Centrifugal Differential Mobility Analysis—Validation and First Two-Dimensional Measurements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Fundamentals
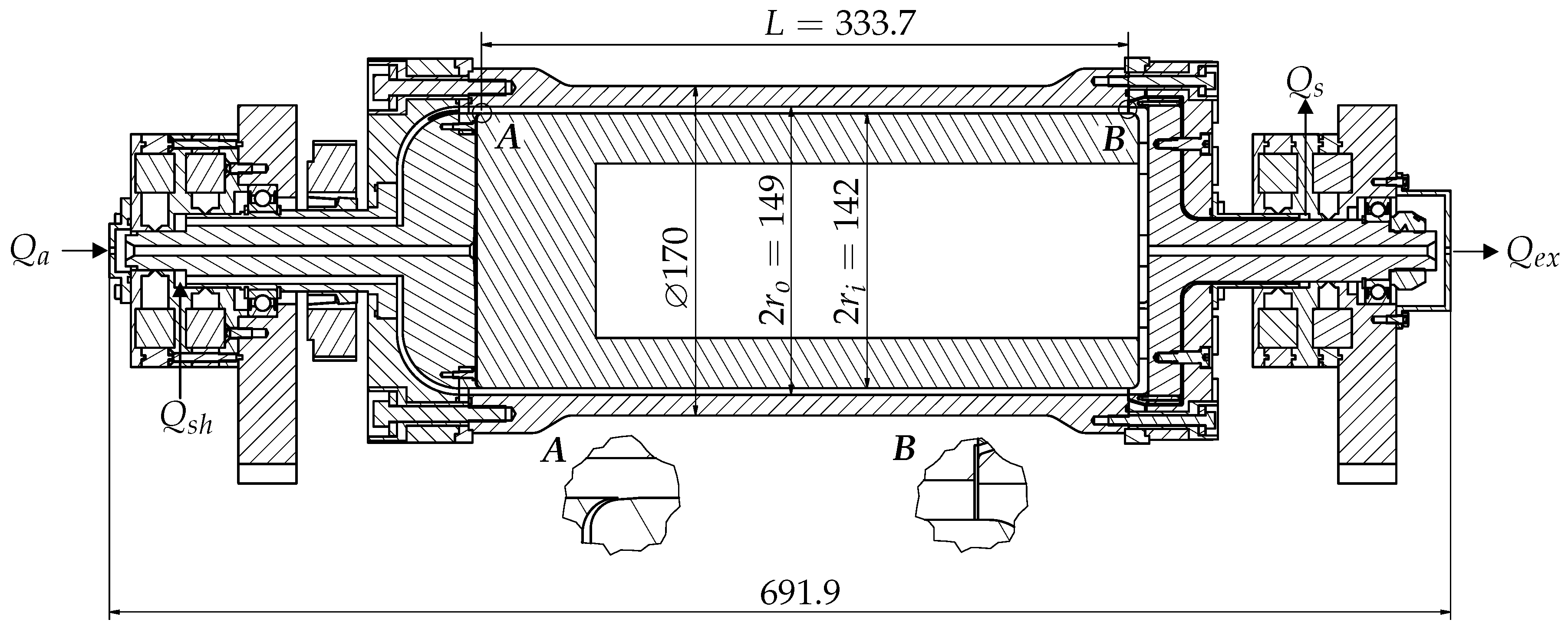
3. Design
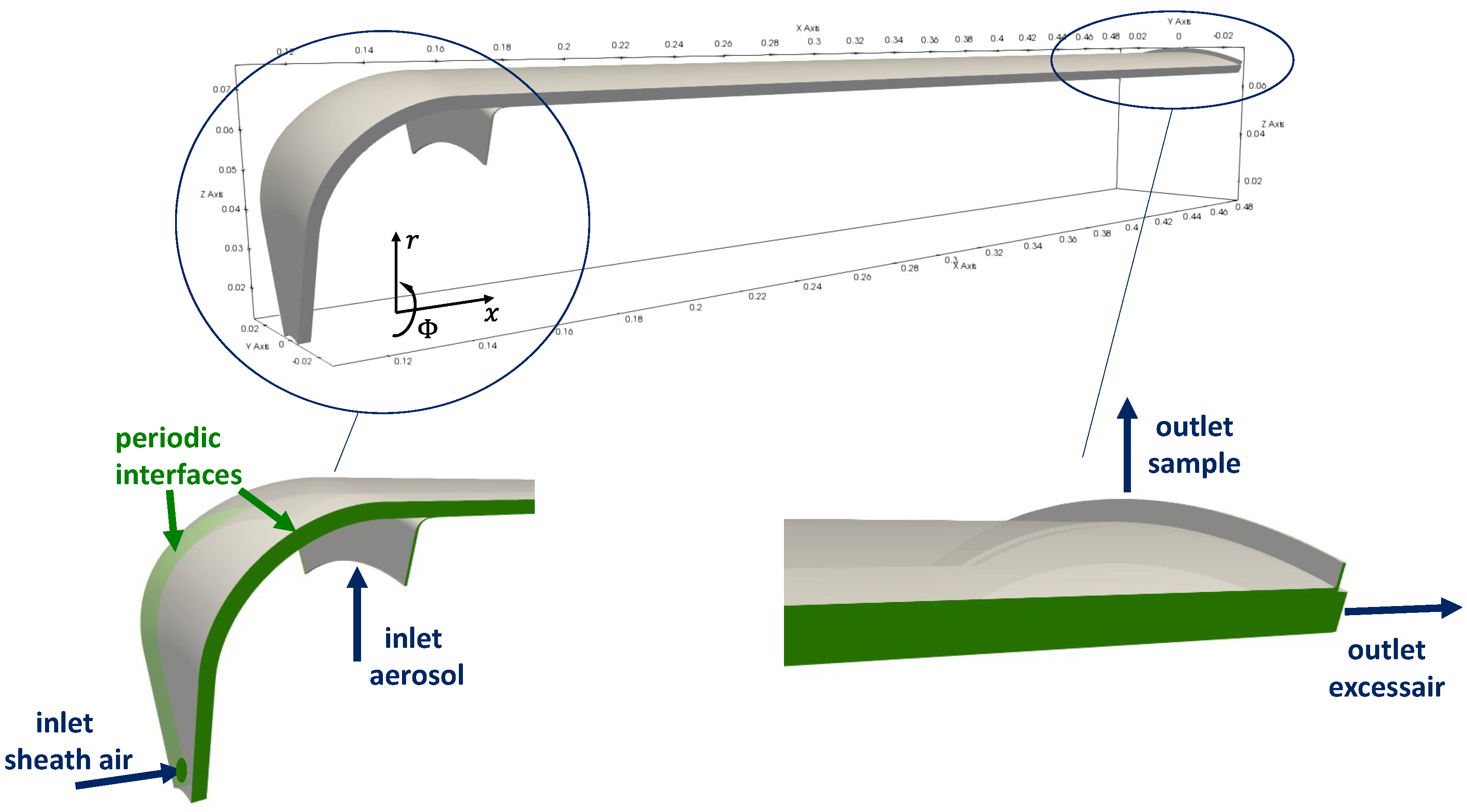
4. Numerical Flow Simulations
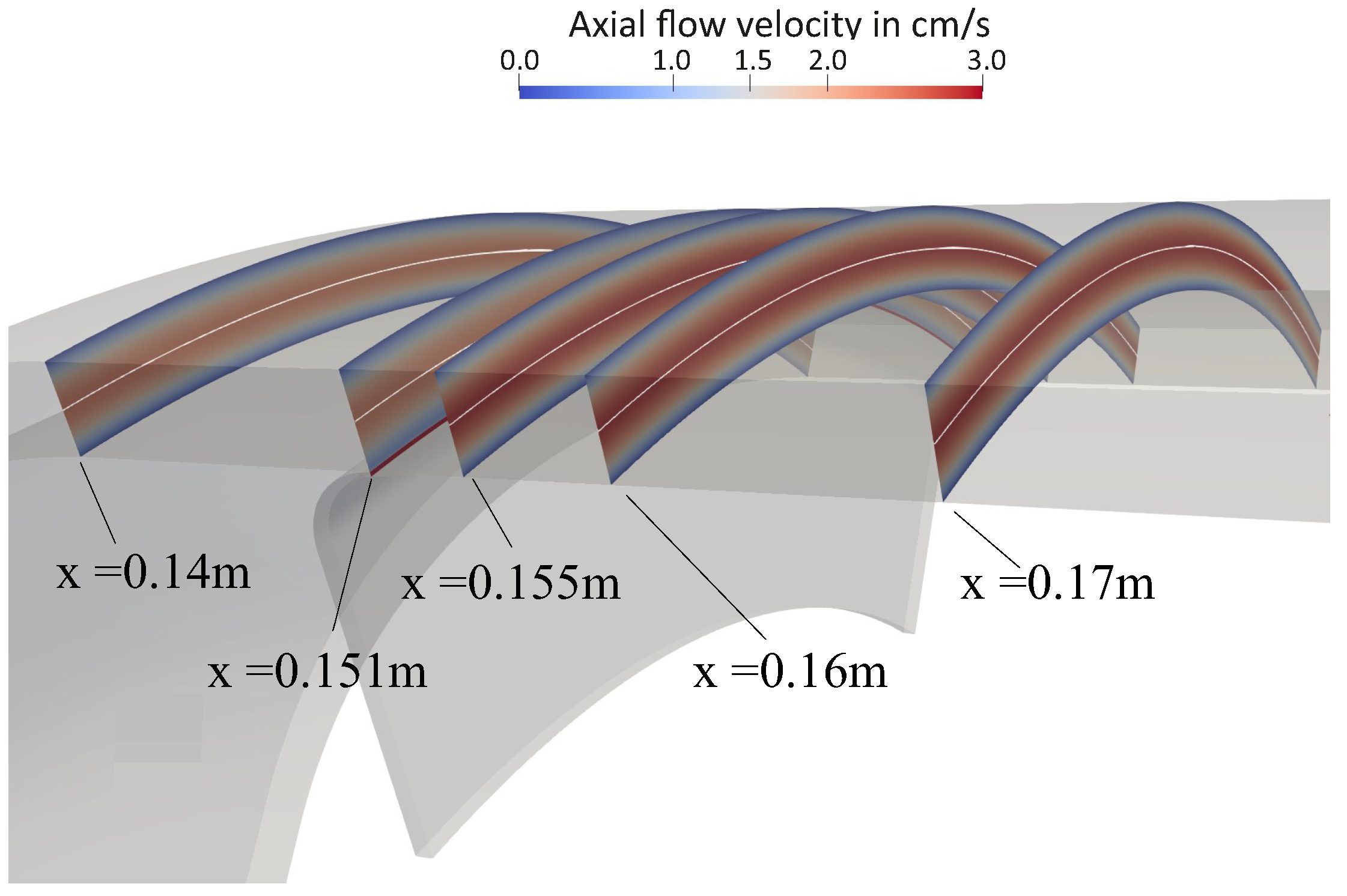
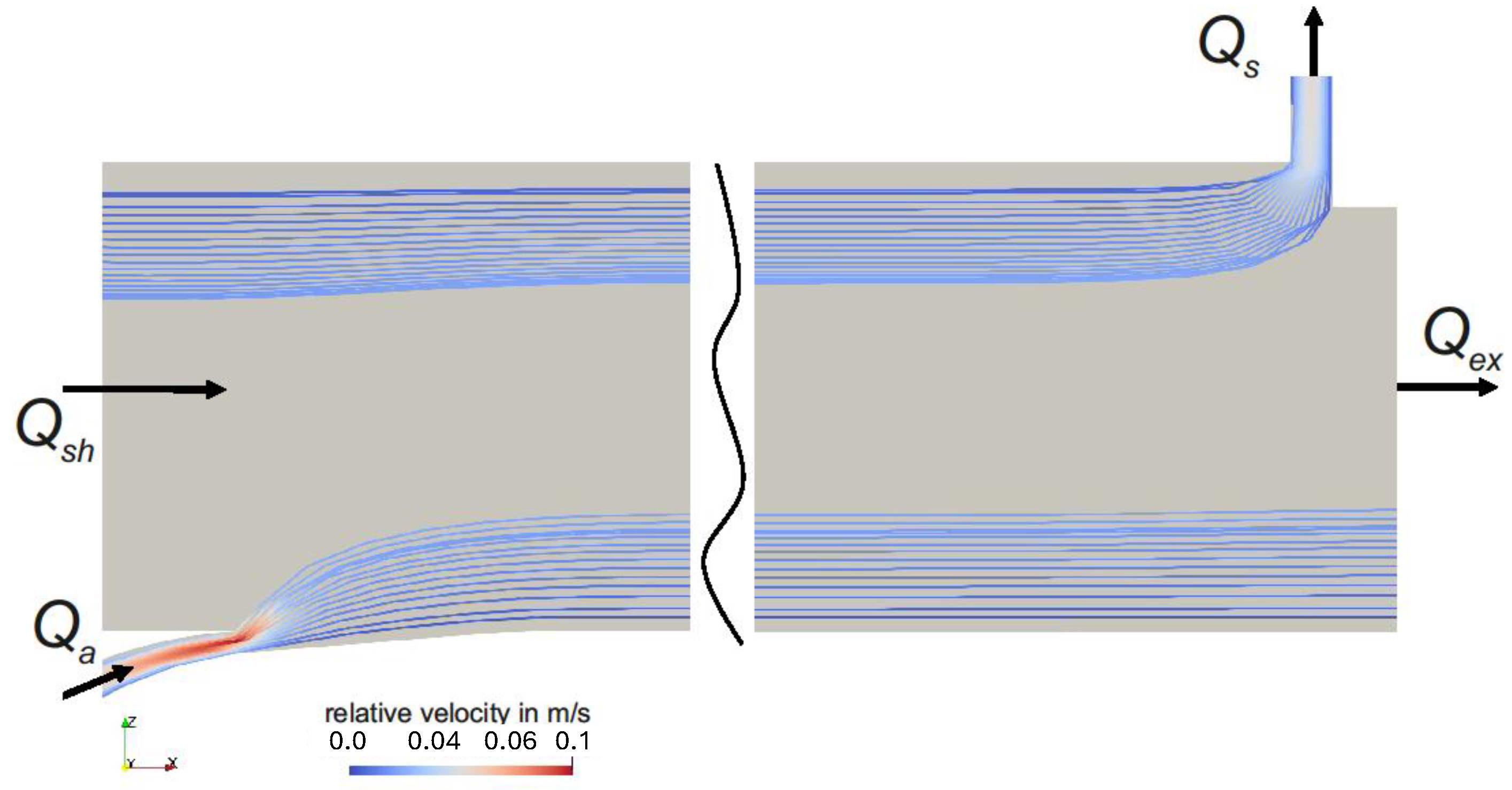
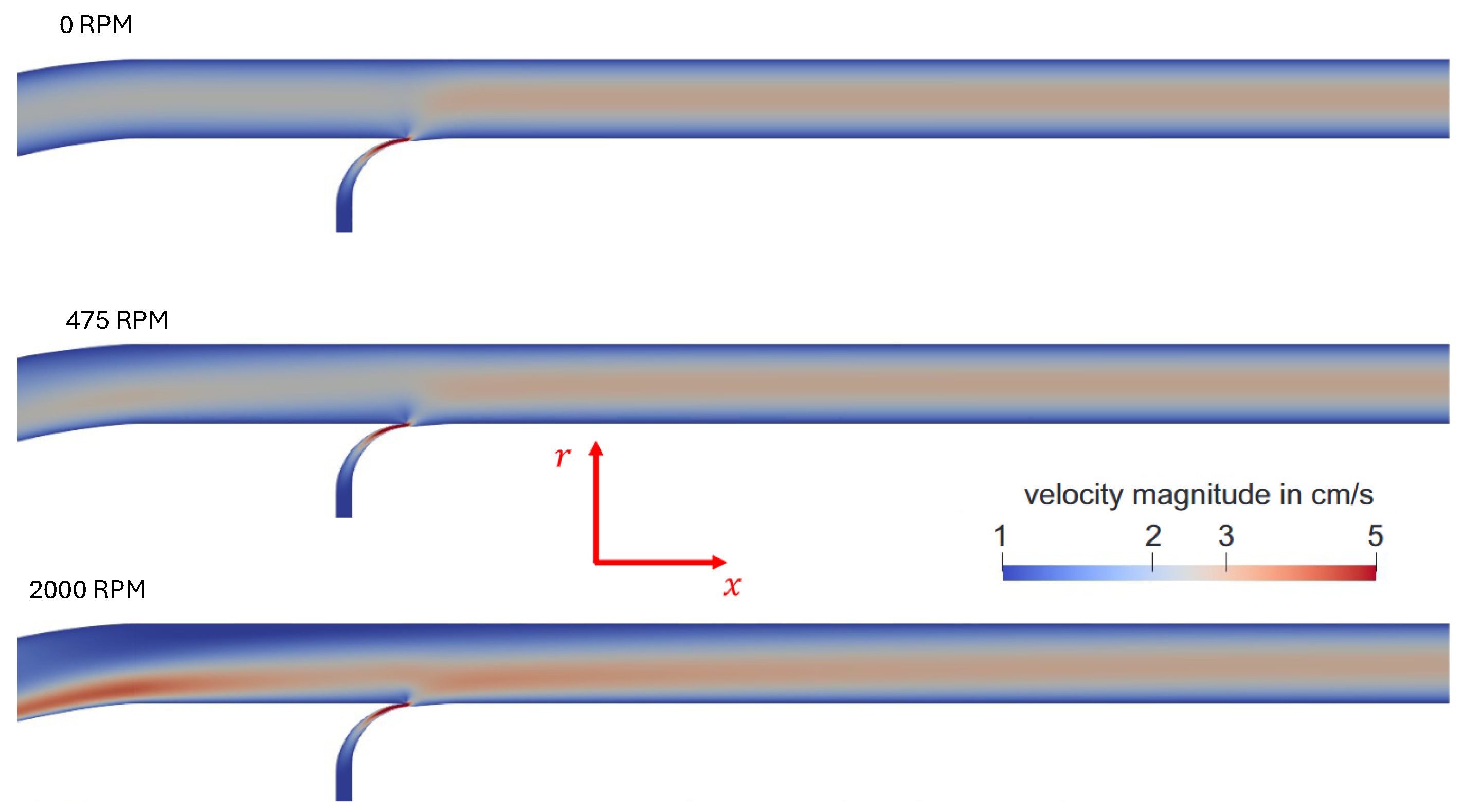
4.1. Flow Behavior Without Rotation
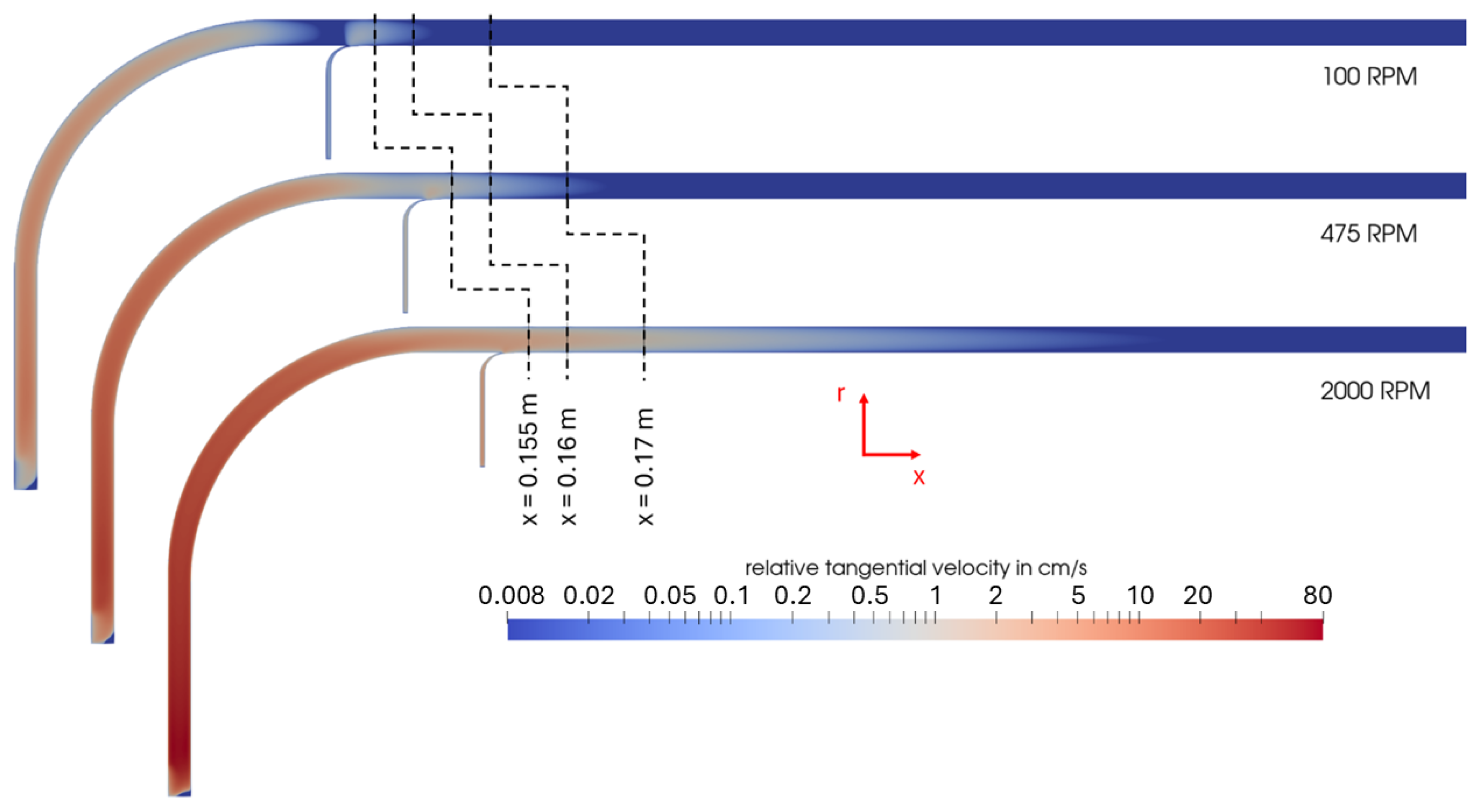
4.2. Flow Behavior with Rotation
5. Transfer Function of the CDMA
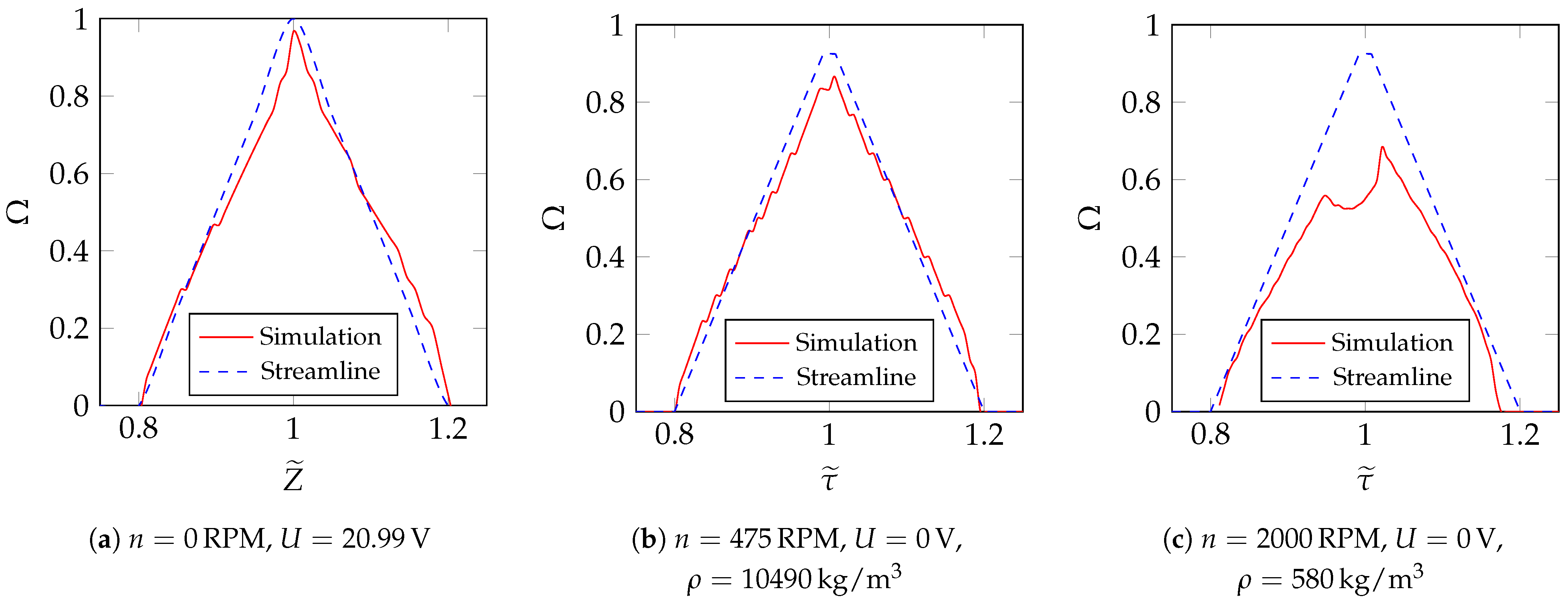
5.1. Transfer Function Based on CFD Simulations
5.2. Ideal Transfer Function Based on Streamline Approach
5.3. Comparison of Transfer Functions
6. Measurement of Transfer Functions
6.1. Theory
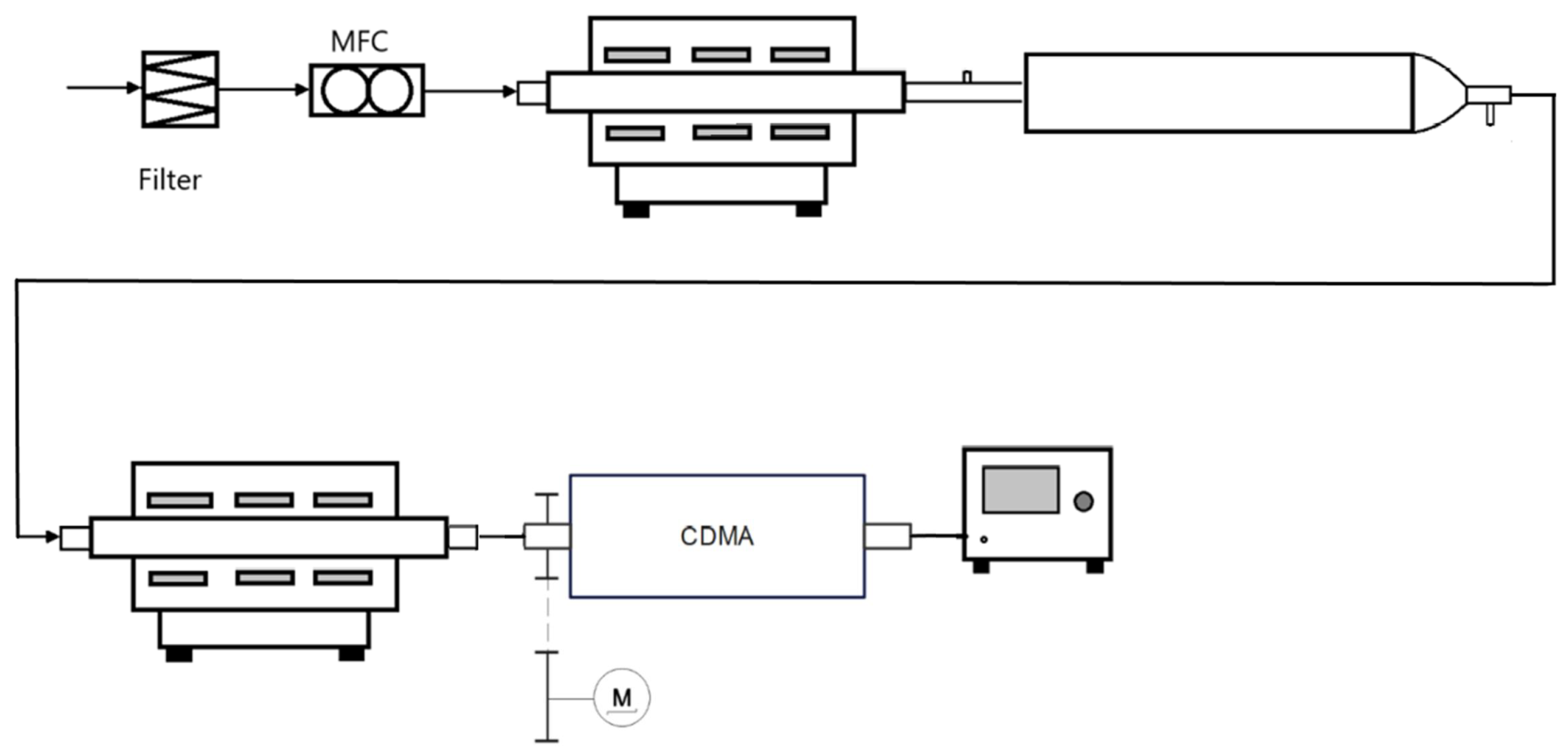
6.2. Production of the Test Aerosol and Measurement Setup
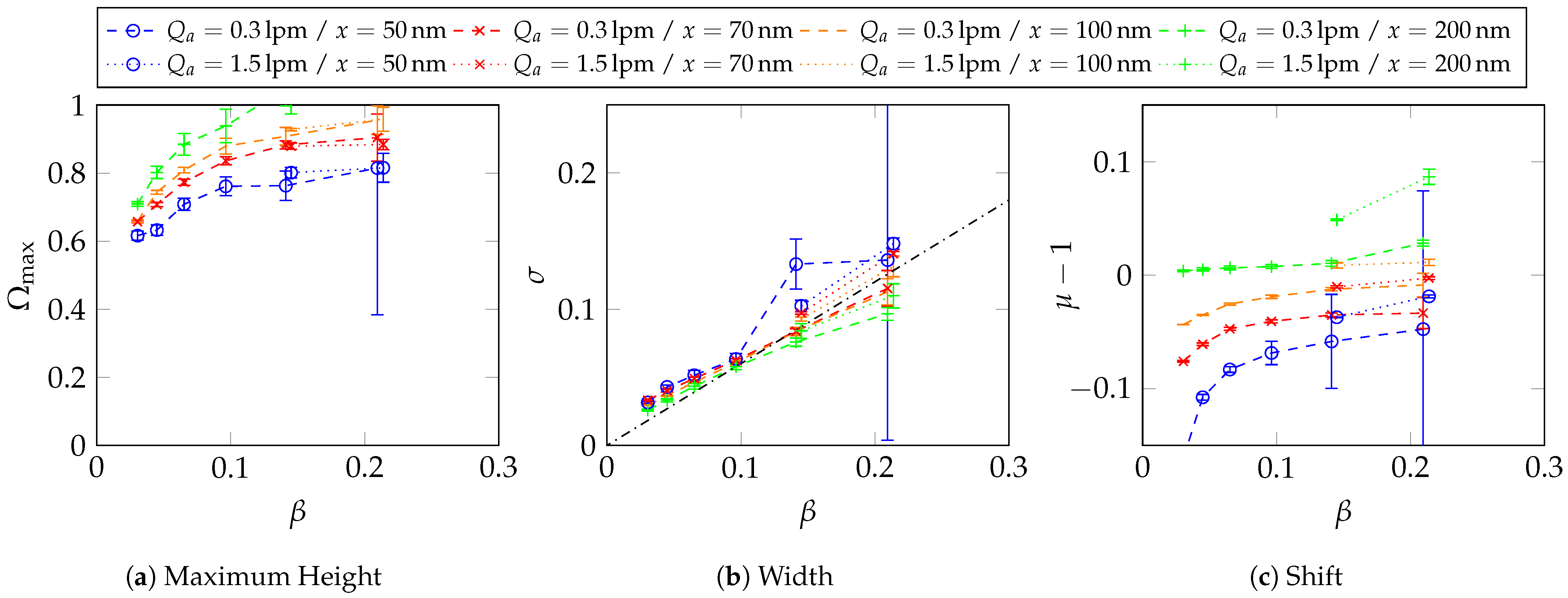
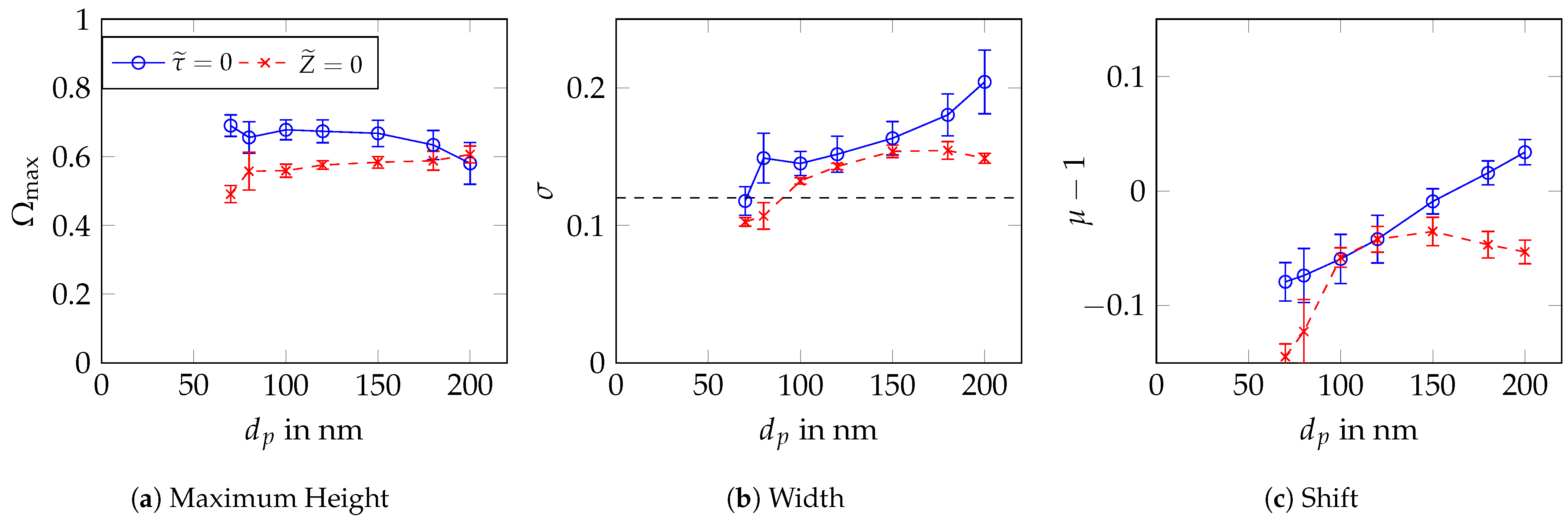
6.3. Experimental Determination of the CDMA Transfer Function for and at Different -Values
6.4. Experimental Determination of the Transfer Function for and at
7. Measurement Results and Analysis of Two-Dimensional Size Distributions for Different Sintering Stages of Silver Nanoparticles
7.1. Production of the Aerosol and Measurement Setup for Two-Dimensional Distributions
7.2. Derivation of Further Properties
