Patterns of Supplement Consumption and Interaction Risks Among Polymedicated Older Adults: A Descriptive Study †
7th CiiEM International Congress 2025—Empowering One Health to Reduce Social Vulnerabilities
)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maher, R.L.; Hanlon, J.; Hajjar, E.R. Clinical consequences of polypharmacy in elderly. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2014, 13, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morin, L.; Johnell, K.; Laroche, M.-L.; Fastbom, J.; Wastesson, J.W. The epidemiology of polypharmacy in older adults: Register-based prospective cohort study. Clin. Epidemiol. 2018, 10, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahverdian, A.; Jafari, M. Dietary supplement safety in older adults: A review of published case reports. Sr. Care Pharm. 2025, 40, 32–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asher, G.N.; Corbett, A.H.; Hawke, R.L. Common herbal dietary supplement-drug interactions. Am. Fam. Physician 2017, 96, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Auxtero, M.D.; Chalante, S.; Abade, M.R.; Jorge, R.; Fernandes, A.I. Potential Herb-Drug Interactions in the Management of Age-Related Cognitive Dysfunction. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Chan, E.; Pan, S.-Q.; Huang, M.; Lee, E.J.D. Pharmacokinetic interactions of drugs with St John’s wort. J. Psychopharmacol. 2004, 18, 262–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzo, A.A.; Ernst, E. Interactions between herbal medicines and prescribed drugs: An updated systematic review. Drugs 2009, 69, 1777–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzanti, G.; Menniti-Ippolito, F.; Moro, P.A.; Cassetti, F.; Raschetti, R.; Santuccio, C.; Mastrangelo, S. Hepatotoxicity from green tea: A review of the literature and two unpublished cases. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2009, 65, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teschke, R.; Schwarzenboeck, A.; Hennermann, K.-H. Kava hepatotoxicity: A clinical survey and critical analysis of 26 suspected cases. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 20, 1182–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bent, S.; Tiedt, T.N.; Odden, M.; Shlipak, M.G. The relative safety of Ephedra compared with other herbal products. Ann. Intern. Med. 2003, 138, 1006–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DrugBank Online. Available online: https://go.drugbank.com (accessed on 21 May 2025).
