Abstract
Oncolytic viruses (OV) promote anti-tumour responses through the initiation of immunogenic cancer cell death which activates the host’s systemic anti-tumour immunity. We have previously shown that intravenously administered HSV1716 is an effective treatment for mammary cancer. However, intravenous administration of a virus has the potential to result in neutralization and sequestration of the virus which may reduce efficacy. Here, we show that the oncolytic virus HSV1716 can be administered within a cellular carrier (macrophages). PyMT and 4T1 murine mammary cancer cell lines were implanted into immuno-competent murine models (orthotopic primary, early metastatic and brain metastasis models). HSV1716 or macrophages armed with HSV1716 (M-HSV1716) were administered intravenously, and tumour size was quantified using caliper measurement or bioluminescence imaging. Administration of M-HSV1716 led to tumour shrinkage and increased the survival of animals. Furthermore, these results were achieved with a 100-fold lower viral load, which has the potential for decreased toxicity. Our results demonstrate that M-HSV1716 is associated with activity against murine mammary cancers and provides an alternative platform for the systemic delivery of OV.
1. Introduction
Breast cancer is the most commonly occurring cancer and the leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide, with an estimated 2.3 million new cases and 684,996 deaths in 2020. It accounts for 15.5% of cancer death in females [1], and of these, the triple-negative subtype of breast cancer (TNBC) is often one of the most challenging to treat.
Tumour-associated macrophages (TAMs) are common in breast cancers, and it has been described that the breast cancer microenvironment may educate macrophages to become more “M2” like [2]. Furthermore, high numbers of TAMs in TNBC have been associated with an increase in tumour aggressiveness and metastases [3]. The increased tumour progression and decreased survival may be manipulated if TAMs are reprogrammed, aiding the immune system’s recognition of cancer and enhancing the response to cancer therapeutics. The use of macrophages as a cell-based therapy is increasing in popularity within the healthcare setting. One such example is the use of macrophages to reverse and repair the damage caused by liver cirrhosis [4]. Within the cancer setting, macrophage-based therapies have been investigated with varying success. Therapies include the modification of macrophage numbers through depletion within the tumour site or interfering with TAM recruitment, and macrophage reprogramming using inhibitors of receptors/protein involved in the innate immune response including CD47, CD40 and toll-like receptors [5]. We have recently shown that macrophages can also be reprogrammed using an oncolytic virus (HSV1716) resulting in decreased tumour burden and increased survival in murine breast cancer models [6]. In this study, we describe the changes in macrophage phenotype from “M2-like” to “M1-like”, and if macrophages were depleted using clodronate liposome, anti-tumour efficacy was suppressed.
Oncolytic viruses (OV) are a novel class of cancer therapeutics which have the ability, either intrinsicallyor more commonly in genetically altered form, to preferentially divide and replicate in cancer cells rather than non-cancer cells. Although the mechanism behind individual viruses delivering their cytotoxic effect differs, the broad effect of the virus is to directly lyse tumour cells and generate immunogenic cell death, thus presenting tumour antigens which will be recognised and targetable by the host’s own immune system. Immunogenic cell death is the term given to the release of host of pro-inflammatory markers including calreticulin, heat shock proteins, ATP and HMGB1. This environment is particularly appealing to dendritic cells which then phagocytose tumour associated antigens and presents these to T cells.
The most commonly studied of these are adenoviruses, reoviruses and herpes simplex viruses (HSV). These have been trialed in a number of tumour types with preclinical and clinical efficacy, whilst advanced melanoma represents the leading tumour subtype to be treated with the first FDA-approved herpes simplex virus (T-VEC). T-VEC is a modified HSV that carries the transgene for granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (GMCSF). The landmark phase 3 virotherapy trial (OPTIM) described increased response and overall survival in patients compared with GM-CSF alone [7]. In breast cancer, oncolytic virotherapy is an expanding area of interest, with a number of preclinical studies and a few early phase studies showing early markers of response [8,9,10,11,12,13,14]. However, to date, most clinical studies using OV have relied on intratumoural injection due to the challenges of systemic therapy.
Injection of OV into the circulation may lead to suboptimal viral concentrations reaching the tumour and exerting its anti-tumour effects. This is mainly a result of neutralisation via the patient’s immune system and non-specific uptake in tissues, predominantly the liver and spleen [15,16]. Intratumoural injection of OV has been used in melanoma metastases, however, intratumoural injection would prove technically challenging in treating TNBC metastases, which are primarily located in the liver, lung, brain and bone. One of the approaches to systemic delivery of virotherapy is to exploit the cellular components of the tumour microenvironment. A number of cell carriers have been reported to provide viral protection and carry the virus to the tumour in a “Trojan horse” style. These cells include T cells, dendritic cells, mesenchymal stem cells, neural progenitor cells, endothelial progenitor cells and macrophages [17]. Of these, macrophages are of particular interest, as they are present in high numbers in tumours [18] and may have a prognostic implication in breast cancer [19,20]. Using the macrophage as a vector for virotherapy, also known as macrophage virotherapy, has been shown to protect the virus in circulation and target inaccessible prostate tumours in murine models [21,22]. Others have recently published data of an in vitro co-culture model of monocyte-derived macrophages, a paramyxovirus and TNBC [23]. Here we describe the potential for macrophage virotherapy using an oncolytic HSV1716 virus within murine primary and metastatic breast cancer.
