Abstract
The study introduces a theory about a giant impact on the surface of Dione. Our study suspects a relatively low-velocity (≤5 km/s) collision between a c.a. 50–80 km diameter object and Dione, which might have resulted in the resurfacing of its intermediate cratered terrain. The source of the impactor might have been a unique satellite-centric debris, a unique impactor population, suspected in the Saturnian system. Other possible candidates are asteroid(s) appearing during the outer Solar System heavy bombardment period, or a collision, which might have happened during the “giant impact phase” in the early Saturnian system (coinciding with the Late Heavy Bombardment, or not).
1. Introduction
The target of the study is Dione, one of Saturn’s satellites, and its surface characteristics, especially with a focus on the possible relationship between the distribution pattern of certain-sized craters and resurfacing processes. The pivot of the study is the region, located westward from the Eurotas and Palatine chasmata (faulted terrain), defined as one of the intermediate cratered terrains (ICTs) [1]. Chronologically, intermediate cratered terrain might have formed between, (or following) the formation of the two oldest terrains (so-called dense cratered terrain, DCT 1 and 2; both c.a. 4.1 Ga), during the expected outer Solar System heavy bombardment period (independently from its spike-like or steady decline nature) (3.5 +1.0/−2.6 Ga) [1]. Kirchoff and Schenk [1] suggest that the region resurfaced at some point through a still unknown process, which erased all the previous craters. Some theories have been built to explain such process, including burial by material “snowing” down from the ring [2,3], thermal activity from tidal dissipation [4,5,6,7,8], and the subsequent formation of larger (D ≥ 50 km) craters and their ejecta blanket [1].
We propose a working hypothesis that suggests a hemisphere-scale impact or collision as an alternative cause and trigger of the surface renewal processes. The goal of our research is to support or deny such a hypothesis by the study of crater distribution patterns in Dione (with a focus on one of the ITCs) which may indicate the appearance of secondary crater formation related to the putative impact.
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Calculations Supporting the Estimation of the Primary Impactor and Secondary Crater Size
The transient crater size (Dt, km) is determined from the observed crater size (D, km) [9,10]:
The size of the primary impactor (d, km) is derived from Dt [9]:
where d is the impactor diameter in km with a density ρi (0.6 g/cm3; [10]), velocity vi (in the original study—U; for detailed information, please see Section 2.1.1), and incidence angle α (for detailed information, please see Section 2.1.1). ρt is the density of the icy crust (910 kg/m3), and g is the acceleration of gravity in km/s2 at the target surface, which is 2.32 × 10−4 km/s2 in the case of Dione.
The average size of the secondary impactors is determined by the following [11]:
where lAVG is the average size (m) of the ejected fragments, and T is the tension fracture, equal to 0.17 × 108 Pa in ice [12]. As described in the previous equations, d is the size of the impactor (km), ρt is the density of the ice at the target location: 0.91 g/cm3 [10], ve is the speed of the ejecta (for “rubble ejecta”: 1.98 km/s; [10]), and vi is the velocity of the impactor (please see detailed information in Section 2.1.1).
The maximum size of the secondary projectiles was derived from lAVG [11]:
where lMAX is the maximum size (m) of the ejected fragments, lAVG is the average fragment size (m), and mW is the so-called Weibulls constant, which is 8.7 for ice [12].
The ejected mass (Mtot; kg) in the case of the theoretical impact (if a secondary crater ring or any pattern is found, and the original impactor/impact crater size can be estimated) is calculated from:
where Dt is the transient crater diameter of the putative crater in km, indicated by the secondary craters, and ρt is the density of the ice at the target location: 0.91 g/cm3 [10].
