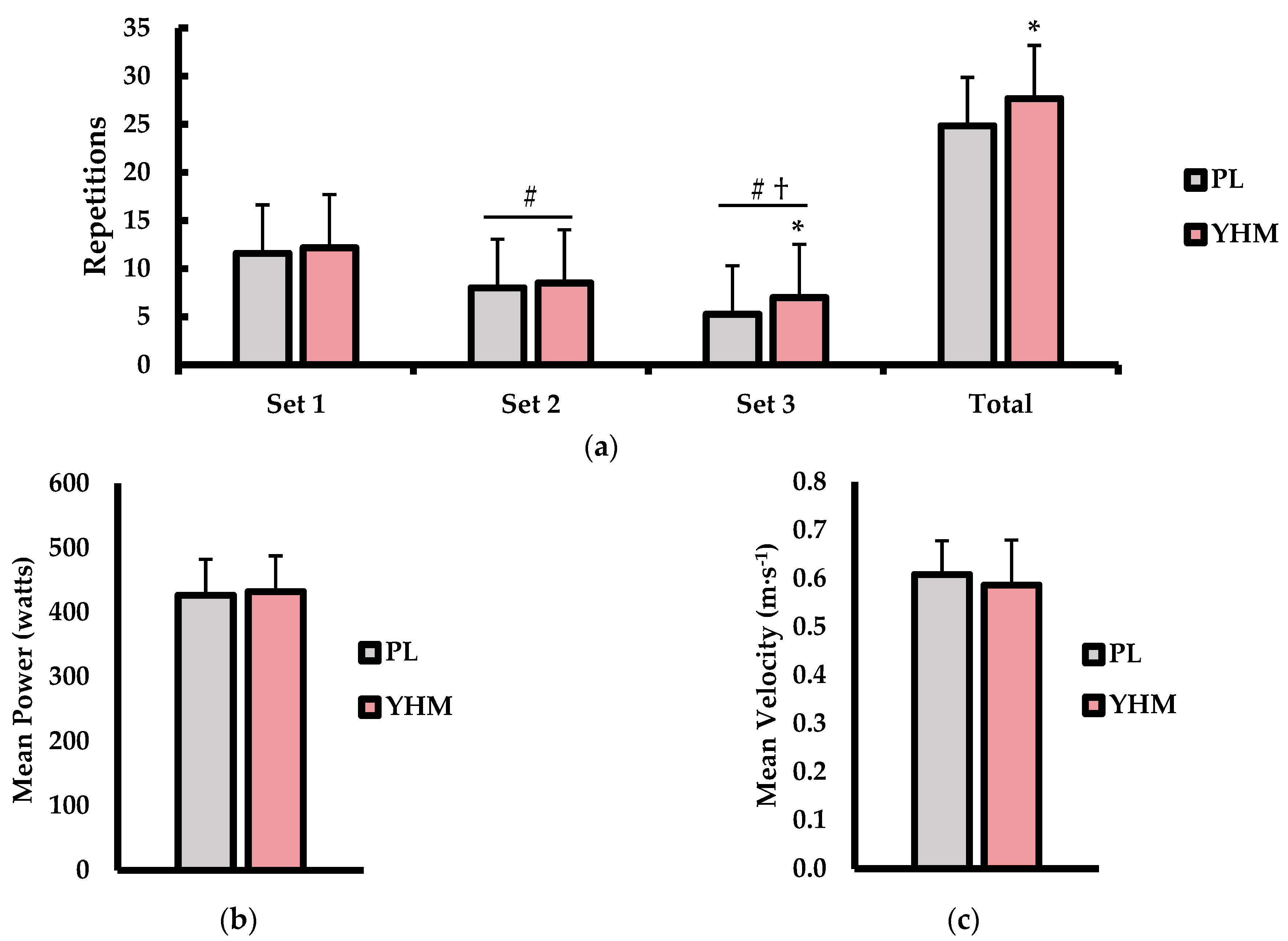
The RTF (repetitions), mean power (watts), and mean velocity (m·s−1) values are shown in Figure 1. The set-to-set and total RTF analysis (Figure 1a) showed the main effects for the treatment (p = 0.002; η2 = 0.021) and set (p < 0.001; η2 = 0.564) variables but no interaction effect (p = 0.082; η2 = 0.008). Specifically, the YHM ingestion resulted in a greater RTF value compared to PL (p = 0.002; d = 0.82; %Δ: +11.1%). The RTF values decreased from set-to-set in a manner whereby the reps performed in set 2 (p < 0.001; d = 2.07; %Δ: −30.4%) and set 3 (p < 0.001; d = 3.07 %Δ: −47.7%) were lower than in set 1. The RTF value in set 2 was also higher than in set 3 (p < 0.001; d = 0.93). For the total RTF, the YHM treatment resulted in a significantly higher repetition volume cumulatively over the 3 sets compare to PL (p = 0.015; d = 0.82; %Δ: +11.1%). For the mean power (Figure 1b), there were no significant differences between YHM and PL treatments (p = 0.431; d = 0.24; %Δ: +1.3%). Furthermore, the mean velocity (Figure 1c) values did not different between YHM and PL (p = 0.242; d = 0.36%Δ: −3.2%).
