Prevalence and Management of Phytopathogenic Seed-Borne Fungi of Maize
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Duration
2.2. Maize Seed Varieties
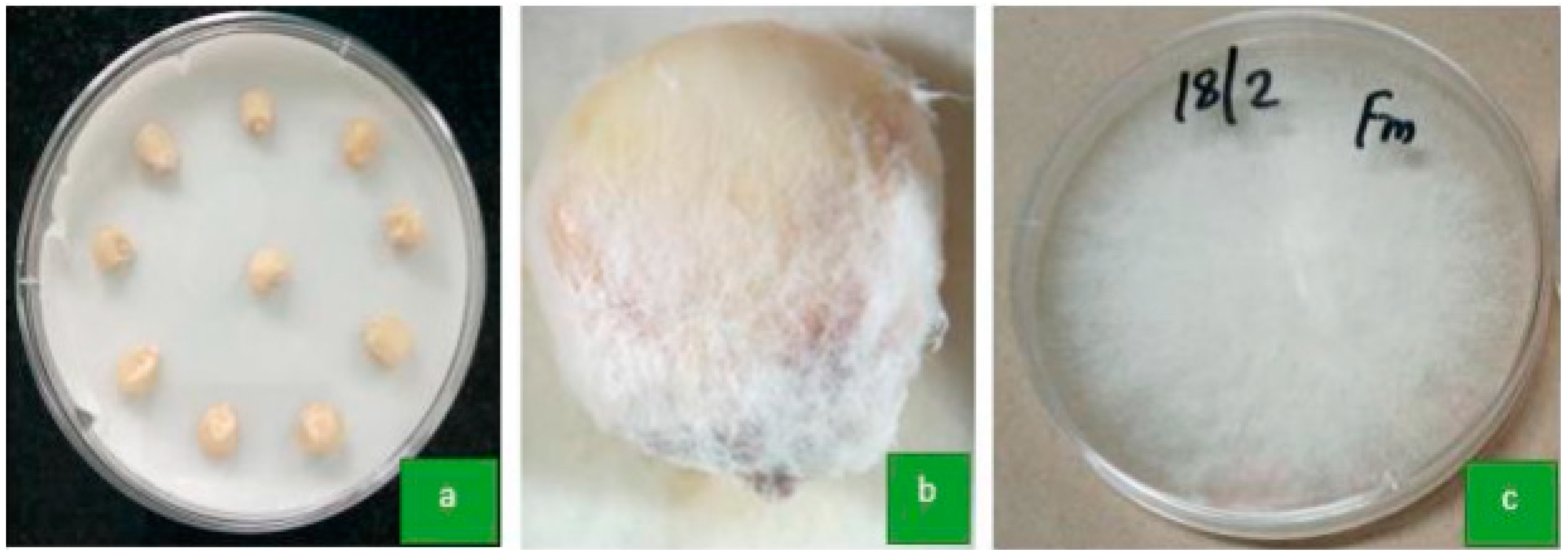
- Experiment 1: Detection and Identification of Seed-Borne Fungi
2.3. Data Collection and Processing
- Experiment 2: Efficacy of Bio-Fungicides on Seed-Borne F. verticillioides under Aseptic Culture
2.4. Preparation of Fungal Inoculum
2.5. Preparation of Bio-Fungicides
2.6. Co-Inoculation of F. verticillioides and Bio-Fungicides In Vitro