Mtot = 3.75 × 10−2 ρtDt3
2.1.1. Scenarios of the Secondary Crater Formation
To determine the characteristic of the impact causing hemisphere-scale renewal, the size variation of secondary craters was simulated as a result of various size impactors. As already indicated above, two variables were used during the simulation: the speed of the impactor and the impact angle. A set of impact velocities, including 3.93, 5.81, and 7.69 km/s, and 20.4 km/s was used. The former three represent the collision velocity calculated for main asteroid belt collisions [13], and the latter was applied in the various studies targeting asteroid impact reconstructions in icy planetary bodies [9,10]. As a second variable, two different impact angles were set: one is the average, commonly applied at 45° [9,10], and a relatively low, 20° incidence angle, which appears in a certain study, modeling low-angle impacts and their effects on planetary surfaces [14].
2.2. The Studied Location and the Crater Distribution Map
The studied region, one of the so-called intermediate cratered terrains [1] spreads approximately between latitude 50° and −50° and longitude c.a. 300° to 60° (westward) (Figure 1). The source of the map of Dione is based on Cassini—Voyager Global Mosaic 154 m v1 map, and can be found at Astropedia—Lunar and Planetary Cartographic Catalog [15,16,17,18]. The applied nomenclature follows the recommendation of the Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature [19].
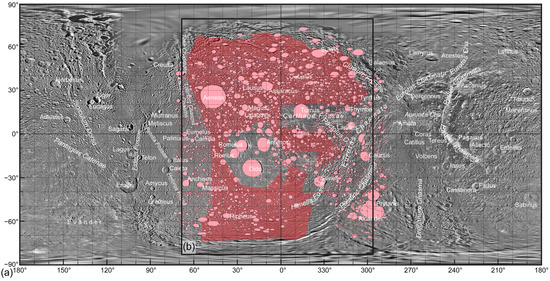
Figure 1.
(a) Cassini–Voyager Global Mosaic 154 m v1 map (can be found at https://astrogeology.usgs.gov/search/map/Dione/Voyager/Dione_Cassini_Voyager_mosaic_global_154m; accesed on 14 February 2023) Reprinted/adapted with permission from Refs. [15,16,17,18]. Batson, R. 1984; Greely, R. and Batson, R. 2007; Roatsch, T. et al. 2016; and Schneck, P. 2016. (b) the region of study, consisting of the ICT (red, transparent polygon) [1]. The ⌀ ≥ 4 km craters used in the analysis are indicated by pink ellipsoids. Dashed red lines: areas with crater mapping uncertainties (see Section 2.2).
The remote sensing and GIS research was performed by QGIS 3.22 software (“Firenze” version; released: 21st October 2022; international developer team; https://www.qgis.org/en/site/; accessed on 14 February 2023). In previous studies, the mapping of craters in Dione was limited to craters with ⌀ ≥ 4 km crater diameter due to problems during the identification of smaller craters in image mosaics with lower resolution [1]. To avoid the increasing bias in the results due to the use of barely identifiable smaller craters, this study also applies such a criterion. Over 8800 craters fulfilling the minimum ⌀ ≥ 4 km size limit were identified, including about 5400 craters found in the studied area (Figure 1b). The crater distribution maps were created by using the centroids of the craters and a grid with a 100 km × 100 km basic cell size, overlapping the map. The distribution map is based on the number of certain-sized craters, appearing in the cells of the grid (Figure 2).
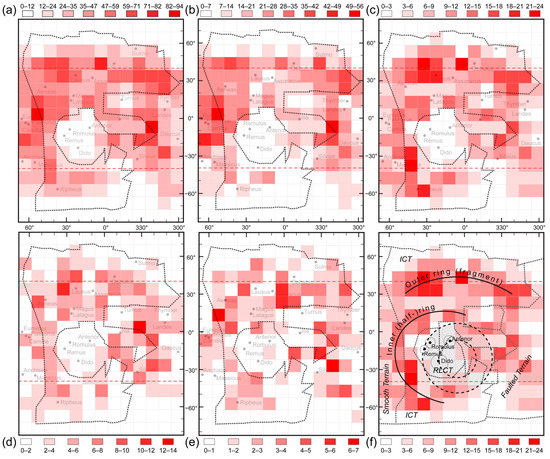
Figure 2.