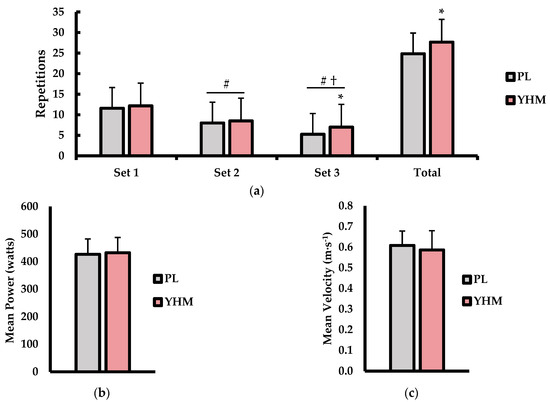
Figure 1.
(a) Repetitions to failure (repetitions) for each of the three sets and total accumulated repetitions (Total) over the three sets. (b) Mean power (watts) and (c) mean velocity (m·s−1) values as compared between the placebo (PL; grey bars) and yohimbine HCl (YHM; red bars) treatments. Data are presented as means ± SD. Note: # indicates significantly different from set 1 (p < 0.05); † indicates significantly different from set 2 (p < 0.05); * indicates significantly different from PL (p < 0.05).
2.2. Subjective Measures—Motivation, Energy, Fatigue, Alertness, Focus
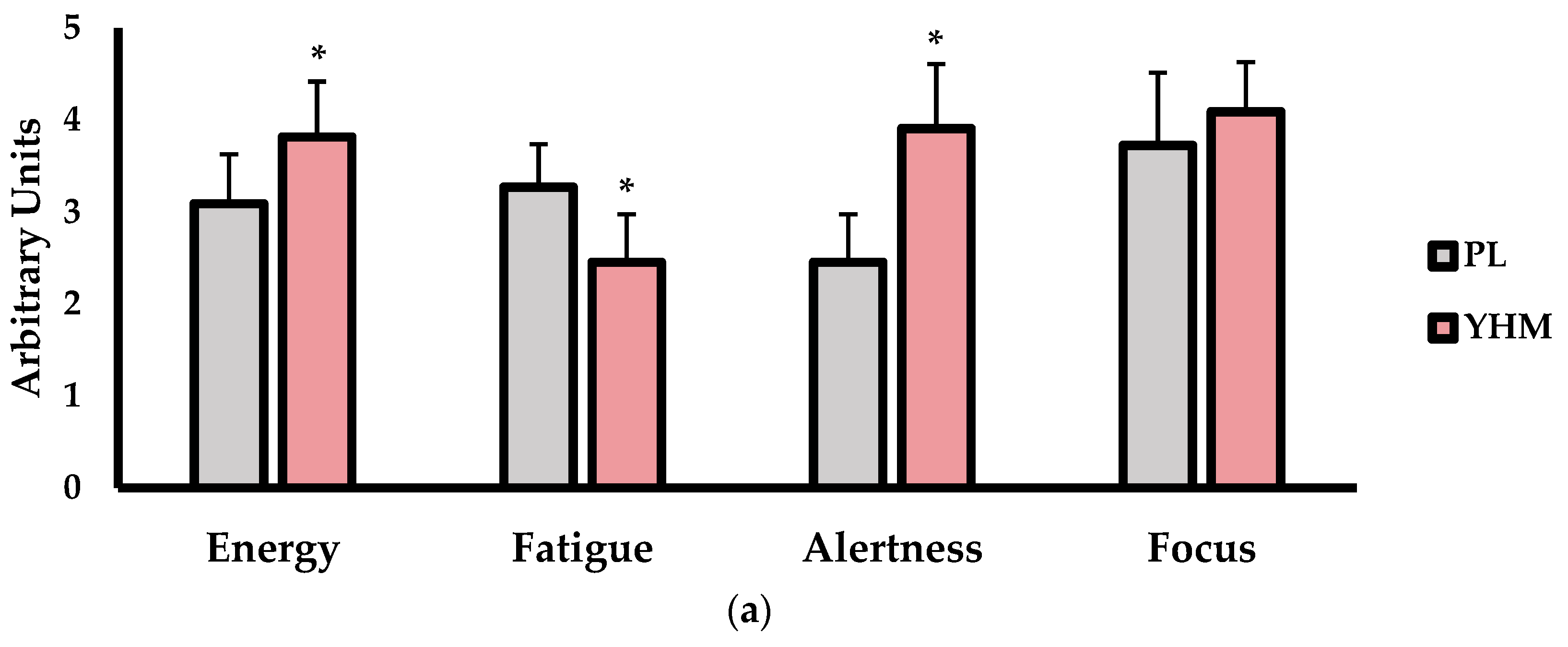
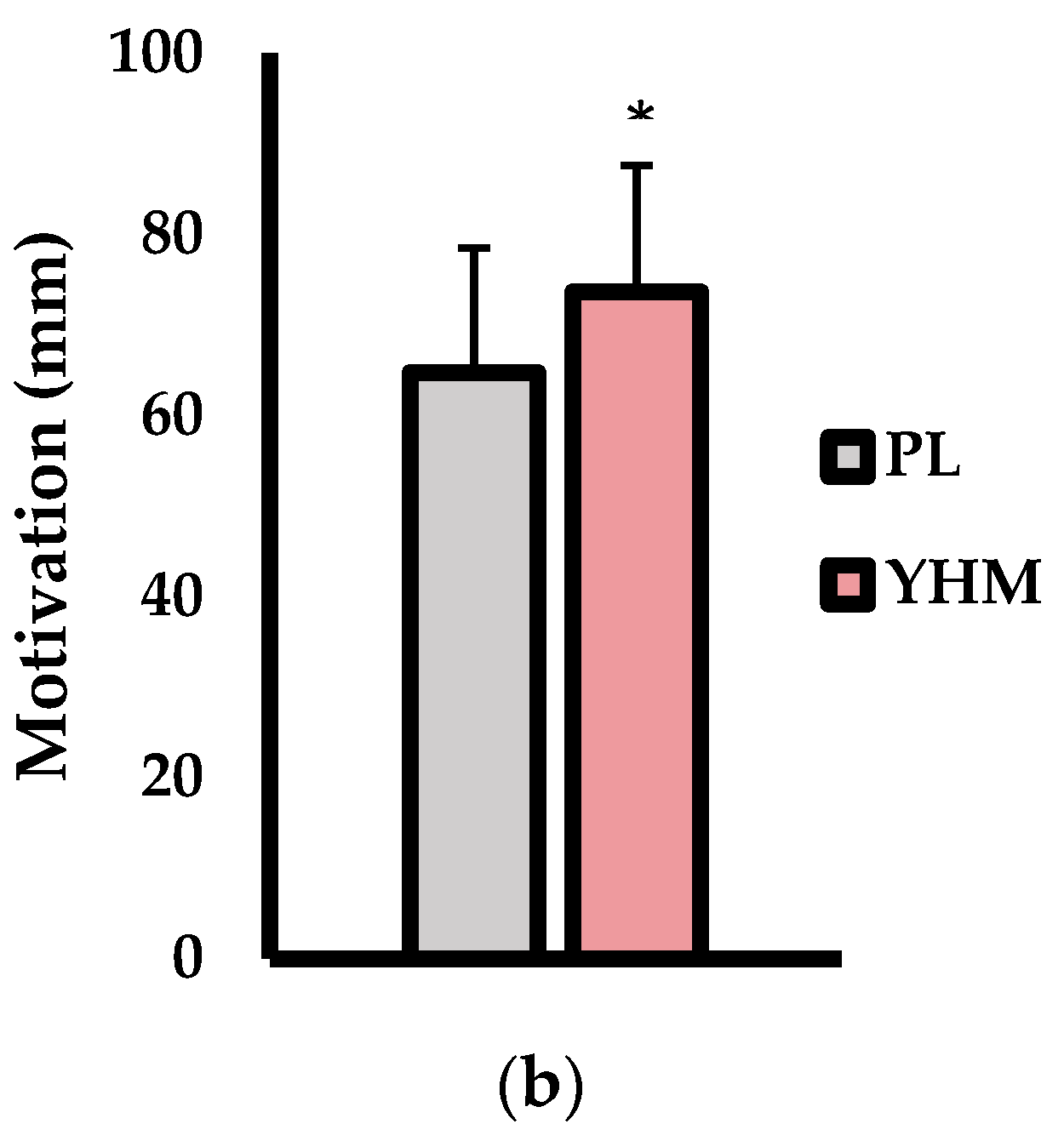
