An Overview of High-Entropy Alloys Prepared by Mechanical Alloying Followed by the Characterization of Their Microstructure and Various Properties
Abstract
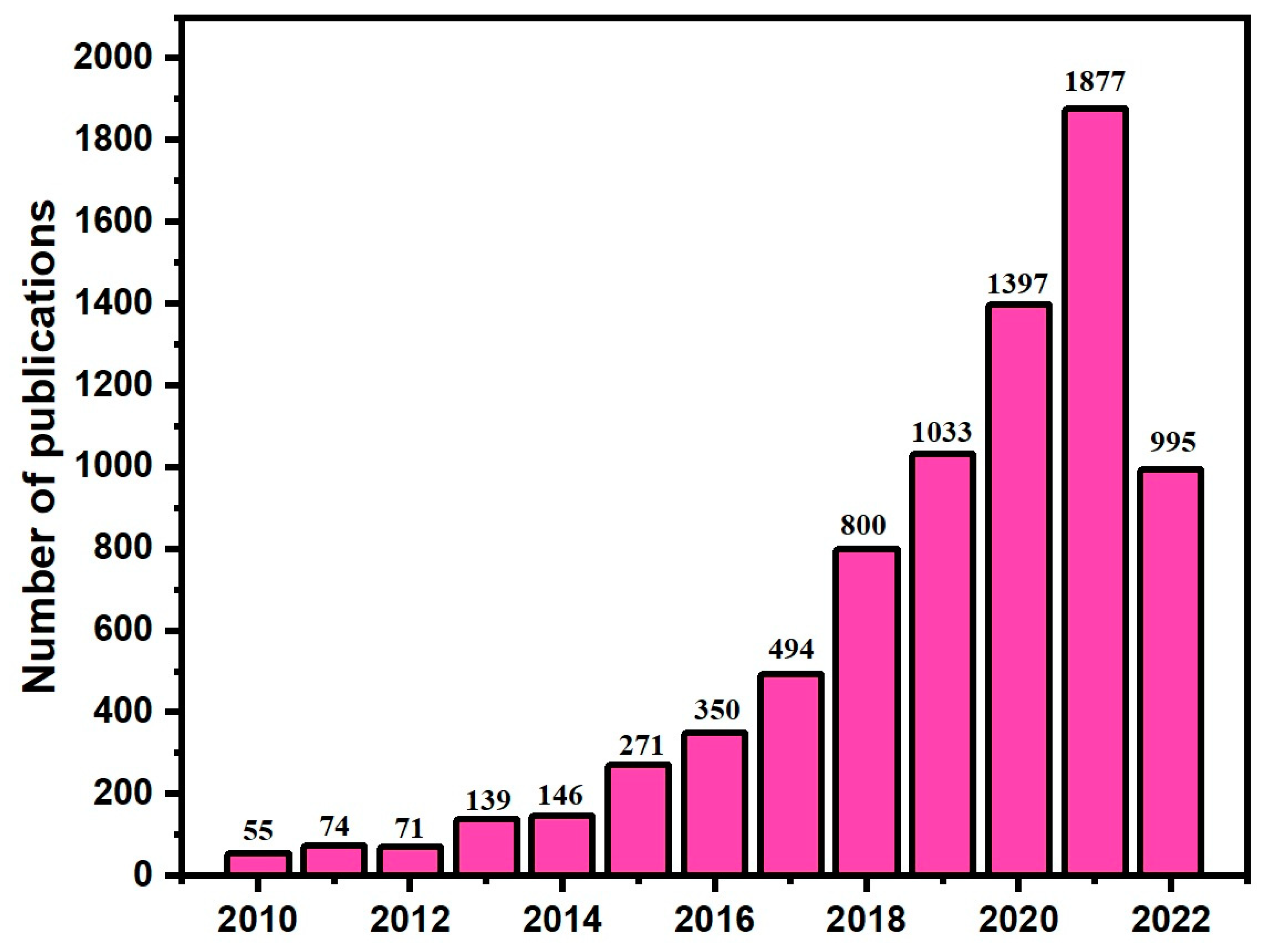
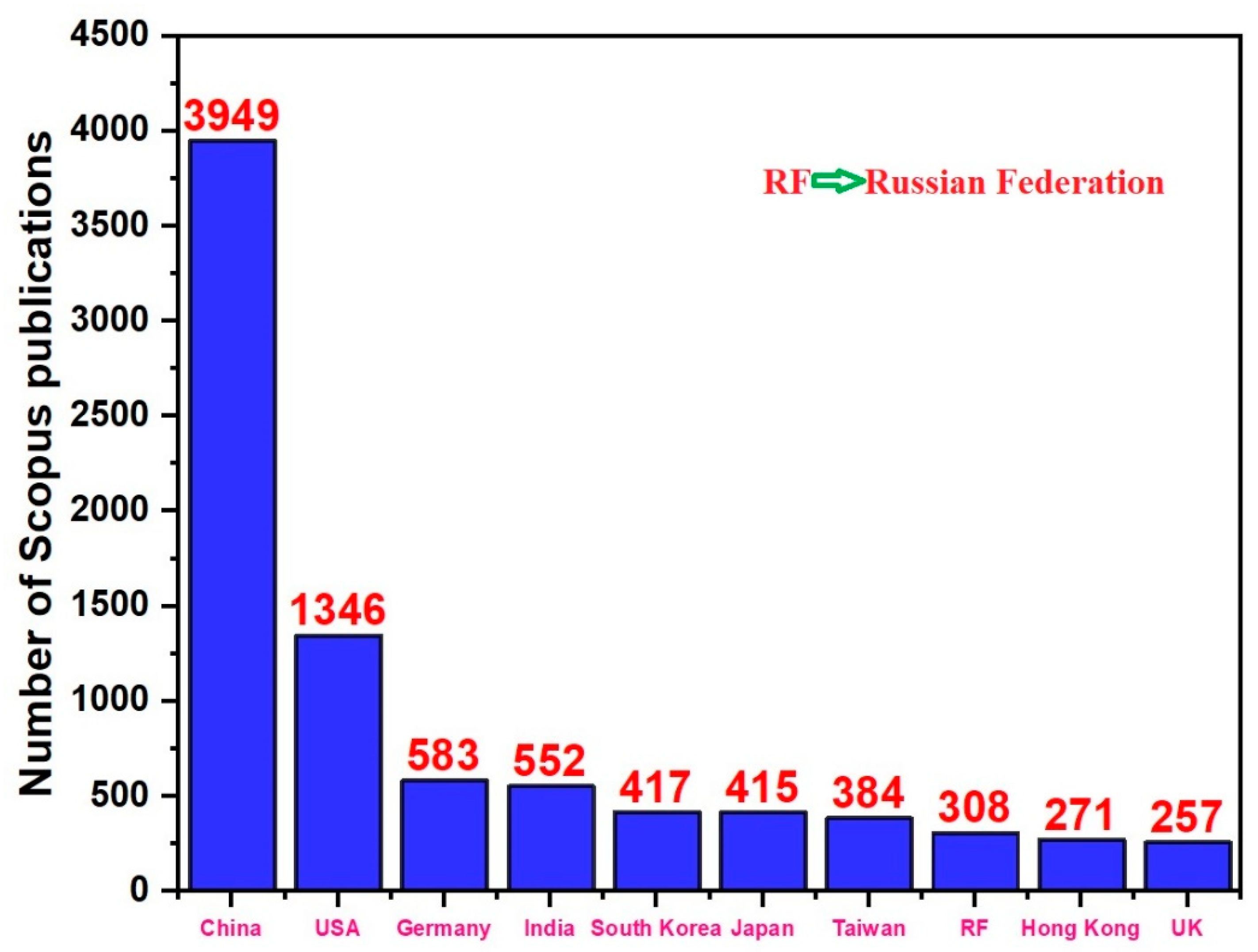
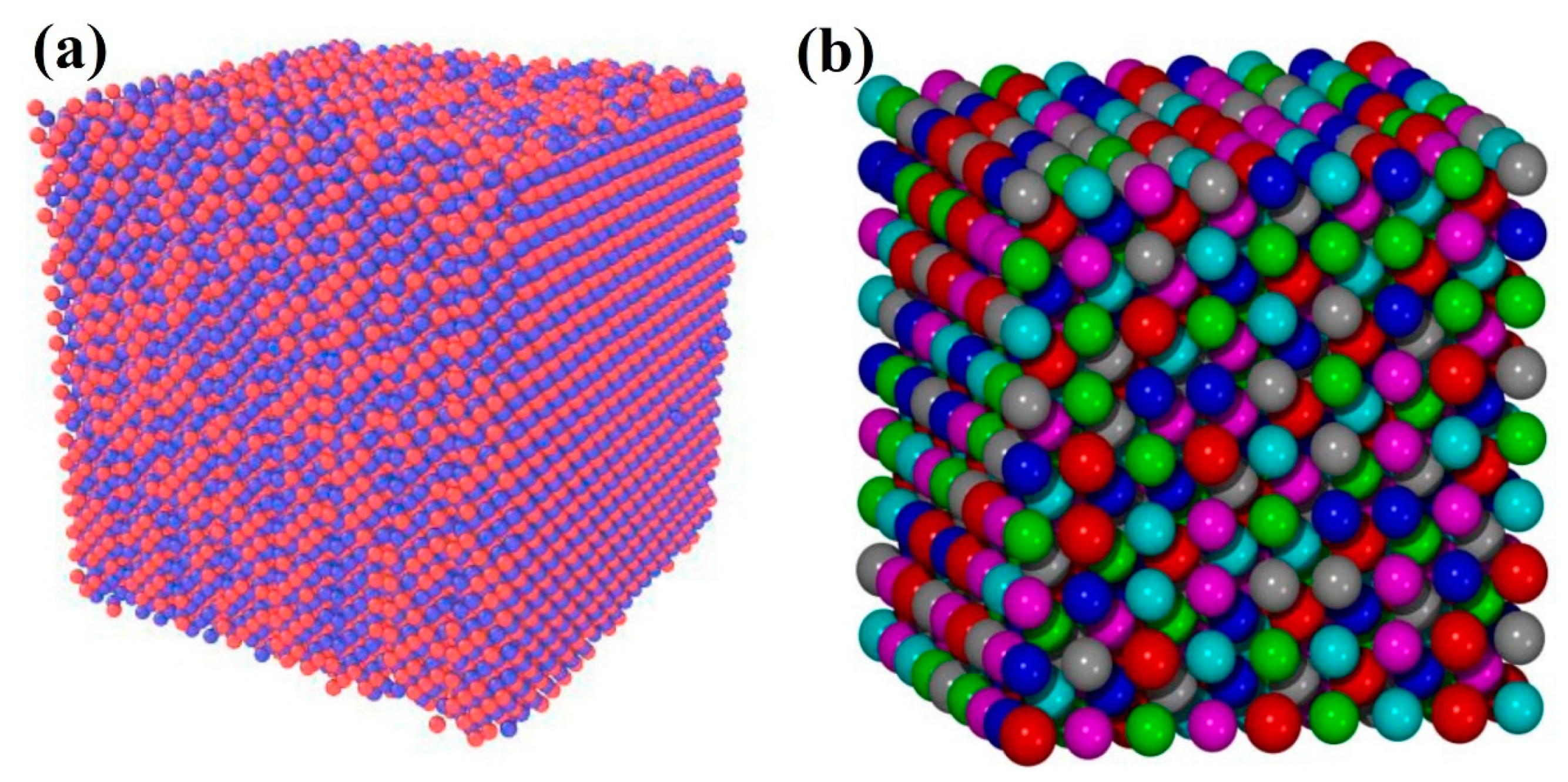
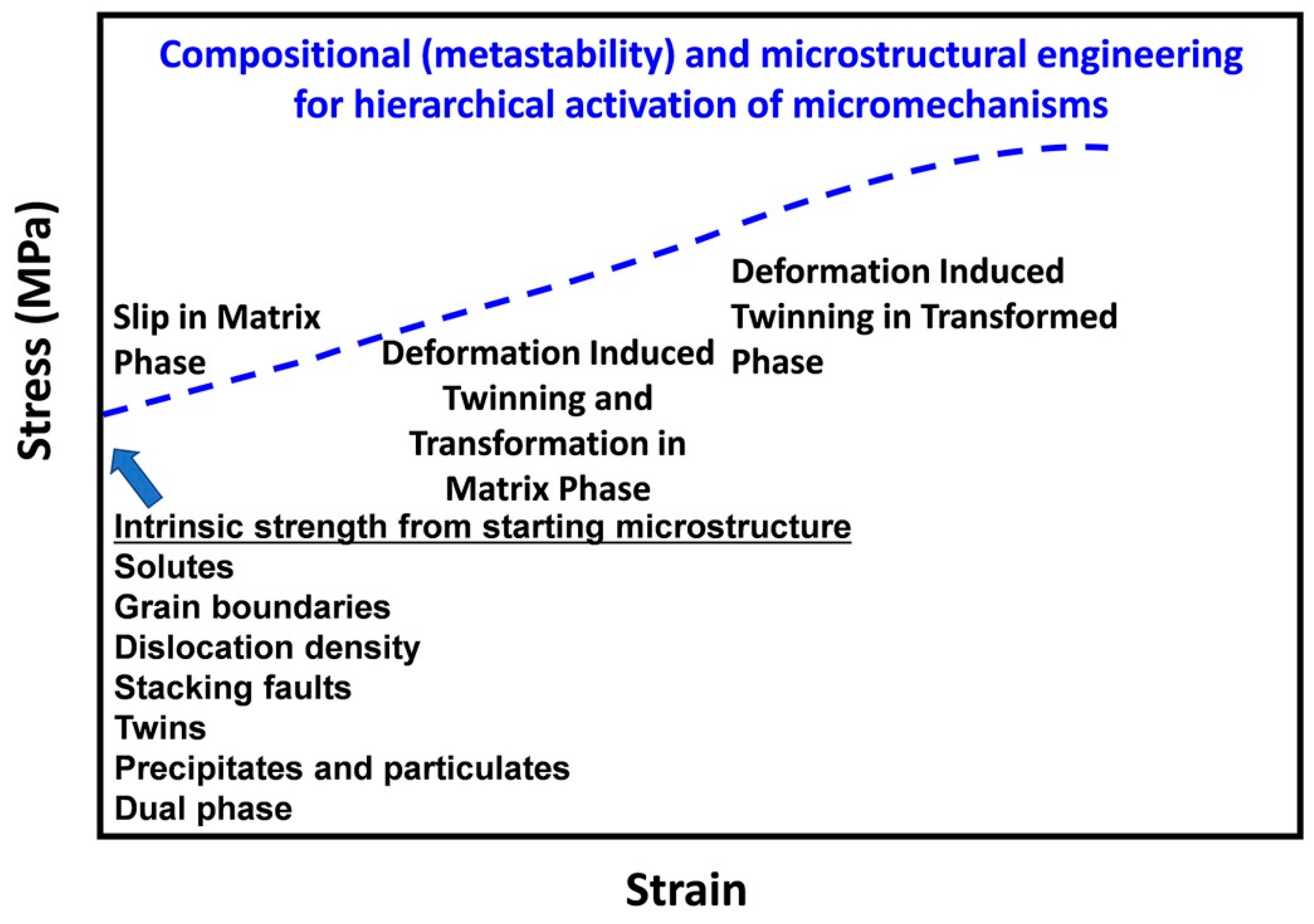
:1. Introduction
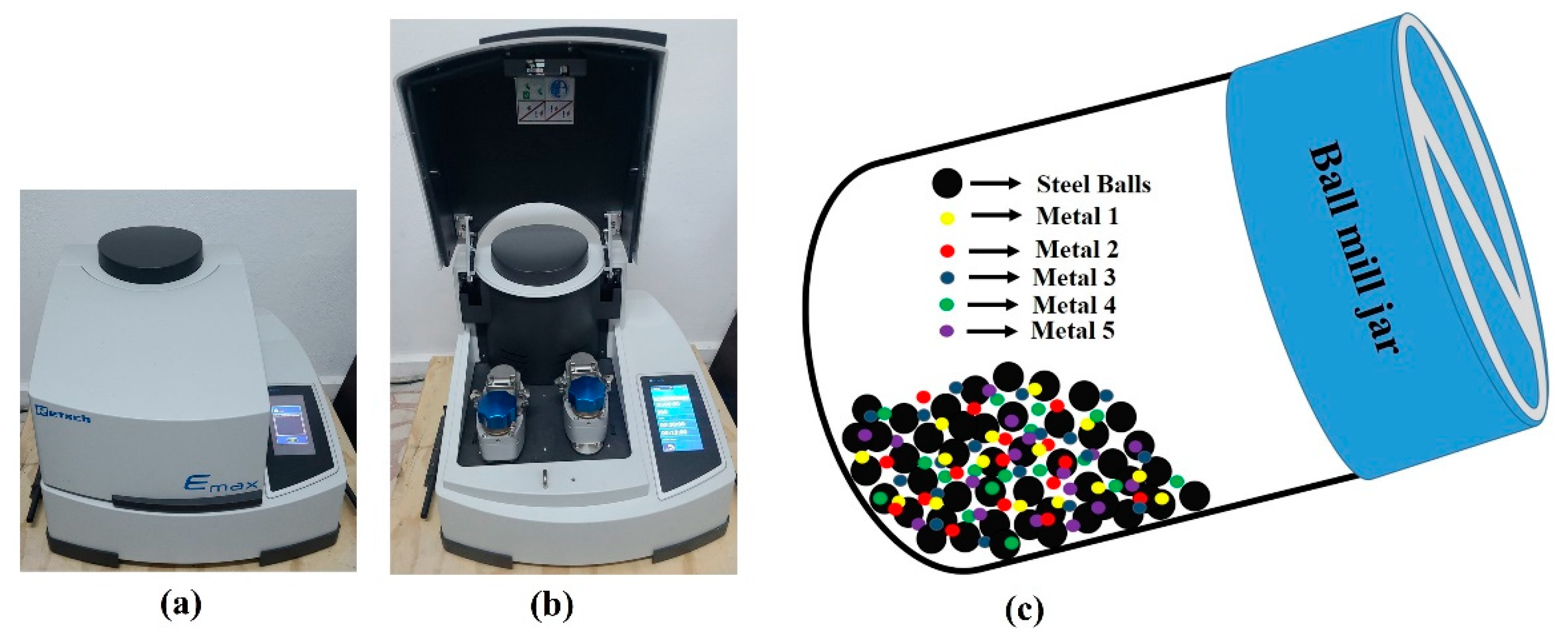
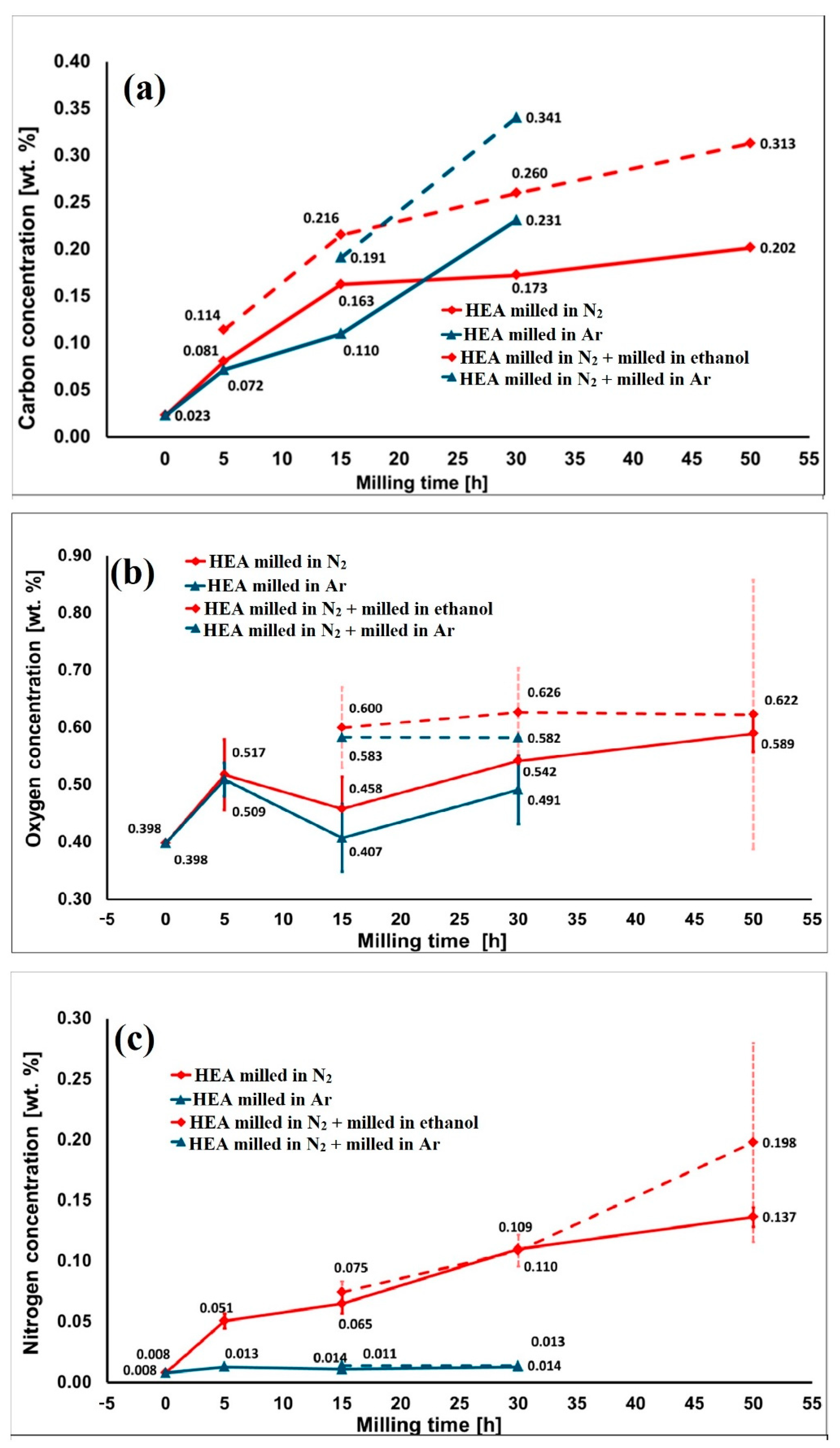
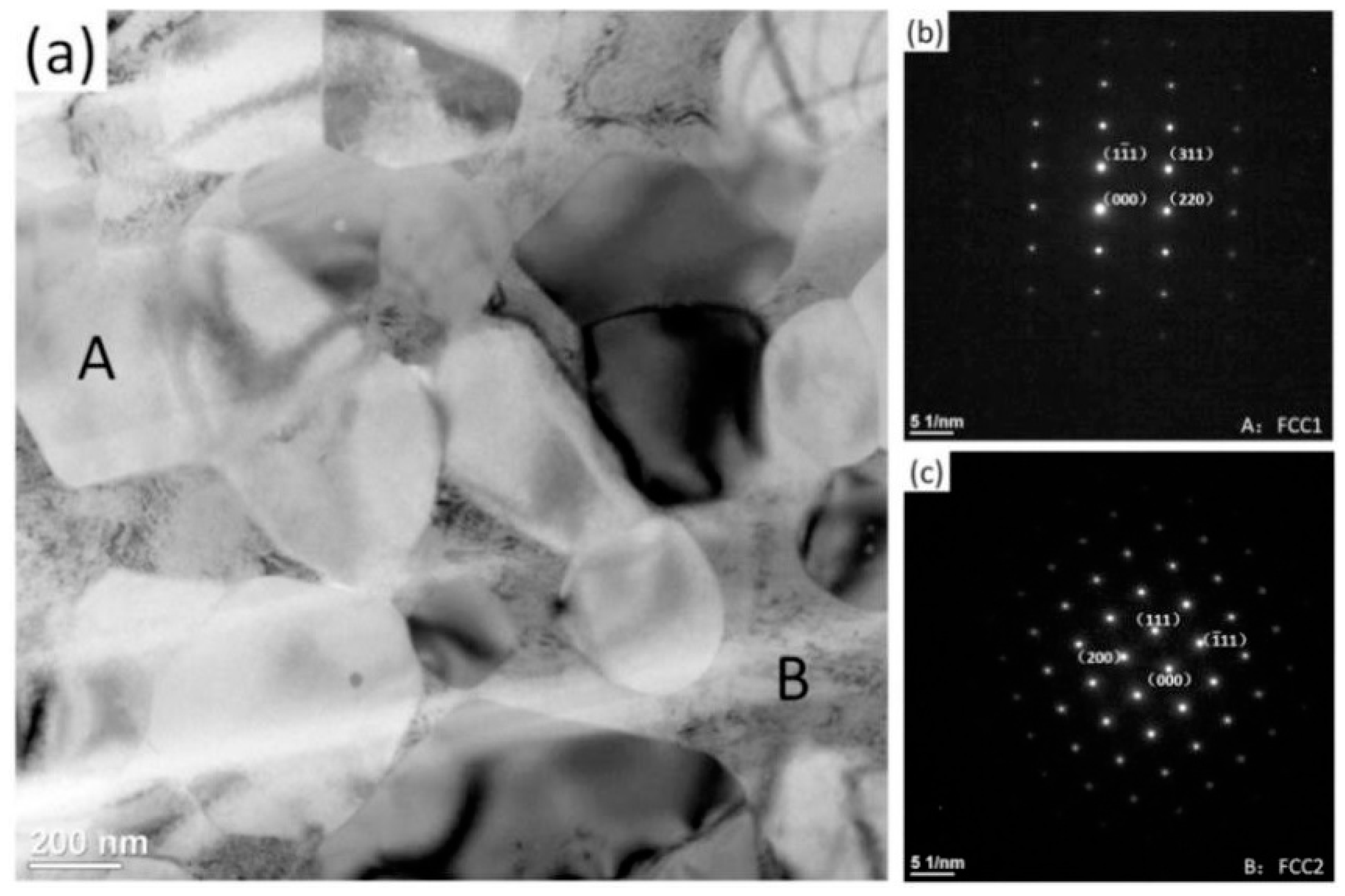
2. Preparation of HEAs by Mechanical Alloying
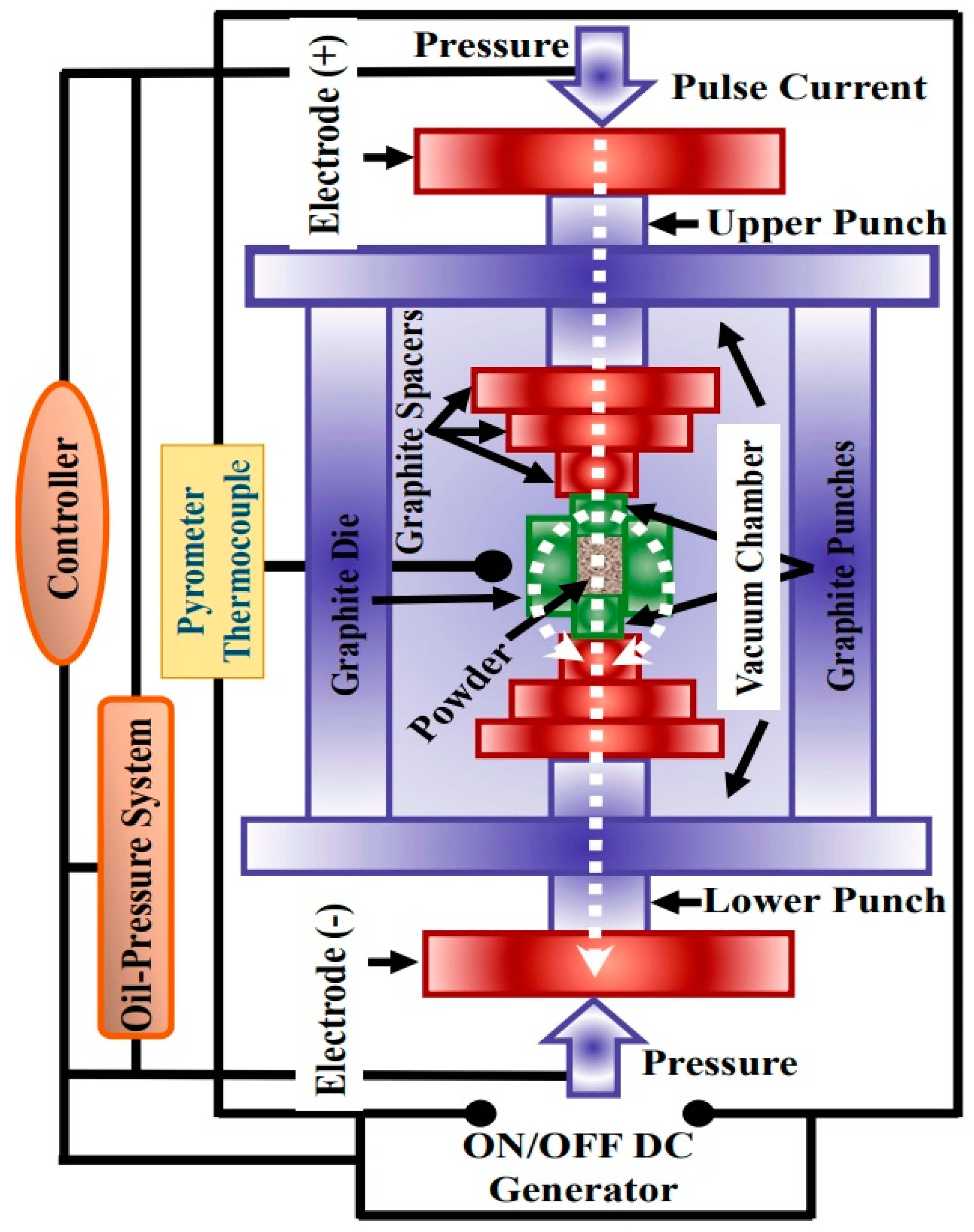
3. Spark Plasma Sintering of Various HEAs
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ding, J.; Xu, H.; Li, X.; Liu, M.; Zhang, T. The similarity of elements in multi-principle element alloys based on a new criterion for phase constitution. Mater. Des. 2021, 207, 109849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.; Senadeera, M.; Chao, Q.; Rana, S.; Gupta, S. Computational design of thermally stable and precipitation-hardened Al-Co-Cr-Fe-Ni-Ti high entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 888, 161496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.W. Overview of High-Entropy Alloys, High-Entropy Alloys, Fundamentals and Applications; Gao, M.C., Yeh, J.W., Liaw, P.K., Zhang, Y., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Liaw, P.K.; Zhang, Y. Preparation of Bulk TiZrNbMoV and NbTiAlTaV High-Entropy Alloys by Powder Sintering. Metals 2021, 11, 1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.J.; Gan, J.Y.; Chin, T.S.; Shun, T.T.; Tsau, C.H.; Chang, S.Y. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: Novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, B.; Chang, I.T.H.; Knight, P.; Vincent, A.J.B. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 375–377, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Zhou, X.; Meng, Q. Atomic-Scale Mechanism Investigation of Mass Transfer in Laser Fabrication Process of Ti-Al Alloy via Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Metals 2020, 10, 1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. Atomic Structure