Electron Spin Resonance Spectroscopy Suitability for Investigating the Oxidative Stability of Non-Alcoholic Beers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Beer Samples
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. ESR Spin-Trapping Experiments
2.4. DPPH Assay
2.5. ThioBarbituric Index (TBI)
2.6. Data Elaboration and Multivariate Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Radical Scavenging Activity (RSA)
3.2. Total Phenolic Compounds (TPC)
3.3. ThioBarbituric Index (TBI)
3.4. ESR Spin Trapping Experiments
3.5. Multivariate Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABV | Alcohol content by Volume |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| DPPH | 2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl |
| DTE | Days to Expiration |
| EC50 | Half maximal Effective Concentration |
| ESR | Electron Spin Resonance |
| I150 | Intensity at 150 min |
| NAB | Non-alcoholic Beer |
| NABLAB | Non-alcoholic and Low-alcohol Beer |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| PBN | N-tert-Butyl-α-phenylnitrone |
| RDS | Refractometric Dry Substance |
| TBI | ThioBarbituric Index |
| TPC | Total Phenolic Compounds |
References
- Waehning, N.; Wells, V.K. Product, individual and environmental factors impacting the consumption of no and low alcoholic drinks: A systematic review and future research agenda. Food Qual. Prefer. 2024, 117, 105163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K. The emergence of lower-alcohol beverages: The case of beer. J. Wine Econ. 2023, 18, 66–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katainen, A.; Uusitalo, L.; Saarijärvi, H.; Erkkola, M.; Rahkonen, O.; Lintonen, T.; Fogelholm, M.; Nevalainen, J. Who buys non-alcoholic beer in Finland? Sociodemographic characteristics and associations with regular beer purchases. Int. J. Drug Policy 2023, 113, 103962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gliszczyńska-Świgło, A.; Klimczak, I.; Klensporf-Pawlik, D.; Rybicka, I. Quality characteristics and consumer perception of non-alcoholic beers in the context of responsible alcohol consumption. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 7145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Alcohol Action Plan 2022–2030; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024.
- Kokole, D.; Jané Llopis, E.; Anderson, P. Non-alcoholic beer in the European Union and UK: Availability and apparent consumption. Drug Alcohol Rev. 2022, 41, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackmore, H.; Hidrio, C.; Yeomans, M.R. How sensory and hedonic expectations shape perceived properties of regular and non-alcoholic beer. Food Qual. Prefer. 2022, 99, 104562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gernat, D.C.; Brouwer, E.; Ottens, M. Aldehydes as Wort Off-Flavours in Alcohol-Free Beers—Origin and Control. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2020, 13, 195–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, I.; Yang, Q.; Fisk, I.; Ford, R. Understanding the sensory and physicochemical differences between commercially produced non-alcoholic lagers, and their influence on consumer liking. Food Chem. X 2021, 9, 100114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rettberg, N.; Lafontaine, S.; Schubert, C.; Dennenlöhr, J.; Knoke, L.; Diniz Fischer, P.; Fuchs, J.; Thörner, S. Effect of Production Technique on Pilsner-Style Non-Alcoholic Beer (NAB) Chemistry and Flavor. Beverages 2022, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staub, C.; Contiero, R.; Bosshart, N.; Siegrist, M. You are what you drink: Stereotypes about consumers of alcoholic and non-alcoholic beer. Food Qual. Prefer. 2022, 101, 104633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quain, D.E. The enhanced susceptibility of alcohol-free and low alcohol beers to microbiological spoilage: Implications for draught dispense. J. Inst. Brew. 2021, 127, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, M.; Collin, S. Why Oxidation Should Be Still More Feared in NABLABs: Fate of Polyphenols and Bitter Compounds. Beverages 2022, 8, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piornos, J.A.; Koussissi, E.; Balagiannis, D.P.; Brouwer, E.; Parker, J.K. Alcohol-free and low-alcohol beers: Aroma chemistry and sensory characteristics. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2023, 22, 233–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salanță, L.C.; Coldea, T.E.; Ignat, M.V.; Pop, C.R.; Tofană, M.; Mudura, E.; Borșa, A.; Pasqualone, A.; Zhao, H. Non-Alcoholic and Craft Beer Production and Challenges. Processes 2020, 8, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozłowski, R.; Dziedziński, M.; Stachowiak, B.; Kobus-Cisowska, J. Non- and low-alcoholic beer—Popularity and manufacturing techniques. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2021, 20, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montanari, L.; Marconi, O.; Mayer, H.; Fantozzi, P. 6—Production of Alcohol-Free Beer. In Beer in Health and Disease Prevention; Preedy, V.R., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2009; pp. 61–75. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, C.; Neves, L.E.; Gomes, L.; Guimarães, M.; Ghesti, G. Processes for alcohol-free beer production: A review. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 40, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilarski, D.W.; Gerogiorgis, D.I. Progress and modelling of cold contact fermentation for alcohol-free beer production: A review. J. Food Eng. 2020, 273, 109804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perpète, P.; Collin, S. Influence of beer ethanol content on the wort flavour perception. Food Chem. 2000, 71, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, L.; Nikulin, J.; Juvonen, R.; Krogerus, K.; Magalhães, F.; Mikkelson, A.; Nuppunen-Puputti, M.; Sohlberg, E.; de Francesco, G.; Perretti, G.; et al. Sourdough cultures as reservoirs of maltose-negative yeasts for low-alcohol beer brewing. Food Microbiol. 