Abstract
Researchers and health practitioners seek to understand the upper limit of muscle hypertrophy under different conditions. Although there are models to estimate the muscle-building threshold in drug-free resistance training practitioners, little is known about the population using anabolic–androgenic steroids (AASs) in this regard. Because of a plateau effect of muscle hypertrophy upon AAS regimens, there is a hypothesis among clinicians and enthusiasts that AASs downregulate skeletal muscle androgen receptors (ARs). Conversely, in this narrative review, we show that seminal and recent evidence—primarily using testosterone and oxandrolone administration as human experimental models—support that AASs upregulate ARs, eliciting greater anabolic effects on skeletal muscle receptors through a dose-dependent relationship. Thus, to date, there is no scientific basis for claiming that myocyte AR downregulation is the cause of the AAS-induced plateau in muscle gains. This phenomenon is likely driven by the neutral nitrogen balance, but further research is imperative to clarify the intrinsic mechanisms related to this landscape.
1. Introduction
The use of anabolic–androgenic steroids (AASs) is targeted at clinical populations suffering from loss of strength and muscle mass [1,2,3]. Testosterone (T) administration is mainly used in the treatment of male hypogonadism as a means of improving a range of clinical symptoms and body composition [4,5,6].
T, as well as its synthetic derivatives (e.g., oxandrolone, stanozolol, oxymetholone, and nandrolone) can be used in muscle wasting disorders, such as burns, sarcopenia, osteoporosis, and cancer [7,8,9,10,11,12]. Notwithstanding the therapeutic proposals for AAS regimens, it is known that there is serious growth aimed at aesthetic improvement, within which muscle hypertrophy is one of the main goals [13]. Such a practice is not supported by the medical literature, with no consensus on dosing regimens and types of drugs, therefore resulting in an undecipherable field. However, due to the high prevalence of AAS use among non-athletes and athletes of different sports, as well as in resistance training practitioners [14,15], this scenario should not be neglected among health professionals who deal with these individuals.
Androgen receptors (ARs) are ligand-responsive transcription regulators regarded as a central tenet of muscle hypertrophy [16]. ARs are localized in the cytoplasm and translocate to the nucleus in the presence of AASs, thereby modulating AR-responsive genes [17]. There is a strong belief by health practitioners and enthusiasts that the constant AAS use at supraphysiological doses in bodybuilders and recreational AAS users can lead to a downregulation of ARs by virtue of putative saturation [18,19]. Such a hypothesis is based on the concept that AAS-induced muscle gains reach a plateau after a certain period of AAS use, but this concept is still not well documented.
To the best of our knowledge, there is no narrative review to distinguish misunderstandings from pragmatic molecular and clinical insights in this regard; therefore, a critical appraisal of different areas of medical research is needed to draw better conclusions and future directions. That said, in this narrative review, we discuss the nuances of AR regulation over AAS use, focusing on lean body mass and related molecular parameters (satellite cells, myofibrillar protein synthesis, etc.) as well.
2. Downregulation of Hormone Receptors: Androgen Receptors vs. Other Receptors
Recognizably, many hormone receptors can be downregulated, such as adrenergic receptors (i.e., alpha 1-, alpha 2-, and beta-adrenergic receptors) and insulin receptors [20,21,22,23,24]. Chronic exposure to high levels of insulin and adiposity (i.e., obesity) leads to the downregulation of insulin receptors [25,26,27], while physical exercise and weight/fat loss not only upregulate these receptors and their substrates (insulin-receptor substrates 1 and 2) but also peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha (PPAR-α) and -gamma (PPAR-γ), thus enhancing insulin sensibility and lipid metabolism [28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36].
Nevertheless, taking into account the relationship between ARs and skeletal muscle receptors, it is unsubstantiated to claim that there is downregulation of ARs in response to AAS administration. There is an undeniable lack of evidence to support AAS use downregulating ARs, even when considering animal studies. Amid the paucity of direct evidence, a single, older study using cells from the corpus cavernosum of rats reported that T led to downregulation of ARs [37]; however, instead of administrating T, finasteride was used as a means of increasing T concentration because of its actions in inhibiting 5-alpha reductase—then converting T to dihydrotestosterone [37]. In contrast to this study, another in vitro experiment showed that T administration upregulates AR in cultured the skeletal muscle satellite cells and myotubes of a porcine [38]. Thus, the latter study [38] portrays the biological nexus between AASs and AR regulation with more specificity in an attempt to understand the mechanisms inherent in the muscle-building plateau than the former one [37]. Furthermore, a couple of human studies show that T and oxandrolone upregulate myocyte AR [39,40], as discussed thoroughly in Section 4.
In addition to AASs, thermogenic drugs are widespread in bodybuilding and fitness [41,42]. Beta-2 adrenergic receptor agonists, such as clenbuterol and ephedrine, markedly promote the downregulation and desensitization of beta-2 receptors in the medium- and long-term, especially at high doses [43]. For this reason, these drugs lose effectiveness with chronic use this is quite different from long-term AAS use, which at least can maintain the muscle mass accretion induced by the initial and middle phases of AAS therapy [44,45]. As with AASs, it is crucial to emphasize that thermogenic drugs lack consensus as an approach to improving body composition due to adverse effects related to the cardiovascular system [46]—so much so, that they are not considered first-line therapy for obesity [47].