Modeling of Multi-Principal-Element Alloys by the Principle of Maximum Entropy. Entropy 2013, 15, 5536–5548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Díaz-del-Castilloa, P.E.J.; Fu, H. Strengthening mechanisms in high-entropy alloys: Perspectives for alloy design. J. Mater. Res. 2018, 33, 2970–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.S.; Haridas, R.S.; Agrawal, P. High entropy alloys—Tunability of deformation mechanisms through integration of compositional and microstructural domains. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 812, 141085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joele, M.; Matizamhuka, W.R. A Review on the High Temperature Strengthening Mechanisms of High Entropy Superalloys (HESA). Materials 2021, 14, 5835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moravcikova-Gouvea, L.; Moravcik, I.; Pouchly, V.; Kovacova, Z.; Kitzmantel, M.; Neubauer, E.; Dlouhy, I. Tailoring a Refractory High Entropy Alloy by Powder Metallurgy Process Optimization. Materials 2021, 14, 5796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moravcikova-Gouveaa, L.; Moravcika, I.; Omastab, M.; Veselýc, J.; Cizeka, J.; Minárikc, P.; Cupera, J.; Záděrab, A.; Jana, V.; Dlouhy, I. High-strength Al0.2Co1.5CrFeNi1.5Ti high-entropy alloy produced by powder metallurgy and casting: A comparison of microstructures, mechanical and tribological properties. Mat. Charact. 2020, 159, 110046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.S. Four Outstanding Researchers in Metallurgical History; American Society for Testing and Materials: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zuo, T.T.; Zhi, T.; Gao, M.C.; Dahmen, K.A.; Liaw, P.K.; Lu, Z.P. Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2014, 61, 1–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Ma, H.; Spolenak, R. Ultrastrong ductile and stable high-entropy alloys at small scales. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, C.Z.; Zhang, P.; Liu, M.; Li, G.R.; Ye, J.Q.; Liu, P.; Tong, Y.X. Electrochemical preparation and magnetic study of Bi–Fe–Co–Ni–Mn high-entropy alloy. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 8359–8365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, K.M.; Zaddach, A.J.; Niu, C.; Irving, D.L.; Koch, C.C. A Novel Low-Density, High-Hardness, High-entropy Alloy with Close-packed Single-phase Nanocrystalline Structures. Mater. Res. Lett. 2014, 3, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, J.; Weimin, W.; Hao, W.; Jinyong, Z.; Yucheng, W.; Fan, Z.; Zhengyi, F. Alloying behavior and novel properties of CoCrFeNiMn high-entropy alloy fabricated by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. Intermetallics 2015, 56, 24–27. [Google Scholar]
- Nayak, A.K.; Shashanka, R.; Chaira, D. Effect of Nanosize Yittria and Tungsten Addition to Duplex Stainless Steel During High Energy Planetary Milling. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 115, 012008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Esparza, C.D.; Baldenebro-López, F.; González Rodelas, L.; Baldenebro-López, J.; Martínez-Sánchez, R. Series of nanocrystalline NiCoAlFe(Cr, Cu, Mo, Ti) highentropy alloys produced by mechanical alloying. Mater. Res. 2016, 19, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Li, P.; Xi, S.; Zhou, Y.; Li, S.; Yang, X. A new type of high entropy alloy composite Fe18Ni23Co25Cr21Mo8WNb3C2 prepared by mechanical alloying and hot pressing sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 2018, 728, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, M.; Muralikrishna, G.M.; Murty, B.S. High-entropy alloys by mechanical alloying: A review. J. Mater. Res. 2019, 34, 664–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashanka, R. Effect of Sintering Temperature on the Pitting Corrosion of Ball Milled Duplex Stainless Steel by using Linear Sweep Voltammetry. Anal. Bioanal. Electrochem. 2018, 10, 349–361. [Google Scholar]
- Shashanka, R.; Uzun, O.; Chaira, D. Synthesis of nano-structured duplex and ferritic stainless steel powders by dry milling and its comparison with wet milling. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2020, 65, 5–14. [Google Scholar]
