De Novo Drug Design of Potential Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Papain-like Protease †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Computational Details
2.1. Target Preparation
2.2. De Novo Drug Design
2.3. Molecular Dynamics
2.4. Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion, and Toxicity (ADMET) Study
2.5. Organic Retrosynthesis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structure of Papain-like Protease
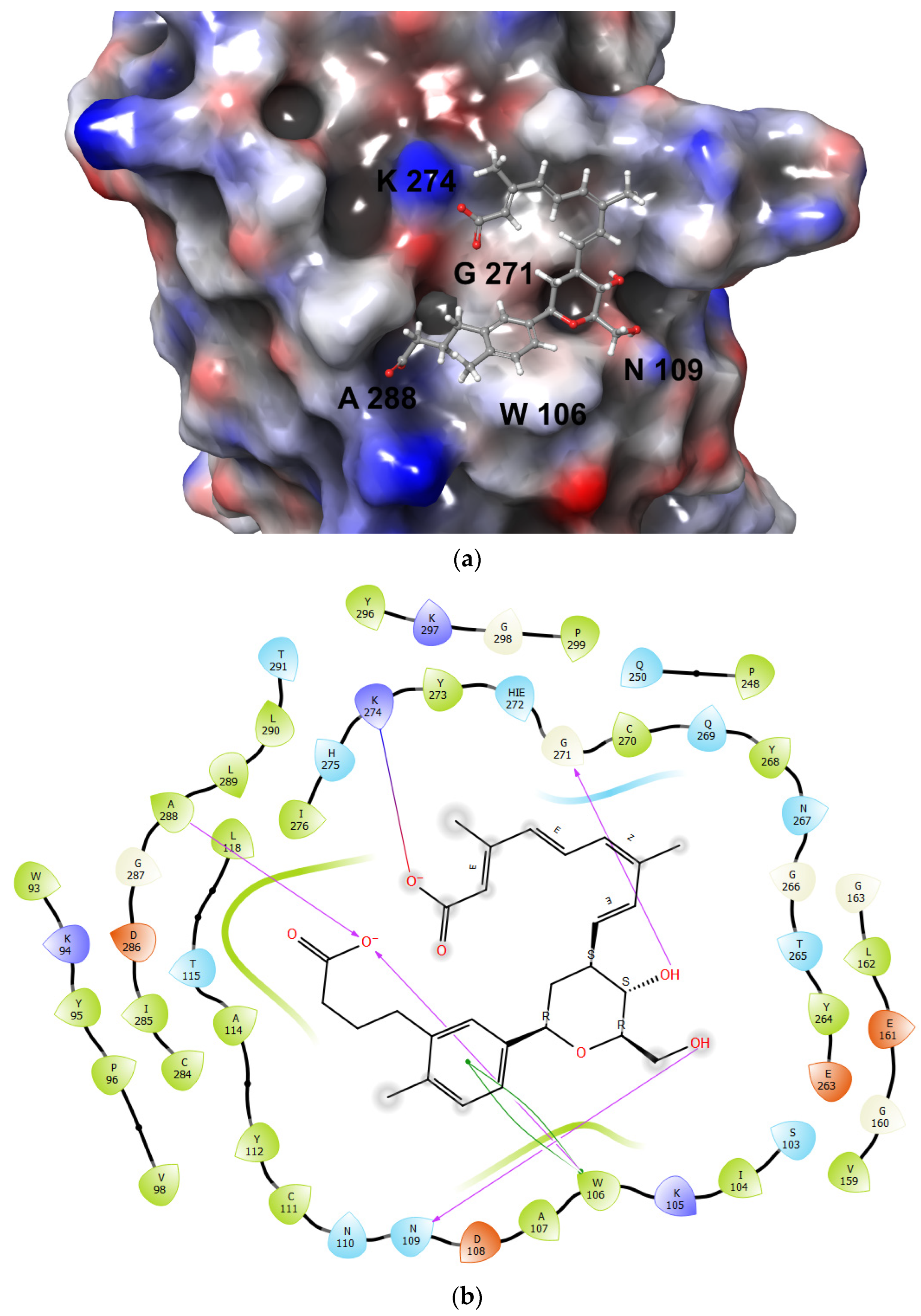
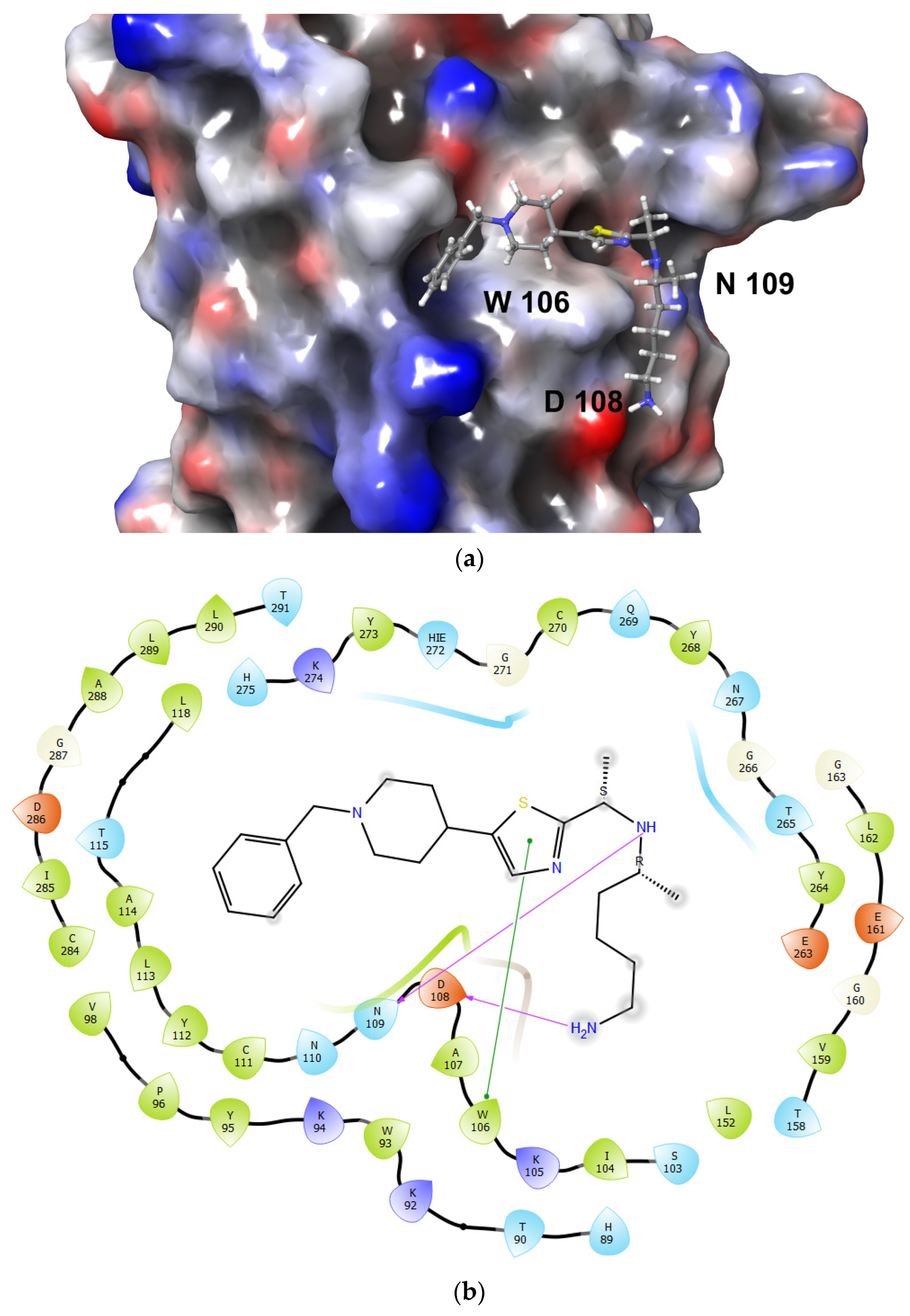
3.2. De Novo Drug Design
3.3. Molecular Dynamics Analysis
3.4. Organic Retrosynthesis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gorbalenya, A.E.; Baker, S.C.; Baric, R.S.; de Groot, R.J.; Drosten, C.; Gulyaeva, A.A.; Haagmans, B.L.; Lauber, C.; Leontovich, A.M.; Neuman, B.W.; et al. The species Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: Classifying 2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyahya, A.; El Omari, N.; Elmenyiy, N.; Hakkour, M.; Balahbib, A.; Guaouguaou, F.E.; Benali, T.; El Baaboua, A.; Belmehdi, O. Therapeutic strategies of COVID-19: From natural compounds to vaccine trials. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2021, 11, 8318–8373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazafa, A.; Ur-Rahman, K.; Haq, I.-U.; Jahan, N.; Mumtaz, M.; Farman, M.; Naeem, H.; Abbas, F.; Naeem, M.; Sadiqa, S.; et al. The broad-spectrum antiviral recommendations for drug discovery against COVID-19. Drug Metab. Rev. 2020, 52, 408–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousefi, H.; Mashouri, L.; Okpechi, S.C.; Alahari, N.; Alahari, S.K. Repurposing existing drugs for the treatment of COVID-19/SARS-CoV-2 infection: A review describing drug mechanisms of action. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 183, 114296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Solidarity Trial Consortium. Repurposed Antiviral Drugs for COVID-19—Interim WHO Solidarity Trial Results. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chellapandi, P.; Saranya, S. Genomics insights of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) into target-based drug discovery. Med. Chem. Res. 2020, 29, 1777–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, G.U.; Song, H.; Yoon, G.Y.; Kim, D.; Kwon, Y.