Abstract
On the quest of discovering novel local strains of microalgal species that can be effectively cultured with industrial perspectives, two cyanobacterial strains Anabaena sp. and Cyanothece sp. were isolated from the lagoonal and saltworks waters of the Messolonghi lagoon (W. Greece). They were batch cultured at 20–21.5 °C in six combinations of three salinities (20, 40 and 60 ppt) and two light intensities (2000 and 8000 lux) resulting in: (a) Anabaena grew best at 20 and 40 ppt at high light of 8000 lux. (b) Cyanothece grew best at 40 and 60 ppt at high light. (c) Low light of 2000 lux resulted in much reduced growth in all treatments. (d) Maximal biomass yield was 1.27 and 1.77 g d.w./L for Anabaena and Cyanothece, respectively. Overall, both species have culture potential yielding biomass comparable to the average (or above) relevant values reported in the literature for various cultured cyanobacteria.
1. Introduction
Microalgae are sources of various products (e.g., aquaculture feedstuff, biofuels, healthy food pills, antioxidants, pharmaceuticals, etc.) for various uses in our modern world [1,2] and the quest for novel species suitable for culture and with characteristics that facilitate the implementation of cost-effective culture techniques is always welcomed. Nowadays, problems of tackling increasing fossil fuel emissions, struggle for fresh water in an expanding human population, finding cheap energy alternatives to fossil fuel sources, creating sea farms as a relief to crop land and replacing meat with plant-like equivalent organisms, all lead to algae and their culture.
Among microalgae, cyanobacteria occupy a prominent part of interest for mass cultivation and among them Spirulina (Arthrospira) species were the starting point for exploitation [3]. Besides Spirulina, many other cyanobacterial species, filamentous or coccoid, have been the target of research, expanding the spectrum of cyanobacteria with the capability to grow fast and massively in various environmental conditions [1,4].
To be commercially exploitable a candidate species must be easily cultured. There is practically little benefit in the quest for valuable substances (e.g., lipids, pigments, proteins) if the species under investigation is cumbersome in mass production because of small yield or need for difficultly attainable or costly conditions (e.g., high temperature) for an adequate outcome. Considering temperature, it is well known that temperatures of 25–30 °C can boost the growth rate of algae [5,6] but this range is rather costly to maintain in temperate regions during the colder months. In this respect, we experimented at around 20 °C which we consider an economically feasible indoors temperature during the cold months. We also left pH uncontrolled because its fine tuning is difficult and practically of no decisive importance, the culture will create its own pH.
Light is the most essential and critical factor because it directly affects the photosynthesis from which biosynthesis of biomass ensues [2]. Low illumination has a limiting effect on the growth of microalgae, so, increasing the light intensity in mass cultivation of algae is a common practice to enhance growth but care should be taken as too much of it can cause photoinhibition [7,8].
Salinity affects the growth of microalgae acting directly on the osmoregulatory mechanism of the cell. Cyanobacteria can endure several ranges of salinity but the existing information in the literature is rather complicated on conclusions about both the range of tolerance and the optimum value. There are studies suggesting that the elevated salinities negatively affect the growth of microalgae acting directly on their photosynthetic apparatus [9,10,11].
In the present work, the filamentous diazotroph Anabaena sp. and the coccoid diazotroph Cyanothece sp., two local strains isolated from lagoonal and hypersaline waters, respectively, were cultured on the assumption that these species that originated from lagoons (and of course hypersaline ponds) with the harshest water environments might tolerate intense seasonal fluctuations in salinity, light, temperature, and nutrient input. Therefore, it is logical to assume that species encountered there are sturdy because of their adaptability to such constantly changing water bodies. Furthermore, these local strains can enrich the collections of algae preserved worldwide in order to create an expanding deposit of strains of sibling or novel species. In this respect, the objective of this study is to examine the response of these local strains of cyanobacteria to salinity and light intensity to gain an initial basic understanding of the effect of these two key parameters on their pace of culture growth and maximization of biomass yield.
