Growth of Matter Perturbations in an Interacting Dark Energy Scenario Emerging from Metric-Scalar-Torsion Couplings †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. MST Cosmology in the Einstein Frame and the Emergent DEM Interacting Scenario
3. Growth of Matter Density Perturbations
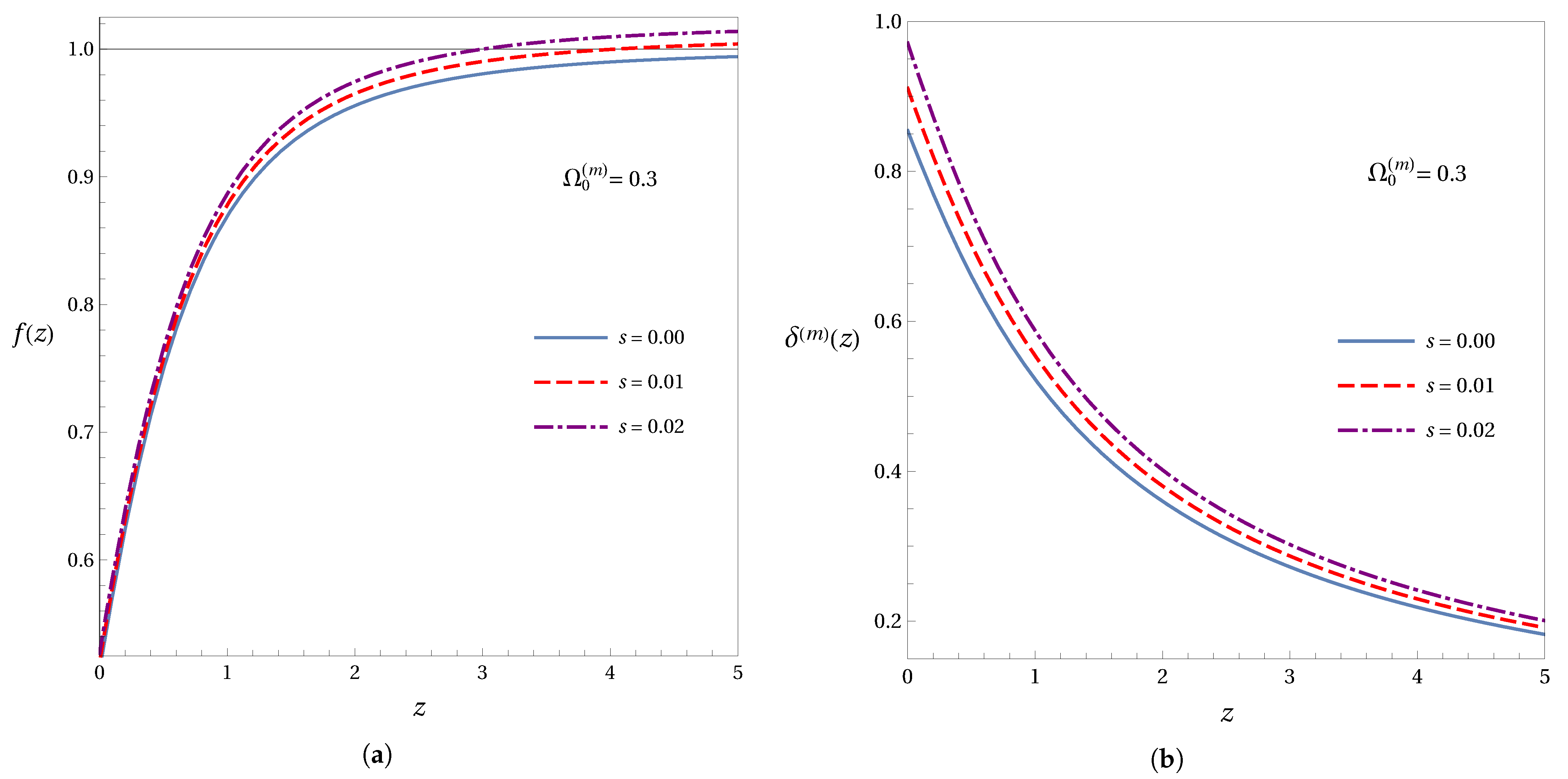
3.1. Growth Factor Parametrization
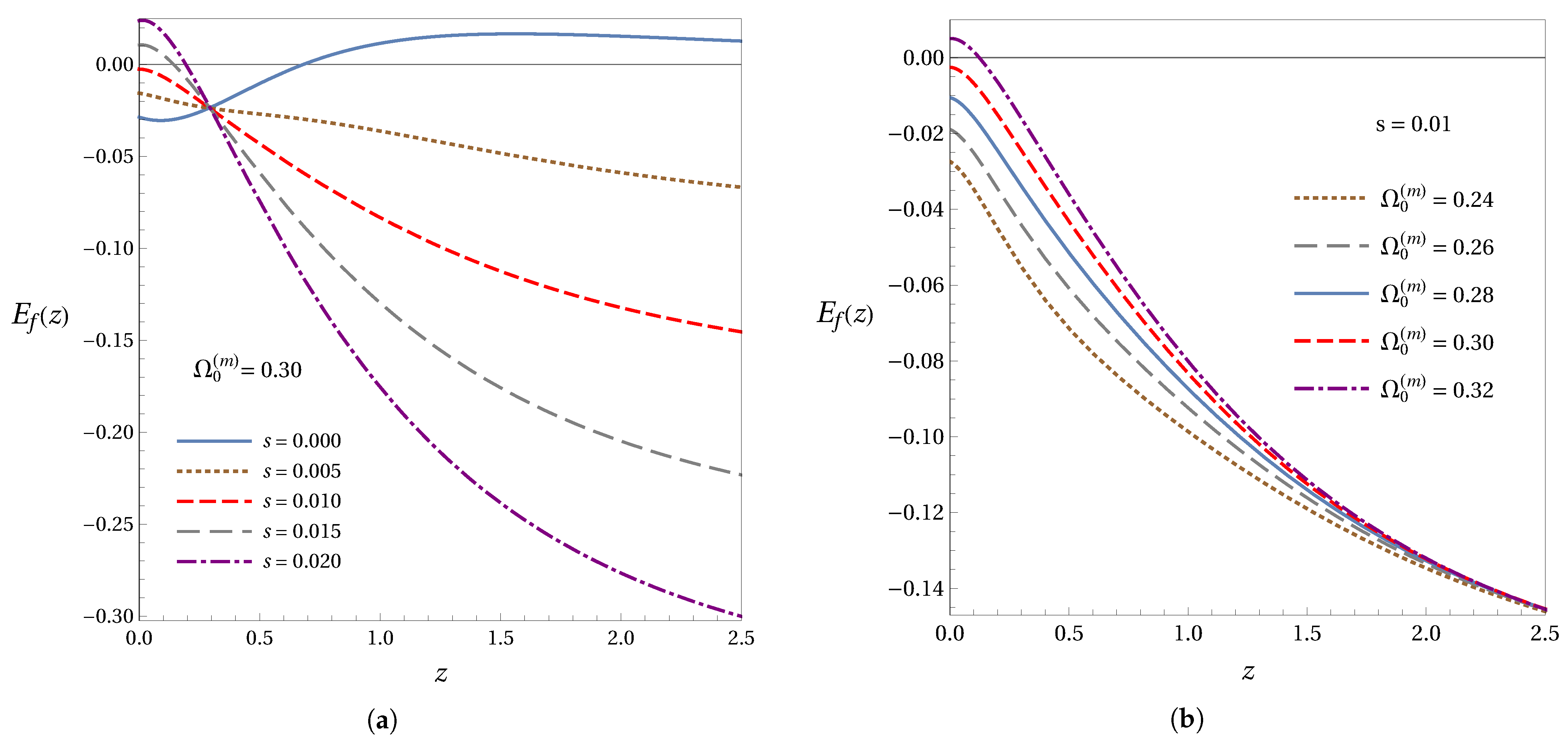
3.2. Numerical Fitting of the Growth Index
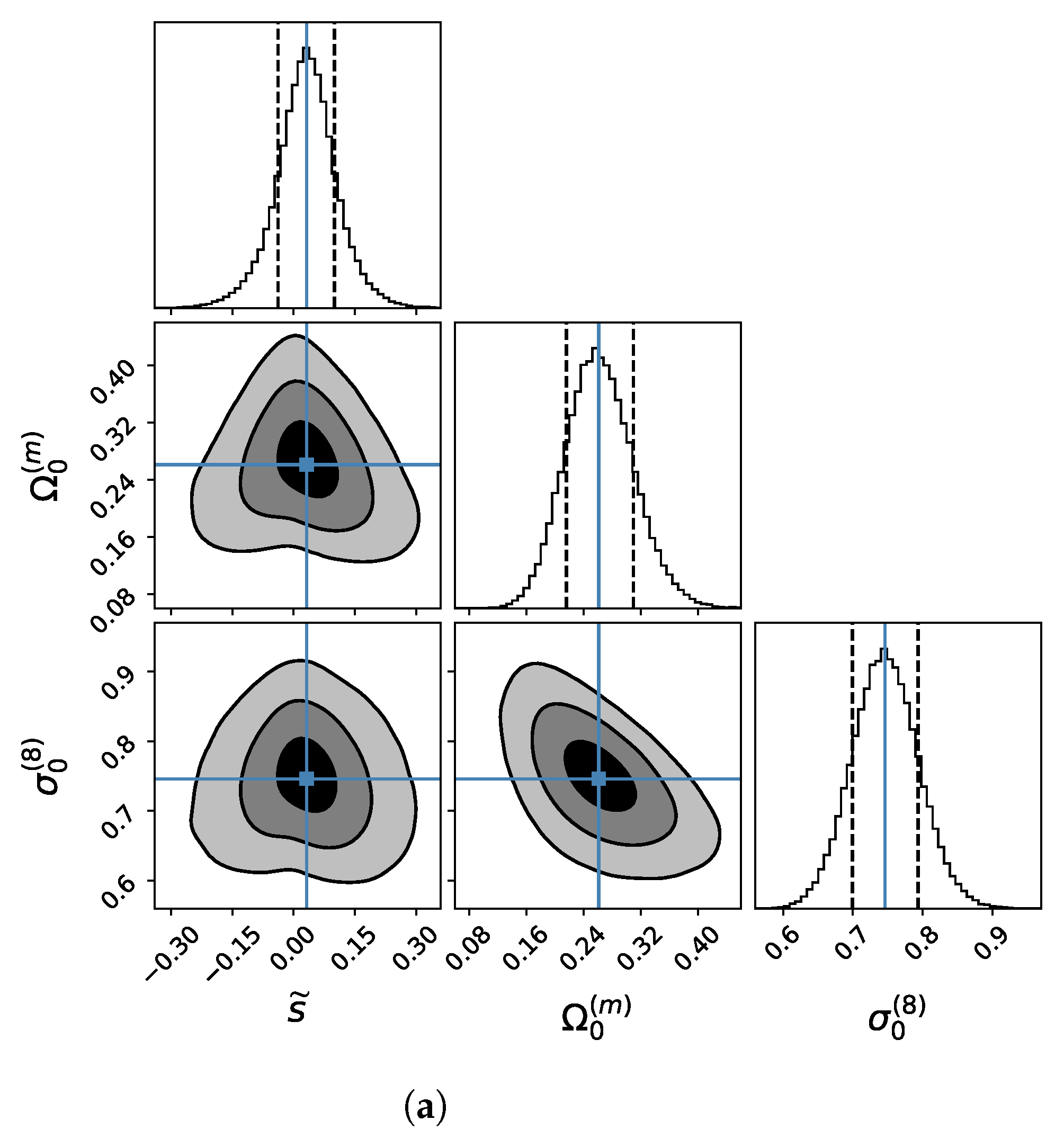
4. Parametric Estimations from RSD and Hubble Observations
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Copeland, E.J.; Sami, M.; Tsujikawa, S. Dynamics of dark energy. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2006, 15, 1753–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frieman, J.A.; Turner, M.S.; Huterer, D. Dark energy and the accelerating universe. Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 46, 385–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, L.; Tsujikawa, S. Dark Energy: Theory and Observations; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wolschin, G. Lectures on Cosmology: Accelerated Expansion of the Universe; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Matarrese, S.; Colpi, M.; Gorini, V.; Moschella, U. Dark Matter and Dark Energy: A Challenge for Modern Cosmology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hinshaw, G.; Larson, D.; Komatsu, E.; Spergel, D.N.; Bennett, C.; Dunkley, J.; Nolta, M.R.; Halpern, M.; Hill, R.S.; Odegard, N.; et al. Nine-year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) Observations: Cosmological Parameter Results. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 2013, 208, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, C.L.; Larson, D.; Weiland, J.L.; Jarosik, N.; Hinshaw, G.; Odegard, N.; Smith, K.M.; Hill, R.S.; Gold, B.; Halpern, M.; et al. Nine-Year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) Observations: Final Maps and Results. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 2013, 208, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betoule, M.E.; Kessler, R.; Guy, J.; Mosher, J.; Hardin, D.; Biswas, R.; Astier, P.; El-Hage, P.; Konig, M.; Kuhlmann, S.; et al. Improved cosmological constraints from a joint analysis of the SDSS-II and SNLS supernova samples. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 568, A22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ade, P.A.; Aghanim, N.; Arnaud, M.; Ashdown, M.; Aumont, J.; Baccigalupi, C.; Banday, A.J.; Barreiro, R.B.; Bartlett, J.G.; Bartolo, N.; et al. Planck 2015 results, XIII. Cosmological parameters. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 594, A13. [Google Scholar]
- Ade, P.A.; Aghanim, N.; Arnaud, M.; Ashdown, M.; Aumont, J.; Baccigalupi, C.; Banday, A.J.; Barreiro, R.B.; Bartolo, N.; Battaner, E.; et al. Planck 2015 results, XIV. Dark energy and modified gravity. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 594, A14. [Google Scholar]
- Scolnic, D.M.; Jones, D.O.; Rest, A.; Pan, Y.C.; Chornock, R.; Foley, R.J.; Huber, M.E.; Kessler, R.; Narayan, G.; Riess, A.G.; et al. The Complete Light-curve Sample of Spectroscopically Confirmed SNe Ia from Pan-STARRS1 and Cosmological Constraints from the Combined Pantheon Sample. Astrophys. J. 2018, 859, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planck Collaboration; Aghanim, N.; Akrami, Y.; Ashdown, M.; Aumont, J.; Baccigalupi, C.; Ballardini, M.; Banday, A.J.; Barreiro, R.B.; Bartolo, N.; et al. Planck 2018 results. VI. Cosmological parameters. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 641, A6. [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell, R.R.; Dave, R.; Steinhardt, P.J. Cosmological imprint of an energy component with general equation of state. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 80, 1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeland, E.J.; Liddle, A.R.; Wands, D. Exponential potentials and cosmological scaling solutions. Phys. Rev. D 1998, 57, 4686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujikawa, S. Quintessence: A Review. Class. Quant. Grav. 2013, 30, 214003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armendariz-Picon, C.; Mukhanov, V.; Steinhardt, P.J. A Dynamical Solution to the Problem of a Small Cosmological Constant and Late-time Cosmic Acceleration. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armendariz-Picon, C.; Mukhanov, V.; Steinhardt, P.J. Essentials of k-essence. Phys. Rev. D 2001, 63, 103510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malquarti, M.; Copeland, E.J.; Liddle, A.R.; Trodden, M. A New view of k-essence. Phys. Rev. D 2003, 67, 123503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherrer, R.J. Purely kinetic k-essence as unified dark matter. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 93, 011301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sur, S.; Das, S. Multiple kinetic k-essence, phantom barrier crossing and stability. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2009, 901, 007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sur, S. Crossing the cosmological constant barrier with kinetically interacting double quintessence. arXiv 2009, arXiv:0902.1186. [Google Scholar]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D. Introduction to modified gravity and gravitational alternative for dark energy. Int. J. Geom. Methods Mod. Phys. 2007, 4, 115–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujikawa, S. Modified gravity models of dark energy. Lect. Notes Phys. 2010, 800, 99–145. [Google Scholar]
- Clifton, T.; Ferreira, P.G.; Padilla, A.; Skordis, C. Modified Gravity and Cosmology. Phys. Rep. 2012, 513, 1–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papantonopoulos, E. Modifications of Einstein’s Theory of Gravity at Large Distances; Lecture Notes in Physics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D.; Oikonomou, V.K. Modified Gravity Theories on a Nutshell: Inflation, Bounce and Late-time Evolution. Phys. Rep. 2017, 692, 1–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wand, L.; Steinhardt, P.J. Cluster abundance constraints for cosmological models with a time-varying, spatially inhomogeneous energy component with negative pressure. Astrophs. J. 1998, 508, 483. [Google Scholar]
- Amendola, L. Coupled quintessence. Phys. Rev. D 2000, 62, 043511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comelli, D.; Pietroni, M.; Riotto, A. Dark energy and dark matter. Phys. Lett. B 2003, 571, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrar, G.R.; Peebles, P.J.E. Interacting dark matter and dark energy. Astrophys. J. 2004, 604, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.G.; Wang, A. Cosmology with interaction between phantom dark energy and dark matter and the coincidence problem. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2005, 3, 002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, S.; Herrera, R.; Olivares, G.; Pavon, D. Interacting models of soft coincidence. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 74, 023501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, L.; Appleby, S.; Avgoustidis, A.; Bacon, D.; Baker, T.; Baldi, M.; Bartolo, N.; Blanchard, A.; Bonvin, C.; Borgani, S.; et al. Cosmology and fundamental physics with the Euclid satellite. Living Rev. Relativ. 2018, 21, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertacca, D.; Bartolo, N.; Mataresse, S. Unified Dark Matter Scalar Field Models. Adv. Astron. 2010, 2010, 904379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertacca, D.; Bruni, M.; Piattella, O.F.; Pietrobon, D. Unified Dark Matter scalar field models with fast transition. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2011, 1102, 018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Guendelman, E.; Nissimov, E.; Pacheva, S. Unified Dark Energy and Dust Dark Matter Dual to Quadratic Purely Kinetic K-Essence. Eur. Phys. J. C 2016, 76, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, E.G.M.; Franzmann, G.; Khoury, J.; Brandenberger, R. Unified Superfluid Dark Sector. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2019, 8, 027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamseddine, A.H.; Mukhanov, V.; Vikman, A. Cosmology with Mimetic Matter. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2014, 1406, 017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzagholi, L.; Vikman, A. Imperfect Dark Matter. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2015, 1506, 028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D.; Oikonomou, V.K. Viable Mimetic Completion of Unified Inflation-Dark Energy Evolution in Modified Gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 94, 104050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastiani, L.; Vagnozzi, S.; Myrzakulov, R. Mimetic gravity: A review of recent developments and applications to cosmology and astrophysics. Adv. High Energy Phys. 2017, 2017, 3156915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langlois, D.; Mancarella, M.; Noui, K.; Vernizzi, F. Mimetic gravity as DHOST theories. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2019, 2, 036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemseddine, A.H.; Mukhanov, V. Ghost Free Mimetic Massive Gravity. J. High Energy Phys. 2018, 1806, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemseddine, A.H.; Mukhanov, V. Mimetic Massive Gravity: Beyond Linear Approximation. J. High Energy Phys. 2018, 1806, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamseddine, A.H.; Mukhanov, V.; Russ, T.B. Asymptotically Free Mimetic Gravity. Eur. Phys. J. C 2019, 79, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chothe, H.R.; Dutta, A.; Sur, S. Cosmological Dark sector from a Mimetic-Metric-Torsion perspective. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2019, 28, 1950174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sur, S.; Dutta, A.; Chothe, H.R. Mimetic-Metric-Torsion with induced Axial mode and Phantom barrier crossing. Eur. Phys. J. C 2021, 81, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, Y.; Maeda, K. The Scalar-Tensor Theory of Gravitation; Cambridge Monographs on Mathematical Physics, Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Faraoni, V. Cosmology in Scalar-Tensor Gravity; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bartolo, N.; Pietroni, M. Scalar-tensor gravity and quintessence. Phys. Rev. D 2000, 61, 023518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisseau, B.; Esposito-Farese, G.; Polarski, D.; Starobinsky, A.A. Reconstruction of a scalar tensor theory of gravity in an accelerating universe. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsujikawa, S.; Uddin, K.; Mizuno, S.; Tavakol, R.; Yokoyama, J.I. Constraints on scalar-tensor models of dark energy from observational and local gravity tests. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 77, 103009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elizalde, E.; Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D. Late-time cosmology in (phantom) scalar-tensor theory: Dark energy and the cosmic speed-up. Phys. Rev. D 2004, 70, 043538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, S.; Herrera, R.; Labrana, P. Emergent universe in a Jordan-Brans-Dicke theory. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2007, 0711, 030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisseau, B.; Giacomini, H.; Polarski, D. Bouncing Universes in Scalar-Tensor Gravity Around Conformal Invariance. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2016, 1605, 048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saridakis, E.N.; Tsoukalas, M. Cosmology in new gravitational scalar-tensor theories. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 93, 124032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kase, R.; Tsujikawa, S. Weak cosmic growth in coupled dark energy with a Lagrangian formulation. Phys. Lett. B 2020, 804, 135400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koivisto, T. Growth of perturbations in dark matter coupled with quintessence. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 72, 043516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- di Porto, C.; Amendola, L. Observational constraints on the linear fluctuation growth rate. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 77, 083508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polarski, D.; Gannouji, R. On the growth of linear perturbations. Phys. Lett. B 2008, 660, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gannouji, R.; Polarski, D. The growth of matter perturbations in some scalar-tensor DE models. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2008, 5, 018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Yu, H.; Fu, X. A parametrization for the growth index of linear matter perturbations. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2009, 6, 019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- di Porto, C.; Amendola, L.; Branchini, E. Growth factor and galaxy bias from future redshift surveys: A study on parametrizations. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 2011, 419, 985–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belloso, A.B.; Garcia-Bellido, J.; Sapone, D. A parametrization of the growth index of matter perturbations in various Dark Energy models and observational prospects using a Euclid-like survey. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2011, 10, 010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basilakos, S.; Pouri, A. The growth index of matter perturbations and modified gravity. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 2012, 423, 3761–3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steigerwald, H.; Bel, J.; Marinoni, C. Probing non-standard gravity with the growth index: A background independent analysis. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2014, 5, 042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Batista, R.C. The impact of dark energy perturbations on the growth index. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 89, 123508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekjani, M.; Basilakos, S.; Mehrabi, A.; Davari, Z.; Rezaei, M. Agegraphic dark energy: Growth index and cosmological implications. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 2016, 464, 1192–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polarski, D.; Starobinsky, A.A.; Giacomini, H. When is the growth index constant? J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2016, 12, 037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basilakos, S.; Anagnostopoulos, F.K. Growth index of matter perturbations in the light of Dark Energy Survey. Eur. Phys. J. C 2020, 80, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjona, R.; García-Bellido, J.; Nesseris, S. Cosmological constraints on non-adiabatic dark energy perturbations. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 103526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basilakos, S.; Nesseris, S.; Perivolaropoulos, L. Observational constraints on viable f(R) parametrizations with geometrical and dynamical probes. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 87, 123529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sur, S.; Bhatia, A.S. Weakly dynamic dark energy via metric-scalar couplings with torsion. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2017, 1707, 039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, A.S.; Sur, S. Dynamical system analysis of dark energy models in scalar coupled metric-torsion theories. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2017, 26, 1750149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, A.S.; Sur, S. Phase Plane Analysis of Metric-Scalar Torsion Model for Interacting Dark Energy. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1611.06902. [Google Scholar]
- Buchbinder, I.L.; Odintsov, S.D.; Shapiro, I.L. Nonsingular Cosmological Model with Torsion induced by Vacuum Quantum effects. Phys. Lett. B 1985, 162, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchbinder, I.L.; Odintsov, S.D.; Shapiro, I.L. Effective Action in Quantum Gravity; IOP: Bristol, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Helayël-Neto, J.A.; Penna-Firme, A.; Shapiro, I.L. Conformal symmetry, anomaly and effective action for metric-scalar gravity with torsion. Phys. Lett. B 2000, 479, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca-Neto, J.B.; Romero, C.; Martinez, S.P.G. Scalar torsion and a new symmetry of general relativity. Gen. Relativ. Grav. 2013, 45, 1579–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shapiro, I.L. Physical aspects of the space-time torsion. Phys. Rep. 2002, 357, 113–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einstein, A. The Meaning of Relativity: Including the Relativistic Theory of the Non-Symmetric Field, 5th ed.; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Trautman, A. Spin and torsion may avert gravitational singularities. Nature 1973, 242, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hehl, F.W.; von der Heyde, P.; Kerlick, G.; Nester, J. General Relativity with Spin and Torsion: Foundations and Prospects. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1976, 48, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raychaudhuri, A.K. Theoretical Cosmology; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- de Sabbata, V.; Gasperini, M. Introduction to Gravitation; World Scientific: Singapore, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- de Sabbata, V.; Sivaram, C. Spin Torsion and Gravitation; World Scientific: Singapore, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Hehl, F.W.; Obukhov, Y.N. How does the electromagnetic field couple to gravity, in particular to metric, nonmetricity, torsion and curvature? Lect. Notes Phys. 2001, 562, 479–504. [Google Scholar]
- Blagojevic, M. Gravitation and Gauge Symmetries; IOP Publishing: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Capozziello, S.; de Laurentis, M. Extended Theories of Gravity. Phys. Rep. 2011, 509, 167–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poplawski, N. Affine theory of gravitation. Gen. Relativ. Grav. 2014, 46, 1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westman, H.F.; Zlosnik, T.G. An introduction to the physics of Cartan gravity. Ann. Phys. 2015, 361, 330–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Capozziello, S.; Lambiase, G.; Stornaiolo, C. Geometric classification of the torsion tensor of space-time. Ann. Phys. 2001, 10, 713–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloomer, I. A maximally symmetric space with torsion. Gen. Relativ. Grav. 1978, 9, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsamparlis, M. Cosmological principle and torsion. Phys. Lett. A 1979, 75, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangopadhyay, D.; SenGupta, S. The meaning of Maximal Symmetry in presence of Torsion. arXiv 1997, arXiv:hep-th/9710139. [Google Scholar]