- Experiment 3: Efficacy of Bio-Fungicides on F. verticillioides under Screenhouse Conditions
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
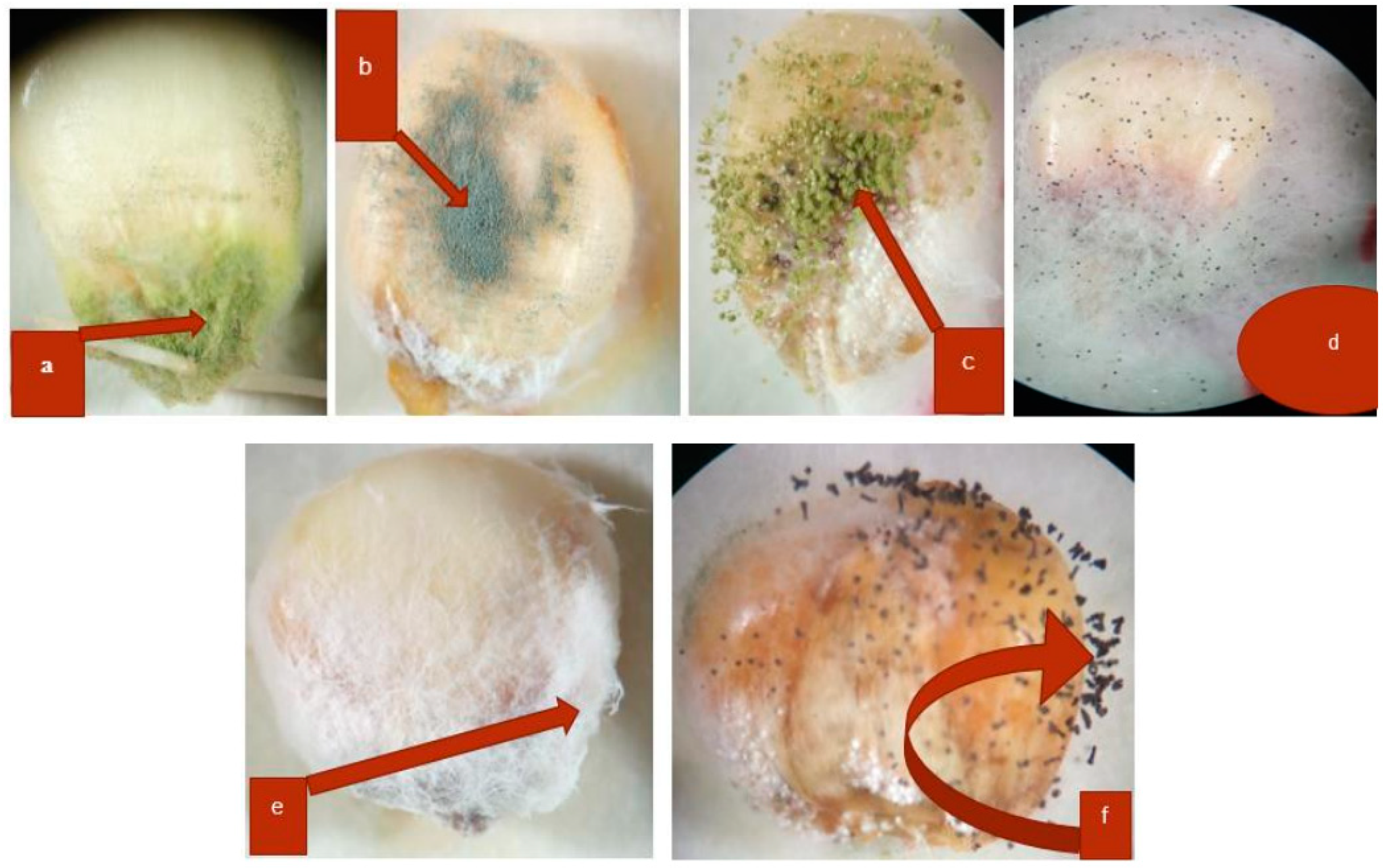
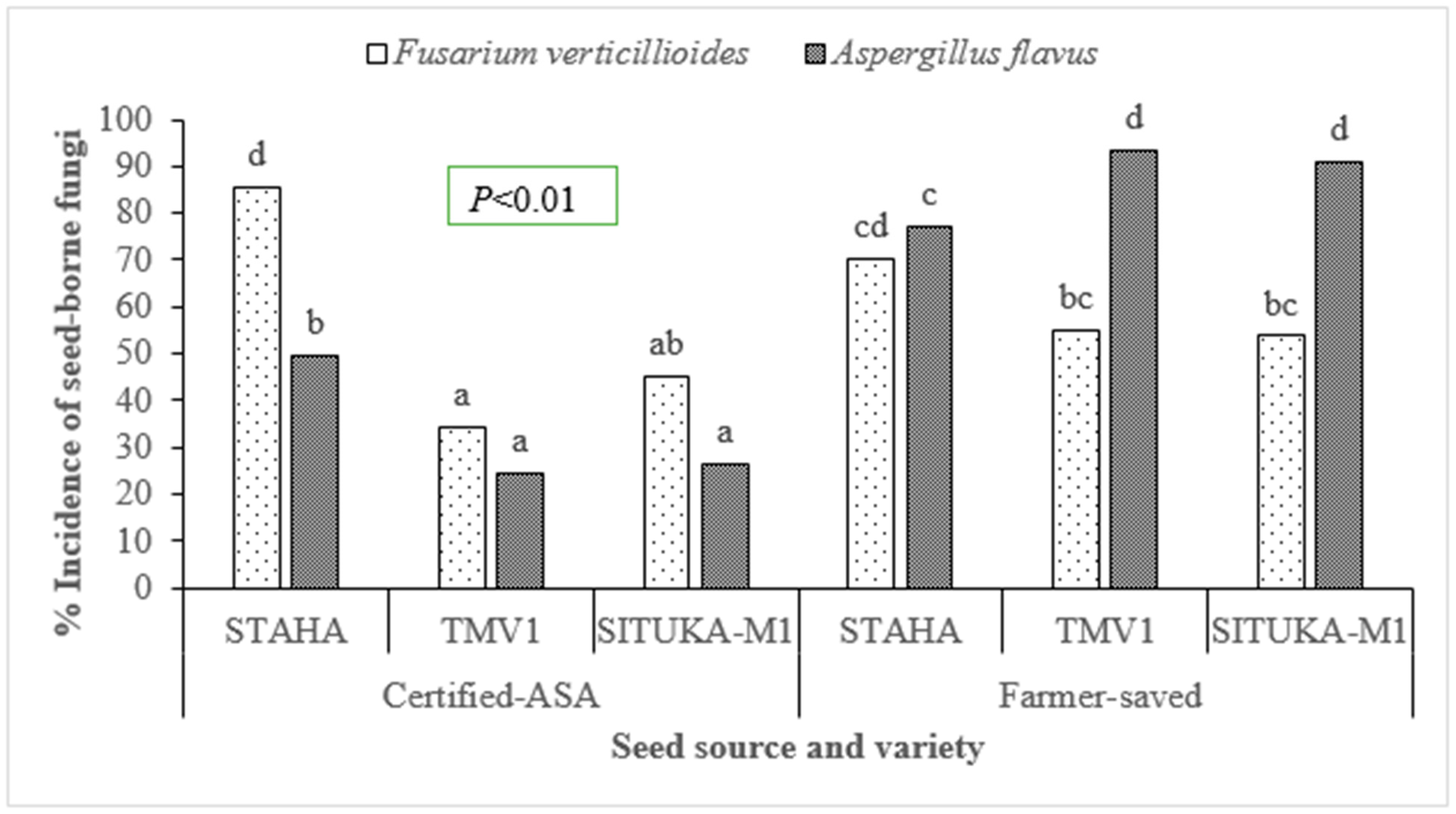
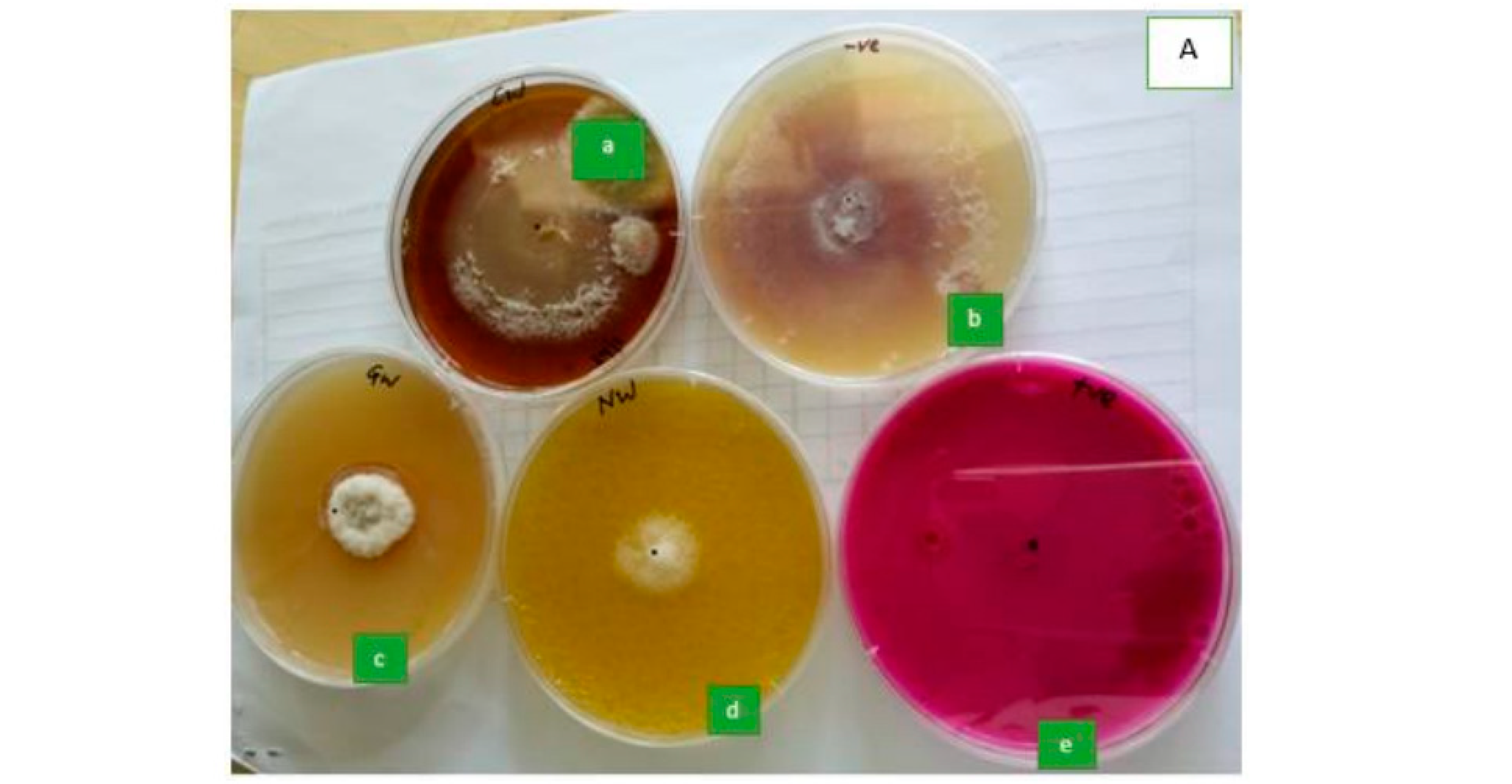
3.1. Identification of Seed-Borne Fungi
3.2. Inhibition of Fungal (F. Verticillioides) Mycelial Growth
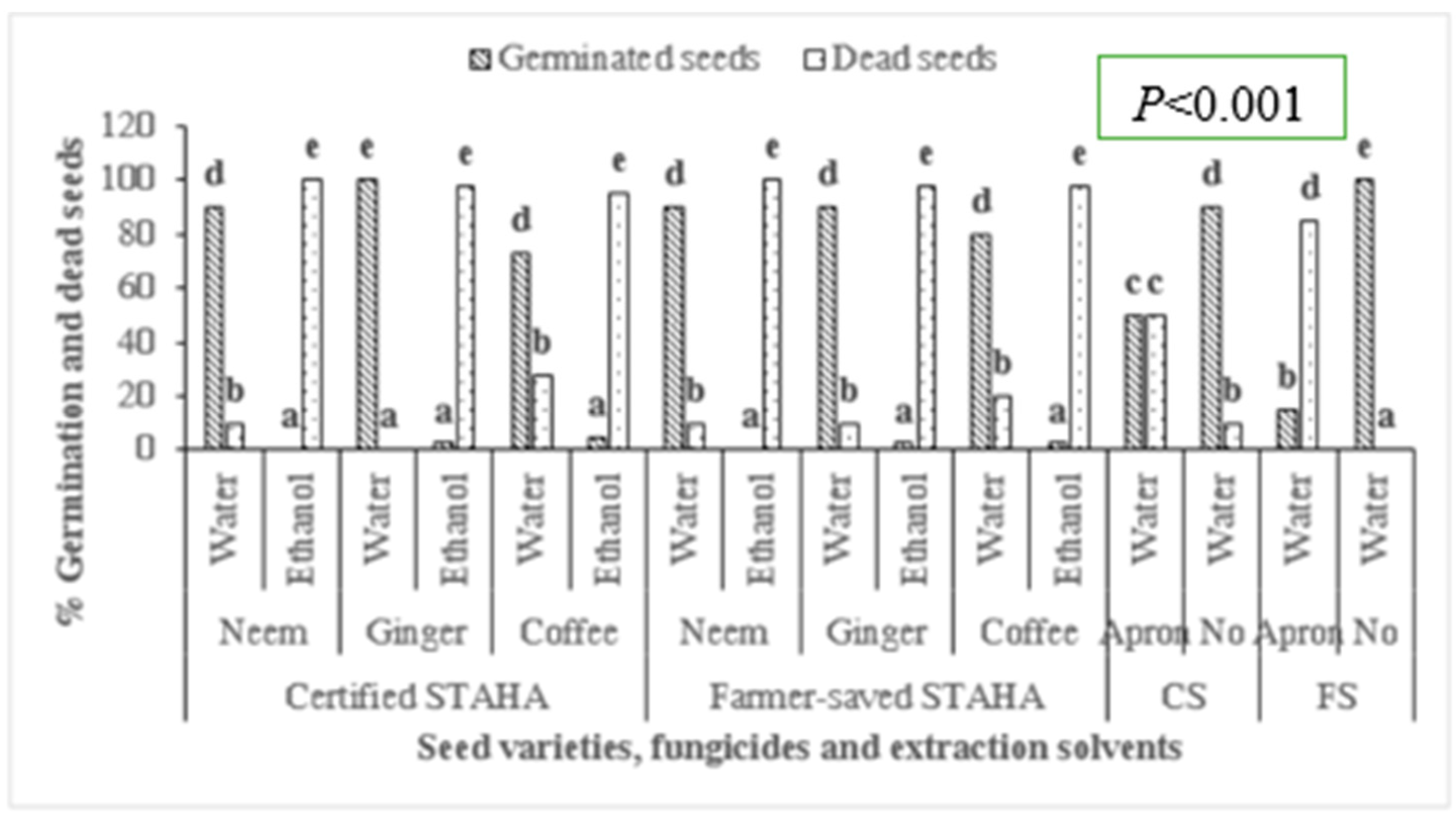
3.3. Seed Germination and Seedling Vigor after Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Recommendation
