An Investigation into the Impact of a Glutaminase Inhibitor, Compound 968, on Nrf2 Signaling
Abstract
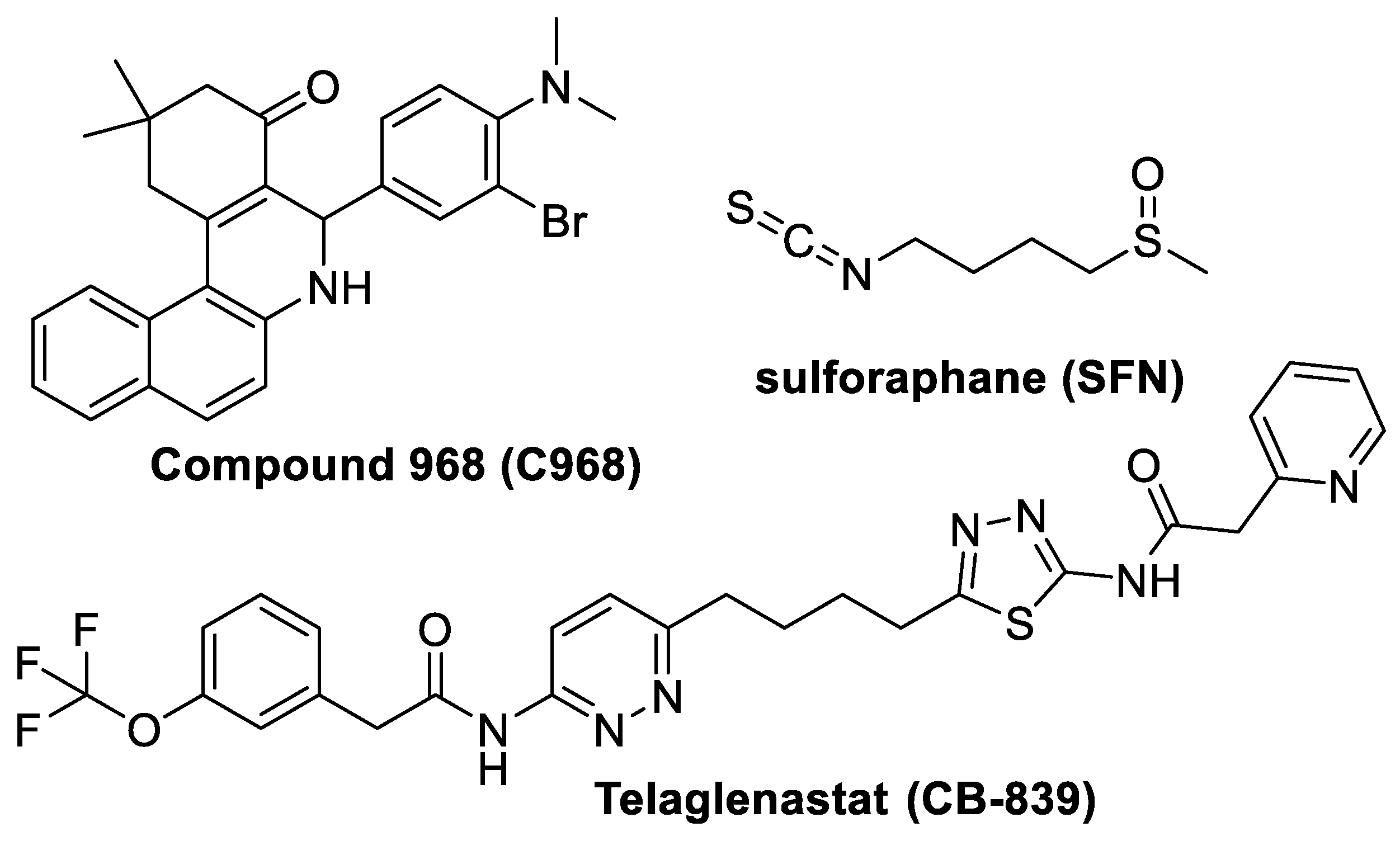
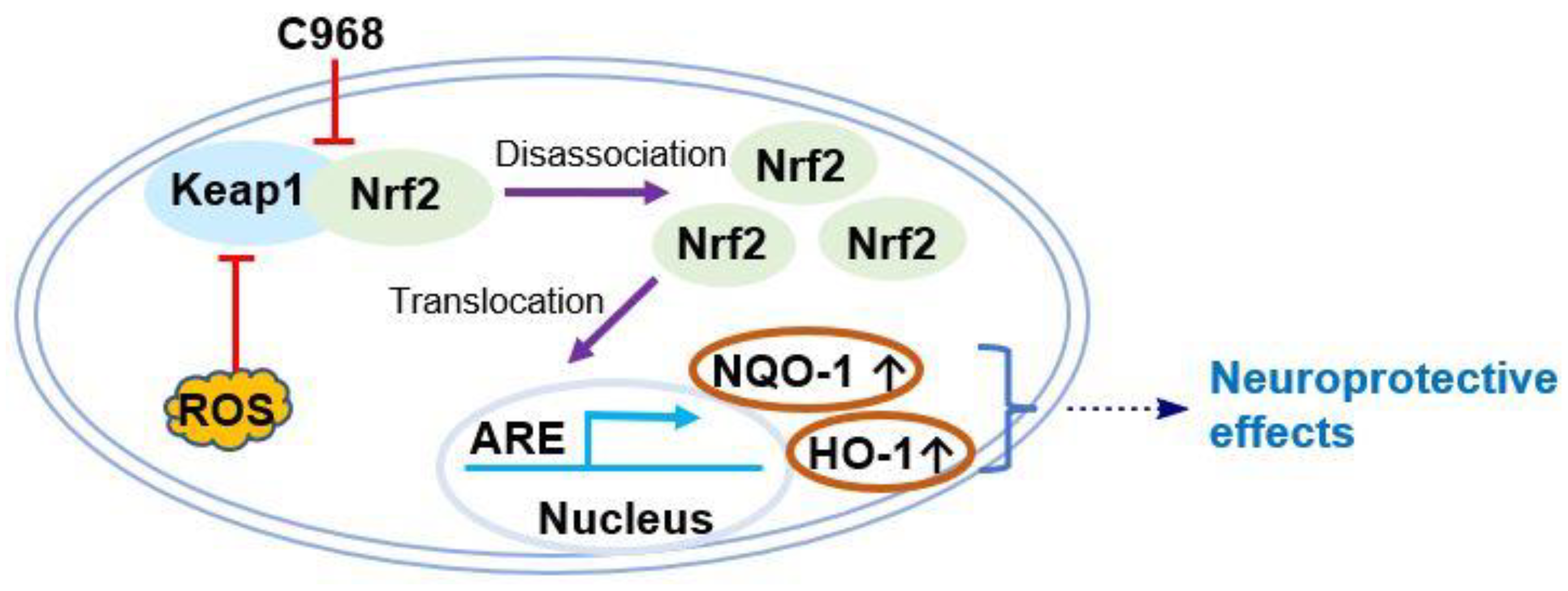
:1. Introduction
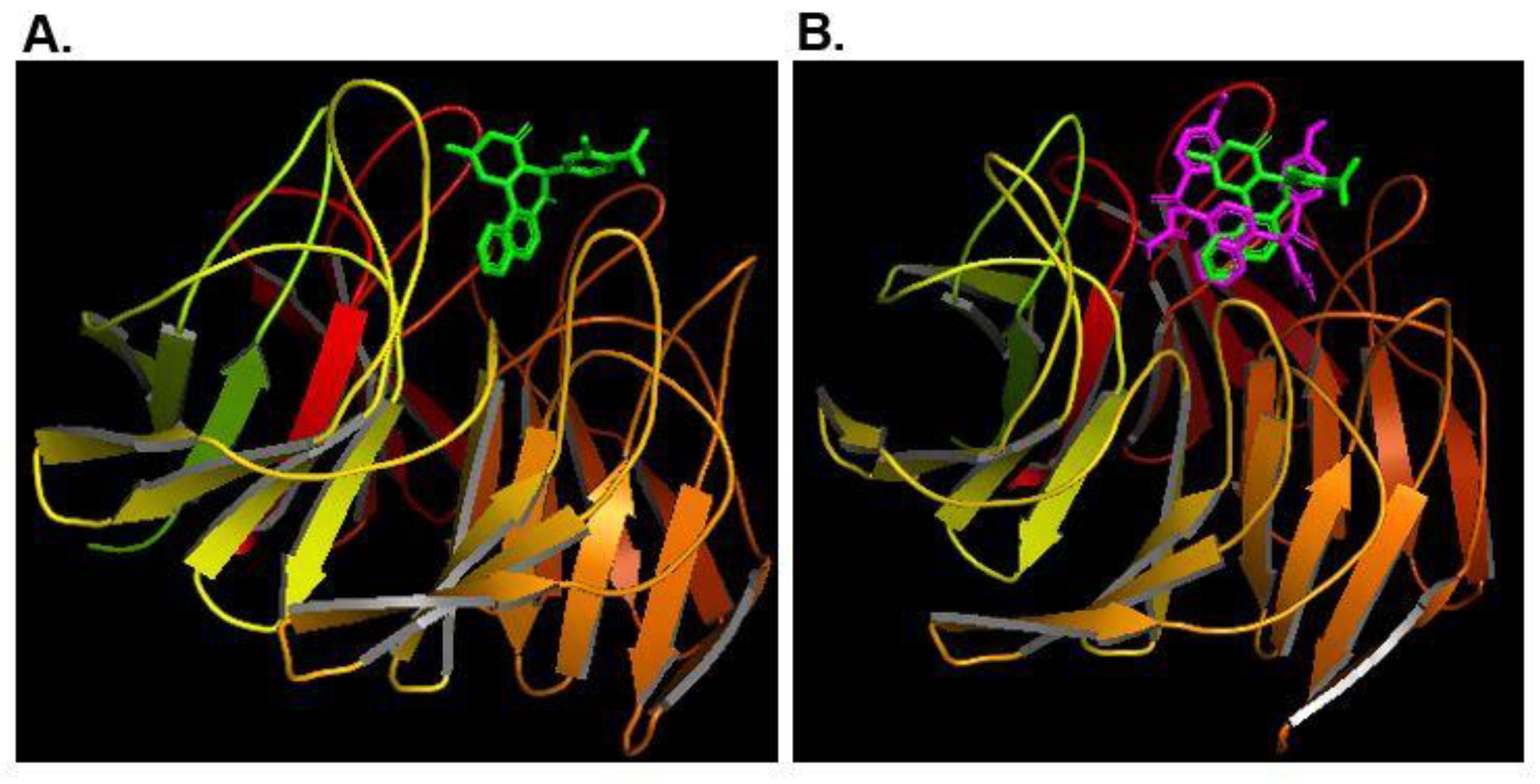
2. Materials and Methods
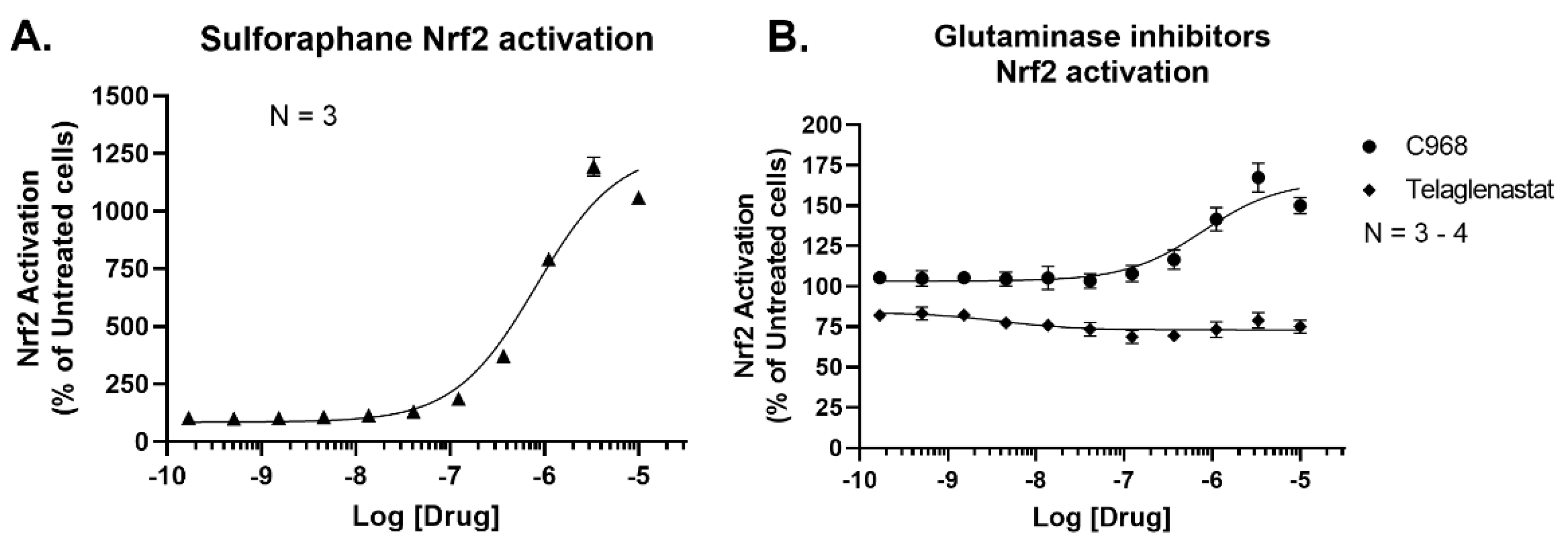
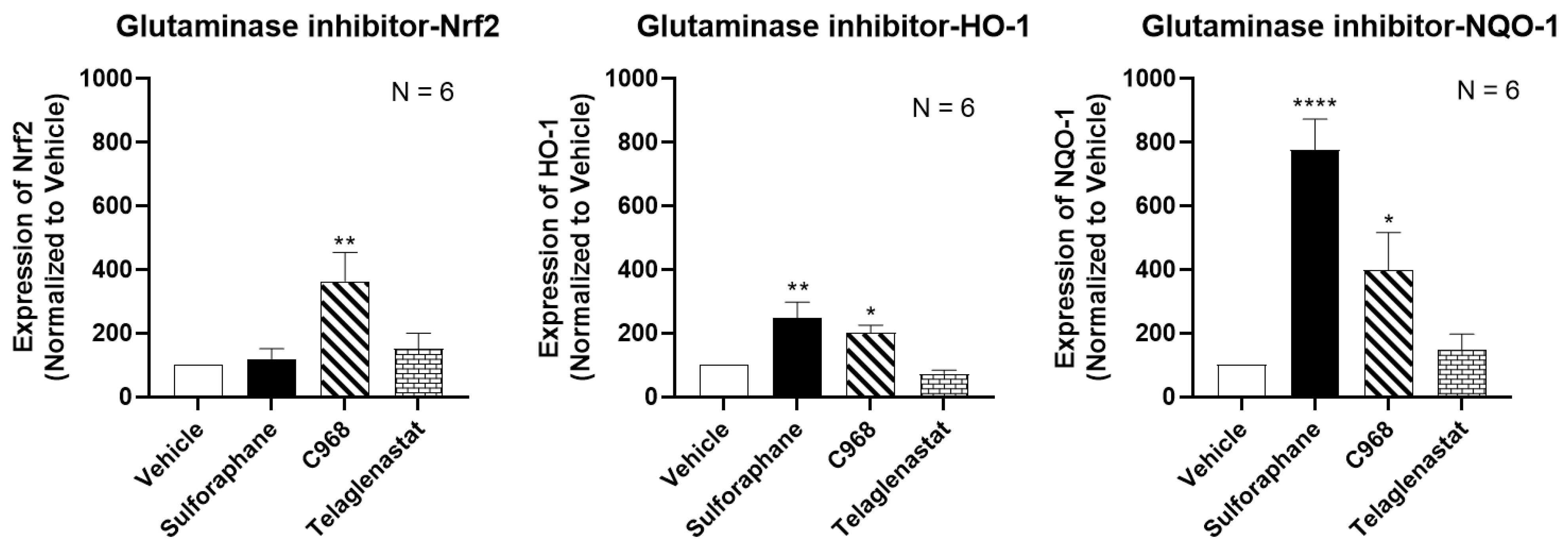
3. Results and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, P.; Malik, D.; Perkons, N.; Huangyang, P.; Khare, S.; Rhoades, S.; Gong, Y.-Y.; Burrows, M.; Finan, J.M.; Nissim, I.; et al. Targeting glutamine metabolism slows soft tissue sarcoma growth. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.-B.; Erickson, J.W.; Fuji, R.; Ramachandran, S.; Gao, P.; Dinavahi, R.; Wilson, K.F.; Andre, L.B.A.; Dias, S.M.G.; Dang, C.V.; et al. Targeting mitochondrial glutaminase activity inhibits oncogenic transformation. Cancer Cell 2010, 18, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Masisi, B.K.; El Ansari, R.; Alfarsi, L.; Rakha, E.A.; Green, A.R.; Craze, M.L. The role of glutaminase in cancer. Histopathology 2020, 76, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, L.M.; Lagies, S.; Klar, R.F.U.; Hussung, S.; Fritsch, R.; Kammerer, B.; Wittel, U.A. Metabolic Profiling of Early and Late Recurrent Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Using