- Gangopadhyay, D.; SenGupta, S. Duality invariance of cosmological solutions with torsion. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 1999, 14, 4953–4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sur, S.; Bhatia, A.S. Constraining torsion in maximally symmetric (sub)spaces. Class. Quant. Grav. 2014, 31, 025020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Majumdar, P.; SenGupta, S. Parity violating gravitational coupling of electromagnetic fields. Class. Quant. Grav. 1999, 16, L89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, R.T. Strings in gravity with torsion. Gen. Relativ. Grav. 2000, 32, 2007–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SenGupta, S.; Sur, S. Spherically symmetric solutions of gravitational field equations in Kalb-Ramond background. Phys. Lett. B 2001, 521, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, S.; Majumdar, P.; SenGupta, S.; Sinha, A. Does a Kalb-Ramond field make space-time optically active? Eur. Phys. J. C 2002, 23, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kar, S.; Majumdar, P.; SenGupta, S.; Sur, S. Cosmic optical activity from an inhomogeneous Kalb-Ramond field. Class. Quant. Grav. 2002, 19, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, S.; SenGupta, S.; Sur, S. Static spherisymmetric solutions, gravitational lensing and perihelion precession in Einstein-Kalb-Ramond theory. Phys. Rev. D 2003, 67, 044005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SenGupta, S.; Sur, S. Does curvature dilaton coupling with a Kalb-Ramond field lead to an accelerating universe? J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2003, 312, 001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Maity, D.; SenGupta, S.; Sur, S. Spinning test particle in Kalb-Ramond background. Eur. Phys. J. C 2005, 42, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sur, S.; Das, S.; SenGupta, S. Charged black holes in generalized dilaton-axion gravity. J. High Energy Phys. 2005, 510, 064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Cesare, M.; Mavromatos, N.E.; Sarkar, S. On the possibility of tree-level leptogenesis from Kalb-Ramond torsion background. Eur. Phys. J. C 2015, 75, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyaya, B.; Sen, S.; SenGupta, S. Does a Randall-Sundrum scenario create the illusion of a torsion free universe? Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 121101, Erratum in 2002, 89, 259902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SenGupta, S.; Sur, S. Gravitational Redshift in Einstein-Kalb-Ramond space-time and Randall-Sundrum scenario. Europhys. Lett. 2004, 65, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Maity, D.; SenGupta, S.; Sur, S. Observable signals in a string inspired axion-dilaton background and Randall-Sundrum scenario. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 72, 066012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyaya, B.; Sen, S.; SenGupta, S. A Randall-Sundrum scenario with bulk dilaton and torsion. Phys. Rev. D 2009, 79, 124029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Chatterjee, A. Gauge invariant coupling of fields to torsion: A string inspired model. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 8, 106007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Mukhopadhyaya, B.; SenGupta, S. Why has spacetime torsion such negligible effect on the Universe? Phys. Rev. D 2014, 90, 107901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojman, S.; Rosenbaum, M.; Ryan, M.P. Propagating torsion and gravitation. Phys. Rev. D 1979, 19, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, S.M.; Field, G.B. Consequences of propagating torsion in connection dynamic theories of gravity. Phys. Rev. D 1994, 50, 3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saa, A. Propagating torsion from first principles. Gen. Relativ. Grav. 1997, 29, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belyaev, A.S.; Shapiro, I.L. The action for the (propagating) torsion and the limits on the torsion parameters from present experimental data. Phys. Lett. B 1998, 425, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hojman, R.; Mukku, C.; Sayed, W.A. Parity violation in metric torsion theories of gravitation. Phys. Rev. D 1980, 22, 1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyaya, B.; SenGupta, S.; Sur, S. Space-time torsion and parity violation: A gauge invariant formulation. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2002, 17, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyaya, B.; Sen, S.; SenGupta, S.; Sur, S. Parity violation and torsion: A study in four-dimensions and higher dimensions. Eur. Phys. J. C 2004, 35, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, D.; Majumdar, P.; SenGupta, S. Parity violating Kalb-Ramond-Maxwell interactions and CMB anisotropy in a brane world. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2004, 406, 005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freidel, L.; Minic, D.; Takeuchi, T. Quantum gravity, torsion, parity violation and all that. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 72, 104002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercuri, S. From the Einstein-Cartan to the Ashtekar-Barbero canonical constraints, passing through the Nieh-Yan functional. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 77, 024036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, K. Some Aspects of Holst and Nieh-Yan Terms in General Relativity with Torsion. Class. Quant. Grav. 2010, 27, 135012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, I.L.; Teixeira, P.M. Quantum Einstein-Cartan theory with the Holst term. Class. Quant. Grav. 2014, 31, 185002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hehl, F.W.; Obukhov, Y.N.; Rubilar, G.F.; Blagojevic, M. On the theory of the skewon field: From electrodynamics to gravity. Phys. Lett. A 2005, 347, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rubilar, G.F.; Obukhov, Y.N.; Hehl, F.W. Torsion nonminimally coupled to the electromagnetic field and birefringence. Class. Quant. Grav. 2003, 20, L185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, W.-T. Skewon field and cosmic wave propagation. Phys. Lett. A 2014, 378, 1217–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yo, H.-J.; Nester, J.M. Dynamic Scalar Torsion and an Oscillating Universe. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2007, 22, 2057–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shie, K.-F.; Nester, J.M.; Yo, H.-J. Torsion Cosmology and the Accelerating Universe. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 78, 023522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baekler, P.; Hehl, F.W.; Nester, J.M. Poincaré gauge theory of gravity: Friedmann cosmology with even and odd parity modes. Analytic part. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 83, 024001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blagojevic, M.; Hehl, F.W. Gauge Theories of Gravitation: A Reader with Commentaries; World Scientific: Singapore, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Chee, G. Cosmology in Poincaré gauge gravity with a pseudoscalar torsion. J. High Energy Phys. 2016, 1605, 024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiforova, V.; Randjbar-Daemi, S.; Rubakov, V. Self-accelerating Universe in modified gravity with dynamical torsion. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 95, 024013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengochea, G.R.; Ferraro, R. Dark torsion as the cosmic speed-up. Phys. Rev. D 2009, 79, 124019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Sotiriou, T.P.; Barrow, J.D. Large-scale Structure in f(T) Gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 83, 104017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.-F.; Chen, S.-H.; Dent, J.B.; Dutta, S.; Saridakis, E.N. Matter Bounce Cosmology with the f(T) Gravity. Class. Quant. Grav. 2011, 28, 215011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, C.-Q.; Lee, C.-C.; Saridakis, E.N.; Wu, Y.-P. “Teleparallel” dark energy. Phys. Lett. B 2011, 704, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.-F.; Capozziello, S.; de Laurentis, M.; Saridakis, E.N. f(T) teleparallel gravity and cosmology. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2016, 79, 106901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahamonde, S.; Capozziello, S.; Faizal, M.; Nunes, R.C. Nonlocal Teleparallel Cosmology. Eur. Phys. J. C 2017, 77, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vignolo, S.; Fabbri, L.; Stornaiolo, C. A square-torsion modification of Einstein-Cartan theory. Ann. Phys. 2012, 524, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilev, T.B.; Cembranos, J.A.R.; Valcarcel, J.G.; Martín-Moruno, P. Stability in quadratic torsion theories. Eur. Phys. J. C 2017, 77, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, R.K.; Sengupta, S. Degenerate spacetimes in first order gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 93, 084026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanagan, E.E.; Rosenthal, E. Can gravity probe B usefully constrain torsion gravity theories? Phys. Rev. D 2007, 75, 124016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostelecky, V.A.; Russell, N.; Tasson, J. New Constraints on Torsion from Lorentz Violation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 111102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babourova, O.V.; Frolov, B.N. Interaction of the 4-rotational gauge field with orbital momentum, gravidiamagnetic effect and orbit experiment ‘Gravity Probe B’. Phys. Rev. D 2010, 82, 027503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hehl, F.W.; Obukhov, Y.N.; Puetzfeld, D. On Poincaré gauge theory of gravity, its equations of motion and Gravity Probe B. Phys. Lett. A 2013, 377, 1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camera, S.; Cardone, V.F.; Radicella, N. Detectability of Torsion Gravity via Galaxy Clustering and Cosmic Shear Measurements. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 89, 083520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Felisola, O.; Corral, C.; Schmidt, I.; Zerwekh, A.R. Updated limits on extra dimensions through torsion and LHC data. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2014, 29, 1450081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucat, S.; Prokopec, T. Observing Geometrical Torsion. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1705.00889. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson, T.; Mattingly, D. Gravity with a dynamical preferred frame. Phys. Rev. D 2001, 64, 024028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, T.; Mattingly, D. Einstein-Aether waves. Phys. Rev. D 2004, 70, 024003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, T.; Liberati, S.; Mattingly, D. Lorentz violation at high energy: Concepts, phenomena and astrophysical constraints. Ann. Phys. 2006, 321, 150–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, J.; Doshi, S.; Ratra, B. Constraints on dark energy dynamics and spatial curvature from Hubble parameter and baryon acoustic oscillation data. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 480, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, J.E.; Alcaniz, J.S.; Carvalho, J.C. Non-parametric reconstruction of cosmological matter perturbations. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2016, 2016, 016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Benisty, D.; Guendelman, E.I.; Nissimov, E.; Pacheva, S. ΛCDM as a Noether Symmetry in Cosmology. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.13146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderon, R.; Felbacq, D.; Gannouji, R.; Polarski, D.; Starobinsky, A.A. Global properties of the growth index of matter inhomogeneities in the Universe. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 100, 083503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khyllep, W.; Dutta, J. Linear growth index of matter perturbations in Rastall gravity. Phys. Lett. B 2019, 797, 134796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujikawa, S.; Gannouji, R.; Moraes, B.; Polarski, D. Dispersion of growth of matter perturbations in f(R) gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2009, 80, 084044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beutler, F.; Blake, C.; Colless, M.; Jones, D.H.; Staveley-Smith, L.; Poole, G.B.; Campbell, L.; Parker, Q.; Saunders, W.; Watson, F. The 6dF Galaxy Survey: z ≈ 0 measurements of the growth rate and σ8. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 423, 3430–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ata, M.; Baumgarten, F.; Bautista, J.; Beutler, F.; Bizyaev, D.; Blanton, M.R.; Blazek, J.A.; Bolton, A.S.; Brinkmann, J.; Brownstein, J.R.; et al. The clustering of the SDSS-IV extended Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey DR14 quasar sample: First measurement of baryon acoustic oscillations between redshift 0.8 and 2.2. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 473, 4773–4794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beutler, F.; Seo, H.J.; Saito, S.; Chuang, C.H.; Cuesta, A.J.; Eisenstein, D.J.; Gil-Marín, H.; Grieb, J.N.; Hand, N.; Kitaura, F.S.; et al. The clustering of galaxies in the completed SDSS-III Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey: Anisotropic galaxy clustering in Fourier space. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 466, 2242–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, A.G.; Montesano, F.; Kazin, E.A.; Aubourg, E.; Beutler, F.; Brinkmann, J.; Brownstein, J.R.; Cuesta, A.J.; Dawson, K.S.; Eisenstein, D.J.; et al. The clustering of galaxies in the SDSS-III Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey: Cosmological implications of the full shape of the clustering wedges in the data release 10 and 11 galaxy samples. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 440, 2692–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feix, M.; Nusser, A.; Branchini, E. Growth rate of cosmological perturbations at z∼0.1 from a new observational test. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 115, 011301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blake, C.; Baldry, I.K.; Bland-Hawthorn, J.; Christodoulou, L.; Colless, M.; Conselice, C.; Driver, S.P.; Hopkins, A.M.; Liske, J.; Loveday, J.; et al. Galaxy In addition, Mass Assembly (GAMA): Improved cosmic growth measurements using multiple tracers of large-scale structure. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 2013, 436, 3089–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.S.; Percival, W.J. Reconstructing the history of structure formation using redshift distortions. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2009, 10, 004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Yang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Mo, H.J.; van den Bosch, F.C.; Luo, W.; Tweed, D.; Li, S.; Liu, C.; et al. Mapping the Real Space Distributions of Galaxies in SDSS DR7: II. Measuring the growth rate, linear mass variance and biases of galaxies at redshift 0.1. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1712.04163. [Google Scholar]
- Howlett, C.; Staveley-Smith, L.; Elahi, P.J.; Hong, T.; Jarrett, T.H.; Jones, D.H.; Koribalski, B.S.; Macri, L.M.; Masters, K.L.; Springob, C.M. 2MTF—VI. Measuring the velocity power spectrum. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 471, 3135–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Torre, S.; Jullo, E.; Giocoli, C.; Pezzotta, A.; Bel, J.; Granett, B.R.; Guzzo, L.; Garilli, B.I.; Scodeggio, M.; Bolzonella, M.; et al. The VIMOS Public Extragalactic Redshift Survey (VIPERS)-Gravity test from the combination of redshift-space distortions and galaxy-galaxy lensing at 0.5 < z < 1.2. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 608, A44. [Google Scholar]
- Gil-Marín, H.; Percival, W.J.; Verde, L.; Brownstein, J.R.; Chuang, C.H.; Kitaura, F.S.; Rodríguez-Torres, S.A.; Olmstead, M.D. The clustering of galaxies in the SDSS-III Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey: RSD measurement from the power spectrum and bispectrum of the DR12 BOSS galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 465, 1757–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samushia, L.; Percival, W.J.; Raccanelli, A. Interpreting large-scale redshift-space distortion measurements. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 420, 2102–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazantzidis, L.; Perivolaropoulos, L.; Skara, F. Constraining power of cosmological observables: Blind redshift spots and optimal ranges. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99, 063537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesseris, S.; Pantazis, G.; Perivolaropoulos, L. Tension and constraints on modified gravity parametrizations of Geff(z) from growth rate and Planck data. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 96, 023542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, R.; Luongo, O. Growth of matter perturbations in nonminimal teleparallel dark energy. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 124013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’Huillier, B.; Shafieloo, A.; Kim, H. Model-independent cosmological constraints from growth and expansion. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 476, 3263–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazantzidis, L.; Perivolaropoulos, L. Evolution of the fσ8 tension with the Planck 15/ΛCDM determination and implications for modified gravity theories. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 97, 103503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Observational Datasets | Parametric Estimations (Best Fit & 68% Limits) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. GOLD | - | ||||
| 2. GOLD | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sharma, M.K.; Sur, S. Growth of Matter Perturbations in an Interacting Dark Energy Scenario Emerging from Metric-Scalar-Torsion Couplings. Phys. Sci. Forum 2021, 2, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECU2021-09293
Sharma MK, Sur S. Growth of Matter Perturbations in an Interacting Dark Energy Scenario Emerging from Metric-Scalar-Torsion Couplings. Physical Sciences Forum. 2021; 2(1):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECU2021-09293
Chicago/Turabian StyleSharma, Mohit Kumar, and Sourav Sur. 2021. "Growth of Matter Perturbations in an Interacting Dark Energy Scenario Emerging from Metric-Scalar-Torsion Couplings" Physical Sciences Forum 2, no. 1: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECU2021-09293
APA StyleSharma, M. K., & Sur, S. (2021). Growth of Matter Perturbations in an Interacting Dark Energy Scenario Emerging from Metric-Scalar-Torsion Couplings. Physical Sciences Forum, 2(1), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECU2021-09293