2. Results
2.1. Characterisation of M-HSV1716
Bone marrow was isolated from immune-competent mice as described in Section 4.3. At day 0 the majority of cells were found to be undifferentiated monocytes (Figure 1A). After 7 days of incubation in macrophage differentiation medium, these cells demonstrated a shift towards F4/80-expressing macrophages, with over 95% of adherent cells expressing CD45+ CD11b+ F4/80+ and a loss of Ly6G expression (Figure 1B). These bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDM) were infected with HSV1716 at an MOI of 10 in serum-free medium for 2 h. Of note, an MOI of 10 was used because at higher MOI’s (greater than MOI 10) BMDMs were susceptible to cell death (over 90% of macrophages died at MOI 25 with 50% cell death at MOI 5) at 96 h following infection (data not shown). Unbound virus was washed off, and cells underwent an additional 2 h incubation; flow cytometry revealed a viral infection efficiency of 53% s (p = 0.0004, Figure 1C). Patency of the virus within BMDMs (M-HSV1716) was demonstrated by a significant difference in the expression of genes responsible for viral replication (Figure 1D) compared to control BMDMs 24 h post-infection. We also confirmed viral replication in the standard plaque assay using vero cells (Figure 1E). Viral concentration of M-HSV1716 demonstrated 100-fold fewer viral particles compared to HSV1716. This was most likely associated with the infection efficiency during the preparation of the treatment. Due to the retrospective nature of quantifying infectious inoculations, together with the loss of viability associated with the storage and preparation of such treatments, a matching virus-alone control is problematic. We have, however, demonstrated that the cytotoxic activity of HSV1716 is dose dependent, with 99% of TS1 cells succumbing 7 days post infection (p < 0.0001, Figure 1F). Additionally, we have previously shown that HSV1716 can infect and lyse a number of breast cancer cell lines in vitro [6]. To examine whether this can be replicated with M-HSV1716, PyMT-TS1 spheroids were co-cultured with HSV1716 or M-HSV1716 for 72 h hours, and tumour cell lysis was assessed via flow cytometry with TOPRO-3. Here, equivalent cell death was seen with both HSV1716 alone and when delivered via macrophages; however, macrophages alone did not induce any significant cell death over the untreated control cells (Figure 1G).
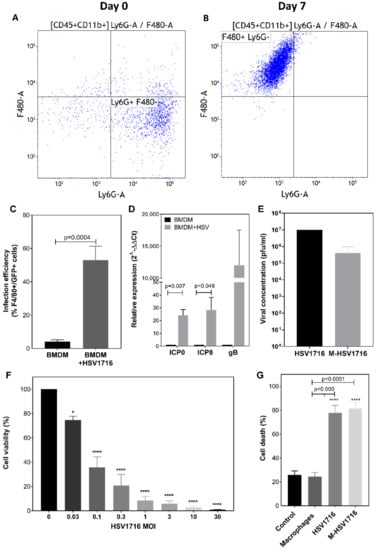
Figure 1.
Characterisation of M-HSV1716. Isolation of BMDM at day 0 was characterised as predominantly undifferentiated monocytes (A), x-axis—Ly6G (neutrophil marker), y-axis—F480 (macrophage marker). Following 7 days of incubation, these differentiated into F4/80-expressing macrophages (B). The infection efficiency of BMDM with HSV1716 (MOI 5) was quantified by flow cytometry of dual-stained F4/80 macrophage marker with GFP-expressing HSV1716 (C). Low-level non-specific binding of antibody was noted in untreated cells. (D) HSV1716 patency within BMDMs was assessed by measuring viral replication genes 24 h post infection. M-HSV1716 was prepared by incubating BMDM with HSV1716 at MOI 25 for 2 h. Cells were harvested and washed in PBS prior to administration, and plaque assays were performed to ascertain viral titre of treatment groups (E). (F) HSV1716 was used to infect PyMT-TS1 cells at a concentration range of MOI 0.03–30, and the effects on cell viability were determined by Alamar blue assay 7 days post infection. (G) FACS data showing equivalence in cell death (TOPRO-3) when spheroids were infected with HSV1716 and M-HSV1716. Data represents the mean ± SEM of assays performed in triplicate. Statistical significance was analysed by unpaired t-test (C,D). * = p < 0.05, **** = p < 0.0001 one-way ANOVA (F,G).
2.2. Macrophage-Mediated Delivery of HSV1716 Slows Primary Breast Tumour Growth
Previously, we have shown that HSV1716 alone slows the rate of breast cancer growth in three murine models of primary breast cancer [6]. This oncolytic effect resulted from both direct cell lysis and changes in the tumour microenvironment, notably a change in macrophage behavior and T-cell activation, which has been shown to result in immunogenic cell death. Additionally, viral replication within macrophages was observed, resulting in the use of this strategy to enhance HSV1716 delivery to tumours in this study.
In this study we investigated the effect of M-HSV1716 treatment in a primary model of breast cancer. PyMT-TS1 cells were implanted into the mammary fat pads of Balb/c mice. Treatment was initiated when tumours had grown to an average of 500 mm3 (Figure 2A). The effect on the breast tumour growth post-treatment was quantified by caliper measurements, whereby M-HSV1716 significantly slowed tumour growth compared with HSV1716 (p < 0.001) and BMDM (p < 0.05) alone up to day 11 post-treatment (Figure 2B). Notably, our recent studies demonstrate that HSV1716 needs to be administered repeatedly in order to suppress tumour growth; despite this, once the treatment stops, tumours did regrow [6]. We did not expect BMDM to have an inhibitory effect, as these cells were not stimulated to be anti-tumour-like, and their purpose was only for delivery of HSV1716.
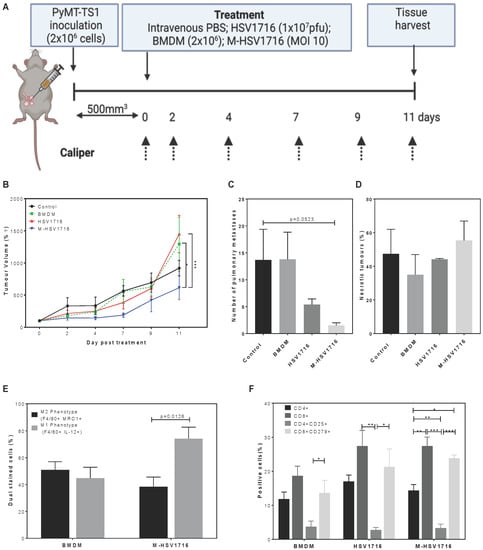
Figure 2.
