In Vitro Effects of Retinoic Acid and Sodium Selenite on Neuroblastoma Cell Line (SH-SY5Y)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Neuroblastoma Cell Line
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Compounds
2.4. Exposure to the Compounds
2.5. Cell Viability
2.6. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.7. Colony Formation Assay
2.8. Cell Migration Assay
2.9. RT-qPCR Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
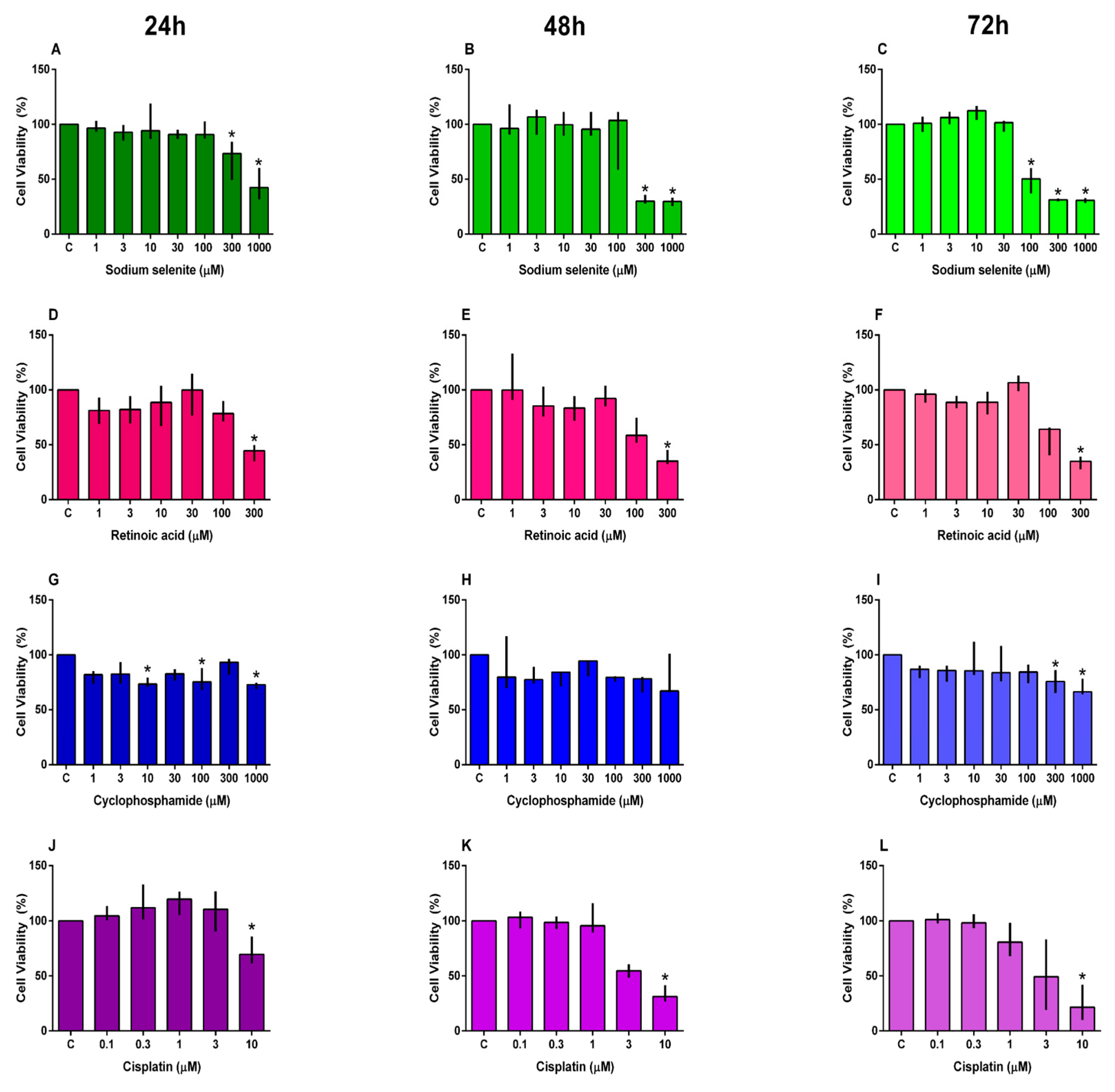
3.1. Cell Viability
3.2. Cell Cycle
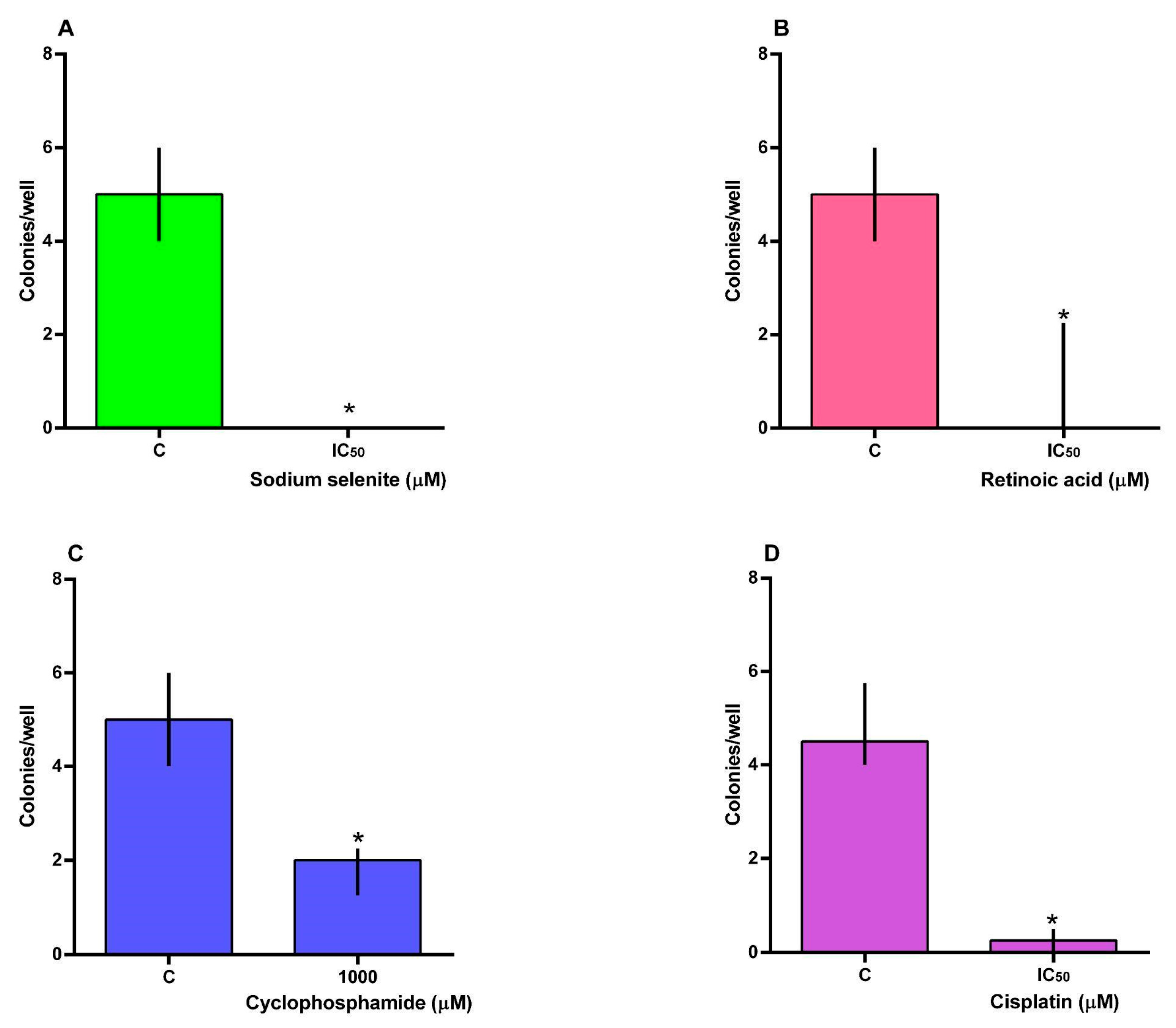
3.3. Clonogenic Assay
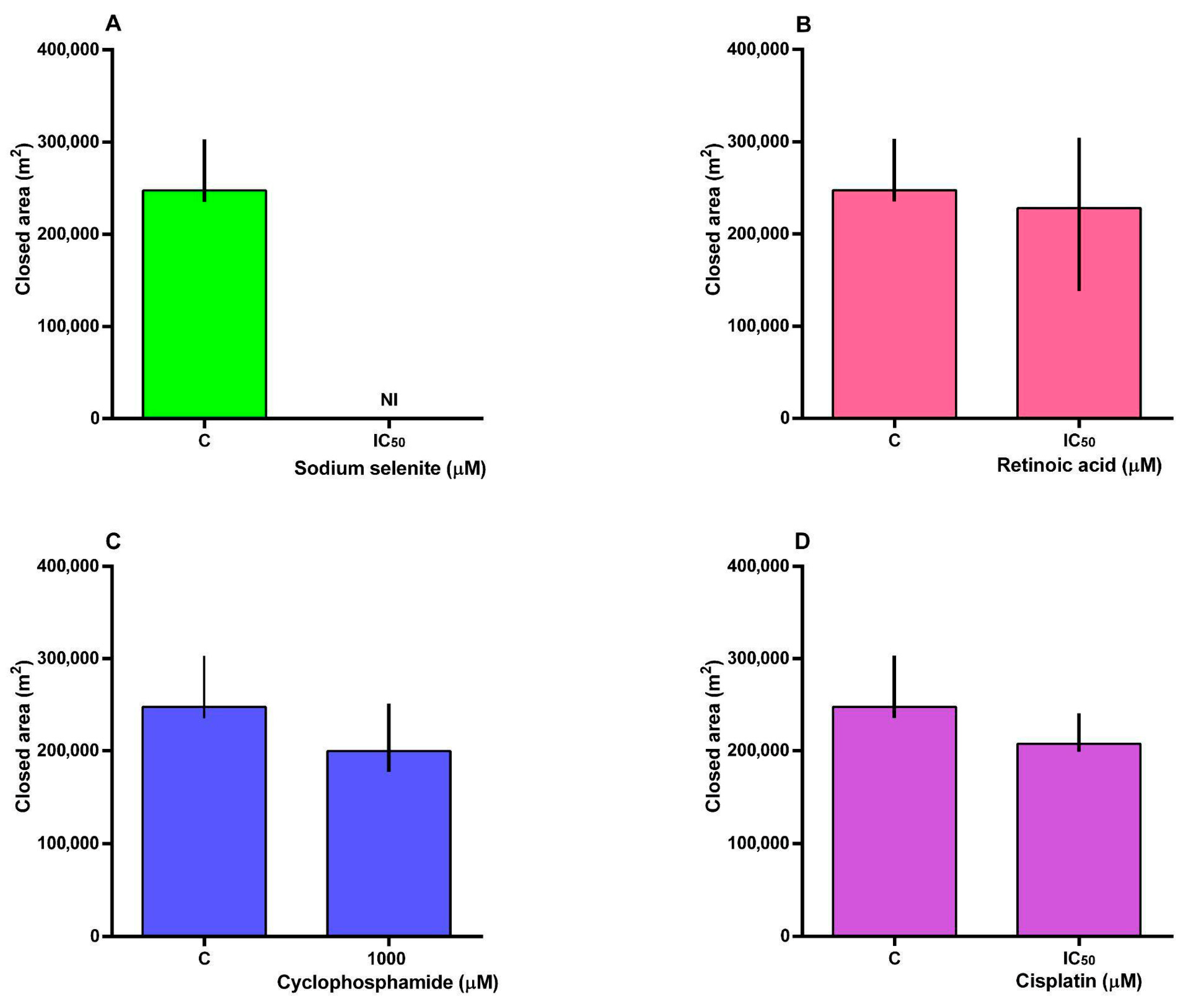
3.4. Cell Migration
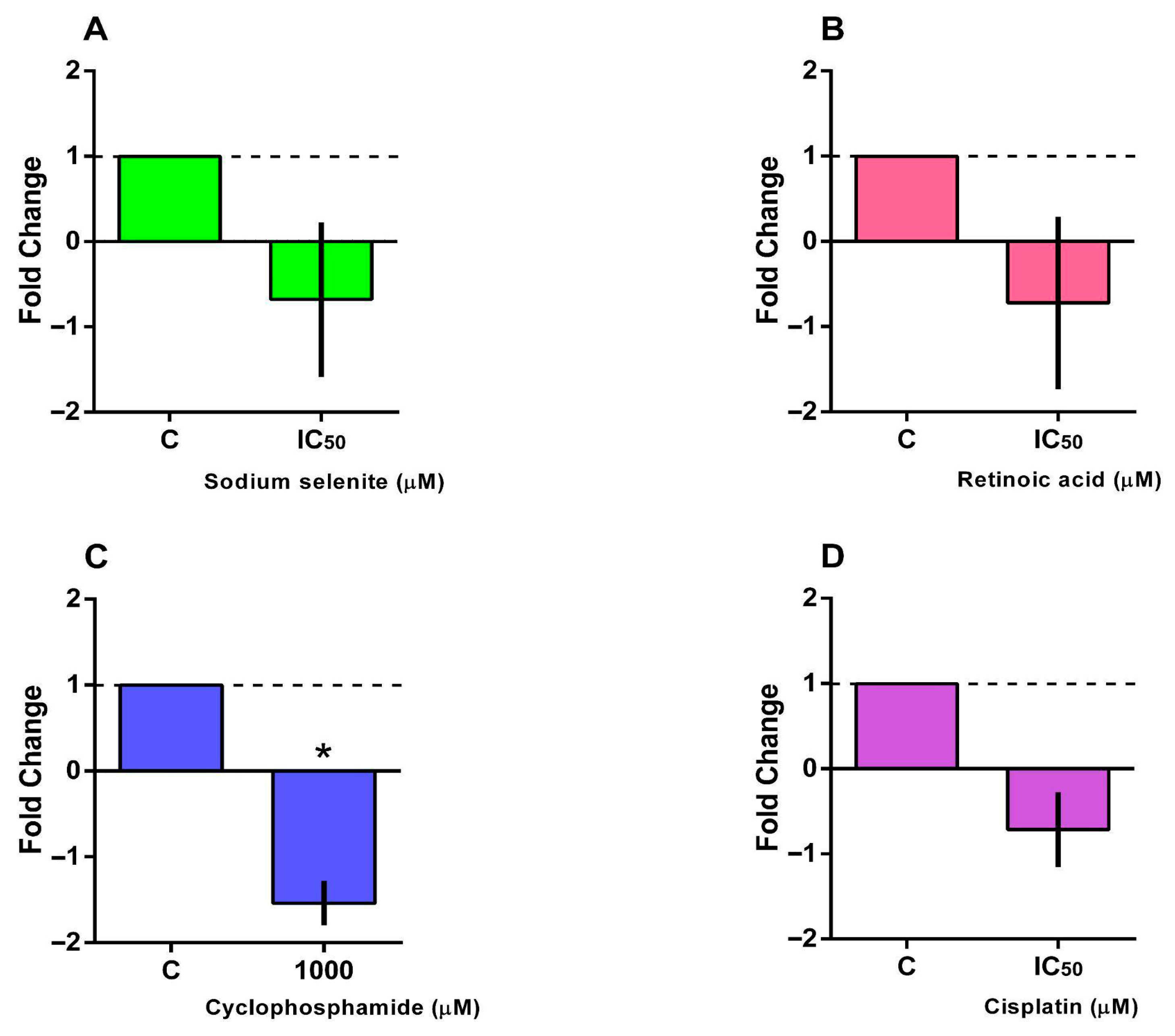
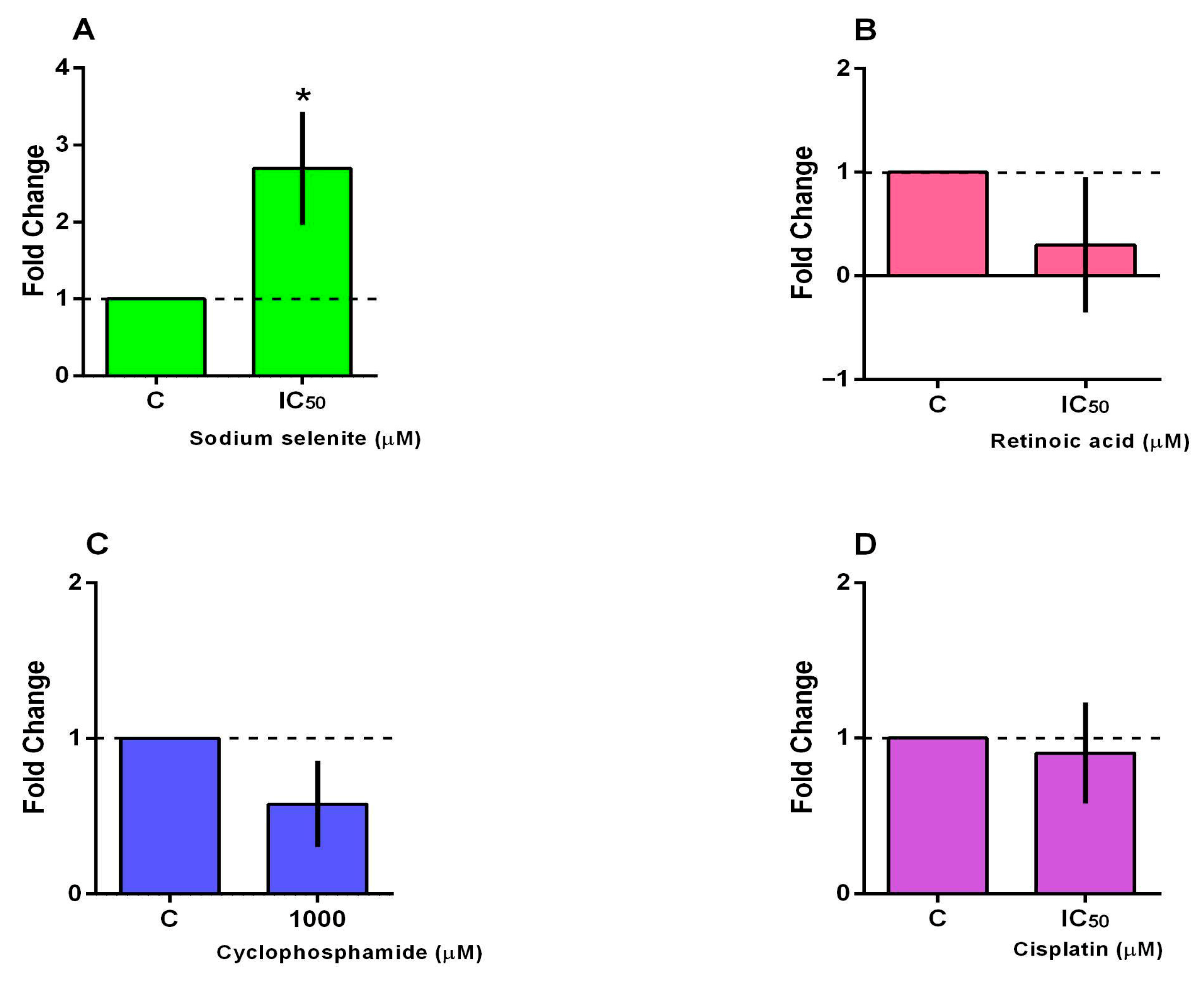
3.5. BCL2 and BAX Gene Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Limitations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lam, C.G.; Howard, S.C.; Bouffet, E.; Pritchard-Jones, K. Science and health for all children with cancer. Science 2019, 363, 1182–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Childhood Cancer. WHO Website 2025. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer-in-children (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Zafar, A.; Khatoon, S.; Khan, M.J.; Abu, J.; Naeem, A. Advancements and limitations in traditional anti-cancer therapies: A comprehensive review of surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and hormonal therapy. Discov. Oncol. 2025, 16, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pudela, C.; Balyasny, S.; Applebaum, M.A. Nervous system: Embryonal tumors: Neuroblastoma. Atlas Genet. Cytogenet. Oncol. Haematol. 