Blockchain Architecture for IoT: Comparative Survey †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Comparison of Existing BCoT Architectures
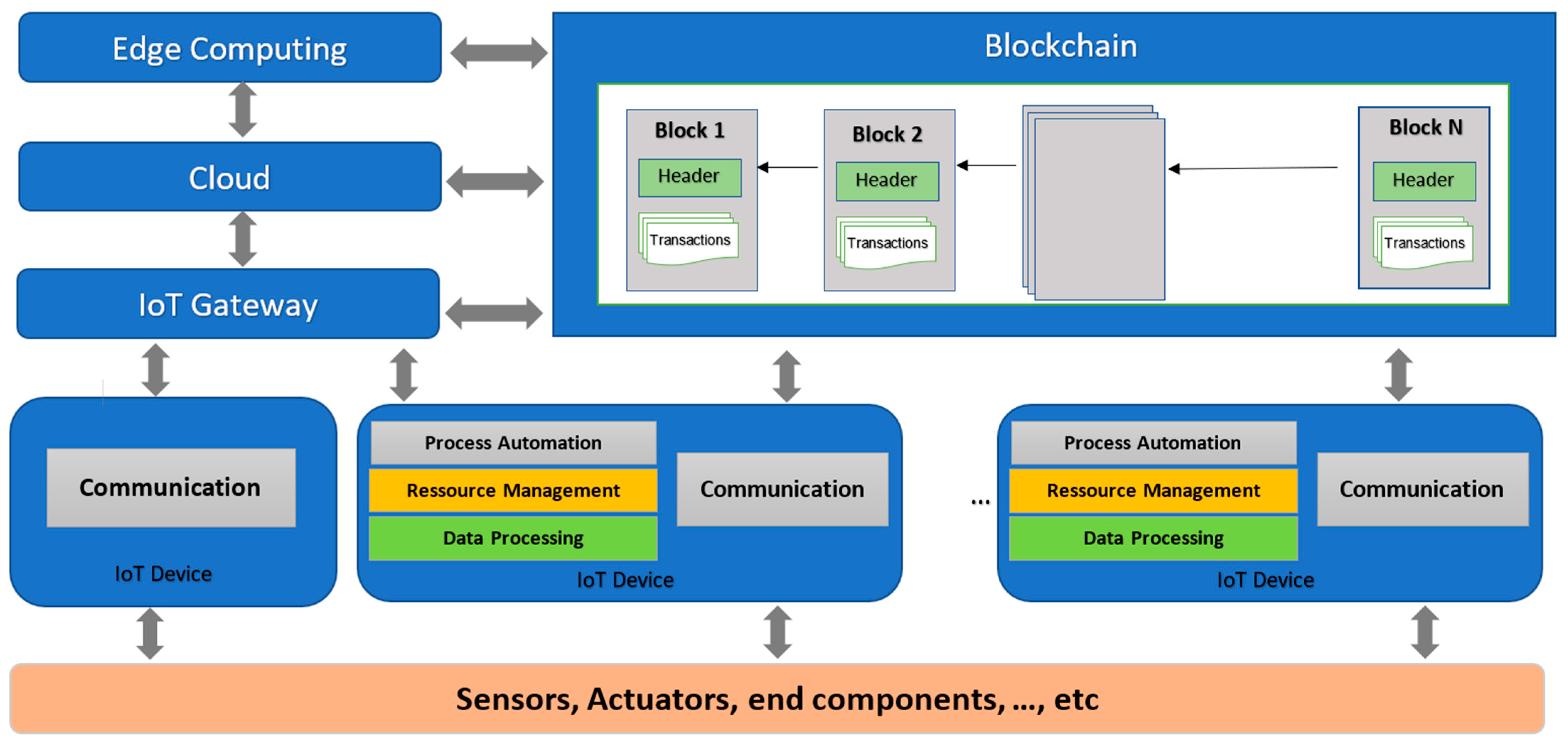
2.1. A Generic BCoT Architecture
2.2. Comparison of BCoT Architectures
- The type of storage used: Blockchain enables decentralized, distributed, and secure data storage. For IoT, there are several methods of storage in the blockchain, such as storing raw data, data hashes, data proofs, or smart contracts.
- The consensus used: In a literal sense, consensus refers to a state of agreement. According to Seibold and Samman [6], a consensus mechanism refers to a technique used for verifying or validating a transaction or value on a blockchain or distributed ledger without having to depend on or trust a central authority.
- Security: In BCoT, the encryption layer is a critical component that guarantees the security, confidentiality, and integrity of both the data exchanged between connected objects and the blockchain, and the transactions executed on the blockchain. It can be used at different levels including encryption of data in transit, encryption of stored data, and transaction protection.