- Shashanka, R.; Chaira, D. Phase transformation and microstructure study of nano-structured austenitic and ferritic stainless steel powders prepared by planetary milling. Powder. Technol. 2014, 259, 125–136. [Google Scholar]
- Varalakshmi, S.; Kamaraj, M.; Murty, B.S. Synthesis and characterization of nanocrystalline AlFeTiCrZnCu high entropy solid solution by mechanical alloying. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 460, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Su, K.; Zhang, J.; Liang, X.; Peng, H.; Li, X. Enhanced Strength of a Mechanical Alloyed NbMoTaWVTi Refractory High Entropy Alloy. Materials 2018, 11, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaidya, M.; Karati, A.; Marshal, A.; Pradeep, K.G.; Murty, B.S. Phase evolution and stability of nanocrystalline CoCrFeNi and CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 770, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moravcik, I.; Kubicek, A.; Moravcikova-Gouvea, L.; Adam, O.; Kana, V.; Pouchly, V.; Zadera, A.; Dlouhy, I. The Origins of High-Entropy Alloy Contamination Induced by Mechanical Alloying and Sintering. Metals 2020, 10, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geambazu, L.E.; Cotrut, C.M.; Miculescu, F.; Csaki, I. Mechanically Alloyed CoCrFeNiMo0.85 High-Entropy Alloy for Corrosion Resistance Coatings. Materials 2021, 14, 3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Wu, H.; Zhou, R.; Zhang, N.; Yin, Y.; Liang, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Shan, Q.; Li, Q.; et al. Microstructures and Tribological Properties of TiC Reinforced FeCoNiCuAl High-Entropy Alloy at Normal and Elevated Temperature. Metals 2020, 10, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Ke, B.; Li, Y.; Yang, K.; Yang, M.; Ji, W.; Fu, Z. Phases, Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of CoCrNiCuZn High-Entropy Alloy Prepared by Mechanical Alloying and Spark Plasma Sintering. Entropy 2019, 21, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fourmont, A.; Gallet, S.L.; Politano, O.; Desgranges, C.; Baras, F. Effects of planetary ball milling on AlCoCrFeNi high entropy alloys prepared by Spark Plasma Sintering: Experiments and molecular dynamics study. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 820, 153448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Dai, T.; Lu, T.; Ni, X.; Dai, J.; Li, M. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Nb25Mo25Ta25W25 and Ti8Nb23Mo23Ta23W23 high entropy alloys prepared by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 738, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.R.; Zhang, G.P.; Zhi, Q.; Liu, Z.X. Effects of milling on the microstructure and hardness of Al2NbTi3V2Zr high entropy alloy. Mater. Des. 2016, 109, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashanka, R.; Chaira, D.; Chakravarty, D. Fabrication of Nano-Yttria Dispersed Duplex and Ferritic Stainless Steels by Planetary Milling Followed by Spark Plasma Sintering and Non-Lubricated Sliding Wear Behaviour Study. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2016, 6, 111–125. [Google Scholar]
- Shashanka, R.; Chaira, D.; Kumara Swamy, B.E. Effect of Y2O3 nanoparticles on corrosion study of spark plasma sintered duplex and ferritic stainless steel samples by linear sweep voltammetric method. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2018, 63, 749–763. [Google Scholar]
- Shashanka, R. Non-lubricated dry sliding wear behavior of spark plasma sintered nano-structured stainless steel. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2019, 10, 767–777. [Google Scholar]
- Rayappa, S.M.; Shamanth, V.; Sharath, P.C.; Shashanka, R.; Hemanth, K. A Review on Spark Plasma Sintering of Duplex Stainless Steels. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 45, 138–144. [Google Scholar]
- Nisar, A.; Zhang, C.; Boesl, B.; Agarwal, A. Unconventional Materials Processing Using Spark Plasma Sintering. Ceramics 2021, 4, 20–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopeliovich, D. Spark Plasma Sintering. SubsTech Substances & Technologies. Available online: http://www.substech.com/dokuwiki/doku.php?id=spark_plasma_sintering (accessed on 20 March 2022).