2020, 24, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Matthay, K.K. Advancing therapy for neuroblastoma. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 19, 515–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martina-Perez, S.F.; Heirene, L.A.; Kasemeier, J.C.; Kulesa, P.M.; Baker, R.E. Modeling cell differentiation in neuroblastoma: Insights into development, malignancy, and treatment relapse. J. Theor. Biol. 2025, 2502, 20939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinly, B.E.; Grant, C.N. Cell adhesion molecules in neuroblastoma: Complex roles, therapeutic potential. Front. Oncol. 2022, 2, 782186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogo, S.C.; Nascimento, T.G.F.C.; Pinhatti, F.A.B.; Junior, N.F.; Rodrigues, B.S.; Cavalli, L.R.; Elifio-Esposito, S. An overview of neuroblastoma cell lineage phenotypes and in vitro models. Exp. Biol. Med. 2020, 245, 1637–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, M.G.; Gomes, J.R.; Costa, M.D.M. Methods used to achieve different levels of neuronal differentiation in SH-SY5Y and Neuro2a cell lines: An integrative review. Cell Biol. Int. 2023, 47, 1883–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Hickey, R.J.; Malkas, L.H. Therapeutic targeting of DNA replication stress in cancer. Genes 2023, 14, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaster, M.; McNaull, P.P.; Davis, P.J. The opioid epidemic in pediatrics: A 2020 update. Curr. Opin. Anesthesiol. 