Abstract
Climate change is enhancing the frequency of cyanobacterial blooms not only during summer but also in spring and autumn, leading to increased ecological impacts. The bacterioplankton community composition (BCC), in particular, is deeply affected by these blooms, although at the same time BCC can also play important roles in blooms’ dynamics. However, more information is still needed regarding BCC during species-specific cyanobacterial blooms. The goal of this study was to assess BCC succession in a hypereutrophic shallow lake (Vela Lake, Portugal) during a warm spring using a metagenomic approach to provide a glimpse of the changes these communities experience during the dominance of Aphanizomenon-like bloom-forming species. BCC shifts were studied using 16S rRNA gene metabarcoding and multivariate analyses. A total of 875 operational taxonomic units (OTUs) were retrieved from samples. In early spring, the dominant taxa belonged to Proteobacteria (mainly Alphaproteobacteria—Rickettsiales) and Bacteroidetes (Saprospirales, Flavobacteriales and Sphingobacteriales). However, at the end of May, a bloom co-dominated by cyanobacterial populations of Aphanizomenon gracile, Sphaerospermopsis aphanizomenoides and Synechococcus sp. developed and persisted until the end of spring. This led to a major BCC shift favouring the prevalence of Alphaproteobacteria (Rickettsiales and also Rhizobiales, Caulobacteriales and Rhodospirillales) and Bacteroidetes (Saprospirales, followed by Flavobacteriales and Sphingobacteriales). These results contribute to the knowledge of BCC dynamics during species-specific cyanobacterial blooms, showing that BCC is strongly affected (directly or indirectly) by Aphanizomenon-Sphaerospermopsis blooms.
1. Introduction
Climate change is enhancing the occurrence and persistence of cyanobacterial blooms across the globe, with impacts on aquatic ecosystems but also posing risks to human health. Harmful Cyanobacterial Blooms (HCBs) are caused by cyanobacteria that can produce toxins that can lead to dermatotoxic, hepatotoxic, neurotoxic or cytotoxic effects on water users/consumers [1,2,3,4]. Under the global warming scenario, there has been a special concern related to tropical invasive bloom-forming species such as Raphidiopsis raciborskii (formerly named Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Woloszynska) Seenayya & Subba Raju [5,6,7,8]), Cuspidothrix issatschenkoi (previously Aphanizomenon issatschenkoi (Usačev) Proshkina-Lavrenko [9]) and Sphaerospermopsis aphanizomenoides (also formerly named Aphanizomenon aphanizomenoides (Forti) Horecká & Komárek/Anabaena aphanizomenoides Forti [6,7,8]), which have been spreading north to higher latitudes in Europe, America and Asia [10,11,12,13,14]. These invasive cyanobacteria have been detected in Portuguese water bodies, including Raphidiopsis raciborskii [15,16,17,18], Cuspidothrix issatschenkoi [19,20] and Sphaerospermopsis aphanizomenoides [19]. These species include potentially toxic strains that are able to produce cyanotoxins such as cylindrospermopsin, saxitoxins and anatoxin-a [21,22,23,24], thus increasing the diversity of potentially HCBs at higher latitudes and subsequently enhancing health risks for water users.
On the other hand, cyanobacterial blooms are being increasingly reported for extended periods not only for tropical but also for subtropical and temperate lakes [25,26,27,28,29,30], which makes the related potential health hazards from the exposure to HCBs no longer exclusive to the late spring/summer/early autumn seasons but rather occurring during most of the year. Therefore, research and monitoring should be intensified in early spring and late autumn in order to better understand the successional dynamics of blooms and the particular environmental requirements and triggering conditions for a given species (or strain) to bloom.
For each cyanobacterial species, growth conditions can vary greatly [31,32,33,34]. This physiological diversity can even occur at the strain level, with impacts on the cyanobacterial growth [19,35,36] but also on the synthesis of cyanotoxins [37,38]. Therefore, infra-specific conclusions retrieved from classical approaches per se have become limited considering the wider and strain-specific information provided by molecular methodologies and which is impossible to track under a microscope. Moreover, the morphological variation and the suggestion of a polyphyletic nature of Nostocales genera such as Anabaena and Aphanizomenon has been controversial [39,40,41,42], and only polyphasic approaches over the past two decades have contributed to put some consensual order onto their taxonomy [6,8,43,44,45]. However, this long-lasting taxonomic controversy and difficulties related to the correct morphological identification of Anabaena/Aphanizomenon taxa has led to many microscopic misidentifications, which inevitably have compromised a deeper assessment of biogeography and toxicity patterns of bloom-forming species. Nevertheless, through DNA-based approaches, new insights of biogeographic/phylogeographic patterns of harmful bloom-forming Nostocacean cyanobacteria were revealed [46,47,48,49].
High-throughput sequencing (HTS) analysis of the 16S rRNA gene (or 16S rRNA gene metabarcoding), in particular, have provided an in-depth overview of spatial and/or temporal variations in cyanobacterial communities either from different geographical origins [50,51,52] or from the same waterbody [53,54] as well as the assessment of the potential toxicity risks of a bloom [55]. Moreover, it became possible to track the eventual re-incidence of specific cyanobacterial populations in target water bodies directly from complex environmental samples, with evident major implications for subsequent modelling and water management design strategies. Additionally, this approach can also be useful to simultaneously study the cyanobacterial and heterotrophic bacterial communities from the same sample [56,57,58]. Bacterioplankton is essential for the biogeochemical cycling of nutrients and the ecological dynamics of waterbodies. The bacterioplankton community composition in HCBs plays an important dual role: (1) as an indicator of potential toxic risks, as it can be strongly affected by cyanobacterial blooms; (2) or as an active player on the bloom dynamics by promoting or inhibiting cyanobacterial growth [59,60] or even lysing bloom-forming cyanobacteria [61] and degrading cyanotoxins [62,63]. These interactions thus have implications for the toxicity potential and health risks of a bloom. However, the bacterial community succession during species-specific cyanobacterial blooms is still a research path that has not been extensively explored in order to hypothesize potential global dynamic patterns, particularly under a global climate change scenario. Therefore, more studies on the dynamics of bacterioplankton communities could bring more insights to this still unravelled topic, particularly under a species-specific scope regarding Aphanizomenon-like blooms.
Under a global warming scenario and increasingly extended warmer seasons, the present work aimed to study the bacterioplankton community dynamics during the development of cyanobacterial blooms through a warm and dry spring at a Portuguese temperate shallow lake (Vela Lake). The present study results will contribute to go further in the understanding of the relationships between cyanobacteria and heterotrophic bacteria, particularly during diazotrophic species-specific blooms.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area, Sampling and Environmental Parameters
Vela Lake is a shallow eutrophic lake located in Central Western Portugal (Quiaios, Figueira da Foz), surrounded by forest, agriculture fields, livestock farms and urban areas. It has a depth range of 0.9–2.4 m and a flooding area of approximately 70 ha. Agricultural land, in particular, is a source of high amounts of fertilizers and pesticides that are lixiviated into the lake water with rainfall. The lake is mainly used for recreation and irrigation of crop fields. During spring 2006, a total of 12 water samples were collected from April to June, with a sampling interval from 2 to 10 days (Table 1), depending on the development stage of the bloom. Samples were taken sub-superficially at about 1 m from the shore (40°16′24.0″ N 8°47′35.0″ W) using 2L sterile bottles and were immediately placed at 4 °C in the dark until further treatment in the laboratory for DNA extraction and determination of environmental parameters. Water temperature, conductivity, pH and dissolved oxygen were determined in situ using portable water testing meters (WTW LF 330 conductivity meter, WTW 340-A pH meter and WTW OXI 320 oxygen meter). Preliminary sampling and analyses along several points of the lake showed this sampling site was representative of the BCC at Vela Lake during late spring. In the laboratory, the total suspended solids (TSS), chlorophyll a (Chl a), soluble reactive phosphorus (SRP), ammonium (N-NH4) and nitrate (N-NO3) concentrations were determined according to standard procedures [64].

Table 1.
Environmental data recorded during the study period (April to June 2006) at Vela Lake (Portugal).