Crater distribution map of (a) all ⌀ ≥ 4 km craters; (b) ⌀ 4–5.9 km craters; (c) ⌀ 6–7.9 km craters; (d) ⌀ 8–9.9 km craters; (e) ⌀ 10–11.9 km craters. The dashed red lines: crater mapping uncertainties. The dotted black line (a–e): margin of ICT and other terrains (f). The cell size of the light grey grid is 100 km × 100 km. Abbreviations: ICT—intermediate cratered terrain, RLCT—recent large cratered terrain. The grey area with black, dashed margins indicates the location of the putative impact crater (inner circle—⌀ 300 km; outer circle—⌀ 550 km).
Please note that the crater mapping had some limitations in certain areas located between latitude 40° to 90°, and especially between −40° to −90°, due to the quality of the image mosaics and the distortion of the map. This limitation may bias the results and therefore the areas with such potential uncertainty are marked by dashed red lines in Figure 1b and the maps of Figure 2.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Simulation of Secondary Crater Formation
Comparing the eight scenarios based on various impact and collision velocities and angles (Scen. 1 to 8; Table 1), the main results can be summarized as followings:

Table 1.
Relationship between the primary impactor and secondary crater formation on Dione. Columns 1 to 8 shows various scenarios, using various combination of impact velocity (U or vi) and angles (ψ), such as 1 (vi: 3.93 km/s; ψ: 20°), 2 (vi: 5.81 km/s; ψ: 20°), 3 (vi: 7.69 km/s; ψ: 20°), 4 (vi: 20.4 km/s; ψ: 20°), 5 (vi: 3.93 km/s; ψ: 45°), 6 (vi: 5.81 km/s; ψ: 45°), 7 (vi: 7.69 km/s; ψ: 45°), and 8 (vi: 20.4 km/s; ψ: 45°). Bold data: primary impactor size; red data: primary impacts which result in ⌀ < 4 km secondary craters; grey background: collision scenarios that might have happened in the early history of Dione (based on the crater distribution results, see Section 3.2).
The change in impact angle from the commonly applied 45° [9,10] to a low, 20° incidence angle [14] does not significantly influence the secondary crater size.
The increasing collision velocity significantly decreases the size of ejectiles and thus the size of secondary craters. With high impact velocity, the secondary crater size would barely reach 1 km, even in the case of a relatively big impactor (Scen. 4 and 8; Table 1). It suggests that even if a larger impact happened, if the velocity was higher (c.a. >10 m/s), the secondary craters would blend into the mass of similar sized, common primary craters.
The minimum crater size requirement seems to limit the further interpretation of the results, i.e., ⌀ < 4 km secondary craters may be formed by large impacts, but they were not mapped due to the uncertainty during their identification.
In a summary, crater distribution patterns observed in this study can indicate relatively low velocity, “asteroid-belt-like” collisions between Dione and a minimum c.a. ⌀ 30–40 km impactor (resulting in a minimum c.a. ⌀ 200–250 km primary craters).
3.2. Distribution Patterns of Various Crater Classes
The distribution pattern of craters falling in four different diameter size classes was studied and compared to the general distribution pattern (all ⌀ ≥ 4 km craters; Figure 2a).
The pattern of the ⌀ 4–5.9 km crater class is similar to the general distribution, suggesting that even if there is some pattern, it melts into the general crater allocation (Figure 2b).
The fragments of two concentric rings were identified in the distribution map of the ⌀ 6–7.9 km crater class (Figure 2c). An inner one at the edge of the relatively crater-clean area, named RLCT (recent large crater terrain), and an outer one roughly around latitude 30° (Figure 2c,f). The inner ring may be the result of impacts forming the larger craters in the area, such as Dido, Romulus, and Remus. The outer ring, if it is created by a putative impact, may be the result of a low angle collision (20°) with a c.a. ⌀ 48–57 km, relatively low-velocity object (Scen. 1), or bigger, ⌀ 69–75 km, and faster object (Scen. 2). A similar ring may form, if a bigger object ⌀ 49–59 km (Scen. 4) or ⌀ 71–79 km (Scen. 5), collides with the same speeds (3.93 and 5.81 km/s, respectively), but at a greater impact angle (45°) (Table 1).
