A Short Review on Dye-Wastewater Valorization Using Up-Flow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket Reactors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
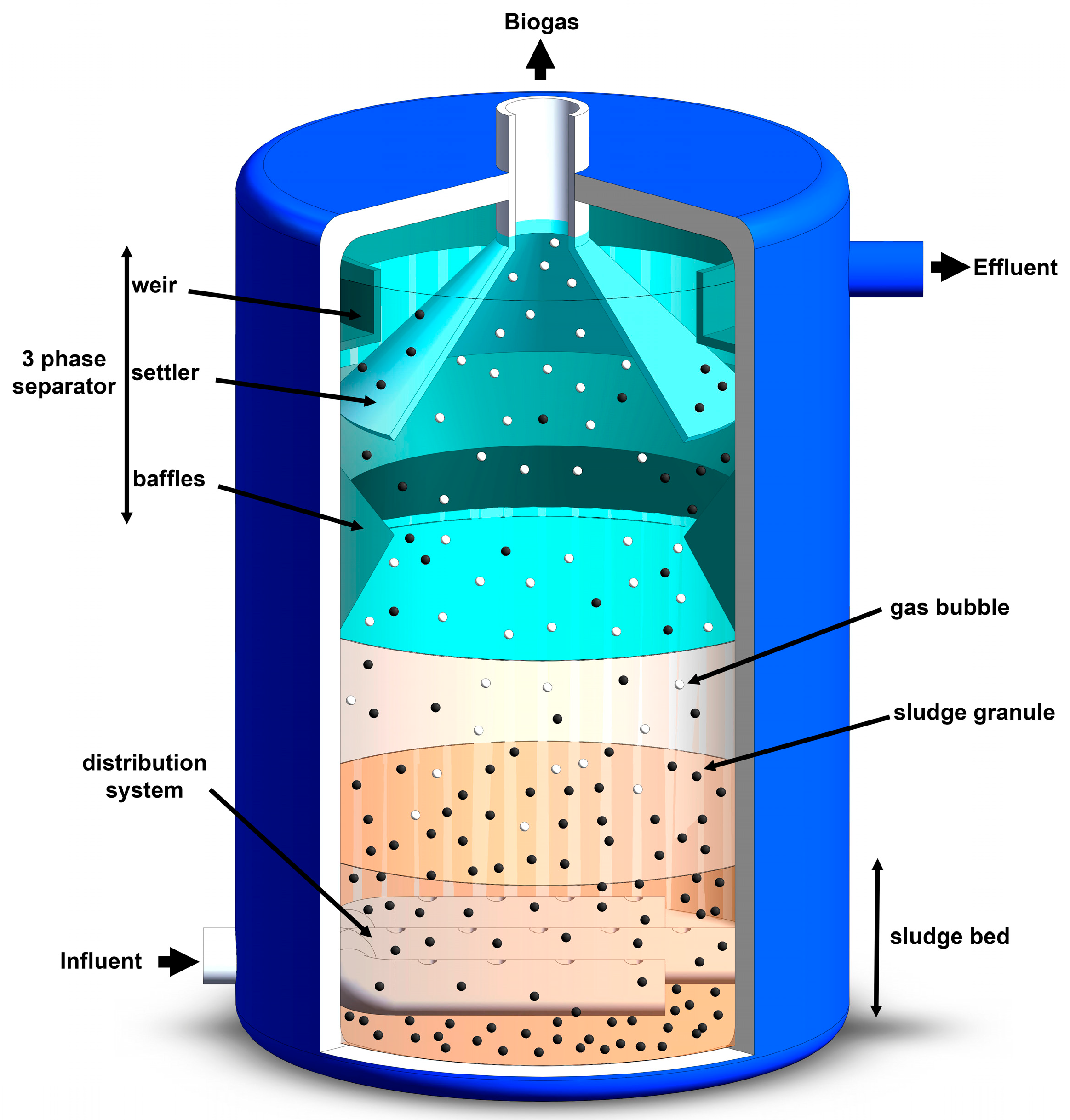
2. Up-Flow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket Reactors
3. Mechanisms and Influencing Parameters in Textile Decolorization in UASB Reactors
3.1. Mechanisms of Dye Removal
3.2. Influence Parameters of Dye Removal
4. UASB Reactor’s Performance in Treating Dye-Containing Effluents
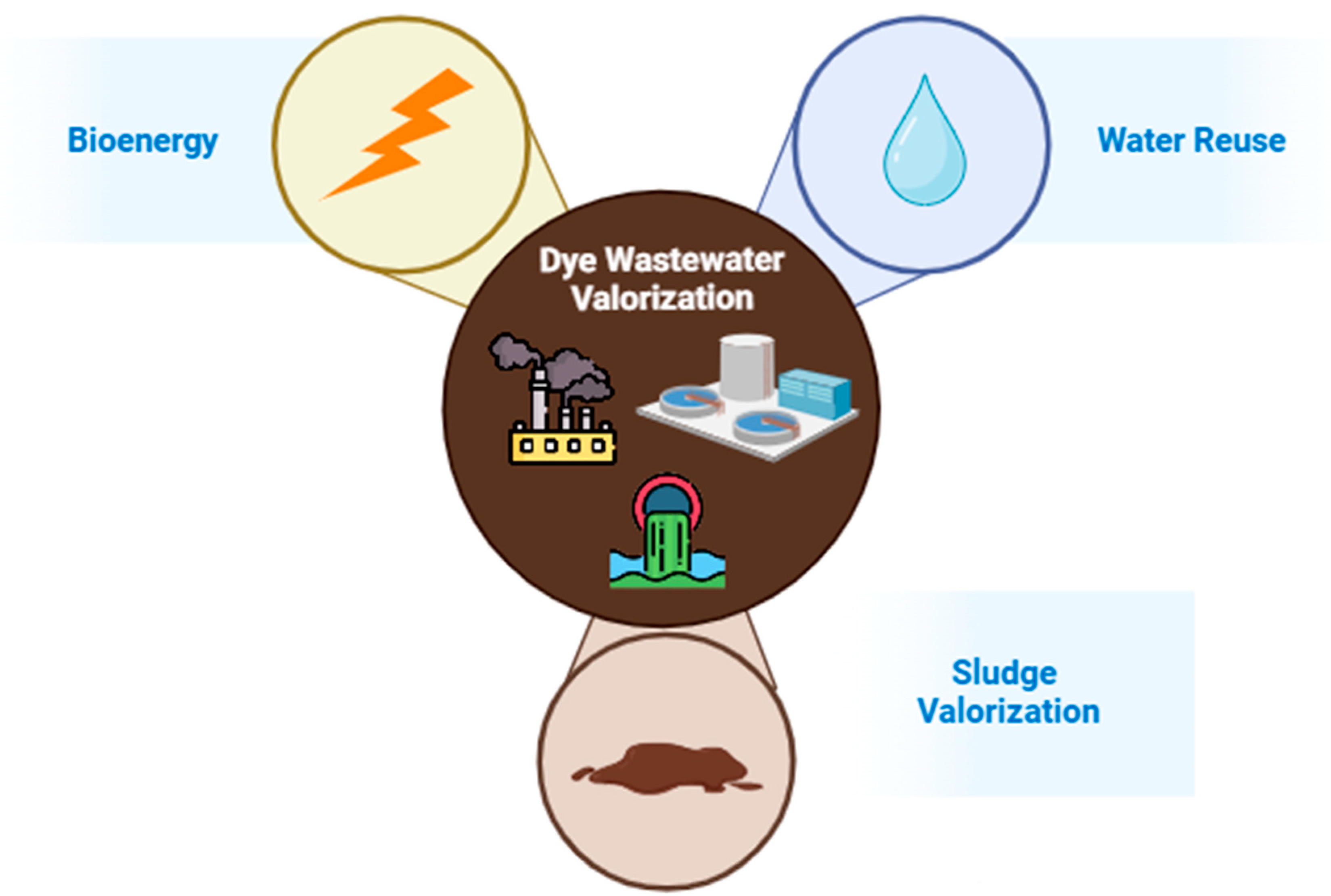
5. Dye-Wastewater Valorization
5.1. Bioenergy Production
| Scheme | UASB Reactor Conditions | Dye Compound | Biogas Production | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UASB reactor | Temperature of 37 °C, HRT 20 h, OLR 3.86 kg COD m−3 d−1 | Azo dye mixture: Reactive Black 5, Direct Red 28, Direct Black 38, Direct Brown 2, and Direct Yellow 12 (250 mg L−1) | 2.26 L d−1 (70%CH4, v/v) | [61] |
| UASB reactor + CSTR reactor | Temperature of 37 °C. HRT 3–30 h, OLR 2–15 kg COD m−3 d−1 | Real textile wastewater | 0.36–0.94 L d−1 | [60] |
| UASB reactor | Temperature of 37 °C, HRT 18.3 h, OLR 0.286 kg m−3 d−1 | Red Congo azo dye (100 mg L−1) | 2.0–2.7 L d−1 | [42] |
| Two-phase UASB reactor | Ambient temperature, HRT 12 h, OLR 8 kg COD m−3 d−1 | Real dye wastewater + starch effluent (40:60% v/v) | 24.5 L d−1 | [64] |
| UASB reactor | Ambient temperature, HRT 24 h, OLR * | Real dye wastewater + starch effluent (30:70% v/v) | 355 L d−1 | [63] |
| Two-phase UASB reactor | Ambient temperature, HRT 24 h, OLR * | Real textile wastewater + sago effluent (30:70% v/v) | 312 L d−1 | [8] |
| UASB reactor | Temperature of 33 °C, HRT 50 h, OLR 12 kg COD m−3 d−1 | Real textile wastewater | 36.04 L d−1 (79%CH4, v/v) | [59] |
| UASB reactor | Temperature of 45 °C, HRT of 24 h, OLR * | Textile sludge | 1.48 ± 0.89 L d−1 (36.7% CH4, v/v) | [62] |
| UASB reactor + aerobic system | Temperature of 37 ± 1 °C, HRT 6 h, OLR 12.97 kg COD m−3 d−1 | 2-Naphthol Red (100 mg L−1) | 3.86 L CH4 m−3 d−1 | [48] |
5.2. Reclaimed Water
5.3. Sludge Valorization
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Tohamy, R.; Ali, S.S.; Li, F.; Okasha, K.M.; Mahmoud, Y.A.G.; Elsamahy, T.; Jiao, H.; Fu, Y.; Sun, J. A Critical Review on the Treatment of Dye-Containing Wastewater: Ecotoxicological and Health Concerns of Textile Dyes and Possible Remediation Approaches for Environmental Safety. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 231, 113160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holkar, C.R.; Jadhav, A.J.; Pinjari, D.V.; Mahamuni, N.M.; Pandit, A.B. A Critical Review on Textile Wastewater Treatments: Possible Approaches. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 182, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkaczyk-Wlizło, A.; Mitrowska, K.; Błądek, T. Quantification of Twenty Pharmacologically Active Dyes in Water Samples Using UPLC-MS/MS. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariraj Mohan, S.; Swathi, T. A Review on Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket Reactor: Factors Affecting Performance, Modification of Configuration and Its Derivatives. Water Environ. Res. 2022, 94, e1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira Silva, T.; Guimarães de Oliveira, M.; Marques Mourão, J.M.; Bezerra dos Santos, A.; Lopes Pereira, E. Monte Carlo-Based Model for Estimating Methane Generation Potential and Electric Energy Recovery in Swine Wastewater Treated in UASB Systems. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 51, 103399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcaraz-Ibarra, S.; Mier-Quiroga, M.A.; Esparza-Soto, M.; Lucero-Chávez, M.; Fall, C. Treatment of Chocolate-Processing Industry Wastewater in a Low-Temperature Pilot-Scale UASB: Reactor Performance and in-Situ Biogas Use for Bioenergy Recovery. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 142, 105786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, P.M.A.; Konaté, Y.; Sawadogo, B.; Sagoe, G.; Dwumfour-Asare, B.; Ahmed, I.; Williams, M.N.V. Performance Evaluation of a Full-Scale Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket Reactor Coupled with Trickling Filters for Municipal Wastewater Treatment in a Developing Country. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senthilkumar, M.; Gnanapragasam, G.; Arutchelvan, V.; Nagarajan, S. Treatment of Textile Dyeing Wastewater Using Two-Phase Pilot Plant UASB Reactor with Sago Wastewater as Co-Substrate. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 166, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, R.; de Souza Guimarães, C. Up-Flow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket Reactors in Dye Removal: Mechanisms, Influence Factors, and Performance. In Biological Approaches in Dye-Containing Wastewater: Volume 1; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 201–227. ISBN 9789811905452. [Google Scholar]
