SMAD1 Is Dispensable for CDX2 Induction but Required for the Repression of Ectopic Small-Intestinal Gene Expression in Human-Pluripotent-Stem-Cell-Derived Colonic Organoids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Generation of SMAD1-Deficient Cells
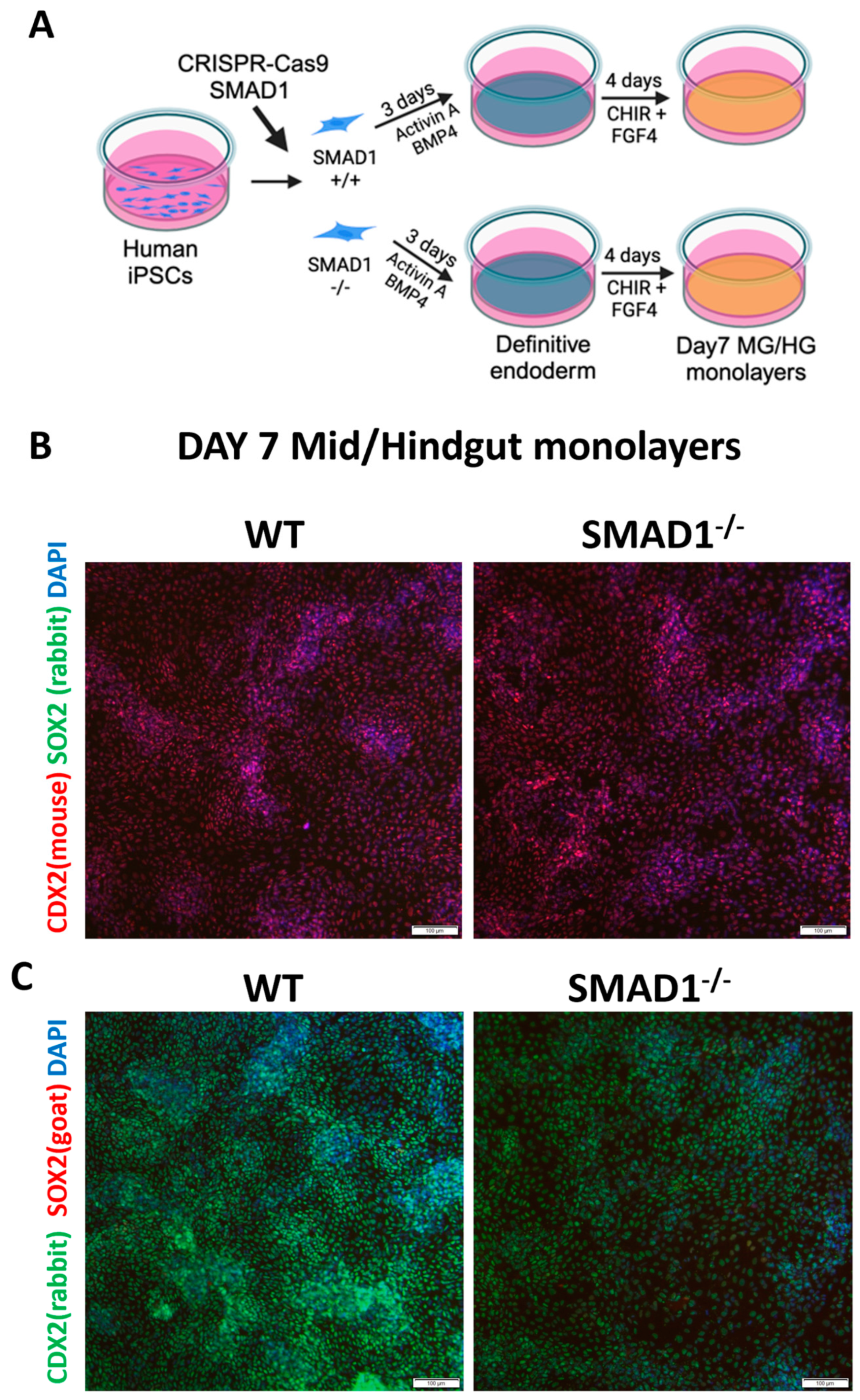
2.3. Generation of Human Gut Tube Cultures
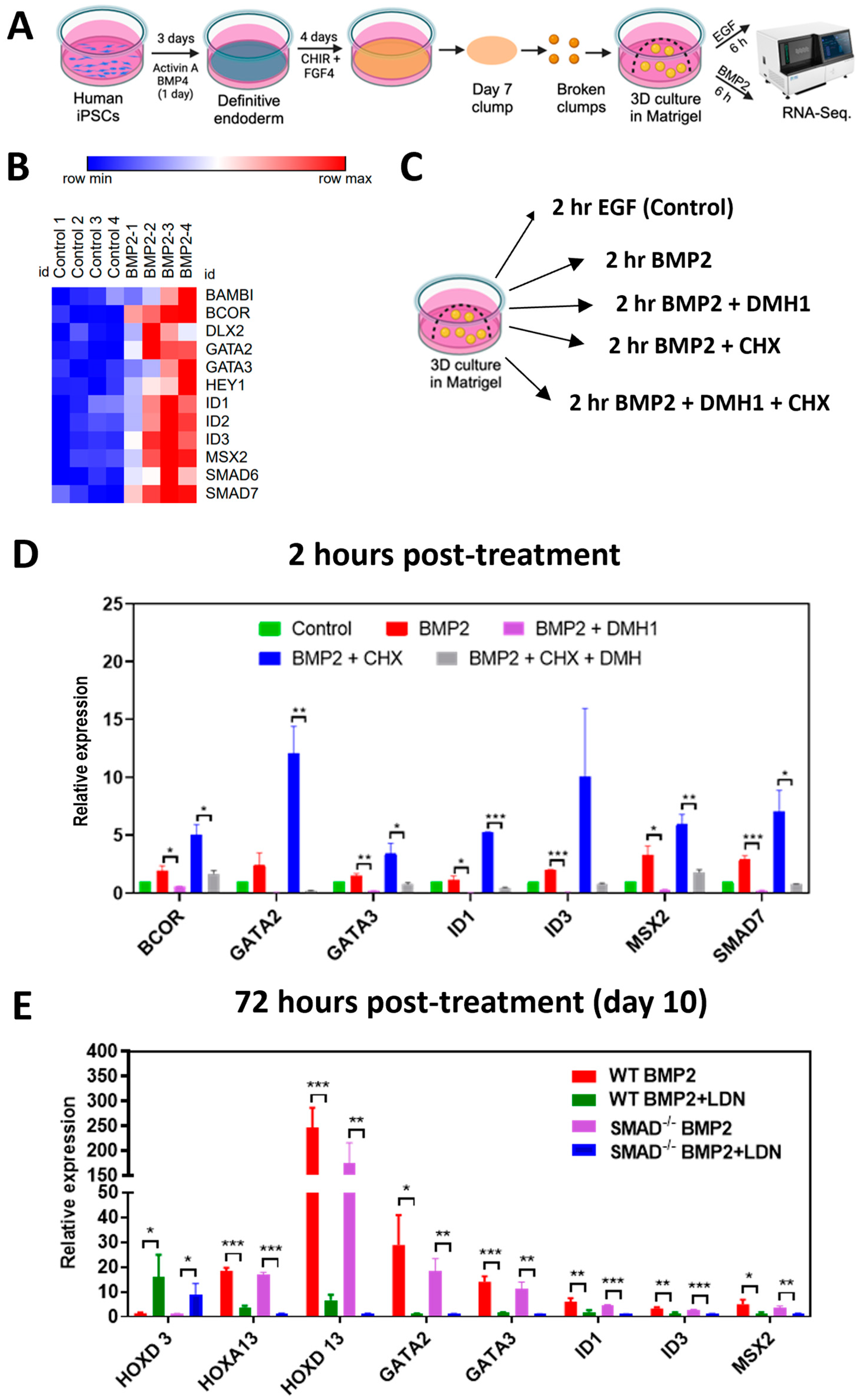
2.4. Three-Dimensional Culture and Posterior Patterning of Dissociated Mid/Hindgut Endoderm
2.5. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.6. Western Blot
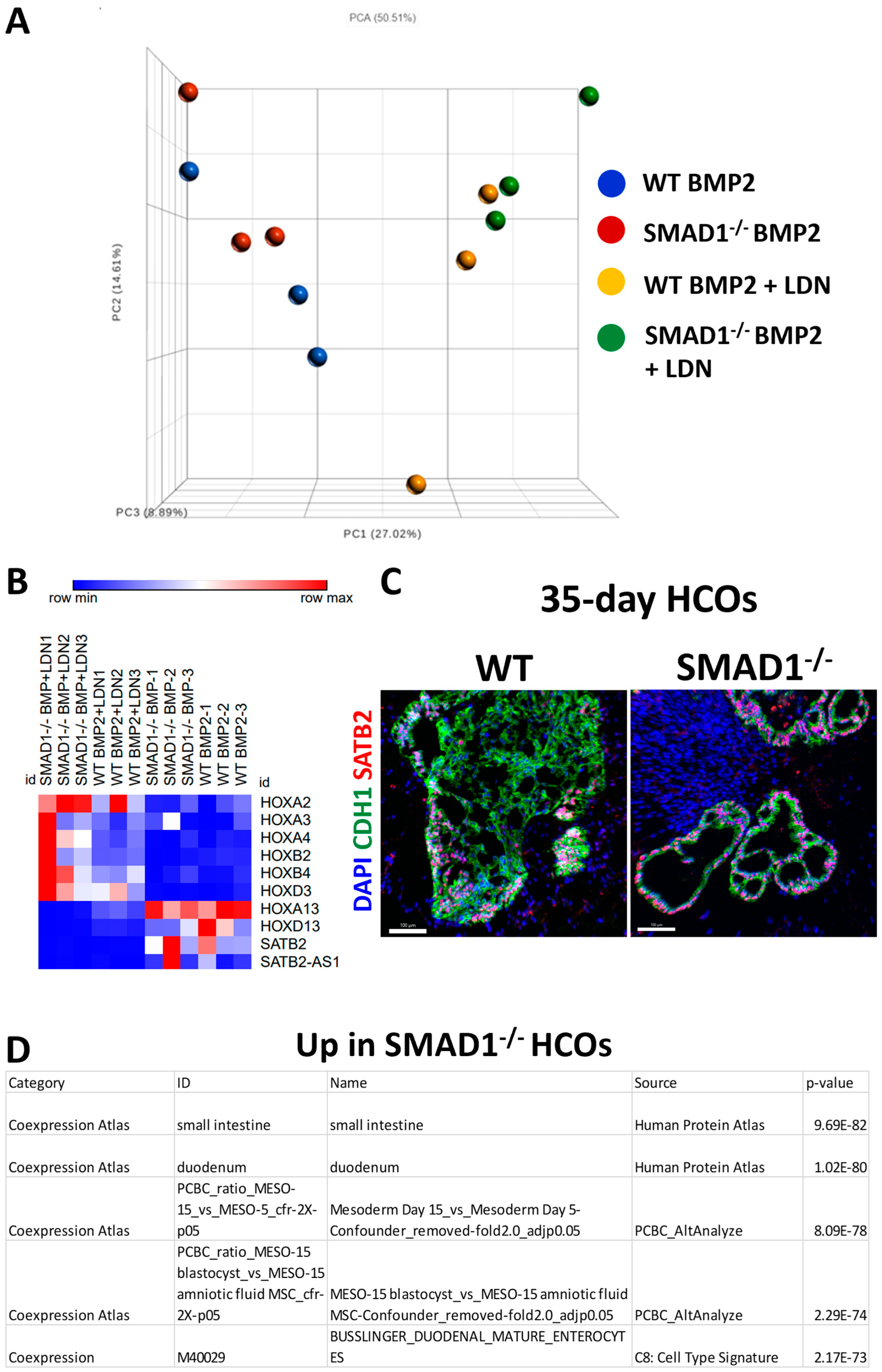
2.7. RNA-Seq Processing and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. SMAD1-Deficient Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Are Competent to Generate CDX2-Expressing Mid/Hindgut
3.2. Immediate Early and Late Targets of BMP Signaling Are Not Affected by SMAD1 Deficiency
3.3. SMAD1-Deficient HCOs Ectopically Express Small-Intestinal Markers Following Long-Term Culture
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trisno, S.L.; Philo, K.E.D.; McCracken, K.W.; Cata, E.M.; Ruiz-Torres, S.; Rankin, S.A.; Han, L.; Nasr, T.; Chaturvedi, P.; Rothenberg, M.E.; et al. Esophageal Organoids from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells Delineate Sox2 Functions during Esophageal Specification. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 23, 501–515.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCracken, K.W.; Aihara, E.; Martin, B.; Crawford, C.M.; Broda, T.; Treguier, J.; Zhang, X.; Shannon, J.M.; Montrose, M.H.; Wells, J.M. Wnt/beta-catenin promotes gastric fundus specification in mice and humans. Nature 2017, 541, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCracken, K.W.; Cata, E.M.; Crawford, C.M.; Sinagoga, K.L.; Schumacher, M.; Rockich, B.E.; Tsai, Y.H.; Mayhew, C.N.; Spence, J.R.; Zavros, Y.; et al. Modelling human development and disease in pluripotent stem-cell-derived gastric organoids. Nature 2014, 516, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spence, J.R.; Mayhew, C.N.; Rankin, S.A.; Kuhar, M.F.; Vallance, J.E.; Tolle, K.; Hoskins, E.E.; Kalinichenko, V.V.; Wells, S.I.; Zorn, A.M.; et al. Directed differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into