2. Materials and Methods
The two N-fixing cyanobacterial strains Anabaena sp. and Cyanothece sp. (Figure 1 A,B, respectively) originated from a screening survey of the adjacent saline waters of Messolonghi lagoon (38°20′05.16″ N, 21°25′28.51″ E) and the hypersaline ponds of Messolonghi saltworks (38°23′37.61″ N, 21°24′29.68″ E), respectively, in W. Greece. Water samples from these areas were continuously cultured and renovated in the laboratory and finally through continuous serial dilutions the monospecific cultures of both species were stabilized and kept at a salinity of 40 ppt.
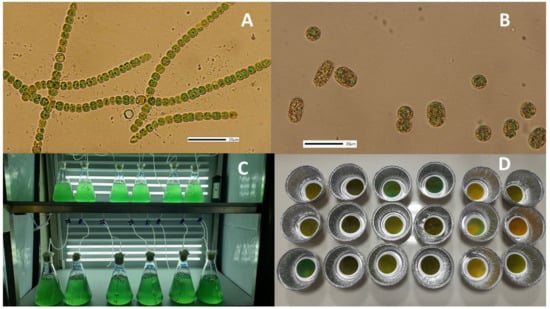
Figure 1.
Photos of the treated material. (A) Filaments of Anabaena sp. (B) Cells of Cyanothece sp. Scale bars in both photos are 20 μm. (C) Culture vessels of Anabaena on the 4th day. (D) Dried GF/C filters with dry material of Cyanothece masses during dry weight measurements.
Both cyanobacteria were batch-cultured using 2 L glass conical Erlenmeyer flasks in 2 replicates for each combination of salinity and light intensity (Figure 1C). Water of three salinities, 20, 40 and 60 ppt, and two light intensities of 2000 and 8000 lux from 20 watt 1600 lm LED lamps, measured at the middle of the outer surface of the vessel (Lux meter BIOBLOCK LX-101), were combined to create 6 treatments (3 salinities × 2 light intensities). Temperature was maintained at 20–21.5 °C by a 18,000 BTU air conditioner. A 16 hL:8 hD light duration was maintained by an electric timer controller. The water used to prepare the various salinities originated from the nearby seacoast. It was first autoclaved at 121 °C for 20 min in order to eliminate all organisms and then adjusted to 20 ppt by sterilized distilled water or to 60 ppt by the dilution of the proper quantity of sterilized artificial salt (Instant Ocean®, Blacksburg, Virginia, USA). After the filling of the culture vessels with the proper amount of sterilized water (1900 mL), 100 mL of stock mature culture (in exponential phase) of the respective species were added. Then, 1 mL/L of each of Walne’s final nutrient solutions of metals, micronutrients, and vitamins were finally added. In Figure 2, the whole procedure is depicted schematized as a flow chart.
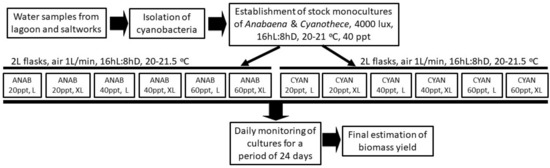
Figure 2.
Flow chart of the experimental procedure. ANAB: Anabaena; CYAN: Cyanothece; L: light 2000 lux; XL: light 8000 lux.
