Abstract
This study aimed to explore the efficiency of hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents (HDESs) composed of menthol and fatty acids for extracting carotenoids from tomato by-products. A selection of nine different HDESs and fatty acid mixtures were prepared and evaluated for their carotenoid extraction potential. The highest extraction yield was obtained with menthol/hexanoic acid 2:1 (94.5 ± 3.3 μg CtE/g dm), demonstrating the influence of the specific composition of DES components on extraction efficiency. An optimization process employing a Box–Behnken design was conducted to identify the optimal extraction conditions. The solvent-to-solid ratio, extraction time, and temperature were studied, resulting in an extraction yield increase of up to 48.5% under optimized conditions (solvent-to-solid ratio of 25:1, extraction time of 90 min, and temperature of 50 °C). Furthermore, potent antioxidant properties, including antiradical activity (63.7 ± 4 μmol AAE/g dm) and reducing power (26.7 ± 1.8 μmol AAE/g dm), were recorded. Comparative analyses with conventional organic solvents (hexane, ethyl acetate, and acetone) highlighted the superiority of HDES in both carotenoid extraction and antioxidant capacity. A color analysis of the extracts showed distinctive color profiles, with the HDES extract displaying higher redness and reduced yellowness compared to organic solvent extracts. Principal component analysis (PCA) and multivariate correlation analysis (MCA) revealed strong correlations between total carotenoid content and antioxidant parameters, underscoring the relationship between carotenoid extraction and antioxidant potential. In conclusion, this study highlights the potential of HDESs, particularly Men/Hex 2:1, as efficient and sustainable solvents for carotenoid extraction. These findings offer valuable insights for the development of innovative and environmentally friendly methods for extracting carotenoids with potential applications in various industries.
1. Introduction
The agri-food industry plays a pivotal role in the sustenance of the food supply to address the needs of the growing global population [1]. However, aside from edible products, substantial amounts of waste are also generated. One such example is the tomato processing industry, which produces a significant amount of discarded material during the production of tomato-based products such as sauces, pastes, and juices [2,3,4]. This waste comprises tomato skins, seeds, and pulp, and is often treated as low-value or even disposed of, leading to environmental concerns and missed opportunities for resource utilization [5]. Tomato waste, although considered a by-product, contains valuable bioactive compounds, including carotenoids [3,6,7]. Carotenoids are lipid-soluble pigments that contribute not only to the color of fruits and vegetables but also confer health benefits [8,9]. Among the numerous carotenoids found in tomatoes, lycopene stands out due to its well-documented antioxidant and anti-carcinogenic properties [10,11]. As such, the extraction of carotenoids from tomato waste can be advantageous in a dual way. At first, it reduces the environmental impact of waste disposal while, simultaneously, it contributes to the supply of health-promoting ingredients, which can be further used in various industries [6,12].
To date, various approaches have been employed to extract carotenoids from plant sources [13,14]. Traditional extraction methods for carotenoids, such as Soxhlet extraction and solvent reflux, are often accompanied by drawbacks such as high solvent consumption, long extraction times, and potential degradation due to elevated temperatures. Furthermore, the usage of organic solvents raises concerns about safety, environmental pollution, and the increased cost of the overall procedure. In this context, there is a growing need to develop extraction methods that are both effective and sustainable [15,16]. To this end, there are various techniques for extracting carotenoids from natural sources, each possessing distinct advantages in terms of cost-effectiveness, environmental sustainability, and efficiency. Ultrasonic-assisted extraction (UAE) is one such method that merits attention. The application of ultrasonic waves enhances the penetration of solvents into plant matrices, promoting efficient carotenoid extraction. This technique not only reduces extraction times but also minimizes solvent consumption, addressing concerns raised by traditional methods [17]. Pulsed electric field (PEF) extraction represents another noteworthy approach. By subjecting plant materials to short bursts of electric pulses, PEF facilitates the disruption of cell membranes, aiding in the release of carotenoids. This method not only accelerates the extraction process but also contributes to maintaining the quality of extracted compounds [18]. Microwave-assisted extraction (MAE) stands out for its ability to harness microwave energy for targeted and rapid extraction. This method offers advantages such as reduced extraction times and lower energy consumption, aligning with the principles of sustainability and efficiency in extraction processes. Supercritical fluid extraction (SFE), utilizing supercritical carbon dioxide (SC-CO2), represents a cutting-edge and environmentally friendly technique [16]. The unique properties of SC-CO2 allow for the selective extraction of carotenoids while avoiding the use of organic solvents. This not only addresses safety and environmental concerns but also contributes to the overall economic viability of the extraction process. Enzyme-assisted extraction (EAE) emerges as a biotechnological alternative, harnessing the catalytic power of enzymes to break down cell walls and facilitate carotenoid release. This approach is characterized by its specificity, reducing the need for harsh conditions and ensuring the preservation of target compounds [19,20,21,22,23].
One innovative approach that has gained prominence in recent years is the use of deep-eutectic solvents (DESs) in various extraction procedures [24]. These solvents are formed through the combination of two or more components, typically a hydrogen bond donor and an acceptor, resulting in a mixture with a lower melting point than each component [25]. DESs offer unique properties such as tunable physicochemical characteristics, low volatility, and the ability to solubilize a wide range of compounds. However, they exhibit low efficiency in extracting lipophilic compounds, due to their polar nature [26]. As such, hydrophobic DESs (HDESs) have been developed [27]. HDESs are a novel class of environmentally benign solvents with remarkable potential for diverse applications, particularly in the extraction of lipophilic compounds. HDESs are synthesized by combining hydrophobic constituents, in specific ratios, to create a eutectic mixture with a considerably lower melting point than the individual components [28]. This unique attribute grants HDESs a liquid form at ambient temperatures, facilitating their use as extraction media [29]. Their hydrophobic nature bestows them with good extraction properties for lipophilic molecules, such as essential oils, fats, and bioactive compounds, from various matrices [30]. This versatility, combined with their reduced environmental impact, low volatility, and biodegradability, renders HDESs promising alternatives to conventional organic solvents in extraction processes, contributing to sustainable and greener approaches to chemical and material processing [30].
