RNase P Ribozyme Effectively Inhibits Human CC-Chemokine Receptor 5 Expression and Human Immunodeficiency Virus 1 Infection
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. HIV and Cells
2.2. Synthesis of M1GS RNA and Its Substrate
2.3. Analysis In Vitro
2.4. Ribozyme and Human Gene Expression in Human Cells
2.5. Studies of the Anti-HIV Effect
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cleaving CCR5 mRNA In Vitro by RNase P Ribozyme
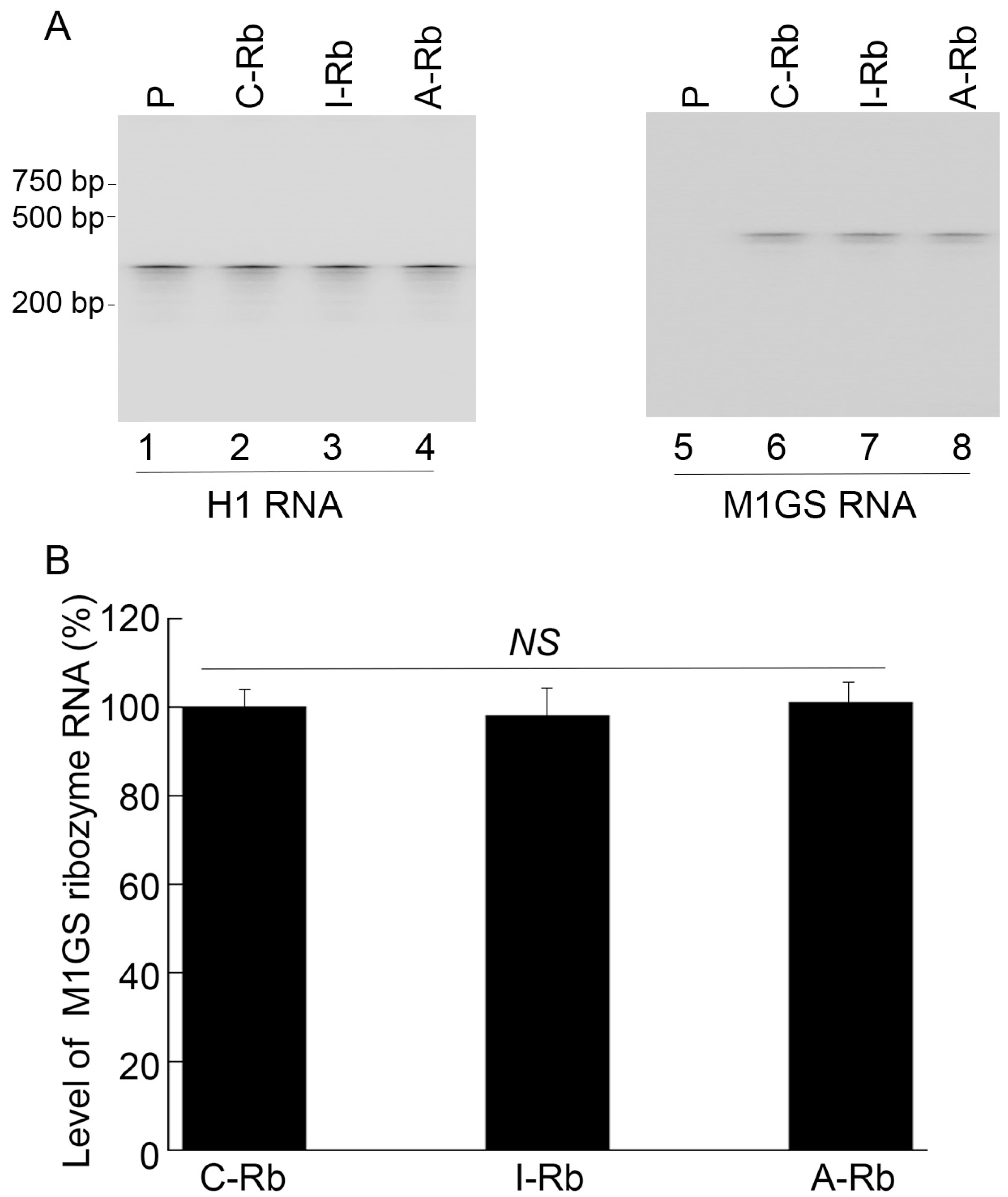
3.2. Anti-CCR5 Ribozyme Expression in Human Cells
3.3. Ribozyme-Mediated Inhibition of Human CCR5 Expression
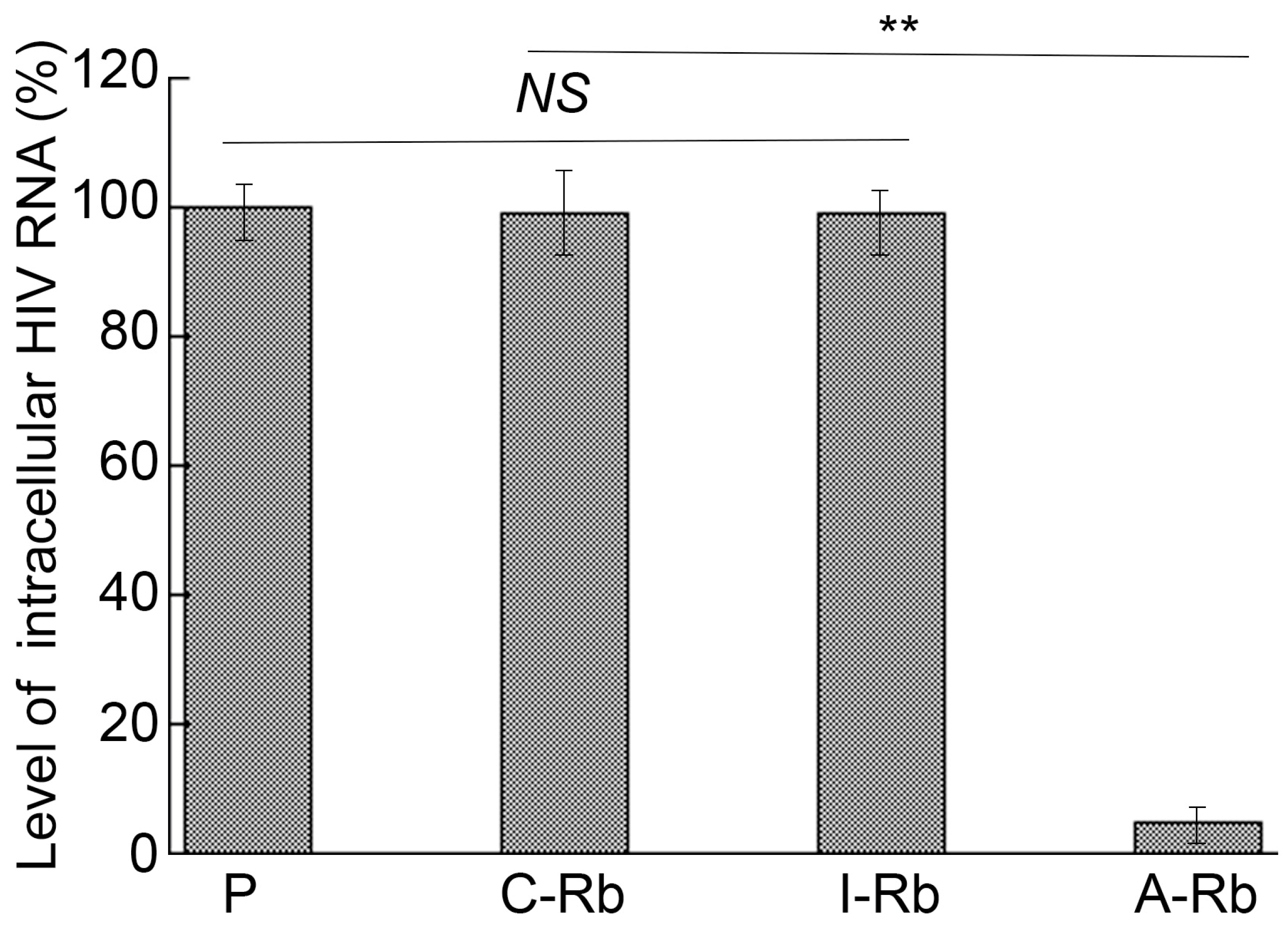
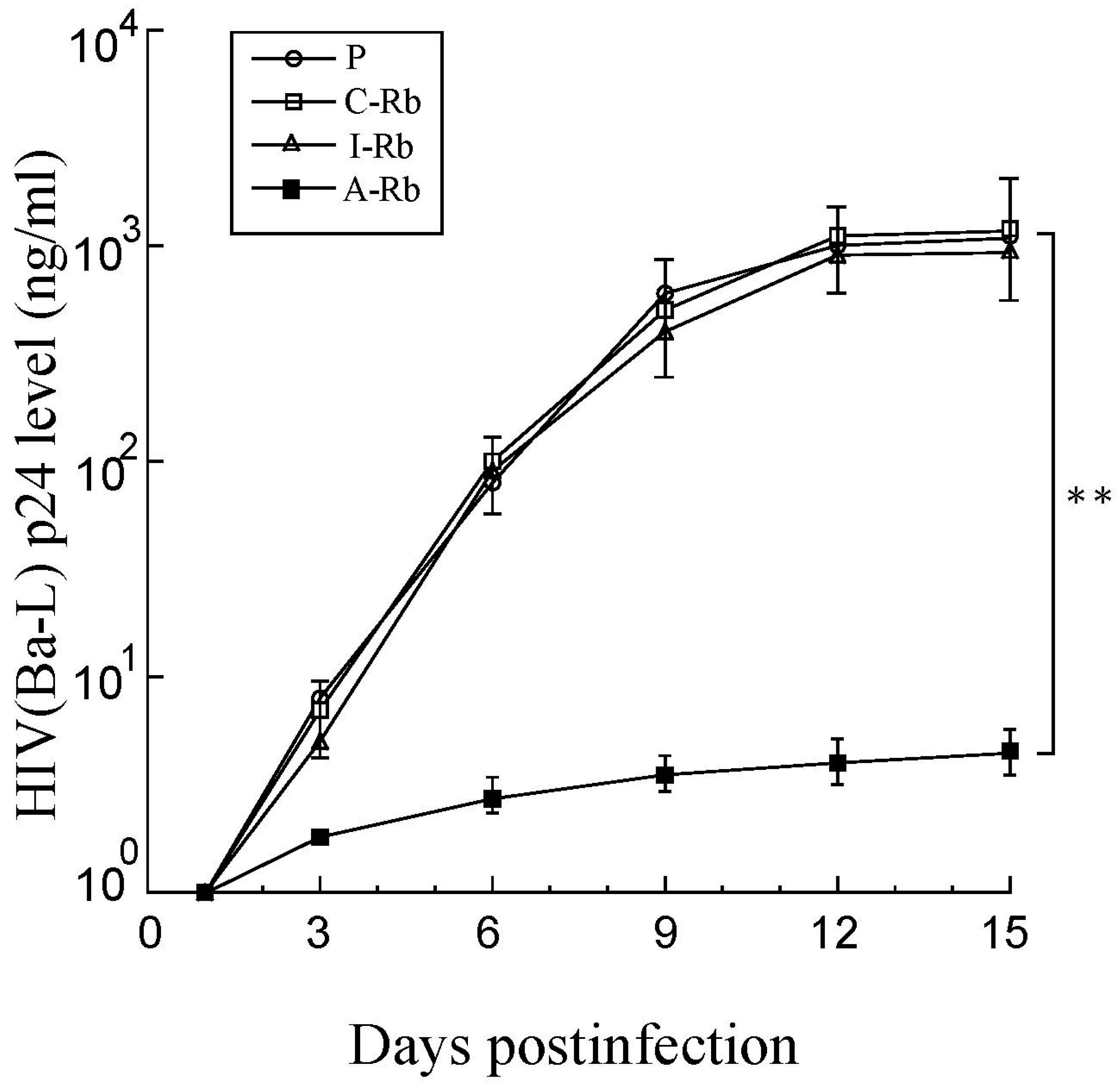
3.4. Anti-HIV Effects of M1GS in Cells
3.5. Strain-Specific Anti-HIV Effects of M1GS Ribozymes
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gopalan, V.; Vioque, A.; Altman, S. RNase P: Variations and uses. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 6759–6762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, S.M.; Liu, F. Engineering of RNase P ribozyme for gene-targeting applications. Gene 2003, 313, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawa, D.; Wang, J.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, F. Inhibition of viral gene expression by human ribonuclease P. RNA 1998, 4, 1397–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnett, J.C.; Rossi, J.J. RNA-based therapeutics: Current progress and future prospects. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, L.J.; Reoma, L.B.; Kovacs, J.A.; Nath, A. Advances toward Curing HIV-1 Infection in Tissue Reservoirs. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00375-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richman, D.D.; Margolis, D.M.; Delaney, M.; Greene, W.C.; Hazuda, D.; Pomerantz, R.J. The challenge of finding a cure for HIV infection. Science 2009, 323, 1304–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doranz, B.J.; Berson, J.F.; Rucker, J.; Doms, R.W. Chemokine receptors as fusion cofactors for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1). Immunol. Res. 1997, 16, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, E.A. HIV entry and tropism: The chemokine receptor connection. Aids 1997, 11, S3–S16. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, J.; Rossi, J.J.; Jung, U. Current progress and challenges in HIV gene therapy. Future Virol. 2011, 6, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Rossi, J.J. Current progress in the development of RNAi-based therapeutics for HIV-1. Gene Ther. 2011, 18, 1134–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Leavitt, M.; Tritz, R.; Duarte, E.; Kang, D.; Mamounas, M.; Gilles, P.; Wong-Staal, F.; Kennedy, S.; Merson, J.; et al. Inhibition of CCR5-dependent HIV-1 infection by hairpin ribozyme gene therapy against CC-chemokine receptor 5. Virology 2000, 276, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagnon, L.; Rossi, J.J. Downregulation of the CCR5 beta-chemokine receptor and inhibition of HIV-1 infection by stable VA1-ribozyme chimeric transcripts. Antisense Nucleic Acid. Drug. Dev. 2000, 10, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.; Akkina, R. CXCR4 and CCR5 shRNA transgenic CD34+ cell derived macrophages are functionally normal and resist HIV-1 infection. Retrovirology 2005, 2, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, E.; Lee, S.-K.; Dykxhoorn, D.M.; Novina, C.; Zhang, D.; Crawford, K.; Cerny, J.; Sharp, P.A.; Lieberman, J.; Manjunath, N.; et al. Sustained small interfering RNA-mediated human immunodeficiency virus type 1 inhibition in primary macrophages. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 7174–7181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilani, A.F.; Trang, P.; Jo, S.; Hsu, A.; Kim, J.; Nepomuceno, E.; Liou, K.; Liu, F. RNase P ribozymes selected in vitro to cleave a viral mRNA effectively inhibit its expressionin cell culture. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 10611–10622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lusso, P.; Cocchi, F.; Balotta, C.; Markham, P.D.; Lioue, A.; Farci, P.; Pal, R.; Gallo, R.C.; Reitz, M.S. Growth of macrophage-tropic and primary human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) isolates in a unique CD4+ T-cell clone (PM1): Failure to downregulate CD4 and to interfere with cell-line-tropic HIV-1. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 3712–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.J.; Kilani, A.F.; Zhan, X.; Altman, S.; Liu, F. The protein cofactor allows the sequence of an RNase P ribozyme to diversify by maintaining the catalytically active structure of the enzyme. RNA 1997, 3, 613–623. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, A.D.; Rosman, G.J. Improved retroviral vectors for gene transfer and expression. Biotechniques 1989, 7, 980–990. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Altman, S. Inhibition of viral gene expression by the catalytic RNA subunit of RNase P from Escherichia coli. Genes Dev. 1995, 9, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Chen, W.; He, L.; Sheng, J.; Liu, Y.; Vu, G.-P.; Yang, Z.; Li, W.; Trang, P.; Wang, Y.; et al. Inhibition of human cytomegalovirus immediate early gene expression and growth by a novel RNase P ribozyme variant. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Yan, B.; Sun, X.; Tang, W.; Trang, P.; Yang, Z.; Gong, H.; Wang, Y.; et al. Inhibition of human cytomegalovirus major capsid protein expression and replication by ribonuclease P-associated external guide sequences. RNA 2019, 25, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, W.; Vu, G.-P.; Bai, Y.; Chen, Y.-C.; Trang, P.; Lu, S.; Xiao, G.; Liu, F. RNase P-associated external guide sequence effectively reduces the expression of human CC-chemokine receptor 5 and inhibits the infection of human immunodeficiency virus 1. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 509714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daftarian, P.M.; Kumar, A.; Kryworuchko, M.; Diaz-Mitoma, F. IL-10 production is enhanced in human T cells by IL-12 and IL-6 and in monocytes by tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J. Immunol. 1996, 157, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, H.K.; Unutmaz, D.; KewalRamani, V.N.; Littman, D.R. Expression cloning of new receptors used by simian and human immunodeficiency viruses. Nature 1997, 388, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, F.; Lee, H.