Abstract
The objective of this study was to investigate the antibacterial and antioxidant effect of Greek oregano and rosemary by-products from essential oil distillation on pathogenic and spoilage bacteria. The antibacterial effect of raw material of oregano and rosemary before distillation and post distillation, the dried residues, was tested against the following bacteria: Escherichia coli, Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica ser. Typhimurium, Listeria monocytogenes, Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus licheniformis, and Bacillus cereus strains. Results showed that rosemary distillation by-products were able to inhibit the growth of all Bacillus (B. subtilis, B. licheniformis, B. cereus) strains and L. monocytogenes while oregano affected the growth of L. monocytogenes and S. aureus, even at the minimum concentration. However, it affected B. cereus, at the maximum concentration. The total phenolic content in oregano/rosemary raw material and their by-products was approximately similar; however, antioxidant activity was reduced in oregano solid residue, whereas it was surprisingly increased in the rosemary by-products after distillation. These results suggest the potential use of oregano and rosemary distillation by-products as antimicrobial and bioactive agents.
1. Introduction
Numerous medicinal and aromatic plants have been known for their healing properties since antiquity, and nowadays, there is increased research interest in the bioactive compounds associated with the pharmacological properties of many herbs. In this context, Greek oregano (Origanum vulgare subsp. hirtum L.) and rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) have been studied for their antioxidant, antibacterial, and antifungal properties [1,2,3,4,5]. Oregano essential oil and its main constituents, thymol and carvacrol, and their precursor monoterpenes, γ-terpinene and p-cymene, have been attributed with significant antioxidant properties against lipid oxidation [6], while several reports have documented its antibacterial effect against foodborne and food-spoilage bacteria [7,8,9]. Bioactive effects have also been reported for rosemary essential oil and its extracts [2,4]. More specifically, carnosic acid, carnosol, and rosmanol, identified as the main active components in rosemary extracts, are well known for their antioxidant activity [2]. However, some negative attributes limit the use of essential oils for food preservation, e.g., their odor and the strong effect on food sensory characteristics [10]. Although the essential oils of oregano and rosemary have a significant commercial value and their pharmacological properties have been well documented [11], the bioactivity and particularly the antibacterial potential of the distillation by-products have not been studied yet.
The essential oil distillation procedure generates large amounts of post distillation residues, thus causing environmental problems. Therefore, valorization of the essential oil industry by-products into valuable bioactive constituents is an attractive perspective, and it is also in accordance with the bioeconomy aspects. Taking into consideration the above, the aim of the present study was to assess in vitro the antibacterial and antioxidant activities of the post distillation material of Origanum vulgare subsp. hirtum L. and Rosmarinus officinalis L., as potential candidates for use as antimicrobial and bioactive substances.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Preparation of Samples
Aerial parts of Origanum vulgare subsp. hirtum L. (oregano) and Rosmarinus officinalis L. (rosemary) were collected during the flowering season, from cultivated accessions in the Department of Aromatic and Medicinal Plant Hellenic Agricultural Organization (Demeter, Plant Breeding and Genetic Resources Institute, Thessaloniki, Greece).
The plant material was dried under shade until the moisture content reached about 10% (raw) and then subjected to steam distillation in pilot-scale distillation equipment. After the removal of the essential oil, the remining solid residue was collected immediately and dried as follows: (a) sun-dried (SD) for 48 h and (b) oven-dried (OD) at 60 °C for 2 h (oregano) or 40 °C for 1 h (rosemary) according to preliminary tests to achieve a moisture content in the wet solid residue below 10%.
Following the drying process, solid materials were separated from stalks and finally were ground to pass through a 0.5 mm sieve in a Retsch Model ZM1000 mill (Haan, Germany). Ground samples were stored in plastic bags in a cool, dry, and dark place until the analyses.
2.2. Bacterial Strains and Cultures
The antibacterial activity was tested against the following well-known pathogen and spoilage bacteria: Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 (American Type Culture Collection, Manassas, VA 20110, USA), Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923, Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica ser. Typhimurium DC 193 (provided by the Lab. of Food Microbiology and Biotechnology, Agricultural University of Athens, Athens, Greece), Listeria monocytogenes Scott A, Bacillus subtilis NCIMB 3610 (National Collection of Industrial, Food and Marine Bacteria, NCIMB Ltd., Aberdeen, Scotland, UK), Bacillus subtilis NCFB 1069 (National Collection of Food Bacteria, Reading, UK, which incorporated with NCIMB), Bacillus licheniformis NCDO 735, (National Collection of Dairy Organisms, which incorporated in NCFB), Bacillus licheniformis DSM 13 (DSMZ-German Collection of Microorganisms and Cell Cultures GmbH, Braunschweig, Germany), and Bacillus cereus DSM 31.