- Drug Interactions Checker-Medscape Drug Reference Database. Available online: https://reference.medscape.com/drug-interactionchecker (accessed on 21 May 2025).
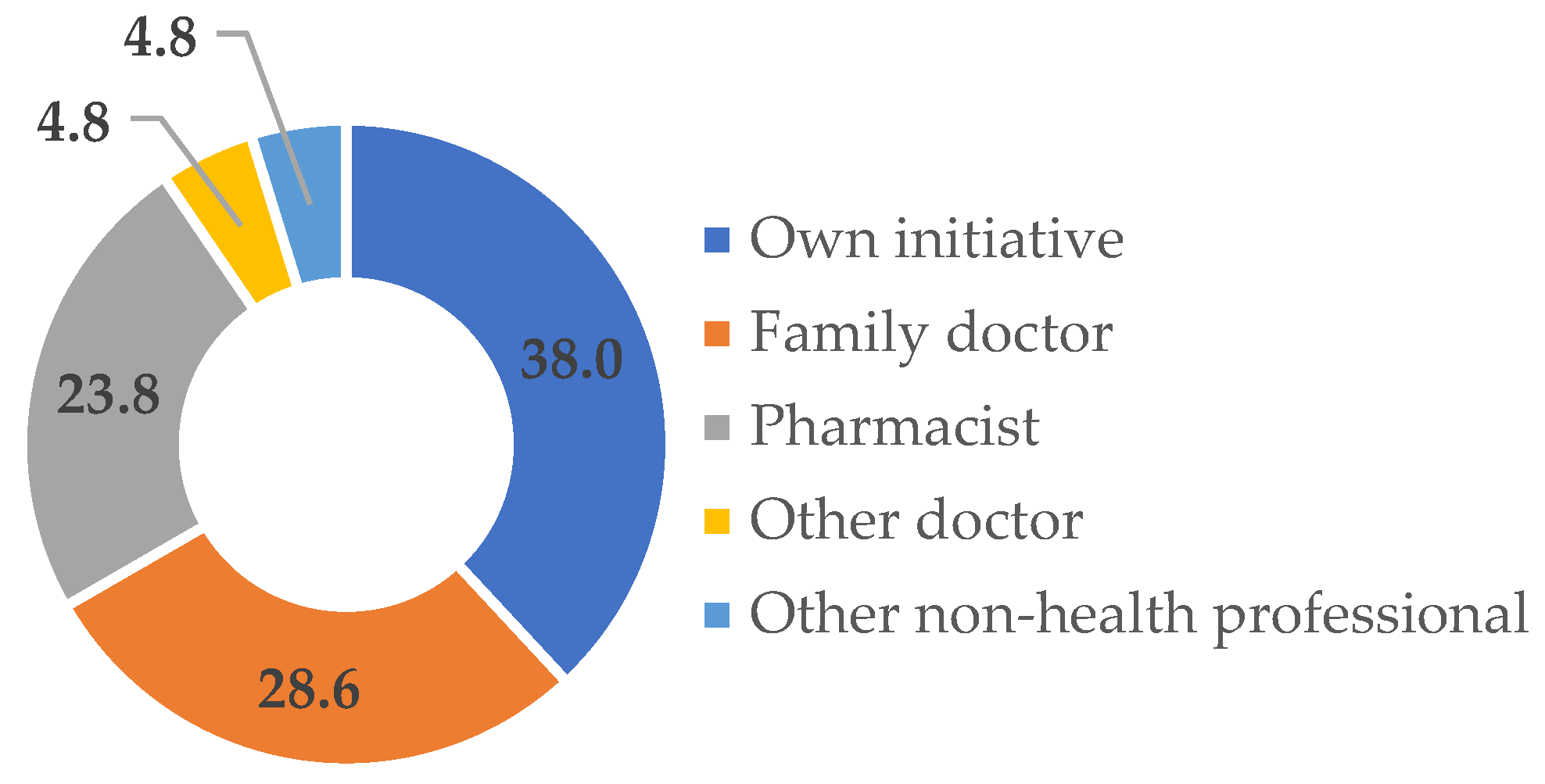
| P | FS | Bioactive | CYP ↑ | CYP ↓ | P-gP ↓ | Drugs Affected (CYP/Transporter Involved) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A | Biotin | 1B1 | - | No | - |
| Lutein | - | 2C19 | No | Simvastatin; Bromazepam; Pantoprazole (2C19) | ||
| Resveratrol | 1A2 | 1A2; 1A1; 1B1; 3A4; 2D6; 2B6; 2C19; 2C9 | No | Betahistine (2D6); Simvastatin (3A4; 2D6; 2C19); Calcitriol (3A4); Acetylsalicylic acid (2C9); Bromazepam (1A2, 2C19; 3A4); Pantoprazole (2C19; 3A4); Spironolactone (3A4) | ||
| Vitamin A | 26A1 | - | No | - | ||
| Vitamin B1 | 4B1 | - | No | - | ||
| Riboflavin | - | CYP1A2; CYP2C19 | No | Simvastatin (2C19); Bromazepam (1A2; 2C19); Pantoprazole (2C19) | ||
| Vitamin B6 | - | CYP1A1 | No | - | ||
| Vitamin D3 | - | CYP1A1; CYP2C8 | No | Simvastatin (2C8) | ||
| Vitamin E | 3A4 | - | No | Simvastatin; Calcitriol; Bromazepam; Pantoprazole; Spironolactone (3A4) | ||
| 2–4 | B | Vitamin D3 | 1A1; 2C8 | No | Atorvastatin (2C8) | |
| 5 | C | Biotin | 1B1 | - | No | - |
| Niacin | - | 2D6; 3A4; 2E1 | No | Bisoprolol (3A4; 2D6); Simvastatin (3A4; 2D6); Diazepam (3A4); Budesonide (3A4) | ||
| Vitamin B6 | - | 1A1 | No | - | ||
| 6 | D | DHA | - | 2C9 | No | - |
| 7 | E | Vitamin B6 | - | 1A1 | No | - |
| Vitamin D3 | - | 1A1; 2C8 | No | - | ||
| 8 | F | DHA | - | 2C9 | No | Venlafaxine |
| EPA | - | 1A2 | No | - | ||
| Curcumin | - | 3A4; 2C9; 2B6; 1A2; 2D6 | Yes | Atorvastatin (3A4/P-gP); Venlafaxine (2D6; 3A4; 2C9/P-gP) | ||
| Piperine | - | 3A4 | Yes | Atorvastatin (3A4/P-gP); Venlafaxine (3A4/P-gP) | ||
| Vitamin E | 3A4 | - | No | Atorvastatin; Venlafaxine (3A4) | ||
| 9 | G | Vitamin D3 | - | 1A1; 2C8 | No | Atorvastatin (2C8) |
| H | EPA | - | 1A2 | No | - | |
