Molecular Docking Study of Natural Compounds Targeting the β2-Adrenergic Receptor (β2-AR) †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Receptor and Ligand Preparation
2.2. Docking Protocol
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schiöth, H.B.; Fredriksson, R. The GRAFS classification system of G-protein coupled receptors in comparative perspective. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2005, 142, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S.; Rahimi, N.; Dimri, M. Biochemistry, G protein coupled receptors. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Benovic, J.L. Novel β2-adrenergic receptor signaling pathways. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002, 110, S229–S235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tandale, A.; Joshi, M.; Sengupta, D. Structural insights and functional implications of inter-individual variability in β2-adrenergic receptor. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, P.J. Biochemical basis of asthma therapy. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 32899–32905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, S.J. G-protein-coupled receptors: Past, present and future. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 147, S27–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Marín, J.; Reyes-Resina, I.; Martínez-Pinilla, E.; Navarro, G.; Franco, R. Natural compounds as guides for the discovery of drugs targeting G-protein-coupled receptors. Molecules 2020, 25, 5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saqib, U.; Kelley, T.T.; Panguluri, S.K.; Liu, D.; Savai, R.; Baig, M.S.; Schürer, S.C. Polypharmacology or promiscuity? Structural interactions of resveratrol with its bandwagon of targets. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabarczyk, M.; Justyńska, W.; Czpakowska, J.; Smolińska, E.; Bielenin, A.; Glabinski, A.; Szpakowski, P. Role of plant phytochemicals: Resveratrol, curcumin, luteolin and quercetin in demyelination, neurodegeneration, and epilepsy. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiou, N.; Kakava, M.G.; Routsi, E.A.; Petsas, E.; Stavridis, N.; Freris, C.; Zoupanou, N.; Moschovou, K.; Kiriakidi, S.; Mavromoustakos, T. Quercetin: A potential polydynamic drug. Molecules 2023, 28, 8141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, N.N.; Armide, N.; Akbari, A.; Rahimi, V.B.; Askari, V.R. Quercetin a promising functional food additive against allergic diseases: A comprehensive and mechanistic review. J. Funct. Foods 