2020, 33, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makimoto, A.; Fujisaki, H.; Matsumoto, K.; Takahashi, Y.; Cho, Y.; Morikawa, Y.; Yuza, Y.; Tajiri, T.; Iehara, T. Retinoid therapy for neuroblastoma: Historical overview, regulatory challenges, and prospects. Cancers 2024, 16, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, M.; Pang, C.; Wang, J.; Hu, L. Sodium selenite inhibits proliferation and metastasis through ROS-mediated NF-κB signaling in renal cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, J.B.T.; Piccoli, B.C.; Oliveira, C.S. Biological and chemical interest in selenium: A brief historical account. Arkivoc 2017, 2, 457–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, J.B.T.; Oliveira, C.S.; Nogara, P.A. Toxicology and Anticancer Activity of Synthetic Organoselenium Compounds. In Chemistry Beyond Chlorine; Jain, V.K., Priyadarsini, K.I., Eds.; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2017; Chapter 13; pp. 342–376. [Google Scholar]
- da Costa, N.S.; Lima, L.S.; Oliveira, F.A.M.; Galiciolli, M.E.A.; Manzano, M.I.; Garlet, Q.I.; Oliveira, C.S. Antiproliferative effect of inorganic and organic selenium compounds in breast cell lines. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid Colorimetric Assay for Cellular Growth and Survival: Application to Proliferation and Cytotoxicity Assays. J. Immunol. Methods. 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veiga, A.A.; Irioda, A.C.; Mogharbel, B.F.; Bonatto, S.J.R.; Souza, L.M. Quercetin-Rich Extracts from Onions (Allium cepa) Play Potent Cytotoxicity on Adrenocortical Carcinoma Cell Lines, and Quercetin Induces Important Anticancer Properties. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotiropoulou, P.A.; Perez, S.A.; Salagianni, M.; Baxevanis, C.N.; Papamichail, M. Characterization of the optimal culture conditions for clinical scale production of human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells 2006, 24, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, V.M.; Bezerra, M.A., Jr.; Nascimento, J.C.; Amorim, L.M.F. Anticancer drug screening: Standardization of in vitro wound healing assay. J. Bras. Patol. Med. 2019, 55, 606–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−∆∆CT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahba, A.; Wolters, R.; Foster, J.H. Neuroblastoma in the era of precision medicine: A clinical review. Cancers 2023, 15, 4722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, C.; Zeng, Q.; Qi, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Sun, H.; Du, L.; Hao, S.; Li, G.; Feng, C.; et al. Sodium Selenite Induces Autophagy and Apoptosis in Cervical Cancer Cells via Mitochondrial ROS-Activated AMPK/mTOR/FOXO3a Pathway. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Cai, Y.S.; Xu, K.; Zhu, J.L.; Li, Y.B.; Wu, X.Q.; Sun, J.; Lu, S.M.; Xu, P. Sodium selenite induces apoptosis and inhibits autophagy in human synovial sarcoma cell line SW982 in vitro. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 6560–6568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wright, W.C.; Liu, X.; Passaia, B.; Currier, D.; Low, J.; Chapple, R.H.; Steele, J.A.; Connelly, J.P.; et al. Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling determines neuroblastoma cell fate and sensitivity to retinoic acid. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illendula, A.; Fultang, N.; Peethambaran, B. Retinoic acid induces differentiation in neuroblastoma via ROR1 by modulating retinoic acid response elements. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 44, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, E.R.; Moreno-Vicente, J.; Easton, A.; Lanati, S.; Taylor, M.; James, S.; Williams, E.L.; English, V.; Penfold, C.; Beers, S.A.; et al. Cyclophosphamide depletes tumor infiltrating T regulatory cells and combined with anti-PD-1 therapy improves survival in murine neuroblastoma. iScience. 2022, 25, 104995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger-Genge, A.; Köhler, S.; Laube, M.; Haileka, V.; Lemm, S.; Majchrzak, K.; Kammerer, S.; Schulz, C.; Storsberg, J.; Pietzsch, J.; et al. Anti-Cancer Prodrug Cyclophosphamide Exerts Thrombogenic Effects on Human Venous Endothelial Cells Independent of CYP450 Activation, Relevance to Thrombosis. Cells 2023, 12, 1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanova, L.; Careccia, S.; De Maria, R.; Fiori, M.E. Micro-Economics of Apoptosis in Cancer: ncRNAs Modulation of BCL-2 Family Members. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewidar, S.A.; Hamdy, O.; Soliman, M.M.; El Gayar, A.M.; El-Mesery, M. Enhanced therapeutic efficacy of doxorubicin/cyclophosphamide in combination with pitavastatin or simvastatin against breast cancer cells. Med. Oncol. 