The subjective measures of energy, fatigue, alertness, focus, and motivation (mm) are shown in Figure 2. As shown in Figure 2a, energy (p < 0.001; d = 1.27; %Δ: +18.2%) and alertness (p < 0.001; d = 2.7; %Δ: +35.8%) were significantly higher with the YHM treatment versus PL. Furthermore, the subjective fatigue was significantly lower with the YHM treatment compared to PL (p < 0.001; d = 1.65; %Δ: −21.2%). Focus was not significantly altered as a consequence of the treatment (p = 0.167; d = 0.45; %Δ: +9.8%). For the motivation to exercise (Figure 2b), the YHM ingestion resulted in significantly greater feelings of motivation compared to PL (p = 0.011; d = 0.64; %Δ: +12.1%).
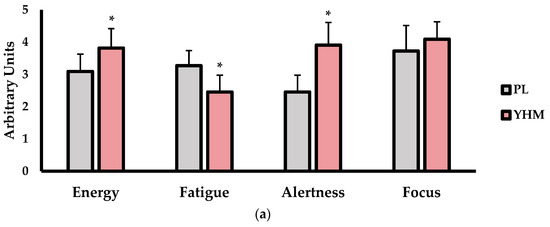
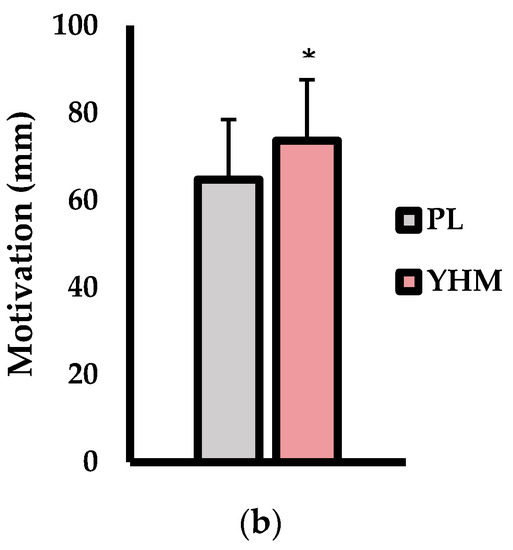
Figure 2.