-H.; Farber, J.M. Cloning of STRL22, a new human gene encoding a G-protein-coupled receptor related to chemokine receptors and located on chromosome 6q27. Genomics 1997, 40, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, E.; Castanotto, D.; Zhou, C.; Carbonnelle, C.; Lee, N.S.; Good, P.; Chatterjee, S.; Grange, T.; Pictet, R.; Kohn, D.; et al. The expression cassette determines the functional activity of ribozymes in mammalian cells by controlling their intracellular localization. RNA 1997, 3, 75–88. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Hwang, E.S.; Altman, S. Targeted cleavage of mRNA by human RNase, P. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 8006–8010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, E.A.; Murphy, P.M.; Farber, J.M. Chemokine receptors as HIV-1 coreceptors: Roles in viral entry, tropism, and disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1999, 17, 657–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieniasz, P.D.; Cullen, B.R. Chemokine receptors and human immunodeficiency virus infection. Front. Biosci. 1998, 3, 44–58. [Google Scholar]
- Scherer, L.J.; Rossi, J.J. Approaches for the sequence-specific knockdown of mRNA. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 1457–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, S.W.; Joyce, G.F. A general purpose RNA-cleaving DNA enzyme. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 4262–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, C.A.; Cheng, Y.C. Antisense oligonucleotides as therapeutic agents—Is the bullet really magical? Science 1993, 261, 1004–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong-Staal, F.; Poeschla, E.M.; Looney, D.J. A controlled, Phase 1 clinical trial to evaluate the safety and effects in HIV-1 infected humans of autologous lymphocytes transduced with a ribozyme that cleaves HIV-1 RNA. Hum. Gene Ther. 1998, 9, 2407–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amado, R.G.; Mitsuyasu, R.T.; Rosenblatt, J.D.; Ngok, F.K.; Bakker, A.; Cole, S.; Chorn, N.; Lin, L.-S.; Bristol, G.; Boyd, M.P.; et al. Anti-human immunodeficiency virus hematopoietic progenitor cell-delivered ribozyme in a phase I study: Myeloid and lymphoid reconstitution in human immunodeficiency virus type-1-infected patients. Hum. Gene Ther. 2004, 15, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macpherson, J.L.; Boyd, M.P.; Arndt, A.J.; Todd, A.V.; Fanning, G.C.; Ely, J.A.; Elliott, F.; Knop, A.; Raponi, M.; Murray, J.; et