Abstract
Andean maize is produced in the Argentine Northwest and can be used in gluten-free bread formulations. Water has an important role in the technological properties of flour and consequently in gluten-free bread quality. Processing whole-grain flour is difficult but improves the final product’s nutritional profile. The work aimed to evaluate the effect of different levels of water (100, 110, and 120% based on flour weight) on the flow properties of dough, textural properties and cooking of bread. For the formulation of the mold bread, Andean maize (Capia and Bolita) whole-grain flour was used. The flow properties of dough, weight losses and textural properties in breads were determined. The flow tests showed a drop in the consistency index with increasing dough hydration. In contrast, the flow index increased with respect to its initial value in both varieties of maize. The weight loss after baking tended to increase significantly from 4.60 to 5.8% with hydration increasing in Capia maize bread. However, this trend was not observed in Bolita. The hardness, springiness, gumminess and chewiness determined varied significantly only in Bolita maize bread due to the effects of hydration. More consistent dough resulted in harder, more elastic, rubbery and chewier bread.
1. Introduction
Gluten-free breads have several textural and sensory defects because they lack a three-dimensional structure like gluten capable of retaining the incorporated air. The combination of various ingredients and additives (hydrocolloids, modified starches, protein isolates, among others) is the most widely used strategy to imitate the viscoelastic properties of gluten necessary to obtain gluten-free bread of acceptable quality [1].
Vidaurre-Ruiz et al. [2] studied four gluten-free bread formulations using two starches (corn and potato) and hydrocolloids (tara and xanthan gum), finding that depending on the starch source, due to their morphology and sticking characteristics, they can interact with hydrocolloids differently, affecting the rheological properties of dough and the baking and textural properties of baked goods. In addition, the chemical structure of the hydrocolloid also influences the mentioned properties. Subsequently, Vidaurre-Ruiz et al. [3] experimented with the replacement of potato starch with quinoa, kiwicha and tarwi flour in different proportions, showing that in multicomponent systems the physicochemical interactions between flour components affecting the rheological and textural properties of gluten-free dough, making the study of these systems more complex.
Various methods are used to evaluate the effect of varying the water content in gluten-free dough, such as farinographic, adjustment calculations based on the water absorption capacity of the ingredients, retro-extrusion, and flow tests. The gluten-free dough, made with different ingredients, can be considered a structured system and show different viscoelastic and flow properties depending on the water content and the composition of the raw material used [4]. There are few studies on the relationship between the baking properties of gluten-free whole-grain flours from Andean grains and the flow properties of their doughs for adjusting the water content.
The aim of this work was to evaluate the effect of different levels of water (100, 110, and 120% based on flour weight) on the flow properties of dough, textural properties and cooking of bread.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Andean maizes (Capia and Bolita varieties) grown in the Ocumazo-Humahuaca province of Jujuy, Argentina, was used. The grains were milled in a hammer mill (Polymix System PX-MFC) to obtain whole-grain flour with grain size <710 µm. The maize had 10.33% and 10.07% moisture content, respectively. Commercial xanthan gum (9.58% moisture content) was used.
2.2. Breadmaking Process
The mold bread was made with whole-grain native maize flour; initially, the flour was mixed for 1 min to achieve homogenization of the samples. For every 100 g of substituted flours, 100, 110 and 120 mL of water (30 °C), 1.5 g of previously activated commercial dry yeast, 1.5 g salt (NaCl), 3 g sugar, 3 g of milk powder, 10 g butter, 0.5% xanthan gum and 2% egg albumin were added and mixed to low speed in hand mixer for 5 min. The dough obtained was put in molds and placed in a fermentation chamber for 50 min at 30 °C and 80–90% relative humidity. The fermented dough was baked at 150 °C for 50 min. The bread’s technological properties were evaluated 24 h after baking.
2.3. Technological Properties
2.3.1. Dough Rheological Properties
Dough samples for the rheological tests were prepared without adding yeast. The rheological measurements were conducted using a TA rheometer (DHR 10, TA Instrument, EE.UU). All measurements were carried out at 25 °C, using parallel plate geometry of 40 mm diameter and 1 mm gap. The dough sample was placed between the plates and the edges were carefully trimmed with a spatula. The flow experiments were conducted under steady-shear conditions with shear rates ranging from 0.01 to 50 L/s. The consistency index and flow behavior index or flow index values were obtained by applying the power law to the shear stress vs. shear rate curves. The measurements were made in duplicate.
2.3.2. Weight Loss (WL)
Weight loss or baking loss was computed as [initial loaf weight before baking—the loaf weight after 24 h baking × 100]/initial loaf weight before baking. The measurements were made in duplicate.
