Abstract
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) has the poorest BC prognosis, chemotherapy being the mainstream treatment. Prior studies revealed potential synergistic effects of natural compounds with drugs, such as doxorubicin (Dox), frequently used for TNBC. Fucosterol (Fct), a phytosterol of brown seaweeds, because of its antioxidant and antitumor effects, is one of these promising compounds. Using a TNBC cell line (MDA-MB-231), we aimed to test the effects of Fct alone and in combination with Dox on cell viability and proliferation, in monolayer and three-dimensional (3D) cultures. At this stage of the research, data demonstrated that Fct (5 µM) alone did not affect cell viability and proliferation. In monolayer, Dox (≥1 µM) decreased cell viability and proliferation, while in 3D only cell viability was affected at Dox 5 µM. The combination of Fct/Dox (5/0.1 µM), in monolayer, significantly decreased cell viability and proliferation, differing from the control and both compounds alone; hence, this suggests that Fct enhanced the Dox effect. These promising Fct effects in monolayer were not observed in 3D. We suggest that Fct may increase Dox effects, under certain conditions. Our results corroborate other studies reporting more treatment resistance of cells in 3D culture, reinforcing the need to use more complex models for more realistic drug screening.
1. Introduction
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is a cancer subtype that lacks expression of hormonal receptors (estrogen and progesterone receptors—ER and PR), and overexpression of human epidermal growth factor receptor-type 2 (HER-2). Owing to the lack of these targets, which are nowadays the available BC target therapies, TNBC is of poor prognosis, systemic chemotherapy being the mainstream treatment [1,2,3]. Drug resistance is a major problem in the treatment of TNBC [4]; thus, the investigation of new drugs or drug adjuvants to overcome drug resistance or reduce drug toxicity is of utmost importance. Recently, some in vitro studies revealed a potential synergistic effect of selected natural compounds in combination therapy with anti-cancer drugs [5,6], such as doxorubicin (Dox) [7], which is frequently used for TNBC.
Fucosterol (Fct), an abundant phytosterol of brown seaweeds, has been described as a promising compound due to its antioxidant [8,9,10] and antitumor effects [11,12]. However, the use of natural compounds that act as antioxidants in cancer treatment is controversial [13]. Many antioxidants can often exert both anti-oxidant and pro-oxidant properties, depending on the type of antioxidants [14], concentration used, cell type, exposure time, and environmental conditions [15]. In relation to BC in particular, studies are also inconsistent, suggesting that it will depend on the dose intake [16]. Some data recommend the avoidance of antioxidants during BC treatment [17], while others associate the intake of antioxidants in the first six months after BC diagnosis with reduced risk of mortality and recurrence [18].
In light of the presented scenario, it is critical to study the effects of an antioxidant in a specific set of conditions and evaluate their possible interplay with the anticancer drugs. In this study, we selected the antioxidant Fct and the anti-cancer drug Dox, used in TNBC treatment. Our aim was to test the effects of Fct and Dox, alone and in combination, on the viability and proliferation of a triple-negative breast cancer cell line (MDA-MB-231), using them in monolayer and 3D aggregate cultures.
2. Experiments
2.1. Cell Line
The MDA-MB-231 cell line was purchased from the American Tissue Culture Collection (ATCC). Cells were cultivated with Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium (DMEM) with high glucose content deprived of phenol red, supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1% antibiotic solution (streptomycin/penicillin), maintained as monolayer cultures in T75 cm3 culture flasks (Orange Scientific, Braine-l’Alleud, Belgium) and were kept in the incubation chamber MCO 19AIC (Sanyo, Osaka, Japan) at 37 °C with 5% CO2. For cells’ growth and maintenance, the medium was replaced every two days. Cells were regularly observed using the Olympus CKX41 inverted phase-contrast.
2.2. Chemicals for Exposure
Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) was purchased from VWR Chemicals (Solon, OH, USA). 3-(4,5-Dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT), 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole, Dox, Fct, were obtained from Sigma Aldrich (St.Louis, MO, USA). DMEM without glutamine and without phenol red, FBS, streptomycin/penicillin solution and trypsin/ ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) solution, were acquired from Biochrom KG (Berlin, Germany). Resazurin was acquired from Cayman (AnnArbor, MI, USA) and BrdU (colorimetric) from Roche (Basel, Switzerland).