al. Long-term survival and concomitant gene expression of ribozyme-transduced CD4+ T-lymphocytes in HIV-infected patients. J. Gene Med. 2005, 7, 552–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michienzi, A.; Castanotto, D.; Lee, N.; Li, S.; Zaia, J.A.; Rossi, J.J. RNA-mediated inhibition of HIV in a gene therapy setting. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2003, 1002, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiGiusto, D.L.; Krishnan, A.; Li, L.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Rao, A.; Mi, S.; Yam, P.; Stinson, S.; Kalos, M.; et al. RNA-based gene therapy for HIV with lentiviral vector-modified CD34(+) cells in patients undergoing transplantation for AIDS-related lymphoma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2010, 2, 36ra43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Autran, B.; Carcelain, G.; Li, T.S.; Blanc, C.; Mathez, D.; Tubiana, R.; Katlama, C.; Debre, P.; Leibowitch, J. Positive effects of combined antiretroviral therapy on CD4 + T cell homeostasis and function in advanced HIV disease. Science 1997, 277, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeni, P. Update on HAART in HIV. J. Hepatol. 2006, 44, S100–S103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palella, F.J., Jr.; Delaney, K.M.; Moorman, A.C.; Loveless, M.O.; Fuhrer, J.; Satten, G.A.; Aschman, D.J.; Holmberg, S.D.; the HIV Outpatient Study Investigators. Declining morbidity and mortality among patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. HIV Outpatient Study Investigators. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freed, E.O.; Martin, M.A. HIVs and their replication. In Fields Virology; Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Griffin, D.E., Martin, M.A., Lamb, R.A., Roizman, B., Straus, S.E., Eds.; Lippincott-William & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007; pp. 2108–2185. [Google Scholar]
- Kuritzkes, D.R.; Walker, B.D. HIV-1: Pathogenesis, Clinical Manifestations, and Treatment. In Fields Virology; Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Griffin, D.E., Martin, M.A., Lamb, R.A., Roizman, B., Straus, S.E., Eds.; Lippincott-William & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007; pp. 2188–2214. [Google Scholar]