-C. Therapeutic Strategies Against COVID-19 and Structural Characterization of SARS-CoV-2: A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.; Mukherjee, R.; Grewe, D.; Bojkova, D.; Baek, K.; Bhattacharya, A.; Schulz, L.; Widera, M.; Mehdipour, A.R.; Tascher, G.; et al. Papain-like protease regulates SARS-CoV-2 viral spread and innate immunity. Nature 2020, 587, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, B.K. Can Papain-like Protease Inhibitors Halt SARS-CoV-2 Replication? ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2020, 3, 1017–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou-Yang, S.; Lu, J.; Kong, X.; Liang, Z.; Luo, C.; Jiang, H. Computational drug discovery. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2012, 33, 1131–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechelane-Maia, E.H.; Assis, L.C.; Alves de Oliveira, T.; Marques da Silva, A.; Gutterres Taranto, A. Structure-based virtual screening: From classical to artificial intelligence. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionta, E.; Spyrou, G.; Vassilatis, D.K.; Cournia, Z. Structure-Based Virtual Screening for Drug Discovery: Principles, Applications and Recent Advances. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 1923–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danishuddin, M.; Khan, A.U. Structure based virtual screening to discover putative drug candidates: Necessary considerations and successful case studies. Methods 2015, 71, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tresadern, G.; Bemporad, D. Modeling approaches for ligand-based 3D similarity. Futur. Med. Chem. 2010, 2, 1547–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, C.; Coop, A.; Polli, J.E.; MacKerell, A.D. Recent advances in ligand-based drug design: Relevance and utility of the conformationally sampled pharmacophore approach. Curr. Comput. Aided-Drug Des. 2010, 7, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Rani, C.; Pant, P.; Vijayan, V.; Vikram, N.; Kaur, P.; Singh, T.P.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, P. Structure-Based Virtual Screening and Biochemical Validation to Discover a Potential Inhibitor of the SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 33151–33161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carli, M.; Sormani, G.; Rodriguez, A.; Laio, A. Candidate Binding Sites for Allosteric Inhibition of the SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease from the Analysis of Large-Scale Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2020, 12, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osipiuk, J.; Azizi, S.