Patient-Derived Organoid Cultures. Cancers 2020, 12, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altman, B.J.; Stine, Z.E.; Dang, C.V. From Krebs to clinic: Glutamine metabolism to cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 619–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.; Kim, S.-H.; Im, C.Y.; Hwang, H.-J. Recent Development of Small Molecule Glutaminase Inhibitors. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Márquez, J.; Martín-Rufián, M.; Segura, J.A.; Matés, J.M.; Campos-Sandoval, J.A.; Alonso, F.J. Brain glutaminases. Biomol. Concepts 2010, 1, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, R.; Wu, B.; Lanoha, B.; Tong, Z.; Peer, J.; Liu, J.; Xiong, H.; Huang, Y.; et al. Glutaminase C overexpression in the brain induces learning deficits, synaptic dysfunctions, and neuroinflammation in mice. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 66, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Xu, X.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Xia, X.; Zheng, J.C. Glutaminase in microglia: A novel regulator of neuroinflammation. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 92, 139–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Bonay, M.; Vanhee, V.; Vinit, S.; Deramaudt, T.B. Comparative effectiveness of 4 natural and chemical activators of Nrf2 on inflammation, oxidative stress, macrophage polarization, and bactericidal activity in an in vitro macrophage infection model. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajares, M.; Jiménez-Moreno, N.; García-Yagüe, Á.J.; Escoll, M.; de Ceballos, M.L.; van Leuven, F.; Rábano, A.; Yamamoto, M.; Rojo, A.I.; Cuadrado, A. Transcription factor NFE2L2/NRF2 is a regulator of macroautophagy genes. Autophagy 2016, 12, 1902–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Villavicencio, T.F.; Quintanilla, R. Contribution of the Nrf2 Pathway on Oxidative Damage and Mitochondrial Failure in Parkinson and Alzheimer’s Disease. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajares, M.; Jiménez-Moreno, N.; Dias, I.H.; Debelec, B.; Vucetic, M.; Fladmark, K.E.; Basaga, H.; Ribaric, S.; Milisav, I.; Cuadrado, A. Redox control of protein degradation. Redox Biol. 2015, 6, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cuadrado, A.; Rojo, A.I.; Wells, G.; Hayes, J.D.; Cousin, S.P.; Rumsey, W.L.; Attucks, O.C.; Franklin, S.; Levonen, A.-L.; Kensler, T.W.; et al. Therapeutic targeting of the NRF2 and KEAP1 partnership in chronic diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 