- Muduli, M.; Chanchpara, A.; Choudhary, M.; Saravaia, H.; Haldar, S.; Ray, S. Critical Review on Sustainable Bioreactors for Wastewater Treatment and Water Reuse. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2022, 8, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Lier, J.B.; van der Zee, F.P.; Frijters, C.T.M.J.; Ersahin, M.E. Celebrating 40 Years Anaerobic Sludge Bed Reactors for Industrial Wastewater Treatment. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio Technol. 2015, 14, 681–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugen, F.; Bakke, R.; Lie, B.; Hovland, J.; Vasdal, K. Optimal Design and Operation of a UASB Reactor for Dairy Cattle Manure. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2015, 111, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Han, K.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Huang, Y.; Shen, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y. Performance, Granule Conductivity and Microbial Community Analysis of Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB) Reactors from Mesophilic to Thermophilic Operation. Biochem. Eng. J. 2018, 133, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainardis, M.; Buttazzoni, M.; Goi, D. Up-Flow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (Uasb) Technology for Energy Recovery: A Review on State-of-the-Art and Recent Technological Advances. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinde, R.; Hackula, A.; O’Shea, R.; Barth, S.; Murphy, J.D.; Wall, D.M. Demand-Driven Biogas Production from Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB) Reactors to Balance the Power Grid. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 385, 129364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirmohamadsadeghi, S.; Karimi, K.; Tabatabaei, M.; Aghbashlo, M. Biogas Production from Food Wastes: A Review on Recent Developments and Future Perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2019, 7, 100202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariraj Mohan, S.; Swathi, T. Enhanced Biogas Production and Substrate Degradation through the Intermittent Operation of Modified Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket–Static Granular Bed Reactor Series. Water Environ. Res. 2022, 94, e10775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernicharo, C.A.L.; Almeida, P.G.S.; Lobato, L.C.S.; Couto, T.C.; Borges, J.M.; Lacerda, Y.S. Experience with the Design and Start up of Two Full-Scale UASB Plants in Brazil: Enhancements and Drawbacks. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 60, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, H.-L.; Yang, S.-F.; Tay, J.-H. Mechanisms and Models for Anaerobic Granulation in Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket Reactor. Water Res. 2003, 37, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulshoff Pol, L.W.; de Castro Lopes, S.I.; Lettinga, G.; Lens, P.N.L. Anaerobic Sludge Granulation. Water Res. 2004, 38, 1376–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Show, K.-Y.; Yan, Y.; Yao, H.; Guo, H.; Li, T.; Show, D.-Y.; Chang, J.-S.; Lee, D.-J. Anaerobic Granulation: A Review of Granulation Hypotheses, Bioreactor Designs and Emerging Green Applications. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 300, 122751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Wang, Q.; Yoza, B.A.; Li, Q.X.; Chen, C.; Ming, J.; Yu, J.; Li, J.; Ke, M. Rapid Granulation Using Calcium Sulfate and Polymers for Refractory Wastewater Treatment in Up-Flow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket Reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 305, 123084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, N.; Tahmid, M.; Shoronika, A.Z.; Fariha, A.; Roy, H.; Pervez, M.N.; Cai, Y.; Naddeo, V.; Islam, M.S. A Comprehensive Review on the Sustainable Treatment of Textile Wastewater: Zero Liquid Discharge and Resource Recovery Perspectives. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Gutierrez, L.V.; Escamilla-Silva, E.M. Reactive Red Azo Dye Degradation in a UASB Bioreactor: Mechanism and Kinetics. Eng. Life Sci. 2009, 9, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saratale, R.G.; Saratale, G.D.; Chang, J.S.; Govindwar, S.P. Bacterial Decolorization and Degradation of Azo Dyes: A Review. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2011, 42, 138–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Arora, S. Removal of Synthetic Textile Dyes From Wastewaters: A Critical Review on Present Treatment Technologies. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 41, 807–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volschan Junior, I.; de Almeida, R.; Cammarota, M.C. A Review of Sludge Pretreatment Methods and Co-Digestion to Boost Biogas Production and Energy Self-Sufficiency in Wastewater Treatment Plants. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 40, 101857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, R.; Chen, X.; Luo, Y.; Ma, P.; Ni, S.; Xiang, X.; Li, G. Inhibitory Effect and Mechanism of Azo Dyes on Anaerobic Methanogenic Wastewater Treatment: Can Redox Mediator Remediate the Inhibition? Water Res. 2016, 104, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, F.M.; Kato, M.T.; Florêncio, L.; Gavazza, S. Color, Organic Matter and Sulfate Removal from Textile Effluents by Anaerobic and Aerobic Processes. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 163, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, J.A.; Cervantes, F.J.; van der Zee, F.P.; Lettinga, G. Role of Quinones in the Biodegradation of Priority Pollutants: A Review. Water Sci. Technol. 2000, 42, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes, F.J.; Garcia-Espinosa, A.; Moreno-Reynosa, M.A.; Rangel-Mendez, J.R. Immobilized Redox Mediators on Anion Exchange Resins and Their Role on the Reductive Decolorization of Azo Dyes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1747–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baêta, B.E.L.; Aquino, S.F.; Silva, S.Q.; Rabelo, C.A. Anaerobic Degradation of Azo Dye Drimaren Blue HFRL in UASB Reactor in the Presence of Yeast Extract a Source of Carbon and Redox Mediator. Biodegradation 2012, 23, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, A.B.; Traverse, J.; Cervantes, F.J.; van Lier, J.B. Enhancing the Electron Transfer Capacity and Subsequent Color Removal in Bioreactors by Applying Thermophilic Anaerobic Treatment and Redox Mediators. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2005, 89, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.-L.; Patel, B.K.C.; Ollivier, B. Taxonomic, Phylogenetic, and Ecological Diversity of Methanogenic Archaea. Anaerobe 2000, 6, 205–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Feng, L.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Q. Biodegradation and Detoxification of Direct Black G Textile Dye by a Newly Isolated Thermophilic Microflora. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 250, 650–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuchiwal, S.; Gola, D.; Malik, A. Decolourization of Textile Effluent Using Native Microbial Consortium Enriched from Textile Industry Effluent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatas, M.; Dursun, S.; Argun, M.E. The Decolorization of Azo Dye Reactive Black 5 in a Sequential Anaerobic-Aerobic System. Ekoloji 2010, 19, 15–23. [Google Scholar]
- Ryue, J.; Lin, L.; Kakar, F.L.; Elbeshbishy, E.; Al-Mamun, A.; Dhar, B.R. A Critical Review of Conventional and Emerging Methods for Improving Process Stability in Thermophilic Anaerobic Digestion. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2020, 54, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Schnürer, A.; Björkmalm, J.; Willquist, K.; Kreuger, E. Diversity and Abundance of Microbial Communities in UASB Reactors during Methane Production from Hydrolyzed Wheat Straw and Lucerne. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daud, M.K.; Rizvi, H.; Akram, M.F.; Ali, S.; Rizwan, M.; Nafees, M.; Jin, Z.S. Review of Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket Reactor Technology: Effect of Different Parameters and Developments for Domestic Wastewater Treatment. J. Chem. 2018, 2018, 1596319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, F.M.; Florêncio, L.; Kato, M.T.; Santa-Cruz, P.A.; Gavazza, S. Hydraulic Retention Time Influence on Azo Dye and Sulfate Removal during the Sequential Anaerobic–Aerobic Treatment of Real Textile Wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 3319–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Işik, M.; Sponza, D.T. Effects of Alkalinity and Co-Substrate on the Performance of an Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB) Reactor through Decolorization of Congo Red Azo Dye. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Haadel, A.; van der Lubbe, J. UASB Reactor Design Guidelines. In Anaerobic Sewage Treatment: Optimization of Process and Physical Design of Anaerobic and Complementary Processes; van Haandel, A., van der Lubbe, J., Eds.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2019; pp. 133–192. ISBN 9781780409627. [Google Scholar]
- Haider, A.; Khan, S.J.; Nawaz, M.S.; Saleem, M.U. Effect of Intermittent Operation of Lab-Scale Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB) Reactor on Textile Wastewater Treatment. Desalin. WATER Treat. 2018, 136, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Barros, A.N.; da Silva, M.E.R.; Firmino, P.I.M.; de Vasconcelos, E.A.F.; dos Santos, A.B. Impact of Microaeration and the Redox Mediator Anthraquinone-2,6-Disulfonate on Azo Dye Reduction and By-Products Degradation. CLEAN Soil Air Water 2018, 46, 1700518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahia, M.; Passos, F.; Adarme, O.F.H.; Aquino, S.F.; Silva, S.Q. Anaerobic-Aerobic Combined System for the Biological Treatment of Azo Dye Solution Using Residual Yeast. Water Environ. Res. 2018, 90, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazal, S.; Huang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ullah, Z.; Ali, A.; Xu, H. Biological Treatment of Red Bronze Dye through Anaerobic Process. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadow, S.I.; Li, Y.-Y. Development of an Integrated Anaerobic/Aerobic Bioreactor for Biodegradation of Recalcitrant Azo Dye and Bioenergy Recovery: HRT Effects and Functional Resilience. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2020, 9, 100388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, J.R.S.; Amaral, F.M.; Florencio, L.; Kato, M.T.; Delforno, T.P.; Gavazza, S. Microaerated UASB Reactor Treating Textile Wastewater: The Core Microbiome and Removal of Azo Dye Direct Black 22. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahia, M.; Borges, T.A.; Passos, F.; de Aquino, S.F.; Silva, S.d.Q. Evaluation of a Combined System Based on an Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket Reactor (UASB) and Shallow Polishing Pond (SPP) for Textile Effluent Treatment. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2020, 63, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Soto, I.C.; García-Gómez, C.; Álvarez-Valencia, L.H.; Meza-Escalante, E.R.; Leyva-Soto, L.A.; Camacho-Ruiz, M.A.; Concha-Guzmán, M.O.; Ulloa-Mercado, R.G.; Díaz-Tenorio, L.M.; Gortáres-Moroyoqui, P. Sequential Congo Red Elimination by UASB Reactor Coupled to Electrochemical Systems. Water 2021, 13, 3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, R.A.; Vistanty, H.; Suhardi, S.H. Performance of Anaerobic Co-Digestion with Honey Processing Wastewater as Co-Substrate for Treating Synthetic Wastewater Containing Commercial Anthraquinone Dye Remazol Blue RSP: Effect of C:N Ratio and HRT. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2022, 19, 101157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.U.; Khan, S.J.; Shahzad, H.M.A.; Zeshan. Performance Evaluation of Integrated Anaerobic and Aerobic Reactors for Treatment of Real Textile Wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 10325–10336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albahnasawi, A.; Yüksel, E.; Gürbulak, E.; Duyum, F. Fate of Aromatic Amines through Decolorization of Real Textile Wastewater under Anoxic-Aerobic Membrane Bioreactor. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, S.; Suhan, M.B.K.; Islam, M.S. Recent Advances and Perspective of Electrocoagulation in the Treatment of Wastewater: A Review. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2022, 17, 100643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varjani, S.; Rakholiya, P.; Shindhal, T.; Shah, A.V.; Ngo, H.H. Trends in Dye Industry Effluent Treatment and Recovery of Value Added Products. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 39, 101734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavičić, J.; Novak Mavar, K.; Brkić, V.; Simon, K. Biogas and Biomethane Production and Usage: Technology Development, Advantages and Challenges in Europe. Energies 2022, 15, 2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampese, L.C.; Sganzerla, W.G.; Di Domenico Ziero, H.; Mudhoo, A.; Martins, G.; Forster-Carneiro, T. Research Progress, Trends, and Updates on Anaerobic Digestion Technology: A Bibliometric Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 331, 130004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katal, R.; Zare, H.; Rastegar, S.O.; Mavaddat, P.; Darzi, G.N. Removal of Dye and Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) Reduction from Textile Industrial Wastewater Using Hybrid Bioreactors. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2014, 13, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Işik, M.; Sponza, D.T. Anaerobic/Aerobic Sequential Treatment of a Cotton Textile Mill Wastewater. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2004, 79, 1268–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Işik, M. Efficiency of Simulated Textile Wastewater Decolorization Process Based on the Methanogenic Activity of Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket Reactor in Salt Inhibition Condition. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2004, 35, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, J.; Pinheiro, A.; da Silva, J.D. Tratabilidade Do Lodo Biológico Têxtil e Produção de Biogás Em Reator UASB Em Diferentes Temperaturas. Eng. Sanit. Ambient. 2018, 23, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanapragasam, G.; Senthilkumar, M.; Arutchelvan, V.; Sivarajan, P.; Nagarajan, S. Recycle in Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket Reactor on Treatment of Real Textile Dye Effluent. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 26, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar, M.; Arutchelvan, V.; Kanakasabai, V.; Venkatesh, K.R.; Nagarajan, S. Biomineralisation of Dye Waste in a Two-Phase Hybrid UASB Reactor Using Starch Effluent as a Co-Substrate. Int. J. Environ. Waste Manag. 2009, 3, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volschan, I.; Cammarota, M.C.; De Almeida, R.; Lobato, L.C.S.; de Aquino, S.F. Part B: Sludge Sewage Pre-Treatment and Codigestion Technical Note 2—Contributions about Sewage Sludge Pre-Treatment Techniques. Cad. Técnicos Eng. Sanit. Ambient. 2022, 2, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Dou, X.; Pan, F.; Wu, Q.; Li, C.; Zhou, B.; Hao, L. Optimal Planning of Local Biomass-Based Integrated Energy System Considering Anaerobic Co-Digestion. Appl. Energy 2022, 316, 119075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrispim, M.C.; Scholz, M.; Nolasco, M.A. Biogas Recovery for Sustainable Cities: A Critical Review of Enhancement Techniques and Key Local Conditions for Implementation. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 72, 103033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadow, S.I.; Estrada, A.L.; Li, Y.-Y. Characterization and Potential of Two Different Anaerobic Mixed Microflora for Bioenergy Recovery and Decolorization of Textile Wastewater: Effect of C/N Ratio, Dye Concentration and PH. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2022, 17, 100886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Hao, X.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Li, J. Feasibility Analysis of Anaerobic Digestion of Excess Sludge Enhanced by Iron: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 89, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattier, M.; Jimenez, J.A.; Miller, M.W.; Dhanasekar, A.; Willis, J.; Keller, J.; Batstone, D. Long-Term Comparison of Pilot UASB and AnMBR Systems Treating Domestic Sewage at Ambient Temperatures. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.-H.; Min, K.-S.; Speece, R.E. Full Scale UASB Reactor Performance in the Brewery Industry. Environ. Technol. 2001, 22, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, A.P.; Lobato, L.C.S.; Chernicharo, C.A.L. Mathematical Model to Predict the Energy Potential of UASB-Based Sewage Treatment Plants. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 37, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CIBiogas BIOGASMAP. Available online: https://app.powerbi.com/view?r=eyJrIjoiNDZiYTYyNGQtYzliYS00NTMyLTk1Y2EtOWZmZjE4OTgwY2VkIiwidCI6ImMzOTg3ZmI3LTQ5ODMtNDA2Ny1iMTQ2LTc3MGU5MWE4NGViNSJ9 (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- Apollo, S.; Onyango, M.S.; Ochieng, A. Integrated UV Photodegradation and Anaerobic Digestion of Textile Dye for Efficient Biogas Production Using Zeolite. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 245, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.; Hwang, J.-E.; Jegal, J.; Kim, J. Pretreatment of a Dyeing Wastewater Using Chemical Coagulants. Dye. Pigment. 2007, 72, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, M.; Anees, M.; Qadeer, S.; Khalid, A.; Kumar, R.; Barakat, M.A. A Recent Progress in the Leachate Pretreatment Methods Coupled with Anaerobic Digestion for Enhanced Biogas Production: Feasibility, Trends, and Techno-Economic Evaluation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, R.; Porto, R.F.; Quintaes, B.R.; Bila, D.M.; Lavagnolo, M.C.; Campos, J.C. A Review on Membrane Concentrate Management from Landfill Leachate Treatment Plants: The Relevance of Resource Recovery to Close the Leachate Treatment Loop. Waste Manag. Res. 2023, 41, 264–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, R.; Pimenta de Oliveira, T.J.; Maurício Gouvea, R.; Carbonelli Campos, J. Technical and Economic Aspects of a Sequential MF + NF + Zeolite System Treating Landfill Leachate. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2022, 57, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, R.; Campos, J.C. Análise Tecnoeconômica Do Tratamento de Lixiviado de Aterro Sanitário. Rev. Ineana 2020, 8, 6–27. [Google Scholar]
- Shindhal, T.; Rakholiya, P.; Varjani, S.; Pandey, A.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Ng, H.Y.; Taherzadeh, M.J. A Critical Review on Advances in the Practices and Perspectives for the Treatment of Dye Industry Wastewater. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Wen, D.; Shen, J.; Wang, J. Zero Discharge Process for Dyeing Wastewater Treatment. J. Water Process Eng. 2016, 11, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkanlı, M.; Yilmaz, L.; Çulfaz-Emecen, P.Z.; Yetis, U. Brackish Water Recovery from Reactive Dyeing Wastewater via Ultrafiltration. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 165, 1204–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, A.; Karimi, M.; Ebrahimi, H.; Fallah, N. Sequencing Batch Reactor/Nanofiltration Hybrid Method for Water Recovery from Textile Wastewater Contained Phthalocyanine Dye and Anionic Surfactant. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gripa, E.; Dario, S.; Daflon, A.; De Almeida, R.; Valéria, F.; Campos, J.C. Landfill Leachate Treatment by High-Presssure Membranes and Advanced Oxidation Techniques with a Focus on Ecotoxicity and By-Products Management: A Review. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 173, 747–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obotey Ezugbe, E.; Rathilal, S. Membrane Technologies in Wastewater Treatment: A Review. Membranes 2020, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Almeida, R.; de Souza Couto, J.M.; Gouvea, R.M.; de Almeida Oroski, F.; Bila, D.M.; Quintaes, B.R.; Campos, J.C. Nanofiltration Applied to the Landfill Leachate Treatment and Preliminary Cost Estimation. Waste Manag. Res. 2020, 38, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, R.; Campos, J.; Oroski, F.d.A. Techno-economic evaluation of landfill leachate treatment by hybrid lime application and nanofiltration process. Detritus 2020, 10, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendón-Castrillón, L.; Ramírez-Carmona, M.; Ocampo-López, C.; González-López, F.; Cuartas-Uribe, B.; Mendoza-Roca, J.A. Treatment of Water from the Textile Industry Contaminated with Indigo Dye: A Hybrid Approach Combining Bioremediation and Nanofiltration for Sustainable Reuse. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2023, 8, 100498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćurić, I.; Dolar, D.; Karadakić, K. Textile Wastewater Reusability in Knitted Fabric Washing Process Using UF Membrane Technology. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 299, 126899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahinkaya, E.; Tuncman, S.; Koc, I.; Guner, A.R.; Ciftci, S.; Aygun, A.; Sengul, S. Performance of a Pilot-Scale Reverse Osmosis Process for Water Recovery from Biologically-Treated Textile Wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 249, 109382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Qiu, P.; Qian, Y.; Kong, Z.; Zheng, X.; Tang, Z.; Guo, H. Textile Wastewater Treatment for Water Reuse: A Case Study. Processes 2019, 7, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, R.A.; Ali, E.A. Polyethersulfone/Gelatin Nano-Membranes for the Rhodamine B Dye Removal and Textile Industry Effluents Treatment under Cost Effective Condition. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskin, B.; Korkut, S.; Ormancı-Acar, T.; Turken, T.; Tas, C.E.; Menceloglu, Y.Z.; Unal, S.; Koyuncu, I. Pilot Scale Nanofiltration Membrane Fabrication Containing Ionic Co-Monomers and Halloysite Nanotubes for Textile Dye Filtration. Water Sci. Technol. 2023, 87, 1529–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Ye, K.; Lin, F.; Liu, H.; Jiang, M.; Wang, J.; Liu, R.; Lin, J. Enhanced Fractionation of Dye/Salt Mixtures by Tight Ultrafiltration Membranes via Fast Bio-Inspired Co-Deposition for Sustainable Textile Wastewater Management. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 379, 122321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanasekaran, G.; Sudhakaran, M.S.P.; Kulmatova, D.; Han, J.; Arthanareeswaran, G.; Jwa, E.; Mok, Y.S. Efficient Removal of Anionic, Cationic Textile Dyes and Salt Mixture Using a Novel CS/MIL-100 (Fe) Based Nanofiltration Membrane. Chemosphere 2021, 284, 131244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cieślik, B.M.; Namieśnik, J.; Konieczka, P. Review of Sewage Sludge Management: Standards, Regulations and Analytical Methods. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 90, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratina, B.; Šorgo, A.; Kramberger, J.; Ajdnik, U.; Zemljič, L.F.; Ekart, J.; Šafarič, R. From Municipal/Industrial Wastewater Sludge and FOG to Fertilizer: A Proposal for Economic Sustainable Sludge Management. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 183, 1009–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, X.; Chen, X.; Dai, R.; Luo, Y.; Ma, P.; Ni, S.; Ma, C. Anaerobic Digestion of Recalcitrant Textile Dyeing Sludge with Alternative Pretreatment Strategies. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 222, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xiang, X.; Dai, R.; Wang, Y.; Ma, P. Effect of Low Temperature of Thermal Pretreatment on Anaerobic Digestion of Textile Dyeing Sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 243, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Tuersun, N.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, C.; Chen, X. Optimization and System Energy Balance Analysis of Anaerobic Co-Digestion Process of Pretreated Textile Dyeing Sludge and Food Waste. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirir, E.; Ballice, L. Supercritical Water Gasification of Wet Sludge from Biological Treatment of Textile and Leather Industrial Wastewater. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2019, 146, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Influencing Parameters | Main Aspects | Main Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dye structure and concentration |
|
| [28,29] |
| Electron donors and redox mediators |
|
| [30,31,32,33] |
| pH |
|
| [34,35] |
| Temperature |
|
| [33,36] |
| OLR |
|
| [37,38,39] |
| HRT |
|
| [40,41,42] |
| Scheme | Scale | UASB Reactor Conditions | Dye Compounds | Treatability Results | Reference | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Name | Concentration/Amount | Color | COD | ||||
| UASB reactor | Lab | Continuous mode, 27 °C, HRT 24 h, OLR * | Azo dye | Reactive Red 2 | 50 mg L−1 | 51% | 89% | [45] |
| UASB reactor + Activated sludge process | Lab | Continuous mode, 16 °C–29 °C, HRT 24 h, OLR * | Azo dye | Yellow Gold Remazol | 50 mg L−1 | 85% | 67–88% | [46] |
| UASB reactor + shallow polishing pond | Lab | Continuous mode, 16 °C–29 °C, HRT 24 h, OLR * | Azo dye | Yellow Gold Remazol | 50 mg L−1 | 85% | 67–88% | [46] |