Strains were kept in brain heart infusion (BHI) broth plus 25% glycerol at −80 °C, and activated with 2 successive cultures in BHI broth (Oxoid, Basingstoke, UK) incubated overnight at 30 °C for Bacillus species and at 37 °C for the other bacteria.
2.3. Assessment of Antibacterial Activity
The agar dilution method was applied [12]. The raw material (raw), the sun-dried (SD), and the oven-dried (OD) solid residues were incorporated in Mueller–Hinton (MH) agar (Oxoid, Basingstoke, UK) in various concentrations (5, 10, and 20 mg/mL) before sterilization. Following sterilization, the media was distributed in the plates and 10 μL of activated culture were spot inoculated on the solidified agar plates in triplicate. After incubation for 5 days at 30 °C for bacilli and 37 °C for the other bacteria, plates were examined for visible bacterial growth [12], recording optimum (+), weak (w), or no growth (–), compared to the control. To discriminate the mode of action of raw, SD, or OD samples on bacterial cell viability (bacteriostatic or bactericidal action), a part of the inoculated agar surface from plates where no growth occurred after 5 days of incubation was transferred aseptically to brain heart infusion (BHI) broth. Growth in BHI broth after 24–48 h of incubation indicated bacteriostatic activity while no growth indicated bactericidal activity [13].
2.4. Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Activity Assay
The total phenolic contents (TPCs) of solid residues were determined using the modified Folin–Ciocalteau’s method according to Irakli et al. [14]. Briefly, 0.05 g of dried solid residue was extracted with 10 mL of 70% methanol with the aid of an ultrasonic bath for 15 min. After centrifugation at 4500 rpm for 10 min, the above extraction was repeated one more time. An aliquot of mixed supernatants (0.2 mL) was mixed with 0.8 mL of 10% Folin–Ciocalteau reagent and allowed to react for 2 min. Consequently, 2 mL of sodium carbonate (7.5% w/v) solution and 7 mL of distilled water were added to the mixture and the absorbance at 725 nm was measured after incubation for 60 min in a dark place. The results were expressed as mg of gallic acid equivalents per g of sample on a dry weight basis (mg GAE/g dw). All analyses were performed in triplicate.
To determine the antioxidant activity of the solid residues’ extracts, the 2,2’-azinobis-(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulphonate) radical (ABTS·+) scavenging activity (ABTS assay) was assessed according to Irakli et al. [15]. Trolox was used as the standard compound for the calibration curve and the results were expressed in mg of Trolox equivalents (TE) per g of sample on a dry basis (mg TE/g dw). Analyses were performed in triplicate.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Values were reported as the mean ± standard deviation of triplicate measurements. All parameters were subjected to 1-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), and when ANOVA revealed significant differences between means, a Tukey’s test at p ≤ 0.05 was used to separate means using the Minitab 17 (Minitab Inc., State College, PA, USA) software.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Antibacterial Effect of Oregano and Rosemary
The antibacterial capacity of the raw material and the solid residues against pathogenic and spoilage bacteria was clearly verified throughout this study. Oregano and Rosemary distillation solid residues showed certain antibacterial activity against specific bacteria (Table 1 and Table 2). The antibacterial activity of three different concentrations (5, 10, and 20 mg/mL) of raw, SD, and OD samples was examined against E. coli ATCC 25922, S. aureus ATCC 25923, S. Typhimurium DC 193, L. monocytogenes Scott A, B. subtilis NCIMB 3610, B. subtilis NCFB 1069, B. licheniformis NCDO 735, B. licheniformis DSM 13, and B. cereus DSM 31 (Table 1). All strains showed optimum growth in control agar plates. All concentrations of raw samples inhibited the growth of all bacteria tested, exhibiting mostly bacteriocidal action, except against E. coli and S. Typhimurium, which withstood the lower concentration (5 mg/mL) used. Oregano SD and OD residues presented a similar antibacterial activity pattern against the tested strains. Both strongly inhibited L. monocytogenes growth at all concentrations used while the growth of S. aureus and B. cereus was only inhibited at the higher concentration (20 mg/mL), exhibiting bacteriocidal action, whereas the growth of S. aureus was weakened at the lower concentrations (5 and 10 mg/mL) of SD and OD compared to the control. The oregano residues showed no antibacterial activity against E. coli, S. Typhimurium, or the two B. subtilis strains. Limited activity (noted as weak growth) was observed against B. cereus and the two B. licheniformis strains, and only at the maximum concentration (20 mg/mL). The limited antibacterial activity of the SD and OD samples is possibly explained by the fact that the main constituents of oregano essential oil, carvacrol and thymol, known for their strong antimicrobial activity, were removed during the distillation process, and are not present in the post distillation material [7,8,9].