M-HSV1716 reduces tumour burden in a primary mouse model. PyMT-TS1 cells were implanted into the 4th mammary fat pads to assess the effectiveness of HSV1716 or M-HSV1716 in primary tumours (A). Tumour growth was measured by digital calipers for 11 days following treatment (B). Pulmonary metastases (C) and necrosis (D) were quantified histologically postmortem from an average of 2–4 different sections of lung tissue over 100 μm apart from 2–4 slides. Immune cell changes within the TME were seen when M-HS1716 was given compared to macrophage alone. Flow cytometric analysis of dispersed tumours showed a skewing to M1 macrophage phenotype (E) and an increase in CD8+ T cells (F). Data are mean ± SEM, n = 6–8 mice per group. * = p < 0.05, ** = p < 0.01, *** = p < 0.001 analysed using one-way ANOVA. Panel A was created with BioRender.com, accessed on 6 October 2022.
A difference in the number of lung metastases was also seen between the control (untreated) and M-HSV1716 group (p = 0.0523), as well as a trend for improvement between the HSV1716 and M-HSV1716 group (Figure 2C). There was no difference in tumour necrosis between groups (Figure 2D). As viral titre was significantly lower in the M-HSV1716 group compared to HSV1716 treatment alone (Figure 1E), we speculate that this may be a result of improved tumour targeting and shielding of the virus from immunosurveillance whilst in the circulation in comparison to naked virus (as described in our previous work [21,22]) or an increase in viral replication within the macrophage carriers [6].
Interestingly, a greater proportion of M1-like macrophages were seen when phenotyping BMDM vs M-HSV1716 (p = 0.0126, Figure 2E). Macrophage expression of MRC1 decreased from 51% to 32%, whilst the percentage of F4/80+ cells expressing IL12 within tumours increased from 48% to 74% following treatment with M-HSV1716 (Figure 2E). Additionally, M-HSV1716 mirrors the changes in CD8+ T cell numbers and phenotype which we have previously described (Figure 2F). These changes are not seen when macrophages alone are given. In view of this, we did not include macrophage controls for subsequent studies.
2.3. Equivalence of HSV1716 and M-HSV1716 in an Early Metastatic Model despite Decrease in Viral Load
To investigate whether M-HSV1716 could prevent the development of metastatic disease, an early metastatic model was performed [6]. In this study, a highly metastatic 4T1 cell line was used to model the aggressive nature of TNBC. Luciferase-labeled 4T1 cells were implanted into the left ventricle of female Balb/c mice. Five days later treatment was initiated, and animals were monitored regularly for tumour burden using an in vivo luminescent imaging system (IVIS) (Figure 3A). We have shown previously that multiple dosing of HSV1716 improved metastatic disease compared to single dosing [6]. Therefore, comparison with multi-dosing HSV1716 and M-HSV1716 was performed in this experiment. This consisted of 3 treatments given 48 h apart. A significant improvement in disease survival was seen in the HSV1716 and M-HSV1716 treatment groups as compared to controls (p < 0.0001, Figure 3B). At day 50 we saw no development of luciferase-measurable metastatic disease in either group (Figure 3C,D), suggesting that both regimes effectively prevented metastatic disease in this early setting.
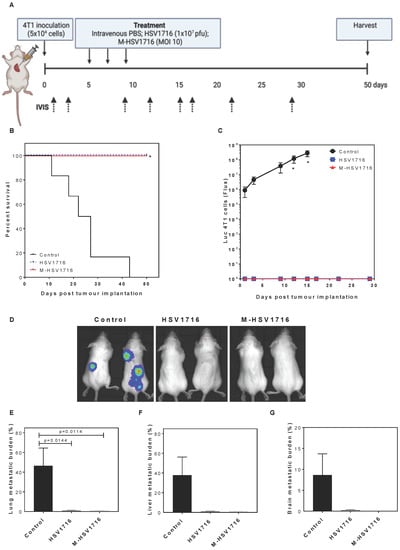
Figure 3.
M-HSV1716 is equivalent to intravenous HSV in an early metastatic model. Luciferase-labeled 4T1 cells were injected into the left ventricle of the heart via intracardiac injection of female Balb/C mice. At days 5, 7 and 9, mice were treated with PBS, HSV1716 (1 × 107 pfu/mL) or M-HSV1716 ((1 × 106 macrophages infected at MOI 10), and the development of metastases was monitored by IVIS up to day 50 (A). M-HSV1716 provided a survival advantage (B, Log-Rank test) corresponding with an absence of visible metastatic disease quantified by flux analysis of luciferase-expressing 4T1 cells (C,D). The burden of metastases was calculated as the percentage of the organ with metastatic involvement calculated as an average of 2–4 different sections of lung (E), liver (F) and brain (G), over 100 μm apart from 2–4 slides. Data shown are mean ± SEM, n = 4–6 animals. Panel A was created with BioRender.com, accessed on 6 October 2022.
Metastatic burden was quantified by H&E histological staining in the lung, liver and brain (Figure 3E–G). This confirmed that there was no metastatic disease in both the HSV1716 and the M-HSV1716 treatment arms.