2.2. 16S rRNA Gene Metabarcoding
Total DNA was extracted as previously described [65]. Briefly, 100 mL water samples were filtered through 0.22 µm polycarbonate sterile filters; collected cells were resuspended in 2 mL of TE buffer (10 mM Tris HCl, 1 mM EDTA, pH 8.0), centrifuged and resuspended in 200 µL of TE. Lysis was performed using lysozyme (1 mg mL−1) over 1 h at 37 °C. DNA extraction and purification was performed using the Genomic DNA Purification Kit (MBI Fermentas, Vilnius, Lithuania) and DNA was resuspended in TE buffer and stored at −20 °C. Pyrosequencing libraries were obtained using the 454 Genome Sequencer FLX platform (Roche Diagnostics Ltd., West Sussex, UK). Bacterial 16S rRNA gene fragments from the V3V4 hypervariable region were amplified using barcoded fusion primers with the Roche-454 Titanium sequencing adapters A and B (an eight-base barcode sequence), the forward primer 5′-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAG-3′ (338F) and the reverse primer 5′-TACNVRRGTHTCTAATYC-3′ (802R) [66]. PCR amplifications were carried out in 20 µL reactions with Advantage Taq (Clontech) using 0.2 M of each primer, 0.2 mM dNTPs, 1× of polymerase mix, 6% DMSO and 1–2 µL of template DNA. PCR conditions were 94 °C for 4 min, followed by 25 cycles of 94 °C for 30 s, 44 °C for 45 s and 68 °C for 60 s and a final elongation step at 68 °C for 10 min. Amplicons were quantified by fluorometry with PicoGreen (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA), pooled at equimolar concentrations and sequenced in the A direction with GS 454 FLX Titanium chemistry, according to manufacturer’s instructions (Roche, 454 Life Sciences, Brandford, CT, USA), at Biocant (Cantanhede, Portugal). Pyrosequencing sequence analysis was performed using previously described methods [67].
2.3. Statistical Analysis
A cluster analysis of samples, based on operational taxonomic units (OTUs) distribution, was performed using the unweighted pair group method with mathematical averages (UPGMA). The dendrogram was created using the Pearson correlation coefficient and the PAST software package [68]. Canonical correspondence analysis (CCA) [69] was performed to reveal relationships between environmental variables and the distribution of OTUs across the sampling period, using CANOCO 4.5 (Scientia Software) software. Environmental variables were standardized and OTUs abundance data were log transformed. Furthermore, only OTUs with a contribution of more than 1% (of total sequence reads) in at least one sample were considered. Forward selection was applied to choose the significant (p ≤ 0.05) environmental parameters for the CCA using a Monte Carlo permutation test (499 unrestricted permutations).
3. Results
3.1. Environmental Parameters
The recorded environmental parameters and sample codes are summarised in Table 1. From early to late spring samples, it was possible to detect a general environmental gradient mainly characterized by water temperature, Chl a, TSS, pH and conductivity levels. The lowest values for water temperature (18.0 °C) and conductivity (560 mS cm−1) were recorded on the 10th of April whereas the highest temperature (27.5 °C) and conductivity (647 μS cm−1) were observed on the 28th of May and 25th of June, respectively. The highest Chl a (98.1 μg L−1), pH (9.82) and oxygen (13.70 mg L−1 and 173.3%) levels were recorded on the 5th of June. The lowest values for pH (8.00) and oxygen (5.99 mg L−1 and 71.4%) were detected on the 4th of May and 11th of June, respectively. On the 10th of May, the lowest Chl a (10.3 μg L−1) and TSS (51.0 mg L−1) values were recorded whereas maximum concentration of TSS (51.0 mg L−1) was recorded on the 11th of June. Nitrogen inorganic sources (nitrate and ammonium) were undetectable in all samples, except for the 20th of April where ammonium levels (0.04 mg L−1) were slightly above the detection limit (0.01 mg L−1). Soluble reactive phosphorus was only detectable on the 22nd of May (0.01 mg L−1).
3.2. 16S rRNA Gene Metabarcoding
For the 16S rRNA gene metabarcoding analysis, a total of 25,705 sequences corresponding to 875 OTUs were obtained after quality checking. BLAST results for the most abundant OTUs (>3% of total bacterial sequence reads in at least one sample) are presented in Table 2. In general, for Vela Lake samples, a high phylogenetic diversity was recorded at phylum and class levels. By considering the main groups (Figure 1A), it was possible to observe that, from the 10th of April until the 22nd of May, the most abundant bacterial phylum was Proteobacteria (always >50% of total sequence reads), followed by Bacteroidetes (ranging between 18 and 28%). Actinobacteria members were also persistent across samples, although at lower abundances (between 4 and 14%). From the 28th May onwards, Cyanobacteria became progressively dominant, reaching an abundance peak on the 5th of June (46%), although Proteobacteria remained co-dominant (ranging from 28 to 44%).

Table 2.
Phylogenetic denomination, closest relative (after a BLAST search) and corresponding percentage similarity for the 16S rRNA gene partial sequences (408–425 bp) of the most abundant OTUs (above 2% of total reads in at least one sample). Phylogenetic affiliation determined using RDP database is also presented.
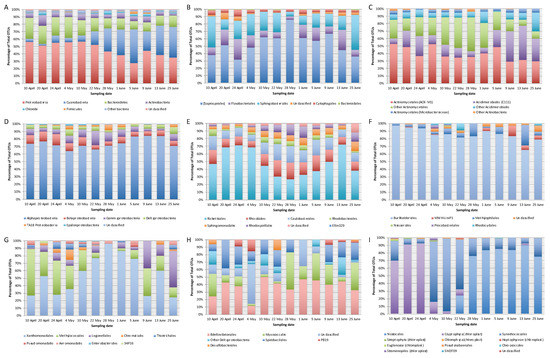
Figure 1.
Relative abundance of bacterial OTUs of 12 samples from Vela Lake analysed using 16S rRNA gene metabarcoding: (A) total bacteria at the phylum level; (B) Bacteroidetes at the order level; (C) Actinobacteria at the order/family level; (D) Proteobacteria at the class level; (E) Alphaproteobacteria at the order level; (F) Betaproteobacteria at the order level; (G) Gammaproteobacteria at the order level; (H) Deltaproteobacteria at the order level; (I) Cyanobacteria at the order or similar level; Ribosomal Database Project (RDP) was used for the classification of OTUs. Please view the web version of this article for a better interpretation of the colour gradients.
The major bacterial phylum found in Vela Lake samples was Proteobacteria and it was clearly dominated by Alphaproteobacteria (from 64 to 84% of total sequence reads within the phylum) during the study period (Figure 1D). Alphaproteobacteria OTUs (Figure 1E) mostly belonged to the Rickettsiales order (between 26 and 72% of total reads from the class) and the most dominant and persistent OTU affiliated with Pelagibacteraceae, reaching 21% of total bacterial sequence reads on the 24th of April (Table 2). Between the 10th of May and 1st of June, the relative abundance of Rickettsiales declined and the relative abundance of the orders Caulobacterales (9 to 22% of total class reads) and Rhizobiales (8 to 22%), and Rhodospirales (up to 14%) increased. As seen in Table 2, the dominant Rhizobiales reached 4% of total bacterial sequence reads on the 10th of April, whereas Rhodospirales and the other Alphaproteobacteria OTU reached maximum values of 4 and 3%, respectively, between the 28th of May and 1st of June. The Sphingomonadales order was persistent across samples (with relative abundances varying between 4 and 12% of total Alphaproteobacteria sequence reads and attaining maxima values between the 10th of May and 25th of June). Betaproteobacteria varied from 6 to 14%, Gammaproteobacteria from 2 to 18%, and Deltaproteobacteria from 4 to 10% (Figure 1D). The Burkholderiales order almost completely dominated the betaproteobacterial class, and varied between 66 and 98% of total class sequence reads (Figure 1F). Gammaproteobacteria composition (Figure 1G) oscillated, with the Xanthomonadales order clearly dominating from the 10th of May until the 5th of June (ranging from 60 to 96% of the class sequence reads) and a dominant Sinobacteraceae (Xanthomonadales, Gammaproteobacteria) OTU reached a peak of 4% of total bacterial reads on the 22nd of May (Table 2). The Methylophilales order was most abundant from the 10th of April until the 10th of May (between 26 and 63% of total class reads) and there was an increase in the Legionellales abundance between the 9th and 25th of June (up to 48%), during the later phase of the bloom (Figure 1G). In all samples, Bacteroidetes were generally dominated by members of the Saprospirales order (from 32 to 86% of total sequence reads within the phylum), followed by Sphingobacteriales (from 8 to 46%) and Flavobacteriales (from 4 to 28%), as shown in Figure 1B. Chitinophagaceae were the most abundant Saprospirales members, with maxima on the 10th of April (3% of total bacterial reads), 4th of May (with 5%), and 22nd of May (3%) or 28th of May (with 7%), depending on the OTU (Table 2). Saprospiraceae (Saprospirales) OTUs exhibited pronounced oscillations in abundance throughout the study period, with peaks on the 10th of April (5%) and from the 28th of May until the 1st of June (4%), depending on the OTU. Different dominant OTUs assigned to the Sphingobacteriales order appeared with different peaks on the 10th of April (6%), 20th of April (3%) and 25th of June (6%).