To the best of our knowledge, there are limited data available regarding the usage of HDESs for the extraction of carotenoids from tomatoes and tomato by-products. More specifically, a green extraction method is suggested by Kyriakoudi et al. [31] in their work on the recovery of lycopene from tomato fruits. At various molar ratios, several HDESs based on terpenes (menthol and thymol) and fatty acids (decanoic acid and dodecanoic acid) were produced. In another study, Lazzarini et al. [32] used HDES mixtures (ethyl acetate/ethyl lactate and menthol/lactic acid) to extract carotenoids, particularly lycopene and β-carotene, from tomato pomace, a by-product made of skin and seeds. Also, Diacon et al. [33] extracted carotenoids (i.e., lycopene and β-carotene) from tomato waste products using fatty-acid ethyl esters, a novel green solvent.
This study aimed to investigate the feasibility and effectiveness of HDES synthesized from menthol and fatty acids (i.e., hexanoic acid and octanoic acid) for the extraction of carotenoids from tomato waste. The utilization of HDESs for the extraction of carotenoids from tomato waste is a promising way to address both the challenges of waste management in the tomato processing industry and the demand for the sustainable isolation of bioactive compounds. To this end, various HDESs were synthesized and compared, so as to conclude the most efficient one. Next, the overall extraction process was further optimized using a response surface methodology (RSM) in an effort to further enhance the extraction yield. As such, we aimed to contribute to the development of environmentally friendly and economically viable extraction methodologies. The novelty of this study lies predominantly in the use of DES for the extraction, as well as in the nature of the synthesized DES (vide infra). The use of HDESs, specifically composed of menthol and fatty acids, represents a unique approach to enhance the solubilization of lipophilic compounds like carotenoids. While DESs have been explored in various extraction studies, the emphasis on hydrophobic variants, particularly utilizing menthol (a naturally derived compound with unique properties), introduces a novel dimension to the extraction process while being an environmentally friendly approach.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
Menthol, iron (III) chloride, and lycopene (analytical standard, ≥85%) were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (Steinheim, Germany). Hexanoic and octanoic acid were from Fluorochem (Hadfield, UK). Hexane, ethyl acetate, acetone, sodium carbonate anhydrous (99%), sodium carbonate, 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), and 2,4,6-tris (2-pyridyl)-s-triazine (TPTZ) (99%) were from Penta (Prague, Czech Republic). Absolute ethanol and Folin–Ciocalteu regent were from Panreac (Barcelona, Spain). All solvents used were at least of HPLC grade.
2.2. Tomato Waste Sample Preparation
Fresh tomato waste samples were obtained from a tomato processing facility (Damavand S.A., Filia, Karditsa, Greece). The samples were placed in a Biobase BK-FD10P freeze-dryer (Jinan, China) in order to remove water. The moisture was calculated to be 84.5%. The freeze-dried waste was pulverized and placed in sieves in order to be separated according to size. For the preparation of the extracts, the powdered wastes with an average particle diameter of 250 μm were used.
2.3. Preparation of Deep Eutectic Solvents
A set of 9 HDESs were synthesized using menthol (Men) as the hydrogen bond acceptor (HBA), whereas hexanoic acid (Hex) and octanoic acid (Oct) served as hydrophobic hydrogen bond donors (HBDs). Also, the two fatty acids were combined, so as to develop HDESs. The individual components were combined in different molar ratios, as shown in Table 1. To synthesize the HDESs, appropriate amounts of HBA and HBD were mixed in 25 mL glass bottles and heated at 70 °C under stirring at 350 rpm, until a clear homogeneous liquid was formed. The HDESs were then allowed to cool to room temperature and inspected for the formation of crystals after 24 h. The density of all HDESs was measured using pre-weighed density vials.

Table 1.
Constituents, molar ratios, abbreviations, and densities of the prepared HDESs.
2.4. Extraction Procedure
Initially, the as-synthesized HDESs were evaluated for their efficiency to extract carotenoids. To this end, the dried tomato waste was mixed with each HDESs at a solvent-to-solid ratio of 10:1, and the mixture was stirred at 500 rpm for 60 min, and at room temperature. For means of comparison, extracts were also prepared using three conventional organic solvents (i.e., hexane, ethyl acetate, and acetone). After extraction was completed, the mixtures were centrifuged at 10,000× g for 10 min. The supernatants were retracted and used for further analyses.
2.5. Design of the Experiment and the Response Surface Methodology (RSM) Optimization
An RSM approach was employed so as to optimize the extraction procedure. The response was the extraction yield in total carotenoids (YTCn), which was based on an experiment utilizing a Box–Behnken design with 15 design points, 3 of which were central. Three levels of process variables were defined (Table 2). To achieve optimum extraction, the ratio of liquid-to-solid (X1; RL/S, mL/g), the extraction time (X2; t, min), and the extraction temperature (X3; T, °C) were investigated. The overall model significance (R2, p) was evaluated at a minimum level of 95% using the analysis of variance (ANOVA) and summary-of-fit tests.

Table 2.
The actual and coded levels of the independent variables were used to optimize the process.