intestinal tissue in vitro. Nature 2011, 470, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.H.; Nattiv, R.; Dedhia, P.H.; Nagy, M.S.; Chin, A.M.; Thomson, M.; Klein, O.D.; Spence, J.R. In vitro patterning of pluripotent stem cell-derived intestine recapitulates in vivo human development. Development 2017, 144, 1045–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo, M.; Vilar, E.; Tsai, S.Y.; Chang, K.; Amin, S.; Srinivasan, T.; Zhang, T.; Pipalia, N.H.; Chen, H.J.; Witherspoon, M.; et al. Colonic organoids derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells for modeling colorectal cancer and drug testing. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 878–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munera, J.O.; Sundaram, N.; Rankin, S.A.; Hill, D.; Watson, C.; Mahe, M.; Vallance, J.E.; Shroyer, N.F.; Sinagoga, K.L.; Zarzoso-Lacoste, A.; et al. Differentiation of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells into Colonic Organoids via Transient Activation of BMP Signaling. Cell Stem Cell 2017, 21, 51–64.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorn, A.M.; Wells, J.M. Vertebrate endoderm development and organ formation. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2009, 25, 221–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancho, E.; Batlle, E.; Clevers, H. Signaling pathways in intestinal development and cancer. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2004, 20, 695–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyer, A.E.; Huycke, T.R.; Lee, C.; Mahadevan, L.; Tabin, C.J. Bending gradients: How the intestinal stem cell gets its home. Cell 2015, 161, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, K.D.; Whidden, M.; Kolterud, A.; Shoffner, S.K.; Czerwinski, M.J.; Kushwaha, J.; Parmar, N.; Chandhrasekhar, D.; Freddo, A.M.; Schnell, S.; et al. Villification in the mouse: Bmp signals control intestinal villus patterning. Development 2016, 143, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, D.J.; Johnson, R.L.; Burke, A.C.; Nelson, C.E.; Morgan, B.A.; Tabin, C. Sonic Hedgehog Is an Endodermal Signal Inducing Bmp-4 and Hox Genes during Induction and Regionalization of the Chick Hindgut. Development 