Stock solutions of Dox and Fct were prepared in DMSO and kept at −20 °C until used. Exposure solutions were prepared before each experiment by diluting stock solution into the respective fresh culture medium, maintaining the 0.1% DMSO. Stock solutions of MTT and Resazurin were prepared in phosphate buffer saline (PBS) at a final concentration of 5 mg/mL and 1mM, respectively.
2.3. Monolayer Culture
Cell suspensions were obtained by using a trypsin-EDTA solution and after counting in a Neubauer chamber, cells were seeded in 96-multiwell culture plates (Orange Scientific, Braine-l’Alleud, Belgium) at a density of 0.5 × 106 cells/mL, 100 µl/well, and kept in the incubator at 37 °C and 5% CO2. For monolayer, cells were left overnight for attachment and then exposed to the tested conditions for 72 h.
2.4. Multicellular Aggregates (MCAs) (3D Cultures)
Cells were trypsinized and seeded at 40 × 104 cells/mL, 200 µL/well in ultra-low attachment microplates (Corning, MA, USA), then centrifugated at 200 g for 10 min in a ROTINA 380R centrifuge with swinging buckets (Hettich, Vlotho, Germany), and finally incubated under standard cell culture conditions as monolayer cultures. After seeding, MCAs formed within 72 h, and then the exposure was performed for 96 h.
2.5. Viability Assays
Effects on cell viability were assessed by MTT and resazurin assays. For MTT, stock solution was added to each well in a dilution of 1:10 µL and resazurin in a dilution of 1:100 µL of exposure medium. In monolayers, the metabolization of both reagents was performed for 2 h, while in 3D the time was extended by 4 h; the whole protocol was described previously [19].
2.6. Proliferation Assay
Effects on cell proliferation were evaluated by the BrdU assay according to manufacturer’s instructions as described in detail [6,19].
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Descriptive and inferential statistics were performed using GraphPad Prism 6.0 software (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA, USA), from 3 independent experiments. The normality and homogeneity of variance were confirmed by the Shapiro–Wilk test and the Levene test, respectively. The results are expressed as mean ± standard error of mean (SEM) of three independent experiments (three duplicates per replica). Significant differences (p < 0.05) were assessed by one-way ANOVAs, followed by the post-hoc Holm– Šídák multiple comparison test.
3. Results
3.1. Assessement of Cell Cell Viability
3.1.1. MTT Assay
In monolayer, MTT assay showed that Dox (≥1 µM) induced cytotoxic effects in all tested conditions (alone and in combination), reducing cell viability. Fct alone did not affect cell viability. The combination of Fct 5 µM with Dox 0.1 µM statistically differed from the exposure of each compound alone. In 3D culture, cell viability only differed from the control when cells were exposed to Dox 5 µM (Figure 1).
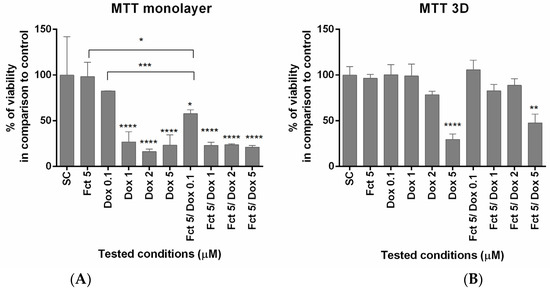
Figure 1.
Effect of fucosterol (Fct) at 5 µM alone and in combination with doxorubicin (Dox) at 0.1, 1 and 2 µM, on cell viability in monolayer (A) and 3D (B), assessed by MTT assay. Cells treated with 0.1% DMSO (SC) and Dox 5 µM were included as negative and positive controls, respectively. The results were expressed as the percentage of cell viability relative to SC (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001).
3.1.2. Resazurin Assay
The results of the resazurin assay were similar to those of the MTT assay. In monolayer, cell viability differed from the SC group in all conditions, except from Fct and Dox 0.1 µM alone. The combination of Fct 5 µM with Dox 0.1 µM also differed statistically from the exposure of either compound alone. The same conditions tested in 3D only revealed effects on cell viability in cells exposed to Dox 5 µM (Figure 2).
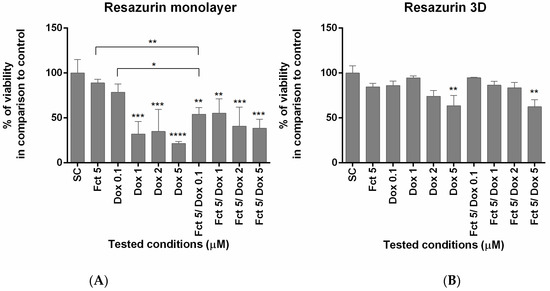
Figure 2.
