Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns and Serological Diversity of Shigella Species from Patient Isolates at University Teaching Hospital in Lusaka, Zambia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation of Shigella Species, Biochemical Tests, and Detection of Strain Serotypes
2.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (AST): The Kirby–Bauer Disk Diffusion Method
2.3. DNA Extraction, Polymerase Chain Reaction, and Gel Electrophoresis
2.4. Analysis of AMR Profiles
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Features and Shigella Isolate Serogroup Distribution
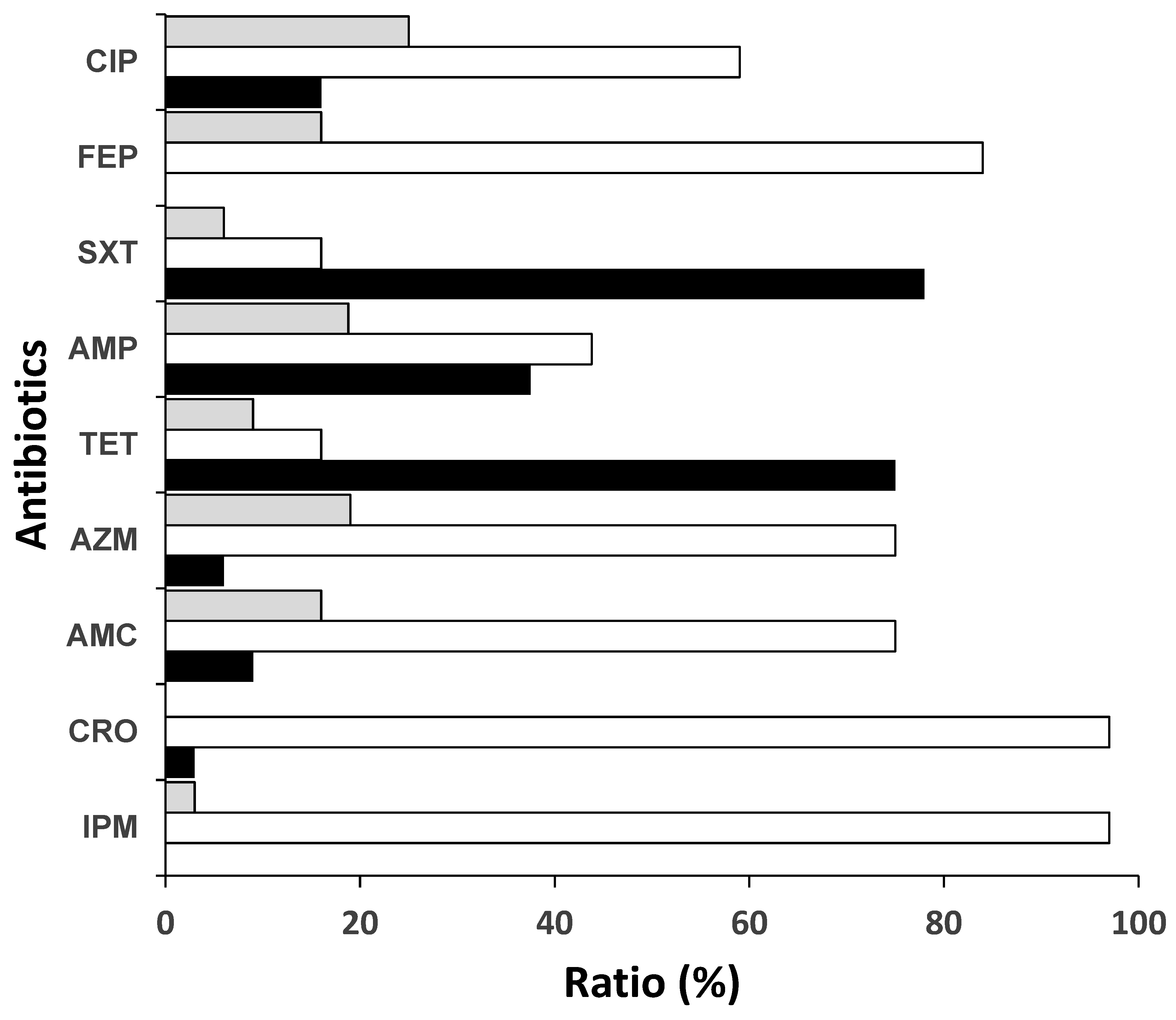
3.2. Antibiotic Resistance Rates to Commonly Used Antibiotics and WHO Priority Shigella Isolates
3.3. Proportion of Multidrug Resistance Shigella Species
3.4. β-Lactamase-Encoding Genes Were Detected Among Shigella Species
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Limitation of This Study
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anderson, M.; Sansonetti, P.J.; Marteyn, B.S. Shigella Diversity and Changing Landscape: Insights for the Twenty-First Century. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, T.L.; Keusch, G.T. Shigella. In Medical Microbiology; University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston: Galveston, TX, USA, 1996. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK8038/ (accessed on 29 January 2025).