Table 1.
Effect of raw dried oregano (raw) and oregano residues obtained from distillation followed by sun-drying (SD) or oven-drying (OD) treatment on the growth 1 of E. coli (Ec), S. Typhimurium (ST), L. monocytogenes (Lm), S. aureus (Sa), B. subtilis (Bs1, Bs2), B. licheniformis (Bl1, Bl2), and B. cereus (Bc) strains. When no growth occurred, the mode of action 2 on cell viability was also recorded.

Table 2.
Effect of raw dried rosemary (raw) and rosemary residues obtained from distillation followed by sun-drying (SD) or oven-drying (OD) treatment on the growth 1 of E. coli (Ec), S. Typhimurium (ST), L. monocytogenes (Lm), S. aureus (Sa), B. subtilis (Bs1, Bs2), B. licheniformis (Bl1, Bl2), and B. cereus (Bc) strains. When no growth occurred, the mode of action 2 on cell viability was also recorded.
The raw rosemary sample inhibited the growth of L. monocytogenes and the three Bacillus species tested, at all concentrations incorporated in the agar medium, mostly exhibiting bactericidal activity, while no growth inhibition was observed against E. coli, S. Typhimurium, and S. aureus (Table 2). A similar trend regarding the antibacterial activity was revealed for SD and OD rosemary residues, except that B. subtilis strains withstood all concentrations of OD used. Therefore, it would be interesting to elucidate the constitution of the two residues to explain the differences observed in their antibacterial capacity and possibly attribute them to specific compounds.
In general, oregano and rosemary were more effective against bacteria tested in their initial form (raw), while rosemary residues maintained their antibacterial activity after the distillation process against L. monocytogenes and Bacillus species.
3.2. Antioxidant Effect of Oregano and Rosemary
The content of total phenols (TPC) in the oregano solid residues ranged from 89.9 mg GAE/g dw for the SD residue to 90.5 mg GAE/g dw for the OD residue, which is statistically (p ≤ 0.05) similar to the raw material (93.8 mg GAE/g dw) (Figure 1). On the contrary, the SD- and OD-treated oregano solid residues exhibited lower antioxidant activity using the ABTS test than the raw sample. This could be attributed to the antioxidant effect of its essential oil components [1,2,3].
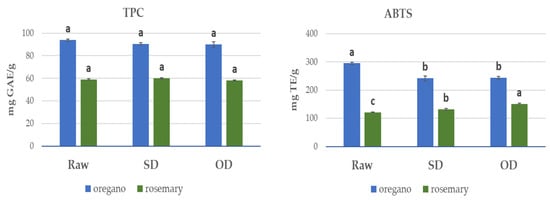
Figure 1.
Main effects plot for the total phenolic content (TPC, mg GAE/g) and ABTS radical scavenging activity (mg TE/g) of raw and solid residues after steam distillation of oregano and rosemary; values followed by different letters in the bars in the same attribute are significantly different (p ≤ 0.05) according to Tukey’s test.
On the other hand, the TPC in rosemary solid residues ranged from 58.0 mg GAE/g dw in the case of the OD residue to 60.1 mg GAE/g dw for the SD residue, which was statistically (p ≤ 0.05) similar to the raw material (59.0 mg GAE/g dw). However, the antioxidant activity of SD and OD rosemary residues, evaluated using the ABTS assay, was statistically (p ≤ 0.05) higher than the raw material (Figure 1). This may explain the retained antibacterial activity of the rosemary residues. Therefore, it would be interesting to elucidate the constitution of the two residues to explain the differences observed in their antibacterial capacity and possibly attribute them to specific compounds.
In general, in the case of raw materials, oregano showed approximately 2.5-fold higher antioxidant activity than rosemary, whereas in the respective solid residues, the ratio was, on average, 1.7.