Effect of fucosterol (Fct) at 5 µM alone and in combination with doxorubicin (Dox) at 0.1, 1 and 2 µM, on cell viability in monolayer (A) and 3D (B), assessed by resazurin assay. Cells treated with 0.1% DMSO (SC) and Dox 5 µM were included as negative and positive controls, respectively The results were expressed as the percentage of cell viability relative to SC (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001; **** p < 0.0001).
3.2. Assessement of Cell Proliferation
The effects on cell proliferation were studied by BrdU assay. In monolayer, proliferation was reduced in Dox concentration of 1–5 µM and in all Fct plus Dox combinations. Fct and Dox 0.1 µM alone did not have any effect on cell proliferation, but in combination reduced significatively the percentage of cell proliferation in relation to the control. In 3D culture, none of the tested conditions revealed effects on cell proliferation (Figure 3).
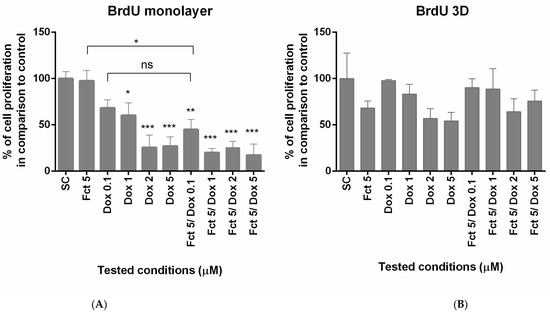
Figure 3.
Effect of fucosterol (Fct) at 5 µM alone and in combination with doxorubicin (Dox) at 0.1, 1 and 2 µM, on cell proliferation in monolayer (A) and 3D (B), assessed by BrdU assay. Cells treated with 0.1% DMSO (SC) and Dox 5 µM were included as negative and positive controls, respectively. The results were expressed as the percentage of cell viability relative to SC (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001).
4. Discussion
At the tested conditions, Fct alone did not have cytotoxic or anti-proliferative effects on the MDA-MB-231 cells; this is similar to previous studies using colon cell lines [6]. However, another study [20] reported the opposite, revealing Fct to have cytotoxic effects, but this was using concentrations four to twenty times higher than those used in this study. Here, the fact that Fct in low concentration seemed to have potentiated the Dox action is a very interesting result that needs to be further explored. Of particular importance would be to study the mechanisms related to the interplay between Fct and Dox, namely using a pathway-focused gene expression analysis and additional cell-based assays. As for the latter, and because Fct may change the levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) [20,21], the fine balance of which is critical for cancer cells to thrive, the determination of ROS would be a particularly interesting target.
5. Conclusions
We conclude that Fct seems to have potential to increase Dox effects, under certain conditions. Our results corroborate other studies reporting more resistance of cancer cells to treatments when cultured in 3D. In this case, more resistance to the cytotoxic activity of Dox and its combination with Fct further highlights the importance of using these more complex models for drug screening.
Author Contributions
F.M., A.A.R. and E.R. conceived and designed the experiments; F.M. performed the experiments; F.M. analyzed the data; E.R. contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools; F.M. wrote the paper. A.A.R and E.R. reviewed it. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The Strategic Funding UIDB/04423/2020 and UIDP/04423/2020 partially supported this research, through national funds provided by FCT and ERDF to CIIMAR/CIMAR, under the framework of the program PT2020. Further support was attributed by the Doctoral Program in Biomedical Sciences of the ICBAS.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| BC | Breast Cancer |
| Dox | doxorubicin |
| Fct | Fucosterol |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| TNBC | Triple-Negative Breast Cancer |
References
- Kumar, P.; Aggarwal, R. An overview of triple-negative breast cancer. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2016, 293, 247–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.; Li, T.; Bai, Z.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhan, J.; Shi, B. Breast cancer intrinsic subtype classification, clinical use and future trends. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 2929–2943. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, L.N.; Wilkinson, K.H.; Kong, A. Triple-negative breast cancer: Who should receive neoadjuvant chemotherapy? Surg. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 27, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedeljković, M.; Damjanović, A. Mechanisms of Chemotherapy Resistance in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer—How We Can Rise to the Challenge. Cells 2019, 8, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lopes-Costa, E.; Abreu, M.; Gargiulo, D.; Rocha, E.; Ramos, A.A. Anticancer effects of seaweed compounds fucoxanthin and phloroglucinol, alone and in combination with 5-fluorouracil in colon cells. J. Toxicol. Environ. Heal. Part A 2017, 80, 776–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, A.; Almeida, T.; Lima, B.; Rocha, E. Cytotoxic activity of the seaweed compound fucosterol, alone and in combination with 5-fluorouracil, in colon cells using 2D and 3D culturing. J. Toxicol. Environ. Heal. Part A 2019, 82, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.