- Liu, H.; Zhu, B.; Qiu, S.; Xia, Y.; Liang, B.; Yang, C.; Dong, N.; Li, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Wang, S.; et al. Dominant serotype distribution and antimicrobial resistance profile of Shigella spp. in Xinjiang, China. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieper, R.; Zhang, Q.; Parmar, P.P.; Huang, S.; Clark, D.J.; Alami, H.; Donohue-Rolfe, A.; Fleischmann, R.D.; Peterson, S.N.; Tzipori, S. The Shigella dysenteriae serotype 1 proteome, profiled in the host intestinal environment, reveals major metabolic modifications and increased expression of invasive proteins. Proteomics 2009, 9, 5029–5045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethuvel, D.M.; Ragupathi, N.D.; Anandan, S.; Veeraraghavan, B. Update on: Shigella new serogroups/serotypes and their antimicrobial resistance. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 64, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Pholwat, S.; Zhang, J.; Taniuchi, M.; Haque, R.; Alam, M.; Ochieng, J.B.; Jones, J.A.; Platts-Mills, J.A.; Tennant, S.M.; et al. Evaluation of Molecular Serotyping Assays for Shigella flexneri Directly on Stool Samples. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e02455-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CDC. CDC Yellow Book 2023; CDC: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Miti, S.; Chilyabanyama, O.N.; Chisenga, C.C.; Chibuye, M.; Bosomprah, S.; Mumba, C.; Chitondo, S.; Siziya, S.; Cohen, D.; Chilengi, R.; et al. Sensitivity and predictive value of dysentery in diagnosing shigellosis among under five children in Zambia. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0279012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisenga, C.C.; Bosomprah, S.; Simuyandi, M.; Mwila-Kazimbaya, K.; Chilyabanyama, O.N.; Laban, N.M.; Bialik, A.; Asato, V.; Meron-Sudai, S.; Frankel, G.; et al. Shigella-specific antibodies in the first year of life among Zambian infants: A longitudinal cohort study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, A.; Okafor, C.N. Shigella; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- DuPont, H.L.; Levine, M.M.; Hornick, R.B.; Formal, S.B. Inoculum Size in Shigellosis and Implications for Expected Mode of Transmission. J. Infect. Dis. 1989, 159, 1126–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, W.; Formal, S.; Giannella, R.; Dammin, G. Pathophysiology of Shigella Diarrhea in the Rhesus Monkey: Intestinal Transport, Morphological, and Bacteriological Studies. Gastroenterology 1975, 68, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattock, E.; Blocker, A.J. How Do the Virulence Factors of Shigella Work Together to Cause Disease? Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, R.; Farahani, A. Shigella: Antibiotic-Resistance Mechanisms And New Horizons For Treatment. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 3137–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Singh, A.; Dar, M.A.; Kaur, R.J.; Charan, J.; Iskandar, K.; Haque, M.; Murti, K.; Ravichandiran, V.; Dhingra, S. Menace of antimicrobial resistance in LMICs: Current surveillance practices and control measures to tackle hostility. J. Infect. Public Health 2021, 15, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sono, T.M.; Yeika, E.; Cook, A.; Kalungia, A.; Opanga, S.A.; Acolatse, J.E.E.; Sefah, I.A.; Jelić, A.G.; Campbell, S.; Lorenzetti, G.; et al. Current rates of purchasing of antibiotics without a prescription across sub-Saharan Africa; rationale and potential programmes to reduce inappropriate dispensing and resistance. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2023, 21, 1025–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulis, G.; Sayood, S.; Gandra, S. Antimicrobial resistance in low- and middle-income countries: Current status and future directions. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2021, 20, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otaigbe, I.I.; Elikwu, C.J. Drivers of inappropriate antibiotic use in low- and middle-income countries. JAC-Antimicrobial Resist. 2023, 5, dlad062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanda, G.-W.; Kayla, V.E.; Naeemah, L. Shigellosis: Travel-Associated Infections & Diseases. 2023. Available online: https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/yellowbook/2024/infections-diseases/shigellosis (accessed on 29 January 2025).