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Seed Testing Association (ISTA). International Rules for Seed Testing; International Seed Testing Association: Bassersdorf, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Roopa, S.V.; Wadje, S.S. In vivo testing of plant extracts against seed-borne pathogens. Int. Res. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 1, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Etten, J.V.; López Noriega, I.; Fadda, C.; Thomas, E. The contribution of seed systems to crop and tree diversity in sustainable food systems. In Mainstreaming Agrobiodiversity in Sustainable Food Systems: Scientific Foundations for an Agrobiodiversity Index; Bioversity International: Rome, Italy, 2017; pp. 81–101. ISBN 978-92-9255-070-7. [Google Scholar]
- Kansiime, M.K.; Bundi, M.; Nicodemus, J.; Ochieng, J.; Marandu, D.; Njau, S.S.; Romney, D. Assessing sustainability factors of farmer seed production: A case of the Good Seed Initiative project in Tanzania. Agric. Food Secur. 2021, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mghweno, O.N.; Mishili, F.J.; Nchimbi-Msolla, S. Farmers’ Decision to Purchase Quality Declared Seeds in Kongwa District, Tanzania. Tanzan. J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 19, 203–215. [Google Scholar]
- Msuya, D.G.; Stefano, J. Responses of Maize (Zea mays L.) Seed Germination Capacity and Vigour to Seed Selection Based on Size of Cob and Selective Threshing. World J. Agric. Sci. 2010, 6, 683–688. [Google Scholar]
- SAT. Sixth Workshop for Participatory Research Design. 2019. Available online: https://kilimo.org/WordPress/sustainable-agriculture-tanzania-sat/training/research/wprd/ (accessed on 21 September 2020).
