Abstract
While mechanical dewatering is widely used in faecal sludge treatment, the agricultural potential of mechanically dewatered faecal sludge (MDFS) combined with anaerobic digestion (AD) remains underexplored, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa where nutrient recovery is critical for food security. This study provides the first comprehensive characterisation of MDFS from Ghana’s largest treatment facility and evaluates anaerobic digestion effectiveness for agricultural application. Over six months, 182 composite MDFS samples from Lavender Hill Faecal Treatment Plant were analysed for physicochemical properties, nutrients, heavy metals, and microbial contaminants before and after AD treatment. MDFS demonstrated exceptional nutrient density, with total nitrogen (2141.05 mg/kg), phosphorus (190.08 mg/kg), and potassium (4434.88 mg/kg) concentrations comparable to commercial organic fertilisers. AD achieved significant pathogen reduction, decreasing total coliforms from 148,808.70 to 493.33 cfu/100 g (p < 0.001) and Ascaris lumbricoides eggs from 12.08 to 3.33 eggs/L, while maintaining nutrient integrity and keeping heavy metals within safe agricultural limits. Statistical modelling revealed a significant correlation between treatment duration and pathogen reduction efficiency. Despite substantial improvements, treated MDFS still exceeded some regulatory thresholds, indicating a need for complementary post-treatment strategies. This research establishes AD as an effective primary treatment for converting MDFS into a nutrient-rich organic fertiliser, supporting circular economy principles in urban sanitation systems and providing a sustainable pathway for agricultural nutrient recovery in resource-constrained settings.
1. Introduction
Global sanitation challenges persist as a critical impediment to sustainable development, with approximately 3.6 billion people lacking access to safely managed sanitation and 1.9 billion still practicing open defecation [1,2]. This crisis disproportionately affects developing countries, particularly in Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia, where over 80% of the population relies on onsite sanitation systems such as septic tanks, aqua privies, and pit latrines [3,4]. The inadequate sanitation infrastructure and unsafe handling of faecal sludge contributes to the spread of waterborne diseases including diarrhoea, cholera, dysentery, and parasitic infections. Globally, these conditions cause nearly 1.5 million deaths annually, with children under five years in developing countries bearing the greatest burden [5,6].
Achieving universal access to adequate sanitation by 2030, a key target under UN Sustainable Development Goal 6.2, requires estimated annual investments exceeding USD 110 billion [7,8]. Recent data from 2023 indicate that in Ghana, over 90% of urban households depend on onsite sanitation systems, yet most urban authorities lack proper infrastructure for conveyance, treatment, and disposal of faecal sludge (FS) [9]. Only approximately 4% of Ghana’s urban population is served by centralised sewer systems, predominantly around Accra [10,11]. Consequently, of the 55 million litres of FS emptied annually in Accra, less than 16% undergoes any form of treatment [12]. This situation mirrors broader regional patterns, with about 85% of faecal sludge in Africa lacking proper treatment [1,13].
The environmental and public health implications of inadequate FS management are severe. Raw or partially treated faecal sludge is frequently discharged into water bodies, including the Gulf of Guinea and Densu River, which supply drinking water to major cities like Accra [14,15]. Recent studies from 2023 show that less than 10% of FS nationwide is safely managed, posing major health and environmental risks [16]. However, this crisis presents an opportunity for resource recovery, as FS contains valuable resources, including organic matter, essential nutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium), and trace elements crucial for plant growth [17,18].
Recent research has demonstrated significant nutrient potential in FS, with average concentrations of 41.5 g/kg organic carbon and typical ranges of 2–7% nitrogen, 1.5–7% phosphorus, and 0.5–2.5% potassium, meeting common deficiency levels in agricultural soils [19,20]. Resource recovery through safe agricultural reuse could simultaneously address waste management challenges and improve food security, particularly given that approximately half of the world’s population experiences severe water scarcity for at least part of the year [21,22]. However, safe utilisation requires effective treatment to eliminate pathogens while preserving nutrient content, as WHO guidelines mandate 1–2 log reduction of Ascaris eggs and absence of Salmonella spp. and E. coli in treated biosolids for food crop application [23].
Various treatment technologies have been explored for FS management, including composting, drying beds, alkaline treatment, vermicomposting, and thermal processes such as pyrolysis and gasification [24,25]. Among these approaches, mechanical dewatering (MD) has emerged as a crucial pre-processing step, reducing FS volume by over 95% and improving subsequent treatment efficiency due to high water content [26,27]. Mechanically dewatered faecal sludge (MDFS) undergoes solid–liquid separation through screw press technology, producing a concentrated solid fraction suitable for further biological treatment. Anaerobic digestion (AD) has gained particular attention as an effective stabilisation method that reduces pathogen loads while recovering nutrients through controlled microbial decomposition under oxygen-free conditions, making it suitable for agricultural applications [28,29,30,31]. The combination of MD and AD represents a promising integrated approach for sustainable FS management, where MDFS serves as feedstock for AD reactors operating at mesophilic temperatures (35 ± 2 °C), with hydraulic retention times of 60–90 days.
Despite the potential benefits of integrated FS treatment systems, several critical research questions remain inadequately addressed. Understanding the comprehensive physicochemical and microbiological characteristics of mechanically dewatered faecal sludge from urban treatment facilities in Ghana requires systematic investigation. The effectiveness of anaerobic digestion in reducing pathogen loads while preserving essential nutrients for agricultural use needs quantitative assessment. Optimal treatment parameters and post-processing strategies required to meet international safety standards for agricultural application remain unclear. Additionally, the nutrient profile and bioavailability of treated MDFS compared with conventional organic fertilisers requires comprehensive evaluation.
Although MD has gained widespread adoption in FS treatment facilities globally [32,33], empirical data characterising mechanically dewatered faecal sludge (MDFS) and its transformation through AD remain limited, particularly in sub-Saharan African contexts [34,35,36]. Current research limitations are evident in several areas. Most existing studies from 2020 to 2023 have focused on co-composting with municipal waste without adequately addressing pathogen safety concerns [37,38,39], with investigations by Manga et al. [40,41] showing persistent Ascaris ova even after extended treatment periods of 200 days. Similarly, recent work by Verbyla et al. [42] documented inadequate pathogen reduction in conventional composting systems. Furthermore, insufficient scientific evidence exists regarding treatment technology performance and product safety, particularly concerning heavy metals and pharmaceutical residues, as highlighted by recent reviews [43,44,45,46,47].
Research gaps become more apparent when examining treatment method limitations identified in recent studies. Thermophilic composting, while effective for pathogen reduction, requires strict process control and continuous monitoring, as demonstrated by Wang et al. [48] and Zhou et al. [49]. Solar drying approaches, investigated by Mawejje et al. [50] and Nan-norl et al. [51], demand significant space requirements and extended treatment times that may be impractical for urban settings. Alkaline stabilisation methods face constraints from FS buffering capacity, as documented by Novais et al. [52] and Toutian et al. [53] in recent publications. Advanced thermal methods, though achieving rapid disinfection, require energy-intensive drying processes and specialised equipment [54,55,56].