(a) Subjective feelings of energy, fatigue, alertness, and focus as assessed by 5-point Likert scale questioning. (b) Motivation (mm) assessed by a 100-mm visual analog scale as compared between placebo (PL; grey bars) and yohimbine HCl (YHM; red bars) treatments. Data are presented as means ± SD. Note: # indicates significantly different from set 1 (p < 0.05); † indicates significantly different from set 2 (p < 0.05); * indicates significantly different from PL (p < 0.05).
3. Discussion
Despite its pervasive availability in pre-workout and energy supplements, YHM has been relatively understudied regarding exercise performance. Repeated sprint performance and indices of fatigue have been shown to be improved with acute YHM ingestion [8]. However, the current findings are the first to delineate whether YHM may impart ergogenic benefits during resistance exercise. The present observations show that acute YHM ingestion did not enhance the power or velocity but increased the total RTF, which was mainly manifested in the third set. Furthermore, the subjective feelings of energy, alertness, and motivation were higher with the YHM treatment, while also diminishing the subjective fatigue. While the physiological determinants of the improvements in performance remain unknown, these findings reveal important information on how YHM may influence muscular strength-endurance and psychophysiological responses during resistance exercise.
Previous investigations have reported increased power output values with acute YHM ingestion during repeated sprints, which are in opposition to the current findings [8,14]. While not confirmed currently, the disparities in findings may be due to the exercise duration or fatigue state. Previous studies reporting enhanced power output and performance values with YHM treatment noted an attenuation in fatigue as a principal underlying mechanism [8,14]. Indeed, the indirect markers of fatigue, such as La, have been shown to be lower following intense repeated exercise [8]. Since non-fatiguing exercise was used to measure power and velocity, the benefits from YHM ingestion may have eluded the current exercise protocol. Although context- and intensity-dependent, this is partially supported by the previous evidence suggesting that stimulants and sympathomimetics in moderate doses may be more effective later into exercise rather than at the onset of the exercise bout [16,17]. Since no optimal dosing or training protocols have been identified to accompany YHM ingestion, future research will be necessary to establish which performance variables may benefit the most from acute supplementation. Contrary to the lack of changes in explosive performance, the participants were able to accumulate a greater repetition volume with YHM treatment, which was most pronounced in the last of the three bench press sets. While speculative, these changes may be possibly due to changes in blood flow and nociception. YHM has been widely researched and used to improve blood flow to combat impotence [18]. However, YHM and other α2-adrenergic antagonists have been shown to also induce hyperemia in neural and skeletal muscle tissues in rodents and humans [4,19]. YHM ingestion has been shown to lower La levels during anaerobic exercise and is possibly implicated in greater lactate clearance [8]. While La was not measured in the current study, while the increased blood flow from YHM ingestion may have resulted in greater La clearance, thereby attenuating pH disturbances and fatigue and allowing for greater RTF values. Furthermore, YHM has been shown to have antinociceptive actions, although these appear to be dose-dependent [20,21]. This has been elucidated in exercising rodent models, where YHM ingestion blunted pain perception during cold water swimming tests [21]. Mechanistically, this may be due to the inhibition of sodium ion channels and vanilloid receptors (TRPV1), which mediate peripheral pain sensations in sensory neurons [22]. In humans, YHM and pain have been primarily studied in clinical populations [23]. Burhel et al. showed that the intravenous delivery of YHM initiated hypoalgesia in individuals with chronic back pain [24]. Furthermore, Park et al. showed that periodic YHM administration resulted in antinociception in patients with peripheral nerve pain [23]. While uncertain, it is plausible that YHM ingestion may have induced mild hypoalgesia, which could have led to a superior ability to endure fatiguing exercise. This is bolstered by previous studies utilizing stimulants where acute ingestion decreased muscle pain and increased RTF values during resistance exercise [25,26]. However, mechanistic studies of how YHM influences resistance exercise performance are non-existent, and further studies will be needed to substantiate the previously discussed performance mediators.