2.3.3. Textural Analysis
Crumb texture profile analysis (TPA) was performed using a texture analyzer (TAXT plus, Stable Micro System, Godalming, UK) equipped with a 5 kg load cell. An aluminum cylindrical probe with a P/35 (35.0 mm) was used for the bread; samples from the center of bread (thickness of 10 mm) were compressed to 50% of their original height. The test speed was 1 mm/s and the waiting time was 5 s. The measurements were made in quadruplicate.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Data obtained were analyzed using the INFOSTAT software (Córdoba, Argentina, version 2017.1.2). The results were evaluated via analysis of variance with a significance level (α) 0.05, followed by the post hoc test with LSD Fisher.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Dough Properties
Figure 1A,B show the variation of the consistency and flow index due to the effect of the water content in the formulated gluten-free doughs.
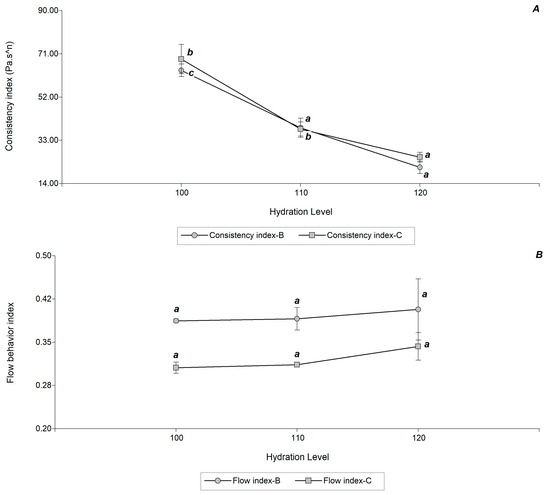
Figure 1.
Diagram of values of (A) Consistency Index and (B) Flow Behavior Index of dough from Andean maize varieties Bolita (circle) and Capia (square), whit hydration levels 100, 110 and 120% in base of flour. Different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) between hydration levels by maize.
The consistency of Bolita and Capia maize dough decreased significantly (p < 0.05) between 33.13 and 37.27%, respectively with increasing hydration. However, the values between maize did not vary significantly at the same level of hydration.
The flow behavior index did not show a significant difference with the hydration level in Bolita and Capia maize dough, although significant differences were observed between maize varieties (p < 0.05). The flow behavior index values obtained are within the range of values reported for other gluten-free dough formulations e indicate that the formulated dough with the flours of both maize varieties presented a pseudo plastic or shear thinning behavior [4]. However, in other formulations, we found an increment in the flow behavior index with increasing hydration that would be related with the greater mobility of the flour components. In this work, the high variability of this factor at the point of greatest hydration could be due to the greater ease of incorporation of air by the egg albumen, which would cause greater instability of the mass due to coalescence. Dermikersen et al. [5] indicated the existence of this unstable behavior, with phase separation, in control dough prepared only with rice flour (without gum or emulsifier) and in dough with pectin.
The studied maize varieties have morphological differences in their starch granules, with smaller sizes and greater size distribution in Bolita maize (unpublished results). In addition, their whole-grain flours have a compositional difference in lipid content (almost 20% higher in Capia) and fiber (almost 60% higher in Bolita). Despite this, they did not show differences in the flow behavior, possibly the native state of the whole-grain flours and the low stability provided by xanthan gum in the formulation dose.
3.2. Technological Characteristics of Bread
The weight losses (WL) by baking of the formulated breads are shown in Figure 2. In Capia maize WL increased from 4.60 to 5.8% in a statistically significant way (p < 0.05) with the level of hydration. In the Bolita maize bread, a trend similar to that of Capia maize at 100 and 110% hydration was observed, with a drop in WL to 120%, due to effect of water retention by the fiber. In some works, a direct relationship between bread quality and WL was observed; lower WL gave rise to loaves of lower volumes and defective textural characteristics [6]. In addition, the association of higher water contents with higher WL was highlighted, as observed in this work. The textural properties of the formulated bread can be shown in Figure 3. It was observed that increasing the hydration of the doughs had no significant effect on the textural properties of the Capia maize bread. In contrast, only a slight tendency to increase the hardness and elasticity of bread with 110% hydration was observed. In Bolita maize, a statistically significant decrease (p < 0.05) was observed in hardness, gumminess, chewiness, and elasticity at 100 and 110% hydration. No significant differences were found in cohesion or resilience in any sample. Higher values of elasticity, cohesion, and resilience in the bread are indicators of structural stability [7]. Encina-Zelada et al. [6] found that gluten-free bread with a low water content has greater hardness, which is consistent with the results of this work.
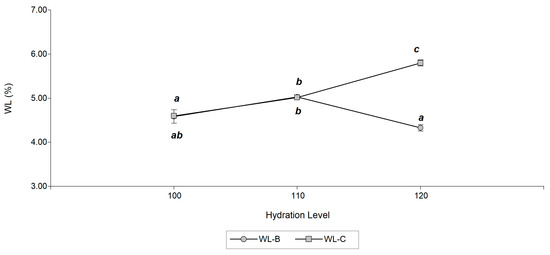
Figure 2.