Critical knowledge gaps persist across multiple research domains, as identified in recent systematic reviews [57,58,59]. Limited understanding exists regarding the optimisation of treatment parameters for effective pathogen reduction while preserving nutrient content [60,61]. Field validation studies assessing crop responses to treated FS products remain scarce, with most evaluations conducted under controlled laboratory conditions rather than real agricultural settings [62,63,64]. Additionally, systematic investigations of nutrient bioavailability and long-term soil health impacts following MDFS application are conspicuously absent from the current literature [65,66,67].
This study addresses these research gaps by providing the first systematic characterisation of MDFS from Ghana’s largest treatment facility and evaluating the effectiveness of anaerobic digestion for safe agricultural application. This research aims to establish evidence-based guidelines for MDFS treatment that balance pathogen reduction with nutrient preservation, contributing to sustainable sanitation and circular economy initiatives in resource-constrained urban settings.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Facility Description
This study was conducted at the Lavender Hill Faecal Treatment Plant (LHFTP), located in Accra-James Town, Ghana (5°32′ N, 0°12′ W). The facility, operated by Sewerage Systems Ghana Limited since 2017, is one of the largest faecal sludge treatment plants in West Africa, with a design capacity of 3500 m3/day, making it a representative site for urban FS management research in the region. The plant serves the Greater Accra Metropolitan Area (GAMA) and surrounding communities, receiving and processing faecal sludge collected from onsite sanitation systems including septic tanks (both public and private), aqua privies, and pit latrines.
LHFTP operates a comprehensive treatment train consisting of preliminary screening (5 mm step screens), flow regulation tanks, steel tanks for solid–liquid separation, flocculation units with cationic polymer addition, and mechanical dewatering using screw press technology (Figure 1). The dewatered faecal sludge (DFS) undergoes mechanical dewatering through screw press technology, removing approximately 95% of water content from the original faecal sludge (FS). The facility processed approximately 322,920 m3 of FS during the six-month study period (January to June 2024), representing both dry and wet seasonal conditions typical of Ghana’s bimodal rainfall pattern.
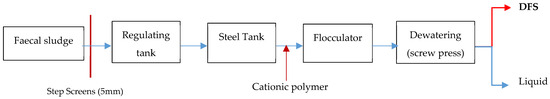
Figure 1.
Summary process flow chart of LHFTP.
2.2. Study Design and Sampling Strategy
2.2.1. Sample Collection Protocol
This study employed a systematic composite sampling approach designed to capture temporal and spatial variability in FS characteristics following standard protocols [68]. During the study period, an average of 177 cesspit trucks per day delivered approximately 1770 m3 of septage to LHFTP. As shown in Figure 2a, the mechanical dewatering system utilised a screw press (Model SP-3000, capacity 15 m3/h, Manufacturer: EMO, Rennes, France) coupled with cationic polymer dosing at 2 kg/m3 concentration to optimise solid–liquid separation efficiency.
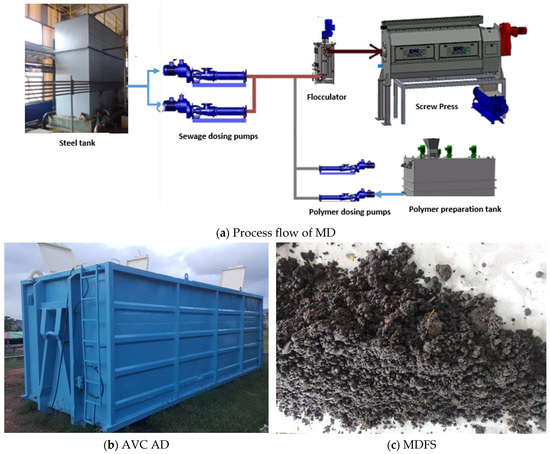

Figure 2.
Process flow of mechanical dewatering (a), AVC anaerobic digester (b), Mechanically dewatered faecal sludge (c).
Mechanically dewatered faecal sludge (MDFS) samples were collected using a stratified random sampling protocol. Daily composite samples were prepared by collecting 5–10 sub-samples from multiple locations within the dewatered sludge pile immediately after discharge from the screw press. Sub-samples (approximately 500 g each) were collected from different depths (surface, middle, and bottom layers) and locations across the pile to ensure representativeness. These sub-samples were thoroughly mixed to create a homogeneous daily composite sample of 2–3 kg, which was immediately stored in sterile, air-tight containers under controlled refrigeration (4–10 °C) to prevent microbial activity and preserve sample integrity.
2.2.2. Sample Processing and Temporal Compositing
To address seasonal variability concerns, the sampling period (January–June 2024) was specifically selected to capture both the dry season (January–March) and the onset of the wet season (April–June), representing approximately 70% of Ghana’s annual rainfall variability. Daily composite samples were stored under controlled conditions and composited monthly to create six monthly representative samples. Each monthly composite was prepared by mixing equal masses (300–400 g) from each daily sample within that month, ensuring temporal representativeness.
2.2.3. Anaerobic Digestion Setup
As shown in Figure 2b,c MDFS was digested using an AVC anaerobic digester (Model AVC-740, Simon Moos A/S, Sydals, Denmark) with a 90-day hydraulic retention time following established protocols [69]. The digester specifications include an empty weight of 3000 kg, total volume of 42,210 L (42.21 m3), dimensions of 6.552 m length × 2.5 m width × 2.576 m height, and operating temperature maintained at 35 ± 2 °C (mesophilic conditions). The digester was equipped with automated pH monitoring, a gas collection system, and mechanical mixing capabilities (30 rpm, 15 min every 4 h).
The digester was inoculated with active anaerobic sludge from the Mudor wastewater treatment plant (20% v/v) and operated at an organic loading rate of 2.5 kg volatile solids/m3/day. Monthly sampling of anaerobically digested MDFS was conducted to monitor physicochemical changes, microbial reduction kinetics, and heavy metal stabilisation throughout the digestion period.
2.3. Laboratory Analyses
2.3.1. Physicochemical Characterisation
Physicochemical properties were analysed following standard methods for examination of water and wastewater [68]. pH measurements were conducted using a calibrated digital pH meter (Hanna HI-2020, accuracy ±0.01 pH units, Chiba, Japan). Moisture content was determined gravimetrically by drying samples at 105 °C for 24 h until constant weight according to APHA Method 2540G (APHA, 2023) [68]. Organic matter content was quantified through loss on ignition at 550 °C for 4 h in a muffle furnace following APHA Method 2540E (APHA, 2023) [68]. Electrical conductivity was measured using a conductivity meter (Hanna HI-2300, accuracy ±1% of reading). Total solids were measured following APHA method 2540B (APHA, 2023) whereas volatile solids, and ash content were determined gravimetrically according to APHA Method 2540E [68].