2024, 116, 106152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vansal, S.S.; Feller, D.R. Direct effects of ephedrine isomers on human β-adrenergic receptor subtypes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1999, 58, 807–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yashima, M.; Sato, Y.; Kazama, I. Catechin synergistically potentiates mast cell-stabilizing property of caffeine. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2021, 17, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, S.; Miyoshi, N.; Kawabata, K.; Yasuda, M.; Shimoi, K. Quercetin-3-O-glucuronide inhibits noradrenaline-promoted invasion of MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells by blocking β2-adrenergic signaling. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 557, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, A.; Kumar, M.; Kaur, P.; Kumar, B.; Sagi, S.S. Efficacy of Quercetin as a potent sensitizer of β2-AR in combating the impairment of fluid clearance in lungs of rats under hypoxia. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2020, 273, 103334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chikazawa, M.; Sato, R. Identification of a Novel Function of Resveratrol and Genistein as a Regulator of β2-Adrenergic Receptor Expression in Skeletal Muscle Cells and Characterization of Promoter Elements Required for Promoter Activation. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1800530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanzione, F.; Giangreco, I.; Cole, J.C. Use of molecular docking computational tools in drug discovery. Prog. Med. Chem. 2021, 60, 273–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, F.J.; Grandordy, B.; Douglas, J.S. Functional and binding characteristics of long-acting beta 2-agonists in lung and heart. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 153, 1489–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherezov, V.; Rosenbaum, D.M.; Hanson, M.A.; Rasmussen, S.G.; Thian, F.S.; Kobilka, T.S.; Choi, H.-J.; Kuhn, P.; Weis, W.I.; Kobilka, B.K. High-resolution crystal structure of an engineered human β2-adrenergic G protein–coupled receptor. Science 2007, 318, 1258–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, S.G.; DeVree, B.T.; Zou, Y.; Kruse, A.C.; Chung, K.Y.; Kobilka, T.S.; Thian, F.S.; Chae, P.S.; Pardon, E.; Calinski, D. Crystal structure of the β2 adrenergic receptor–Gs protein complex. Nature 2011, 477, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Chen, J.; Cheng, T.; Gindulyte, A.; He, J.; He, S.; Li, Q.; Shoemaker, B.A.; Thiessen, P.A.; Yu, B. PubChem 2025 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D1516–D1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Hachem, N.