- Williams, P.C.M.; Berkley, J.A. Guidelines for the treatment of dysentery (shigellosis): A systematic review of the evidence. Paediatr. Int. Child Health 2018, 38, S50–S65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, N.C.; Cunha, B.A. Third-generation cephalosporins. Med. Clin. N. Am. 1995, 79, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNICEF. Annual Report; For Every Child, Every Right; United Nations Children’s Fund: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yeboah-Antwi, K.; MacLeod, W.B.; Biemba, G.; Sijenyi, P.; Höhne, A.; Verstraete, L.; McCallum, C.M.; Hamer, D.H. Improving Sanitation and Hygiene through Community-Led Total Sanitation: The Zambian Experience. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019, 100, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO; UNICEF. Simple Solution Improves Water and Sanitation in Zambian Health-Care Facilities. 2015. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/feature-stories/detail/simple-solution-improves-water-and-sanitation-in-zambian-health-care-facilities (accessed on 29 January 2025).
- INDEX GHS. Global Health Security Index scores for Zambia; INDEX GHS. 2021. Available online: https://ghsindex.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/Zambia.pdf (accessed on 29 January 2025).
- Chiyangi, H.; Muma, J.B.; Malama, S.; Manyahi, J.; Abade, A.; Kwenda, G.; Matee, M.I. Identification and antimicrobial resistance patterns of bacterial enteropathogens from children aged 0–59 months at the University Teaching Hospital, Lusaka, Zambia: A prospective cross sectional study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, J.; Ries, A.A.; Chimba, R.M.; Perera, C.U.; Bean, N.H.; Griffin, P.M. Antimicrobial-Resistant Epidemic Shigella Dysenteriae Type 1 in Zambia: Modes of Transmission. J. Infect. Dis. 1995, 171, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyogi, S.K. Shigellosis. J. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hudzicki, J. Kirby-Bauer Disk Diffusion Susceptibility Test Protocol. Am. Soc. Microbiol. 2009, 15, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- McFaland, J. Nephelometer: An instrument for media used for estimating the number of bacteria in suspensions used for calculating the opsonic index and for vaccines. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1907, 49, 1176–1178. [Google Scholar]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 31st ed.; CLSI: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mabilat, C.; Courvalin, P. Development of “oligotyping” for characterization and molecular epidemiology of TEM beta-lactamases in members of the family Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1990, 34, 2210–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X.; Zhao, J.; Song, W.; Li, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Sun, R.; et al. Synergistic effects of baicalein with cefotaxime against Klebsiella pneumoniae through inhibiting CTX-M-1 gene expression. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhrel, R.H.; Thapa, B.; Kafle, R.; Shah, P.K.; Tribuddharat, C. Co-existence of beta-lactamases in clinical isolates of Escherichia coli from Kathmandu, Nepal. BMC Res. Notes 2014, 7, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawa, M.; Furuta, Y.; Mulenga, G.; Mubanga, M.; Mulenga, E.; Zorigt, T.; Kaile, C.; Simbotwe, M.; Paudel, A.; Hang’ombe, B.; et al. Novel chromosomal insertions of ISEcp1-blaCTX-M-15 and diverse antimicrobial resistance genes in Zambian clinical isolates of Enterobacter cloacae and Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2021, 10, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiorakos, A.-P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharpure, R.; Marsh, Z.A.; Tack, D.M.; Collier, S.A.; Strysko, J.; Ray, L.; Payne, D.C.; Garcia-Williams, A.G. Disparities in Incidence and Severity of Shigella Infections Among Children—Foodborne Diseases Active Surveillance Network (FoodNet), 2009-2018. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2021, 10, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCrickard, L.S.; Crim, S.M.; Kim, S.; Bowen, A. Disparities in severe shigellosis among adults—Foodborne diseases active surveillance network, 2002–2014. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikfar, R.; Shamsizadeh, A.; Darbor, M.; Khaghani, S.; Moghaddam, M. A Study of prevalence of Shigella species and antimicrobial resistance patterns in paediatric medical center, Ahvaz, Iran. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2017, 9, 277–283. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, W.; Cao, M.; Zhu, Q.; Ma, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, G.; Zhou, X.; Li, B.; Shi, Y.; et al. Virulence factors and molecular characteristics of Shigella flexneri isolated from calves with diarrhea. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taneja, N.; Mewara, A. Shigellosis: Epidemiology in India. Indian J. Med. Res. 2016, 143, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drews, S.J.; Lau, C.; Andersen, M.; Ferrato, C.; Simmonds, K.; Stafford, L.; Fisher, B.; Everett, D.; Louie, M. Laboratory based surveillance of travel-related Shigella sonnei and Shigella flexneri in Alberta from 2002 to 2007. Glob. Health 2010, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sack, D.; Hoque, S.; Etheridge, M.; Huq, A. Is protection against shigellosis induced by natural infection with Plesiomonas shigelloides? Lancet 1994, 343, 1413–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toro, C.; Arroyo, A.; Iglesias, N.; Sarria, A.; Enríquez, A.; Baquero, M.; de Guevara, C.L. Shigellosis in Subjects with Traveler’s Diarrhea Versus Domestically Acquired Diarrhea: Implications for Antimicrobial Therapy and Human Immunodeficiency Virus Surveillance. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 93, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’souza, A.W.; Moodley-Govender, E.; Berla, B.; Kelkar, T.; Wang, B.; Sun, X.; Daniels, B.; Coutsoudis, A.; Trehan, I.; Dantas, G. Cotrimoxazole Prophylaxis Increases Resistance Gene Prevalence and α-Diversity but Decreases β-Diversity in the Gut Microbiome of Human Immunodeficiency Virus–Exposed, Uninfected Infants. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 71, 2858–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shambaugh, G.E. History of Sulfonamides. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1966, 83, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeta, K.I.; Michelo, C.; Jacobs, C. Antimicrobial Resistance among Pregnant Women with Urinary Tract Infections Attending Antenatal Clinic at Levy Mwanawasa University Teaching Hospital (LMUTH), Lusaka, Zambia. Int. J. Microbiol. 2021, 2021, 8884297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, M.; Griffin, S.; Chitah, B.; Walker, A.S.; Mulenga, V.; Kalolo, D.; Hawkins, N.; Merry, C.; Barry, M.G.; Chintu, C.; et al. The cost-effectiveness of cotrimoxazole prophylaxis in HIV-infected children in Zambia. AIDS 2008, 22, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ud-Din, A.I.M.S.; Wahid, S.U.H.; Latif, H.A.; Shahnaij, M.; Akter, M.; Azmi, I.J.; Hasan, T.N.; Ahmed, D.; Hossain, M.A.; Faruque, A.S.G.; et al. Changing Trends in the Prevalence of Shigella Species: Emergence of Multi-Drug Resistant Shigella sonnei Biotype g in Bangladesh. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salleh, M.Z.; Zuraina, N.M.N.N.; Hajissa, K.; Ilias, M.I.; Singh, K.K.B.; Deris, Z.Z. Prevalence of Multidrug-Resistant and Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase-Producing Shigella Species in Asia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Finance and National Planning. Socio-Economic Transformation for Improved Livelihoods. 2022. Available online: https://www.mot.gov.zm/?wpdmpro=eighth-national-development-plan-8ndp-2022-2026&wpdmdl=972&refresh=6799924eb4f741738117710 (accessed on 29 January 2025).