| UASB reactor | Lab | Continuous mode, temperature *, TRH 24 h, OLR * | Azo dye | Red Bronze | 40–325 mg L−1 | 75–94% | 60–91% | [47] |
| UASB reactor + Aerated bioreactor | Lab | Continuous mode, 37 ± 1 °C, HRT 6 h, OLR 12.97 kg C.O.D. m−3 d−1 | Azo dye | 2-Naphthol Red | 0.1 g L−1 | 96% | 85.6% | [48] |
| UASB reactor + microaerated UASB reactor | Lab | Continuous mode, 25.0 ± 1.4 °C, HRT *, OLR 1.27–1.50 kg m−3 d−1 | Azo dye | Direct Black 22 | 0.6 mM | 70–78% | 67–72% | [49] |
| UASB reactor + shallow polishing pond | Lab | Continuous mode, 16–29 °C, HRT 24 h, OLR * | − | Real textile wastewater | − | 50% | 80% | [50] |
| UASB reactor + EC system | Lab | Continuous mode, Temperature *, HRT 8–12 h, OLR * | Congo Red dye | 100 mg L−1 | >96% | >82% | [51] | |
| UASB reactor | Lab | Continuous mode, 27–29 °C, HRT 24 h, OLR 6.20 kg COD m−3 d−1 | Simulated wastewater containing Remazol blue RSP | 12.5 mg L−1 | 97.37 ± 3.62% | 76.69 ± 2.83% | [52] | |
| UASB reactor + SBR | Lab | Intermitent mode, 35 °C, HRT 48 h, OLR 0.74–0.90 kg COD m−3 d−1 | Real textile wastewater | − | 87.7% | 90.4% | [53] | |
| Treatment Scheme | Features | Main Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| SBR + NF | Dye: raw textile wastewater; Membrane: Alfa Laval (Alfa Laval, Sweden); Operating conditions: TPM = 5 bars, 20 °C. | COD and color removal of >80% and >96%; Water flux of 23.71 LMH; Combined SBR and NF treatment cost estimated at 0.97 USD m−3. | [88] |
| UF | Dye: raw textile wastewater; Membrane: UF-GH 2 kDa GE (Water and Process Technologies); Operating conditions: TPM = 10 bars, 25 °C. | COD and color removal of 56% and >95% Water flux of 20–30 LMH; Treated water was suitable for dyed knitted cotton fabric washing. | [89] |
| SBR + NF | Dyes: Reactive Blue 21 and Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate; Membrane: NP010 (Microdyn Nadir); Operating conditions: TPM = 10 bars, 25 °C. | COD and dye removal of 97% and 96%; Water flux of 15.4 LMH for 1 h; NF process could produce reclaimed water. | [83] |
| RO | Dye: Biologically treated textile wastewater; Membrane: 8-inch DOW FILMTEC™ FORTILIFE™ CR100 RO element; Operating conditions: TPM = 8–20 bars, recovery of 70%, 30–40 °C. | Water flux of 19 LMH; COD, color, and conductivity parameters within required limits for reuse in the dyeing process. | [90] |
| Two-step UF | Dye: raw textile wastewater; Membranes: UF-GH 2 kDa and UF-PT 5 kDa (GE Osmonics); Operating conditions: TPM = 2–4 bars, volume reduction factor of 2.5–10, 25 °C. | TOC removal of >70%; Water flux of 4.5–16 LMH; The proposed treatment produced salty water for reuse. | [82] |
| Ozonation + UF + RO | Dye: Biologically treated textile wastewater; Membranes *; Operating conditions: UF, TPM *; RO, TPM = 15–25 bars. | COD and color removal of >99% in RO; The reuse rate of reclaimed water is equal to 86.6%; UF treatment cost = 0.04 USD m−3 and RO treatment cost = 0.14 USD m−3; The proposed treatment produced high-quality water for reuse. | [91] |
| RO + EO + BMED | Dye: raw textile wastewater; Membrane: SG1812 (GE Power and Water Technologies) Operating conditions: TPM = 12 bars, recovery of 70%, 25 °C. | COD and color removal of >70 and 100%; Water flux of 19 LMH; The energy demand of combined RO–EO–BMED is equal to 24.6 kWh m−3 RO permeate meets the requirements for water reuse. | [81] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Almeida, R.; de Souza Guimarães, C. A Short Review on Dye-Wastewater Valorization Using Up-Flow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket Reactors. Waste 2023, 1, 960-976. https://doi.org/10.3390/waste1040055
de Almeida R, de Souza Guimarães C. A Short Review on Dye-Wastewater Valorization Using Up-Flow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket Reactors. Waste. 2023; 1(4):960-976. https://doi.org/10.3390/waste1040055
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Almeida, Ronei, and Claudinei de Souza Guimarães. 2023. "A Short Review on Dye-Wastewater Valorization Using Up-Flow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket Reactors" Waste 1, no. 4: 960-976. https://doi.org/10.3390/waste1040055
APA Stylede Almeida, R., & de Souza Guimarães, C. (2023). A Short Review on Dye-Wastewater Valorization Using Up-Flow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket Reactors. Waste, 1(4), 960-976. https://doi.org/10.3390/waste1040055