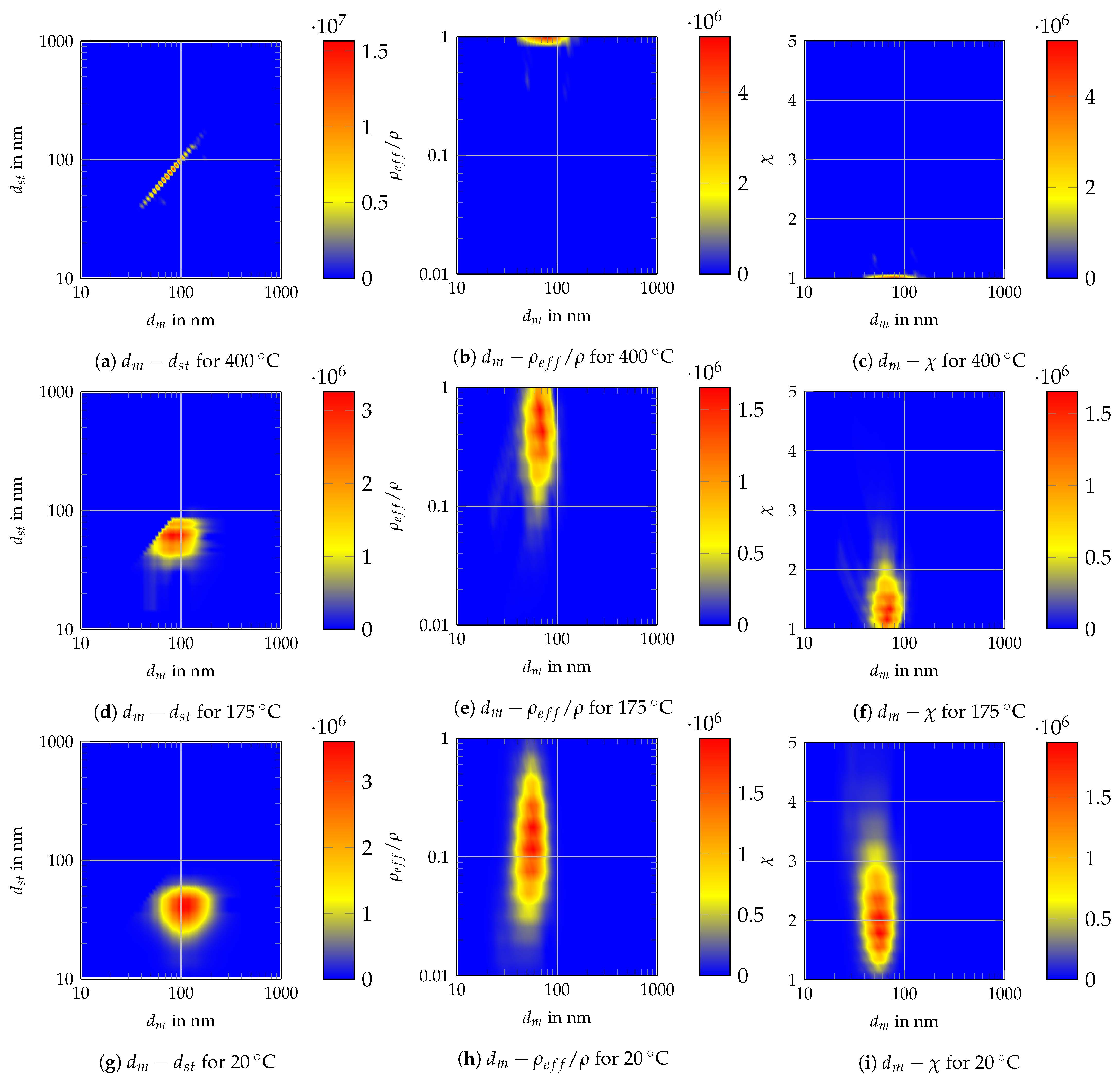
7.3. Measurement Results
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CDMA | Centrifugal Differential Mobility Analyzer |
| DMA | Differential Mobility Analyzer |
| AAC | Aerodynamic Aerosol Classifier |
| CPC | Condensation Particle Counter |
| lpm | Standard liters per minute |
| RPM | Revolutions per minute |
| MFC | Mass-flow Controller |
Nomenclature
| κ | ratio of ri to ro | − |
| β | ratio of Qa to Qsh | − |
| χ | shape factor | − |
| η | dynamic viscosity | Pas |
| Ω | transfer function of classifier | − |
| Ω | transfer function | − |
| ω | angular speed ω = 2π · n | 1/s |
| ρ | particle density | kg/m3 |
| ρ0 | assumed reference density of 1000 kg/m3 | kg/m3 |
| ρeff | effective density | kg/m3 |
| σ | standard deviation of Gaussian shaped transfer function | − |
| σ | width of the transfer function | − |
| τ | particle relaxation time | s |
| τ* | nominal particle relaxation time | s |
| Kernel matrix | ||
| fit parameters for the shift of a Gaussian function | − | |
| normalized particle relaxation time | − | |
| ratio of the gap width to the mean radius | − | |
| normalized particle mobility | − | |
| ac | centrifugal acceleration | m/s2 |
| Cu | Cunningham slip correction factor | − |
| dm | mobility equivalent diameter | m |
| dv | volume equivalent diameter | m |