2.4. Macrophage Mediated Delivery of HSV Improves Survival of Mice with Stereotactically Inserted Brain Metastases
Brain metastases pose a therapeutic challenge in TNBC. Once developed, these are often aggressive and difficult to treat systemically. As viruses are small, there is a potential they may cross the blood–brain barrier. We performed a survival model of an aggressive brain metastatic breast cancer cell line, inoculating luciferase-labeled brain-seeking 4T1 cells into the brain parenchyma of female Balb/c mice (Figure 4A). In this small study, n = 5 mice per group were implanted with tumours; once these were visible using IVIS (Figure 4B), mice were treated with intravenous treatments of either PBS control, IV HSV1716 or M-HSV1716 combination. Mice demonstrated a median survival time of 9, 14 and 15.5 days when treated with PBS, HSV1716 or M-HSV1716, respectively. Treatment with M-HSV1716 demonstrated a survival advantage when compared to control mice (p = 0.0167, Mantel–Cox test) (Figure 4C).
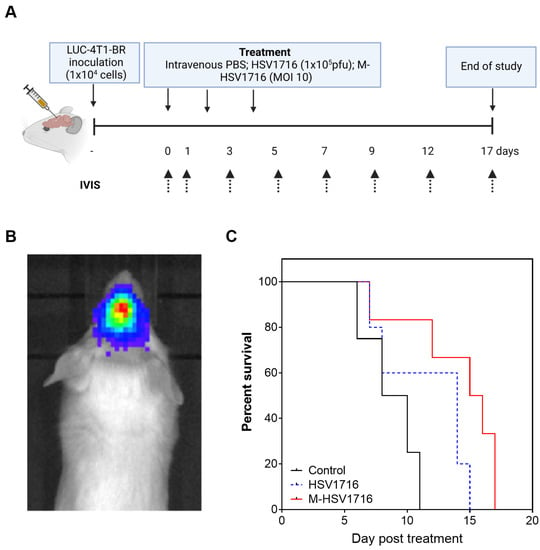
Figure 4.
M-HSV1716 improves survival of mice with stereotactically implanted brain metastases. A brain metastases model was formed by the inoculation of 1 × 104 LUC-4T1-BR cells intracranially, to a depth of 3 mm, using a Hamilton syringe. Animals were imaged until the intracranial lesion was visible and then treated with either PBS, HSV1716 or macrophage-HSV1716 (A). (B) A representative image of a brain metastases as seen on IVIS. (C) A Kaplan–Meier curve demonstrated a survival advantage with M-HSV1716 compared to other treatment groups (Log-Rank test). Mice were culled when tumours reached the maximum permitted size as determined by the IVIS, at which point tissues were harvested. Only mice treated with M-HSV1716 survived beyond day 15. Data shown are mean ± SEM, n = 5 animals. Panel A was created with BioRender.com, accessed on 6 October 2022.
3. Discussion
Understanding the immune system and enhancing immunotherapies is a topical area of research. Here we show that improvements in treatment efficacy are seen when macrophages are used to deliver an oncolytic viral immunotherapy to murine mammary tumours. Of particular interest is that the viral dose carried within macrophages was found to be 100-fold less than that of the intravenous dose and still showed similar efficacy. This has the potential of reducing a patient’s viral-associated off-target effects by both allowing for more-specific tumour targeting and enabling a lower dose of viral particles to be administered for the desired effect. Therefore, although there are costs involved in the production of M-HSV1716, these costs may be offset by a reduction in the dose of treatment required and the downstream costs of patient-related hospital admissions secondary to toxicities. One possible explanation of this finding could be related to the ability of some viruses to replicate within macrophages. Studies have shown that this occurs in pathological infections with viruses such as influenza [24] and HIV [25]. Indeed, we recently described how the oncolytic herpes virus HSV1716 has the ability replicate within MDM in vitro [6]. Perhaps this could account for the increased effectiveness of macrophage-delivered virus over virus alone, especially in view of the discrepancy in viral doses.
Nevertheless, cell delivery of anticancer drugs is a growing area of interest [17]. Research carried out by Muthana et al. [21,22], demonstrated the potential of cell carriers, namely macrophages, as vectors to deliver a prostate-specific adenovirus. Given that high numbers of macrophages are present in the hypoxic areas of prostate tumours, the researchers opted to exploit this and used macrophages to deliver OV to prostate tumours grown in spherical cell complexes that mimic the TME in vitro and in xenograft models of prostate cancer. The Macrophage–OV complex successfully delivered the virus to the tumours resulting in efficient viral replication under hypoxic conditions, tumour oncolysis and inhibition of tumour growth in mice. More importantly, when co-cultured with high-titre neutralising antibodies in human serum, the macrophages protected the virus, and this was significantly more effective compared to adenovirus on its own, which was completely neutralised [21].
As we know, high concentrations of virus are required for an efficacious anti-tumour response when delivered intravenously due to its rapid neutralisation by circulating antibodies and removal by the reticular endothelial system. However, our group has observed dose-dependent tolerability issues in murine models resulting in recoverable subacute piloerection, pallor and reduced mobility to death in the most severe cases. This phenomenon is seen in tumour-bearing mice only and is also dependent on mouse strain. The maximum tolerated dose of HSV1716 has been elucidated (unpublished observation) in these models, and we are confident that the shielding of viral epitopes by macrophage delivery negates immunosurveillance thus facilitating the use of lower doses resulting in the absence of observable toxicities. Both of these observations support the use of macrophages as vectors to improve viral delivery (Figure 5).
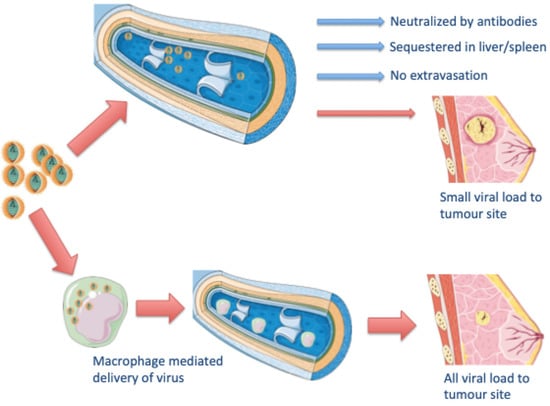
Figure 5.