- Castellari, C.; Marcos, F.V.; Mutti, J.; Cardoso, L.; Bartosik, R. Toxigenic fungi in Corn (maize) stored in hermetic plastic bags. In Proceedings of the 10th International Working Conference on Stored Product Protection, Estoril, Portugal, 27 June–2 July 2010; National Institute of Agricultural Technologies, Mardel Plata University: Mar del Plata, Argentina, 2010; pp. 115–297. [Google Scholar]
- Gyasi, E.; Kwoseh, C.; Moses, E. Identification of seed-borne fungi of farmer-saved seeds of pepper and their control with some selected botanicals. Ghana J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 55, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, N.; Hussain, A.; Ishtiaq, M.; Azam, S.; Hussain, T. Pathogenicity of two seed-borne fungi commonly involved in maize seeds of eight districts of Azad Jammu and Kashmir, Pakistan. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 12, 1363–1370. [Google Scholar]
- Madege, R.R.; Audenaert, K.; Kimanya, M.; Tiisekwa, B.; De Meulenaer, B.; Bekaert, B.; Haesaert, G. Control of Fusarium verticillioides (Sacc.) Nirenberg and fumonisins by using a combination of crop protection products and fertilization. Toxins 2018, 10, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahender, A.; Anandan, A.; Pradhan, S.K. Early seedling vigor, an imperative trait for direct-seeded rice: An overview on physio-morphological parameters and molecular markers. Planta 2015, 241, 1027–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsedaley, B. Detection and identification of major storage fungal pathogens of maize (Zea mays L.) in Jimma, Southwestern Ethiopia. Eur. J. Agric. For. Res. 2016, 4, 38–49. [Google Scholar]
- Charity, A.; Amienyo, J.; Dauda, T. Effect of relative humidity on spore determination and growth of Aspergillus flavus. Niger. J. Bot. 2010, 23, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Niaz, I.; Dawar, S. Detection of seed-borne mycoflora in maize (Zea mays L.). Pak. J. Bot. 2009, 4, 443–451. [Google Scholar]
- Ismaiel, A.A.; Jutta, P. Mycotoxins: Producing fungi and mechanisms of phytotoxicity. Agriculture 2015, 5, 492–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, F.u.; Adnan, M.; Kalsoom, M.; Naz, N.; Husnain, M.G.; Ilahi, H.; Ahmad, U. Seed-borne fungal diseases of Maize (Zea mays L.): A review. Agrinula J. Agroteknologi Dan Perkeb. 2021, 4, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, J.; Mabagala, R.B.; Mamiro, D.P. Efficacy of selected plant extracts against Pyricularia grisea, the causal agent of rice blast disease. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbega, E.R.; Mortensen, C.N.; Mabagala, R.B.; Wulff, E.G. The effect of plant extracts as seed treatments to control bacterial leaf spot of tomato in Tanzania. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2012, 78, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, M.; Sultana, A.; Rashid, A.Q.M.B. Effect of seed-borne fungi on the germinating seeds and their bio-control in Maize. J. Environ. Sci. Nat. Resour. 2012, 5, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelló, A.; Gruhlke, M.; Slusarenko, A.J. Effect of garlic extract on seed germination, seedling health, and vigor of pathogen-infested wheat. J. Plant Prot. Res. 2013, 53, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amadioha, A.C. Controlling Rice Blast In Vitro and In Vivo with Extracts of Azadirachta indica. J. Crop Prot. 2000, 19, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, N.K.; Mojumdar, A.; Chatterje, S.K.; Banerjee, A.; Datta, J.K.; Gupta, S. Antifungal activities and chemical characterization of Neem leaf extracts on the growth of some selected fungal species in vitro culture medium. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag. 2009, 13, 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Luzi-Kihupi, A.; Kashenge-Killenga, S.; Bonsi, C. A review of maize, rice, tomato, and banana research in Tanzania. Tanzan. J. Agric. Sci. 2015, 14, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Mathur, S.B.; Kongsdal, O. Common Laboratory Seed Health Testing Methods for Detecting Fungi; International Seed Testing Association (ISTA): Bassersdorf, Switzerland, 2003; p. 89. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.Y.; Qi, Y.L.; Cai, L. Induction of sporulation in plant pathogenic fungi. Mycology 2012, 3, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasas, W.F.O.; Burgess, L.W.; Anelich, R.Y.; Lamprecht, S.C.; van Schalkwyk, D.J. Survey of Fusarium species associated with plant debris in South African soils. S. Afr. J. Bot. 1988, 54, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, S.B.; Kongsdal, O. Common Laboratory Seed Healthy Testing Methods for Detecting Fungi, 2nd ed.; International Seed Testing Association (ISTA): Bassersdorf, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Akinbode, O.A.; Ikotun, T. Evaluation of Some Bio-Agents and Botanicals in in Vitro Control of Colletotrichuwm destructivum. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 7, 868–872. [Google Scholar]
- Mamiro, D.P.; Royse, D.J. Laboratory Efficacy of Selected Fungicides and Rhododendron catawbiense Leaf Extracts on the Growth of Vericillium fungicola. Acta Edulis Fungi 2004, 12, 390–396. [Google Scholar]
- Nduagu, C.; Ekefan, E.J.; Nwankiti, A.O. Effect of Some Crude Plant Extracts on Growth of Colletotrichum capsici (Synd) Butler and Bisby, Causal Agent of Pepper Anthracnose. J. Appl. Biosci. 2008, 6, 184–190. [Google Scholar]
- Rauha, J.P.; Remes, S.; Heinonen, M.; Hopia, A.; Kahkonen, M.; Kujala, T.; Pihlaja, K.; Vuorela, H.; Vuorela, P. Antimicrobial effects of Finnish plant extracts containing flavonoids and other phenolic compounds. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2000, 56, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zida, E.P.; Sereme, P.; Leth, V.; Sankara, P. Effect of Acacia gourmaensis A. Chev and Eclipta alba (L.) Hassk. on Seed Health, Seedling Vigour and Grain Yield of Sorghum and Pearl Millet. Asian J. Plant Pathol. 2008, 2, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degraeve, S.; Madege, R.R.; Audenaert, K.; Kamala, A.; Ortiz, J.; Kimanya, M.; Haesaert, G. Impact of local pre-harvest management practices in maize on the occurrence of Fusarium species and associated mycotoxins in two agro-ecosystems in Tanzania. Food Control 2016, 59, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagtap, G.P.; Dhavale, M.C.; Dey, U. Evaluation of natural plant extracts, antagonists and fungicides in controlling root rot, collar rot, fruit (brown) rot and gummosis of citrus caused by Phytophthora spp.. in vitro. Sci. J. Microbiol. 2012, 1, 27–47. [Google Scholar]
- Kamalakannan, A.; Shanmugam, V. Controlling Downy Mildew of Maize Caused by Peronosclerospora sorghi by Prosopis chilensis, Azadirachta indica and Foliar Sprays of a Talc-Based Formulation of a Pseudomonas fluorescens. Plant Pathol. 2005, 18, 115–118. [Google Scholar]
- Harlapur, S.I.; Kulkarni, M.S.; Wali, M.C.; Kulkarni, S. Evaluation of Plant Extracts, Bio-Agents and Fungicides against Exserohilum turcicum (Pass.) Leonard and Suggs. Causing Turcicum Leaf Blight of Maize. J. Agric. Sci. 2007, 20, 541–544. [Google Scholar]
- Ogbebor, N.; Adekunle, A.T. Inhibition of Conidial Germination and Mycelial Growth of Corynespora cassiicola (Berk and Curt) of Rubber (Hevea Brasiliensis Muell. Arg.) Using Extracts of Some Plants. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2005, 4, 996–1000. [Google Scholar]
- Namai, T.; Ehara, Y. Studies on Variation in Virulence of Rice Blast Fungus, Pyricularia oryzae Cavara. J. Agric. Res. 1986, 36, 3–4. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez, K.A.; Gomez, A.A. Statistical Procedures for Agricultural Research; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1984; pp. 298–308. [Google Scholar]