- Strayer, D.S.; Akkina, R.; Bunnell, B.A.; Dropulic, B.; Planelles, V.; Pomerantz, R.J.; Rossi, J.J.; Zaia, J.A. Current status of gene therapy strategies to treat HIV/AIDS. Mol. Ther. 2005, 11, 823–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Kim, J.; Kilani, A.F.; Kim, K.; Dunn, W.; Jo, S.; Nepomuceno, E.; Liu, F. In vitro selection of external guide sequences for directing RNase P-mediated inhibition of viral gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 30112–30120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Altman, S. Selection of guide sequences that direct efficient cleavage of mRNA by human ribonuclease P. Science 1994, 263, 1269–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Enzyme | (kcat/Km)s (µM−1·min−1) | Kd (nM) |
|---|---|---|
| M1-Rb | 0.21 ± 0.08 | 0.31 ± 0.08 |
| A-Rb | 6.5 ± 2.5 | 0.35 ± 0.09 |
| I-Rb | <5 × 10−5 | 0.32 ± 0.08 |
| C-Rb | <5 × 10−5 | ND |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, B.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.-C.; Zhang, I.; Liu, F. RNase P Ribozyme Effectively Inhibits Human CC-Chemokine Receptor 5 Expression and Human Immunodeficiency Virus 1 Infection. Zoonotic Dis. 2023, 3, 93-103. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis3020009
Yan B, Liu Y, Chen Y-C, Zhang I, Liu F. RNase P Ribozyme Effectively Inhibits Human CC-Chemokine Receptor 5 Expression and Human Immunodeficiency Virus 1 Infection. Zoonotic Diseases. 2023; 3(2):93-103. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis3020009
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Bin, Yujun Liu, Yuan-Chuan Chen, Isadora Zhang, and Fenyong Liu. 2023. "RNase P Ribozyme Effectively Inhibits Human CC-Chemokine Receptor 5 Expression and Human Immunodeficiency Virus 1 Infection" Zoonotic Diseases 3, no. 2: 93-103. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis3020009
APA StyleYan, B., Liu, Y., Chen, Y.-C., Zhang, I., & Liu, F. (2023). RNase P Ribozyme Effectively Inhibits Human CC-Chemokine Receptor 5 Expression and Human Immunodeficiency Virus 1 Infection. Zoonotic Diseases, 3(2), 93-103. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis3020009