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Khalil, A.; Kobeissy, F.H.; Nemer, G. AutoDock and AutoDockTools for protein-ligand docking: Beta-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE1) as a case study. In Neuroproteomics; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrödinger, Inc. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 1.8; Schrödinger, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, A.C.; Laskowski, R.A.; Thornton, J.M. LIGPLOT: A program to generate schematic diagrams of protein-ligand interactions. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 1995, 8, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.-Y.; Zhang, H.-X.; Mezei, M.; Cui, M. Molecular docking: A powerful approach for structure-based drug discovery. Curr. Comput.-Aided Drug Des. 2011, 7, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
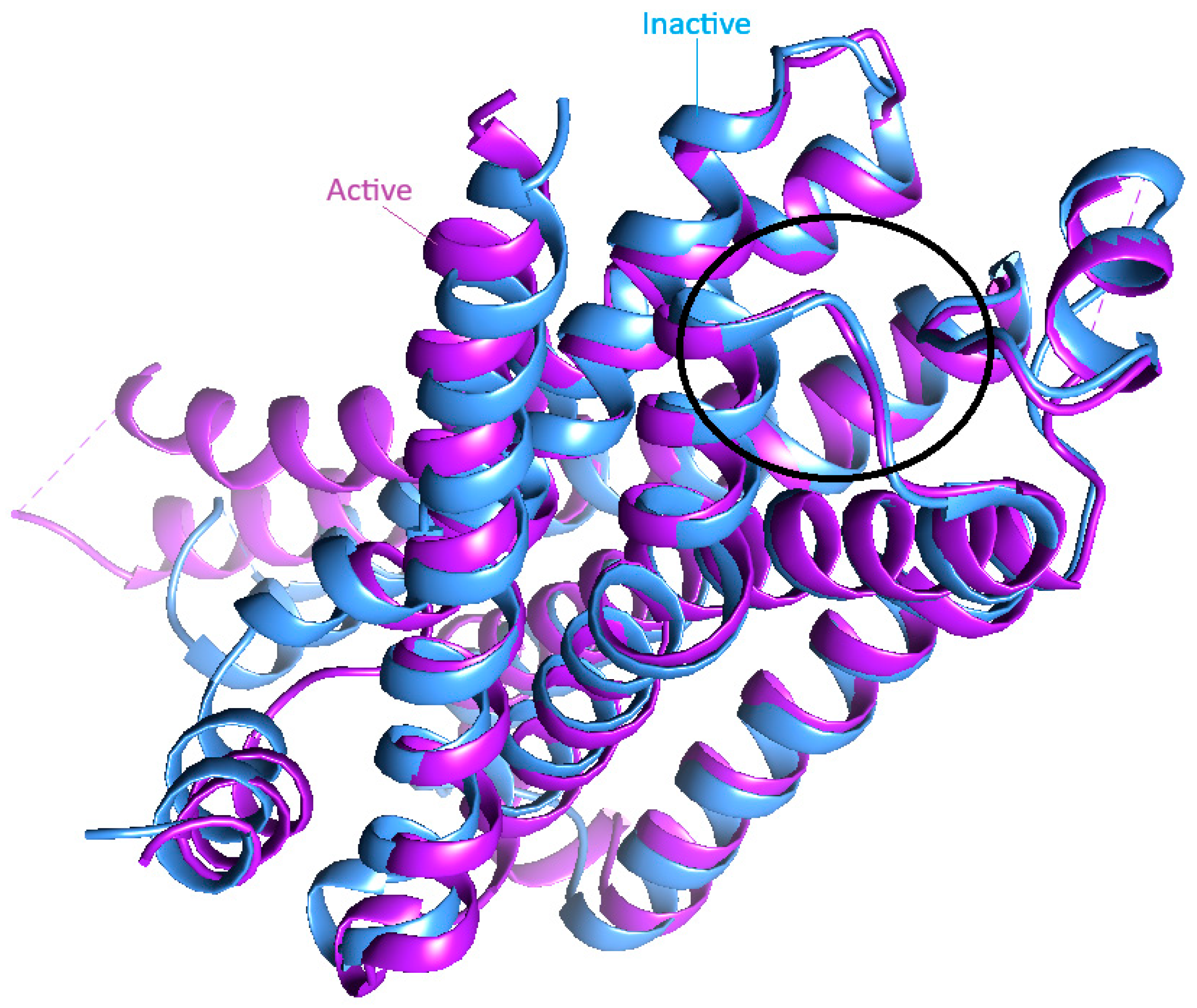
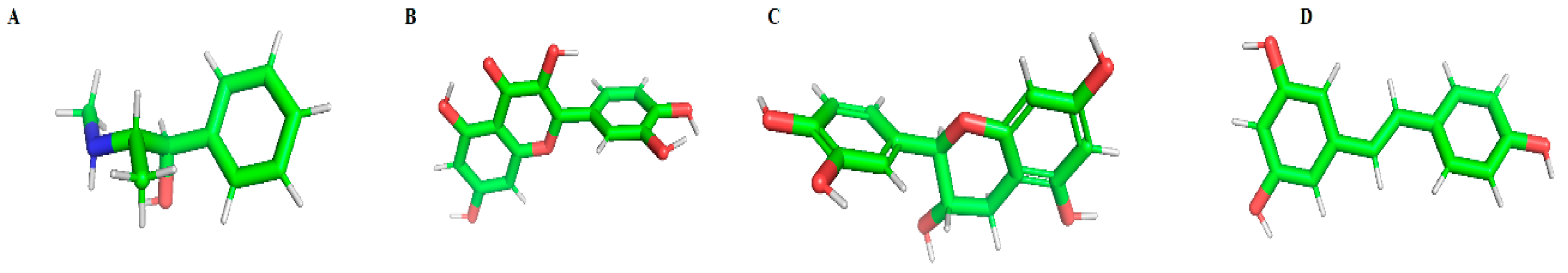

| Compound | Binding Energy (Inactive—2RH1) [kcal/mol] | H-Bonds (2RH1) | Binding Energy (Active—3SN6) [kcal/mol] | H-Bonds (3SN6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Formoterol | −7.86 | 2 | −7.53 | 3 |
| Salbutamol | −6.33 | 4 | −6.53 | 3 |
| Catechin | −5.37 | 5 | −4.65 | 4 |
| Ephedrine | −4.66 | 3 | −4.04 | 2 |
| Quercetin | −5.70 | 5 | −4.00 | 3 |
| Resveratrol | −5.29 | 3 | −4.64 | 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jafari, S.; Bojarska, J. Molecular Docking Study of Natural Compounds Targeting the β2-Adrenergic Receptor (β2-AR). Med. Sci. Forum 2025, 34, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2025034003
Jafari S, Bojarska J. Molecular Docking Study of Natural Compounds Targeting the β2-Adrenergic Receptor (β2-AR). Medical Sciences Forum. 2025; 34(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2025034003
Chicago/Turabian StyleJafari, Sepideh, and Joanna Bojarska. 2025. "Molecular Docking Study of Natural Compounds Targeting the β2-Adrenergic Receptor (β2-AR)" Medical Sciences Forum 34, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2025034003
APA StyleJafari, S., & Bojarska, J. (2025). Molecular Docking Study of Natural Compounds Targeting the β2-Adrenergic Receptor (β2-AR). Medical Sciences Forum, 34(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2025034003