In all the vessels, the suspension of the cells and the supply of CO2 were accomplished using coarse air bubbling through 2 mL glass pipettes (one in every vessel with a supply of half culture volume/min) connected through sterilized plastic hoses to the 0.45 μm filtered central air supply system fed by a blower. The density of Anabaena’s culture vessel in g dry biomass/L was monitored daily by the recording of its optical density at 750 nm in a visible–UV spectrophotometer (Shimadzu UVmini-1240 UV-visible). To accomplish that, the values of optical density were transformed to g d.w./L using a calibration curve’s equation of optical density (OD) vs. g/L or cells/mL at 750 nm [12] that was constructed in advance using a dense culture of each cyanobacterium and subsequent serial dilutions before the start of experimentation (Figure 3A). The density of Cyanothece was daily calculated as cells/mL using a Fuchs–Rosenthal hematocytometer and a relevant calibration curve (Figure 3B). All measurements were conducted in triplicate. The specific growth rate (SGR as doublings day−1) was estimated during the early exponential (log) phase of the culture’s growth curve using the equation: SGR = (lnC2 − lnC1)/(t2 − t1) where C1 and C2 stand for g d.w./L or cells/mL at days t1 and t2, (t2 > t1), respectively. Next, the generation time Tg (in days) of the culture was calculated as days required for duplication using the formula: Tg = 0.6931/SGR. The calculation of the dry weight (in triplicate for each treatment) was made by filtering a known amount of culture through 0.45 μm GF/C filters (Figure 1D) in a vacuum pump (Heto-SUE-3Q), washing the filter with ammonium carbonate, and drying the filter in an oven at 100 °C for 2 h. Then, the filter was weighed to the fourth decimal and the dry weight was calculated as g/L after subtraction of the pre-weighted filter’s tare weight. The pH was measured daily using a digital pH-meter (HACH-HQ30d-flexi). Statistical treatment of the different variables was completed with ANOVA and pair-wise Tukey’s test for comparison of the means at a 0.05 level of significance using the free PAST3 software.
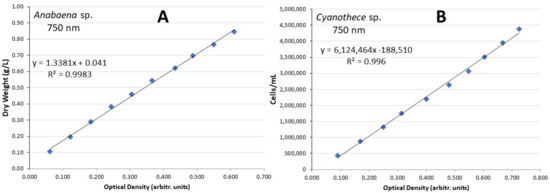
Figure 3.
Calibration lines with the relevant equations of (A) Anabaena sp. and (B) Cyanothece sp. of dry weight/L and cells/mL vs. optical density for Anabaena and Cyanothece, respectively.
3. Results
3.1. Anabaena sp.
The culture of Anabaena sp. lasted 24 days (Figure 4A–C) and presented the highest value of g dry weight/L at the salinity of 20 ppt on the 22nd day (Figure 4A). At all salinities the initial lag phase was very short and after the third day all cultures entered a long exponential phase that lasted until the 21st day. Thereafter, in all treatments the cultures entered the stationary phase. The daily records of g/L were accomplished by using the relevant calibration curve (Figure 3A) which presented an excellent fit. The specific growth rate (SGR) remained above 0.13 in all treatments, presenting its highest value (0.213) at the salinity of 40 ppt-XL and the lowest (0.131) at 60 ppt-XL (Figure 4D, Table 1).
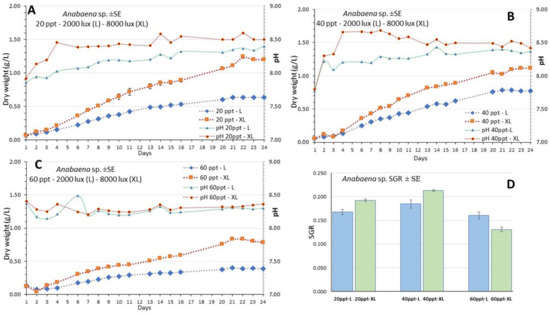
Figure 4.
The growth curve (g dry weight/L) of the culture of Anabaena sp. at the salinities of (A) 20 ppt, (B) 40 ppt and (C) 60 ppt and at each light intensity (L: 2000 lux; XL: 8000 lux). Also depicted are the pH daily values in each condition. Values are means of 3 measurements ± standard error (SE). In (D) there the values of Specific Growth Rate (SGR) ± SE are depicted for the time interval of the 4th to 9th day for each treatment.

Table 1.
Data (± SE) on specific growth rate (SGR) and generation of doubling time (Tg) of Anabaena and Cyanothece cultures at salinities of 20, 40, and 60 ppt and at each light intensity (L: 2000 lux; XL: 8000 lux). The different superscripts indicate a statistically significant difference at the 0.05 level of confidence (statistical processing with ANOVA and then pair-wise comparison with Tukey’s test). The second superscript indicates the statistically equal value of the condition of the corresponding letter.