- Sukwa, N.; Bosomprah, S.; Somwe, P.; Muyoyeta, M.; Mwape, K.; Chibesa, K.; Luchen, C.C.; Silwamba, S.; Mulenga, B.; Munyinda, M.; et al. The Incidence and Risk Factors for Enterotoxigenic E. coli Diarrheal Disease in Children under Three Years Old in Lusaka, Zambia. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Health Zambia NFC. Standard Treatment Guidelines, Essential Medicines List, Essential Laboratory Supplies for Zambia, 5th ed.; Zambia Ministry of Health: Lusaka, Zambia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Neu, H.C.; Fu, K.P. Clavulanic Acid, a Novel Inhibitor of β-Lactamases. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1978, 14, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
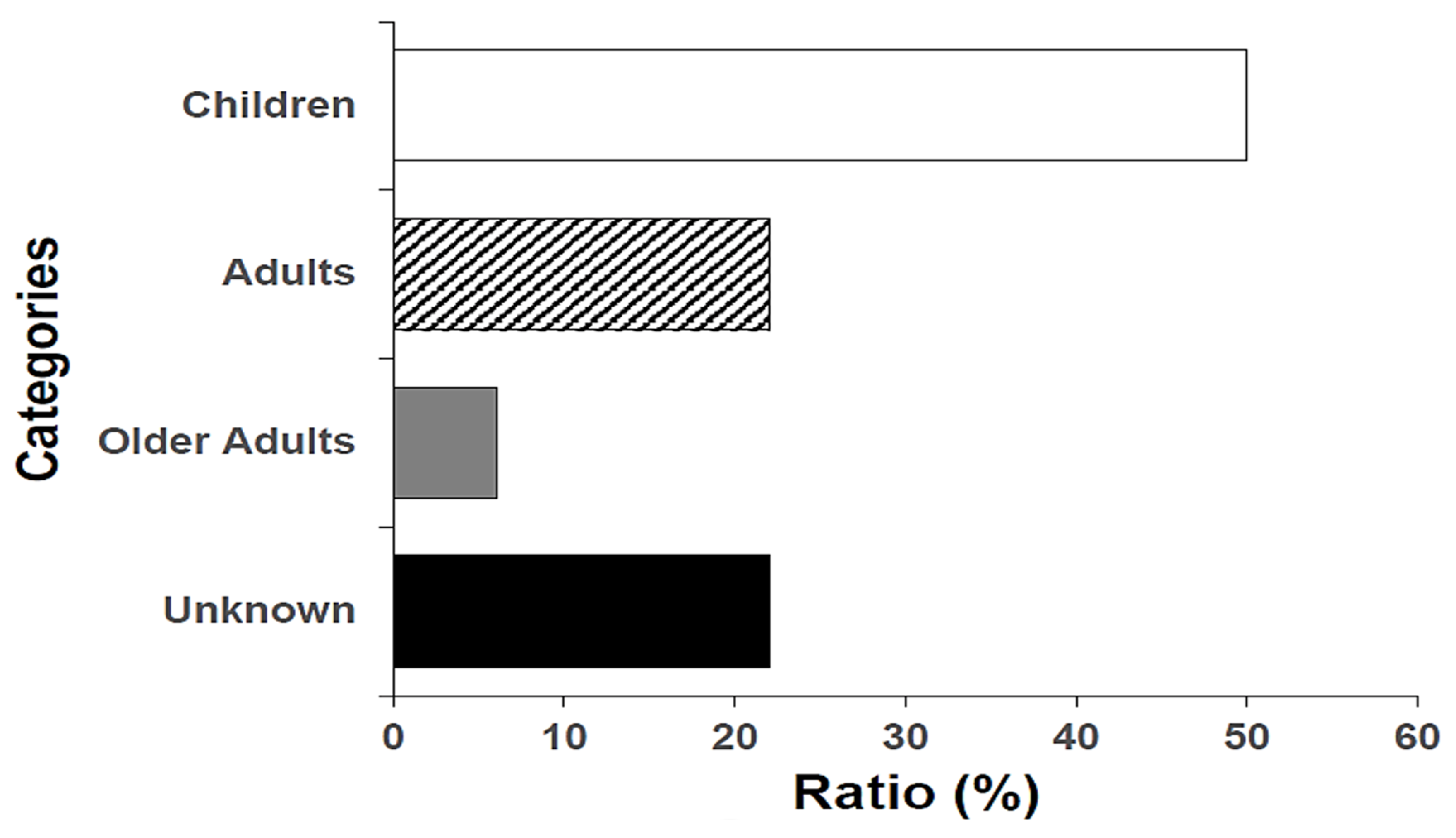

| Name of Species | Most Prevalent Age Category | Number (n) | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S. flexneri | Children (6/16; 37.5%) * | 16 | 50 |
| S. sonnei | Children (10/14; 71.4%) | 14 | 44 |
| S. dysenteriae | Unknown (1; 100%) | 1 | 3 |
| S. boydii | Older adult (1; 100%) | 1 | 3 |
| Total | 32 | 100 | |
| MDR Phenotype | Strain ID | Facility of Origin | No. of Isolates | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SXT/TET/AMP/CIP | MN_12 | UTH Adult | 2 | 25 |
| MN_13 | UTH Adult | |||
| SXT/AMP/TET | MN_14 | Matero Hospital | 2 | 25 |
| MN_28 | UTH Paeds | |||
| AMC/TET/SXT | MN_22 | UTH Paeds | 1 | 12.5 |
| CIP/TET/SXT | MN-10 | Chilanga Hospital | 1 | 12.5 |
| CIP/AZM/AMC/CRO/TET | MN_11 | UTH Adult | 1 | 12.5 |