1995, 121, 3163–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiso, N.; Filippi, A.; Pauls, S.; Bortolussi, M.; Argenton, F. BMP signalling regulates anteroposterior endoderm patterning in zebrafish. Mech. Dev. 2002, 118, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dye, B.R.; Hill, D.R.; Ferguson, M.A.; Tsai, Y.H.; Nagy, M.S.; Dyal, R.; Wells, J.M.; Mayhew, C.N.; Nattiv, R.; Klein, O.D.; et al. In vitro generation of human pluripotent stem cell derived lung organoids. eLife 2015, 4, e05098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noto, F.K.; Determan, M.R.; Cai, J.; Cayo, M.A.; Mallanna, S.K.; Duncan, S.A. Aneuploidy is permissive for hepatocyte-like cell differentiation from human induced pluripotent stem cells. BMC Res. Notes 2014, 7, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munera, J.O.; Wells, J.M. Generation of Gastrointestinal Organoids from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1597, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, C.L.; Mahe, M.M.; Munera, J.; Howell, J.C.; Sundaram, N.; Poling, H.M.; Schweitzer, J.I.; Vallance, J.E.; Mayhew, C.N.; Sun, Y.; et al. An in vivo model of human small intestine using pluripotent stem cells. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 1310–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, N.; Jeffcoat, B.; Maity, P.; Christensen, R.K.; Munera, J.O. Retinoic Acid Promotes the In Vitro Growth, Patterning and Improves the Cellular Composition of Human Pluripotent Stem-Cell-Derived Intestinal Organoids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, F.A.; Hsu, P.D.; Wright, J.; Agarwala, V.; Scott, D.A.; Zhang, F. Genome engineering using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 2281–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunne-Braden, A.; Sullivan, A.; Gharibi, B.; Sheriff, R.S.M.; Maity, A.; Wang, Y.F.; Edwards, A.; Jiang, M.; Howell, M.; Goldstone, R.; et al. GATA3 Mediates a Fast, Irreversible Commitment to BMP4-Driven Differentiation in Human Embryonic Stem Cells. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 26, 693–706.