2.3.2. Nutrient Analysis
Macronutrient analysis included total nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium quantification following established protocols [70]. Total nitrogen was determined using the APHA Method 4500-N (APHA, 2023) [68], with sulfuric acid digestion followed by steam distillation and titration. Total phosphorus was analysed spectrophotometrically (UV-Vis spectrophotometer, Hach DR3900, Tokyo, Japan) after acid digestion using the APHA Method 4500-P (APHA, 2023) [68]. Potassium content was quantified using flame photometry (Jenway PFP7, detection limit 0.1 mg/L, Synergy Plus, London, UK) after acid extraction. All nutrient analyses were performed in triplicate with appropriate quality control measures including blanks, spikes, and certified reference materials.
2.3.3. Microbiological and Parasitological Analysis
Comprehensive microbiological assessment included enumeration of indicator organisms and pathogens following standard protocols [71]. Total coliforms and faecal coliforms were quantified using the membrane filtration technique in accordance with APHA Method 9222B and 9222D respectively (APHA, 2023) [68]. Escherichia coli enumeration was conducted using the EC-MUG method with a fluorogenic substrate. Salmonella spp. detection involved pre-enrichment in buffered peptone water, selective enrichment in Rappaport-Vassiliadis broth, and isolation on selective agar media following ISO 6579:2017 protocols [72].
Parasitological analysis focused on helminth eggs including Ascaris lumbricoides, Strongyloides stercoralis, and Trichuris trichiura using the flotation concentration method described by Moodley et al. [73]. Samples were processed using zinc sulphate flotation (specific gravity 1.18) and examined microscopically at 400× magnification [74]. Enterococci enumeration was performed using membrane filtration on mE agar [75]. Giardia lamblia cysts and Cryptosporidium parvum oocysts were detected using immunofluorescence microscopy following EPA Method 1623 [76].
2.3.4. Heavy Metal Analysis
Heavy metals (Pb, Ni, Cd, Hg, As) were analysed using atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) following acid digestion protocols [77]. Samples were digested using a 3:1 mixture of concentrated HNO3:HCl (aqua regia) in a microwave digestion system (CEM Mars 6). Metal concentrations were determined using a flame atomic absorption spectrometer according to APHA Method 3111B (APHA, 2023) [68], using PerkinElmer Analyst 400 spectrometer. Mercury analysis was conducted using cold vapour atomic absorption spectroscopy (CV-AAS). Quality control included NIST certified reference materials 2781 (NIST, 2025) [78], method blanks, and matrix spikes with recovery rates between 85 and 115%.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS version 26.0. Descriptive statistics including means, standard deviations, and minimum and maximum values were calculated for all parameters. One-sample t-tests were conducted to compare nutrient concentrations with threshold values. Multiple regression analysis was performed to examine relationships between nutrients and physicochemical parameters using the model Y = β0 + β1X1 + β2X2 + β3X3, where Y is nutrient concentration, X1 is pH, X2 is organic matter content, and X3 is moisture content. Paired t-tests were used to compare pre- and post-AD treatment parameters. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
2.5. Economic Analysis
Economic viability assessment was conducted, comparing treatment costs with potential revenue from fertiliser sales. Operational costs included energy consumption for mechanical dewatering (2.5 kWh/m3), anaerobic digestion (1.8 kWh/m3), labour (2 operators at USD 150/month each), and maintenance (5% of capital costs annually). Capital costs for a screw press (USD 45,000) and anaerobic digester (USD 85,000) were amortised over 15 years at an 8% interest rate. Revenue projections were based on the nutrient content equivalent to commercial fertiliser prices: nitrogen (USD 1.2/kg), phosphorus (USD 2.8/kg), and potassium (USD 0.8/kg).
3. Results
3.1. Characterisation of MDFS
The characteristics of MDFS are presented in Table 1, indicating the nutrient, microbial, metal, and physicochemical concentrations. Physicochemical analysis of MDFS recorded a near-neutral pH (7.24 ± 0.20) and high moisture content (60.20 ± 8.57%). The organic matter content of 28.5 ± 2.62% and organic carbon of 14.83 ± 0.72% indicate significant potential for soil amendment applications. The electrical conductivity (528.62 ± 16.71 μS/cm) suggests a moderate salt content, avoiding phytotoxicity concerns associated with high-salinity organic amendments.

Table 1.
Average physicochemical, nutrient, microbial, parasitological, and heavy metal concentration of mechanical dewatered faecal sludge (N = 182).
The near-neutral pH observed aligns closely with findings from recent studies by Strande et al. [79], who reported similar pH ranges in urban FS across sub-Saharan Africa, suggesting favourable conditions for biological treatment processes. The high moisture content demonstrates the effectiveness of mechanical dewatering in reducing water content from the typical > 95% found in raw FS [80], though it remains within ranges reported by Englund and Strande [81] for mechanically processed sludge in 2019. This moisture level represents a critical balance between dewatering efficiency and subsequent processing requirements, as excessive moisture complicates handling while over-dewatering can increase operational costs [82].
Table 1 presents a considerable nutrient content, with potassium (K2O) being the most abundant at 4434.88 ± 35.88 mg/kg, followed by total nitrogen at 2141.05 ± 27.37 mg/kg, and phosphorus (P2O5) at 190.08 ± 3.34 mg/kg. One-sample t-tests indicate that all primary nutrient concentrations are significantly different from typical agricultural soil requirements (p < 0.001), with MDFS exceeding standard soil nutrient levels. The nutrient profile suggests potential value for agricultural applications, particularly given the high potassium and phosphorus content. The relatively low standard deviations indicate consistent nutrient concentrations across dewatered samples.
The substantial organic matter content (28.50 ± 2.62%) and organic carbon (14.83 ± 0.72%) demonstrate remarkable potential for soil amendment applications, corroborating recent research by Brooker [83], who found similar concentrations in septage samples during 2022–2023. These values exceed typical organic matter requirements for soil conditioning, suggesting that MDFS could significantly enhance soil structure and water retention capacity when properly treated [84]. The potassium oxide concentrations significantly exceed typical soil requirements, supporting previous assertions by Wang et al. [85] regarding the high potassium content in urban FS, attributable to dietary patterns and metabolic processes. The total nitrogen content compares favourably with commercial organic fertilisers, validating the resource recovery potential identified by recent studies in West Africa [86].
Statistical correlation and regression analysis were performed to examine relationships between nutrients (TN, K2O, P2O5) and physicochemical (pH, OM, MC) parameters. The regression analysis (Table 2) reveals strong relationships between nutrient concentrations and physicochemical parameters (R2 > 0.77, p < 0.001), with R2 values ranging from 0.768 to 0.823, indicating that approximately 77–82% of the variance in nutrient concentrations can be explained by these parameters.

Table 2.
Multiple regression results for nutrient content.