Additionally, the response variable was predicted using a second-order polynomial model presented in the following Equation (1), as a function of the investigated independent factors:
where Yk is the predicted response variable; Xi and Xj are the independent variables; β0, βi, βii, and βij are the intercept, regression coefficients of the linear, quadratic, and interaction terms of the model, respectively.
The RSM was also used to calculate the greatest peak area and to examine the impact of a significant independent variable on the response. To display the model equation visually, the 3D surface response graphs were built.
2.6. Total Carotenoid Content (TCC)
The TCC of the extracts was evaluated using a previously described method, with minor modifications [34]. More specifically, 200 μL of the extract was combined with 800 μL of ethanol, and the mixture was vortexed for 30 s. Using a Shimadzu spectrophotometer (UV-1700, Shimadzu Europa GmbH, Duisburg, Germany), the absorbance was measured at 471 nm. Using lycopene as a reference substance (since it is the main carotenoid of tomatoes), a calibration curve was created and used for the quantification of TCC.
2.7. DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
A DPPH assay was carried out, as previously described [35]. To assess the DPPH radical scavenging activity, 25 µL of the prepared extract was added to 975 µL of DPPH solution (100 µM). Following thorough mixing, the absorbance of the solution was measured at 515 nm (A515(i)), as well as after 30 min of incubation, in the absence of light (A515(f)). The capacity to scavenge the DPPH radical is expressed as
Using an ascorbic acid calibration curve (for comparison with other published articles) and the following equation, antiradical activity (AAR) was calculated as μmol of ascorbic acid equivalents (AAEs) per g of dry weight:
where V is the volume of the extraction medium (in L) and w is the dry weight of the sample (in g).
2.8. Ferric Reducing Antioxidant Power (FRAP) Assay
The FRAP assay was carried out according to a previous report [36]. For the evaluation of the FRAP, an Eppendorf tube was filled with 50 μL of FeCl3 solution (4 mM in 0.05 M HCl) and was mixed with the sample extracts (50 μL). The solutions were incubated for 30 min at 37 °C. Afterward, 900 μL of TPTZ solution (1 mM in 0.05 M HCl) was added, and, after 5 min, the absorbance at 620 nm was measured. A calibration curve was prepared using ascorbic acid as a standard compound. Ascorbic acid was used for means of comparison with other studies. Reducing power (PR) was determined as µmol ascorbic acid equivalents (AAEs) per g of dw, using the following Equation (4):
where V is the volume of the extraction medium (in L) and w is the dry weight of the sample (in g).
2.9. Color Analysis
The color of the extracts was analyzed using two different approaches. The first approach was with a colorimeter and the second approach was based on a spectrophotometric method.
2.9.1. Colorimeter Method
The extracts were colored using a Lovibond CAM-System 500 Imaging Colorimeter (CIE L*, a*, b*). The parameters L*, a*, and b* represent lightness, redness, and yellowness, respectively [37]. Equations (5) and (6) were used to determine the parameters’ values to calculate chroma () and hue-angle ():
2.9.2. Absorbance Method
An aliquot of 200 μL of the material was combined with 800 μL of ethanol, and the mixture was agitated ferociously for 30 s. At 420, 520, and 620 nm, the absorbance of the solution was measured. The color intensity (CI) is calculated by adding the absorbance at the aforementioned wavelengths, and the hue is calculated by dividing the absorbance at 420 nm by that at 520 nm (Equations (7) and (8)) [38]. Additionally, the following Equations (9)–(11) were used to determine the color composition, or the proportion contribution of the three components (yellow, red, and blue):
2.10. Statistical Analysis
The JMP® Pro 16 (SAS, Cary, NC, USA) program was used to create the experimental design, statistical analysis linked to the response surface methodology, and distribution analysis. The results were presented as mean values alongside the standard deviation.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Selection of Solvent
The first part of the study was to determine the most efficient HDESs among those prepared. Nine HDESs composed of menthol and two fatty acids were prepared, as well as HDESs composed of the two fatty acids, since fatty acids can simultaneously act as HBAs and HBDs owing to the presence of ‒OH groups [39]. Menthol is a monoterpenoid used in various industrial processes and commercial products. Because of its very low solubility in water and relatively low price, menthol is a good candidate to prepare sustainable and cheap HDESs [39,40,41]. The total carotenoid extraction yield (mainly lycopene, which is the major carotenoid in tomatoes [42]) of the extracts obtained by the various HDESs, as well as of the extracts obtained with three common organic solvents, can be seen in Table 3. Significant variations in extraction yields among different solvents can be seen, shedding light on their effectiveness for carotenoid extraction. In general, the HDESs based on menthol and the two fatty acids exhibited potential for carotenoid extraction. The extraction yields varied depending on the composition of the DES. The highest extraction yield was achieved with Men/Hex 2:1 (94.5 ± 3.3 μg CtE/g dm), which was significantly higher (p < 0.05) than in all other DES systems. This highlights the importance of the specific composition of DES components, where an excess of menthol relative to hexanoic acid seems to enhance the solubility and extraction efficiency of carotenoids. Interestingly, the extraction yield decreased as the hexanoic acid content in the DES was increased (Men/Hex 1:2, 68.0 ± 2.3 μg CtE/g dm). Comparatively, HDESs formulated with octanoic acid exhibited lower extraction yields than those containing hexanoic acid. Men/Oct 2:1 (74.4 ± 3.7 μg CtE/g dm) displayed nearly a 30% lower extraction yield compared to Men/Hex 2:1, albeit a similar extraction yield to Men/Hex 1:1, indicating the potential of octanoic acid as an alternative component for designing HDESs for carotenoid extraction. When considering the effect of solvent composition within the DES systems, it was observed that the molar ratio of menthol to hexanoic acid or octanoic acid does not profoundly influence the extraction efficiency, since the differences in yields in most cases were not statistically significant (p > 0.05). This suggests that within a certain range, the alteration of molar ratios may not profoundly impact carotenoid solubility and extraction. Similar to the above, the HDESs composed of the two fatty acids exhibited similar extraction properties as the HDES containing menthol. Recent publications also reported the efficiency of fatty acid mixtures as extraction yields in regard to carotenoid extraction from tomatoes [31]. In all cases, no additives or alternative methods were employed, so as to stabilize the obtained extract. Although carotenoids are known to be unstable upon exposure to light, oxygen, and high temperatures, no stability issues were observed during the experiments. However, further experiments are needed to further ensure the stability of the extract and to overcome potential issues.