Potential for M-HSV1716 in TNBC. A schematic representation of how macrophages with virus may be used to target breast cancer.
In other studies, improved tumour growth in vivo was shown when macrophages were used to transport chemotherapy particles, SN38, a derivative of irinotecan [26]. Another showed that loading M1-polarised macrophages with a sorafenib nanoparticle improved drug targeting and was effective at treating hepatocellular cancer in vitro and in vivo [27]. Furthermore, non-malignant disease areas are exploring the use of macrophage carriers to treat diseases such as atherosclerosis [28] and liver cirrhosis [29].
However, the reduction of breast tumours was not curative with virus alone. This suggests that perhaps virus alone is unable to stimulate a sufficient immune response despite improved delivery with macrophage carriers. Combination therapy of OV and established cancer therapeutics is of significant interest to a number of research groups. Of particular promise are the trials involving checkpoint inhibition and OV. For example, Bourgeois–Daigneault et al. [8] described the use of a rhabdovirus Maraba virus prior to the removal of a breast tumour in immunocompetent murine models. Here, they administered a course of intravenous OV treatment 7 days prior to mammary tumour resection, followed by an adjuvant course of checkpoint inhibitor treatment. They demonstrated that use of virotherapy prior to surgery allowed for sensitisation to immune checkpoint therapy given adjuvantly, and that on re-challenge, the immunological effects were long lasting [8]. Similarly, Mostafa et al. [30] demonstrated that the oncolytic effect of reovirus can be enhanced with the addition of a PD-1 inhibitor in an EMT6 immunocompetent murine model of breast cancer, causing a reduction in tumour growth in comparison to monotherapy, and this change resulted from cytotoxic changes in the TME including an increase in CD8+ cells and a decrease in CD4+ T cells. Given these promising preclinical data, there are a few ongoing clinical trials combining oncolytic viruses with a checkpoint inhibitor in breast cancer. Viruses under investigation at present include HSV, vaccinia and reovirus, with the likelihood that other viral groups will be included as data matures.
Another area this research highlights is the potential for targeting brain metastases. We show that macrophage-delivered treatment enhances the survival of animals treated for brain metastases. The potential to cross the blood–brain barrier, a clinically challenging niche, needs to be explored further. Macrophages have been used as carriers to effectively transport nanoparticles loaded within them to target gliomas in the brain [31]. Furthermore, some groups are exploring the use of macrophages as vector-carrying nanoparticles which enhance photo thermal ablative therapies to the brain [32,33].
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines
PyMT-TS1 [34] (a kind gift from Prof. Johanna Joyce, MSKCC, Manhattan, NY, USA), and LUC-4T1-BR [35] (obtained from Prof. Sanjay Srivastava, University of Texas, Austin, TX, USA) were used in vivo. Vero cells were purchased from the ATCC. Cells were maintained in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS. All cells were used within 20 passages and were cultured at 37 °C in 5% CO2. All cell lines were routinely tested for mycoplasma and microsatellite analysis. All culture reagents were purchased from Lonzo BioWhittaker Ltd.
4.2. Virus Production and Handling
HSV1716 was obtained from Virttu Biologics (Glasgow, UK) in stocks of 1 × 108 particle-forming units (PFU) in compound sodium lactate (Hartmann’s solution) with 10% glycerol. All vials were stored at −80 °C and freshly thawed on ice before each experiment.
4.3. Production of Murine Bone Marrow Derived Macrophages
Bone marrow was obtained from both femurs and tibias of Balb/C mice under aseptic conditions. The lower abdominal cavity and both hind limbs of animals were sprayed with 70% ethanol before tibias and femurs were isolated. Joints were taken from above the pelvis and the muscles removed by blunt dissection and then cleaned with sterile gauze. Femurs were transported in sterile PBS to the tissue culture lab, where they were washed in sterile 70% ethanol. The epiphyses of bones were cut, and the shafts of the bones were flushed with 1 mL of DMEM using a sterile 25G needle. The bone marrow was then centrifuged at 1000 rpm for 5 min. The pellet was resuspended and incubated in differentiation DMEM which contained 10% heat-inactivated FCS and 20% L929 cell-conditioned medium. Non-adherent cells were removed on day 5, and adherent cells were matured by incubating at 37 °C, 5% CO2 ready for infection on day 7.
4.4. HSV1716 Infection of Macrophages In Vitro
Virus was allowed to gradually thaw on ice. Cells were washed in PBS, and 500 μL serum free RMPI medium was added to each well followed by virus at the desired multiplicity of infection (MOI). Macrophages were incubated, at 37 °C, 5% CO2, with virus for 2 h and then free virus was removed by washing with PBS. M-HSV1716 complex was incubated for 2 more hours before use in experiments. Cells were analyses 24–48 h post infection.
4.5. Spheroids
For tumour spheroid experiments, 96-well plates were coated with DMEM containing aga rose prior to seeding with TS1 cells at 2 × 104 cells/well. Following incubation for 5 days and an approximate cell density of 105 cells, spheroids were inoculated with HSV1716 or M-HSV1716 at an MOI of 5. For these experiments HSV1716 GFP was used, and for controls, spheroids were either untreated or infiltrated with BMDM at a concentration of 1 × 105. Spheroids were monitored by light microscopy (Leica DM1000) at ×10 magnification. Flow cytometry as described above was used to assess cellular death and GFP infection on day 3 post-infection.