For Cyanobacteria there was a clear temporal succession in taxa (Figure 1I). During early spring, cyanobacterial abundance was low (between 2 and 10% of total bacterial reads) (Figure 1A). From the 10th to 24th of April, cyanobacterial abundance was mostly dominated (from 70 and 93% of cyanobacterial sequence reads) with different sequences affiliating with chloroplasts from the microalga Cryptomonas (Cryptophyta) which attained a total maximum of 12% of total bacterial sequence reads on the 24th of April (Table 2). From the 4th until the 22nd of May, the Synechococcales order became dominant (varying between 67 and 96% of cyanobacterial reads) with a Synechococcus OTU attaining a maximum of 21% of total bacterial sequence reads on the 22nd of May (Table 2). From the 22nd of May onwards, Cyanobacteria abundance increased and coincided with the rise in the Nostocales, which dominated until the end of the study period (reaching 90% of cyanobacterial sequence reads on the 13th of June). The OTUs that achieved the highest abundance levels were assigned to the cyanobacterial species Aphanizomenon gracile (reaching 34% of total bacterial reads on the 5th of June) and Sphaerospermospis aphanizomenoides (formerly Aphanizomenon aphanizomenoides [7,8,36] which reached 22% on the 25th of June) (Table 2). Interestingly, the S. aphanizomenoides OTU was similar to sequences retrieved from strains isolated from Vela Lake in 2004 and 2006, during the summer season [70]. On the 25th of June, when the Aphanizomenon gracile density began to decline (to 15% of total bacterial reads), another Synechococcus OTU increased its abundance reaching 11% of total bacterial sequence reads.
Actinobacteria were ubiquitous throughout samples and dominated by the orders Actinomycetales (with different dominant OTUs showing maxima in distinct samples: 4 or 5% of total bacterial reads on the 10th of May or 20th of April, respectively) and Acidimicrobiales (with an OTU showing a peak of 4% of total bacterial reads on the 9th of June).
Other dominant OTUs were assigned to the Candidate division OD1 (with a peak of 9% of total bacterial sequence reads on the 1st of June) and the phyla Chlorobi (present in all samples, with a peak of 5% on the 20th of April) and Firmicutes (also with a maximum relative abundance on the 5th of June at 4%).
3.3. Analysis of BCC vs. Environmental Conditions
Despite the variability of environmental parameters, cluster analysis of samples (Figure 2) according to OTUs distribution revealed two distinct temporal clusters: one from the 10th of April to the 22nd of May (cluster I—before the establishment of the bloom) and another from the 28th of May till the 25th of June (cluster II—during the bloom). The major shifts in BCC coincided with the establishment of the Aphanizomenon-like spp. bloom on the 28th of May. CCA (Figure 3) showed that the significant parameters relating to OTUs distribution were total suspended solids and conductivity levels, rather than temperature (although a gradient could be recorded throughout the study period). The first two canonical axes explained 30.7% of the total variance. The first axis explained 19.3% of total variance and it was significantly related to conductivity (0.92) and TSS (0.86). Samples 11JN and 25JN (and OTUs 9, 45, 79, 100, 75 and 22, belonging to Sphingobacteriales, Flavobacteriales and Cytophagales (Bacteroidetes), as well as to Rhodobacterales and Sphingomonadales (Alphaproteobacteria)) defined the positive side of the axis whereas samples 10AP and 24AP (and a cluster of OTUs from mixed groups) defined its negative side. The second axis explained 11.4% of the total variation in OTU composition and it showed a lower correlation with conductivity and TSS (both with 0.44). Sample 5JN (and OTU 35, a Bacillales (Firmicutes)) defined its positive side and 10MAY and 22MAY (and a cluster of OTUs (e.g., 90, 7, 89) belonging to several groups) defined its negative side.
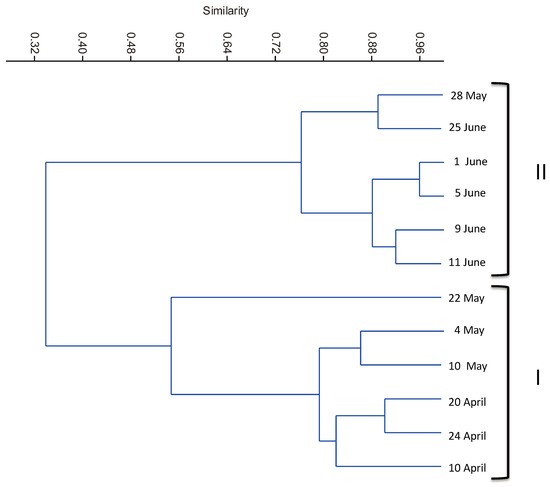
Figure 2.
Dendrogram derived from hierarchical cluster analysis based on Pearson correlation between the 12 temporal samples, according to the distribution of OTUs (with a contribution of 1% or more in at least one sampling date).
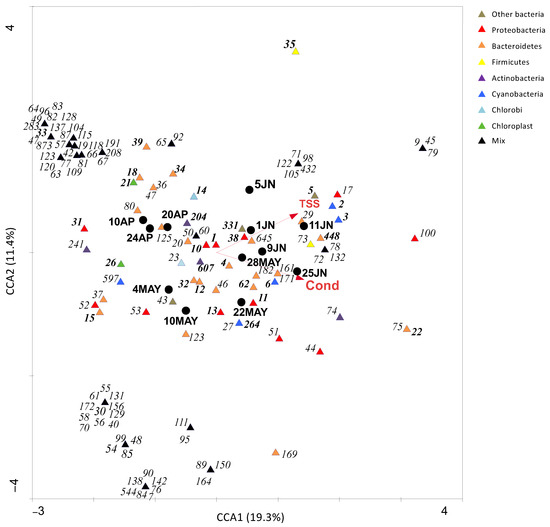
Figure 3.
Canonical Correspondence Analysis (CCA) ordination triplot of OTUs (obtained from 16S rRNA gene metabarcoding) and only significant (p < 0.05) environmental parameters (TSS: total suspended solids; Cond: conductivity) recorded during the corresponding sampling dates. The circles represent the samples and the triangles represent the OTUs (different colours represent different bacterial groups—please view the coloured web version of this article). OTUs with a contribution of less than 1% in at least one sampling date were not considered for multivariate analysis. Dominant OTUs (corresponding to the ones described in Table 2) are highlighted in bold.
4. Discussion
The occurrence of cyanobacterial blooms has been reported in Portugal for the past 30 years with many references to cyanotoxin production [71,72,73]. Recurrent cyanobacterial blooms have been recorded at Vela Lake, with the dominance of taxa belonging to genera such as Microcystis, Anabaena, Aphanizomenon, Cuspidothrix or Cylindrospermopsis [18,19,26,70,74,75]. However, as for most Portuguese freshwater bodies, information on the environmental BCC at Vela Lake is very scarce [76,77].
Vela Lake is a shallow lake characterized as eutrophic decades ago [78], with a trend for increasing eutrophication [76,77]. In fact, conductivity levels recorded in the present study showed a two-fold increase in comparison to data from spring 2001 [26], although temperature, pH and nutrient values fell into or below the range previously reported. More recent data, from 2012, reported a further intensification of eutrophication in the summer season (achieving a very high value for conductivity (802 μS cm−1)) and dense toxic blooms of Microcystis sp. with the production of microcystins (MC-LR) [79].
Over the past decades, spring seasons have become warmer in many regions of the world, enhancing the occurrence of cyanobacterial blooms earlier in the year [25,29]. For Vela Lake, the dominance of diazotrophic cyanobacteria (namely Aphanizomenon spp.) during late spring was also recorded in 2012 [80], supporting the recurrence of these earlier blooms. In the present study, the peak of the bloom coincided with higher values for temperature, pH, conductivity and TSS. The abundance of the Aph. gracile OTU was significantly correlated (p < 0.05) to temperature (r = 0.65), chlorophyll a (r = 0.79) and TSS (r = 0.92). The S. aphanizomenoides OTU also significantly correlated (p < 0.05) with chlorophyll a (r = 0.64) and TSS (r = 0.81), but also conductivity (r = 0.74), suggesting species-specific conditions to bloom. The Synechococcus OTU was only significantly related to conductivity (r = 0.65). In eutrophic shallow lakes, the occurrence of cyanobacterial blooms has been also associated with an increase in temperature, conductivity and pH levels, but also scarcity or undetectable nutrient levels, particularly from inorganic nitrogen sources when diazotrophic species are dominant [81,82,83,84], such as in the present case. Nevertheless, it should be kept in mind that the increase in conductivity, TSS and chlorophyll a levels are certainly a direct consequence of the bloom development.
16S rRNA gene metabarcoding results showed that dominant OTUs were generally assigned to Alphaproteobacteria, Cyanobacteria, Bacteroidetes and Actinobacteria groups, which are usually found dominating bacterial communities in eutrophic shallow lakes [65,77,85,86]. However, the results also revealed a high diversity and successional dynamics below phylum and class levels, which highlights the need to go deeper into the phylogenetic affiliation effort for ecological surveys. Dominant groups belonging to Proteobacteria (Alphaproteobacteria—Rickettsiales, Caulobacterales, Rhizobiales and Sphingomonadales; and Betaproteobacteria—Burkholderiales), Bacteroidetes (Saprospirales, Sphingobacteriales and Flavobacteriales) and Actinobacteria (Actinomycetales) remained abundant throughout the sampling period.
