Overview of Pharmacological Therapies for Diffuse Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Pathogenesis
4. Systemic Therapies Targeting the CSF1-CSF1R Axis (Figure 1)
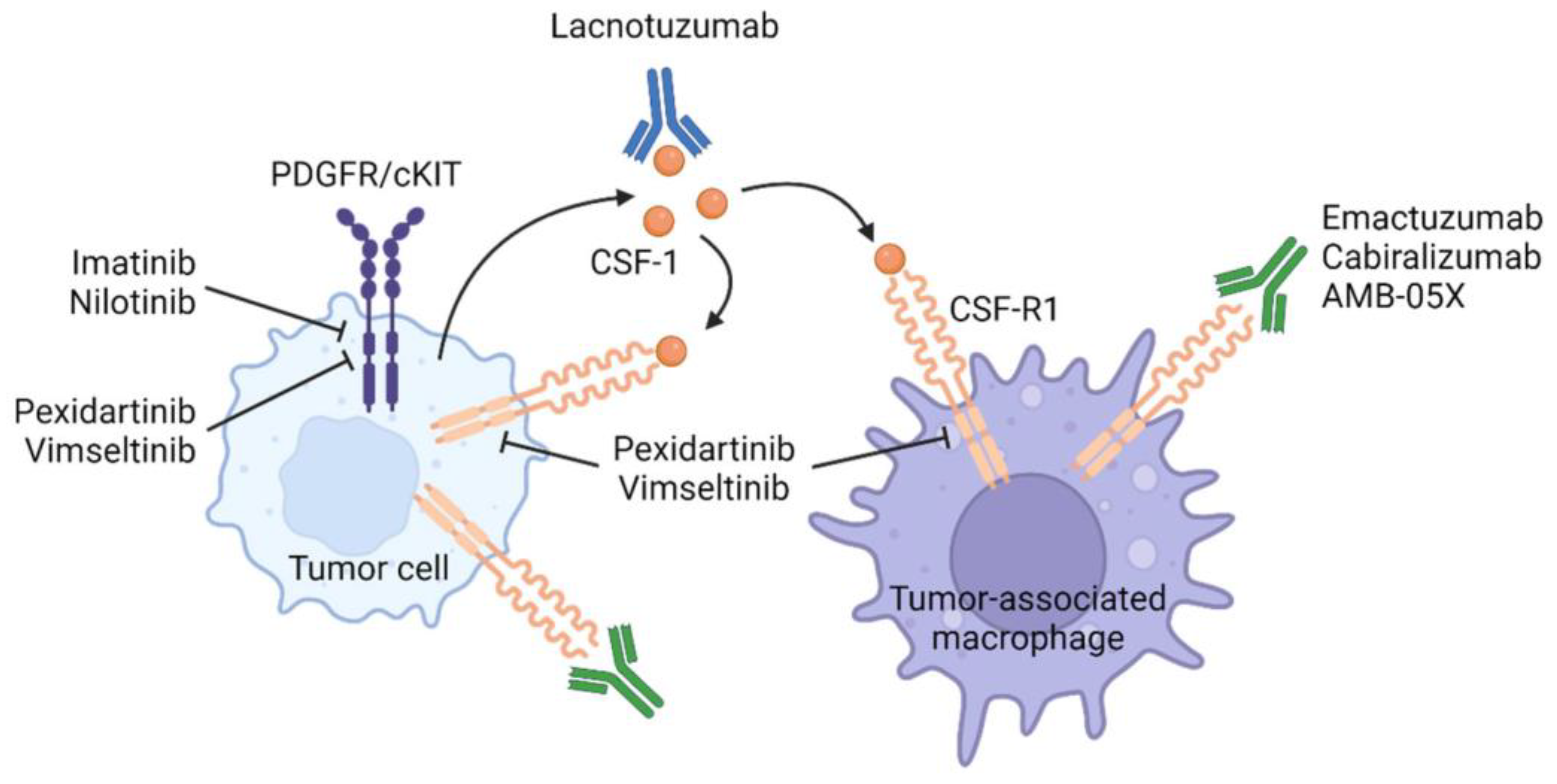
4.1. CSF1R TKIs
4.1.1. Imatinib (Table 1)
| Phase | N | ORR (%) | PFS | Symptomatic Improvement (%) | AEs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cassier et al. (2012) [23] | R | 27 | 19 1 CR 4 PR | 20.9 months | 73 | Fatigue, edema, rash Grade ≥ 3.3% |
| Verspoor et al. (2019) [24] | R | 62 | 31 2 CR | 1 year 71% 5 years 48% (metastatic patients excluded) | 78 | Fatigue, edema, rash Grade ≥ 3.11% |
| Mastboom et al. (2020) [25] | R | 25 | 32 | N/A | N/A | Diarrhea, nausea Grade ≥ 3.12% |
4.1.2. Nilotinib (Table 2)
| Phase | N | ORR (%) | PFS | AEs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gelderblom et al. (2018) [28] | II | 56 | 6 | 12 weeks 92.6% 4 years 57% | Headache, nausea, increased ALT Grade ≥ 3.11% One treatment-related SAE (skin toxicity) |
| Spierenburg et al. (2022) [29] | II | 48 | N/A | 77 months | No long-term AEs |
| NCT01207492 [32] | II | 17 | 0 | 6 months 82% | Fatigue, nausea, constipation SAEs 12% |
4.1.3. Pexidartinib (Table 3)
| Phase | N | ORR RECIST 1.1 (%) | ORR TVS (%) | mDoR (months) | AEs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tap et al. (2015) [34] | II (expansion) | 23 | 52 | 78 | 8 (at data cutoff) | Fatigue, hair color changes, nausea, dysgeusia, periorbital edema, ALT elevation |
| Tap et al. (2022) [33] | I (extension) | 39 | 65 | 71 | 51 | Fatigue, hair color changes, nausea, periorbital edema, dysgeusia and pruritus Grade ≥ 3: hypophosphatemia, ALT increase, AST increase |
| Tap et al. (2019) [14] | III ENLIVEN | 120 a 30 b | 39 a 53 b | 56 a 67 b | Not reached at data cutoff | Any grade 98% vs. 93% Grade ≥ 3.44% vs. 2% (increases in liver enzymes) SAEs 13% vs. 2% |
| Gelderblom et al. (2021) [39] | Pooled analysis | 39 c 61 d 30 e | 60 | 65 | 46.8 (TVS) | Hair color changes, fatigue, and nausea SAEs 18% (hepatic) |
5. Vimseltinib (Table 4)
| Phase | N | ORR (%) | AEs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gelderblom et al. (2021) [41] | I/II | 32 | 33–50 | Mostly grade ≤ 2 2 SAEs |
| Blay et al. (2022) [42] | II | 46 a 11 b | 49 a 44 b | Mostly grade ≤ 2 Grade ≥ 3 > 5% (elevated CK) |
5.1. Anti-CSFR1 Antibodies (Table 5)
5.1.1. Emactuzumab
5.1.2. Cabiralizumab
5.1.3. Lacnotuzumab (MCS110)
| Phase | Drug | N | ORR (%) | AEs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cassier et al. (2015) (2020) [45] | I | Emactuzumab | 12 a 51 b | 71 | Pruritus, asthenia, edema Five SAEs (periorbital edema, lupus erythematosus, erythema, and dermohypodermitis) |
| Sankhala et al. (2017) [48] | I/II | Cabiralizumab | 66 | 45 (5/11) | CK elevation, rash, fatigue, edema Four SAEs (hypertension, fever, CRP elevation, and myocarditis) |
| Cheng et al. (2015) | II | Lacnotuzumab (MCS110) | 36 | 100% (4/4) | No drug-related adverse events |
6. Local Treatments
AMB-05X (Table 6)
| Phase | Administration | N | ORR (%) | AEs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT04731675 [50] | II | Intra-articular injections | 11 | 100 (5/5) | Few low-grade AEs |
| NCT04938180 | II | Intravenous injections | 4 | N/A | N/A |
| NCT05349643 | II | Intra-articular injections | 48 | N/A | N/A |
7. Potential Therapies
7.1. TNFa Blockade
7.2. Immunotherapy
7.3. Intra-Articular Application of Bevacizumab
7.4. Zaltoprofen