The high significant correlation of TN (R2 = 0.823, p < 0.001) suggests that TN levels in MDFS can be predicted with over 82% accuracy using physicochemical parameters. The P2O5 model indicates that about 77% of the variance in phosphorus content is attributed to organic matter content and pH. Potassium (K2O) results confirm that potassium retention in MDFS is largely influenced by moisture and organic matter levels. These predictive relationships could facilitate rapid quality assessment protocols for treatment facilities, reducing analytical costs while maintaining quality control standards [87].
3.1.1. Microbiological Contamination Assessment
The microbiological analysis reveals substantial contamination in the MDFS that exceeds safe limits for agricultural use. Total coliforms show the highest concentration at 148,808.70 ± 223.15 cfu/100 g, substantially exceeding WHO guidelines of <1000 cfu/100 g for safe agricultural use. Faecal Streptococci and Enterococci recorded similar levels around 37,000 cfu/100 g, both far exceeding maximum allowable concentrations. Escherichia coli, a key indicator of faecal contamination, is present at 9286.30 ± 131.12 cfu/100 g, while Salmonella spp. show lower but significant numbers at 1899.86 ± 90.26 cfu/100 g. These levels are consistent with high contamination levels documented by Berendes et al. [88] in Accra’s sanitation systems during 2022–2023 studies.
The parasitological examination identifies five main species, with Strongyloides stercoralis showing the highest concentration at 25.02 ± 0.65 eggs/L, followed by Ascaris lumbricoides at 12.08 ± 1.71 eggs/L. All parasitological concentrations substantially exceed WHO guidelines of <1 egg/L for safe agricultural application. The presence of Giardia lamblia and Cryptosporidium parvum further emphasises the diverse pathogen risks, supporting the comprehensive treatment approach advocated by recent studies [89]. These findings align with regional studies by Manga et al. [90], documenting persistent parasite contamination in African FS management systems during 2021–2023.
3.1.2. Heavy Metal Safety Assessment
Heavy metal analysis provides reassuring results, with all concentrations remaining within acceptable limits for agricultural application. Lead concentrations (45.43 ± 0.56 mg/kg), while representing the highest metal content, remain below international standards for biosolids application [91]. The relatively low concentrations of cadmium, arsenic, and mercury suggest minimal industrial contamination in the source waste streams, contrasting with findings from more industrialized urban areas [92]. These results support the potential for safe agricultural application following appropriate pathogen treatment. This align with broader understanding that low levels of heavy metal and pathogen control in organic amendments or directly in crops is fundamental to ensuring safe plant production, as emphasized by Czembor et al. [93].
3.2. Effect of Anaerobic Digestion
The AD process resulted in significant changes to both beneficial and concerning parameters in MDFS (Table 3). Post-digestion reductions were observed in key nutrients: TN decreased from 2141.05 ± 27.37 mg/kg to 733 ± 208.32 mg/kg (66% reduction), P2O5 remained relatively stable at 140 ± 18.19 mg/kg (26% reduction), and K2O dramatically decreased from 4434.88 ± 35.88 mg/kg to 171.67 ± 46.46 mg/kg (96% reduction). These nutrient losses during the three-month anaerobic digestion period can be attributed to the conversion of organic matter into gaseous end products such as methane and carbon dioxide, as well as to leaching and nutrient mobilisation processes, consistent with observations by Di Costanzo et al. [94] in recent review study.

Table 3.
Physicochemical, nutrient, microbial, parasitological, and heavy metal concentration of AD-MDFS (N = 182).
The significant decrease in total nitrogen reflects the conversion of organic nitrogen to ammonia and subsequent volatilisation, a phenomenon well-documented in anaerobic digestion processes [95]. This 66% nitrogen loss substantially reduces the fertiliser value of the treated product, necessitating nutrient recovery or supplementation strategies to maintain agricultural effectiveness. The phosphorus reduction, while proportionally smaller, still represents meaningful nutrient loss that could be minimised through process optimisation strategies [96].
The dramatic potassium reduction presents the most concerning nutrient loss, potentially reflecting leaching or incorporation into microbial biomass during digestion. This finding contradicts expectations of potassium stability during AD and warrants further investigation into retention mechanisms [97]. The substantial potassium loss significantly reduces the fertiliser value of treated MDFS, potentially requiring supplementation to achieve balanced NPK ratios for agricultural application.
3.2.1. Pathogen Reduction Effectiveness
Microbial analysis reveals significant levels of pathogen reduction in AD-MDFS compared with untreated MDFS (p < 0.001). Total coliforms decreased from 148,808.70 to 493.33 cfu/100 g, representing a 99.7% reduction. Escherichia coli and Salmonella spp. were reduced by >95% (p < 0.001), demonstrating the effectiveness of AD in reducing key indicator organisms. The substantial decrease supports findings by Seruga et al. [98] regarding pathogen reduction potential in organic waste digestion during extended retention periods. However, the persistence of detectable pathogen levels emphasises the need for additional treatment steps to achieve complete safety, as recommended for agricultural applications [99].
Parasitological reduction during AD shows promising trends, with complete elimination of Giardia lamblia, Trichuris trichiura, and Cryptosporidium parvum by the third month. This achievement aligns with extended retention time effects documented in recent tropical composting systems [100]. The substantial reduction in Ascaris lumbricoides eggs from 12.08 to 3.33 eggs/L demonstrates the particular vulnerability of these resistant pathogens to prolonged anaerobic conditions, though levels still exceed WHO guidelines requiring <1 egg/L for safe agricultural use [23].
3.2.2. Heavy Metal Concentration Changes
The increase in nickel concentrations from 9.01 to 73.56 mg/kg during AD raises important monitoring considerations, though levels remain well within agricultural safety limits of 420 mg/kg [101]. This accumulation likely reflects concentration effects as organic matter is converted to gas, similar to phenomena observed in thermal treatment systems [102]. Continued monitoring of heavy metal concentrations throughout extended digestion periods provides valuable insights into accumulation patterns and potential mitigation strategies.
3.3. Economic Viability Assessment
The economic analysis reveals mixed prospects for MDFS treatment and agricultural application. Operational costs for the integrated MD-AD system total approximately USD 28.50 per cubic meter of processed FS, including energy consumption (USD 4.30/m3), labour costs (USD 8.20/m3), maintenance (USD 3.40/m3), and amortised capital costs (USD 12.60/m3). Revenue potential from nutrient recovery averages USD 18.40 per cubic meter based on nitrogen content (USD 2.64/m3), phosphorus content (USD 1.12/m3), and potassium content (USD 14.64/m3 before AD treatment).
However, post-AD treatment significantly reduces revenue potential to USD 6.20 per cubic meter due to substantial nutrient losses, particularly potassium (96% reduction). This creates a negative economic balance of USD −22.30 per cubic meter, indicating current treatment approaches are not economically viable without additional revenue streams or cost reduction strategies. The findings align with recent economic assessments by Pausta et al. [103], highlighting the need for integrated resource recovery approaches to achieve economic sustainability.