3. Crosstalk between Androgen Receptors and Satellite Cell-Mediated Hypertrophy
Muscle AR content has emerged as a determining factor for skeletal muscle hypertrophy, at least in men [48,49]. Albeit satellite cells are the predominant site of AR expression, ARs are expressed in various cell types in human skeletal muscle, such as fibroblasts, vascular endothelial, smooth muscle cells, mast cells, and CD34+ precursor cells [50]. Moreover, ARs are expressed in motor neurons, whose cells are located in the central nervous system and innervated to a target muscle, rendering a stimulus for myonuclear production due to the binding of AASs to ARs [51,52].
Satellite cells proliferate, differentiate, and fuse with each other, generating new myofibers with ensuing incorporation into an existing muscle fiber by donating their nucleus and yielding skeletal muscle hypertrophy [53]. The stimulus for the first step (i.e., proliferation) is triggered by resistance training or AAS use—or by their combination [54,55,56,57].
Many animal and human studies support that T administration leads to satellite cell proliferation and increases the number of myonuclei [58,59,60]. More importantly, supraphysiological doses of T increase the number of satellite cells and myonuclei in healthy men [60]. After 20 wk of 125, 300, or 600 mg weekly doses of T enanthate, Sinha-Hikim et al., detected significant increases in myonuclear number for those subjects who received 300 (2.5 ± 0.8 to 5.0 ± 0.8%, n = 8) and 600 mg (2.5 ± 0.5 to 15.0 ± 1.5%, n = 5) [60]. Equally important, the increase in satellite cell number correlated with changes in total (r = 0.548) and free T concentrations (r = 0.468) [60].
Given the well-established effects of AASs on orchestrating satellite cells, one can contemplate crosstalk between ARs and signaling pathways involved in activating satellite cells from quiescence to proliferation, as the binding of AASs to ARs is imperative to afford satellite cell-mediated hypertrophy [61].
Hence, based on the available literature, the hypothesis that the use of T and other AASs promote AR downregulation in skeletal muscle is an unwarranted assumption, as their effects on muscle mass accretion are evident, as discussed below.
4. Androgen Receptor Content, Accompanying Hypertrophy Mediators, and Lean Body Mass
Satellite cells and ARs regulate many genes in skeletal muscles. In a recent randomized clinical trial examining physically active men without obesity (n = 50) over 28 days of an exercise- and diet-induced 55% energy deficit, muscle AR protein and total RNA content were higher for those receiving 200 mg of T enanthate/wk than the placebo group while reducing fibroblast growth factor-inducible 14 and interleukin-6 receptor signaling [39]. In other words, T administration was able to attenuate proteolytic gene expression and enhance the translational capacity of myofibers, which collectively ensure greater myofibrillar protein synthesis and muscle hypertrophy. Not surprisingly, a lean body mass accretion of 3.8 ± 1.2 kg was found for the T group, with a reduction of 0.9 ± 1.0 kg for the placebo group (p < 0.01 between groups) [39].
The seminal study by Bhasin et al., tested triple the dose of the study above, observing that 600 mg/wk of T enanthate plus a resistance training program for 20 wk increased fat-free mass by ~6 kg (65.3 ± 1.8 to 71.4 ± 1.8) in healthy men, whereas resistance training alone (placebo administration) showed an increase of 2 kg (72.1 ± 2.3 to 74.1 ± 2.2) [62]. Additionally, in another study, Bhasin et al., demonstrated that T enanthate at 25, 50, 125, 300, or 600 mg for 20 wk (resulting in mean total T levels of 253, 306, 542, 1345, and 2370 ng/dL, respectively) increased fat-free mass in a dose-dependent manner when supraphysiological was administered (i.e., >100 mg/wk) in healthy young men (n = 61), with a fat-free mass accretion of 3.4, 5.2, and 7.9 kg for 125, 300, or 600 mg of T weekly, respectively [63].
Besides T administration, oxandrolone increases AR expression in skeletal muscle along with myofibrillar protein synthesis, as confirmed by a short-term study (6 healthy men) consisting of 15 mg/d oxandrolone for 5 days [40]. Such a daily dose is often given in a variety of clinical populations for which oxandrolone may be recommended [64,65,66,67]. Interestingly, Grunfeld et al., tested different doses of oxandrolone (20, 40, or 80 mg/d) for men with HIV-associated weight loss, and through a dose-dependent manner, found that only the 40 and 80 mg oxandrolone groups increased body weight and body cell mass compared to a placebo group over a 12 wk treatment period [68]. Body weight increased by 2.8 ± 3.3 and 2.3 ± 2.9 kg, and body cell mass increased by 1.5 ± 2.5 and 1.8 ± 1.8 kg, for 40 and 80 mg of oxandrolone, respectively, compared to their baselines.
These data are, therefore, a nail in the coffin for the unproven premise that myocyte AR are dose-dependently affected by AAS use. Indeed, insights into AAS dose-dependent muscle adaptations are proven by many studies [63,69,70,71], supporting a dose-dependent increase in skeletal muscle mass along with leg strength and power rather than AR downregulation and early muscle-building plateau in response to AASs. Not surprisingly, particular facets of muscle morphology are also dose-dependent, so athletes using a higher AAS dosage (>2500 mg/wk) have larger muscle fiber areas than athletes using a “lower” AAS dosage (<500 mg/wk) and drug-free athletes [71]. Based on molecular results, greater muscle fiber nuclei and capillarization can be detected in doped athletes regardless of AAS dosage compared to drug-free athletes, hence favoring muscle hypertrophy and sports performance [71].