The most abundant bacterial group was Alphaproteobacteria, with the most abundant OTU assigned to “Candidatus Pelagibacter” (Pelagibacteraceae, Rickettsiales), and was recorded in all samples. However, its abundance declined during the bloom development—a negative correlation was observed with cyanobacterial OTUs from Aph. gracile, S. aphanizomenoides and Synechococchus sp. (r = −0.61 to −0.59, p < 0.05). Strains of Pelagibacter spp. are frequent in marine environments but can also dominate in freshwaters where cyanobacterial blooms occur, namely from Microcystis spp. [87] or Planktothrix rubescens [88]. Caulobacteraceae (Caulobacterales) bacteria have also been found in European lakes with blooms of Cyanobacteria [89], namely co-dominated by Aphanizomenon and Cylindrospermopsis spp. [90]. Sphingomonadaceae (Sphingomonadales) have been associated with cyanobacterial co-dominance of Aphanizomenon/Anabaena [89] and some strains have been shown to degrade cyanobacterial toxins, namely microcystins [63,91,92,93]. The microcystin-degrading potential has also been reported for Rhizobiales [94], a group well represented during the study period at Vela Lake, particularly during the bloom peak. In fact, S. aphanizomenoides was dominant in the bloom and strains of this species have proven to be able to produce microcystins [95].
Burkholderiales (Betaproteobacteria), particularly from the Comamonadaceae family, were less abundant but persistently represented across Vela Lake samples. This family has been related to eutrophic lakes [65,96,97] during blooms dominated by diazotrophic cyanobacteria including Dolichospermum spp. [89,96,97]. A Polynucleobacter (Oxalobacteraceae, Burkholderiales, Betaproteobacteria) OTU was also persistent throughout the sampling period, although studies reported a decrease in the relative abundances of Polynucleobacter OTUs just before blooms co-dominated by Microcystis and Dolichospermum [98]. Nevertheless, Polynucleobacter OTUs have been also recorded during blooms of Microcystis, Anabaena, Aphanizomenon and Dolichospermum spp. [90,98] and some strains have been related to microcystin degradation [94].
Bacteroidetes (Saprospirales, Sphingobacteriales and Flavobacteriales orders) were recorded in all Vela Lake samples and there was a positive correlation with the Aph. gracile OTU (r = 0.72, p < 0.05). Saprospirales members have been recorded during Microcystis spp. blooms [99,100,101] and Sphingobacteriales have been related to high densities of Synechococcus sp. and Anabaena flos-aquae [102]. However, in the present study, some OTUs of Saprospirales (Chitinophagaceae) showed a negative correlation with Aph. gracile, S. aphanizomenoides and Synechococcus sp. (r = −0.72 to −0.60, p < 0.05) while another showed a positive relationship with S. aphanizomenoides (r = 0.65, p < 0.05). This highlights the need for a deeper taxonomic study to distinguish below the family and even genus level. The occurrence of Flavobacteriales (Bacteroidetes) in shallow lakes is also very frequent and has been linked to cell lysis and the declining phase of cyanobacterial blooms of Microcystis [87,100] but has also been associated with Synechococcus strains in culture [101]. In the present study, Flavobacteriales had high OTU diversity and succession, before and during the Aphanizomenon-like spp. bloom, suggesting differential sensitivity to environmental conditions and/or bloom-forming strains. However, no significant positive or negative correlations were recorded for this order while for Sphingobacteriales positive (r = 0.58 to 0.76, p < 0.05) and negative (r = −0.67 to −0.60, p < 0.05) correlations were found with the bloom-forming cyanobacteria Aph. gracile, S. aphanizomenoides and Synechococcus sp.
Actinobacteria, particularly from the Actinomycetales order, were also found persistently in samples although there was a clear succession of different OTUs during the study period and several OTUs had significantly negative correlations with Aph. gracile, S. aphanizomenoides and Synechococcus sp. (r = −0.74 to −0.66, p < 0.05). Actinomycetales are characteristic of shallow lakes and persist across seasons [65,76,86] but negative relationships have been reported with bloom-forming diazotrophic Dolichospermum spp. although a positive correlation was found with Synechococcus spp. [96]. Moreover, this group also includes strains capable of microcystin degradation [63].
Before the bloom development, we observed peaks of dominant OTUs belonging to Chlorobi (OPB56), Cyanobacteria (Synechococcales) and chloroplasts from Cryptophyta. Chlorobi have been found to be abundant in hypolimnetic waters of lakes and ponds where Cyanobacteria (such as Synechococcus) are also present [99]. Synechococcus spp. (Cyanobacteria) are ubiquitous in marine and freshwater environments but with different temporal and/or spatial successional strain patterns [102,103]. In the present study, several Synechococcus OTUs had different abundance patterns from April to June. Cryptophyta OTUs were negatively correlated with the bloom-forming cyanobacterial OTUs, but only one was significant, with the Synechococcus OTU (r = −0.59, p < 0.05). In eutrophic shallow lakes, the prevalence of microalgae belonging to Cryptophyta during winter and spring seasons is frequent [86,104,105]. In fact, microscopic analysis detected a strong presence of Cryptomonas (Cryptophyta) in samples from Vela Lake during spring 2006 [74]. However, 16S rRNA gene metabarcoding analysis did not provide much more relevant information on the remaining phytoplankton.
From the 22nd of May onwards, there were major shifts in BCC, with the increasing dominance of Cyanobacteria over the bacterioplankton community. The successional dominant cyanobacterial OTUs were affiliated with Aphanizomenon gracile, Sphaerospermopsis aphanizomenoides and Synechococcus sp. As already mentioned, these taxa can be frequently found in high densities in lentic freshwaters and have been linked to cyanotoxin production [95,106,107,108,109]. Strains of S. aphanizomenoides and Synechococcus spp. can produce microcystins [95,106] and Aph. gracile has been reported to produce saxitoxins [23,107,109,110] and cylindrospermopsin [111]. Blooms of Aph. gracile and S. aphanizomenoides have been previously recorded at Vela Lake during warmer months and both these OTUs were positively correlated (r = 0.63, p < 0.05). Their growth can be successful under nitrogen depletion [19,26]. In the present study, S. aphanizomenoides was also favoured by water temperatures between 24 and 28 °C during undetectable levels of NO3− and SRP and pH values higher than 9.0. The strong dominance of S. aphanizomenoides in cyanobacterial blooms under high temperatures (25–28 °C) and very low nutrient levels have also been reported for other shallow lakes [95]. Although S. aphanizomenoides is known for its ecological plasticity under different nutrient and temperature levels [112], severe fitness differences may also be observed among different strains under nutrient depletion [19,113]. Interestingly, the S. aphanizomenoides OTU was similar to sequences retrieved from strains isolated from Vela Lake from 2004 to 2006 [70] suggesting an interannual re-incidence of this bloom-forming cyanobacterium. This is a major advantage of using DNA-based approaches that enables the matching of sequences from diverse origins and times, either from isolates or environmental samples.
Moreover, in microscopic phytoplankton analyses from samples collected during the 2006 sampling period at Vela Lake, only a Nostocacean bloom-forming species was considered to bloom and identified as Aph. flos-aquae [74]. Classical microscopic-based analyses do not allow distinguishing unequivocally between Aphanizomenon species [24,114], particularly in the absence of heterocysts and/or akinetes in filaments. Moreover, a bloom of Aph. flos-aquae had been also reported during late spring of 2001, through microscopic identification based on phenotype characteristics [26] but it was re-identified as Aph. gracile after molecular analysis [70], highlighting the problems related to morphological identification but also taxonomic revisions. Indeed, Aph. gracile was previously known as Aph. flos-aquae f. gracile [40] and S. aphanizomenoides that was formerly Aphanizomenon aphanizomenoides or Anabaena aphanizomenoides [7,8,36]. The taxonomic vs. molecular features of Anabaena and Aphanizomenon-like cyanobacteria have been controversial for the past decades, but consensus is beginning to arise and bring light on how to identify Nostocales cyanobacteria using polyphasic approaches for new revisions and modern cyanobacterial taxonomy [115,116,117]. Nevertheless, these differences in nomenclature and potential misidentifications add a considerable variability to the historical ecological data recorded for each bloom-forming cyanobacterial species. Therefore, molecular approaches are essential to overcome these classical taxonomic ambiguities and provide robust information for specific distribution and ecological patterns of cyanobacterial blooms. Next generation sequencing should be considered for monitoring strategies [118], with the advantage of providing species-specific essential information concerning bloom-forming cyanobacteria but also information on the whole community and ribotype re-incidence, which is very important to go deeper in ecological studies and modelling approaches. In fact, an OTU matching the invasive Cuspidothrix issatschenkoi (previously reported at Vela Lake in 2004 [70]) was also detected in samples, although less representative within the cyanobacterial group. One of the bloom-forming Synechococcus (OTU 6) showed a significant positive correlation (r = 0.67, p < 0.05) with S. aphanizomenoides but not with Aph. gracile, emphasising the potential affinities for succession in the cyanobacterial dominance. However, despite Synechococcus-like OTUs being recorded at high densities during June, microscopic analyses from this sampling period [74] did not report this genus in the cell counts, probably due to their small size. Nevertheless, Synechococcus strains are able to produce cyanotoxins, namely microcystins [106], which makes this genus important to quantify for bloom risk assessment. Once more, 16S rRNA gene-based methodologies can overcome the subjectivity and limitations of classical identification approaches and provide a better basis for health risk assessment.