Table 3.
Total carotenoid extraction yield (YTCn), measured in μg of total carotenoids per g of dry matter, and obtained using the produced HDESs and standard solvents.
Comparisons were made between DES systems and conventional organic solvents including hexane, ethyl acetate, and acetone. The HDESs generally exhibited higher extraction yields than hexane (49.9 ± 1.5 μg CtE/g dm). Ethyl acetate (70.7 ± 5.0 μg CtE/g dm) and acetone (58.4 ± 4.1 μg CtE/g dm) showed intermediate extraction yields, with ethyl acetate being more efficient in carotenoid extraction compared to acetone. According to previous studies, ethyl acetate presents higher solubility for polar carotenoids compared to hexane [42]. All the above demonstrate the potential of HDESs as alternative solvents for carotenoid extraction, surpassing the yields of some commonly used organic solvents. Even more importantly, the HDES can be used directly, without any other steps (such as solvent removal). The key feature underscoring the direct usability of the extract lies in the nature of the components comprising the HDES. Menthol, derived from natural sources such as mint, and hexanoic acid, a fatty acid, are well-established as non-toxic, food-grade ingredients and hold a recognized status in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Due to this, the extracts with this HDES are suitable for direct application, aligning with the stringent standards that the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries demand. As such, the extracts can be used for the production of new products or for the fortification of existing ones.
3.2. Extraction Optimization
A Box–Behnken design was applied to test the effect of solvent-to-solid ratio (X1), extraction time (X2), and temperature (X3) on total carotenoid content (TCC). In all cases, the range of the examined variables was selected based on preliminary experiments. The choice of the liquid-to-solid ratio is pivotal in solvent-based extraction processes as it directly influences the efficiency of compound extraction. In this study, the selected range of 10 to 40 mL/g encompasses the variability commonly encountered in extraction processes. A lower liquid-to-solid ratio may be insufficient for the optimal solubilization of target compounds, while a higher ratio may lead to excess solvent usage without proportional increases in extraction efficiency. By choosing these levels, we aimed to explore a range that balances extraction efficiency with solvent economy, ensuring practical relevance and efficiency in real-world applications. The extraction time is a critical parameter that governs the kinetics of the extraction process. The chosen range of 30 to 90 min was based on a consideration of both practical constraints and optimum recovery. A shorter extraction time might be insufficient for achieving maximum extraction efficiency, while an excessively long duration could lead to lower recovery and the potential degradation of target compounds. The selected range seeks to capture the optimum extraction time that balances efficiency with practical considerations. Finally, the extraction temperature plays a fundamental role in influencing the solubility of target compounds and the kinetics of extraction. The chosen range of 20 to 50 °C is grounded in the practical considerations of energy consumption and the stability of carotenoids. Lower temperatures might result in slower extraction rates, while higher temperatures could risk thermal degradation. The selected range aims to explore a temperature spectrum that optimizes extraction efficiency while considering both the practical aspects of energy consumption and the preservation of target compounds. The agitation speed was not examined, since in the preliminary experiments it was not found to affect the extraction recovery. A total of 15 experiments were conducted, as seen in Table 4, and the results were analyzed via ANOVA (Figure 1) to evaluate the statistical significance of the model. Model fitting was assessed with the square coefficient of correlation (R2) which was over 0.98 and suggests a satisfactory agreement between measured and predicted values. Figure 2 shows the generated response surface plots. The optimum extraction conditions, as calculated by the statistical analysis, were a solvent-to-solid ratio of 25:1, extraction time of 90 min, and temperature of 50 °C. Compared to the least efficient combination of parameters for the extraction (i.e., design point 1) under the optimum conditions, a 48.5% increase in the extraction yield was recorded, highlighting the importance of optimizing the extraction parameters.

Table 4.
The dependent variable’s measured and predicted responses were reported as μg of total carotenoids per g of dry matter in the experimental design.
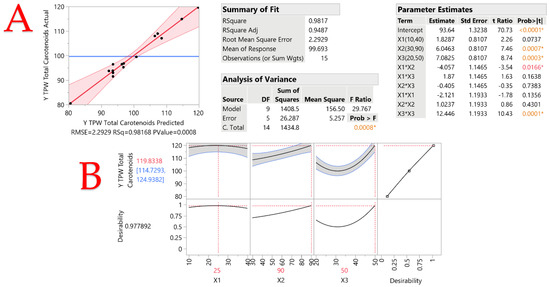
Figure 1.
Plot of predicted vs. actual values of the response (YTCn) (plot (A)), and desirability function (plot (B)), describing the effect of three independent variables considered (solvent-to-solid ratio X1, extraction time X2, temperature X3) on the YTCn upon simultaneous variation. Asterisks and colored values denote statistically significant values, while inset tables include statistics relevant to the evaluation of the resulting model.