The sum of potential mechanisms for AR-mediated hypertrophy discussed in Section 3 and Section 4 can be seen in Figure 1.
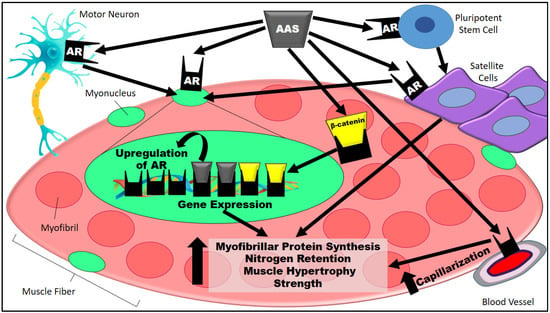
Figure 1.
AAS-induced muscle hypertrophy is triggered by the binding of AASs to ARs in many muscle fiber-associated cells, such as motor neurons, pluripotent stem cells, satellite cells, and endothelial cells. AASs bind to ARs in pluripotent stem cells and, hence, originate in satellite cells [72]. In addition, AASs bind directly to satellite cells [73]. Satellite cells stimulate new myonuclear accretion [74]. Likewise, motor neurons stimulate myonuclei formation upon the binding of AASs to ARs [51,52]. In the myonucleus, ARs are upregulated by the presence of AASs [50]. ARs are capable of activating muscle hypertrophy-related gene expression without the nuclear presence of AASs, but the sarcoplasmic AAS-dependent stimulus of the AR/β-catenin complex is a fundamental process that affords the β-catenin translocation to the nucleus [75,76]. Additionally, the binding of AASs to ARs stimulates vascular cell proliferation via upregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor A and cyclins (e.g., cyclin A and D1), thus entailing capillarization and consequently improving the influx of nutrients as well as the supply of oxygen and growth factors to skeletal muscle [50,77,78]. Taken together, the aforementioned pathways elicit greater myofibrillar protein synthesis and nitrogen retention, thereby translating into muscle hypertrophy and strength [79]. AAS, anabolic–androgenic steroid; AASs, anabolic–androgenic steroids; AR, androgen receptors.
5. Why Can Downregulation of Myocyte Androgen Receptors in Response to Anabolic–Androgenic Steroids Be Considered a Flawed Hypothesis?
Taking into consideration the real bodybuilding scenario, i.e., competition without doping tests, the loss of muscle mass under high doses of T and associated AASs with high anabolic potential (e.g., nandrolone and oxymetholone) is almost illogical despite the assumed threshold for skeletal muscle gains. The same is true for clinical populations (female-to-male transgender persons, patients with HIV/AIDS, sarcopenia, etc.), whose muscle anabolism is the expected effect induced by AAS regimens, seemingly reaching a plateau with the maintenance of a therapeutic dosage [80,81,82,83,84]. In these cases, the muscle-building plateau must not be considered an AR-disrupting factor, as if the chronic use of T and general AASs promoted the downregulation of ARs, muscle mass gains would not be sustainable irrespective of the population.
If there was downregulation of ARs upon AAS administration, T and its derivatives should cease to be effective over time in order to avoid a putative reduction in myofibrillar protein synthesis and muscle mass. On the other hand, there is considerable muscle mass loss after ceasing AAS use—particularly for those agents with greater anabolic potential [85]—due to a negative nitrogen balance (i.e., less muscle protein synthesis and more protein breakdown) [86,87,88].
6. AAS Misuse vs. Therapeutic Use
Although AAS users (i.e., recreational exercise practitioners) are prone to practice polypharmacy, such as combining AASs with diuretics, stimulant thermogenic substances (ephedrine, clenbuterol, caffeine, etc.), and illegal psychotropic substances (e.g., cocaine) [42,89,90], there is an alarming amount of caution geared toward AAS abuse. In light of this, the dose-dependent effect of AASs on pathophysiological responses must be considered. In a survey consisting of 500 AAS users (78% noncompetitive bodybuilders and non-athletes), ~60% reported using at least 1000 mg of T or its derivatives per week [91]. AAS misuse of this magnitude ought to be considered detrimental to health and therefore prohibited, as the traditional dosing regimen of TRT tends to be ~100 mg weekly or ~200 mg every 2 weeks (at least intramuscularly) [92].
Recreational AAS use is associated with many side effects, such as low gonadotropin and T levels, infertility, irritability, acne, and unfavorable liver and cardiovascular profiles, among others [19,93,94]. Viewed collectively, AAS abuse is associated with a harmful cardiometabolic profile due to increasing blood pressure as well as circulating levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and total cholesterol while decreasing high-density lipoprotein cholesterol [95]. Correspondingly, sudden cardiac death in AAS users is associated with cardiomegaly and left ventricular hypertrophy, accompanied by fibrosis and necrosis of myocardial tissue, as well as atherosclerosis, inflammatory infiltrate, and coronary stenosis [96]. These macroscopic and histological alterations contribute to the intertwined link between pathophysiological cardiac remodeling and life-threatening arrhythmias [96].