During the bloom, besides the already mentioned dominance of Alphaproteobacteria and Bacteroidetes orders (in all samples), we also observed high abundance peaks for the groups Candidate division OD1 (Mb-NB09) and Firmicutes (Bacillales) (both with a positive correlation with Aph. gracile, r = 0.72 and 0.67, respectively, p < 0.05). Bacillus strains (Bacillales, Firmicutes) have been shown to lyse cells from Aphanizomenon flos-aquae [61] and Anabaena flos-aquae [116]. This could help explain the highest abundance recorded for Bacillales during the Aph. gracile bloom peak. Several Bacillus strains can also degrade microcystins [63]. The Candidate division OD1 has been found within Microcystis bloom samples [117]. Other bacteria such as Actinobacteria (C111, Acidimicrobiales) had negative correlations with the bloom-forming cyanobacterial abundances, namely Synechococcus sp. (r = −0.63, p < 0.05). Members of Acidiomicrobiales, namely C111, have also been observed during bloom events dominated by Microcystis spp. [118]. Although negative correlations between Gammaproteobacteria (Xanthomonadales) and the cyanobacterial bloom-forming OTUs were not statistically significant, references report Xanthomonadales to be associated with blooms of Microcystis spp. [100] but also with blooms of Planktothrix spp. or co-dominated by strains of Microcystis, Dolichospermum, Cylindrospermopsis and Synechococcus [119]. Moreover, Gammaproteobacteria comprise many pathogens, and can potentially increase health risks during cyanobacterial blooms [120,121,122].
5. Conclusions
This study provides new insights into bacterial succession during a cyanobacterial bloom co-dominated by Aphanizomenon gracile and Sphaerospermopsis aphanizomenoides, but also Synechococcus sp. at a later phase. The dominance of Aph. gracile was correlated with high water temperatures, and S. aphanizomenoides with high conductivity levels. The bloom occurred during NO3− and SRP concentrations below detection levels, highlighting the ability of these diazotrophic species to bloom under low-nutrient conditions. A clear shift in BCC coincided with the establishment of the cyanobacterial bloom, suggesting an impact on the bacterioplankton succession dynamics. In fact, significant negative correlations were recorded between the bloom-forming cyanobacteria and some OTUs of Saprospirales and Sphingobacteriales (both Bacteroidetes), Rhizobiales (Alphaproteobacteria) and Burkholderiales (Betaproteobacteria). Nevertheless, bacterial groups such as Rickettsiales, Caulobacterales, Rhizobiales and Sphingomonadales (Alphaproteobacteria); Saprospirales, Flavobacteriales and Sphingobacteriales (Bacteroidetes); and Actinomycetales (Actinobacteria) remained dominant throughout the study period. Actually, these groups have been frequently associated with cyanobacterial blooms and some strains are capable of degrading cyanotoxins such as microcystins, highlighting the potential BCC influence on the dynamics and impacts of blooms. Nevertheless, only during the bloom event did we observe an increase in Mb-NB09 (Candidate division) and Bacillales (Firmicutes) members (both with a positive correlation with Aph. gracile); Acidimicrobiales (Actinobacteria), in addition to Xanthomonadales (Gammaproteobacteria).
There is still the need to go further in our understanding of HCBs’ dynamics by considering the occurrence patterns of species-specific cyanobacterial blooms and the whole BCC dynamics. The repeatability of patterns of the bacterioplankton dynamics is probable to occur during species-specific blooms, which makes it important to record every possible temporal and spatial dataset from waterbodies prone to HCBs. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) approaches can thus provide important species-specific bloom information for that purpose: (i) considering shifts in the overall community and (ii) avoiding the constraints of culture-dependent approaches and classical ambiguous microscopic identifications. In the near future, modelling, and ultimately management strategic plans, will rely on robust time-series data provided by such technological support.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.R.d.F.; methodology, A.R.M.P., M.J.P., A.R.L., D.R.d.F. and D.F.R.C.; software analysis, D.F.R.C.; validation, N.C.M.G.; investigation, D.R.d.F. and A.R.L.; funding acquisition, F.G. and B.B.C.; data curation, D.R.d.F., M.J.P. and D.F.R.C.; writing—original draft preparation, D.R.d.F.; writing—review and editing, D.R.d.F., D.F.R.C., N.C.M.G. and B.B.C.; visualization, D.R.d.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work had the financial support from CESAM (UID/AMB/50017/2019), FCT/MCTES and FEDER (PT2020 Partnership Agreement and Compete 2020). FCT (Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia) funded a post-doc grant SFRH/BPD/74184/2010 and a research contract for D.R.d.F. supported by national funds (OE), according to the DL 57/2016. A.R.M.P. was supported by a postdoctoral scholarship (SFRH/BPD/117563/2016) funded by the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology (FCT)/national funds (MCTES) and by the European Social Fund (ESF)/EU.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The DNA sequences generated in this study can be downloaded from the NCBI SRA: PRJNA905074.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- de Figueiredo, D.R.; Azeiteiro, U.M.; Esteves, S.M.; Gonçalves, F.J.M.; Pereira, M.J. Microcystin-producing blooms—A serious global public health issue. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2004, 59, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Otten, T.G. Harmful cyanobacterial blooms: Causes, consequences, and controls. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 65, 995–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbel, S.; Mougin, C.; Bouaïcha, N. Cyanobacterial toxins: Modes of actions, fate in aquatic and soil ecosystems, phytotoxicity and bioaccumulation in agricultural crops. Chemosphere 2014, 96, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring and Management, 2nd ed.; Chorus, I., Welker, M., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; ISBN 9788490225370. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilera, A.; Gómez, E.B.; Kaštovský, J.; Echenique, R.O.; Salerno, G.L. The polyphasic analysis of two native Raphidiopsis isolates supports the unification of the Genera raphidiopsis and Cylindrospermopsis (Nostocales, cyanobacteria). Phycologia 2018, 57, 130–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapomělová, E.; Jezberová, J.; Hrouzek, P.; Hisem, D.; Řeháková, K.; Komárková, J.; Zapomelová, E.; Jezberová, J.; Hrouzek, P.; Hisem, D.; et al. Polyphasic characterization of three strains of Anabaena reniformis and Aphanizomenon aphanizomenoides (Cyanobacteria) and their reclassification to Sphaerospermum gen. nov. (incl. Anabaena kisseleviana). J. Phycol. 2009, 45, 1363–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zapomělová, E.; Skácelová, O.; Pumann, P.; Kopp, R.; Janeček, E. Polyphasic characterization of three strains of Anabaena reniformis and Aphanizomenon aphanizomenoides (cyanobacteria) and their reclassification to Sphaerospermum gen. nov. (incl. Anabaena kisseleviana) (45:1363-73). J. Phycol. 2010, 46, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapomělová, E.; Hrouzek, P.; Řezanka, T.; Jezberová, J.; Řeháková, K.; Hisem, D.; Komárková, J. Polyphasic characterization of Dolichospermum spp. and Sphaerospermopsis spp. (Nostocales, cyanobacteria): Morphology, 16S rRNA gene sequences and fatty acid and secondary metabolite profiles. J. Phycol. 2011, 47, 1152–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaniemi, P.; Komárek, J.; Willame, R.; Hrouzek, P.; Kaštovská, K.; Hoffmann, L.; Sivonen, K. Taxonomic consequences from the combined molecular and phenotype evaluation of selected Anabaena and Aphanizomenon strains. Algol. Stud./Arch. Hydrobiol. 2005, 117, 371–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Park, H.K.; Kim, I.S. Invasion and toxin production by exotic nostocalean cyanobacteria (Cuspidothrix, Cylindrospermopsis, and Sphaerospermopsis) in the Nakdong river, Korea. Harmful Algae 2020, 100, 101954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, J.T.; Leão, P.N.; Vasconcelos, V.M. Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii: Review of the distribution, phylogeography, and ecophysiology of a global invasive species. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokociński, M.; Gagala, I.; Jasser, I.; Karosiene, J.; Kasperovičiene, J.; Kobos, J.; Koreiviene, J.; Soininen, J.; Szczurowska, A.; Woszczyk, M.; et al. Distribution of invasive Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in the east-central Europe is driven by climatic and local environmental variables. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93, fix035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stüken, A.; Rücker, J.; Endrulat, T.; Preussel, K.; Hemm, M.; Nixdorf, B.; Karsten, U.; Wiedner, C. Distribution of three alien cyanobacterial species (Nostocales) in northeast Germany: Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii, Anabaena bergii and Aphanizomenon aphanizomenoides. Phycologia 2006, 45, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaštovský, J.; Hauer, T.; Mareš, J.; Krautová, M.; Bešta, T.; Komárek, J.; Desortová, B.; Heteša, J.; Hindáková, A.; Houk, V.; et al. A review of the alien and expansive species of freshwater cyanobacteria and algae in the Czech Republic. Biol. Invasions 2010, 12, 3599–3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valério, E.; Pereira, P.; Saker, M.L.; Franca, S.; Tenreiro, R. Molecular characterization of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii strains isolated from portuguese freshwaters. Harmful Algae 2005, 4, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saker, M.L.; Nogueira, I.C.G.; Vasconcelos, V.M.; Neilan, B.A.; Eaglesham, G.K.; Pereira, P. First report and toxicological assessment of the cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii from portuguese freshwaters. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2003, 55, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saker, M.L.; Nogueira, I.C.G.; Vasconcelos, V.M. Distribution and toxicity of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (cyanobacteria) in portuguese freshwaters. Limnetica 2003, 22, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, C.; Martins, A.; Azevedo, J.; Freitas, M.; Regueiras, A.; Vale, M.; Antunes, A.; Vasconcelos, V. Application of real-time PCR in the assessment of the toxic cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii abundance and toxicological potential. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 92, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Figueiredo, D.R.; Gonçalves, A.M.M.; Castro, B.B.; Gonçalves, F.; Pereira, M.J.; Correia, A. Differential inter-and intra-specific responses of Aphanizomenon strains to nutrient limitation and algal growth inhibition. J. Plankton Res. 2011, 33, 1606–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, P.; Dias, E.; Franca, S.; Pereira, E.; Carolino, M.; Vasconcelos, V. Accumulation and depuration of cyanobacterial paralytic shellfish toxins by the freshwater mussel Anodonta cygnea. Aquat. Toxicol. 2004, 68, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, T.K.; Costa, L.D.F.; Yunes, J.S.; Resgalla, C.; Barufi, J.B.; Bastos, E.d.O.; Horta, P.A.; Rörig, L.R. Saxitoxins from the freshwater cyanobacterium Raphidiopsis raciborskii can contaminate marine mussels. Harmful Algae 2021, 103, 102004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawong, W.; Pongcharoen, P.; Nishimura, T.; Adachi, M. Molecular characterizations of thai Raphidiopsis raciborskii (Nostocales, cyanobacteria) based on 16s rDNA, rbcLX, and cylindrospermopsin synthetase genes. Plankton Benthos Res. 2019, 14, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirés, S.; Wörmer, L.; Ballot, A.; Agha, R.; Wiedner, C.; Velázquez, D.; Casero, M.C.; Quesada, A. Phylogeography of cylindrospermopsin and paralytic shellfish toxin-producing Nostocales cyanobacteria from mediterranean Europe (Spain). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 1359–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, S.A.; Rasmussen, J.P.; Holland, P.T.; Campbell, R.; Crowe, A.L.M. First report of the cyanotoxin anatoxin-a from Aphanizomenon issatschenkoi (cyanobacteria). J. Phycol. 2007, 43, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Qin, B.; Paerl, H.W.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, J.; Chen, Y. Earlier and warmer springs increase cyanobacterial (Microcystis spp.) blooms in subtropical lake Taihu, China. Freshw. Biol. 2014, 59, 1076–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Figueiredo, D.R.; Reboleira, A.S.S.P.; Antunes, S.C.; Abrantes, N.; Azeiteiro, U.; Gonçalves, F.; Pereira, M.J.; Gonçalves, F.; Figueiredo, D.R. The effect of environmental parameters and cyanobacterial blooms on phytoplankton dynamics of a portuguese temperate lake. Hydrobiologia 2006, 568, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Ma, J.; Wang, X.; Tan, Q. Rising atmospheric CO2 levels result in an earlier cyanobacterial bloom-maintenance phase with higher algal biomass. Water. Res. 2020, 185, 116267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderley, R.F.; Ger, K.A.; Becker, V.; Bezerra, M.G.T.A.; Panosso, R. Abiotic factors driving cyanobacterial biomass and composition under perennial bloom conditions in tropical latitudes. Hydrobiologia 2021, 848, 943–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Deng, J.; Shi, K.; Wang, J.; Brookes, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Paerl, H.W.; Wu, L. Extreme climate anomalies enhancing cyanobacterial blooms in eutrophic lake Taihu, China. Water. Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2020WR029371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, N.M.; Haig, H.A.; Simpson, G.L.; Leavitt, P.R. Effects of lake warming on the seasonal risk of toxic cyanobacteria exposure. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2020, 5, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Otten, T.G. Duelling “CyanoHABs”: Unravelling the environmental drivers controlling dominance and succession among diazotrophic and non-N2-fixing harmful cyanobacteria. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neil, J.M.; Davis, T.W.; Burford, M.A.; Gobler, C.J. The rise of harmful cyanobacteria blooms: The potential roles of eutrophication and climate change. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 313–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanvir, R.U.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, J. Cyanobacterial community succession and associated cyanotoxin production in hypereutrophic and eutrophic freshwaters. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 290, 118056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chorus, I.; Fastner, J.; Welker, M. Cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins in a changing environment: Concepts, controversies, challenges. Water 2021, 13, 2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvanese, E.F.; Padial, A.A.; Aubriot, L. Acclimation at high temperatures increases the ability of Raphidiopsis raciborskii (cyanobacteria) to withstand phosphate deficiency and reveals distinct strain responses. Eur. J. Phycol. 2019, 54, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapomělová, E.; Řeháková, K.; Jezberová, J.; Komárková, J. Polyphasic characterization of eight planktonic Anabaena strains (cyanobacteria) with reference to the variability of 61 Anabaena populations observed in the field. Hydrobiologia 2010, 639, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burford, M.A.; Davis, T.W.; Orr, P.T.; Sinha, R.; Willis, A.; Neilan, B.A. Nutrient-related changes in the toxicity of field blooms of the cyanobacterium, Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 89, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, L.; Lei, M.; Cheng, N.; Chen, Z.; Xiao, L.; Han, B.P.; Lin, Q. Nutrient regulation of relative dominance of cylindrospermopsin-producing and non-cylindrospermopsin-producing Raphidiopsis raciborskii. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 793544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirés, S.; Ballot, A. A review of the phylogeny, ecology and toxin production of bloom-forming Aphanizomenon spp. and related species within the Nostocales (cyanobacteria). Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 21–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindák, F. Morphological variation of four planktic nostocalean cyanophytes—Members of the genus Aphanizomenon or Anabaena? Hydrobiologia 2000, 438, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Carmichael, W.W.; Liu, Y.; Watanabe, M.M. Taxonomic re-evaluation of Aphanizomenon flos-aquae NH-5 based on morphology and 16S rRNA gene sequences. Hydrobiologia 2000, 438, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komárek, J.; Zapomelová, E. Planktic morphospecies of the cyanobacterial genus Anabaena = subg. Dolichospermum—2. Part: Straight types. Fottea 2008, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komárek, J. Modern taxonomic revision of planktic nostocacean cyanobacteria: A short review of genera. Hydrobiologia 2010, 639, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komárek, J. A Polyphasic approach for the taxonomy of cyanobacteria: Principles and applications. Eur. J. Phycol. 2016, 51, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komárek, J. Cyanobacterial taxonomy: Current problems and prospects for the integration of traditional and molecular approaches. Algae 2006, 21, 349–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, C.; Fathalli, A.; Vasconcelos, V.; Antunes, A. Genetic diversity and structure of the invasive toxic cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Curr. Microbiol. 2011, 62, 1590–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haande, S.; Rohrlack, T.; Ballot, A.; Røberg, K.; Skulberg, R.; Beck, M.; Wiedner, C. Genetic characterisation of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Nostocales, cyanobacteria) isolates from Africa and Europe. Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 692–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugger, M.; Molica, R.; Le Berre, B.; Dufour, P.; Bernard, C.; Humbert, J.-F. Genetic diversity of Cylindrospermopsis strains (cyanobacteria) isolated from four continents. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 1097–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zapomělová, E.; Skácelová, O.; Pumann, P.; Kopp, R.; Janeček, E. Biogeographically interesting planktonic Nostocales (cyanobacteria) in the Czech Republic and their polyphasic evaluation resulting in taxonomic revisions of Anabaena bergii Ostenfeld 1908 (Chrysosporum gen. nov.) and A. tenericaulis Nygaard 1949 (Dolichospermum tenericaule comb. nova). Hydrobiologia 2012, 698, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiler, A.; Drakare, S.; Bertilsson, S.; Pernthaler, J.; Peura, S.; Rofner, C.; Simek, K.; Yang, Y.; Znachor, P.; Lindström, E.S. Unveiling distribution patterns of freshwater phytoplankton by a next generation sequencing based approach. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steven, B.; McCann, S.; Ward, N.L. Pyrosequencing of plastid 23S rRNA genes reveals diverse and dynamic cyanobacterial and algal populations in two eutrophic lakes. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 82, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, M.M.; Li, Z.; Effler, T.C.; Hauser, L.J.; Boyer, G.L.; Wilhelm, S.W. Comparative Metagenomics of Toxic Freshwater Cyanobacteria Bloom Communities on Two Continents. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hur, M.; Lee, I.; Tak, B.-M.; Lee, H.J.; Yu, J.J.; Cheon, S.U.; Kim, B.-S. Temporal Shifts in Cyanobacterial Communities at Different Sites on the Nakdong River in Korea. Water Res. 2013, 47, 6973–6982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelm, S.W.; Farnsley, S.E.; LeCleir, G.R.; Layton, A.C.; Satchwell, M.F.; DeBruyn, J.M.; Boyer, G.L.; Zhu, G.; Paerl, H.W. The Relationships between Nutrients, Cyanobacterial Toxins and the Microbial Community in Taihu (Lake Tai), China. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casero, M.C.; Velázquez, D.; Medina-Cobo, M.; Quesada, A.; Cirés, S. Unmasking the Identity of Toxigenic Cyanobacteria Driving a Multi-Toxin Bloom by High-Throughput Sequencing of Cyanotoxins Genes and 16S RRNA Metabarcoding. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 665, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, P.B.; Patel, B.K.C. Metagenomic Analysis of a Freshwater Toxic Cyanobacteria Bloom. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2008, 64, 9–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, T.; Wang, Q.; Li, L.; Shen, T.; Gao, G. Bacterial Community Composition in Aquatic and Sediment Samples with Spatiotemporal Dynamics in Large, Shallow, Eutrophic Lake Chaohu, China. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2019, 34, 575–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yang, J.; Lv, H.; Yu, Z. Synchronous Dynamics and Correlations between Bacteria and Phytoplankton in a Subtropical Drinking Water Reservoir. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 90, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomon, P.S.; Janson, S.; Granéli, E. Molecular Identification of Bacteria Associated with Filaments of Nodularia spumigena and Their Effect on the Cyanobacterial Growth. Harmful Algae 2003, 2, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, K.A.; Lyra, C.; Sivonen, K.; Paulin, L.; Suomalainen, S.; Tuomi, P.; Rapala, J. High Diversity of Cultivable Heterotrophic Bacteria in Association with Cyanobacterial Water Blooms. ISME J. 2008, 3, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shunyu, S.; Yongding, L.; Yinwu, S.; Genbao, L.; Dunhai, L. Lysis of Aphanizomenon flos-aquae (Cyanobacterium) by a Bacterium Bacillus cereus. Biol. Control 2006, 39, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, K.; Maseda, H.; Okano, K.; Itayama, T.; Kawauchi, Y.; Chen, R.; Utsumi, M.; Zhang, Z.; Sugiura, N. How Microcystin-Degrading Bacteria Express Microcystin Degradation Activity. Lakes Reserv. 2011, 16, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kormas, K.A.; Lymperopoulou, D.S. Cyanobacterial Toxin Degrading Bacteria: Who Are They? BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 463894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 19th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- de Figueiredo, D.R.; Pereira, M.J.; Correia, A.; de Figueiredo, D.R. Seasonal Modulation of Bacterioplankton Community at a Temperate Eutrophic Shallow Lake. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 26, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qian, P.-Y. Conservative Fragments in Bacterial 16S RRNA Genes and Primer Design for 16S Ribosomal DNA Amplicons in Metagenomic Studies. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleary, D.F.R.; Becking, L.E.; de Voogd, N.J.; Pires, A.C.C.; Polónia, A.R.M.; Egas, C.; Gomes, N.C.M. Habitat- and Host-Related Variation in Sponge Bacterial Symbiont Communities in Indonesian Waters. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 85, 465–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. Past: Paleontological Statistics Software Package for Education and. Data Analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 4. [Google Scholar]
- ter Braak, C.J.F. Canonical Correspondence Analysis: A New Eigenvector Technique for Multivariate Direct Gradient Analysis. Ecology 1986, 67, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Figueiredo, D.R.; Alves, A.; Pereira, M.J.; Correia, A. Molecular Characterization of Bloom-Forming Aphanizomenon Strains Isolated from Vela Lake (Western Central Portugal). J. Plankton Res. 2010, 32, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, V.M. Toxic Cyanobacteria (Blue-Green Algae) in Portuguese Fresh Waters. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1994, 130, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, V.M.; Sivonen, K.; Evans, W.R.; Carmichael, W.W.; Namikoshi, M. Hepatotoxic Microcystin Diversity in Cyanobacterial Blooms Collected in Portuguese Freshwaters. Water Res. 1996, 30, 2377–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, C.; Gomes, C.; Vasconcelos, V.; Antunes, A. Cyanotoxins Occurrence in Portugal: A New Report on Their Recent Multiplication. Toxins 2020, 12, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, A.R.; Azeiteiro, U.M.; Bessa, V.S.; Pereira, C.; Salvador, S.; Almeida, A.; Cunha, M.A.; Pereira, M.J. Spring Pelagic Communities of Phytoplankton, Cyanobacteria, Associated Heterotrophic Bacteria and Viruses in an Eutrophic Shallow Temperate Lake. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2009, 18, 875–884. [Google Scholar]
- Vasconcelos, V.M.; Campos, T.; Amorim, A.; Soares, A.M.V.M. Toxicidade de Estirpes de Cianobactérias Isoladas a partir das Lagoas das Braças, Vela e Mira. Bol. UCA Univ. Algarve UCTRA 1993, 1, 193–201. [Google Scholar]
- de Figueiredo, D.R.; Pereira, M.J.; Moura, A.; Silva, L.; Bárrios, S.; Fonseca, F.; Henriques, I.; Correia, A. Bacterial Community Composition over a Dry Winter in Meso- and Eutrophic Portuguese Water Bodies. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2007, 59, 638–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Figueiredo, D.R.; Pereira, M.J.; Castro, B.B.; Correia, A. Bacterioplankton Community Composition in Portuguese Water Bodies under a Severe Summer Drought. Community Ecol. 2012, 13, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, P.; Silveira, S.; Ribeiro, R.; Gonçalves, F.; Vasconcelos, V.; Soares, A.M.V.M. Estrutura Populacional Fitoplanctónica nas Lagoas das Braças, Vela e Mira (Região Centro-Litoral). Resultados Preliminares. Bol. UCA Univ. Algarve UCTRA 1993, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Macário, I.P.E.; Castro, B.B.; Nunes, I.M.S.; Pizarro, C.; Coelho, C.; Gonçalves, F.; de Figueiredo, D.R. Stepwise Strategy for Monitoring Toxic Cyanobacterial Blooms in Lentic Water Bodies. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, C.; Mendes, R.; Azevedo, J.; Vasconcelos, V.; Antunes, A. First Occurrence of Cylindrospermopsin in Portugal: A Contribution to Its Continuous Global Dispersal. Toxicon 2017, 130, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, C.; Adrian, R. Cyanobacteria Dominance: Quantifying the Effects of Climate Change. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 2460–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokulil, M.T.; Teubner, K. Cyanobacterial Dominance in Lakes. Hydrobiologia 2000, 438, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burford, M.A.; Davis, T.W. Physical and Chemical Processes Promoting Dominance of the Toxic Cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2011, 29, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taton, A.; Grubisic, S.; Brambilla, E.; De Wit, R.; Wilmotte, A. Cyanobacterial Diversity in Natural and Artificial Microbial Mats of Lake Fryxell (McMurdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica): A Morphological and Molecular Approach. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 5157–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allgaier, M.; Grossart, H.P. Seasonal Dynamics and Phylogenetic Diversity of Free-Living and Particle-Associated Bacterial Communities in Four Lakes in Northeastern Germany. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2006, 45, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Shen, H.; Chen, J.; Xie, P.; Yang, X.; Tao, M.; Ma, Z.; Qi, M. Phytoplankton Community Succession Shaping Bacterioplankton Community Composition in Lake Taihu, China. Water Res. 2011, 45, 4169–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, A.; Wu, J.; Xiao, J.; Sun, Y.; Cheng, C.; Zaichao, Z.; Aizhong, D.; Jiayan, W.; et al. Bar-Coded Pyrosequencing Reveals the Bacterial Community during Microcystis Water Bloom in Guanting Reservoir, Beijing. Procedia Eng. 2011, 18, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Salcher, M.M.; Pernthaler, J.; Posch, T. Seasonal Bloom Dynamics and Ecophysiology of the Freshwater Sister Clade of SAR11 Bacteria “that Rule the Waves” (LD12). ISME J. 2011, 5, 1242–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiler, A.; Bertilsson, S. Composition of Freshwater Bacterial Communities Associated with Cyanobacterial Blooms in Four Swedish Lakes. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 6, 1228–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Razzano, M.; Mou, X. Cyanobacterial Blooms Alter the Relative Importance of Neutral and Selective Processes in Assembling Freshwater Bacterioplankton Community. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 135724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, T.; Park, H.-D.; Ozawa, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Sumino, T.; Hamana, K.; Hiraishi, A.; Kato, K. Sphingosinicella microcystinivorans gen. nov., sp. nov., a microcystin-degrading bacterium. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 92. Amé, V.; Echenique, R.; Pflugmacher, S.; Wunderlin, A. Degradation of Microcystin-RR by Sphingomonas sp. CBA4 Isolated from San Roque Reservoir (Córdoba—Argentina). Biodegradation 2006, 17, 447–455. [Google Scholar]