The distributions pattern of the craters falling into the ⌀ 8–9.9 km and the ⌀ 10–11.9 km crater classes are similar; they consist of some “randomly” located crater groups in the studied area, without any convincing pattern (Figure 2d,e).
3.3. Surface Renewal Model for the Studied Intermediate Cratered Terrain
Kirchoff and Schenk [1] suggested that one possible explanation for the renewal of the surface in the ICT region is the results of impactors and their ejecta creating the ⌀ ≥ 50 km impact craters. Our working theory suggests that such impactors may be accompanied by a much bigger size, c.a. ⌀ 50–80 km impactor, resulting in the formation of a ⌀ 300–350 to ⌀ 500–550 km crater (Figure 3). During the excavation phase of such a collision, 3.3–5.5 × 105 t (⌀ 300–350 km crater) to 1.3–1.7 × 106 t (⌀ 500–550 km crater) of debris might be ejected into space, and return to the surface, covering large areas of the ICT with an ejecta blanket (Figure 3b,c).
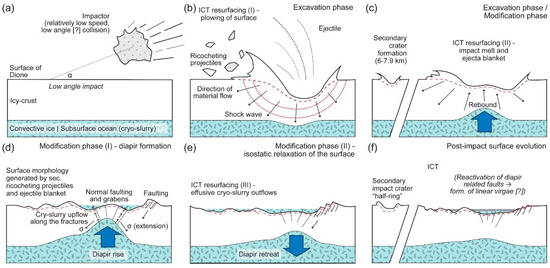
Figure 3.
The surface main steps of surface renewal of intermediate cratered terrain, following asteroid impact. (a) Low-angle collision; (b) Excavation phase of impact and the “plowing” of the ICT`s surface; (c) Excavation/modification phase transition and the ongoing deposition of ejecta blanket; (d,e) Modification phase with diapir formation and intensification of cryotectonic and cryovolcanic activity; and (f) post-impact surface evolution.
In addition to the ejecta blanket, in the case of a low-angle collision, the sliding and ricocheting ejectiles [14] might cause surface planning by “plowing” and partial melts.
Following the excavation phase of the impact, such a size impactor may cause the uplift of the ice crust (rebound) and the rise of a subsurface diapir-like structure, made by the convective ice layer and/or the cryo-slurry at the center of the impact crater during the modification stage of the impact (Figure 3d,e). The diapir and central peak formed in the convective ice crust might later retreat due to isostatic relaxation of the surface. Diapir formation may cause the intensification of cryotectonic and cryovolcanic activity in the region, accompanied by faulting and cryo-slurry outflows. Such secondary processes might have a significant role in the surface renewal of ICT (Figure 3d,e).
Here, we introduced a working theory about a giant impact on the surface of Dione, which might have contributed to the resurfacing of ICT, a region with an unrevealed astrogeological history. Our putative impactor might have originated from a unique impactor population, suspected in the Saturnian system [20], or appeared during the outer Solar System heavy bombardment period, or during the so-called “giant impact phase” (c.a., 4 Ga; coinciding with the Late Heavy Bombardment or not), a period leaving middle-sized satellite remnants, such as Dione, behind [21].