| DHA | - | 2C9 | No | Candesartan (2C9) | ||
| 10 | I | Quercetin | - | 2C8; 2D6; 2C9; 1A2; 2E1; 2C19 | Yes | Alprazolam (2C9); Bisoprolol (2D6/P-gP) |
| 11 | J | DHA | - | 2C9 | No | Acetylsalicylic acid; Pitavastatin (2C9) |
| EPA | - | 1A2 | No | - | ||
| Vitamin E | 3A4 | - | No | Pantoprazole; Amlodipine; Silodosin (3A4) | ||
| 12 | K | Vitamin B1 | 4B1 | - | No | - |
| Riboflavin | - | 1A2; 2C19 | No | Esomeprazole (2C19); Simvastatin (2C19); Clozapine (1A2; 2C19); Vortioxetine (2C19) | ||
| Niacin | - | 2D6; 3A4; 2E1 | No | Clonazepam (3A4); Esomeprazole (3A4); Simvastatin (3A4; 2D6); Clozapine (3A4; 2D6); Betahistine (2D6); Vortioxetine (3A4; 2D6) | ||
| Vitamin B6 | - | 1A1 | No | - | ||
| Biotin | 1B1 | - | No | - | ||
| 13 | L | Pyridoxine | - | 1A1 | No | - |
| 14 | M | DHA | - | 2C9 | No | Trimipramine; Valsartan; Rosuvastatin (2C9) |
| EPA | - | 1A2 | No | - | ||
| 15 | N | Niacin | - | 2D6; 3A4; 2E1 | No | Pantoprazole (3A4); Imatinib (3A4; 2D6) |
| Riboflavin | - | 1A2; 2C19 | No | Pantoprazole (2C19); Imatinib (1A2; 2C19) | ||
| 16 | O | DHA | - | 2C9 | No | Omeprazole; Fluoxetine (2C9) |
| EPA | - | 1A2 | No | Fluoxetine (1A2) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Auxtero, M.D.; Fernandes, A.I. Patterns of Supplement Consumption and Interaction Risks Among Polymedicated Older Adults: A Descriptive Study. Med. Sci. Forum 2025, 37, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2025037004
Auxtero MD, Fernandes AI. Patterns of Supplement Consumption and Interaction Risks Among Polymedicated Older Adults: A Descriptive Study. Medical Sciences Forum. 2025; 37(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2025037004
Chicago/Turabian StyleAuxtero, Maria Deolinda, and Ana Isabel Fernandes. 2025. "Patterns of Supplement Consumption and Interaction Risks Among Polymedicated Older Adults: A Descriptive Study" Medical Sciences Forum 37, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2025037004
APA StyleAuxtero, M. D., & Fernandes, A. I. (2025). Patterns of Supplement Consumption and Interaction Risks Among Polymedicated Older Adults: A Descriptive Study. Medical Sciences Forum, 37(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2025037004