- Quezada, M.Y.; Moreno, J.; Vázquez, M.E.; Mendoza, M.; Méndez-Albores, A.; Moreno-Martínez, E. Hermetic storage system preventing the proliferation of Prostephanus truncatus Horn and storage fungi in maize with different moisture contents. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2006, 39, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godefroid, S.; Van de Vyver, A.; Vanderborght, T. Germination capacity and viability of threatened species collections in seed banks. Biodivers. Conserv. 2010, 19, 1365–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmachari, G. Neem-An Omnipotent Plant: A Retrospection. ChemBioChem 2004, 5, 408–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemzadeh, A.; Jaafar, H.Z.; Rahmat, A. Synthesis of phenolics and flavonoids in ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) and their effects on the photosynthesis rate. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 4539–4555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keta, J.N.; Suberu, H.A.; Shehu, K.; Yahayya, U.; Mohammad, N.K.; Gudu, G.B. Effect of neem (Azadirachta indica A. Juss) leaf extract on the growth of Aspergillus species isolated from foliar diseases of rice (Oryza sativa). Sci. World J. 2019, 14, 98–102. [Google Scholar]
- Mahapatra, S.; Karnes, R.J.; Holmes, M.W.; Young, C.Y.; Cheville, J.C.; Kohli, M.; Klee, E.W.; Tindall, D.J.; Donkena, K.V. Novel Molecular targets of A. indica associated with inhibition of tumor growth in prostate cancer. Am. Assoc. Pharm. Sci. J. 2014, 13, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usharani, K.V. Neem as an organic plant protectant in agriculture. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2019, 8, 4176–4184. [Google Scholar]
- Hallsworth, J.E.; Nomura, Y.; Iwahara, M. Ethanol-induced water stress, and fungal growth. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 1998, 86, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Seed Types × Fungicides × Extraction Solvents (A × B × C) | Shoot Length (cm) | Shoot Weight (g) |
| Certified STAHA × neem × water | 17.1 cd | 8 ef |
| Certified STAHA × neem × ethanol | 0 a | 0.00 a |
| Certified STAHA × ginger × water | 18.38 cd | 10 ef |
| Certified STAHA × ginger × ethanol | 1.5 a | 0.2 a |
| Certified STAHA × coffee × water | 14.28 cd | 4 d |
| Certified STAHA × coffee × ethanol | 3.6 ab | 0.425 ab |
| Farmer-saved STAHA × neem × water | 20.2 cd | 10 ef |
| Farmer-saved STAHA × neem × ethanol | 0 a | 0.00 a |
| Farmer-saved STAHA × ginger × water | 21.2 d | 11 f |
| Farmer-saved STAHA × ginger × ethanol | 2.75 a | 0.325 ab |
| Farmer-saved STAHA × coffee × water | 19.1 cd | 7 e |
| Farmer-saved STAHA × coffee × ethanol | 1.28 a | 0.125 a |
| Certified STAHA × Apron Star® 42 WS | 7.3 bc | 1.5 c |
| Certified STAHA × water | 19.15 cd | 10 ef |
| Farmer-saved STAHA × Apron Star® 42 WS | 9 bcd | 0.85 bc |
| Farmer-saved STAHA × water | 17.65 cd | 9 ef |
| F-value | 0.641 | 0.025 |
| Sum of squares | 0.894 | 0.635 |
| Mean sum of squares | 0.298 | 0.212 |
| CV | 2.1 | 1.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Erasto, R.; Kilasi, N.; Madege, R.R. Prevalence and Management of Phytopathogenic Seed-Borne Fungi of Maize. Seeds 2023, 2, 30-42. https://doi.org/10.3390/seeds2010003
Erasto R, Kilasi N, Madege RR. Prevalence and Management of Phytopathogenic Seed-Borne Fungi of Maize. Seeds. 2023; 2(1):30-42. https://doi.org/10.3390/seeds2010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleErasto, Rehema, Newton Kilasi, and Richard Raphael Madege. 2023. "Prevalence and Management of Phytopathogenic Seed-Borne Fungi of Maize" Seeds 2, no. 1: 30-42. https://doi.org/10.3390/seeds2010003
APA StyleErasto, R., Kilasi, N., & Madege, R. R. (2023). Prevalence and Management of Phytopathogenic Seed-Borne Fungi of Maize. Seeds, 2(1), 30-42. https://doi.org/10.3390/seeds2010003