| AMC/AZM/CIP/TET | MN_30 | State House Clinic | 1 | 12.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nundwe, M.; Chizimu, J.Y.; Mwaba, J.; Shawa, M.; Katete, R.S.; Mutengo, M.M.; Nakazwe, R.; Mulunda, N.R.; Sialubanje, C.; Kalumbi, M.M.; et al. Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns and Serological Diversity of Shigella Species from Patient Isolates at University Teaching Hospital in Lusaka, Zambia. Bacteria 2025, 4, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/bacteria4020018
Nundwe M, Chizimu JY, Mwaba J, Shawa M, Katete RS, Mutengo MM, Nakazwe R, Mulunda NR, Sialubanje C, Kalumbi MM, et al. Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns and Serological Diversity of Shigella Species from Patient Isolates at University Teaching Hospital in Lusaka, Zambia. Bacteria. 2025; 4(2):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/bacteria4020018
Chicago/Turabian StyleNundwe, Mike, Joseph Yamweka Chizimu, John Mwaba, Misheck Shawa, Rodrick S. Katete, Mable Mwale Mutengo, Ruth Nakazwe, Namwiinga R. Mulunda, Cephas Sialubanje, Mox Malama Kalumbi, and et al. 2025. "Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns and Serological Diversity of Shigella Species from Patient Isolates at University Teaching Hospital in Lusaka, Zambia" Bacteria 4, no. 2: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/bacteria4020018
APA StyleNundwe, M., Chizimu, J. Y., Mwaba, J., Shawa, M., Katete, R. S., Mutengo, M. M., Nakazwe, R., Mulunda, N. R., Sialubanje, C., Kalumbi, M. M., Kaunda, Y., Chanda, R., Chambaro, H., Kamboyi, H. K., Kapalamula, T., Mudenda, S., Chabala, F. W., Hang’ombe, B. M., Chilengi, R., ... Suzuki, Y. (2025). Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns and Serological Diversity of Shigella Species from Patient Isolates at University Teaching Hospital in Lusaka, Zambia. Bacteria, 4(2), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/bacteria4020018