| dae | aerodynamic equivalent diameter | m |
| dP | diameter of a spherical particle | m |
| dst | stokes equivalent diameter | m |
| E | electric field | V/m |
| L | length of the CDMA classification gap | m |
| mP | particle mass | kg |
| n | number of particle charges | − |
| Ntot | total number of simulated streamlines | # |
| Ntraversed | number of successfully traversed streamlines | # |
| q | particle density distribution | − |
| Qa | aerosol volume flow | m3/s |
| QP | particle charge | As |
| Qs | sample volume flow | m3/s |
| Qex | excess air volume flow | m3/s |
| Qsh | sheath air volume flow | m3/s |
| ri | inner radius | m |
| ro | outer radius | m |
| rae | outer radius of the aerosol air streamlines | m |
| rs | inner radius of the sampling air streamlines | m |
| U | voltage | V |
| wDr | particle drift velocity | m/s |
| x | length coordinate in axial direction | m |
| Z* | nominal particle mobility | m2/(Vs) |
| Zp | particle mobility | m2/(Vs) |
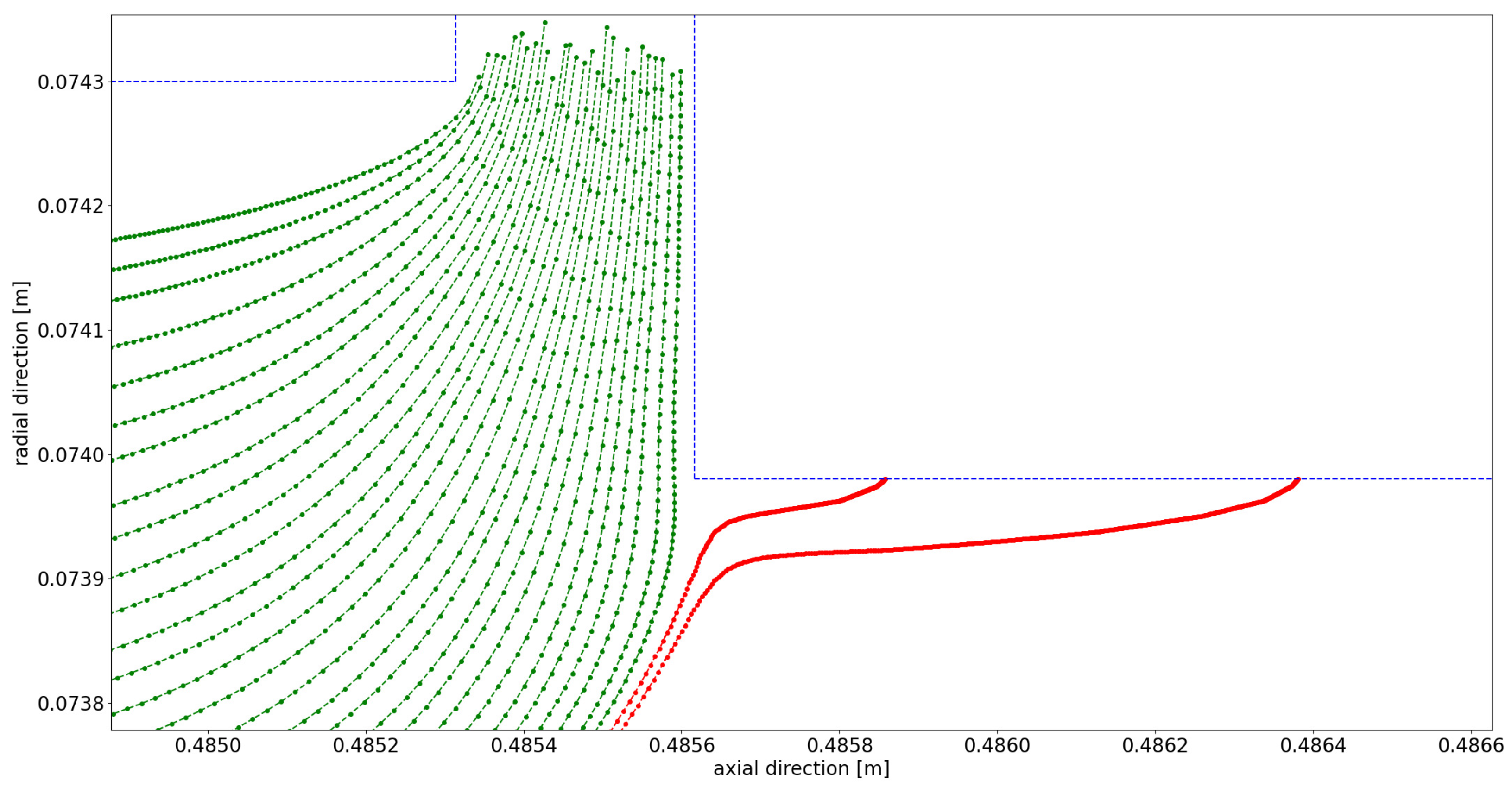
Appendix A. Further Illustration of the CFD Simulation
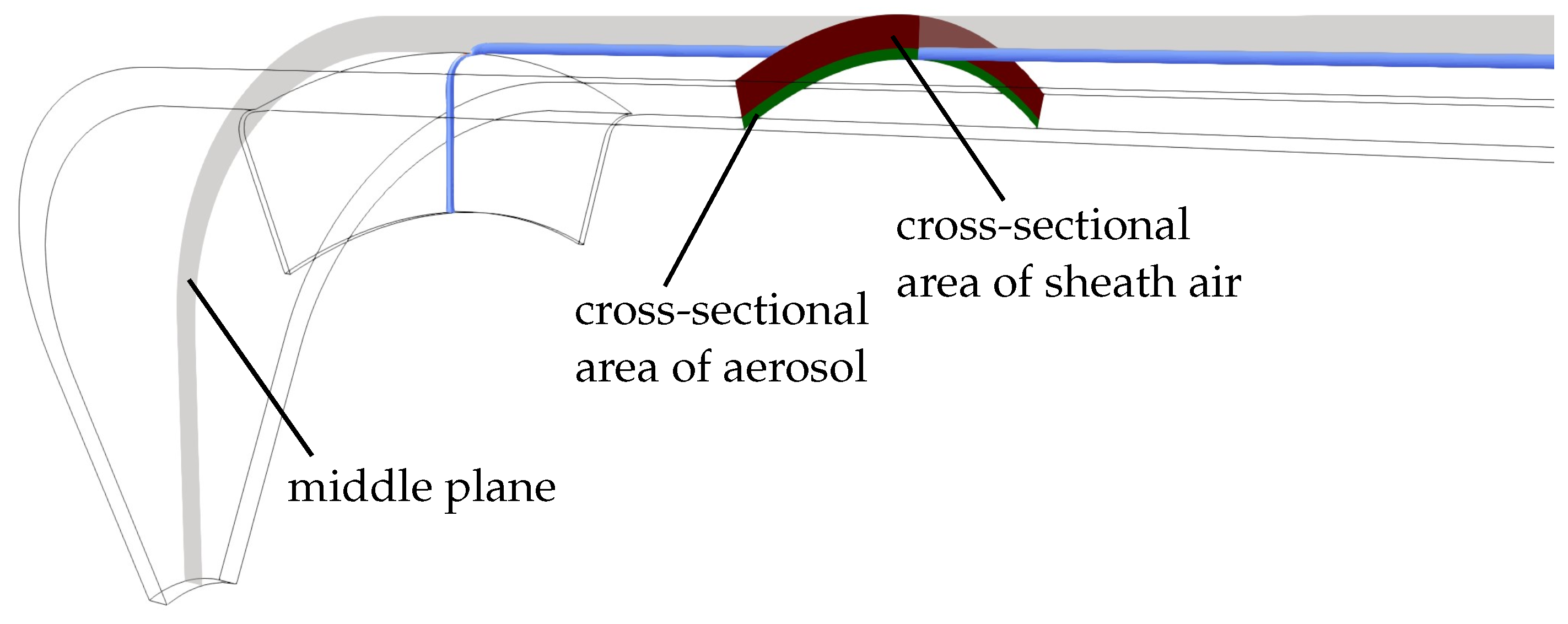
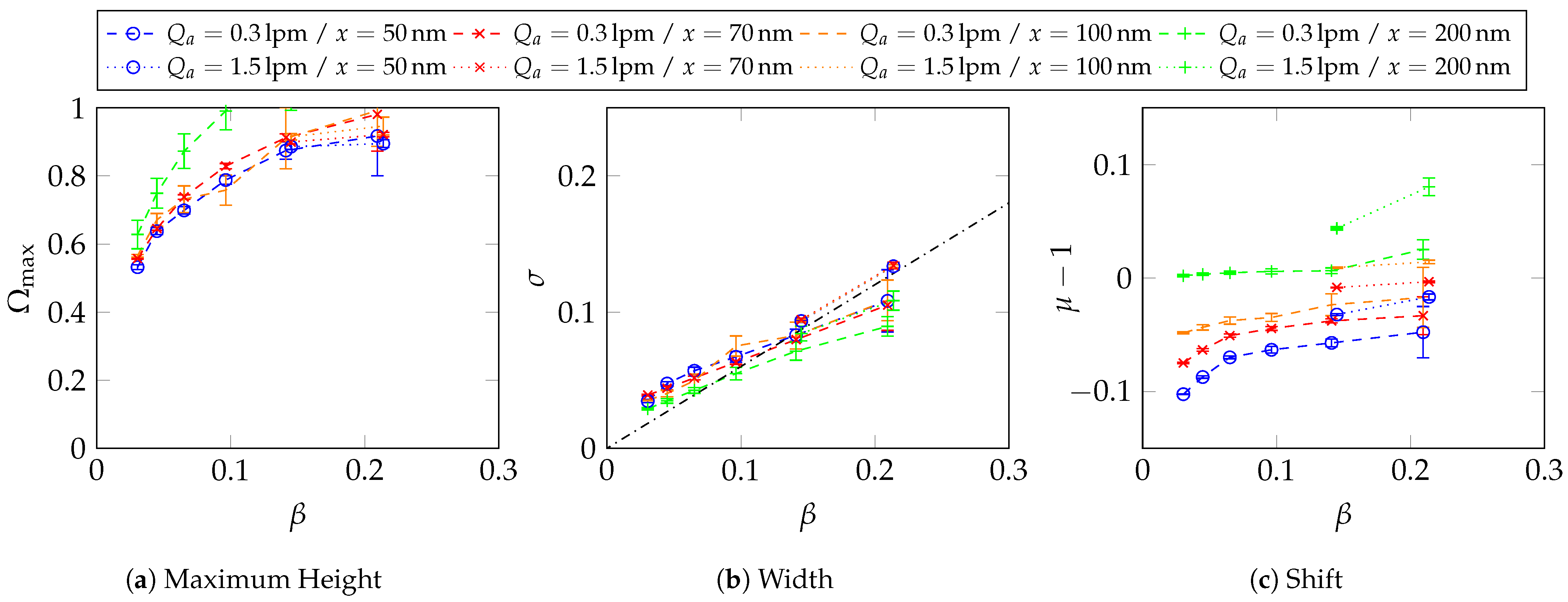
Appendix B. Transfer Function Parameter Determination
| DMA Combination | 1-2 | 1-3 | 2-1 | 2-3 | 3-1 | 3-2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.6778 | 1.0173 | 0.6964 | 1.0443 | 0.8622 | 0.8950 | |