At each salinity, there were considerably higher values each day at the high light intensity (XL-8000 lux) compared to its counterpart at low intensity (L-2000 lux). With time advancing, the gap between them increased and this was very prominent at the salinities of 20 and 60 ppt. At the cultures with salinities of 20 and 40 ppt, pH started from values slightly lower than 8.0 and then increased steadily to values exceeding 8.5 at high light remaining always higher than its counterparts of low light which remained under 8.5. Their gap was very prominent during the first 14 days and thereafter the gap narrowed. At the salinity of 60 ppt both light treatments had similar pH under 8.5 during the whole period.
Total biomass yield calculated on the 22nd day was much higher (p < 0.05) at 20 and 40 ppt salinities (1.27 and 0.97 g d.w./L at XL, respectively) compared to 60 ppt (0.78 g/L, XL). The same was observed also at low light (L) with ~0.6 g/L at 20 and 40 ppt compared to 0.37 g/L at 60 ppt (Figure 5A).
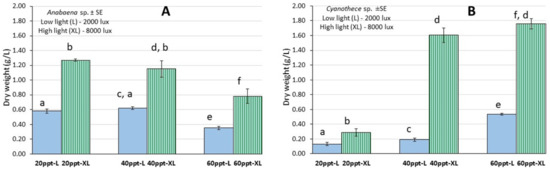
Figure 5.
Data on biomass yield (g d.w./L) of (A) Anabaena and (B) Cyanothece cultures at salinities of 20, 40 and 60 ppt and at each light intensity (L: 2000 lux; XL: 8000 lux). The different superscripts indicate a statistically significant difference at the 0.05 level of confidence (statistical processing with ANOVA and then pair-wise comparison with Tukey’s test). Where there is a second superscript it means statistically equal (p > 0.05) to the value of the condition of the corresponding letter.
3.2. Cyanothece sp.
The culture of Cyanothece sp. lasted 24 days (Figure 4) and presented the highest value of 7.5–8.0 × 106 cells/mL at the salinities of 40 and 60 ppt on the 20th day (Figure 6B,C, respectively). Contrary to these salinities, at the salinity of 20 ppt growth was much lower reaching 2.0 × 106 cells/mL (Figure 6A). At all salinities, the initial lag phase lasted 4 days and thereafter all cultures entered a long exponential phase that lasted until the 20th day. The daily records of cell density were accomplished by using the calibration curve (Figure 3B) which presented an excellent fit. The specific growth rate (SGR) was maximal at the salinities of 40 ppt-XL and 60 ppt XL (0.281 ± 0.003 and 0.260 ± 0.005, respectively) and minimal (0.041 ± 0.004—0.084 ±0.002) at the salinity of 20 ppt in both light regimes (Figure 6D, Table 1). At the higher salinities (40 and 60 ppt), there were considerably higher values each day at the high light intensity (XL-8000 lux) compared to their counterparts at low intensity (L-2000 lux). With time advancing, the gap between them increased enormously and this was very prominent at the salinities of 40 and 60 ppt. In the cultures with salinities of 20 and 40 ppt, pH started from values slightly lower than 8.0 and then increased steadily (with much fluctuation) to values between 8.0 and 8.5 at high light remaining always higher than its counterparts of low light. At the salinity of 60 ppt, both light treatments had similar values around 8.3 during the whole period. Total biomass yield calculated on the 20th day reached its highest values at 40 and 60 ppt salinities (1.60 and 1.77 g d.w./L at XL, respectively) compared (p < 0.05) to 20 ppt (0.30 g/L, XL). At all low light regimes, yield was much lower (p < 0.05) in all salinities (0.16 and 0.19 g/L at 20 and 40 ppt, respectively) but the treatment 60 ppt-L gave a considerably higher yield of 0.56 g/L (Figure 5B).
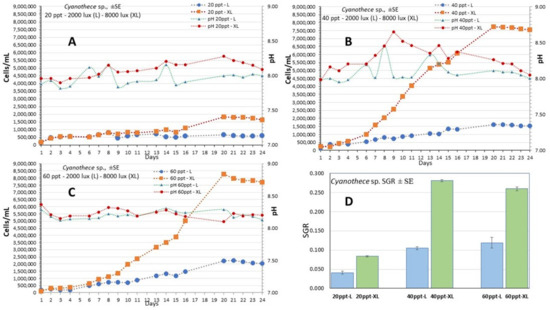
Figure 6.