- Dziallas, C.; Grossart, H. Temperature and Biotic Factors Influence Bacterial Communities Associated with the Cyanobacterium Microcystis sp. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1632–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mou, X.; Lu, X.; Jacob, J.; Sun, S.; Heath, R. Metagenomic Identification of Bacterioplankton Taxa and Pathways Involved in Microcystin Degradation in Lake Erie. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabour, B.; Loudiki, M.; Oudra, B.; Vasconcelos, V.; Oubraim, S.; Fawzi, B. Dynamics and Toxicity of Anabaena aphanizomenoides (Cyanobacteria) Waterblooms in the Shallow Brackish Oued Mellah Lake (Morocco). Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2005, 8, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, P.I.; Millard, A.D.; Miller, A.; Schoen, R.; Raeder, U.; Geist, J.; Zwirglmaier, K. Temporal Dynamics of the Microbial Community Composition with a Focus on Toxic Cyanobacteria and Toxin Presence during Harmful Algal Blooms in Two South German Lakes. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, I.A.; Rachid, C.T.C.C.; Rangel, L.M.; Silva, L.H.S.; Bisch, P.M.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O.; Pacheco, A.B.F. Close Link between Harmful Cyanobacterial Dominance and Associated Bacterioplankton in a Tropical Eutrophic Reservoir. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tromas, N.; Fortin, N.; Bedrani, L.; Terrat, Y.; Cardoso, P.; Bird, D.; Greer, C.W.; Shapiro, B.J. Characterising and Predicting Cyanobacterial Blooms in an 8-Year Amplicon Sequencing Time Course. ISME J. 2017, 11, 1746–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, P.; Laurion, I.; Lovejoy, C. Distribution and Identity of Bacteria in Subarctic Permafrost Thaw Ponds. Aquat. Microbial. Ecol. 2013, 69, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Xiao, L.; Ren, J.; Yang, L. The Effect of a Microcystis aeruginosa Bloom on the Bacterioplankton Community Composition of Lake Xuanwa. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2008, 23, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zheng, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xie, R.; Lang, A.S.; Liu, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhang, X.; Sun, J.; Suttle, C.A.; Jiao, N. Dynamics of Heterotrophic Bacterial Assemblages within Synechococcus Cultures. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e01517-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohit, V.; Archambault, P.; Toupoint, N.; Lovejoy, C. Phylogenetic Differences in Attached and Free-Living Bacterial Communities in a Temperate Coastal Lagoon during Summer, Revealed via High-Throughput 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 2071–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, S.; Richl, P.; Ernst, A. Seasonal and Habitat-Related Distribution Pattern of Synechococcus Genotypes in Lake Constance. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2007, 62, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, M.; Xie, P.; Chen, J.; Qin, B.; Zhang, D.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Q.; Wu, L. Use of a Generalized Additive Model to Investigate Key Abiotic Factors Affecting Microcystin Cellular Quotas in Heavy Bloom Areas of Lake Taihu. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadimitriou, T.; Katsiapi, M.; Kormas, K.A.; Moustaka-Gouni, M.; Kagalou, I. Artificially-Born “Killer” Lake: Phytoplankton Based Water Quality and Microcystin Affected Fish in a Reconstructed Lake. Sci. Total. Environ. 2013, 452–453, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, W.; Li, R. Cyanobacteria Toxins in the Salton Sea. Saline Syst. 2006, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballot, A.; Fastner, J.; Wiedner, C. Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning Toxin-Producing Cyanobacterium Aphanizomenon gracile in Northeast Germany. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 1173–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballot, A.; Sandvik, M.; Rundberget, T.; Botha, C.J.; Miles, C.O. Diversity of Cyanobacteria and Cyanotoxins in Hartbeespoort Dam, South Africa. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2014, 65, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledreux, A.; Thomazeau, S.; Catherine, A.; Duval, C.; Yéprémian, C.; Marie, A.; Bernard, C. Evidence for Saxitoxins Production by the Cyanobacterium Aphanizomenon gracile in a French Recreational Water Body. Harmful Algae 2010, 10, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karosienė, J.; Savadova-Ratkus, K.; Toruńska-Sitarz, A.; Koreivienė, J.; Kasperovičienė, J.; Vitonytė, I.; Błaszczyk, A.; Mazur-Marzec, H. First Report of Saxitoxins and Anatoxin-a Production by Cyanobacteria from Lithuanian Lakes. Eur. J. Phycol. 2020, 55, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokociński, M.; Mankiewicz-Boczek, J.; Jurczak, T.; Spoof, L.; Meriluoto, J.; Rejmonczyk, E.; Hautala, H.; Vehniäinen, M.; Pawełczyk, J.; Soininen, J. Aphanizomenon gracile (Nostocales), a Cylindrospermopsin-Producing Cyanobacterium in Polish Lakes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 5243–5264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savadova-Ratkus, K.; Mazur-Marzec, H.; Jūratė, K.; Jūratė, K.; Paškauskas, R.; Vitonyte, I.; Koreiviene, J. Interplay of Nutrients, Temperature, and Competition of Native and Alien Cyanobacteria Species Growth and Cyanotoxin Production in Temperate Lakes. Toxins 2021, 13, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabour, B.; Loudiki, M.; Vasconcelos, V. Growth Responses of Microcystis ichthyoblabe Kützing and Anabaena aphanizomenoides Forti (Cyanobacteria) under Different Nitrogen and Phosphorus Conditions. Chem. Ecol. 2009, 25, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komárek, J.; Komárková, J. Diversity of Aphanizomenon-like Cyanobacteria. Fottea 2006, 6, 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Komárek, J.; Mareš, J. An Update to Modern Taxonomy (2011) of Freshwater Planktic Heterocytous Cyanobacteria. Hydrobiologia 2012, 698, 327–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Pan, W.; Ma, C. Stimulation and Inhibition Effects of Algae-Lytic Products from Bacillus cereus Strain L7 on Anabaena flos-aquae. J. Appl. Phycol. 2011, 24, 1015–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Jiang, H.; Krumholz, L.R.; Yang, Z. Bacterial Community Composition of Size-Fractioned Aggregates within the Phycosphere of Cyanobacterial Blooms in a Eutrophic Freshwater Lake. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerji, A.; Bagley, M.J.; Shoemaker, J.A.; Tettenhorst, D.R.; Nietch, C.T.; Allen, H.J.; Santo Domingo, J.W. Evaluating Putative Ecological Drivers of Microcystin Spatiotemporal Dynamics Using Metabarcoding and Environmental Data. Harmful Algae 2019, 86, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Cai, Y.; Kong, F.; Yu, Y. Specific Association between Bacteria and Buoyant Microcystis Colonies Compared with Other Bulk Bacterial Communities in the Eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2012, 4, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, K.A.; Lyra, C.; Niemi, R.M.; Heens, B.; Hoppu, K.; Erkomaa, K.; Sivonen, K.; Rapala, J. Virulence Genes of Aeromonas Isolates, Bacterial Endotoxins and Cyanobacterial Toxins from Recreational Water Samples Associated with Human Health Symptoms. J. Water Health 2011, 9, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Cai, Y.; Kong, F.; Yu, Y. Changes in Abundance and Community Structure of Bacteria Associated with Buoyant Microcystis Colonies during the Decline of Cyanobacterial Bloom (Autumn–Winter Transition). Ann. Limnol.—Int. J. Limnol. 2011, 47, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Parveen, B.; Ravet, V.; Djediat, C.; Mary, I.; Quiblier, C.; Debroas, D.; Humbert, J. Bacterial Communities Associated with Microcystis Colonies Differ from Free-Living Communities Living in the Same Ecosystem. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2013, 5, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).