4.6. Flow Cytometric Studies
Dissociated mammary tumours were stained with fluorescent antibodies [36]. Cell viability was determined using the Zombie UV™ Fixable Viability Kit (Biolegend) and ABC™ Anti-Mouse Bead Kit (ThermoFisher Scientific, Loughborough, UK). The following antibodies were used: CD4 (cat no. 100510), CD8 (cat no. 100707), CD25 (cat no. 101909), CD279 (cat no. 109110), LY6-G (127616), F4/80 (AbD Serotec, cat no. MCA497A488, clone C1:A3-1), IL-12 (cat no 505207), GFP (Abcam, Cambridge, UK, cat no. ab290), TOPRO3, MRC1(Abcam, ab64693). All antibodies were purchased from Biolegend unless otherwise stated. All FACS data were analyzed on an LSR II flow cytometer (BD Biosciences, Wokingham, UK) and processed using Flow software (Tree Star, Texas, USA).
4.7. PCR
RNA was isolated from infected MDMs using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen) followed by cDNA synthesis using SuperScript III reverse transcriptase (Life Technologies, Paisley, UK). cDNA was analyzed using the following viral replication genes: ICP0 (Forward primer region AAGCTTGGATCCGAGCCCCGCCC, reverse primer region AAGCGGTGCACGGGAAGGT), ICP8 (Forward primer region GACATTACGTTCACGGCCTTCGAAGCCAG, reverse primer region GGCCGAGTTGGTGCTAAATACCATGGC) and gB (Forward primer region TGTGTACATGTCCCCGTTTTACG, reverse primer region GCGTAGAAGCCGTCAACCT) with GAPDH (forward primer region ACAGTTGCCATGTAGACC, reverse primer region TTTTTGGTTGAGCACAGG) as the housekeeping gene using SYBR Green (Primer Design, Chandler’s Ford, UK). q-PCR reaction was performed in a 384-well plate (three wells per gene and sample), and a 7900HT AbiPrism sequence detection system (Applied Biosystems) was used. The fold change in gene expression between treatment groups was analysed by inserting Ct values into Data Assist V3.01 software (Applied Biosystems), and changes in gene expression were only analysed for genes with a Ct value of ≤25.
4.8. Viral Quantification
As previously described, plaque assays were performed as described in Baer and Kehn-Hall [37]. Briefly, confluent monolayers of Vero cells were inoculated with serial dilutions of HSV1716 for 2 h. Following removal of the viral inoculum, monolayers were overlaid with 1:10 4% agarose:culture medium and allowed to solidify for 15 min at room temperature before the plate was moved to a humidified incubator (37 °C) for 72 h. A total of 4% PFA was applied to agarose plugs for 1–2 h to fix cell monolayers before their removal. Cells were washed with PBS, stained with 1 mL crystal violet for 5 min and rinsed with tap water. Once dried, plaques were counted per well and viral titre was determined.
4.9. In Vivo Studies
All animal procedures were carried out in accordance with the UK Animals Scientific Procedures Act 1986 and with the approval of the University of Sheffield Ethical Committee (PPL70/8670). All mice were obtained from Charles River Laboratory and acclimatised in the biological services laboratory for 7 days prior to the procedure. Animals were anesthetised using 3–4% isofluorane in 70:30% N20:02.
Primary mammary tumours: 1 × 106 PyMT TS1 in 50 μL of 1:1 matrigel:cells, were implanted into the 4th mammary fat pad of 6–7-week-old FVB mice (n = 10/group) as described in [6]. When tumours reached ~500 mm3, mice were randomly divided into groups and received a single injection of 100 µL PBS, 2 × 106 BMDMs, HSV1716 (1 × 107 PFU) or M-HSV1716 (1 × 106 macrophages infected at MOI 10) intravenously. Mice were culled on day 9 for postmortem comparison of tissues or when tumour volumes exceeded the maximum permitted size (1500 mm3) for survival studies. Excised tissues including tumours, brain, liver, lungs, kidney and spleen were embedded in paraffin wax for histological studies. Tumours were also digested, and single-cell suspensions were cryo-stored in 90% FBS and 10% DMSO for flow cytometry.
Metastatic model: 1 × 105 LUC 4T1 cells were filtered and injected via the intracardiac route into the left ventricle of female Balb/C mice as described in [6]. All animals were allowed to recover in a heated chamber. Animals were randomly allocated (n = 6/group) and received either PBS, 1 dose of HSV1716 (1 × 107) or 3 doses of HSV1716 (1 × 107) or M-HSV1716 ((1 × 106 macrophages infected at MOI 10)) given on day 1, 3 and 5). Animals were imaged weekly using the In Vivo Imaging Systems (IVIS Lumina II imaging, Caliper Life Sciences, Preston Brook, UK) following intra-peritoneal injection of luciferin (150 mg/kg). Mice were culled on reaching a humane end point (over 20% weight loss, respiratory distress, physical signs of discomfort) or after 50 days from treatment. Brain, liver, lungs, and spleen were embedded in paraffin wax for histological studies.
Brain metastatic model: Within a stereotactic frame, 1 × 104 LUC 4T1-BR cells were injected intracranially into female Balb/c mice. All animals were allowed to recover in a heated chamber. Animals were given 2 doses of analgesia via subcutaneous injection, metacam (5% solution with 20 µL injected subcutaneously), just prior to intracranial inoculation and at 24 h post recovery. Animals were also given a single dose of antibiotic (Baytril 2.5% solution for injection, diluted 1:10 in saline and injected 20 µL intramuscularly) just following the procedure.
When luminescence of an intracranial lesion was observed, animals received intravenous treatment of either control (PBS), 3 doses of HSV1716 (1 × 107) or M-HSV1716 ((1 × 105 macrophages infected at MOI 10). Animals were observed every 2–3 days with tumour growth progression visualised on the IVIS. All animals were culled if a humane end point was reached or after 26 days post first intracranial tumour implantation and brain and lung were cryopreserved in OCT freezing medium.