The growth curve (cells/mL) of the culture of Cyanothece sp. at the salinities of (A) 20 ppt, (B) 40 ppt and (C) 60 ppt and at each light intensity (L: 2000 lux; XL: 8000 lux). Also depicted are the pH daily values in each condition. Values are means of 3 measurements ± standard error (SE). In (D) the values of Specific Growth Rate (SGR) ± SE are depicted for the time interval of the 4th to 11th day for each treatment.
4. Discussion
The success of any microalgal culture lays primarily on its fast growth which, as expressed by its growth rate, depends on various factors such as photoperiod, light intensity, nutrient composition, salinity, temperature, pH, etc. [13,14]. As the light intensity is a primary and critical factor for growth and nutrient metabolism [15,16,17,18], in order to determine its effect on growth of the local strains Anabaena sp. and Cyanothece sp. we used low (2000 lux) and high (8000 lux) intensities of illumination, continuing a similar previous exploration conducted on another local cyanobacterial strain, that of Phormidium sp. [19]. We also combined the above-mentioned illuminations with several salinities because on the one hand, these are marine species and on the other, future mass cultivation of cyanobacteria for various products is desirable to be conducted in seawater due to the preservation of limited freshwater resources which are destined for drinking and crop irrigation [20,21].
In the present study, the two species exhibited totally different response to the various salinities they were exposed to. Anabaena clearly grew more efficiently at the lower salinity of 20 ppt while Cyanothece at the higher of 40 and 60 ppt. These results reflect obviously the origin of the two species as Anabaena was isolated from the seawater salinity of the lagoon while Cyanothece from the hypersaline ponds of the saltworks [22]. It is true that cyanobacteria can adapt to the variations in salinities [23,24] and many marine species can tolerate lower salinities and optimum growth occurs at a specific range of salinity [25], but not all of them are halotolerant [26,27]. The filaments of Anabaena over the whole range of salinity used remained healthy and normal with no irregular aggregates as reported for the marine filamentous cyanobacterium Trichodesmium which grew best at 33–37 ppt but stopped growing and deformed at 18 ppt [28]. As pH in all treatments of both cyanobacterial cultures remained during the culture period between the acceptable (if not optimum) range of 8.0–8.5 [29,30], the different response of each species to the various salinities can probably be attributed to their inherent physiological capabilities to withstand increased Na+ on regulating respiration, ion flux, PS II electron flow, or nitrogenase activity as mentioned in several studies on cyanobacteria [31,32,33,34] and eukaryotic algae [9,10,11,35,36,37,38,39,40]. However, apart from the salinity alone, it seems that the above-mentioned physiological responses are also influenced by the intensity of light. In Anabaena, the influence of both light intensities exhibited a lesser degree of difference between low and high illumination on both growth rate (Figure 4, Table 1) and biomass yield (Figure 5A), compared to Cyanothece (Figure 6, Table 1 and Figure 5B), where the differences were much higher at all salinities.
The influence of light is catalytic, and we are faced with the need to adjust the light intensity to a compromising level between opposite directions. On the one hand, cyanobacteria grow faster in continuous high light intensities [19,41] and this was corroborated in the present study in both Anabaena with 1.26 g dw/L at high light of 8000 lux as compared to 0.60 g/L in low light of 2000 lux and Cyanothece with 1.75 and 0.55 g/L, respectively. On the other hand, cyanobacteria can grow effectively in low luminosity because they have a low energy requirement for maintenance and a unique flexible photo-capture apparatus that maximizes the spectrum of available low light [42,43]. In reality, it is very difficult to determine the exact optimum range of light intensity which gives the maximum of biomass yield for a particular species at a certain combination of other environmental conditions and exhausting experimentation is needed. What is useful (to start with) is to draw some generalized conclusions about the influence of extreme levels of light intensity and study the responses. In the present work, it was proven beyond any doubt that both cyanobacteria responded more efficiently at the higher level of illumination (8000 lux) than in the lower of 2000 lux and this was more pronounced in Cyanothece.