-R.; Chang, C.-H.; Hsu, C.-F.; Tsai, M.-J.; Cheng, H.; Leong, M.K.; Sung, P.-J.; Chen, J.-C.; Weng, C.-F. Natural compounds as potential adjuvants to cancer therapy: Preclinical evidence. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 1409–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.; Lee, Y.S.; Jung, S.H.; Kang, S.S.; Shin, K.H. Anti-oxidant activities of fucosterol from the marine algae Pelvetia siliquosa. Arch. Pharmacal. Res. 2003, 26, 719–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.S.; Han, Y.R.; Byeon, J.S.; Choung, S.-Y.; Sohn, H.S.; Jung, H.A.; Choi, J.S.; Choung, S.-Y.; Sohn, H.S.; Jung, H.A. Protective effect of fucosterol isolated from the edible brown algae, Ecklonia stoloniferaandEisenia bicyclis, ontert-butyl hydroperoxide- and tacrine-induced HepG2 cell injury. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2015, 67, 1170–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul, Q.A.; Choi, R.J.; Jung, H.A.; Choi, J.S. Health benefit of fucosterol from marine algae: A review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 1856–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.-B.; Ji, C.; Yue, L. Study on human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cells apoptosis induced by fucosterol. Bio-Medical Mater. Eng. 2014, 24, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostad, S.N.; Khanavi, M.; Gheidarloo, R.; Sadati, N.; Ardekani, M.R.S.; Nabavi, S.M.B.; Tavajohi, S. Cytotoxicity of fucosterol containing fraction of marine algae against breast and colon carcinoma cell line. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2012, 8, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Asadi-Samani, M.; Farkhad, N.K.; Mahmoudian-Sani, M.R.; Shirzad, H. Antioxidants as a double-edged sword in the treatment of cancer. In Antioxidants; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greenlee, H.; Kwan, M.L.; Kushi, L.H.; Song, J.; Castillo, A.; Weltzien, E.; Quesenberry, C.P., Jr.; Caan, B.J. Antioxidant supplement use after breast cancer diagnosis and mortality in the Life After Cancer Epidemiology (LACE) cohort. Cancer 2011, 118, 2048–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sznarkowska, A.; Kostecka, A.; Meller, K.; Bielawski, K.P. Inhibition of cancer antioxidant defense by natural compounds. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 15996–16016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pan, S.Y.; Zhou, J.; Gibbons, L.; Morrison, H.; Wen, S.W. for the Canadian cancer registries epidemiology research group, Antioxidants and breast cancer risk—A population-based case-control study in Canada. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jung, A.Y.; Cai, X.; Thoene, K.; Obi, N.; Jaskulski, S.; Behrens, S.; Flesch-Janys, D.; Chang-Claude, J. Antioxidant supplementation and breast cancer prognosis in postmenopausal women undergoing chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 109, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nechuta, S.; Lu, W.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Gu, K.; Cai, H.; Zheng, W.; Shu, X. Vitamin Supplement Use During Breast Cancer Treatment and Survival: A Prospective Cohort Study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2011, 20, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malhão, F.; Ramos, A.; Buttachon, S.; Dethoup, T.; Kijjoa, A.; Rocha, E. Cytotoxic and Antiproliferative Effects of Preussin, a Hydroxypyrrolidine Derivative from the Marine Sponge-Associated Fungus Aspergillus candidus KUFA 0062, in a Panel of Breast Cancer Cell Lines and Using 2D and 3D Cultures. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bae, H.; Lee, J.-Y.; Song, G.; Lim, W. Fucosterol Suppresses the Progression of Human Ovarian Cancer by Inducing Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Li, J.; Chen, A.; Li, Y.; Xia, M.; Guo, P.; Yao, S.; Chen, S. Fucosterol exhibits selective antitumor anticancer activity against HeLa human cervical cell line by inducing mitochondrial mediated apoptosis, cell cycle migration inhibition and downregulation of m-TOR/PI3K/Akt signalling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 3458–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