- Nakajo, H.; Nishimoto, A. Boronizing of CoCrFeMnNi High-Entropy Alloys Using Spark Plasma Sintering. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2022, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvi, S.; Waseem, O.A.; Akhtar, F. High Temperature Performance of Spark Plasma Sintered W0.5(TaTiVCr)0.5 Alloy. Metals 2020, 10, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimoto, T.; Nishimoto, A. Plasma-Nitriding Properties of CoCrFeMnNi High-Entropy Alloys Produced by Spark Plasma Sintering. Metals 2020, 10, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rymer, L.M.; Lindner, T.; Frint, P.; Löbel, M.; Lampke, T. Designing (Ultra)Fine-Grained High-Entropy Alloys by Spark Plasma Sintering and Equal-Channel Angular Pressing. Crystals 2020, 10, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkodich, N.; Sedegov, A.; Kuskov, K.; Busurin, S.; Scheck, Y.; Vadchenko, S.; Moskovskikh, D. Refractory High-Entropy HfTaTiNbZr-Based Alloys by Combined Use of Ball Milling and Spark Plasma Sintering: Effect of Milling Intensity. Metals 2020, 10, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, M.; Kumaresh, B.S.P.; Majhi, J.; Vallimanalan, A.; Mahendran, R. Processing and characterisation of nano crystalline AlCoCrCuFeTix high-entropy alloy. Powder. Metall. 2018, 61, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, S.H.; Kato, H.; Jang, M.J.; Moon, J.; Kim, E.B.; Hong, S.J.; Kim, H.S. Structure and properties of ultrafine-grained CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloys produced by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 698, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Cai, H.; Cheng, X. Effect of Ni/Cr ratio on phase, microstructure and mechanical properties of NixCoCuFeCr2-x (x=1.0, 1.2, 1.5, 1.8 mol) high entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 662, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ji, W.; Fu, Z. Mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering of CoCrFeNiMnAl high-entropy alloy. Adv. Powder Technol. 