The economic viability could be improved through several strategies: implementing nutrient recovery systems to capture volatilised nitrogen and potassium during AD, developing markets for soil conditioning products based on organic matter content, integrating biogas production for energy recovery, and establishing policy frameworks supporting nutrient recovery initiatives. Recent studies suggest that nutrient recovery systems could potentially capture 60–80% of lost nutrients, improving economic viability significantly [104].
3.4. Agricultural Application Potential and Safety Considerations
Despite pathogen reduction achievements, treated MDFS still poses safety concerns for direct agricultural application. Residual pathogen levels, particularly Ascaris lumbricoides eggs (3.33 eggs/L vs. <1 egg/L WHO guideline), necessitate additional post-treatment strategies before safe agricultural use. The nutrient profile, while reduced from original levels, still provides valuable agricultural benefits: treated MDFS nitrogen content (733 mg/kg) exceeds many commercial organic fertilisers, and the high organic matter content (52.21%) offers excellent soil conditioning properties.
Integration with Ghana’s agricultural context reveals both opportunities and challenges. The nutrient content could address documented fertiliser deficiencies in Ghanaian agriculture, supporting food security goals [105]. However, the persistence of pathogen contamination necessitates additional treatment steps, potentially increasing costs beyond municipal capacity [106]. Successful implementation requires coordinated policy frameworks addressing both sanitation and agricultural sectors, as advocated in recent integrated management guidelines [107].
The development of appropriate post-treatment strategies could include the following: solar drying for additional pathogen reduction, alkaline treatment to achieve pH > 12 for pathogen elimination, composting with high-carbon materials to enhance biological pathogen destruction, and thermal treatment for rapid pathogen elimination. Each approach presents trade-offs between effectiveness, cost, and technical complexity that must be evaluated within local contexts [108].
4. Conclusions
This study provides the first comprehensive characterisation of mechanically dewatered faecal sludge from Ghana’s largest treatment facility and demonstrates significant potential for sustainable resource recovery through anaerobic digestion, though with important limitations. MDFS exhibited a substantial nutrient content, with potassium oxide (4434.88 mg/kg), total nitrogen (2141.05 mg/kg), and phosphorus (190.08 mg/kg) concentrations significantly exceeding typical agricultural soil requirements, confirming its value as an organic fertiliser source. However, severe microbial contamination necessitates effective treatment before safe agricultural application. Anaerobic digestion achieved significant pathogen reduction (>99% for total coliforms) and completely eliminated several parasite species within 90 days, though residual contamination levels indicate additional post-treatment strategies are required to meet international safety standards. The substantial nutrient losses, particularly potassium (96% reduction) and nitrogen (66% reduction), highlight the need for optimisation strategies and economic considerations that currently challenge commercial viability at USD –22.30 per cubic meter processing cost.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.O.-A.; Methodology, D.O.-A. and I.A.; Software, E.A.-E.; Validation, E.A.-E.; Formal analysis, D.O.-A.; Resources, D.O.-A.; Data curation, I.A.; Writing—original draft, D.O.-A.; Writing—review & editing, B.G.-K., E.A., H.M.K.E., M.A.-B. and I.A.; Supervision, E.A.-E., B.G.-K., M.A.-B. and D.O.-A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions present in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Dennis Ofori-Amanfo and Issahaku Ahmed were employed by the company Sewerage Systems Ghana Limited. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AD | Anaerobic Digestion |
| MDFS | Mechanically Dewatered Faecal Sludge |
| AD-MDFS | Anaerobic Digested Mechanical Dewatered Faecal Sludge |
| FS | Faecal Sludge |
| TN | Total Nitrogen |
| MC | Moisture Content |
| OM | Organic Matter |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| UNICEF | United Nations Children’s Fund |
| LHFTP | Lavender Hill Faecal Treatment Plant |
| NPK | Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium |
| CFU | Colony Forming Units |
| SDG | Sustainable Development Goals |
| GDP | Gross Domestic Product |
| COD | Chemical Oxygen Demand |
| BOD | Biochemical Oxygen Demand |
| VS | Volatile Solids |
| TS | Total Solids |
| HRT | Hydraulic Retention Time |
| SRT | Solids Retention Time |
| WASH | Water, Sanitation and Hygiene |
| FSM | Faecal Sludge Management |
| WWTP | Wastewater Treatment Plant |
| FSTP | Faecal Sludge Treatment Plant |
| pH | Potential of Hydrogen |
| EC | Electrical Conductivity |
| GIS | Geographic Information System |
| IWA | International Water Association |
| IWMI | International Water Management Institute |
References
- UNICEF; WHO. Progress on Household Drinking Water, Sanitation and Hygiene 2000–2020: Five Years into the SDGs. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240030848 (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- United Nations Statistics Division. Sustainable Development Goals Report 2025: Goal 6—Clean Water and Sanitation. Available online: https://unstats.un.org/sdgs/report/2025/Goal-06/ (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Ofori-Amanfo, D.; Rockson, G.N.K.; Arthur, A.; Ahmed, I. Processing dewatered faecal sludge into unpelletized fertilizer for crop production in Greater Accra-Ghana. Int. J. Environ. Monit. Anal. 2018, 6, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagoe, G.; Danquah, F.S.; Amofa-Sarkodie, E.S.; Appiah-Effah, E.; Ekumah, E.; Mensah, E.K.; Karikari, K.S. GIS-aided optimisation of faecal sludge management in developing countries: The case of the Greater Accra Metropolitan Area, Ghana. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Alam, M.A.U.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Rahman, M.A.; Hasan, M.M.; Ahmed, T. Exploring fecal sludge treatment technologies in humanitarian settings at Cox’s Bazar, Bangladesh: A comprehensive assessment of treatment efficiency through characterization of fecal sludge. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1341176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Health Observatory Data Repository: Water, Sanitation and Hygiene. Available online: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/water-sanitation-and-hygiene (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- United Nations. The Sustainable Development Goals Report 2023. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/sites/default/files/2023-07/The-Sustainable-Development-Goals-Report-2023_0.pdf (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- World Health Organization. UN-Water Global Analysis and Assessment of Sanitation and Drinking-Water (GLAAS) 2017 Report. Available online: https://iris.who.int/server/api/core/bitstreams/b51034ff-9ca6-422e-8046-6acc1115aded/content (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Ghana Statistical Service. Ghana 2021 Population and Housing Census: Water and Sanitation Report. Available online: https://census2021.statsghana.gov.gh/subreport.php?readreport=NjMzMzk0MDg5LjAzNg==&Volume-3M-Water-and-Sanitation&utm (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Ministry of Sanitation and Water Resources. National Environmental Sanitation Strategy and Action Plan. Available online: https://www.ircwash.org/sites/default/files/MLGRD-2010-National.pdf (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Pureco. Ghana: Kumasi, Takoradi and Tamale Start Treating Faecal Sludge. Available online: https://purecoafrica.com/news/takoradi-tamale-are-completed (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Greater Accra Metropolitan Assembly. Faecal Sludge Management Status Report 2023 (In Press). Available online: https://www.gamaswp.org/household-toilet/ (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- African Development Bank. Africa Water Vision 2025: Progress and Challenges. Available online: https://www.afdb.org/fileadmin/uploads/afdb/Documents/Generic-Documents/african%20water%20vision%202025%20to%20be%20sent%20to%20wwf5.pdf (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Water Resources Commission. State of Ghana’s Water Resources 2023. Available online: https://wrc-gh.org (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Environmental Protection Agency. National Water Quality Assessment Report 2023. Available online: https://epa.gov.gh (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- WHO. WHO Global Water, Sanitation and Hygiene: Annual Report 2023. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240106079 (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Pradhan, S.K.; Cofie, O.; Nikiema, J.; Heinonen-Tanski, H. Fecal sludge derived products as fertilizer for lettuce cultivation in urban agriculture. Sustainability 2019, 11, 7101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalulu, K.; Thole, B.; Mkandawire, T.; Kululanga, G. Resource-Efficient Characterisation of Pit Latrine Sludge for Use in Agriculture. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, V.K.; Lo, S.L. Sludge: A waste or renewable source for energy and resource recovery? Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 25, 708–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhou, X.; Ren, X.; Hu, X.; Ji, B. Recent Research on Municipal Sludge as Soil Fertilizer in China: A Review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. United Nations World Water Development Report 2024: Water for Prosperity and Peace; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2024; Available online: https://www.unesco.org/reports/wwdr/en/wwdr/en/2024/statistics (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- UN-Water. The United Nations World Water Development Report 2023: Partnerships and Cooperation for Water. Available online: https://www.unwater.org/publications/un-world-water-development-report-2023 (accessed on 10 March 2024).