4.10. Tissue Analysis
Haematoxylin and Eosin staining was carried out to determine necrosis and metastasis in FFPE tissue (2–4 sections per sample, 10 microns thickness and 1000 microns apart). Slides visualised using the using Hamamatsu NanoZoomer XR (Hamamatsu, Hertfordshire, UK), and quantified using Image Scope (Leica Biosystems, Newcastle Upon Tyne, UK).
4.11. Statistics
All statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism 8, and the tests used are described in the Figure legends. Data are means ± SEMs, and p values of < 0.05 were considered to be significant.
5. Conclusions
Breast cancer is a heterogeneous disease, and although conventional treatments have evolved significantly over the past few years, treatment resistance invariably occurs. Training the immune system to recognize and target cancers has proved curative for select patients in a number of solid tumour types. The hallmark of response appears to be a favourable “inflammatory” TME. Oncolytic viruses are an expanding group of immunotherapeutics with the potential to enhance the TME. Here we show that macrophages may be able to further enhance their effect through improved delivery of virus. Future work involving the combination of M-HSV1716 with other chemotherapeutics or immunotherapies would enhance this study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.M. and A.K.; methodology, M.M., G.C.S., A.K. and P.D.O.; validation, A.K., F.H. and N.W.; formal analysis, A.K. and F.H.; investigation, A.K.; data curation F.H., N.W., A.K., A.J., E.A., R.A. and P.B.P.; writing—original draft preparation A.K. and F.H.; writing—review and editing, F.H., M.M., J.E.B., C.L., P.D.O., G.C.S., C.W., J.C., S.K.S. and S.J.D.; supervision, M.M., C.W. and S.J.D.; project administration, A.K.; funding acquisition, M.M., J.E.B., C.L. and A.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
We would like to thank CRUK (grant reference: C25574/A24321, A.K. & M.M.), Sheffield Teaching Hospitals (grant reference: 12053, M.M., J.E.B., C.L., A.K.) and Team Verrico (grant reference: MS/149394: A.K. and M.M.).
Institutional Review Board Statement
All animal procedures were carried out in accordance with the UK Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act 1986 and with the approval of the University of Sheffield Ethical Committee (PPL70/8670).
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
Thank you to Johanna Joyce (MSKCC, USA) for providing the TS1 cell lines. We are also grateful to Virttu Biologics/Sorrento for providing the HSV1716 for this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, S.; Brion, R.; Lintunen, M.; Kronqvist, P.; Sandholm, J.; Mönkkönen, J.; Kellokumpu-Lehtinen, P.-L.; Lauttia, S.; Tynninen, O.; Joensuu, H.; et al. Human breast cancer cells educate macrophages toward the M2 activation status. Breast Cancer Res. 2015, 17, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.-Y.; Luo, R.-Z.; Peng, R.-J.; Wang, S.-S.; Xue, C. High infiltration of tumor-associated macrophages in triple-negative breast cancer is associated with a higher risk of distant metastasis. OncoTargets Ther. 2014, 7, 1475–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Heide, D.; Weiskirchen, R.; Bansal, R. Therapeutic Targeting of Hepatic Macrophages for the Treatment of Liver Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belgiovine, C.; Digifico, E.; Anfray, C.; Ummarino, A.; Andón, F.T. Targeting Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Anti-Cancer Therapies: Convincing the Traitors to Do the Right Thing. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, A.; Winder, N.; Atkinson, E.; Al-Janabi, H.; Allen, R.J.; Hughes, R.; Moamin, M.; Louie, R.; Evans, D.; Hutchinson, M.; et al. Macrophages Mediate the Antitumor Effects of the Oncolytic Virus HSV1716 in Mammary Tumors. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2021, 20, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andtbacka, R.H.; Kaufman, H.L.; Collichio, F.; Amatruda, T.; Senzer, N.; Chesney, J.; Delman, K.A.; Spitler, L.E.; Puzanov, I.; Agarwala, S.S.; et al. Talimogene Laherparepvec Improves Durable Response Rate in Patients With Advanced Melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2780–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgeois-Daigneault, M.-C.; Roy, D.G.; Aitken, A.S.; El Sayes, N.; Martin, N.T.; Varette, O.; Falls, T.; St-Germain, L.E.; Pelin, A.; Lichty, B.D.; et al. Neoadjuvant oncolytic virotherapy before surgery sensitizes triple-negative breast cancer to immune checkpoint therapy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaao1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramante, S.; Koski, A.; Liikanen, I.; Vassilev, L.; Oksanen, M.; Siurala, M.; Heiskanen, R.; Hakonen, T.; Joensuu, T.; Kanerva, A.; et al. Oncolytic virotherapy for treatment of breast cancer, including triple-negative breast cancer. OncoImmunology 2016, 5, e1078057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, S.; Chen, C.-H.; Gao, S.; Lou, E.; Fujisawa, S.; Carson, J.; Nnoli, J.E.; Chou, T.-C.; Bromberg, J.; Fong, Y. Role of MAPK in oncolytic herpes viral therapy in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 2014, 21, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, S.; Marano, A.; Chen, N.G.; Aguilar, R.J.; Frentzen, A.; Chen, C.-H.; Lou, E.; Fujisawa, S.; Eveno, C.; Belin, L.; et al. A novel vaccinia virus with dual oncolytic and anti-angiogenic therapeutic effects against triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 148, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, M.; Seshadri, M.; Komorowski, M.P.; Abrams, S.I.; Kozbor, D. Targeting CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling with oncolytic virotherapy disrupts tumor vasculature and inhibits breast cancer metastases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E1291–E1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.C.; Coffin, R.S.; Davis, C.J.; Graham, N.J.; Groves, N.; Guest, P.J.; Harrington, K.J.; James, N.D.; Love, C.A.; McNeish, I.; et al. A Phase I Study of OncoVEXGM-CSF, a Second-Generation Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Virus Expressing Granulocyte Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 6737–6747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Li, Y.; Cui, Y.; Li, S.; Zhu, Y.; Shang, C.; Song, G.; Liu, Z.; Xiu, Z.; Cong, J.; et al. Anti-tumour effects of a dual cancer-specific oncolytic adenovirus on Breast Cancer Stem cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, M.S.; Lemoine, N.; Wang, Y. Systemic Delivery of Oncolytic Viruses: Hopes and Hurdles. Adv. Virol. 2012, 2012, 805629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.; Bell, J. Cell carriers for oncolytic viruses: Current challenges and future directions. Oncolytic Virother. 2013, 2, 47–56. [Google Scholar]