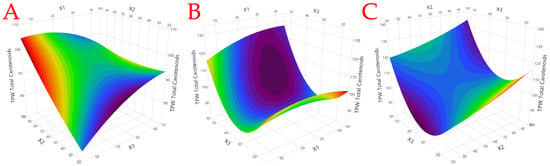
Figure 2.
Response surface plots for the total carotenoid yields (μg CtE/g dm). (A) The interaction between solvent-to-solid ratio (X1) and extraction time (X2), (B) the interaction between solvent-to-solid ratio (X1) and temperature (X3), and (C) the interaction between extraction time (X2) and temperature (X3).
3.3. Total Carotenoids of the Extracts and Antioxidant Activity
After selecting the optimum HDESs and optimizing the extraction conditions, the extraction of total carotenoids using HDESs and organic solvents was examined, as well as the antioxidant properties of the extracts. The results can be seen in Table 5. The HDES exhibited the highest total carotenoid content (127.6 ± 9.4 μg CtE/g dm). This yield was significantly greater (up to 31%) (p < 0.05) than those achieved with hexane, ethyl acetate, and acetone. The higher extraction efficiency of the HDES can be attributed to the tailored solvation environment created by the menthol–hexanoic acid combination, which appears to enhance the solubility of carotenoids and facilitate their extraction from the matrix. This was also the case with previous studies, describing the extraction of carotenoids from tomato [32,33], orange [43], and juice [44] samples using DES.

Table 5.
Total carotenoids extracted from the extracts and their antioxidant capacity were determined under optimum extraction conditions using different solvents.
Aside from the carotenoid content, the antioxidant properties of the extracts were evaluated. The HDES extract exhibited the most potent antiradical activity (63.7 ± 4 μmol AAE/g dm), significantly surpassing (p < 0.05) the values observed for hexane, ethyl acetate, and acetone (up to 164%). The substantial antiradical activity observed in the HDES extract indicates its efficiency in scavenging free radicals, which is important for counteracting oxidative stress. In terms of reducing power, the HDES extract again demonstrated the highest value (26.7 ± 1.8 μmol AAE/g dm), indicating its capacity to donate electrons and potentially mitigate oxidative damage. Ethyl acetate also exhibited notable reducing power, while hexane and acetone displayed comparatively lower values. These findings underscore the superiority of the HDES in terms of both carotenoid extraction yield and antioxidant activity. The performance of the DES, surpassing that of conventional organic solvents, highlights its potential as a more sustainable and efficient alternative for carotenoid extraction.
3.4. Color Analysis of the Extracts
Table 6 displays the values of the color analysis (L*, a*, b*) measured by the Lovibond colorimeter. The color saturation and hue values (represented by the Chroma C* and hue-angle h°, respectively) of the extracts produced using the three organic solvents were quite similar. Their hue angles exceeded 90 degrees (yellow); however, the extract produced by mixing Men/Hex 2:1 was less yellow and redder (90 degrees hue angle equals yellow, and zero degrees equals red), as shown in Figure 3. To this end, it was found that the values of a* increased while the values of h° decreased.

Table 6.
Color parameters of the extracts. Measurements were obtained with a colorimeter.

Figure 3.
Extracts obtained by (A) Men/Hex 2:1, (B) hexane, (C) ethyl acetate, and (D) acetone at optimum conditions.
The three organic solvents showed negative values ranging from ‒6.2 in hexane to ‒3 in ethyl acetate and positive values (2.5) for HDES when the coordinates a* (which takes positive values for reddish colors and negative values for greenish ones) and b* (which is positive for yellowish colors and negative values for bluish colors) were taken into consideration. On the other hand, all solvents had recorded positive b* values between 57.9 and 63.1.
The absorbance of the extracts was measured at 420, 520, and 620 nm as an alternative approach for analyzing the color parameters. Table 7 provides the obtained values for color intensity (CI), hue, and each color’s percentage. As can be seen, the extracts obtained using organic solvents have similar color parameters, while the extract obtained using HDESs is different. The values for ethyl acetate, acetone, and hexane are similar, with hexane having a slightly lower proportion. Men/Hex 2:1 extract had a smaller amount of yellow and a higher percentage of red, which validates our previous findings about higher carotenoid contents.

Table 7.
Color parameters of the extracts. Measurements obtained using UV-Vis spectrophotometer.
3.5. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Multivariate Correlation Analysis (MCA)
A principal component analysis (PCA) was also carried out to reduce the dimensionality of the multivariate data and to obtain a better understanding of the results. The extraction of total carotenoids (TCC) using HDESs and conventional organic solvents (hexane, ethyl acetate, and acetone) was investigated, as well as the antioxidant properties (assessed using the DPPH and FRAP assays) of the extracts, after the optimum ratio of HDESs (Men/Hex 2:1) was chosen and the extraction conditions were optimized. The hue and saturation values of the extracts (shown by the hue-angle h° and the chroma C*, respectively), as well as the results of the color analysis (L*, a*, b*), were also investigated. Further analyses were performed on hue and color intensity (CI) values. Figure 4 demonstrates the two main components that were adopted to explain 83.8% of the variation, which was considered to be a statistically significant parameter (p < 0.0001). The total carotenoid content (TCC), DPPH, FRAP, color intensity (CI), and redness (a*) of PC1 were positively correlated, while L*, b*, C*, h°, and hue were negatively correlated. Additionally, PC1 accounted for 63.4% of the variance. PC2 can explain 20.4% of the variance and exhibits a positive correlation with all of the variables examined, with the exception of TCC, DPPH, and a*. The Men/Hex 2:1 sample parameter provides the same loading directions for DPPH, FRAP, and TCC, but different loading directions for L*, as shown by the PCA plots in Figure 4.