On the other hand, recent evidence supports TRT as a safe and effective strategy for male hypogonadism [97,98,99]. Moreover, proper dosing regimens of certain AASs (e.g., oxandrolone, nandrolone, and stanozolol) may aid in mitigating muscle wasting disorders [7,8,9,10,11,12].
7. Take Home-Messages and Perspectives
Recent and seminal evidence supports that AASs—at least using T and oxandrolone administration in human experimental models—upregulate myocyte ARs, conferring greater anabolic effects on skeletal muscles [38,39,40]. Although there is a lack of compelling research, the data are in line with well-controlled, randomized clinical trials that employed different AAS dosages, since AAS-induced muscle gains are indisputable [62,63,68].
To date, the supposed hypothesis of AR downregulation caused by AAS use is a mere anecdote that cannot be translated into the real-world scenario of muscle hypertrophy because, to the best of our knowledge, only a former study published nearly three decades ago suggests T-induced downregulation of ARs using rat cavernosum smooth muscle, in which finasteride was used to increase T levels instead of T administration [37].
Since AASs upregulate ARs, further studies are warranted to portray the underlying causes of the plateau effect on muscle hypertrophy among the population for which AAS use is prevalent, i.e., bodybuilders, weightlifters, and individuals suffering from muscle wasting disorders. Conversely, it is worth mentioning that AASs are prescription-only medicines that are often used without medical advice to augment muscle mass and enhance sports performance; therefore, health practitioners should counsel patients about the detrimental effects of AAS abuse.
With this caveat in mind, the illegal practice of AAS use should not be endorsed or replicated (i.e., tested) in the spheres of human science; however, further animal research focusing on the effects of different AAS dosing regimens is essential to elucidate AR modulation and related mechanistic aspects of the muscle-building plateau, followed by well-controlled, randomized clinical trials addressing common AAS dosages on tight safety control. Regarding the latter, such a landscape could be explored in clinical populations using AAS dosing regimens approved for muscle wasting disorders, as scientists are endeavoring to understand the upper limit of muscle hypertrophy under different conditions.
Author Contributions
H.O.S.: conceptualization, investigation, supervision, writing—original draft, review, and editing. C.E.F.H.: investigation and writing—original draft. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
H.O.S. has been supported by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brazil (CAPES).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
AASs, anabolic–androgenic steroids; AR, androgen receptors (AR); PPAR-α, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha; PPAR-γ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma; T, Testosterone.
References
- Orr, R.; Fiatarone Singh, M. The anabolic androgenic steroid oxandrolone in the treatment of wasting and catabolic disorders: Review of efficacy and safety. Drugs 2004, 64, 725–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basualto-Alarcon, C.; Varela, D.; Duran, J.; Maass, R.; Estrada, M. Sarcopenia and Androgens: A Link between Pathology and Treatment. Front. Endocrinol. 2014, 5, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demling, R.H.; DeSanti, L. Oxandrolone induced lean mass gain during recovery from severe burns is maintained after discontinuation of the anabolic steroid. Burns 2003, 29, 793–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassil, N.; Alkaade, S.; Morley, J.E. The benefits and risks of testosterone replacement therapy: A review. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2009, 5, 427–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corona, G.; Sforza, A.; Maggi, M. Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Long-Term Safety and Efficacy. World J. Mens Health 2017, 35, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzuti, A.; Stocker, G.; Santos, H.O. Exploring the Role of Testosterone Replacement Therapy in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia and Prostate Cancer: A Review of Safety. URO 2022, 2, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demling, R.H.; Orgill, D.P. The anticatabolic and wound healing effects of the testosterone analog oxandrolone after severe burn injury. J. Crit. Care 2000, 15, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, I.M.; Verreschi, I.T.; Nery, L.E.; Goldstein, R.S.; Zamel, N.; Brooks, D.; Jardim, J.R. The influence of 6 months of oral anabolic steroids on body mass and respiratory muscles in undernourished COPD patients. Chest 1998, 114, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengge, U.R.; Stocks, K.; Wiehler, H.; Faulkner, S.; Esser, S.; Lorenz, C.; Jentzen, W.; Hengge, D.; Goos, M.; Dudley, R.E.; et al. Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phase III trial of oxymetholone for the treatment of HIV wasting. AIDS 2003, 17, 699–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storer, T.W.; Woodhouse, L.J.; Sattler, F.; Singh, A.B.; Schroeder, E.T.; Beck, K.; Padero, M.; Mac, P.; Yarasheski, K.E.; Geurts, P.; et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of nandrolone decanoate in human immunodeficiency virus-infected men with mild to moderate weight loss with recombinant human growth hormone as active reference treatment. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 4474–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisoli, A., Jr.; Chaves, P.H.; Pinheiro, M.M.; Szejnfeld, V.L. The effect of nandrolone decanoate on bone mineral density, muscle mass, and hemoglobin levels in elderly women with osteoporosis: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2005, 60, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falqueto, H.; Junior, J.L.R.; Silverio, M.N.O.; Farias, J.C.H.