| 1.0282 | 1.0568 | 1.0261 | 1.0504 | 0.9900 | 0.9891 |
| DMA | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| k | 0.5732 | 0.5988 | 0.7818 |
| 1.0154 | 1.0117 | 1.0080 |

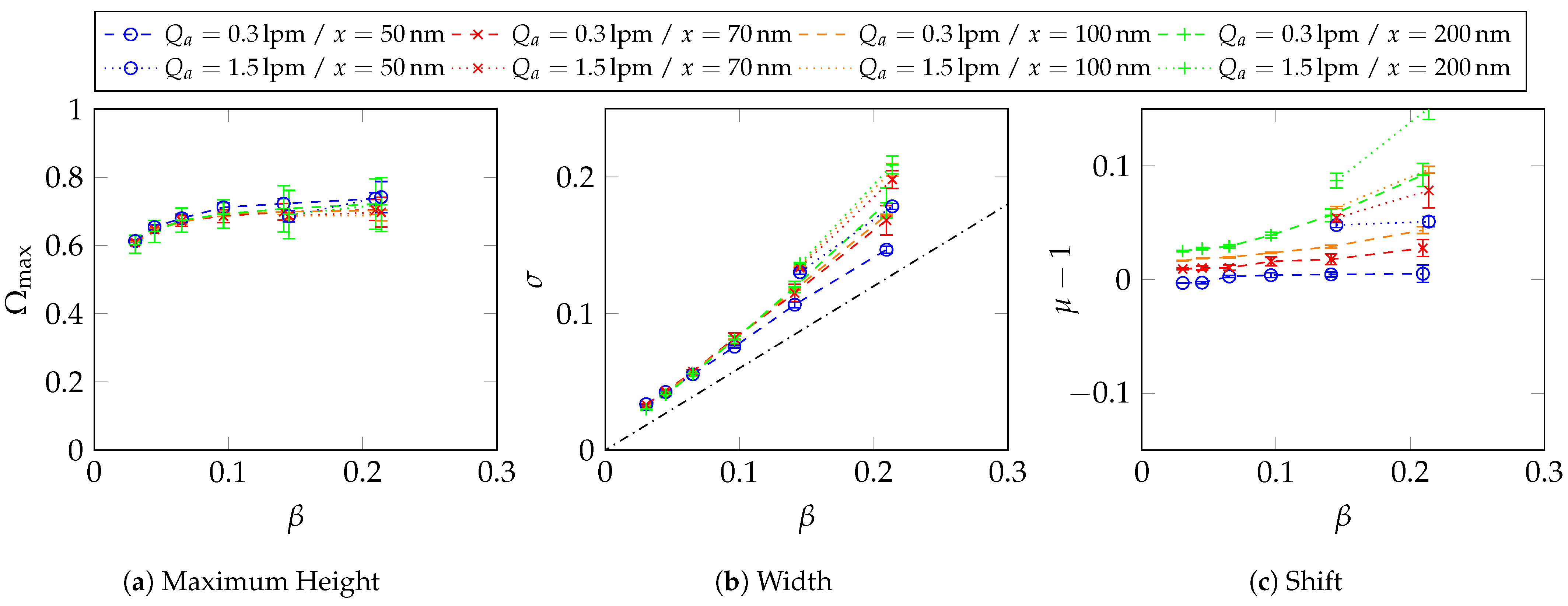
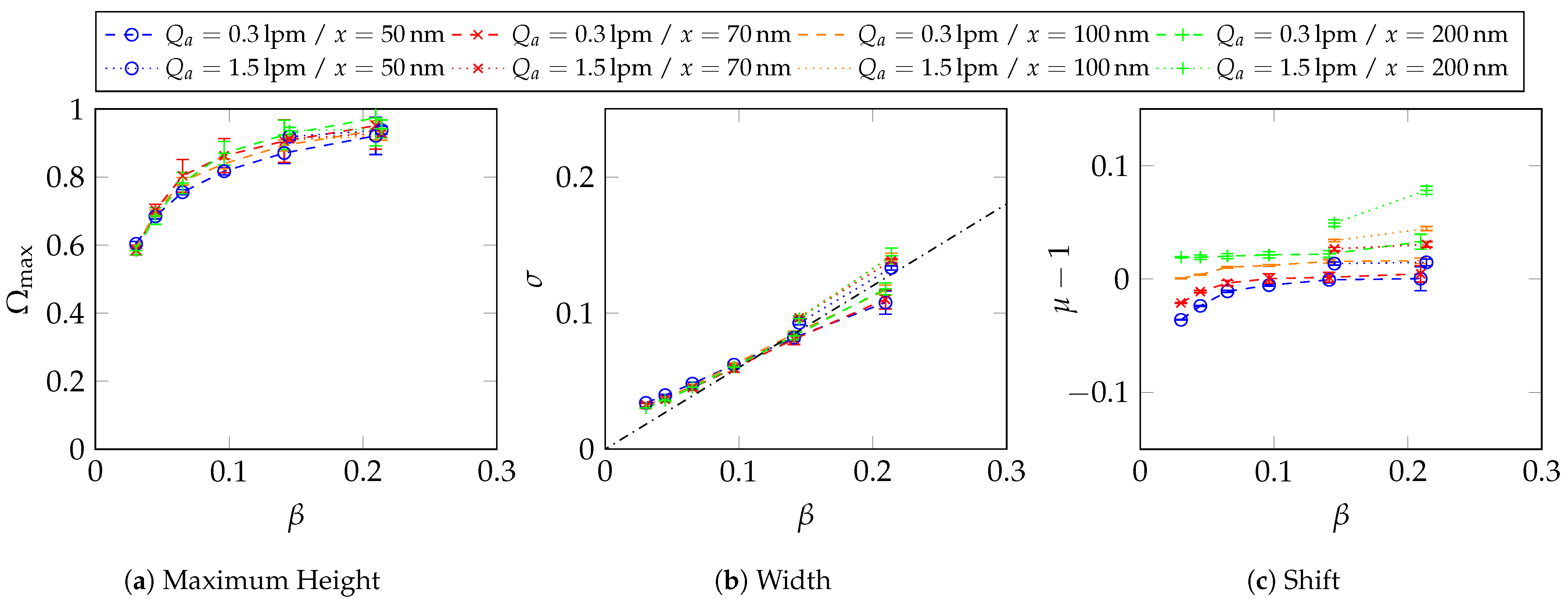

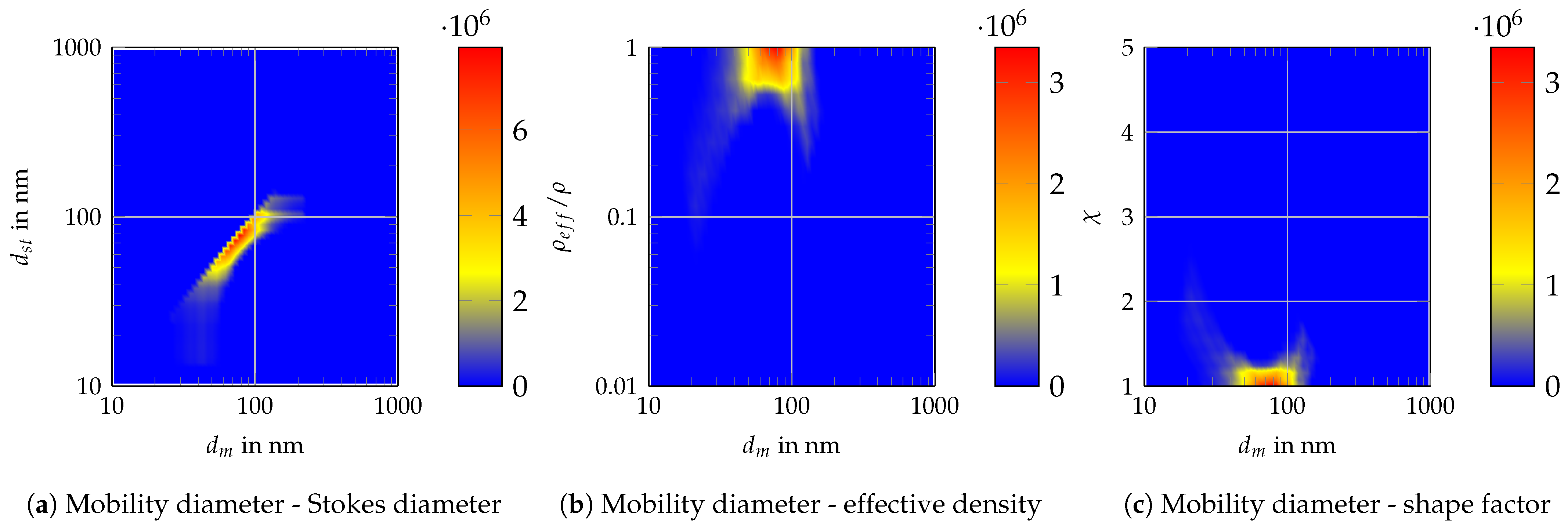
Appendix C. Two-Dimensional Property Distribution for Agglomerated Silver Particles Treated at Different Sintering Temperatures
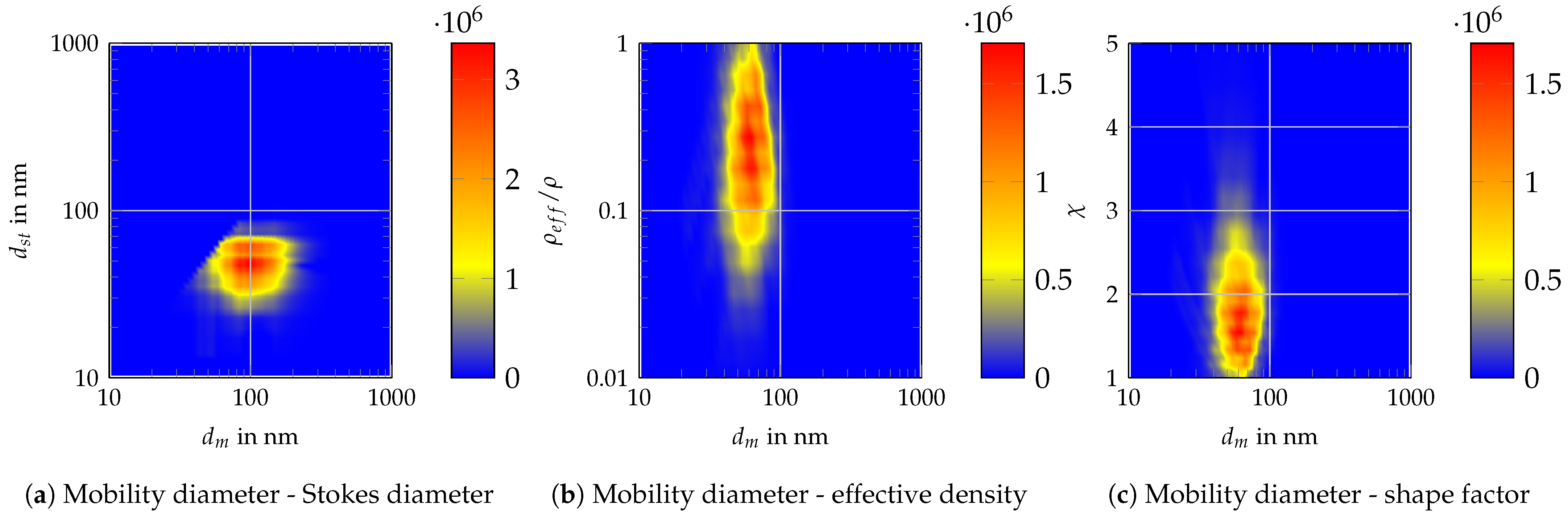
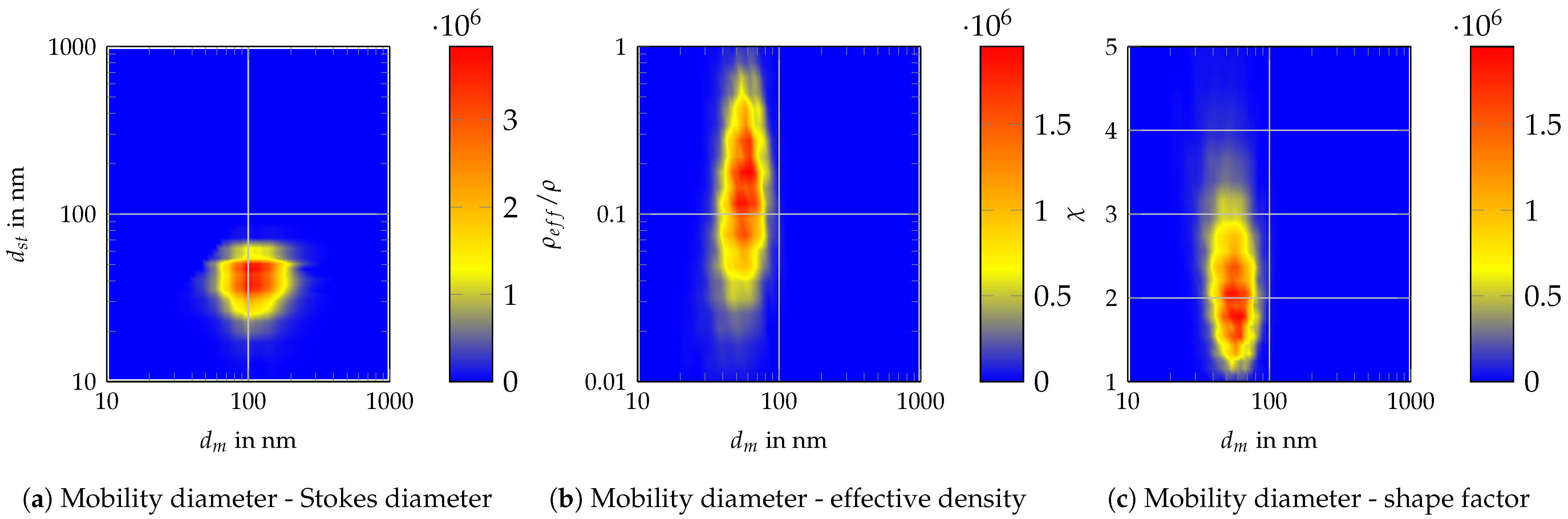
References
- Baron, P.A.; Kulkarni, P.; Willeke, K. Aerosol Measurement: Principles, Techniques, and Applications, 3rd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Friedlander, S.K. Smoke, Dust, and Haze: Fundamentals of Aerosol Dynamics, 2nd ed.; Topics in Chemical Engineering; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Colbeck, I. Aerosol Science: Technology and Applications, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.; Dutcher, D.; Emery, M.; Pagels, J.; Sakurai, H.; Scheckman, J.; Qian, S.; Stolzenburg, M.R.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.; et al. Tandem Measurements of Aerosol Properties—A Review of Mobility Techniques with Extensions. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 801–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, V.K.; Buckley, D.T.; Kimoto, S.; Lee, M.H.; Fukushima, N.; Hogan, C.J. Two dimensional size–mass distribution function inversion from differential mobility analyzer–aerosol particle mass analyzer (DMA–APM) measurements. J. Aerosol Sci. 2016, 92, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, D.T.; Kimoto, S.; Lee, M.H.; Fukushima, N.; Hogan, C.J. Technical note: A corrected two dimensional data inversion routine for tandem mobility-mass measurements. J. Aerosol Sci. 2017, 114, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipkens, T.A.; Olfert, J.S.; Rogak, S.N. Inversion methods to determine two-dimensional aerosol mass-mobility distributions II: Existing and novel Bayesian methods. J. Aerosol Sci. 2020, 146, 105565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broda, K.N.; Olfert, J.S.; Irwin, M.; Schill, G.P.; McMeeking, G.R.; Schnitzler, E.G.; Jäger, W. A novel inversion method to determine the mass distribution of non-refractory coatings on refractory black carbon using a centrifugal particle mass analyzer and single particle soot photometer. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipkens, T.A.; Boies, A.; Corbin, J.C.; Chakrabarty, R.K.; Olfert, J.; Rogak, S.N. Overview of methods to characterize the mass, size, and morphology of soot. J. Aerosol Sci. 2023, 173, 106211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, F.; Olfert, J.S. Determination of particle