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ehrenstein, V.; Andersen, S.L.; Qazi, I.; Sankar, N.; Pedersen, A.B.; Sikorski, R.; Acquavella, J.F. Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumor: Incidence, Prevalence, Patient Characteristics, and Recurrence. A Registry-based Cohort Study in Denmark. J. Rheumatol. 2017, 44, 1476–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gounder, M.M.; Thomas, D.M.; Tap, W.D. Locally Aggressive Connective Tissue Tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastboom, M.J.L.; Palmerini, E.; Verspoor, F.G.M.; Rueten-Budde, A.J.; Stacchiotti, S.; Staals, E.L. Surgical outcomes of patients with diffuse-type tenosynovial giant-cell tumours: An inter-national, retrospective, cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouin, F.; Noailles, T. Localized and diffuse forms of tenosynovial giant cell tumor (formerly giant cell tumor of the tendon sheath and pigmented villonodular synovitis). Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2017, 103, S91–S97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaynrub, A.; Healey, J.H.; Tap, W.; Vaynrub, M. Pexidartinib in the Management of Advanced Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumor: Focus on Patient Selection and Special Considerations. OncoTargets Ther. 2022, 15, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dürr, H.R.; Stäbler, A.; Maier, M.; Refior, H.J. Pigmented villonodular synovitis. Review of 20 cases. J. Rheumatol. 2001, 28, 1620–1630. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, H.S.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, J.-Y.; Yoo, C.; Joo, M.W.; Kim, J.-H. Tenosynovial giant cell tumors of digits: MRI differentiation between localized types and diffuse types with pathology correlation. Skelet. Radiol. 2023, 52, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, J.-Y. MRI Prediction Model for Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumor with Risk of Diffuse-type. Acad. Radiol. 2023, 30, 2616–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling, J.M.; Goldring, S.R.; Harada, Y.; Handel, M.L.; Glowacki, J.; Gravallese, E.M. Multinucleated cells in pigmented villonodular synovitis and giant cell tumor of tendon sheath express features of osteoclasts. Am. J. Pathol. 1997, 150, 1383–1393. [Google Scholar]
- Robert, M.; Farese, H.; Miossec, P. Update on Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumor, an Inflammatory Arthritis with Neoplastic Features. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 820046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamlin, B.R.; Duffy, G.P.; Trousdale, R.T.; Morrey, B.F. Total Knee Arthroplasty in Patients Who Have Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis. Minerva Anestesiol. 1998, 80, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephan, S.R.; Shallop, B.; Lackman, R.; Kim, T.W.B.; Mulcahey, M.K. Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis: A Comprehensive Review and Proposed Treatment Algorithm. JBJS Rev. 2016, 4, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmerini, E.; Staals, E.L. Treatment updates on tenosynovial giant cell tumor. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2022, 34, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tap, W.D.; Gelderblom, H.; Palmerini, E.; Desai, J.; Bauer, S.; Blay, J.-Y.; Alcindor, T.; Ganjoo, K.; Martín-Broto, J.; Ryan, C.W.; et al. Pexidartinib versus placebo for advanced tenosynovial giant cell tumour (ENLIVEN): A random-ised phase 3 trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogrincic, G.S.; O’Connell, J.X.; Gilks, C. Giant cell tumor of tendon sheath is a polyclonal cellular proliferation. Hum. Pathol. 1997, 28, 815–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, M.; Höglund, M.; Panagopoulos, I.; Sciot, R.; Dal Cin, P.; Debiec-Rychter, M.; Mertens, F.; Mandahl, N. Molecular cytogenetic mapping of recurrent chromosomal breakpoints in tenosynovial giant cell tumors. Virchows Arch. 2002, 441, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmi, M.; Vinceneux, A.; Cassier, P.A. Current Systemic Treatment Options for Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumor/Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis: Targeting the CSF1/CSF1R Axis. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2016, 17, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tap, W. ENLIVEN study: Pexidartinib for tenosynovial giant cell tumor (TGCT). Futur. Oncol. 2020, 16, 1875–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagopoulos, I.; Brandal, P.; Gorunova, L.; Bjerkehagen, B.; Heim, S. Novel CSF1-S100A10 fusion gene and CSF1 transcript identified by RNA sequencing in te-nosynovial giant cell tumors. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 44, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hume, D.A.; MacDonald, K.P.A. Therapeutic applications of macrophage colony-stimulating factor-1 (CSF-1) and antagonists of CSF-1 receptor (CSF-1R) signaling. Blood 2012, 119, 1810–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, R.B.; Rubin, B.P.; Miller, M.A.; Subramanian, S.; Kaygusuz, G.; Montgomery, K.; Zhu, S.; Marinelli, R.J.; De Luca, A.; Downs-Kelly, E.; et al. A landscape effect in tenosynovial giant-cell tumor from activation of CSF1 expression by a trans-location in a minority of tumor cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 690–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahmi, M.; Cassier, P.; Dufresne, A.; Chabaud, S.; Karanian, M.; Meurgey, A.; Bouhamama, A.; Gouin, F.; Vaz, G.; Garret, J.; et al. Long term term follow-up of tyrosine kinase inhibitors treatments in inoperable or relapsing diffuse type tenosynovial giant cell tumors (dTGCT). PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassier, P.A.; Gelderblom, H.; Stacchiotti, S.; Thomas, D.; Maki, R.G.; Kroep, J.R.; van der Graaf, W.T.; Italiano, A.; Seddon, B.; Dômont, J.; et al. Efficacy of imatinib mesylate for the treatment of locally advanced and/or metastatic tenosyno-vial giant cell tumor/pigmented villonodular synovitis. Cancer 2012, 118, 1649–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verspoor, F.G.M.; Mastboom, M.J.L.; Hannink, G.; Maki, R.G.; Wagner, A.; Bompas, E.; Desai, J.; Italiano, A.; Seddon, B.M.; van der Graaf, W.T.A.; et al. Long-term efficacy of imatinib mesylate in patients with advanced Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumor. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastboom, M.; Lips, W.; van Langevelde, K.; Mifsud, M.; Ng, C.; McCarthy, C.; Athanasou, N.; Gibbons, C.; van de Sande, M. The effect of Imatinib Mesylate in diffuse-type Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumours on MR imaging and PET-CT. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 35, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blay, J.-Y.; El Sayadi, H.; Thiesse, P.; Garret, J.; Ray-Coquard, I. Complete response to imatinib in relapsing pigmented villonodular synovitis/tenosynovial giant cell tumor (PVNS/TGCT). Ann. Oncol. 2008, 19, 821–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stacchiotti, S.; Crippa, F.; Messina, A.; Pilotti, S.; Gronchi, A.; Blay, J.Y.; Casali, P.G. Response to imatinib in villonodular pigmented synovitis (PVNS) resistant to nilotinib. Clin. Sarcoma Res. 2013, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelderblom, H.; Cropet, C.; Chevreau, C.; Boyle, R.; Tattersall, M.; Stacchiotti, S.; Italiano, A.; Piperno-Neumann, S.; Le Cesne, A.; Ferraresi, A.; et al. Nilotinib in locally advanced pigmented villonodular synovitis: A multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spierenburg, G.; Grimison, P.; Chevreau, C.; Stacchiotti, S.; Piperno-Neumann, S.; Le Cesne, A.; Ferraresi, V.; Italiano, A.; Duffaud, F.; Penel, N.; et al. Long-term follow-up of nilotinib in patients with advanced tenosynovial giant cell tumours: Long-term follow-up of nilotinib in TGCT. Eur. J. Cancer 2022, 173, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verspoor, F.; Mastboom, M.; Weijs, W.; Koetsveld, A.; Schreuder, H.; Flucke, U. Treatments of tenosynovial giant cell tumours of the temperomandibular joint: A report of three cases and a review of literature. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 47, 1288–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouin, F. Nilotinib in locally advanced pigmented villonodular synovitis: Challenges of a new targeted therapy. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 584–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staals, E.L.; Ferrari, S.; Donati, D.M.; Palmerini, E. Diffuse-type tenosynovial giant cell tumour: Current treatment concepts and future perspectives. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 63, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tap, W.D.; Singh, A.S.; Anthony, S.P.; Sterba, M.; Zhang, C.; Healey, J.H.; Chmielowski, B.; Cohn, A.L.; Shapiro, G.I.; Keedy, V.L.; et al. Results from Phase I Extension Study Assessing Pexidartinib Treatment in Six Cohorts with Solid Tumors including TGCT, and Abnormal CSF1 Transcripts in TGCT. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tap, W.D.; Wainberg, Z.A.; Anthony, S.P.; Ibrahim, P.N.; Zhang, C.; Healey, J.H.; Chmielowski, B.; Staddon, A.P.; Cohn, A.L.; Shapiro, G.I.; et al. Structure-Guided Blockade of CSF1R Kinase in Tenosynovial Giant-Cell Tumor. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van De Sande, M.; Tap, W.D.; Gelhorn, H.L.; Ye, X.; Speck, R.M.; Palmerini, E.; Stacchiotti, S.; Desai, J.; Wagner, A.J.; Alcindor, T.; et al. Pexidartinib improves physical functioning and stiffness in patients with tenosynovial giant cell tumor: Results from the ENLIVEN randomized clinical trial. Acta Orthop. 2021, 92, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmerini, E.; Longhi, A.; Donati, D.M.; Staals, E.L. Pexidartinib for the treatment of adult patients with symptomatic tenosynovial giant cell tumor: Safety and efficacy. Expert. Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2020, 20, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, J.H.; Gelderblom, H.; Sande, M.; Stacchiotti, S.; Healey, J.H.; Tap, W.D.; Wagner, A.J.; Pousa, A.L.; Druta, M.; Lin, C.-C.; et al. Pexidartinib Long-Term Hepatic Safety Profile in Patients with Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumors. Oncologist 2021, 26, e863–e873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monestime, S.; Lazaridis, D. Pexidartinib (TURALIO™): The First FDA-Indicated Systemic Treatment for Teno-synovial Giant Cell Tumor. Drugs R D 2020, 20, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelderblom, H.; Wagner, A.J.; Tap, W.D.; Palmerini, E.; Wainberg, Z.A.; Desai, J.; Healey, J.H.; Sande, M.A.J.; Bernthal, N.M.; Staals, E.L.; et al. Long-term outcomes of pexidartinib in tenosynovial giant cell tumors. Cancer 2021, 127, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, O.; Zahir, H.; French, J.; Polhamus, D.; Wang, X.; van de Sande, M.; Tap, W.D.; Gelderblom, H.; Wagner, A.J.; Healey, J.H.; et al. Exposure–response analysis of efficacy and safety for pexidartinib in patients with tenosynovial giant cell tumor. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst. Pharmacol. 2021, 10, 1422–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelderblom, H.; Razak, A.A.; Sánchez-Gastaldo, A.; Rutkowski, P.; Wilky, B.; Wagner, A.; van de Sande, M.; Michenzie, M.; Vallee, M.; Sharma, M.; et al. 1821P Safety and preliminary efficacy of vimseltinib in tenosynovial giant cell tumor (TGCT). Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, S1233–S1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blay, J.-Y.; Gelderblom, H.; Rutkowski, P.; Wagner, A.; van de Sande, M.; Gonzalez, A.F.; Stacchiotti, S.; Le Cesne, A.; Alcindor, T.; Serrano, C.; et al. 1509P Efficacy and safety of vimseltinib in tenosynovial giant cell tumour (TGCT): Phase II expansion. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, S1236–S1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tap, W.D.; Wagner, A.J.; Sharma, M.G.; Vallee, M.; Michenzie, M.F.; Sherman, M.L.; Ruiz-Soto, R.; Stacchiotti, S.; van de Sande, M.A.; Gelderblom, H. MOTION: A randomized, phase 3, placebo-controlled, double-blind study of vimseltinib (DCC-3014) for the treatment of tenosynovial giant cell tumor. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, TPS11590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart, K.; Bröske, A.-M.; Rüttinger, D.; Mueller, C.; Phipps, A.; Walz, A.-C.; Ries, C.; Baehner, M.; Cannarile, M.; Meneses-Lorente, G.; et al. PK/PD Mediated Dose Optimization of Emactuzumab, a CSF1R Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors and Diffuse-Type Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumor. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 108, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassier, P.A.; Italiano, A.; Gomez-Roca, C.A.; Le Tourneau, C.; Toulmonde, M.; Cannarile, M.A.; Ries, C.; Brillouet, A.; Müller, C.; Jegg, A.-M.; et al. CSF1R inhibition with emactuzumab in locally advanced diffuse-type tenosynovial giant cell tumours of the soft tissue: A dose-escalation and dose-expansion phase 1 study. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissinger, S.; Hage, C.; Wagner, V.; Maser, I.-P.; Brand, V.; Schmittnaegel, M.; Jegg, A.-M.; Cannarile, M.; Watson, C.; Klaman, I.; et al. Macrophage depletion induces edema through release of matrix-degrading proteases and prote-oglycan deposition. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassier, P.A.; Italiano, A.; Gomez-Roca, C.; Le Tourneau, C.; Toulmonde, M.; D’Angelo, S.P.; Weber, K.; Loirat, D.; Jacob, W.; Jegg, A.-M.; et al. Long-term clinical activity, safety and patient-reported quality of life for emactuzumab-treated patients with diffuse-type tenosynovial giant-cell tumour. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 141, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankhala, K.K.; Blay, J.-Y.; Ganjoo, K.N.; Italiano, A.; Hassan, A.B.; Kim, T.M.; Ravi, V.; Cassier, P.A.; Rutkowski, P.; Sankar, N.; et al. A phase I/II dose escalation and expansion study of cabiralizumab (cabira; FPA-008), an an-ti-CSF1R antibody, in tenosynovial giant cell tumor (TGCT, diffuse pigmented villonodular synovitis D-PVNS). J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 11078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, A.; Joensuu, H.; Sebastian, M.; Naing, A.; Bang, Y.-J.; Martin, M.; Roda, D.; Hodi, F.S.; Veloso, A.; Mataraza, J.; et al. Phase Ib/II study of lacnotuzumab (MCS110) combined with spartalizumab (PDR001) in patients (pts) with advanced tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelderblom, H.; Huang, M.; van de Sande, M.; Scharschmidt, T.; Kostogryz, O.; Alani, L.; Huang, T.; Hsu, L.; Johnson, K. 1486MO The synovial and systemic pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of in-tra-articular administration of the CSF1 receptor antibody AMB-05X in a phase II proof-of-concept trial in tenosynovial gi-ant cell tumor. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, S1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiocco, U.; Sfriso, P.; Lunardi, F.; Pagnin, E.; Oliviero, F.; Scagliori, E.; Cozzi, L.; Vezzù, M.; Molena, B.; Scanu, A.; et al. Molecular pathways involved in synovial cell inflammation and tumoral proliferation in diffuse pigmented villonodular synovitis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2010, 9, 780–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiocco, U.; Sfriso, P.; Oliviero, F.; Sovran, F.; Scagliori, E.; Pagnin, E.; Vezzu, M.; Cozzi, L.; Botsios, C.; Nardacchione, R.; et al. Intra-articular treatment with the TNF-alpha antagonist, etanercept, in severe diffuse pigmented villonodular synovitis of the knee. Reumatismo 2006, 58, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kroot, E.-J.A.; Kraan, M.C.; Smeets, T.J.M.; Maas, M.; Tak, P.P.; Wouters, J.M.G.W. Tumour necrosis factor blockade in treatment resistant pigmented villonodular synovitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2005, 64, 497–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spierenburg, G.; van der Heijden, L.; van Langevelde, K.; Szuhai, K.; Bovée, J.V.G.M.; van de Sande, M.A.J.; Gelderblom, H. Tenosynovial giant cell tumors (TGCT): Molecular biology, drug targets and non-surgical pharmacological approaches. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets 2022, 26, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Yu, L.; Hu, J.; Xu, H.; Wang, J.; Shi, Y.; Luo, X.; Yan, W. Expression of PD-L1 in mononuclear cells, multinucleated cells, and foam cells in tenosynovial giant cell tumors. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2019, 12, 876–884. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nissen, M.J.; Boucher, A.; Brulhart, L.; Menetrey, J.; Gabay, C. Efficacy of intra-articular bevacizumab for relapsing diffuse-type giant cell tumour. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 947–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, A.; Endo, M.; Kawai, A.; Nishida, Y.; Terauchi, R.; Matsumine, A.; Aiba, H.; Nakamura, T.; Tandai, S.; Ozaki, T.; et al. Randomized placebo-controlled double-blind phase II study of zaltoprofen for patients with diffuse-type and unresectable localized tenosynovial giant cell tumors: The REALIZE study. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 900010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stamatiou, A.; Nguyen-Ngoc, T.; Wetterwald, L.; Dolcan, A.-M.; Dei Tos, G.; Cherix, S.; Omoumi, P.; Digklia, A. Overview of Pharmacological Therapies for Diffuse Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumor. Future Pharmacol. 2023, 3, 926-937. https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol3040056
Stamatiou A, Nguyen-Ngoc T, Wetterwald L, Dolcan A-M, Dei Tos G, Cherix S, Omoumi P, Digklia A. Overview of Pharmacological Therapies for Diffuse Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumor. Future Pharmacology. 2023; 3(4):926-937. https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol3040056
Chicago/Turabian StyleStamatiou, Antonia, Tu Nguyen-Ngoc, Laureline Wetterwald, Ana-Maria Dolcan, Giovanni Dei Tos, Stephane Cherix, Patrick Omoumi, and Antonia Digklia. 2023. "Overview of Pharmacological Therapies for Diffuse Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumor" Future Pharmacology 3, no. 4: 926-937. https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol3040056
APA StyleStamatiou, A., Nguyen-Ngoc, T., Wetterwald, L., Dolcan, A.-M., Dei Tos, G., Cherix, S., Omoumi, P., & Digklia, A. (2023). Overview of Pharmacological Therapies for Diffuse Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumor. Future Pharmacology, 3(4), 926-937. https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol3040056