4. Conclusions
To our knowledge, this is the first published work about the antibacterial properties of Greek oregano and rosemary residues derived from essential oil distillation. The method of incorporating solid residues into the medium to test the antibacterial capacity is simple, quick, and cheap. The results showed that oregano was more effective against all bacteria tested in its initial form (raw), and after distillation (solid residues); inhibition was shown against L. monocytogenes and S. aureus, while the rosemary residues maintained their antibacterial activity after the distillation process, against all three Bacillus species (B. subtilis, B. licheniformis, B. cereus) and L. monocytogenes). In general, L. monocytogenes was the most susceptible strain and the Gram-negative bacteria E. coli and S. Typhimurium were the most resistant. Gram-negative bacteria, in general, are more resistant to the action of various antibacterial substances since they have an outer membrane consisting of lipopolysaccharides that restrict the diffusion of hydrophobic compounds [16]. These results suggest the potential use of the solid residue from the essential oil distillation of oregano and rosemary as an antimicrobial substrate. The absence of aroma (volatile) constituents of solid residues could be considered advantageous when such extracts are intended to be used as additives in food products. Additionally, the antioxidant assessments showed that both solid residues could be used as a bioactive material, although the rosemary residue was a more promising antioxidant matrix than oregano. However, further studies should be conducted to determine the components that are responsible for the antibacterial and antioxidant activity of the essential oil residues.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.I.; E.B. and M.H.; methodology, E.B. and M.H.; validation, E.B., M.H. and M.I.; formal analysis, E.B., M.H.; investigation, M.H.; E.B.; M.I. and A.L.; data curation, E.B., M.H. and M.I.; writing—original draft preparation, E.B.; writing—review and editing, M.H.; P.C.; M.I.; A.L. and C.G.B.; visualization, M.I.; A.L. and P.C.; supervision, C.G.B.; project administration, M.I. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
This research has been co-financed by the European Regional Development Fund of the European Union and Greek national funds through the Operational Program Competitiveness, Entrepreneurship and Innovation, under the call RESEARCH—CREATE—INNOVATE (project code: T2EDK-00946).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Skendi, A.; Irakli, M.; Chatzopoulou, P. Analysis of phenolic compounds in Greek plants of Lamiaceae family by HPLC. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2017, 6, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuppett, S.L.; Hall, C.A. Antioxidant activity of the Labiatae. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 1998, 42, 245–272. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Exarchou, V.; Nenadis, N.; Tsimidou, M.; Gerothanassis, I.P.; Troganis, A.; Boskou, D. Antioxidant activities and phenolic composition of extracts from Greek oregano, Greek sage, and summer savory. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 5294–5299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto, G. Biological Activities of Three Essential Oils of the Lamiaceae Family. Medicines 2017, 4, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skendi, A.; Katsantonis, D.Ν.; Chatzopoulou, P.; Irakli, M.; Papageorgiou, M. Antifungal Activity of Aromatic Plants of the Lamiaceae Family in Bread. Foods 2020, 9, 1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botsoglou, N.A.; Christaki, E.; Fletouris, D.J.; Florou-Paneri, P.; Spais, A.B. The effect of dietary oregano essential oil on lipid oxidation in raw and cooked chicken during refrigerated storage. Meat Sci. 2002, 62, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mith, H.; Dure, R.; Delcenserie, V.; Zhiri, A.; Daube, G.; Clinquart, A. Antimicrobial activities of commercial essential oils and their components against food-borne pathogens and food spoilage bacteria. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 2, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rota, C.; Carraminana, J.J.; Burillo, J.; Herrera, A. In vitro antimicrobial activity of essential oils from aromatic plants against selected foodborne pathogens. J. Food Prot. 2004, 67, 1252–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakkas, H.; Papadopoulou, C. Antimicrobial activity of basil, oregano, and thyme essential oils. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, R.J.V.; Skandamis, P.N.; Coote, P.J.; Nychas, G.-J.E. A study of the minimum inhibitory concentration and mode of action of oregano essential oil, thymol and carvacrol. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 91, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edris, A. Pharmaceutical and therapeutic potentials of essential oils and their individual volatile constituents: A review. Phytother. Res. 2007, 21, 308–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayaud, L.; Carricajo, A.; Zhiri, A.; Aubert, G. Comparison of bacteriostatic and bactericidal activity of 13 essential oils against strains with varying sensitivity to antibiotics. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 47, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biondi, D.; Cianci, P.; Geraci, C.; Ruberto, G.; Piattelli, M. Antimicrobial activity and chemical composition of essential oils from Sicilian aromatic plants. Flavour Fragr. J. 1993, 8, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irakli, M.; Lazaridou, A.; Biliaderis, C.G. Comparative evaluation of the nutritional, antinutritional, functional, and bioactivity attributes of rice bran stabilized by different heat treatments. Foods 2021, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irakli, M.; Tsifodimou, K.; Sarrou, E.; Chatzopoulou, P. Optimization infusions conditions for improving phenolic content and antioxidant activity in Sideritis scardica tea using response surface methodology. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2018, 8, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaara, M. Agents that increase the permeability of the outer membrane. Microbiol. Rev. 1992, 56, 395–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).