3. Discussion
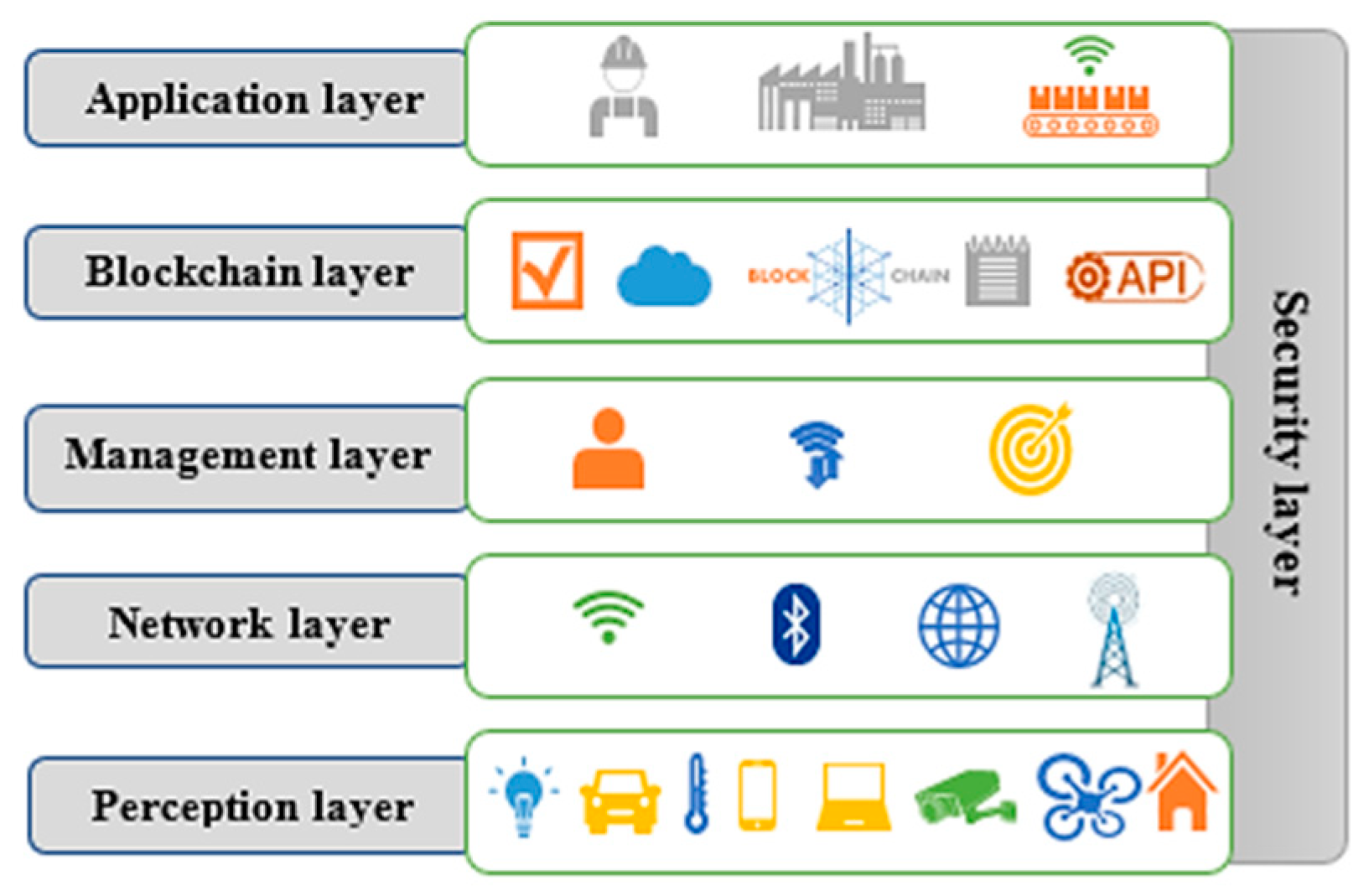
4. Proposed Architecture
- Perception layer: IoT devices collect data and send them to a blockchain network via management nodes.
- Management layer: they are special nodes that connect constrained IoT networks to the blockchain network.
- Blockchain layer: The blockchain network stores data and transactions using decentralized consensus. APIs allow developers to create applications to collect and use IoT data stored on the blockchain network.
- Application layer: an application can be developed to facilitate the management and visualization of IoT data stored on the blockchain network.
- Security layer: this layer is transverse to all previous layers.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Swan, M. Blockchain: Blueprint for a New Economy; O’Reilly Media Inc.: Newton, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pavithran, D.; Shaalan, K.; Al-Karaki, J.N.; Gawanmeh, A. Towards Building a Blockchain Framework for IoT. Cluster Comput. 2020, 23, 2089–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novo, O. Blockchain Meets IoT. An Architecture for Scalable Access Management in IoT. J. Internet Things 2018, 14, 1184–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedeoglu, V.; Jurdak, R.; Putra, G.D.; Dorri, A.; Kanhere, S.S. A Trust Architecture for Blockchain in IoT. In Proceedings of the 16th EAI International Conference on Mobile and Ubiquitous Systems: Computing, Networking and Services (MobiQuitous), Houston, TX, USA, 12–14 November 2019; ACM: New York, NY, USA; pp. 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotb, Y.; Al Ridhawi, I.; Aloqaily, M.; Baker, T.; Jararweh, Y.; Tawfik, H. Cloud-based multi-agent cooperation for IoT devices using workflow-nets. J. Grid Comput. 2019, 17, 625–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibold, S.; Samman, G. Consensus—Immutable Agreement for the Internet of Value. KPMG. 2016. Available online: https://assets.kpmg.com/content/dam/kpmg/pdf/2016/06/kpmg-blockchain-consensus-mechanism.pdf (accessed on 30 August 2019).