Given the results of the study, the hypothesis does not sound as “radical” or “dramatic” as the title of our study after all. Future research aims to complete more simulations about the effect of a giant impactor on the surface of Dione and possible astrogeological mapping and comparison of the surroundings of the putative impact and Evander crater, Dione’s largest impact crater, with a similar size to the estimated size range of our theoretical crater.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.B.; methodology, B.B. and C.G.; formal analysis, B.B., M.N.; investigation, B.B.; writing—original draft preparation, B.B.; writing—review and editing, B.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be provided via email upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kirchoff, M.R.; Schenk, P. Dione’s resurfacing history as determined from a global impact crater database. Icarus 2015, 256, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchoff, M.R.; Schenk, P. Crater modification and geologic activity in Enceladus’ heavily cratered plains: Evidence from the impact crater distribution. Icarus 2009, 202, 656–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenk, P.; Hamilton, D.P.; Johnson, R.E.; McKinnon, W.B.; Paranicas, C.; Schmidt, J.; Showalter, M.R. Plasma, plumes and rings: Saturn system dynamics as recorded in global color patterns on its midsize icy satellites. Icarus 2011, 211, 740–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segatz, M.; Spohn, T.; Ross, M.; Schubert, G. Tidal dissipation, surface heat flow, and figure of viscoelastic models of Io. Icarus 1988, 75, 187–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.M.A.; Nimmo, F. Implications from Ithaca Chasma for the thermal and orbital history of Tethys. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L19203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, J.; Wisdom, J. Tidal evolution of Mimas, Enceladus, and Dione. Icarus 2008, 193, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Nimmo, F. Recent orbital evolution and the internal structures of Enceladus and Dione. Icarus 2009, 204, 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, N.; Phillips, C.; Nimmo, F.; Kattenhorn, S. Flexure on Dione: Investigating subsurface structure and thermal history. Icarus 2013, 223, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarellos, J.L.; Zahnle, K.J.; Dobrovolskis, A.R.; Hamill, P. Fates of satellite ejecta in the Saturn system. Icarus 2005, 178, 104–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarellos, J.L.; Dobrovolskis, A.R.; Zahnle, K.J.; Hamill, P.; Dones, L.; Robbins, S. Fates of satellite ejecta in the Saturn system, II. Icarus 2017, 284, 70–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mileikowsky, C.; Cucinotta, F.A.; Wilson, J.W.; Gladman, B.; Horneck, G.; Lindegren, L.; Melosh, J.; Rickman, H.; Valtonen, M.; Zheng, J.Q. Natural Transfer of Viable Microbes in Space: 1. From Mars to Earth and Earth to Mars. Icarus 2000, 145, 391–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melosh, H. Impact ejection, spallation, and the origin of meteorites. Icarus 1984, 59, 234–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farinella, P.; Davis, D.R. Collision rates and impact velocities in the main asteroid belt. Icarus 1992, 97, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbeshausen, D.; Wünnemann, K.; Collins, G.S. The transition from circular to elliptical impact craters. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2013, 118, 2295–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batson, R. Voyager 1 and 2 Atlas of Six Saturnian Satellites (NASA-SP-474). Available online: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/archive/nasa/casi.ntrs.nasa.gov/19840027171.pdf (accessed on 14 February 2023).
- Greely, R.; Batson, R. Planetary Mapping. Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2007; 312p, ISBN 0-521-30774-0. [Google Scholar]
- Roatsch, T.; Kersten, E.; Matz, K.D.; Scholten, F.; Wagner, R.; Porco, C. Cartography of the Medium-Sized Saturnian Satellites Based on Cassini-ISS Images. Presented at the Enceladus and the Icy Moons of Saturn Conference, Boulder, CO, USA, 26–29 July 2016; p. 2. Available online: https://www.hou.usra.edu/meetings/enceladus2016/pdf/3032.pdf (accessed on 14 February 2023).
- Schneck, P. Global Color and Cartographic Mapping of Saturn’s Midsize Icy Moons. Presented at the Enceladus and the Icy Moons of Saturn Conference, Boulder, CO, USA, 26–29 July 2016; p. 2. Available online: https://www.hou.usra.edu/meetings/enceladus2016/pdf/3053.pdf (accessed on 14 February 2023).
- Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. International Astronomical Union (IAU). Available online: https://asc-planetarynames-data.s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/dione_comp.pdf (accessed on 11 December 2022).
- Ferguson, S.N.; Rhoden, A.R.; Kirchoff, M.R.; Salmon, J.J. A unique Saturnian impactor population from elliptical craters. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2022, 593, 117652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asphaug, E.; Reufer, A. Late origin of the Saturn system. Icarus 2013, 223, 544–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).