Interestingly, YHM ingestion had pronounced effects on psychological measures related to energy and fatigue. The findings of increased energy and alertness with YHM administration are supported by previous findings using a multi-ingredient energy supplement containing YHM [15]. Indeed, α2-adrenergic antagonists, including YHM, have been shown to increase both plasma and cerebral spinal fluid catecholamine levels, which may underlie increased feelings of vigor accompanying performance enhancements [27,28]. For example, Plewnia et al. showed that YHM administration resulted in greater neural recruitment and cortico-motoneuronal excitability, likely through increases in norepinephrine [29]. This is also partially supported by other studies showing that YHM may in turn aid in linking regions of the brain responsible for psychological arousal to locomotor activity [2,30]. Since arousal and alertness are closely linked to optimal performance [31], increases in arousal from YHM may serve as another effective mechanism for the enhancement of strength-endurance. Similarly, the self-reported levels of motivation were higher here with YHM treatment. While the current findings are among the first to describe increases in motivation to exercise with YHM ingestion, other groups have shown that catecholamine stress responses from YHM administration result in increased motivated behavior and impulsivity [32]. Previous studies have suggested that YHM ingestion alters the basal neural signaling in the pre-frontal cortex, which may lead to greater anticipatory drive and impulsive responding [33]. When paired with findings of increased reward-biased decision making with YHM treatment [34], the improvements in strength-endurance may be a psychophysiological manifestation of motivation or a synergistic amalgam of other subjective states, including energy and alertness. However, much of this is speculative as to whether it translates to exercise, which will require further study to form sound conclusions.
Although the current study provides novel findings of the ergogenic potential of YHM, it was not without limitations. First, the dosage protocols are heterogenous in the YHM literature, and the current study was not able to elucidate an optimal YHM regimen. The performance enhancement with the current dose used here may not translate to other doses, protocols, or athletic populations. Dose-response investigations, particularly with YHM in the context of exercise, will be needed to better determine strategies for optimizing performance. Additionally, blood flow and changes in neural activation have been widely reported as mechanistic underpinnings of YHM ingestion [2,4,5,22]. While the present findings support these mechanisms, the precise contribution to the performance enhancement remains elusive. The mechanistic confirmation of YHM responses during exercise in humans will be necessary to substantiate the aforementioned mechanisms. Lastly, only a single upper body resistance exercise and load were tested. Since stimulants may influence upper and lower body resistance exercise performance levels differently [35], the current performance improvements may not appertain to other types of resistance exercise or loads. In conclusion, the current findings reveal that the YHM ingestion had little impact on the explosive bench press performance but improved the muscular strength-endurance results. The adaptive psychophysiological responses of increased energy, alertness, motivation, and lower fatigue accompanied and likely mediated the changes in performance. From a practical perspective, athletes and competitors may use an acute dose of YHM to increase strength-endurance and combat fatigue during repeated sets of resistance exercise or possibly during gameplay where upper body pressing is involved (i.e., American football, rugby, shotput, etc.). While it is still unknown how chronic YHM supplementation influences long-term resistance exercise adaptations, the current findings of acute performance enhancements could suggest greater adaptive responses over time if repeated, and the ergogenic effects of YHM maintaining their efficacy and strength. However, it should be noted that YHM is a potent stimulant, which like many stimulants may have heterogeneous effects, depending on the individual. Thus, athletes and competitors should practice temperance if they are beginning a YHM regimen and should assess their individual tolerance and efficacy. While the current findings alone cannot readily predict how well all individuals will respond to YHM, the increases in strength-endurance and subjective feelings of energy suggest that YHM ingestion may be useful for some athletes and competitors.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design
Using a double-blinded, counterbalanced, crossover study design, this study examined the effects of acute YHM supplementation on explosive bench press performance. Resistance-trained males volunteered to participate and underwent two experimental bench press trials, each with a different randomized condition: (1) YHM; (2) placebo (PL; gluten-free cornstarch). Following supplement ingestion, the participants completed a series of bench press sets while measurements were collected for their mean barbell velocity, power, and repetitions performed. The subjective measures of energy, fatigue, alertness, focus, and motivation were collected following the completion of exercise. The visits were separated by a minimum of 72 h.
4.2. Participants
To determine the appropriate sample size, an a priori power analysis was conducted using statistical software (G * power V 3.1.9.4). A previous investigation from our lab measuring anaerobic sprint performance with YHM supplementation in females showed a lower fatigue index with an estimated effect size of d = 1.08 [8]. To calculate the minimal sample size, the following parameters were used: test = t-test (matched pairs), d = 1.08, α = 0.05, 1-β = 0.8. These were calculated to a minimum sample size range of n = 9 for adequate power. Healthy resistance-trained males (n = 16) participated and their descriptive characteristics are shown in Table 1. In order to be deemed resistance-trained, the participants were required to complete ≥ 2 days of resistance exercise each week, including performance of the barbell bench press regularly [36,37]. To ensure the safety of the exercise protocol, a physical activity readiness questionnaire (PARQ) was completed by each participant for exercise screening [36]. The exclusion criteria included: upper body injuries within the past six months, a current disease or diagnosis limiting exercise ability, and current supplementation with YHM or any of its constituents in any form [38]. The participants were instructed prior to each visit to refrain from consuming caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol 12 h before and engaging in vigorous exercise 24 h before exercise [38]. The participants were also asked to maintain similar sleep and dietary routines for each visit. Preceding any data collection, verbal and written informed consent was obtained from each participant. All experimental procedures were conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Samford University Institutional Review Board.

Table 1.
Descriptive characteristics (n = 16).