2014, 25, 1334–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, K.R.; Bruno da Silva, I.; Leonardo de Souza, V.; Bepe, A.M. Mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering of AlCrCuFeZn high entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 36, 1861–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razumov, N.; Makhmutov, T.; Kim, A.; Shemyakinsky, B.; Shakhmatov, A.; Popovich, V.; Popovich, A. Refractory CrMoNbWV High-Entropy Alloy Manufactured by Mechanical Alloying and Spark Plasma Sintering: Evolution of Microstructure and Properties. Materials 2021, 14, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveen, S.; Anupam, A.; Tilak, R.; Kottada, R.S. Phase evolution and thermal stability of AlCoCrFe high entropy alloy with carbon as unsolicited addition from milling media. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 210, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombini, E.; Rosa, R.; Trombi, L.; Zadra, M.; Casagrande, A.; Veronesi, P. High entropy alloys obtained by field assisted powder metallurgy route: SPS and microwave heating. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 210, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Praveen, S.; Murty, B.S.; Kottada, R.S. Effect of molybdenum and niobium on the phase formation and hardness of nanocrystalline CoCrFeNi high entropy alloys. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 8106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moravcik, I.; Cizek, J.; Gavendova, P.; Sheikh, S.; Guo, S.; Dlouhy, I. Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of spark plasma sintered AlCoCrFeNiTi0.5 high entropy alloy. Mater. Lett. 2016, 174, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
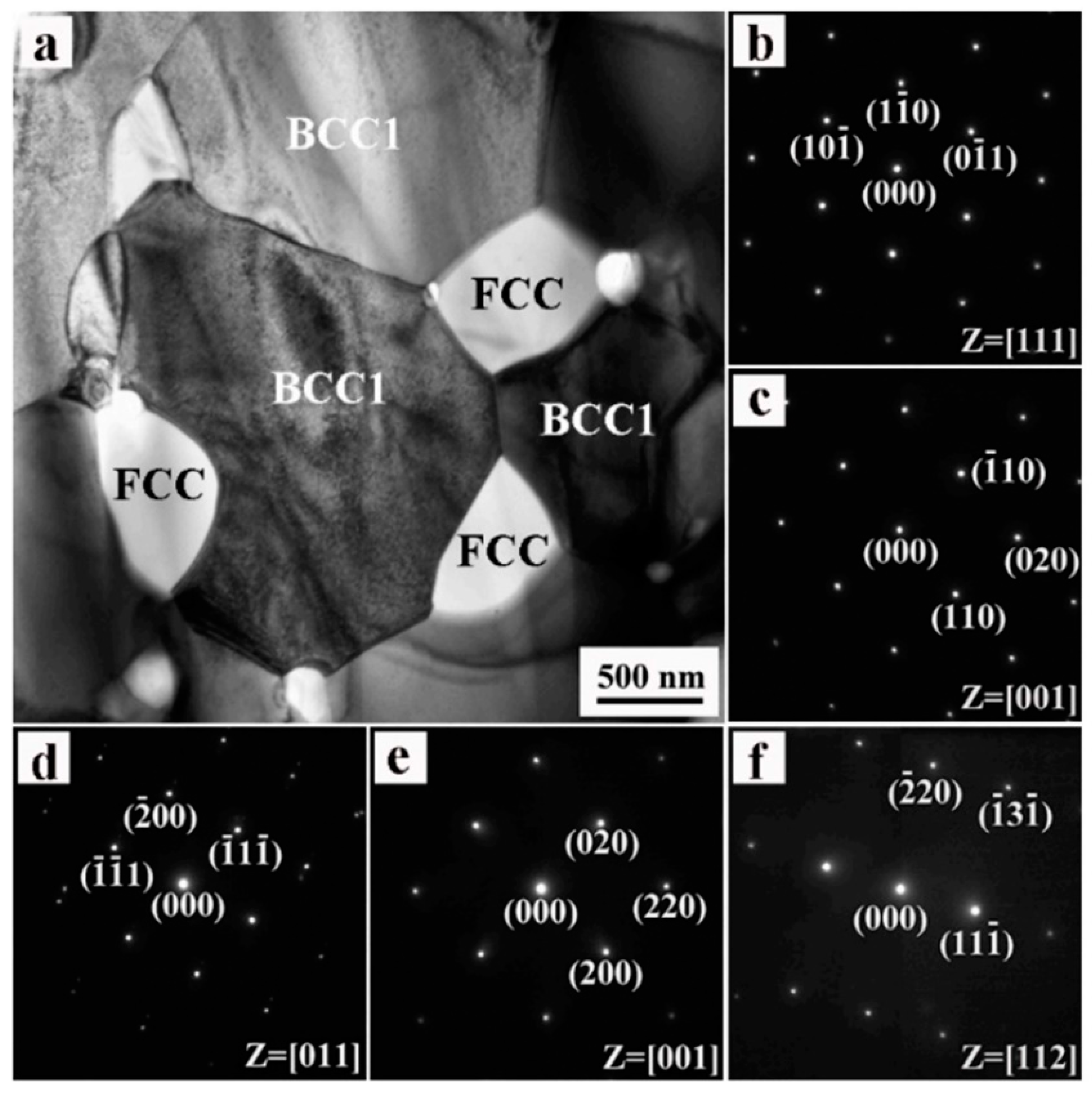
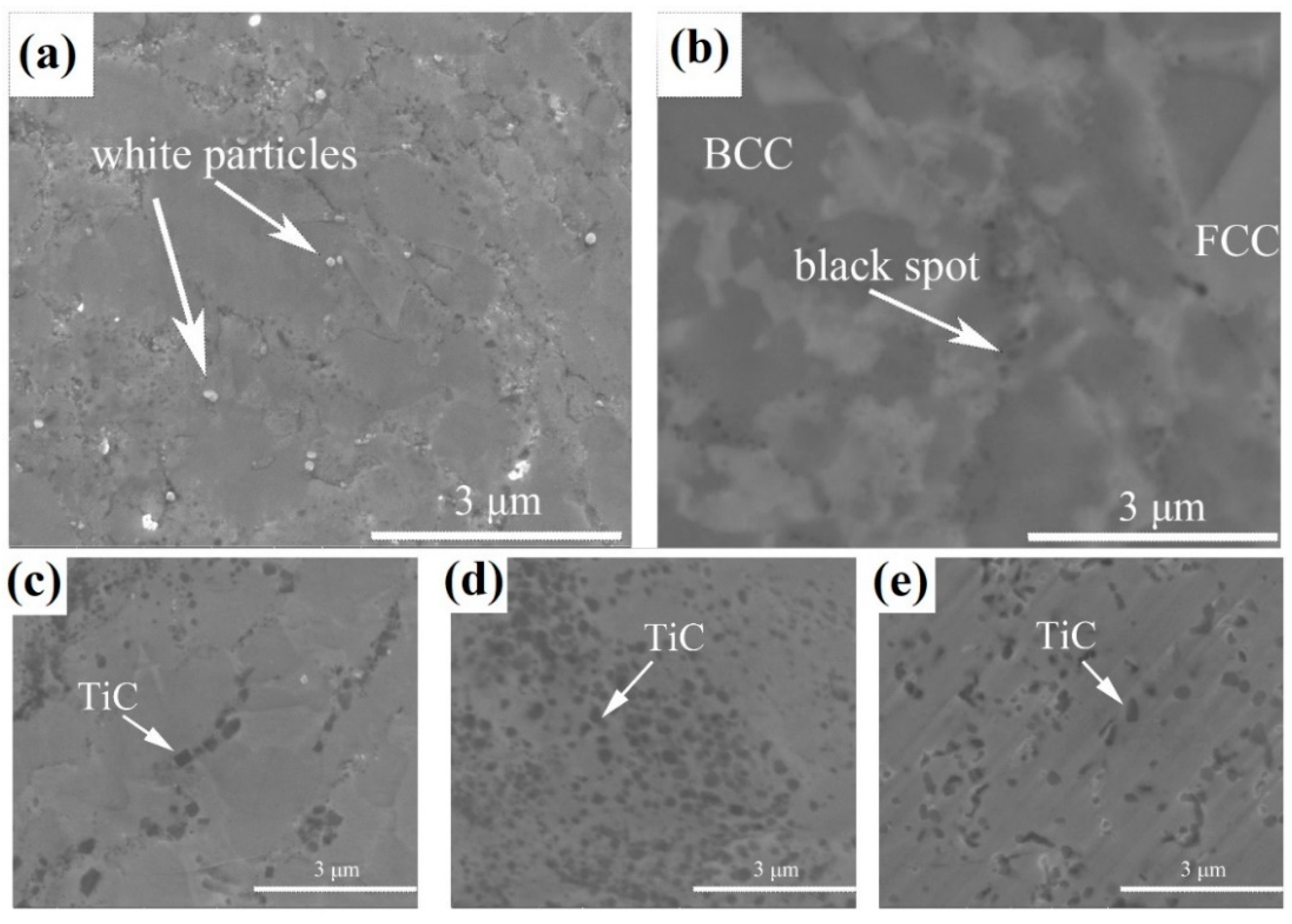



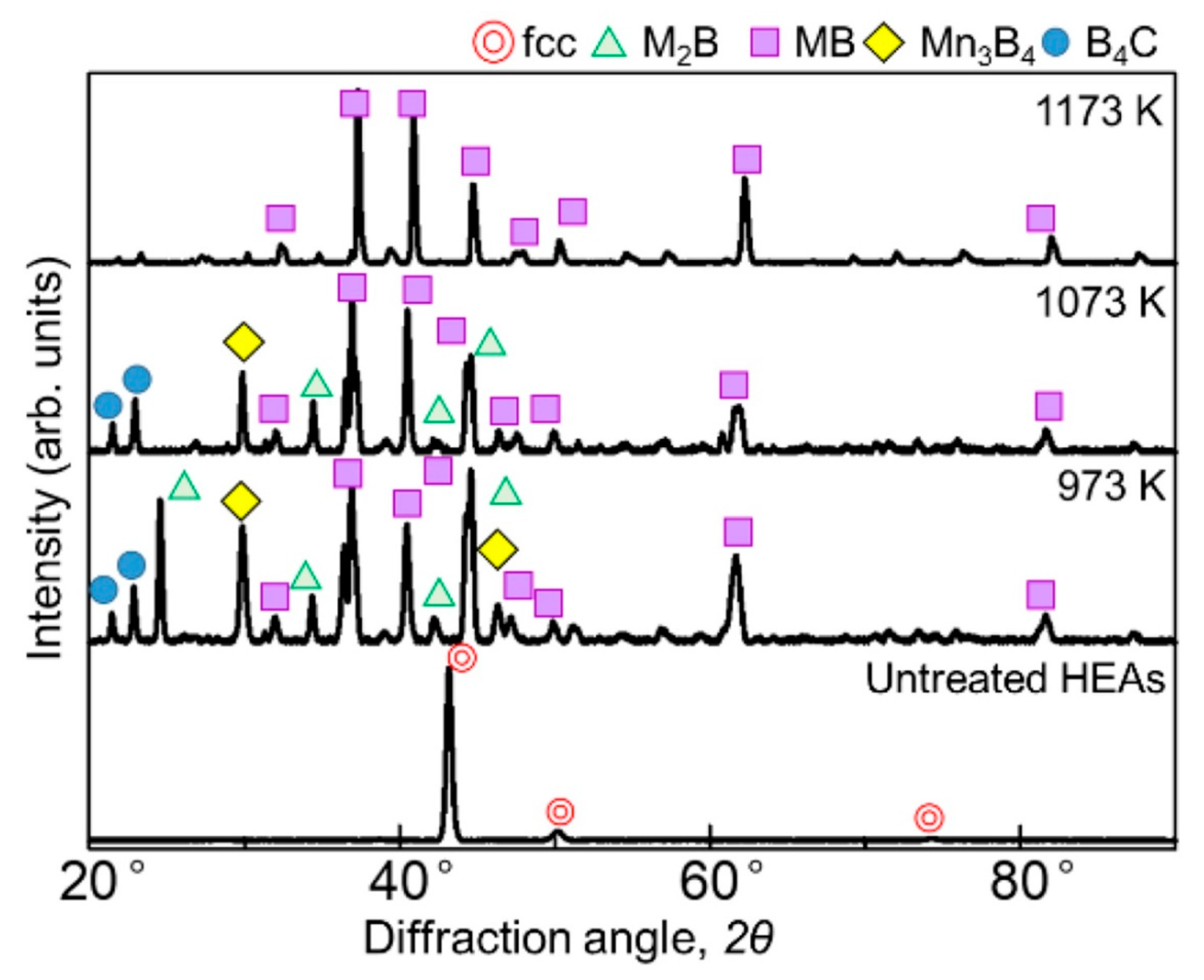
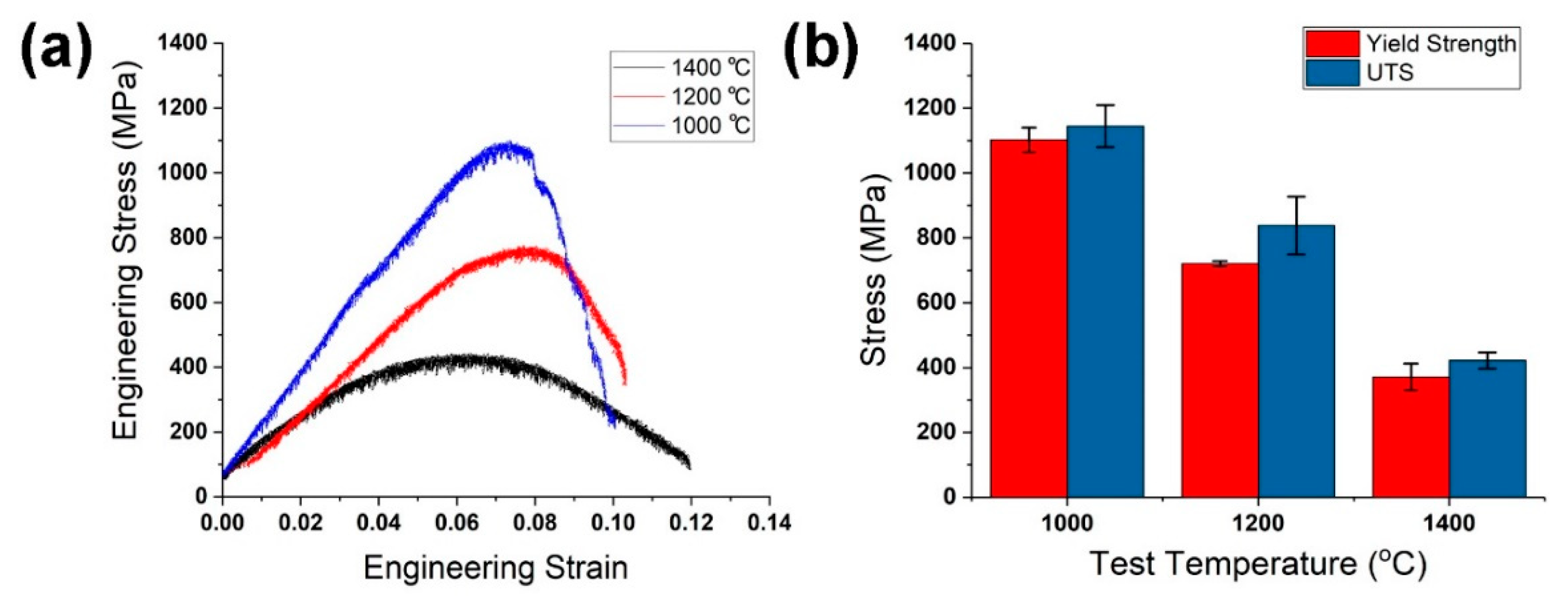

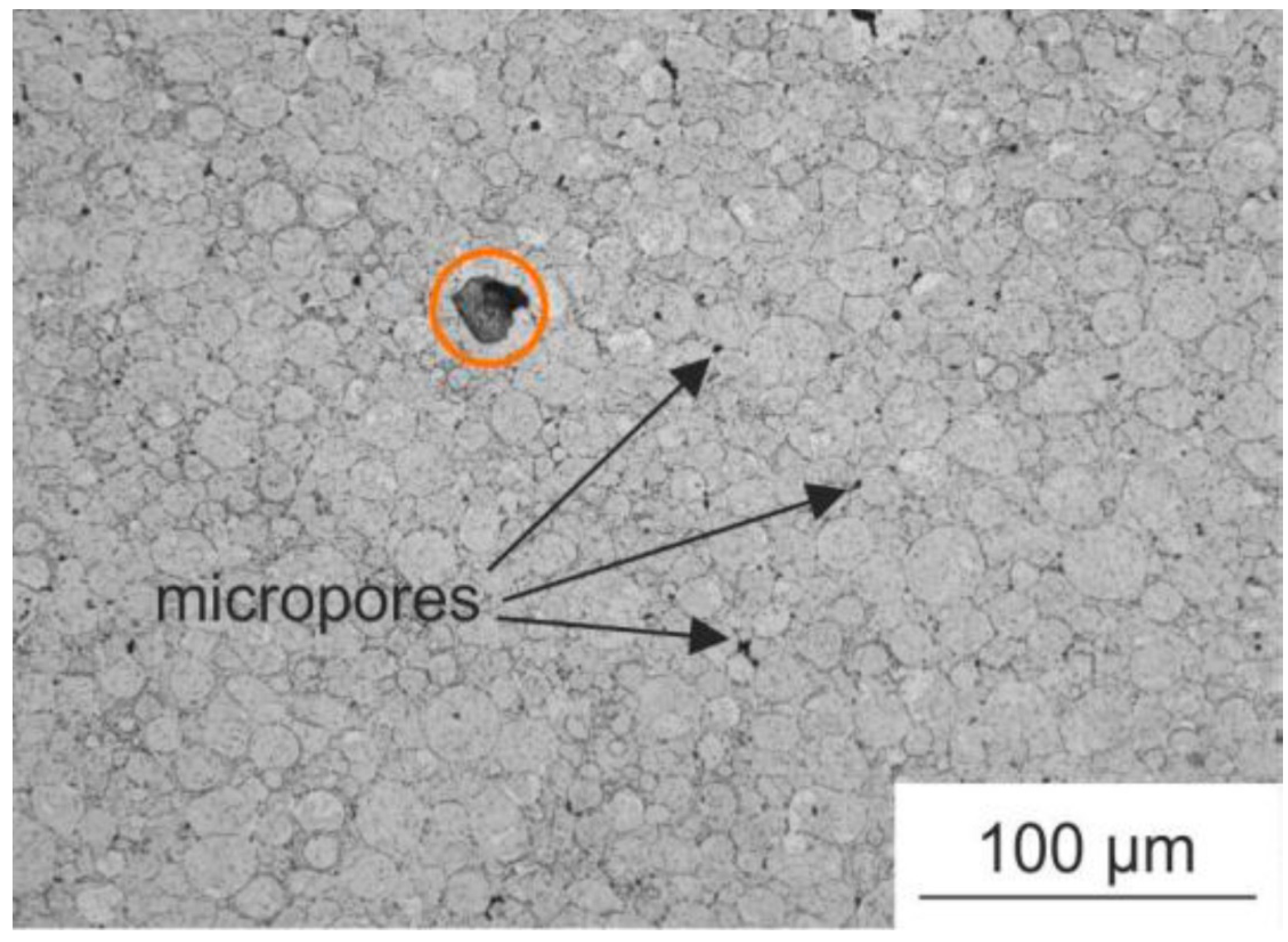
| Composition of HEA | Type of Ball Mill Used | Ball Milling Parameters | SPS Parameters | Mechanical Properties | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CoCrFeNiMnAl | Planetary ball mill | 60 h, 15:1 BPR, argon atmosphere, 200 rpm mill speed, stearic acid as PCA | 20 mm diameter, 800 °C for 10 min under 50 MPa axial pressure in an argon atmosphere | Vickers hardnessof 662 HV and compressive strength of 2142 MPa | [51] |
| AlCrCuFeZn | High-energy planetary ball mill P-5 | 50 h, 15:1 BPR, argon atmosphere, 250 rpm mill speed, n-heptane as PCA | 800 °C for 5 min under 50 MPa uniaxial pressure in an argon atmosphere | 91% density and 627 HV microhardness | [52] |