- Willmon, C.; Harrington, K.; Kottke, T.; Prestwich, R.; Melcher, A.; Vile, R. Cell Carriers for Oncolytic Viruses: Fed Ex for Cancer Therapy. Mol. Ther. 2009, 17, 1667–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingle, L.; Brown, N.; Lewis, C.E. The role of tumour-associated macrophages in tumour progression: Implications for new anticancer therapies. J. Pathol. 2002, 196, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medrek, C.; Pontén, F.; Jirström, K.; Leandersson, K. The presence of tumor associated macrophages in tumor stroma as a prognostic marker for breast cancer patients. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.B.; Yeh, E.S.; Soloff, A.C. Tumor-associated macrophages: Unwitting accomplices in breast cancer malignancy. npj Breast Cancer 2016, 2, 15025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthana, M.; Giannoudis, A.; Scott, S.D.; Fang, H.-Y.; Coffelt, S.B.; Morrow, F.J.; Murdoch, C.; Burton, J.; Cross, N.; Burke, B.; et al. Use of Macrophages to Target Therapeutic Adenovirus to Human Prostate Tumors. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 1805–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthana, M.; Rodrigues, S.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Welford, A.; Hughes, R.; Tazzyman, S.; Essand, M.; Morrow, F.; Lewis, C.E. Macrophage Delivery of an Oncolytic Virus Abolishes Tumor Regrowth and Metastasis after Chemotherapy or Irradiation. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.Q.; Zhang, L.; Ohba, K.; Ye, M.; Ichiyama, K.; Yamamoto, N. Macrophage response to oncolytic paramyxoviruses potentiates virus-mediated tumor cell killing. Eur. J. Immunol. 2016, 46, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cline, T.D.; Beck, D.; Bianchini, E. Influenza virus replication in macrophages: Balancing protection and pathogenesis. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 2401–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, S.M.; Greenwell-Wild, T.; Peng, G.; Ma, G.; Orenstein, J.M. Viral and host cofactors facilitate HIV-1 replication in macrophages. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2003, 74, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Sun, X.; Liu, X.; Shen, Y.; Wang, K. Macrophages as an active tumour-targeting carrier of SN38-nanoparticles for cancer therapy. J. Drug Target. 2017, 26, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.; Wang, T.; Mu, W.; Yang, R.; Liang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, S.; Gao, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, N. Nanoparticle-Loaded Polarized-Macrophages for Enhanced Tumor Targeting and Cell-Chemotherapy. Nano-Micro Lett. 2020, 13, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Huang, Q.; Liu, C.; Kwong, C.H.T.; Yue, L.; Wan, J.-B.; Lee, S.M.Y.; Wang, R. Treatment of atherosclerosis by macrophage-biomimetic nanoparticles via targeted pharmacotherapy and sequestration of proinflammatory cytokines. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroni, F.; Dwyer, B.J.; Graham, C.; Pass, C.; Bailey, L.; Ritchie, L.; Mitchell, D.; Glover, A.; Laurie, A.; Doig, S.; et al. Safety profile of autologous macrophage therapy for liver cirrhosis. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1560–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, A.A.; Meyers, D.E.; Thirukkumaran, C.M.; Liu, P.J.; Gratton, K.; Spurrell, J.; Shi, Q.; Thakur, S.; Morris, D.G. Oncolytic Reovirus and Immune Checkpoint Inhibition as a Novel Immunotherapeutic Strategy for Breast Cancer. Cancers 2018, 10, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.; Qin, J.; Han, L.; Zhao, W.; Liang, J.; Xie, Z.; Yang, P.; Wang, J. Exploiting macrophages as targeted carrier to guide nanoparticles into glioma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 37081–37091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christie, C.; Madsen, S.J.; Peng, Q.; Hirschberg, H. Macrophages as nanoparticle delivery vectors for photothermal therapy of brain tumors. Ther. Deliv. 2015, 6, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen, S.J.; Christie, C.; Hong, S.J.; Trinidad, A.; Peng, Q.; Uzal, F.A.; Hirschberg, H. Nanoparticle-loaded macrophage-mediated photothermal therapy: Potential for glioma treatment. Lasers Med. Sci. 2015, 30, 1357–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shree, T.; Olson, O.C.; Elie, B.T.; Kester, J.C.; Garfall, A.L.; Simpson, K.; Bell-McGuinn, K.M.; Zabor, E.C.; Brogi, E.; Joyce, J.A. Macrophages and cathepsin proteases blunt chemotherapeutic response in breast cancer. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 2465–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjan, A.; Gupta, P.; Srivastava, S.K. Penfluridol: An Antipsychotic Agent Suppresses Metastatic Tumor Growth in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer by Inhibiting Integrin Signaling Axis. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 877–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R.; Qian, B.-Z.; Rowan, C.; Muthana, M.; Keklikoglou, I.; Olson, O.C.; Tazzyman, S.; Danson, S.; Addison, C.; Clemons, M.; et al. Perivascular M2 Macrophages Stimulate Tumor Relapse after Chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 3479–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baer, A.; Kehn-Hall, K. Viral Concentration Determination Through Plaque Assays: Using Traditional and Novel Overlay Systems. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 93, e52065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).