4.3. Supplementation
The acute supplementation protocol was followed in an identical manner to Barnes et al. [8]. Briefly, each participant ingested either a PL (gluten-free cornstarch) or YHM (2.5 mg; Primaforce, Burlington, NC, USA) treatment 20 min prior to exercise. The treatments were orally ingested and delivered in indistinguishable gelatin capsules. The color and shape of the capsules were identical between the PL and YHM treatments. Furthermore, the treatments were distributed in a double-blinded manner, whereby an independent researcher organized non-identifiable opaque bags containing each treatment. The participants were not aware of any experimental hypotheses and remained blinded until the completion of the study.
4.4. One-Repetition Maxium (1-RM) and Familiarization
Prior to the experimental trials, the participants completed a one-repetition maximum (1-RM) and familiarization visit [37,39,40]. A progressive bench press warm-up was completed according to the American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM) recommendations [36]. After the cessation of the warm-up, the barbell load was progressively increased by 2.5–20.0 kg for one attempt until the participant could not finish the concentric phase of the lift. The 1-RM load was attained within four attempts separated by 3–5 min each [40,41]. To ensure that the participants were familiar with completing the bench press explosively, a 20 kg Olympic barbell was lifted as quickly and explosively as possible for three repetitions. This was repeated for a total of three sets and their form was corrected as needed.
4.5. Experimental Procedures
Following the ingestion of the corresponding treatment, the participants completed a repeated bench press test as previously described by Williams et al. [37,42]. First, the participants completed a progressive warm-up consisting of 5 repetitions at 40% of 1-RM and 3 repetitions at 60% of 1-RM, with each set separated by a 2 min rest period [37]. To measure the barbell velocity and power, the participants then completed 2 sets × 2 repetitions of bench press at 75% of 1-RM as explosively as possible. A linear position transducer (GymAware, Kinetic Performance Technology, ACT, Australia) was fixed to the barbell during this time to attain the mean velocity and power measurements. This device had been previously validated for velocity measurements by multiple groups [43,44]. Additionally, our group had previously used this equipment with excellent test-retest reliability in our laboratory (ICC = 0.932) [35,41]. The device was employed according to the manufacturer’s instructions, such that the device was attached to the barbell with an approximate perpendicular angle being achieved throughout the lift [45]. The mean barbell velocity and power values were averaged across the 2 sets × 2 repetitions and used for the analysis. The participants then rested for 5 min before completing 3 sets × repetitions to failure (RTF) of the bench press exercise at 75% 1-RM [37,40,46]. Each set of RTF was separated by 2 min of rest. Failure was deemed by the participant’s inability to complete the concentric phase of the repetition or if the participant deviated from proper form. The repetitions for each set and the total repetitions were recorded for the analysis. Following the completion of the exercise, subjective feelings of energy, fatigue, alertness, focus, and motivation were measured. A 5-point Likert scale questionnaire (1 = very low; 2 = low; 3 = average; 4 = high; 5 = very high) was used to assess energy, fatigue, alertness, and focus levels in an identical manner to Hoffman et al. [15]. The motivation was assessed via a visual analog scale as previously described by our lab [37,40,47,48]. In brief, the participants were presented with a 100 mm line and asked to mark how motivated they felt to exercise, where 0 was “no motivation” and 100 was “extremely motivated”.
4.6. Data Analysis
The data analysis was completed using Jamovi software (Version 0.9; Sydney, Australia). There were no violations of data normality detected with the Shapiro–Wilk method for any comparisons. The mean barbell velocity, mean power, total RTF, energy, fatigue, alertness, focus, and motivation were analyzed using a paired samples t-test. For the analysis of set-to-set RTF values, a 2 × 3 (treatment × set) repeated measures ANOVA was utilized. For the significant main effects, an individual means post-hoc analysis was performed as previously recommended by Wei et al. with a Bonferroni–Holm post-hoc test [49]. Each percent change (%Δ) was also calculated for mean comparisons as ((initial value − final value)/final value) * 100. The estimates of effect size for the main effects were calculated using eta squared (η2) and interpreted as: 0.01—small; 0.06—medium; ≥0.14—large [50,51]. The individual mean effect sizes were calculated via Cohen’s d (d) between conditions and interpreted as: 0.2—small; 0.5—moderate; 0.8—large [50,51]. Significance was set at p ≤ 0.05 a priori.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.D.W., R.R.R. and C.G.B.; data curation, T.D.W., L.E.B., M.L.M., L.H.S. and C.G.B.; formal analysis, T.D.W. and C.G.B.; investigation, T.D.W., L.E.B., C.L.H., M.L.M., R.R.R., L.H.S. and C.G.B.; methodology, T.D.W., L.E.B., C.L.H., M.L.M., R.R.R., L.H.S. and C.G.B.; supervision, C.L.H. and R.R.R.; validation, T.D.W.; writing—original draft, C.G.B.; writing—review and editing, T.D.W., R.R.R. and C.G.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All experimental procedures were conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Samford University Institutional Review Board (EXPD-HP-19-S-29; August 2019).
Informed Consent Statement
Prior to any data collection, verbal and written informed consent was obtained from each participant.