-A.; Dvorkin, S.; Endres, M.; Jedrzejczak, R.; Jones, K.A.; Kang, S.; Kathayat, R.S.; Kim, Y.; Lisnyak, V.G.; et al. Structure of papain-like protease from SARS-CoV-2 and its complexes with non-covalent inhibitors. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douguet, D. e-LEA3D: A computational-aided drug design web server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A. Drug-like properties and the causes of poor solubility and poor permeability. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2000, 44, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benet, L.Z.; Hosey, C.M.; Ursu, O.; Oprea, T.I. BDDCS, the Rule of 5 and drugability. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 101, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skalic, M.; Jiménez, J.; Sabbadin, D.; De Fabritiis, G. Shape-Based Generative Modeling for de Novo Drug Design. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2019, 59, 1205–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Boyle, N.M.; Banck, M.; James, C.A.; Morley, C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Hutchison, G.R. Open babel: An open chemical toolbox. J. Cheminform. 2011, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.-F.; Wang, F.; Chen, Y.-Z.; Hao, G.-F.; Yang, G.-F. LARMD: Integration of bioinformatic resources to profile ligand-driven protein dynamics with a case on the activation of estrogen receptor. Briefings Bioinform. 2019, 21, 2206–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Case, D.A.; Cheatham, T.E., III; Darden, T.; Gohlke, H.; Luo, R.; Merz, K.M., Jr.; Onufriev, A.; Simmerling, C.; Wang, B.; Woods, R.J. The Amber biomolecular simulation programs. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1668–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, J.A.; Martinez, C.; Kasavajhala, K.; Wickstrom, L.; Hauser, K.E.; Simmerling, C. ff14SB: Improving the accuracy of protein side chain and backbone parameters from ff99SB. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2015, 11, 3696–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wolf, R.M.; Caldwell, J.W.; Kollman, P.A.; Case, D.A. Development and testing of a general amber force field. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1157–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Merz, K.M. A Fast QM/MM (Quantum Mechanical/Molecular Mechanical) Approach to Calculate Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Chemical Shifts for Macromolecules. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2006, 2, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, D.J.; Brooks, C.L. A modified TIP3P water potential for simulation with Ewald summation. J. Chem. Phys. 2004, 121, 10096–10103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Chandrasekhar, J.; Madura, J.D.; Impey, R.W.; Klein, M.L. Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGibbon, R.T.; Beauchamp, K.A.; Harrigan, M.P.; Klein, C.; Swails, J.M.; Hernández, C.X.; Schwantes, C.R.; Wang, L.-P.; Lane, T.J.; Pande, V.S. MDTraj: A Modern Open Library for the Analysis of Molecular Dynamics Trajectories. Biophys. J. 2015, 109, 1528–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, B.J.; Rodrigues, A.P.; ElSawy, K.M.; McCammon, J.A.; Caves, L.S. Bio3d: An R package for the comparative analysis of protein structures. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 2695–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Wang, N.-N.; Yao, Z.-J.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, Y.; Ouyang, D.; Lu, A.-P.; Cao, D.-S. ADMETlab: A platform for systematic ADMET evaluation based on a comprehensively collected ADMET database. J. Cheminform. 2018, 10, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Qin, B.; Chen, P.; Zhu, K.; Hou, P.; Wojdyla, J.A.; Wang, M.; Cui, S. Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 papain-like protease. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, 11, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertl, P.; Schuffenhauer, A. Estimation of synthetic accessibility score of drug-like molecules based on molecular complexity and fragment contributions. J. Cheminform. 2009, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lopez, E.C.R. De Novo Drug Design of Potential Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Papain-like Protease. Med. Sci. Forum 2023, 21, 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECB2023-14368
Lopez ECR. De Novo Drug Design of Potential Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Papain-like Protease. Medical Sciences Forum. 2023; 21(1):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECB2023-14368
Chicago/Turabian StyleLopez, Edgar Clyde R. 2023. "De Novo Drug Design of Potential Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Papain-like Protease" Medical Sciences Forum 21, no. 1: 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECB2023-14368
APA StyleLopez, E. C. R. (2023). De Novo Drug Design of Potential Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Papain-like Protease. Medical Sciences Forum, 21(1), 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECB2023-14368