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Manfredi, L.H. Can conditions of skeletal muscle loss be improved by combining exercise with anabolic-androgenic steroids? A systematic review and meta-analysis of testosterone-based interventions. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2021, 22, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagoe, D.; Molde, H.; Andreassen, C.S.; Torsheim, T.; Pallesen, S. The global epidemiology of anabolic-androgenic steroid use: A meta-analysis and meta-regression analysis. Ann. Epidemiol. 2014, 24, 383–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, H.G., Jr.; Kanayama, G.; Athey, A.; Ryan, E.; Hudson, J.I.; Baggish, A. The lifetime prevalence of anabolic-androgenic steroid use and dependence in Americans: Current best estimates. Am. J. Addict. 2014, 23, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahin, O.S.; Sousa, E.C.; Santos, A.M. Prevalence of the use of anabolic-androgenic steroids in Brazil: A systematic review. Subst. Use Misuse 2014, 49, 1156–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallio, P.J.; Poukka, H.; Moilanen, A.; Janne, O.A.; Palvimo, J.J. Androgen receptor-mediated transcriptional regulation in the absence of direct interaction with a specific DNA element. Mol. Endocrinol. 1995, 9, 1017–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Nguyen, M.M.; Dincer, Z.; Wade, J.R.; Alur, M.; Michalak, M.; Defranco, D.B.; Wang, Z. Cytoplasmic localization of the androgen receptor is independent of calreticulin. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2009, 302, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanovic, M.D.; Ostojic, S.M. Limits of Anabolic Steroids Application in Sport and Exercise. J. Intech 2012, 1, 169–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albano, G.D.; Amico, F.; Cocimano, G.; Liberto, A.; Maglietta, F.; Esposito, M.; Rosi, G.L.; Di Nunno, N.; Salerno, M.; Montana, A. Adverse Effects of Anabolic-Androgenic Steroids: A Literature Review. Healthcare 2021, 9, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strosberg, A.D. Structure, function, and regulation of adrenergic receptors. Protein Sci. 1993, 2, 1198–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruffolo, R.R., Jr.; Kopia, G.A. Importance of receptor regulation in the pathophysiology and therapy of congestive heart failure. Am. J. Med. 1986, 80, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadcock, J.R.; Malbon, C.C. Down-regulation of beta-adrenergic receptors: Agonist-induced reduction in receptor mRNA levels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 5021–5025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boden, G.; Chen, X.; Ruiz, J.; Heifets, M.; Morris, M.; Badosa, F. Insulin receptor down-regulation and impaired antilipolytic action of insulin in diabetic patients after pancreas/kidney transplantation. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1994, 78, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okabayashi, Y.; Maddux, B.A.; McDonald, A.R.; Logsdon, C.D.; Williams, J.A.; Goldfine, I.D. Mechanisms of insulin-induced insulin-receptor downregulation. Decrease of receptor biosynthesis and mRNA levels. Diabetes 1989, 38, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wondmkun, Y.T. Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Type 2 Diabetes: Associations and Therapeutic Implications. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 3611–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wigand, J.P.; Blackard, W.G. Downregulation of insulin receptors in obese man. Diabetes 1979, 28, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, A.V.; Kolka, C.M.; Kim, S.P.; Bergman, R.N. Obesity, insulin resistance and comorbidities? Mechanisms of association. Arq. Bras. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 58, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, O.; Beck-Nielsen, H.; Heding, L. Increased insulin receptors after exercise in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 1980, 302, 886–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chibalin, A.V.; Yu, M.; Ryder, J.W.; Song, X.M.; Galuska, D.; Krook, A.; Wallberg-Henriksson, H.; Zierath, J.R. Exercise-induced changes in expression and activity of proteins involved in insulin signal transduction in skeletal muscle: Differential effects on insulin-receptor substrates 1 and 2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musi, N.; Goodyear, L.J. Insulin resistance and improvements in signal transduction. Endocrine 2006, 29, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastaldi, G.; Russell, A.; Golay, A.; Giacobino, J.P.; Habicht, F.; Barthassat, V.; Muzzin, P.; Bobbioni-Harsch, E. Upregulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator gene (PGC1A) during weight loss is related to insulin sensitivity but not to energy expenditure. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 2348–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verreth, W.; De Keyzer, D.; Pelat, M.; Verhamme, P.; Ganame, J.; Bielicki, J.K.; Mertens, A.; Quarck, R.; Benhabiles, N.; Marguerie, G.; et al. Weight-loss-associated induction of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma correlate with reduced atherosclerosis and improved cardiovascular function in obese insulin-resistant mice. Circulation 2004, 110, 3259–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Santos, H.O.; Macedo, R.C.O. Impact of intermittent fasting on the lipid profile: Assessment associated with diet and weight loss. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2018, 24, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macedo, R.C.O.; Santos, H.O.; Tinsley, G.M.; Reischak-Oliveira, A. Low-carbohydrate diets: Effects on metabolism and exercise—A comprehensive literature review. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2020, 40, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, H.O.; Lavie, C.J. Weight loss and its influence on high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) concentrations: A noble clinical hesitation. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2021, 42, 90–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, H.O.; Earnest, C.P.; Tinsley, G.M.; Izidoro, L.F.M.; Macedo, R.C.O. Small dense low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (sdLDL-C): Analysis, effects on cardiovascular endpoints and dietary strategies. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 63, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.C.; Rajfer, J.; Swerdloff, R.S.; Gonzalez-Cadavid, N.F. Testosterone down-regulates the levels of androgen receptor mRNA in smooth muscle cells from the rat corpora cavernosa via aromatization to estrogens. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1993, 45, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doumit, M.E.; Cook, D.R.; Merkel, R.A. Testosterone up-regulates androgen receptors and decreases differentiation of porcine myogenic satellite cells in vitro. Endocrinology 1996, 137, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, E.E.; Margolis, L.M.; Berryman, C.E.; Lieberman, H.R.; Karl, J.P.; Young, A.J.; Montano, M.A.; Evans, W.J.; Rodriguez, N.R.; Johannsen, N.M.; et al. Testosterone supplementation upregulates androgen receptor expression and translational capacity during severe energy deficit. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 319, E678–E688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheffield-Moore, M.; Urban, R.J.; Wolf, S.E.; Jiang, J.; Catlin, D.H.; Herndon, D.N.; Wolfe, R.R.; Ferrando, A.A. Short-term oxandrolone administration stimulates net muscle protein synthesis in young men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1999, 84, 2705–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petroczi, A.; Ocampo, J.A.; Shah, I.; Jenkinson, C.; New, R.; James, R.A.; Taylor, G.; Naughton, D.P. Russian roulette with unlicensed fat-burner drug 2,4-dinitrophenol (DNP): Evidence from a multidisciplinary study of the internet, bodybuilding supplements and DNP users. Subst. Abus. Treat. Prev. Policy 2015, 10, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentil, P.; de Lira, C.A.B.; Paoli, A.; Dos Santos, J.A.B.; da Silva, R.D.T.; Junior, J.R.P.; da Silva, E.P.; Magosso, R.F. Nutrition, Pharmacological and Training Strategies Adopted by Six Bodybuilders: Case Report and Critical Review. Eur. J. Transl. Myol. 2017, 27, 6247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, E.; Loiacono, R.; Summers, R.J. The rush to adrenaline: Drugs in sport acting on the beta-adrenergic system. Br. J. Pharm. 2008, 154, 584–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porro, L.J.; Herndon, D.N.; Rodriguez, N.A.; Jennings, K.; Klein, G.L.; Mlcak, R.P.; Meyer, W.J.; Lee, J.O.; Suman, O.E.; Finnerty, C.C. Five-year outcomes after oxandrolone administration in severely burned children: A randomized clinical trial of safety and efficacy. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2012, 214, 489–502; discussion 502–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, R.; Petersson, S.J.; Christensen, L.L.; Kristensen, J.M.; Sabaratnam, R.; Ortenblad, N.; Andersen, M.; Hojlund, K. Effect of long-term testosterone therapy on molecular regulators of skeletal muscle mass and fibre-type distribution in aging men with subnormal testosterone. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2020, 112, 154347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mladenka, P.; Applova, L.; Patocka, J.; Costa, V.M.; Remiao, F.; Pourova, J.; Mladenka, A.; Karlickova, J.; Jahodar, L.; Voprsalova, M.; et al. Comprehensive review of cardiovascular toxicity of drugs and related agents. Med. Res. Rev. 2018, 38, 1332–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montan, P.D.; Sourlas, A.; Olivero, J.; Silverio, D.; Guzman, E.; Kosmas, C.E. Pharmacologic therapy of obesity: Mechanisms of action and cardiometabolic effects. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morton, R.W.; Sato, K.; Gallaugher, M.P.B.; Oikawa, S.Y.; McNicholas, P.D.; Fujita, S.; Phillips, S.M. Muscle Androgen Receptor Content but not Systemic Hormones Is Associated with Resistance Training-Induced Skeletal Muscle Hypertrophy in Healthy, Young Men. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardaci, T.D.; Machek, S.B.; Wilburn, D.T.; Heileson, J.L.; Willoughby, D.S. High-Load Resistance Exercise Augments Androgen Receptor-DNA Binding and Wnt/beta-Catenin Signaling without Increases in Serum/Muscle Androgens or Androgen Receptor Content. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha-Hikim, I.; Taylor, W.E.; Gonzalez-Cadavid, N.F.; Zheng, W.; Bhasin, S. Androgen receptor in human skeletal muscle and cultured muscle satellite cells: Up-regulation by androgen treatment. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 5245–5255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, R.A.; Clarke, M.V.; Russell, P.K.; Rana, K.; Seto, J.; Roeszler, K.N.; How, J.M.Y.; Chia, L.Y.; North, K.; Zajac, J.D. Androgen Action via the Androgen Receptor in Neurons within the Brain Positively Regulates Muscle Mass in Male Mice. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 3684–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daou, N.; Hassani, M.; Matos, E.; De Castro, G.S.; Costa, R.G.F.; Seelaender, M.; Moresi, V.; Rocchi, M.; Adamo, S.; Li, Z.; et al. Displaced Myonuclei in Cancer Cachexia Suggest Altered Innervation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snijders, T.; Nederveen, J.P.; McKay, B.R.; Joanisse, S.; Verdijk, L.B.; van Loon, L.J.; Parise, G. Satellite cells in human skeletal muscle plasticity. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadi, F.; Schjerling, P.; Andersen, L.L.; Charifi, N.; Madsen, J.L.; Christensen, L.R.; Andersen, J.L. The effects of heavy resistance training and detraining on satellite cells in human skeletal muscles. J. Physiol. 