Data Availability Statement
All data are contained within the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank HS for his support with the study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cimolai, N.; Cimolai, T. Yohimbine use for physical enhancement and its potential toxicity. J. Diet. Suppl. 2011, 8, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, S.W.; Worcel, M.; Wyllie, M. Yohimbine: A clinical review. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 91, 215–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musso, N.R.; Vergassola, C.; Pende, A.; Lotti, G. Yohimbine effects on blood pressure and plasma catecholamines in human hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens. 1995, 8, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, O.G.; Zubieta, J.K.; Grunhaus, L.; Minoshima, S. Effects of yohimbine on cerebral blood flow, symptoms, and physiological functions in humans. Psychosom. Med. 2000, 62, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, M.R.; Hollister, A.S.; Robertson, D. Influence of yohimbine on blood pressure, autonomic reflexes, and plasma catecholamines in humans. Hypertension 1983, 5, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phillips, M.; Szabadi, E.; Bradshaw, C. Comparison of the effects of clonidine and yohimbine on spontaneous pupillary fluctuations in healthy human volunteers. Psychopharmacology 2000, 150, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, J.; Nakatsu, S.; Fenemore, J.; Condra, M.; Surridge, D.; Morales, A. The pharmacokinetics of yohimbine in man. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1987, 32, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, M.E.; Cowan, C.R.; Boag, L.E.; Hill, J.G.; Jones, M.L.; Nixon, K.M.; Parker, M.G.; Parker, S.K.; Raymond, M.V.; Sternenberg, L.H.; et al. Effects of Acute Yohimbine Hydrochloride Supplementation on Repeated Supramaximal Sprint Performance. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gershon, S.; Holmberg, G. Autonomic and psychic effects of yohimbine hydrochloride. Psychopharmacology 1961, 2, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tod, D.; Iredale, F.; Gill, N. ‘Psyching-up’and muscular force production. Sports Med. 2003, 33, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollander, D.B.; Kraemer, R.R. Psychology of resistance exercise. In The Oxford Handbook of Exercise Psychology; Acevedo, E.O., Ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, P.A.; Wang, Y.H.; Maller, G.; DeSouza, R.; Khan, I.A. Pharmaceutical quantities of yohimbine found in dietary supplements in the USA. Drug Test. Anal. 2016, 8, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ostojic, S.M. Yohimbine: The effects on body composition and exercise performance in soccer players. Res. Sports Med. 2006, 14, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Kuraishy, H.M.; AN Abood, H.; Al-Gareeb, I.A. Ergogenic Effects of Yohimbine: Standardized Cycling Clinical Study. Kerbala J. Med. 2014, 7, 1850–1855. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, J.R.; Kang, J.; Ratamess, N.A.; Hoffman, M.W.; Tranchina, C.P.; Faigenbaum, A.D. Examination of a pre-exercise, high energy supplement on exercise performance. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2009, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tarnopolsky, M.A. Caffeine and endurance performance. Sports Med. 1994, 18, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, C.E.; Beneke, R.; Jones, G. Caffeine and other sympathomimetic stimulants: Modes of action and effects on sports performance. Essays Biochem. 2008, 44, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ernst, E.; Pittler, M. Yohimbine for erectile dysfunction: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. J. Urol. 1998, 159, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinonen, I.; Wendelin-Saarenhovi, M.; Kaskinoro, K.; Knuuti, J.; Scheinin, M.; Kalliokoski, K.K. Inhibition of α-adrenergic tone disturbs the distribution of blood flow in the exercising human limb. Am. J. Physiol. -Heart Circ. Physiol. 2013, 305, H163–H172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shannon, H.E.; Lutz, E.A. Yohimbine produces antinociception in the formalin test in rats: Involvement of serotonin1A receptors. Psychopharmacology 2000, 149, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kepler, K.L.; Bodnar, R.J. Yohimbine potentiates cold-water swim analgesia: Re-evaluation of a noradrenergic role. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1988, 29, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessaint, J.; Yu, W.; Krause, J.E.; Yue, L. Yohimbine inhibits firing activities of rat dorsal root ganglion neurons by blocking Na+ channels and vanilloid VR1 receptors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 485, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.H.; Yong, A.; Lee, S.H. Involvement of selective alpha-2 adrenoreceptor in sympathetically maintained pain. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2010, 47, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruehl, S.; Chung, O.Y.; Diedrich, L.; Diedrich, A.; Robertson, D. The relationship between resting blood pressure and acute pain sensitivity: Effects of chronic pain and alpha-2 adrenergic blockade. J. Behav. Med. 2008, 31, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, M.J.; Stanley, M.; Parkhouse, N.; Cook, K.; Smith, M. Acute caffeine ingestion enhances strength performance and reduces perceived exertion and muscle pain perception during resistance exercise. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2013, 13, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, T.R.; Howatson, G. Analgesic and anti-inflammatory drugs in sports: Implications for exercise performance and training adaptations. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2018, 28, 2252–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peskind, E.R.; Elrod, R.; Dobie, D.J.; Pascualy, M.; Petrie, E.; Jensen, C.; Brodkin, K.; Murray, S.; Veith, R.C.; Raskind, M.A. Cerebrospinal fluid epinephrine in Alzheimer’s disease and normal aging. Neuropsychopharmacology 1998, 19, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biaggioni, I.; Robertson, R.M.; Robertson, D. Manipulation of norepinephrine metabolism with yohimbine in the treatment of autonomic failure. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1994, 34, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plewnia, C.; Bartels, M.; Cohen, L.; Gerloff, C. Noradrenergic modulation of human cortex excitability by the presynaptic α2-antagonist yohimbine. Neurosci. Lett. 2001, 307, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnsten, A.F.; Li, B.-M. Neurobiology of executive functions: Catecholamine influences on prefrontal cortical functions. Biol. Psychiatry 2005, 57, 1377–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, D.; Krane, V. The arousal–athletic performance relationship: Current status and future directions. In Advances in Sport Psychology; Horn, T.S., Ed.; Human Kinetics Publishers: Champaign, IL, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.; Messing, R.B.; Sparber, S.B. Learning enhancement and behavioral arousal induced by yohimbine. Life Sci. 1987, 41, 1083–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Green, T.A.; Theobald, D.E.; Birnbaum, S.G.; Graham, D.L.; Zeeb, F.D.; Nestler, E.J.; Winstanley, C.A. Yohimbine increases impulsivity through activation of cAMP response element binding in the orbitofrontal cortex. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montes, D.R.; Stopper, C.M.; Floresco, S.B. Noradrenergic modulation of risk/reward decision making. Psychopharmacology 2015, 232, 2681–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degrange, T.; Jackson, W.; Williams, T.; Rogers, R.R.; Marshall, M.; Ballmann, C. Acute caffeine ingestion increases velocity and power in upper and lower body free-weight resistance exercises. Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2019, 12, 1280–1289. [Google Scholar]
- Riebe, D.; Ehrman, J.K.; Liguori, G.; Magal, M.; Medicine, A.C.o.S. ACSM’s Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription; Wolters Kluwer: Alphen aan den Rijn, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, T.D.; Martin, M.P.; Mintz, J.A.; Rogers, R.R.; Ballmann, C.G. Effect of Acute Beetroot Juice Supplementation on Bench Press Power, Velocity, and Repetition Volume. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2020, 34, 924–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballmann, C.G.; Maze, S.B.; Wells, A.C.; Marshall, M.M.; Rogers, R.R. Effects of short-term Rhodiola Rosea (Golden Root Extract) supplementation on anaerobic exercise performance. J. Sports Sci. 2018, 37, 998–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballmann, C.G.; McCullum, M.J.; Rogers, R.R.; Marshall, M.M.; Williams, T.D. Effects of Preferred vs. Nonpreferred Music on Resistance Exercise Performance. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2018, 35, 1650–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballmann, C.G.; Favre, M.L.; Phillips, M.T.; Rogers, R.R.; Pederson, J.A.; Williams, T.D. Effect of Pre-Exercise Music on Bench Press Power, Velocity, and Repetition Volume. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2021, 128, 1183–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballmann, C.G.; Cook, G.D.; Hester, Z.T.; Kopec, T.J.; Williams, T.D.; Rogers, R.R. Effects of Preferred and Non-Preferred Warm-Up Music on Resistance Exercise Performance. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2021, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, T.D.; Langley, H.N.; Roberson, C.C.; Rogers, R.R.; Ballmann, C.G. Effects of short-term golden root extract (Rhodiola rosea) supplementation on resistance exercise performance. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orange, S.T.; Metcalfe, J.W.; Marshall, P.; Vince, R.V.; Madden, L.A.; Liefeith, A. Test-retest reliability of a commercial linear position transducer (GymAware PowerTool) to measure velocity and power in the back squat and bench press. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2018, 34, 728–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hori, N.; Andrews, W. Reliability of velocity, force and power obtained from the Gymaware optical encoder during countermovement jump with and without external loads. J. Aust. Strength Cond. 2009, 17, 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Helms, E.R.; Storey, A.; Cross, M.R.; Brown, S.R.; Lenetsky, S.; Ramsay, H.; Dillen, C.; Zourdos, M.C. RPE and velocity relationships for the back squat, bench press, and deadlift in powerlifters. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2017, 31, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blazer, H.J.; Jordan, C.L.; Pederson, J.A.; Rogers, R.R.; Williams, T.D.; Marshall, M.R.; Ballmann, C.G. Effects of Time-of-Day Training Preference on Resistance-Exercise Performance. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2021, 92, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nixon, K.M.; Parker, M.G.; Elwell, C.C.; Pemberton, A.L.; Rogers, R.R.; Ballmann, C.G. Effects of Music Volume Preference on Endurance Exercise Performance. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2022, 7, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballmann, C.G.; Maynard, D.J.; Lafoon, Z.N.; Marshall, M.R.; Williams, T.D.; Rogers, R.R. Effects of Listening to Preferred versus Non-Preferred Music on Repeated Wingate Anaerobic Test Performance. Sports 2019, 7, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, J.; Carroll, R.J.; Harden, K.K.; Wu, G. Comparisons of treatment means when factors do not interact in two-factorial studies. Amino Acids 2012, 42, 2031–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fritz, C.O.; Morris, P.E.; Richler, J.J. Effect size estimates: Current use, calculations, and interpretation. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 2012, 141, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc.: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).