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for the Safe Use of Wastewater, Excreta and Greywater—Volume 4: Excreta and Greywater Use in Agriculture. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9241546859 (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Behera, S.; Samal, K. Sustainable approach to manage solid waste through biochar assisted composting. Energy Nexus 2022, 7, 100121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xiao, R.; Klammsteiner, T.; Kong, X.; Yan, B.; Mihai, F.C.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Awasthi, M.K. Recent trends and advances in composting and vermicomposting technologies: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 360, 127591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, B.J.; Nguyen, M.T.; Sam, S.B.; Korir, N.; Niwagaba, C.B.; Morgenroth, E.; Strande, L. Particle size as a driver of de-watering performance and its relationship to stabilization in fecal sludge. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 326, 116801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalulu, K.; Thole, B.; Mkandawire, T.; Kululanga, G. Application of process intensification in the treatment of pit latrine sludge from informal settlements in Blantyre City, Malawi. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strande, L. Integrating recent scientific advances to enhance non-sewered sanitation in urban areas. Nat. Water 2024, 2, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deligiannis, M.; Gkalipidou, E.; Gatidou, G.; Kostakis, M.G.; Gerokonstantis, D.T.; Arvaniti, O.S.; Thomaidis, N.S.; Vyrides, I.; Hale, S.E.; Arp, H.P.; et al. Study on the fate of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances during thermophilic anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge and the role of granular activated carbon addition. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 406, 131013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forbis-Stokes, A.A.; O’Meara, P.F.; Mugo, W.; Simiyu, G.M.; Deshusses, M.A. On-site fecal sludge treatment with the anaerobic digestion pasteurization latrine. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2016, 33, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moura, E.R.; Machado, V.; Hocevar, L.S.; Pereira, J.S.; Torres, F.A.; Alves, C.T. Characterization of sludge for biogas production using anaerobic digestion: A literature review approach. J. Biotechnol. Health 2024, 7, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConville, J.; Niwagaba, C.; Nordin, A.; Ahlström, M.; Namboozo, V.; Kiffe, M. Guide to Sanitation Resource-Recovery Products & Technologies: A Supplement to the Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies; Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences: Uppsala, Sweden, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Andriessen, N.; Ward, B.J.; Strande, L. To char or not to char? Review of technologies to produce solid fuels for resource recovery from faecal sludge. J. Water Sanit. Hyg. Dev. 2019, 9, 210–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jothinathan, H.; Singh, A.P. Faecal sludge characterization, treatment, and resource recovery options: A state-of-the-Art review on faecal sludge management. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 119549–119567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagalwa Nyamugara, L.; Bigumandondera, P.; Bayumbasire, C.; Bukuru Nyabukara, J.J.; Lina Aleke, A.; Ndagano Kamole, K.E.C. Faecal sludge management in the city of Bukavu, Democratic Republic of Congo. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2024, 15, 268–284. [Google Scholar]
- Muoghalu, C.; Semiyaga, S.; Manga, M. Faecal sludge emptying in Sub-Saharan Africa, South and Southeast Asia: A systematic review of emptying technology choices, challenges, and improvement initiatives. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1097716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayilara, M.S.; Olanrewaju, O.S.; Babalola, O.O.; Odeyemi, O. Waste management through composting: Challenges and potentials. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andraskar, J.; Yadav, S.; Khan, D.; Kapley, A. Treatment Options for Municipal Solid Waste by Composting and Its Challenges. Indian J. Microbiol. 2023, 63, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nartey, E.G.; Sakrabani, R.; Tyrrel, S.; Cofie, O. Assessing consistency in the aerobic co-composting of faecal sludge and food waste in a municipality in Ghana. Environ. Syst. Res. 2023, 12, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manga, M.; Camargo-Valero, M.A.; Anthonj, C.; Evans, B.E. Fate of faecal pathogen indicators during faecal sludge composting with different bulking agents in tropical climate. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2021, 232, 113670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manga, M.; Muoghalu, C.C.; Acheng, P.O. Inactivation of faecal pathogens during faecal sludge composting: A systematic review. Environ. Technol. Rev. 2023, 12, 150–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbyla, M.E.; Iriarte, M.M.; Guzmán, A.M.; Coronado, O.; Almanza, M.; Mihelcic, J.R. Pathogens and faecal indicators in waste stabilization pond systems with direct reuse for irrigation: Fate and transport in water, soil and crops. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 551–552, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittencourt, F.L.F.; Martins, M.F. Thermochemically-driven treatment units for faecal matter sanitation: A review addressed to the underdeveloped world. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breukelman, H.; Krikke, H.; Löhr, A. Failing services on urban waste management in developing countries: A review on symptoms, diagnoses, and interventions. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, B.C.; Fowler, G.D.; Templeton, M.R. Critical analytical parameters for faecal sludge characterization informing the application of thermal treatment processes. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 280, 111658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Lin, K.Y.A.; Jung, S.; Kwon, E.E. Hybrid renewable energy systems involving thermochemical conversion process for waste-to-energy strategy. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 452, 139218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandana, N.; Rao, B. A critical review on sludge management from onsite sanitation systems: A knowledge to be revised in the current situation. Environ. Res. 2022, 203, 111812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.K.; Wang, M.H.S.; Cardenas, R.R.; Sabiani, N.H.M.; Yusoff, M.S.; Hassan, S.H.; Kamaruddin, M.A.; George, F.O.; Hung, Y.T. Composting process for disposal of municipal and agricultural solid wastes. In Solid Waste Engineering and Management; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 1, pp. 399–523. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.; Peng, S.; Li, S.