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wills, A.; Dickinson, K.; Khokha, M.; Baker, J.C. Bmp signaling is necessary and sufficient for ventrolateral endoderm specification in Xenopus. Dev. Dyn. Off. Publ. Am. Assoc. Anat. 2008, 237, 2177–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherwood, R.I.; Maehr, R.; Mazzoni, E.O.; Melton, D.A. Wnt signaling specifies and patterns intestinal endoderm. Mech. Dev. 2011, 128, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Jordan, N.; Melton, D.; Grapin-Botton, A. Signals from lateral plate mesoderm instruct endoderm toward a pancreatic fate. Dev. Biol. 2003, 259, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, T.; Xia, K.; Li, Z.; Zhou, B.; Zhu, S.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Z.; Xiao, H.; Han, J.D.; et al. Genome-wide mapping of SMAD target genes reveals the role of BMP signaling in embryonic stem cell fate determination. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, M.L.; Chaturvedi, P.; Rankin, S.A.; Macdonald, M.; Jagannathan, S.; Yukawa, M.; Barski, A.; Zorn, A.M. Genomic integration of Wnt/beta-catenin and BMP/Smad1 signaling coordinates foregut and hindgut transcriptional programs. Development 2017, 144, 1283–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, S.J.; Maretto, S.; Islam, A.; Bikoff, E.K.; Robertson, E.J. Dose-dependent Smad1, Smad5 and Smad8 signaling in the early mouse embryo. Dev. Biol. 2006, 296, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, K.D.; Dunn, N.R.; Robertson, E.J. Mouse embryos lacking Smad1 signals display defects in extra-embryonic tissues and germ cell formation. Development 2001, 128, 3609–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Castilla, L.H.; Xu, X.; Li, C.; Gotay, J.; Weinstein, M.; Liu, P.P.; Deng, C.X. Angiogenesis defects and mesenchymal apoptosis in mice lacking SMAD5. Development 1999, 126, 1571–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Huylebroeck, D.; Verschueren, K.; Guo, Q.; Matzuk, M.M.; Zwijsen, A. Smad5 knockout mice die at mid-gestation due to multiple embryonic and extraembryonic defects. Development 1999, 126, 1631–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.Y.; Wang, H.P.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Sun, Y.H. Transcriptional factors smad1 and smad9 act redundantly to mediate zebrafish ventral specification downstream of smad5. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 6604–6618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orvis, G.D.; Jamin, S.P.; Kwan, K.M.; Mishina, Y.; Kaartinen, V.M.; Huang, S.; Roberts, A.B.; Umans, L.; Huylebroeck, D.; Zwijsen, A.; et al. Functional redundancy of TGF-beta family type I receptors and receptor-Smads in mediating anti-Mullerian hormone-induced Mullerian duct regression in the mouse. Biol. Reprod. 2008, 78, 994–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacroix, B.; Kedinger, M.; Simon-Assmann, P.; Rousset, M.; Zweibaum, A.; Haffen, K. Developmental pattern of brush border enzymes in the human fetal colon. Correlation with some morphogenetic events. Early Hum. Dev. 1984, 9, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raul, F.; Lacroix, B.; Aprahamian, M. Longitudinal distribution of brush border hydrolases and morphological maturation in the intestine of the preterm infant. Early Hum. Dev. 1986, 13, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qu, N.; Daoud, A.; Jeffcoat, B.; Múnera, J.O. SMAD1 Is Dispensable for CDX2 Induction but Required for the Repression of Ectopic Small-Intestinal Gene Expression in Human-Pluripotent-Stem-Cell-Derived Colonic Organoids. Organoids 2023, 2, 192-203. https://doi.org/10.3390/organoids2040015
Qu N, Daoud A, Jeffcoat B, Múnera JO. SMAD1 Is Dispensable for CDX2 Induction but Required for the Repression of Ectopic Small-Intestinal Gene Expression in Human-Pluripotent-Stem-Cell-Derived Colonic Organoids. Organoids. 2023; 2(4):192-203. https://doi.org/10.3390/organoids2040015
Chicago/Turabian StyleQu, Na, Abdelkader Daoud, Braxton Jeffcoat, and Jorge O. Múnera. 2023. "SMAD1 Is Dispensable for CDX2 Induction but Required for the Repression of Ectopic Small-Intestinal Gene Expression in Human-Pluripotent-Stem-Cell-Derived Colonic Organoids" Organoids 2, no. 4: 192-203. https://doi.org/10.3390/organoids2040015
APA StyleQu, N., Daoud, A., Jeffcoat, B., & Múnera, J. O. (2023). SMAD1 Is Dispensable for CDX2 Induction but Required for the Repression of Ectopic Small-Intestinal Gene Expression in Human-Pluripotent-Stem-Cell-Derived Colonic Organoids. Organoids, 2(4), 192-203. https://doi.org/10.3390/organoids2040015