2023, 41, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pally, D.; Naba, A. Extracellular matrix dynamics: A key regulator of cell migration across length-scales and systems. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2024, 86, 102309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chastney, M.R.; Kaivola, J.; Leppänen, V.M.; Ivaska, J. The role and regulation of integrins in cell migration and invasion. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2025, 26, 147–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalevich, J.; Langford, D. Considerations for the use of SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells in neurobiology. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 1078, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Meng, Y.; Cai, W.; Luo, Q.; Gao, H.; Shen, Q.; Shi, D. Docosahexaenoic Acid Coordinating with Sodium Selenite Promotes Paraptosis in Colorectal Cancer Cells by Disrupting the Redox Homeostasis and Activating the MAPK Pathway. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youle, R.J.; Strasser, A. The BLC-2 protein family: Opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varlamova, E.G.; Baimler, I.V.; Gudkov, S.V.; Turovsky, E.A. Comparative study of the anticancer effects of selenium nanoparticles and nanorods: Regulation os Ca2+ signaling, ER stress, and apoptosis. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Compound | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h |
|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 (µM) | IC50 (µM) | IC50 (µM) | |
| Sodium Selenite | 722.10 | 294.20 | 166.30 |
| Retinoic Acid | 251.10 | 174.30 | 178.60 |
| Cisplatin | - | 5.13 | 3.45 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ribeiro, M.M.; Lima, L.S.; da Costa, N.d.S.; Pereira, M.E.; Fonseca, A.S.; Cavalli, L.R.; Garlet, Q.I.; Irioda, A.C.; Oliveira, C.S. In Vitro Effects of Retinoic Acid and Sodium Selenite on Neuroblastoma Cell Line (SH-SY5Y). Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5, 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5040065
Ribeiro MM, Lima LS, da Costa NdS, Pereira ME, Fonseca AS, Cavalli LR, Garlet QI, Irioda AC, Oliveira CS. In Vitro Effects of Retinoic Acid and Sodium Selenite on Neuroblastoma Cell Line (SH-SY5Y). Future Pharmacology. 2025; 5(4):65. https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5040065
Chicago/Turabian StyleRibeiro, Milena Mariano, Luíza Siqueira Lima, Nayara de Souza da Costa, Meire Ellen Pereira, Aline S. Fonseca, Luciane R. Cavalli, Quelen I. Garlet, Ana Carolina Irioda, and Cláudia S. Oliveira. 2025. "In Vitro Effects of Retinoic Acid and Sodium Selenite on Neuroblastoma Cell Line (SH-SY5Y)" Future Pharmacology 5, no. 4: 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5040065
APA StyleRibeiro, M. M., Lima, L. S., da Costa, N. d. S., Pereira, M. E., Fonseca, A. S., Cavalli, L. R., Garlet, Q. I., Irioda, A. C., & Oliveira, C. S. (2025). In Vitro Effects of Retinoic Acid and Sodium Selenite on Neuroblastoma Cell Line (SH-SY5Y). Future Pharmacology, 5(4), 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5040065