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, Y.; Li, X.; Hong, M.; Li, W.; Lu, P. Characterization of microbial communities and functions in shale gas wastewaters and sludge: Implications for pretreatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mawejje, M.N.; Pocock, J.; Septien, S. Solar Thermal Drying Kinetics of Faecal Sludge: Effect of Convection Air Stream Conditions and Type of Sludge. Energy Eng. 2025, 120, 3177–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An-nori, A.; Ezzariai, A.; El Mejahed, K.; El Fels, L.; El Gharous, M.; Hafidi, M. Solar Drying as an Eco-Friendly Technology for Sewage Sludge Stabilization: Assessment of Micropollutant Behavior, Pathogen Removal, and Agronomic Value. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 814590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novais, R.M.; Gameiro, T.; Carvalheiras, J.; Seabra, M.P.; Tarelho, L.A.; Labrincha, J.A.; Capela, I. High pH buffer capacity biomass fly ash-based geopolymer spheres to boost methane yield in anaerobic digestion. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 178, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toutian, V.; Barjenbruch, M.; Loderer, C.; Remy, C. Impact of process parameters of thermal alkaline pretreatment on biogas yield and dewaterability of waste activated sludge. Water Res. 2021, 202, 117465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwapinski, W.; Kolinovic, I.; Leahy, J.J. Sewage sludge thermal treatment technologies with a focus on phosphorus recovery: A review. Waste Biomass Valorization 2021, 12, 5837–5852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladejo, J.; Shi, K.; Luo, X.; Yang, G.; Wu, T. A review of sludge-to-energy recovery methods. Energies 2019, 12, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myszograj, S.; Płuciennik-Koropczuk, E. Thermal Disintegration of Sewage Sludge as a Method of Improving the Biogas Potential. Energies 2023, 16, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Shao, Y.; Qin, S.; Wang, Z. Future Directions of Sustainable Resource Utilization of Residual Sewage Sludge: A Review. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Ye, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, B.; Pan, Z.; Wang, J. Thermochemical conversion of sewage sludge for energy and resource recovery: Technical challenges and prospects. Environ. Pollut. Bioavail. 2021, 33, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Chowdhury, S.; Techato, K. Waste-to-energy in developing countries: A rapid review: Opportunities, challenges, and policies in selected countries of Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia towards sustainability. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oluoch, B.; Mandizvo, T.; Musazura, W.; Badza, T.; Otieno, B.; Ojwach, S.; Odindo, A. A review of pathogen removal from municipal wastewater using advanced oxidation processes: Agricultural application, regrowth risks, and new perspectives. Heliyon 2024, 10, e39625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, R.; Yen, P.; Agarwal, R.; Arshinder, K.; Bajada, C. Collaborative innovation and sustainability in the food supply chain: Evidence from farmer producer organisations. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 168, 105253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karef, S.; Azlaoui, M.; Boussaid, K.; Batana, F.Z.; Bruzzoniti, M.C.; Fodili, M.; Kettab, A. Fertilizer potential and social perception of the agricultural reuse of sewage sludge and treated wastewater. Desalination Water Treat. 2024, 322, 100186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpan, V.E.; Omole, D.O.; Bassey, D.E. Assessing the public perceptions of treated wastewater reuse: Opportunities and implications for urban communities in developing countries. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amegah, A.K. Slum decay in Sub-Saharan Africa: Context, environmental pollution challenges, and impact on dweller’s health. Environ. Epidemiol. 2021, 5, e149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amponsah-Doku, B.; Daymond, A.; Robinson, S.; Atuah, L.; Sizmur, T. Improvement soil health and closing the yield gap of cocoa production in Ghana: A review. Sci. Afr. 2022, 15, e01075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daadi, B.E.; Latacz-Lohmann, U. Organic fertilizer use by smallholder farmers: Typology of management approaches in northern Ghana. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2021, 36, 192–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capodaglio, A.G.; Callegari, A. Energy and resource recovery from excess sewage sludge: A holistic analysis of opportunities and strategies. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. Adv. 2023, 19, 200184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 24th ed.; American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Amenyeku, G. Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Faecal Sludge with Paper or Fruit Waste for Biogas: A Case in Kumasi, Ghana. Master’s Thesis, Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology, Kumasi, Ghana, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Velkushanova, K.; Strande, L.; Ronteltap, M.; Koottatep, T.; Brdjanovic, D.; Buckley, C. Methods for Faecal Sludge Analysis; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2021; pp. 236–395. ISBN 9781780409115. [Google Scholar]
- Butte, G.; Niwagaba, C.; Nordin, A. Assessing the microbial risk of faecal sludge use in Ugandan agriculture by comparing field and theoretical model output. Water Res. 2021, 197, 117068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 6579-1:2017; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Detection, Enumeration and Serotyping of Salmonella—Part 1: Detection of Salmonella spp. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/76671.html (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Moodley, P.; Wilkinson, E.; Connolly, C.; Asafu-Adjei, D.; Sturm, A.W. Standard Methods for the Recovery and Enumeration of Helminth Ova in Wastewater, Sludge, Compost and Urine-Diversion Waste in South Africa. Available online: https://www.wrc.org.za/wp-content/uploads/mdocs/TT%20322-web.pdf (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Ravindran, V.B.; Shahsavari, E.; Soni, S.K.; Ball, A.S. Viability determination of Ascaris ova in raw wastewater: A comparative evaluation of culture-based, BacLight Live/Dead staining and PMA-qPCR methods. Water Sci. Technol. 2019, 80, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Environmental Protection Agency. Method 1600: Enterococci in Water by Membrane Filtration Using Membrane-Enterococcus Indoxyl-β-D-Glucoside Agar (mEI). Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-08/documents/method_1600_2009.pdf (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- US Environmental Protection Agency. Method 1623.1: Cryptosporidium and Giardia in Water by Filtration/IMS/FA. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2021-05/documents/method_1623_1.pdf (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Cai, X.; Du, C. Thermal plasma treatment of medical waste. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2021, 41, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIST. Certificate of Analysis: Standard Reference Material 2781 Domestic Sludge; National Institute of Standards and Technology. Available online: https://tsapps.nist.gov/srmext/certificates/2781.pdf (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Strande, L.; Ronteltap, M.; Brdjanovic, D. Faecal Sludge Management: Systems Approach for Implementation and Operation; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strande, L.; Schoebitz, L.; Bischoff, F.; Ddiba, D.; Okello, F.; Englund, M.; Ward, B.J.; Niwagaba, C.B. Methods to Reliably Estimate Faecal Sludge Quantities and Qualities for the Design of Treatment Technologies and Management Solutions. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 223, 898–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englund, M.; Strande, L. Faecal Sludge Management Highlights and Exercises; Eawag: Dübendorf, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gold, M.; Dayer, P.; Faye, M.C.A.S.; Clair, G.; Seck, A.; Niang, S.; Morgenroth, E.; Strande, L. Locally produced natural conditioners for dewatering of faecal sludge. Environ. Technol. 2016, 37, 2802–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooker, M.R. Advanced Characterization of Organic Waste Streams for Resource Recovery. Ph.D. Thesis, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Capps, K.A.; Bentsen, C.N.; Ramírez, A. Environmental impacts and resource recovery potential from urban waste streams in developing countries. Freshw. Sci. 2016, 35, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xiao, K.; Yang, J.; Yu, Z.; Yu, W.; Xu, Q.; Wu, Q.; Liang, S.; Hu, J.; Hou, H.; et al. Phosphorus recovery from the liquid phase of anaerobic digestate using biochar derived from iron-rich sludge: A potential phosphorus fertilizer. Water Res. 2020, 174, 115629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanda, C.; Kengne, E.S.; Wafo, G.V.D.; Nzouebet, W.A.L.; Nbendah, P.; Ngandjui, Y.A.T.; Zapfack, L.; Noumsi, I.M.K. Quantification and characterisation of faecal sludge from on-site sanitation systems prior the design of a treatment plant in Bangangte, West Region of Cameroon. Environ. Chall. 2021, 5, 100236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, B.J.; Andriessen, N.; Tembo, J.M.; Kabika, J.; Grau, M.; Scheidegger, A.; Morgenroth, E.; Strande, L. Predictive models using “cheap and easy” field measurements: Can they fill a gap in planning, monitoring, and implementing fecal sludge management solutions? Water Res. 2021, 197, 116997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berendes, D.M.; Kirby, A.E.; Clennon, J.A.; Agbemabiese, C.; Ampofo, J.A.; Armah, G.E.; Baker, K.K.; Liu, P.; Reese, H.E.; Robb, K.A.; et al. Urban sanitation coverage and environmental faecal contamination: Links between the household and public environments of Accra, Ghana. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kengne, E.S.; Tekamdjo, S.L.T.; Nzouebet, W.A.L.; Wanda, C.; Nbendah, P.; Tchuifon, D.R.T.; Kengne, I.M.; Nola, M.; Djuikom, E. Treatment of Fecal Sludge (FS) Using Combined Bio-Digester and Stabilization Pond in a Tropical Urban Area. Int. J. Water Wastewater Treat. 2024, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manga, M.; Muoghalu, C.; Camargo-Valero, M.A.; Evans, B.E. Effect of Turning Frequency on the Survival of Fecal Indicator Microorganisms during Aerobic Composting of Fecal Sludge with sawdust. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naidoo, M.K. Water, Sanitation and Hygiene (WASH) Practices and the Incidence of WASH Related Diseases Within the Tamale Metropolitan Area. Master’s Thesis, University for Development Studies, Tamale, Ghana, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ahogle, A.M.A.; Letema, S.; Schaab, G.; Ngure, V.; Mwesigye, A.R.; Korir, N.K. Heavy metals and trace elements contamination risks in peri-urban agricultural soils in Nairobi city catchment, Kenya. Front. Soil Sci. 2023, 2, 1048057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czembor, E.; Tratwal, A.; Pukacki, J.; Krystek, M.; Czembor, J.H. Managing fungal pathogens of field crops in sustainable agriculture and AgroVariety internet application as a case study. J. Plant Prot. Res. 2025, 65, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Costanzo, N.; Cesaro, A.; Di Capua, F.; Esposito, G. Exploiting the Nutrient Potential of Anaerobically Digested Sewage Sludge: A Review. Energies 2021, 14, 8149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhelal, I.; Loetscher, L.; Sharvelle, S.; Reardon, K. Nitrogen Recovery from Anaerobic Digestate Via Ammonia Stripping and Absorbing with a Nitrified Solution. SSRN Electron. J. 2022, 10, 107826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Grimberg, S.; Rogers, S.; Kim, T. Bipolar membrane electrodialysis for nutrient recovery from anaerobic digestion dewatering sidestream. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 488, 150834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.R.; Quinta-Ferreira, R.M.; Castro, L.M. Biological Treatments for VOC-Contaminated Off-Gas: Advances, Challenges, and Energetic Valorization Opportunities. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seruga, P.; Krzywonos, M.; Paluszak, Z.; Urbanowska, A.; Pawlak-Kruczek, H.; Niedźwiecki, Ł.; Pińkowska, H. Enhanced pathogen reduction in anaerobic digestion of organic waste. Molecules 2020, 25, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drechsel, P.; Qadir, M.; Galibourg, D. The WHO Guidelines for Safe Wastewater Use in Agriculture: A Review of Implementation Challenges and Possible Solutions in the Global South. Water 2022, 14, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manga, M.; Evans, B.E.; Ngasala, T.M.; Camargo-Valero, M.A. Recycling of Faecal Sludge: Nitrogen, Carbon and Organic Matter Transformation during Co-Composting of Faecal Sludge with Different Bulking Agents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union. Directive 2018/851 on Waste and Circular Economy: Heavy Metal Standards for Organic Amendments; EU: Brussels, Belgium, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- O’Brien, P.L.; DeSutter, T.M.; Casey, F.X.; Khan, E.; Wick, A.F. Thermal remediation alters soil properties: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 206, 826–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pausta, C.M.; Kalbar, P.; Saroj, D. Life cycle assessment of nutrient recovery strategies from domestic wastewaters to quantify environmental performance and identification of trade-offs. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Qin, Y. Research Progress of Low-Temperature Plasma Technology in the Treatment of Malodorous Gases. Int. J. Appl. Sci. 2021, 8, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebenezer, A.A.; Abdul-Wahab, D.; Archibold, B.K.; Rafeah, W.; Zainab, N.; Charles, K.K.; Ibrahim, K.K.; Crentsil, K.B. Climate change, soil health, and governance challenges in Ghana: A review. Land Use Policy 2025, 157, 107684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, A.A. Municipal Capacity Building for Integrated Waste Management in Ghana. Master’s Thesis, Carleton University, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Rohilla, S.K.; Agyenim, F.B.; Luthra, B.; Padhi, S.K.; Quashie, A.S.; Yadav, A. Integrated Wastewater and Faecal Sludge Management for Ghana Draft Guidelines. Available online: https://cspace.csirgh.com/items/show/999 (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Hotez, P.J. Forgotten People, Forgotten Diseases: The Neglected Tropical Diseases and Their Impact on Global Health and Development; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).