295–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sayin, V.I.; LeBoeuf, S.E.; Singh, S.X.; Davidson, S.M.; Biancur, D.; Guzelhan, B.S.; Alvarez, S.W.; Wu, W.L.; Karakousi, T.R.; Zavitsanou, A.M.; et al. Activation of the NRF2 antioxidant program generates an imbalance in central carbon metabolism in cancer. eLife 2017, 6, e28083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Talalay, P.; Cho, C.G.; Posner, G.H. A major inducer of anticarcinogenic protective enzymes from broccoli: Isolation and elucidation of structure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 2399–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.D.; Hannink, M. Distinct cysteine residues in Keap1 are required for Keap1-dependent ubiquitination of Nrf2 and for stabilization of Nrf2 by chemopreventive agents and oxidative stress. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 8137–8151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holmström, K.M.; Kostov, R.V.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T. The multifaceted role of Nrf2 in mitochondrial function. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2016, 1, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katt, W.; Ramachandran, S.; Erickson, J.W.; Cerione, R.A. Dibenzophenanthridines as inhibitors of glutaminase C and cancer cell proliferation. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marcotte, D.; Zeng, W.; Hus, J.-C.; McKenzie, A.; Hession, C.; Jin, P.; Bergeron, C.; Lugovskoy, A.; Enyedy, I.; Cuervo, H.; et al. Small molecules inhibit the interaction of Nrf2 and the Keap1 Kelch domain through a non-covalent mechanism. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 4011–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Motohashi, H.; Yamamoto, M. Toward clinical application of the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 34, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hur, W.; Gray, N.S. Small molecule modulators of antioxidant response pathway. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2011, 15, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Lu, M.-C.; Xu, L.; Yang, T.-T.; Xi, M.-Y.; Xu, X.-L.; Guo, X.-K.; Zhang, X.-J.; You, Q.-D.; Sun, H.-P. Discovery of potent Keap1-Nrf2 protein-protein interaction inhibitor based on molecular binding determinants analysis. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 2736–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-Chamorro, P.; Redondo, A.; Riego, G.; Leánez, S.; Pol, O. Sulforaphane Inhibited the Nociceptive Responses, Anxiety- and Depressive-Like Behaviors Associated With Neuropathic Pain and Improved the Anti-allodynic Effects of Morphine in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, H.K.; Olayanju, A.; Goldring, C.E.; Park, B.K. The Nrf2 cell defence pathway: Keap1-dependent and-independent mechanisms of regulation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 85, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lei, W.; Kliebe, V.M.; Chen, X. An Investigation into the Impact of a Glutaminase Inhibitor, Compound 968, on Nrf2 Signaling. Future Pharmacol. 2021, 1, 41-47. https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol1010004
Lei W, Kliebe VM, Chen X. An Investigation into the Impact of a Glutaminase Inhibitor, Compound 968, on Nrf2 Signaling. Future Pharmacology. 2021; 1(1):41-47. https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol1010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleLei, Wei, Valentin M. Kliebe, and Xin Chen. 2021. "An Investigation into the Impact of a Glutaminase Inhibitor, Compound 968, on Nrf2 Signaling" Future Pharmacology 1, no. 1: 41-47. https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol1010004
APA StyleLei, W., Kliebe, V. M., & Chen, X. (2021). An Investigation into the Impact of a Glutaminase Inhibitor, Compound 968, on Nrf2 Signaling. Future Pharmacology, 1(1), 41-47. https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol1010004