mass, effective density, mass–mobility exponent, and dynamic shape factor using an aerodynamic aerosol classifier and a differential mobility analyzer in tandem. J. Aerosol Sci. 2014, 75, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutson, E.O.; Whitby, K.T. Aerosol classification by electric mobility: Apparatus, theory, and applications. J. Aerosol Sci. 1975, 6, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slowik, J.G.; Stainken, K.; Davidovits, P.; Williams, L.R.; Jayne, J.T.; Kolb, C.E.; Worsnop, D.R.; Rudich, Y.; DeCarlo, P.F.; Jimenez, J.L. Particle Morphology and Density Characterization by Combined Mobility and Aerodynamic Diameter Measurements. Part 2: Application to Combustion-Generated Soot Aerosols as a Function of Fuel Equivalence Ratio. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 1206–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, F.; Olfert, J.S. An Instrument for the Classification of Aerosols by Particle Relaxation Time: Theoretical Models of the Aerodynamic Aerosol Classifier. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 916–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüther, T.N.; Rasche, D.B.; Schmid, H.J. The Centrifugal Differential Mobility Analyser—A New Device for Determination of Two-Dimensional Property Distributions. Aerosol Res. 2025, 3, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüther, T.N.; Schmid, H.J. Prediction of the transfer function for a Centrifugal Differential Mobility Analyzer by Streamline functions. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2025; submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Rüther, T.N.; Rasche, D.B.; Schmid, H.J. The POCS-Algorithm—An effective tool for calculating 2D particle property distributions via Data Inversion of exemplary CDMA measurement data. Aerosol Sci. 2025; submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, M.D.; Raabe, O.G. Slip correction measurements for aerosol particles of doublet and triangular triplet aggregates of spheres. J. Aerosol Sci. 1985, 16, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolzenburg, M.R. An Ultrafine Aerosol Size Distribution System. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Könözsy, L. The k − ω Shear-Stress Transport (SST) Turbulence Model. In A New Hypothesis on the Anisotropic Reynolds Stress Tensor for Turbulent Flows: Volume I: Theoretical Background and Development of an Anisotropic Hybrid k − ω Shear-Stress Transport/Stochastic Turbulence Model; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, L.; Chen, D.R. Technical Note: A New Deconvolution Scheme for the Retrieval of True DMA Transfer Function from Tandem DMA Data. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 1052–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeCarlo, P.F.; Slowik, J.G.; Worsnop, D.R.; Davidovits, P.; Jimenez, J.L. Particle Morphology and Density Characterization by Combined Mobility and Aerodynamic Diameter Measurements. Part 1: Theory. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 1185–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rüther, T.N.; Gröne, S.; Dechert, C.; Schmid, H.-J. Centrifugal Differential Mobility Analysis—Validation and First Two-Dimensional Measurements. Powders 2025, 4, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/powders4020011
Rüther TN, Gröne S, Dechert C, Schmid H-J. Centrifugal Differential Mobility Analysis—Validation and First Two-Dimensional Measurements. Powders. 2025; 4(2):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/powders4020011
Chicago/Turabian StyleRüther, Torben Norbert, Sebastian Gröne, Christopher Dechert, and Hans-Joachim Schmid. 2025. "Centrifugal Differential Mobility Analysis—Validation and First Two-Dimensional Measurements" Powders 4, no. 2: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/powders4020011
APA StyleRüther, T. N., Gröne, S., Dechert, C., & Schmid, H.-J. (2025). Centrifugal Differential Mobility Analysis—Validation and First Two-Dimensional Measurements. Powders, 4(2), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/powders4020011