The existing data in the literature about culture growth and biomass yield among cyanobacteria are highly variable, not only among species but also among the conditions (temperature, light and vessel used primarily, and secondarily salinity and pH). Most of them are not directly comparable to ours, on the grounds that nothing is found concerning Cyanothece growth and additionally concerning Anabaena, the majority of papers refer to its freshwater species (e.g., [27]) and the rest contain only fragmented limited data on the influence of light and salinity. In this respect, historical data on growth of cyanobacteria must be compared cautiously and only after repeated verifications should be considered of undisputed value.
Our results of the above-mentioned yields of Anabaena and Cyanothece rank among the highest level of those reported in the literature concerning Phormidium (1.20 g/L, [19]), Arthrospira from 0.2 g/L [44], to 1.3 g/L [8], to 1.7 g/L [45], Spirulina 101 mg/L/d [46], Pseudoanabaena 0.55 g/L [47], to refer to some of them. Considering that the optimum temperature range for culturing microalgae in general is 20–30 °C [5,48] and for cyanobacteria in particular 25–35 °C [49], it is logical to assume that the particular strains of Anabaena and Cyanothece used in the present work could attain higher growth rate and yield if cultured at temperatures of 25–30 °C higher than that of our study (20–21.5 °C) which is considered as moderate.
5. Conclusions
These two local strains of Anabaena sp. and Cyanothece sp. have potential for mass culture presenting a long exponential growth phase even at a moderate temperature of ~20 °C. They grow best at 8000 lux yielding from ~1.2 to 1.7 g dry weight per liter and while they present a wide salinity tolerance, Anabaena grows best at 20 ppt and Cyanothece at 40–60 ppt, enabling the proper use of various salinities available in particular locations. Their culture on an industrial scale can thus be implemented using the above salinity optima and a light intensity of at least 8000 lux.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.N.H.; methodology, G.N.H., D.A. and A.S.; validation, G.N.H., D.A. and A.S.; formal analysis, G.N.H.; investigation, G.N.H.; resources, G.N.H. and D.A.; data curation, G.N.H., D.A. and A.S.; writing—original draft preparation, G.N.H.; writing—review and editing, G.N.H.; visualization, G.N.H.; supervision, G.N.H.; project administration, G.N.H.; funding acquisition, G.N.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was financially supported by the research program “ALGAVISION: Isolation and culture of local phytoplankton species aiming to mass production of antibacterial substances. fatty acids. pigments and antioxidants” (MIS 5048496), funded by the General Secretariat of Research and Technology of the Greek Government.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Priyadarshani, I.; Rath, B. Commercial and industrial applications of microalgae—A review. J. Algal Biomass Utln. 2012, 3, 89–100. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Zhao, W.; Mao, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, T.; Chen, F. High-value biomass from microalgae production platforms: Strategies and progress based on carbon metabolism and energy conversion. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2018, 11, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sill, C.; Torzillo, G.; Vonshak, A. Arthrospira (Spirulina). In Ecology of Cyanobacteria II: Their Diversity in Space and Time; Whitton, B.A., Ed.; Springer Science+Business: Berlin, Germany, 2012; p. 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, M.G.; Vaz, B.S.; Morais, E.G.; Costa, J.A.V. Biologically active metabolites synthesized by microalgae. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 835761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renaud, S.M.; Thinh, L.V.; Lambrinidis, G.; Parry, D.L. Effect of temperature on growth, chemical composition and fatty acid composition of tropical Australian microalgae grown in batch cultures. Aquaculture 2002, 211, 195–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatamaneni, B.L.; Orsat, V.; Lefsrud, M. Factors affecting growth of various microalgal species. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2018, 35, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Fu, C.-C.; Liu, Y.-C. Effects of using light-emitting diodes on the cultivation of Spirulina platensis. Biochem. Eng. 2007, 37, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raqiba, H.; Sibi, G. Light emitting diode (LED) illumination for enhanced growth and cellular composition in three microalgae. Adv. Microb. Res. 2019, 3, 007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vonshak, A.; Torzillo, G. Environmental Stress Physiology. In Handbook of Microalgal Culture: Biotechnology and Applied Phycology; Richmond, A., Ed.; Blackwell Science Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; pp. 73–75. ISBN 0–632–05953–2. [Google Scholar]