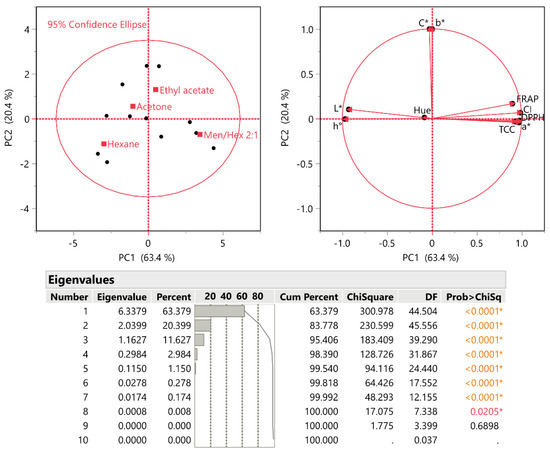
Figure 4.
Principal component analysis (PCA) for the measured variables (total carotenoid content—TCC; DPPH radical scavenging activity; ferric reducing antioxidant power—FRAP assay; L*, a*, b* color coordinates; and other color parameters). The axis scores for PC1 and PC2 are displayed. The inset table includes the eigenvalues. Asterisks and colored values denote statistically significant values.
From Figure 5, it can be deduced that the TCC has a strong positive correlation (>0.9) with the antioxidant parameters but is negatively correlated (‒0.9) with L*. The closer it is to one, the higher the correlation between the measured variables. Additionally, a statistically significant factor (p < 0.0001) was identified in the strongest correlation between the CI and DPPH assay (0.97). This is consistent with another study [45] that found strong positive correlations between the antioxidants, total phenolics, ascorbic acid, total flavonoids, lycopene, β-carotene, and lutein throughout the tomato ripening process. Conversely, both simple and multiple regressions were studied by Stinco et al. [46] to examine the correlations between lycopene content and color parameters in fresh and processed tomato products.
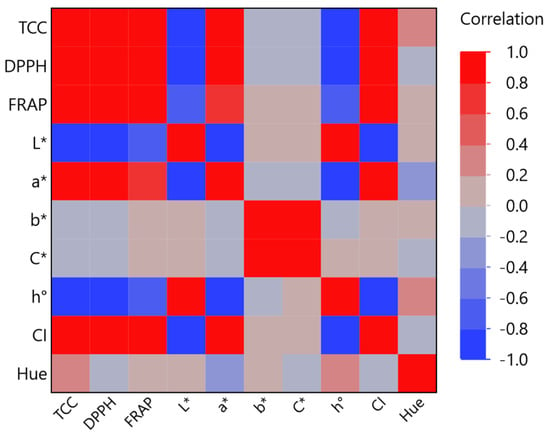
Figure 5.
Multivariate correlation analysis of measured variables (total carotenoid content—TCC; DPPH radical scavenging activity; ferric reducing antioxidant power—FRAP assay; L*, a*, b* color coordinates; and other color parameters).
The study presents valuable insights into carotenoid extraction using HDES. However, it is crucial to acknowledge and elaborate on certain limitations that provide context to the findings and that can guide future research endeavors. Despite the increasing attention on the synthesis of hydrophobic DESs, their availability remains limited. The current lack of commercial availability poses a practical hindrance, restricting the application of HDESs in large-scale usage [28]. The inherent instability of carotenoids, particularly when exposed to light, oxygen, high temperatures, and acidic conditions, constitutes another significant limitation [47]. This instability can lead to the pronounced discoloration of food products, compromising sensory quality, and, in some instances, diminishing biological activity. As such, further studies are needed to examine the stability of carotenoids in HDESs. Moreover, the hydrophobic nature of carotenoids presents challenges in incorporating them into high-water-content food products and functional beverages [48]. This is further strengthened by the hydrophobic nature of HDESs, which makes them less suitable for water-based foods. However, the exploitation of such extracts for use in lipid-based foods and emulsions should be considered.
4. Conclusions
In this study the potential of HDESs for efficient carotenoid extraction from tomato samples was investigated. Our findings provide valuable insights into solvent selection, extraction optimization, carotenoid content, antioxidant activities, and color characteristics. The selection of nine HDESs revealed significant variations in extraction yields, emphasizing the importance of specific solvent compositions for effective carotenoid solubilization. Upon assessing carotenoid content and antioxidant activities, the HDES extract (Men/Hex 2:1) emerged as a standout performer, displaying the highest total carotenoid content and potent antioxidant properties. In summary, this study underscores the potential of HDESs, particularly Men/Hex 2:1, as effective and sustainable solvents for carotenoid extraction. The optimized extraction conditions yielded extracts with enhanced carotenoid content and remarkable antioxidant activities. These findings contribute to the development of innovative and environmentally friendly approaches for carotenoid extraction, with promising applications across various industries. Further investigations could delve into the underlying mechanisms driving the observed enhancements in extraction efficiency and antioxidant potential, paving the way for advanced extraction methodologies and product formulations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.A., T.C. and S.I.L.; methodology, V.A. and T.C.; software, V.A.; validation, V.A. and T.C.; formal analysis, D.V., V.A., E.B. and T.C.; investigation, D.V., V.A. and T.C.; resources, S.I.L.; data curation, V.A. and T.C.; writing—original draft preparation, D.V.; writing—review and editing, D.V., V.A., T.C., E.B. and S.I.L.; visualization, V.A.; supervision, S.I.L.; project administration, V.A., T.C. and S.I.L.; funding acquisition, S.I.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Damavand S.A. tomato processing industry, Filia, Karditsa, Greece, for donating fresh tomato waste samples.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Pawlak, K.; Kołodziejczak, M. The role of agriculture in ensuring food security in developing countries: Considerations in the context of the problem of sustainable food production. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laranjeira, T.; Costa, A.; Faria-Silva, C.; Ribeiro, D.; Ferreira de Oliveira, J.M.P.; Simões, S.; Ascenso, A. Sustainable Valorization of Tomato By-Products to Obtain Bioactive Compounds: Their Potential in Inflammation and Cancer Management. Molecules 2022, 27, 1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, M.C.; Rodrigues, A.S.; Teixeira, J.A.; Pintado, M.E. Integral valorisation of tomato by-products towards bioactive compounds recovery: Human health benefits. Food Chem. 2023, 410, 135319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Wang, J.; Gao, R.; Ye, F.; Zhao, G. Sustainable valorisation of tomato pomace: A comprehensive review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 86, 172–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassino, A.N.; Halambek, J.; Djaković, S.; Rimac Brnčić, S.; Dent, M.; Grabarić, Z. Utilization of tomato peel waste from canning factory as a potential source for pectin production and application as tin corrosion inhibitor. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trombino, S.; Cassano, R.; Procopio, D.; Di Gioia, M.L.; Barone, E. Valorization of Tomato Waste as a Source of Carotenoids. Molecules 2021, 26, 5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Carmona, J.Y.; Ascacio-Valdes, J.A.; Alvarez-Perez, O.B.; Hernández-Almanza, A.Y.; Ramírez-Guzman, N.; Sepúlveda, L.; Aguilar-González, M.A.; Ventura-Sobrevilla, J.M.; Aguilar, C.N. Tomato waste as a bioresource for lycopene extraction using emerging technologies. Food Biosci. 2022, 49, 101966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maoka, T. Carotenoids as natural functional pigments. J. Nat. Med. 2020, 74, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Peña, M.A.; Ortega-Regules, A.E.; Anaya de Parrodi, C.; Lozada-Ramírez, J.D. Chemistry, Occurrence, Properties, Applications, and Encapsulation of Carotenoids—A Review. Plants 2023, 12, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wu, X.; Zhuang, W.; Xia, L.; Chen, Y.; Wu, C.; Rao, Z.; Du, L.; Zhao, R.; Yi, M.; et al. Tomato and lycopene and multiple health outcomes: Umbrella review. Food Chem. 2021, 343, 128396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Goyal, G.K. Dietary lycopene: Its properties and anticarcinogenic effects. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2008, 7, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabo, K.; Teleky, B.-E.; Ranga, F.; Roman, I.; Khaoula, H.; Boudaya, E.; Ltaief, A.B.; Aouani, W.; Thiamrat, M.; Vodnar, D.C. Carotenoid Recovery from Tomato Processing By-Products through Green Chemistry. Molecules 2022, 27, 3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, S.; Yawale, P.; Upadhyay, N. Carotenoids: Extraction strategies and potential applications for valorization of under-utilized waste biomass. Food Biosci. 2022, 48, 101812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R.K.; Prasad, P.; Lokesh, V.; Shang, X.; Shin, J.; Keum, Y.-S.; Lee, J.-H. Carotenoids: Dietary Sources, Extraction, Encapsulation, Bioavailability, and Health Benefits—A Review of Recent Advancements. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adadi, P.; Barakova, N.V.; Krivoshapkina, E.F. Selected Methods of Extracting Carotenoids, Characterization, and Health Concerns: A Review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 5925–5947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miękus, N.; Iqbal, A.; Marszałek, K.; Puchalski, C.; Świergiel, A. Green Chemistry Extractions of Carotenoids from Daucus carota L.—Supercritical Carbon Dioxide and Enzyme-Assisted Methods. Molecules 2019, 24, 4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umair, M.; Jabbar, S.; Nasiru, M.M.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Abid, M.; Murtaza, M.A.; Kieliszek, M.; Zhao, L. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Carotenoids from Carrot Pomace and Their Optimization through Response Surface Methodology. Molecules 2021, 26, 6763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzimitakos, T.; Athanasiadis, V.; Kalompatsios, D.; Mantiniotou, M.; Bozinou, E.; Lalas, S.I. Pulsed Electric Field Applications for the Extraction of Bioactive Compounds from Food Waste and By-Products: A Critical Review. Biomass 2023, 3, 367–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R.K.; Keum, Y.S. Carotenoid extraction methods: A review of recent developments. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kultys, E.; Kurek, M.A. Green Extraction of Carotenoids from Fruit and Vegetable Byproducts: A Review. Molecules 2022, 27, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, I.; Hussain, M.; Imran, A.; Afzaal, M.; Saeed, F.; Javed, M.; Afzal, A.; Ashfaq, I.; Al Jbawi, E.; Saewan, S.A. Traditional and innovative approaches for the extraction of bioactive compounds. Int. J. Food Prop. 2022, 25, 1215–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo, C.; Nieto, G.; Martínez-Zamora, L.; Ros, G.; Kamiloglu, S.; Munekata, P.E.S.; Pateiro, M.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Fernández-López, J.; Viuda-Martos, M.; et al. Novel Approaches for the Recovery of Natural Pigments with Potential Health Effects. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 6864–6883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanasiadis, V.; Chatzimitakos, T.; Kotsou, K.; Palaiogiannis, D.; Bozinou, E.; Lalas, S.I. Optimization of the Extraction Parameters for the Isolation of Bioactive Compounds from Orange Peel Waste. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suthar, P.; Kaushal, M.; Vaidya, D.; Thakur, M.; Chauhan, P.; Angmo, D.; Kashyap, S.; Negi, N. Deep eutectic solvents (DES): An update on the applications in food sectors. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023, 14, 100678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijardar, S.P.; Singh, V.; Gardas, R.L. Revisiting the Physicochemical Properties and Applications of Deep Eutectic Solvents. Molecules 2022, 27, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannavacciuolo, C.; Pagliari, S.; Frigerio, J.; Giustra, C.M.; Labra, M.; Campone, L. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents (NADESs) Combined with Sustainable Extraction Techniques: A Review of the Green Chemistry Approach in Food Analysis. Foods 2023, 12, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Su, E. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents: The new generation of green solvents for diversified and colorful applications in green chemistry. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 314, 127965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makoś, P.; Słupek, E.; Gębicki, J. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents in microextraction techniques—A review. Microchem. J. 2020, 152, 104384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, S.; Oliveira, F.; Ferreira, I.J.; Paiva, A.; Sobral, R.G.; Diniz, M.S.; Gaudêncio, S.P.; Duarte, A.R.C. Hydrophobic DES Based on Menthol and Natural Organic Acids for Use in Antifouling Marine Coatings. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 9989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, M.; Moral, R.; Thakuria, S.; Mitra, A.; Paul, S. Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents as Greener Substitutes for Conventional Extraction Media: Examples and Techniques. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 9702–9728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyriakoudi, A.; Tsiouras, A.; Mourtzinos, I. Extraction of Lycopene from Tomato Using Hydrophobic Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Terpenes and Fatty Acids. Foods 2022, 11, 2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzarini, C.; Casadei, E.; Valli, E.; Tura, M.; Ragni, L.; Bendini, A.; Gallina Toschi, T. Sustainable Drying and Green Deep Eutectic Extraction of Carotenoids from Tomato Pomace. Foods 2022, 11, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diacon, A.; Călinescu, I.; Vinatoru, M.; Chipurici, P.; Vlaicu, A.; Boscornea, A.C.; Mason, T.J. Fatty Acid Ethyl Esters (FAEE): A New, Green and Renewable Solvent for the Extraction of Carotenoids from Tomato Waste Products. Molecules 2021, 26, 4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovanoudis, I.; Athanasiadis, V.; Chatzimitakos, T.; Gortzi, O.; Nanos, G.D.; Lalas, S.I. Development of a Cloud Point Extraction Technique Based on Lecithin for the Recovery of Carotenoids from Liquid Tomato Wastewater. Waste 2022, 1, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makrygiannis, I.; Athanasiadis, V.; Bozinou, E.; Chatzimitakos, T.; Makris, D.P.; Lalas, S.I. Combined Effects of Deep Eutectic Solvents and Pulsed Electric Field Improve Polyphenol-Rich Extracts from Apricot Kernel Biomass. Biomass 2023, 3, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzimitakos, T.; Athanasiadis, V.; Kotsou, K.; Bozinou, E.; Lalas, S.I. Response Surface Optimization for the Enhancement of the Extraction of Bioactive Compounds from Citrus limon Peel. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, A.R. The CIE 1976 Color-Difference Formulae. Color Res. Appl. 1977, 2, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Pérez, M.P.; Bautista-Ortín, A.B.; Pérez-Porras, P.; Jurado, R.; Gómez-Plaza, E. A New Approach to the Reduction of Alcohol Content in Red Wines: The Use of High-Power Ultrasounds. Foods 2020, 9, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.A.R.; Crespo, E.A.; Pontes, P.V.A.; Silva, L.P.; Bülow, M.; Maximo, G.J.; Batista, E.A.C.; Held, C.; Pinho, S.P.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Tunable Hydrophobic Eutectic Solvents Based on Terpenes and Monocarboxylic Acids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 8836–8846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwamena, A. Recent Advances in Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents for Extraction. Separations 2019, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yara-Varón, E.; Fabiano-Tixier, A.S.; Balcells, M.; Canela-Garayoa, R.; Bily, A.; Chemat, F. Is it possible to substitute hexane with green solvents for extraction of carotenoids? A theoretical versus experimental solubility study. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 27750–27759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viñas-Ospino, A.; Panić, M.; Radojčić- Redovniković, I.; Blesa, J.; Esteve, M.J. Using novel hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents to improve a sustainable carotenoid extraction from orange peels. Food Biosci. 2023, 53, 102570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhao, C.; Tian, H.; Yang, Y.; Li, W. Liquid–Liquid Microextraction Based on Acid–Base-Induced Deep Eutectic Solvents for Determination of β-Carotene and Lycopene in Fruit Juices. Food Anal. Methods 2019, 12, 2777–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, S.R.; Lee, J.G. Ripening-Dependent Changes in Antioxidants, Color Attributes, and Antioxidant Activity of Seven Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Cultivars. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2016, 2016, 5498618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stinco, C.M.; Rodríguez-Pulido, F.J.; Escudero-Gilete, M.L.; Gordillo, B.; Vicario, I.M.; Meléndez-Martínez, A.J. Lycopene isomers in fresh and processed tomato products: Correlations with instrumental color measurements by digital image analysis and spectroradiometry. Food Res. Int. 2013, 50, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, G.L.R.; Medeiros, I.; da Cruz Nascimento, S.S.; Viana, R.L.S.; Porto, D.L.; Rocha, H.A.O.; Aragão, C.F.S.; Maciel, B.L.L.; de Assis, C.F.; Morais, A.H. de A.; et al. Antioxidant stability enhancement of carotenoid rich-extract from Cantaloupe melon (Cucumis melo L.) nanoencapsulated in gelatin under different storage conditions. Food Chem. 2021, 348, 129055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verardi, A.; Sangiorgio, P.; Lopresto, C.G.; Casella, P.; Errico, S. Enhancing Carotenoids’ Efficacy by Using Chitosan-Based Delivery Systems. Nutraceuticals 2023, 3, 451–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).