| CrMoNbWV | Planetary mill P-4 | 5 h, 20:1 BPR, argon atmosphere, 350/700 rpm mill speed | Graphite die of 40 mm, 1200, 1300, and 1400 °C under 50 MPa uniaxial pressure for 5 min | Compressive strength of 2700–2870 MPa and microhardness of 1266 HV | [53] |
| AlCoCrFe | P-5 high-energy ball mill | 15 h, 10:1 BPR, 300 rpm mill speed, toluene as PCA | 1000 °C under 30 MPa uniaxial pressure for 3 min | Microhardness of 1050 HV | [54] |
| FeCoCrNiAl | Planetary Ball Mill PM 100 | 35 h, 10:1 BPR, 250 rpm mill speed | 20 mm diameter, 1000 °C for 5 min under 60 MPa axial pressure | Elastic modulus of 260 GPa and microhardness of 550 HV | [55] |
| CoCrFeNiMoNb | Fritsch P5 high-energy ball mill | 30 h, 10:1 BPR, toluene as PCA | 20 mm diameter, 900 and 1000 °C for 5 min under 30–50 MPa axial pressure | Microhardness of 710 HV and relative density of 94% was achieved | [56] |
| AlCoCrFeNiTi0.5 | High-energy ball mill | 24 h, 10:1 BPR, argon atmosphere, 250 rpm mill speed | 20 mm diameter, 1100 °C for 8 min under 60 MPa axial pressure | Microhardness of 762 HV, elastic modulus of 160 GPa | [57] |
| CoCrFeMnNi | Fritsch P5 high-energy ball mill | 15 h, 10:1 BPR, 300 rpm mill speed, toluene as PCA | 15 mm diameter, 1173 K for 5 min under 60 MPa axial pressure | 96% relative density was achieved | [29] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rajendrachari, S. An Overview of High-Entropy Alloys Prepared by Mechanical Alloying Followed by the Characterization of Their Microstructure and Various Properties. Alloys 2022, 1, 116-132. https://doi.org/10.3390/alloys1020008
Rajendrachari S. An Overview of High-Entropy Alloys Prepared by Mechanical Alloying Followed by the Characterization of Their Microstructure and Various Properties. Alloys. 2022; 1(2):116-132. https://doi.org/10.3390/alloys1020008
Chicago/Turabian StyleRajendrachari, Shashanka. 2022. "An Overview of High-Entropy Alloys Prepared by Mechanical Alloying Followed by the Characterization of Their Microstructure and Various Properties" Alloys 1, no. 2: 116-132. https://doi.org/10.3390/alloys1020008
APA StyleRajendrachari, S. (2022). An Overview of High-Entropy Alloys Prepared by Mechanical Alloying Followed by the Characterization of Their Microstructure and Various Properties. Alloys, 1(2), 116-132. https://doi.org/10.3390/alloys1020008