- Barsanti, L.; Gualtiery, P. Algae: Anatomy, Biochemistry and Biotechnology; CRC Taylor & Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bilanovic, D.; Andargatchew, A.; Kroeger, T.; Shelef, G. Freshwater and marine microalgae sequestering of CO2 at different C and N concentrations. Response surface methodology analysis. Energy Convers. Manag. 2009, 50, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotos, G.; Avramidou, D.; Bekiari, V. Calibration curves of culture density assessed by spectrophotometer for three microalgae (Nephroselmis sp., Amphidinium carterae and Phormidium sp.). Eur. J. Biol. Biotechnol. 2020, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutteau, P. Manual on the production and use of live food for aquaculture. FAO Fish. Tech. Pap. 1996, 361, 7–48. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, W.S.; Singh, K.N.; Azam, K. Evaluation of Relationship between Light Intensity (Lux) and Growth of Chaetoceros muelleri. J. Oceanogr. Mar. Res. 2013, 1, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Parmar, A.; Singh, N.K.; Pandey, A.; Gnansounou, E.; Madamwar, D. Cyanobacteria and microalgae: A positive prospect for biofuels. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 10163–10172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahidin, S.; Idris, A.; Muhamad Shaleh, S.R. The influence of light intensity and photoperiod on the growth and lipid content of microalgae Nannochloropsis sp. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 129, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guermazi, W.; Masmoudi, S.; Boukhris, S.; Ayadi, H.; Morant-Manceau, A. Under low irradiation, the light regime modifies growth and metabolite production in various species of microalgae. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 26, 2283–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.P.; Singh, P. Effect of temperature and light on the growth of algae species: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 50, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotos, G.N. Culture Growth of the Cyanobacterium Phormidium sp. in Various Salinity and Light Regimes and Their Influence on Its Phycocyanin and Other Pigments Content. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisti, Y. Constraints to commercialization of algal fuels. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 167, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pade, N.; Hagemann, M. Salt Acclimation of Cyanobacteria and Their Application in Biotechnology. Life 2015, 5, 25–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotos, G.N. A Preliminary Survey on the Planktonic Biota in a Hypersaline Pond of Messolonghi Saltworks (W. Greece). Diversity 2021, 13, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joset, F.; Jeanjean, R.; Hagemann, M. Dynamics of the response of cyanobacteria to salt stress: Deciphering the molecular events. Physiol. Plant 1996, 96, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thajuddin, N.; Subramanian, G. Cyanobacterial biodiversity and potential applications in biotechnology. Curr. Sci. 2005, 89, 47–57. [Google Scholar]
- Rippka, R.; Deruelles, J.; Waterbury, J.B.; Herdman, M.; Stainer, R.Y. Generic assignments, strain histories and properties of pure cultures of cyanobacteria. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1979, 111, 1–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumwald, E.; Tel-Or, E. Osmoregulation and cell composition in salt-adaptation of Nostoc muscorum. Arch. Microbiol. 1982, 132, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, T.A.; Baba, Z.A.; Parvez, S. Effect of NaCl on Growth and Physiological Traits of Anabena cylindrica L. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2006, 9, 2528–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fu, F.X.; Bell, P.R.F. Effect of salinity on growth, pigmentation, N2 fixation and alkaline phosphatase activity of cultured Trichodesmium spp. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 257, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagle, V.L.; Mhalsekar, N.M.; Jagtap, T.G. Isolation, optimization and characterization of selected cyanophycean members. Indian J. Mar. Sci. 2010, 39, 212–218. [Google Scholar]