Diagram of values of weight loss (WL) of Andean maize varieties Bolita (circle) and Capia (square), whit hydration levels 100, 110 and 120% in base of flour. Different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) between hydration levels of maize.
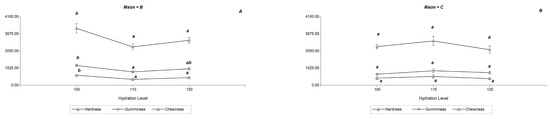
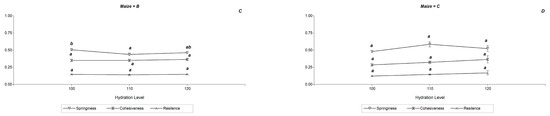
Figure 3.
Diagram of values of Textural properties of Andean maize varieties Bolita (maize = B) and Capia (maize = C), whit hydration levels 100, 110 and 120% in base of flour. (A,B) Diagrams correspond to Hardness (triangle), Gumminess (rhombus) and Chewiness (pentagon); (C,D) diagram correspond to Springiness (inverted triangle), Cohesiveness (sandglass) and Resilience (star). Different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) between hydration levels by maize.
That is, given the greater elasticity, the bread would be more structurally stable at 110% hydration in the case of Capia maize and at 100% hydration in the case of Bolita maize. However, these latter, due to their high hardness, would be less attractive to the consumer, and its dough is difficult to handle due to the high consistency. This agrees with the results of Santos et al. [8], who obtained higher acceptability in gluten-free chickpea bread with high hydration levels and low hardness.
4. Conclusions
The hydration level significantly influenced the consistency of the formulated dough independently of the variety of Andean maize used. On the other hand, the level of hydration significantly influenced the higher values of WL, hardness, elasticity, gumminess, and chewiness of Bolita maize breads at 100 and 110% water contents. In this case, the low structural stability of bread formulated with 120% water, flour in its native state, low gum concentration, and high fiber content of whole-grain flours, could be responsible for the drop in the mentioned parameters. The textural properties of the Capia maize dough did not show variations due to changes in water content, nor was a relationship found with flow properties.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.O.L., R.M.M. and N.C S.; methodology, R.M.M., M.O.L. and N.C.S.; validation, R.M.M. and M.O.L.; formal analysis, R.M.M.; investigation, R.M.M. and N.C.S.; resources, M.O.L. and N.C.S.; data curation, R.M.M., M.O.L. and N.C.S.; writing—original draft preparation, R.M.M. and M.O.L.; writing—review and editing, M.O.L. and N.C.S.; visualization, M.O.L. and N.C.S.; supervision, M.O.L. and N.C.S.; project administration, N.C.S.; funding acquisition, M.O.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This work was support by grant IaValSe-Food (119RT0567), CONICET and Secretaría de Ciencia y Técnica y Estudios Regionales, Universidad Nacional de Jujuy, Argentina.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sciarini, L.S.; Steffolani, M.E.; Leon, A.E. El rol del gluten en la panificación y el desafío de prescindir de su aporte en la elaboración de pan. Agriscientia 2016, 33, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidaurre-Ruiz, J.; Matheus-Diaz, S.; Salas-Valerio, F.; Barraza-Jauregui, G.; Schoenlechner, R.; Repo-Carrasco-Valencia, R. Influence of tara gum and xanthan gum on rheological and textural properties of starch-based gluten-free dough and bread. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 1347–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidaurre-Ruiz, J.; Salas-Valerio, F.; Schoenlechner, R.; Repo-Carrasco-Valencia, R. Rheological and textural properties of gluten-free doughs made from Andean grains. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronda, F.; Pérez-Quirce, S.; Villanueva, M. Rheological properties of gluten-free bread doughs: Relationship with bread quality. In Advances in Food Rheology and Its Applications, 1st ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2016; pp. 297–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirkesen, I.; Mert, B.; Sumnu, G.; Sahin, S. Rheological properties of gluten-free bread formulations. J. Food Eng. 2010, 96, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Encina-Zelada, C.R.; Cadavez, V.; Monteiro, F.; Teixeira, J.A.; Gonzales-Barron, U. Combined effect of xanthan gum and water content on physicochemical and textural properties of gluten-free batter and bread. Food Res. Int. 2018, 111, 544–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De La Hera, E.; Rosell, C.M.; Gomez, M. Effect of water content and flour particle size on gluten-free bread quality and digestibility. Food Chem. 2014, 151, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, F.G.; Fratelli, C.; Muniz, D.G.; Capriles, V.D. The impact of dough hydration level on gluten-free bread quality: A case study with chickpea flour. Int. J. Gastronomy Food Sci. 2021, 26, 100434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).