2004, 558, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalbo, V.J.; Roberts, M.D.; Mobley, C.B.; Ballmann, C.; Kephart, W.C.; Fox, C.D.; Santucci, V.A.; Conover, C.F.; Beggs, L.A.; Balaez, A.; et al. Testosterone and trenbolone enanthate increase mature myostatin protein expression despite increasing skeletal muscle hypertrophy and satellite cell number in rodent muscle. Andrologia 2017, 49, e12622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadi, F. Cellular and molecular mechanisms responsible for the action of testosterone on human skeletal muscle. A basis for illegal performance enhancement. Br. J. Pharm. 2008, 154, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadi, F.; Bonnerud, P.; Eriksson, A.; Thornell, L.E. The expression of androgen receptors in human neck and limb muscles: Effects of training and self-administration of androgenic-anabolic steroids. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2000, 113, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulvaney, D.R.; Marple, D.N.; Merkel, R.A. Proliferation of skeletal muscle satellite cells after castration and administration of testosterone propionate. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1988, 188, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joubert, Y.; Tobin, C. Satellite cell proliferation and increase in the number of myonuclei induced by testosterone in the levator ani muscle of the adult female rat. Dev. Biol. 1989, 131, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha-Hikim, I.; Roth, S.M.; Lee, M.I.; Bhasin, S. Testosterone-induced muscle hypertrophy is associated with an increase in satellite cell number in healthy, young men. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 285, E197–E205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zajac, J.D.; MacLean, H.E. Androgen regulation of satellite cell function. J. Endocrinol. 2005, 186, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhasin, S.; Storer, T.W.; Berman, N.; Callegari, C.; Clevenger, B.; Phillips, J.; Bunnell, T.J.; Tricker, R.; Shirazi, A.; Casaburi, R. The effects of supraphysiologic doses of testosterone on muscle size and strength in normal men. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 335, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhasin, S.; Woodhouse, L.; Casaburi, R.; Singh, A.B.; Bhasin, D.; Berman, N.; Chen, X.; Yarasheski, K.E.; Magliano, L.; Dzekov, C.; et al. Testosterone dose-response relationships in healthy young men. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 281, E1172–E1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halstead, L.S.; Groah, S.L.; Libin, A.; Hamm, L.F.; Priestley, L. The effects of an anabolic agent on body composition and pulmonary function in tetraplegia: A pilot study. Spinal Cord 2010, 48, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavros, Y.; O’Neill, E.; Connerty, M.; Bean, J.F.; Broe, K.; Kiel, D.P.; Maclean, D.; Taylor, A.; Fielding, R.A.; Singh, M.A. Oxandrolone Augmentation of Resistance Training in Older Women: A Randomized Trial. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2015, 47, 2257–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.R.; Pall, L.; Hall, C.D.; Simpson, D.M.; Berry, P.S.; Dudley, R. Oxandrolone in AIDS-wasting myopathy. AIDS 1996, 10, 1657–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demling, R.H.; DeSanti, L. Oxandrolone, an anabolic steroid, significantly increases the rate of weight gain in the recovery phase after major burns. J. Trauma 1997, 43, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunfeld, C.; Kotler, D.P.; Dobs, A.; Glesby, M.; Bhasin, S. Oxandrolone in the treatment of HIV-associated weight loss in men: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2006, 41, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad, F.; Aversa, A.; Isidori, A.M.; Zafalon, L.; Zitzmann, M.; Gooren, L. Onset of effects of testosterone treatment and time span until maximum effects are achieved. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2011, 165, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storer, T.W.; Woodhouse, L.; Magliano, L.; Singh, A.B.; Dzekov, C.; Dzekov, J.; Bhasin, S. Changes in muscle mass, muscle strength, and power but not physical function are related to testosterone dose in healthy older men. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2008, 56, 1991–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.G.; Bonnerud, P.; Eriksson, A.; Stal, P.S.; Tegner, Y.; Malm, C. Effects of long term supplementation of anabolic androgen steroids on human skeletal muscle. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Artaza, J.N.; Taylor, W.E.; Gonzalez-Cadavid, N.F.; Bhasin, S. Androgens stimulate myogenic differentiation and inhibit adipogenesis in C3H 10T1/2 pluripotent cells through an androgen receptor-mediated pathway. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 5081–5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKrell, J.G.; Yaden, B.C.; Bullock, H.; Chen, K.; Shetler, P.; Bryant, H.U.; Krishnan, V. Molecular targets of androgen signaling that characterize skeletal muscle recovery and regeneration. Nucl. Recept. Signal. 2015, 13, e005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou Sawan, S.; Hodson, N.; Babits, P.; Malowany, J.M.; Kumbhare, D.; Moore, D.R. Satellite cell and myonuclear accretion is related to training-induced skeletal muscle fiber hypertrophy in young males and females. J. Appl. Physiol. 2021, 131, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Bhasin, S.; Braga, M.; Artaza, J.N.; Pervin, S.; Taylor, W.E.; Krishnan, V.; Sinha, S.K.; Rajavashisth, T.B.; Jasuja, R. Regulation of myogenic differentiation by androgens: Cross talk between androgen receptor/beta-catenin and follistatin/transforming growth factor-beta signaling pathways. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 1259–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.X.; Hu, J.; Zhu, M.J.; Du, M. Trenbolone enhances myogenic differentiation by enhancing beta-catenin signaling in muscle-derived stem cells of cattle. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2011, 40, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Hong, Y.; Weng, C.; Tan, C.; Imperato-McGinley, J.; Zhu, Y.S. Androgen stimulates endothelial cell proliferation via an androgen receptor/VEGF/cyclin A-mediated mechanism. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2011, 300, H1210–H1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snijders, T.; Nederveen, J.P.; Joanisse, S.; Leenders, M.; Verdijk, L.B.; van Loon, L.J.; Parise, G. Muscle fibre capillarization is a critical factor in muscle fibre hypertrophy during resistance exercise training in older men. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2017, 8, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kicman, A.T. Pharmacology of anabolic steroids. Br. J. Pharm. 2008, 154, 502–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, E.T.; Zheng, L.; Yarasheski, K.E.; Qian, D.; Stewart, Y.; Flores, C.; Martinez, C.; Terk, M.; Sattler, F.R. Treatment with oxandrolone and the durability of effects in older men. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 96, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, E.T.; Vallejo, A.F.; Zheng, L.; Stewart, Y.; Flores, C.; Nakao, S.; Martinez, C.; Sattler, F.R. Six-week improvements in muscle mass and strength during androgen therapy in older men. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2005, 60, 1586–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns, K.; Beddall, M.J.; Corrin, R.C. Anabolic steroids for the treatment of weight loss in HIV-infected individuals. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2005, 19, CD005483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiik, A.; Lundberg, T.R.; Rullman, E.; Andersson, D.P.; Holmberg, M.; Mandic, M.; Brismar, T.B.; Dahlqvist Leinhard, O.; Chanpen, S.; Flanagan, J.N.; et al. Muscle Strength, Size, and Composition Following 12 Months of Gender-affirming Treatment in Transgender Individuals. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, e805–e813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhasin, S.; Storer, T. Anabolic applications of androgens for functional limitations associated with aging and chronic illness. Front. Horm. Res. 2009, 37, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Ronde, W.; Smit, D.L. Anabolic androgenic steroid abuse in young males. Endocr. Connect. 2020, 9, R102–R111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinde, K.L.; O’Leary, T.J.; Greeves, J.P.; Wardle, S.L. Measuring Protein Turnover in the Field: Implications for Military Research. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzulla, M.; Volterman, K.A.; Packer, J.E.; Wooding, D.J.; Brooks, J.C.; Kato, H.; Moore, D.R. Whole-body net protein balance plateaus in response to increasing protein intakes during post-exercise recovery in adults and adolescents. Nutr. Metab. 2018, 15, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pikosky, M.A.; Smith, T.J.; Grediagin, A.; Castaneda-Sceppa, C.; Byerley, L.; Glickman, E.L.; Young, A.J. Increased protein maintains nitrogen balance during exercise-induced energy deficit. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2008, 40, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiller, H.A.; James, K.J.; Scholzen, S.; Borys, D.J. A descriptive study of adverse events from clenbuterol misuse and abuse for weight loss and bodybuilding. Subst. Abus. 2013, 34, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, E.J.; Barnett, M.J.; Tenerowicz, M.J.; Perry, P.J. The Anabolic 500 survey: Characteristics of male users versus nonusers of anabolic-androgenic steroids for strength training. Pharmacotherapy 2011, 31, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, A.B.; Evans, N.A. Anabolic androgenic steroids: A survey of 500 users. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2006, 38, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoskes, J.J.; Wilson, M.K.; Spinner, M.L. Pharmacology of testosterone replacement therapy preparations. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2016, 5, 834–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christou, M.A.; Christou, P.A.; Markozannes, G.; Tsatsoulis, A.; Mastorakos, G.; Tigas, S. Effects of Anabolic Androgenic Steroids on the Reproductive System of Athletes and Recreational Users: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 1869–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggish, A.L.; Weiner, R.B.; Kanayama, G.; Hudson, J.I.; Lu, M.T.; Hoffmann, U.; Pope, H.G., Jr. Cardiovascular Toxicity of Illicit Anabolic-Androgenic Steroid Use. Circulation 2017, 135, 1991–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, M.A.; Magee, C.D.; Combest, T.M.; Allard, R.J.; Douglas, K.M. Physical Effects of Anabolic-androgenic Steroids in Healthy Exercising Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrisi, M.; Pennisi, G.; Russo, I.; Amico, F.; Esposito, M.; Liberto, A.; Cocimano, G.; Salerno, M.; Li Rosi, G.; Di Nunno, N.; et al. Sudden Cardiac Death in Anabolic-Androgenic Steroid Users: A Literature Review. Medicina 2020, 56, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgentaler, A.; Traish, A.; Hackett, G.; Jones, T.H.; Ramasamy, R. Diagnosis and Treatment of Testosterone Deficiency: Updated Recommendations From the Lisbon 2018 International Consultation for Sexual Medicine. Sex. Med. Rev. 2019, 7, 636–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, J.; Cruickshank, M.; Quinton, R.; Aucott, L.; Aceves-Martins, M.; Gillies, K.; Bhasin, S.; Snyder, P.J.; Ellenberg, S.S.; Grossmann, M.; et al. Adverse cardiovascular events and mortality in men during testosterone treatment: An individual patient and aggregate data meta-analysis. Lancet. Healthy Longev. 2022, 3, e381–e393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgentaler, A.; Miner, M.M.; Caliber, M.; Guay, A.T.; Khera, M.; Traish, A.M. Testosterone therapy and cardiovascular risk: Advances and controversies. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2015, 90, 224–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).