- Bao, Z.; Shi, W.; He, D.; Chood, K.K.R. IoTChain: A three-tierblockchain-based IoT security architecture. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.02008. [Google Scholar]
- Sagirlar, G.; Carminati, B.; Ferrari, E.; Sheehan, J.D.; Ragnoli, E. Hybrid-iot: Hybrid blockchain architecture for internet of thingspow sub-blockchains. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Internet of Things (iThings) and IEEE Green Computing and Communications (GreenCom) and IEEE Cyber, Physical and Social Computing (CPSCom) and IEEE Smart Data (SmartData), Halifax, NS, Canada, 30 July–3 August 2018; pp. 1007–1016. [Google Scholar]
- Tuli, S.; Mahmud, R.; Tuli, S.; Buyya, R. Fogbus: A blockchainbased lightweight framework for edge and fog computing. J. Syst. Softw. 2019, 154, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, A.; Liyanage, M.; Braeken, A.; Kanhere, S.S.; Ylianttila, M. Blockchain based proxy re-encryption scheme for secure IoT data sharing. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Blockchain and Cryptocurrency (ICBC), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 14–17 May 2019; pp. 99–103. [Google Scholar]
- Samaniego, M.; Deters, R. Internet of smart things-IoST: Using blockchain and CLIPS to make things autonomous. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Cognitive Computing (ICCC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 June 2017; pp. 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, G. Ethereum: A Secure Decentralised Generalised Transaction Ledger. 2013. Available online: http://gavwood.com/paper.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Birrell, A.D.; Nelson, B.J. Implementing remote procedure calls. ACM Trans. Comput. Syst. 1984, 2, 39–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Jiang, J.; Shu, L.; Niu, J.; Chao, H.C. Management and applications of trust in Wireless Sensor Networks: A survey. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. 2014, 80, 602–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorri, A.; Kanhere, S.S.; Jurdak, R.; Gauravaram, P. LSB: A Lightweight Scalable BlockChain for IoT Security and Privacy. arXiv 2019. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1712.02969.pdf (accessed on 23 January 2023).
- Delgado-Segura, S.; Tanas, C.; Herrera-Joancomarti, J. Reputation and reward: Two sides of the same bitcoin. Sensors 2016, 16, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, S.K.; Liu, Y.; Chia, S.Y.; Xu, X.; Lu, Q.; Zhu, L.; Ning, H. Analysis of blockchain solutions for IoT: A systematic literature review. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 58822–58835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Name | Architecture Type | Consensus Used | Storage Used | Encryption Layer | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IoTchain | Three layers architecture | Any lightweight consensus | Distributed storage | No | [7] |
| Hybrid IoT | A sub-blockchain utilizing proof of work and connected through BFT consensus | Proof of work and BFT | Each sub blockchain has its own transaction pool | No | [8] |
| Fogbus | A cost-effective interface that can be scaled and is not limited to any particular platform | Proof of work | Distributed repository nodes and backing up data to cloud infrastructure at a later time | Yes | [9] |
| Proxy re-encryption scheme | In the absence of a trusted third party, IoT data are encrypted and saved in the cloud. | Ethereum smart contract | Data are kept in the cloud while the location of that data is recorded on the blockchain | Yes | [10] |
| Multichain and arduino | Two layers: FOG et IoT | Round robin | Data processed in FOG | No | [11] |
| Decentralized access control system | Management hub node requests blockchain access information on behalf of IoT devices | One and only smart contract and private Ethereum [12] | Distributed storage in miner nodes | Yes | [3] |
| Trust Architecture | Three layers architecture | Distributed consensus based on reputation, private blockchain | Off-chain storage for data, and on-chain storage for transactions | Yes | [4] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elgountery, Y.; Boushaba, A.; Oualla, M.; Sadki, H. Blockchain Architecture for IoT: Comparative Survey. Comput. Sci. Math. Forum 2023, 6, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmsf2023006007
Elgountery Y, Boushaba A, Oualla M, Sadki H. Blockchain Architecture for IoT: Comparative Survey. Computer Sciences & Mathematics Forum. 2023; 6(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmsf2023006007
Chicago/Turabian StyleElgountery, Yassin, Amal Boushaba, Mohamed Oualla, and Hassain Sadki. 2023. "Blockchain Architecture for IoT: Comparative Survey" Computer Sciences & Mathematics Forum 6, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmsf2023006007
APA StyleElgountery, Y., Boushaba, A., Oualla, M., & Sadki, H. (2023). Blockchain Architecture for IoT: Comparative Survey. Computer Sciences & Mathematics Forum, 6(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmsf2023006007