- Muruga, B.N.; Wagacha, J.M.; Kabaru, J.M.; Amugune, N.; Duboise, S.M. Effect of physicochemical conditions on growth rates of cyanobacteria species isolated from Lake Magadi, a Soda lake in Kenya. WebPub J. Sci. Res. 2014, 2, 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Tel-Or, E. Response of N2-fixing cyanobacteria to salt. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1980, 40, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molitor, V.; Erber, W.; Peschek, G.A. Increased levels of cytochrome oxidase and sodium-proton antiporter in the plasma membrane of Anacystis nidulans after growth in sodium-enriched media. FEBS Lett. 1986, 204, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabbay-Azaria, R.; Schonfeld, M.; Tel-Or, S.; Messinger, R.; Tel-Or, E. Respiratory activity in the marine cyanobacterium Spirulina subsalsa and its role in salt tolerance. Arch. Microbiol. 1992, 157, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeanjean, R.; Bedu, S.; Havaux, M.; Matthijs, H.C.P.; Joset, F. Salt-induced photosystem I cyclic electron transfer restores growth on low inorganic carbon in a type 1 NAD(P)H dehydrogenase deficient mutant Synechocystis PCC6803. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1998, 167, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fava, G.; Martini, E. Effect of inbreeding and salinity on quantitative characters and asymmetry of Tisbe holothuriae (Humes). Hydrobiologia 1988, 167, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Gradinger, R.; Spindler, M. Experimental study on the effect of salinity on growth rates of Arctic-sea-ice algae from the Greenland Sea. Boreal Environ. Res. 1999, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Sudhir, P.; Murthy, S.D.S. Effects of salt stress on basic processes of photosynthesis. Photosynthetica 2004, 42, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Gao, K. Response of growth and fatty acid compositions of Nannochloropsis sp. to environmental factors under elevated CO2 concentration. Biotechnol. Lett. 2006, 28, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, M.; Karseno; Yoshida, T. Effect of salt concentration on intracellular accumulation of lipids and triacylglycerides in marine microalgae Dunaliella cells. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2006, 101, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.W.; Dong, B.Z.; Cai, Z.P.; Duan, S.S. Growth effects on mixed culture of Dunaliella salina and Phaeodactylum tricornutum under different inoculation densities and nitrogen concentrations. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 13164–13174. [Google Scholar]
- Klepacz-Smółka, A.; Pietrzyk, D.; Szeląg, R.; Głuszcz, P.; Daroch, M.; Tang, J.; Ledakowicz, S. Effect of light colour and photoperiod on biomass growth and phycocyanin production by Synechococcus PCC 6715. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 313, 123700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Kulshreshtha, J.; Singh, G.P. Growth and biopigment accumulation of cyanobacterium Spirulina platensis at different light intensities and temperature. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2011, 42, 1128–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.M.; Kumar, K.; Das, D. Physicochemical parameters optimization, and purification of phycobiliproteins from the isolated Nostoc sp. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 166, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, A.; de Carvalho, J.C.; Soccol, V.T.; Bisinella de Faria, A.B.; Ghiggi, V.; Soccol, C.R. Study of Phycocyanin Production from Spirulina platensis Under Different Light Spectra. Brasilian Arch. Biol. Technol. 2011, 54, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, J.P.; Pathak, N.; Tiwari, A. Standardization of pH and Light Intensity for the Biomass Production of Spirulina platensis. J. Algal Biomass Util. 2010, 1, 93–102. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, S.; Liao, J.; Chen, C.; Chang, J. Bioresource Technology Combining light strategies with recycled medium to enhance the economic feasibility of phycocyanin production with Spirulina platensis. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatoon, H.; Leong, L.K.; Rahman, N.A.; Mian, S.; Begum, H.; Banerjee, S.; Endut, A. Effects of different light source and media on growth and production of phycobiliprotein from freshwater cyanobacteria. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 249, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colla, L.M.; Reinehr, C.O.; Reichert, C.; Costa, J.A.V. Production of biomass and nutraceutical compounds by Spirulina platensis under different temperature and nitrogen regimes. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 1489–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robarts, R.D.; Zohary, T. Temperature effects on photosynthetic capacity, respiration and growth rates of bloom-forming cyanobacteria. N. Z. J. Mar. Fresh. Res. 1987, 21, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).