2021, 94, 103629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myncke, E.; Vanderputten, D.; Laureys, D.; Huys, J.; Schlich, J.; Van Opstaele, F.; Schouteten, J.J.; De Clippeleer, J. Navigating yeast selection for NABLAB production: Comparative study of commercial maltose- and maltotriose-negative strains. Food Chem. 2025, 477, 143486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maust, A.; Sen, R.; Lafontaine, S. Exploring Non-traditional Yeast for Flavor Innovation in Non-Alcoholic Beer. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 5, 2007–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canonico, L.; Agarbati, A.; Comitini, F.; Ciani, M. Unravelling the potential of non-conventional yeasts and recycled brewers spent grains (BSG) for non-alcoholic and low alcohol beer (NABLAB). LWT 2023, 190, 115528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gernat, D.C.; Brouwer, E.R.; Faber-Zirkzee, R.C.; Ottens, M. Flavour-improved alcohol-free beer—Quality traits, ageing and sensory perception. Food Bioprod. Process. 2020, 123, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.; Bellut, K.; Tippmann, J.; Becker, T. Physical Methods for Dealcoholization of Beverage Matrices and their Impact on Quality Attributes. ChemBioEng Rev. 2017, 4, 310–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Francesco, G.; Marconi, O.; Sileoni, V.; Freeman, G.; Lee, E.G.; Floridi, S.; Perretti, G. Influence of the dealcoholisation by osmotic distillation on the sensory properties of different beer types. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 1488–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosi, A.; Motke, M.B.; Souza-Silva, É.A.; Zini, C.A.; McCutcheon, J.R.; Cardozo, N.S.M.; Tessaro, I.C. Beer dealcoholization by forward osmosis diafiltration. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 63, 102371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melton, L. Synbio salvages alcohol-free beer. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauwens, J.; Van Opstaele, F.; Karatairis, C.; Weiland, F.; Eggermont, L.; Jaskula-Goiris, B.; De Rouck, G.; De Brabanter, J.; Aerts, G.; De Cooman, L. Assessing the ageing process of commercial non-alcoholic beers in comparison to their lager beer counterparts. J. Inst. Brew. 2022, 128, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, A.; Nomura, Y.; Iwata, H. Sensitive Measurement of Thermal Stress in Beer and Beer-Like Beverages Utilizing the 2-Thiobarbituric Acid (TBA) Reaction. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2011, 69, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, M.; Suga, S.; Ono, M. Improvement for Oxidative Flavor Stability of Beer—Rapid Prediction Method for Beer Flavor Stability by Electron Spin Resonance Spectroscopy. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 1996, 54, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huvaere, K.; Andersen, M.L. 101—Beer and ESR Spin Trapping. In Beer in Health and Disease Prevention; Preedy, V.R., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2009; pp. 1043–1053. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, I.M.; Carvalho, D.O.; Guido, L.F. Impact of storage conditions on the oxidative stability of beer. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2023, 249, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chair, D.B.; Baker, B.; Bosben, S.; Bradshaw, T.; Converse, E.; Daar, A.; Garner, R.; Giarratano, C.; Gonzalez, S.; Hight, H.; et al. Standard Method for Measurement of Oxidative Resistance of Beer by Electron Paramagnetic Resonance. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2008, 66, 259–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, L.; Hernandez, E.M.; William, A.; Foster Ii, R.T. Advancing Flavor Stability Improvements in Different Beer Types Using Novel Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Area and Forced Beer Aging Methods. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2017, 75, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcu, M.C.; Fadda, A.; Sanna, D. Relationship among EPR oxidative stability and spectrophotometric parameters connected to antioxidant activity in beer samples. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2024, 250, 2123–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcu, M.C.; Fadda, A.; Sanna, D. Lag Time Determinations in Beer Samples. Influence of Alcohol and PBN Concentration in EPR Spin Trapping Experiments. Oxygen 2022, 2, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Krofta, K.; Mikyška, A.; Hašková, D. Antioxidant Characteristics of Hops and Hop Products. J. Inst. Brew. 2008, 114, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świeca, M.; Gawlik-Dziki, U.; Kowalczyk, D.; Złotek, U. Impact of germination time and type of illumination on the antioxidant compounds and antioxidant capacity of Lens culinaris sprouts. Sci. Hortic. 2012, 140, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.J.; Chang, S.K.C. A Comparative Study on Phenolic Profiles and Antioxidant Activities of Legumes as Affected by Extraction Solvents. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, S159–S166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanna, V.; Pretti, L. Effect of wine barrel ageing or sapa addition on total polyphenol content and antioxidant activities of some Italian craft beers. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauwens, J.; Van Opstaele, F.; Eggermont, L.; Weiland, F.; Jaskula-Goiris, B.; De Rouck, G.; De Brabanter, J.; Aerts, G.; De Cooman, L. Comprehensive analytical and sensory profiling of non-alcoholic beers and their pale lager beer counterparts. J. Inst. Brew. 2021, 127, 385–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
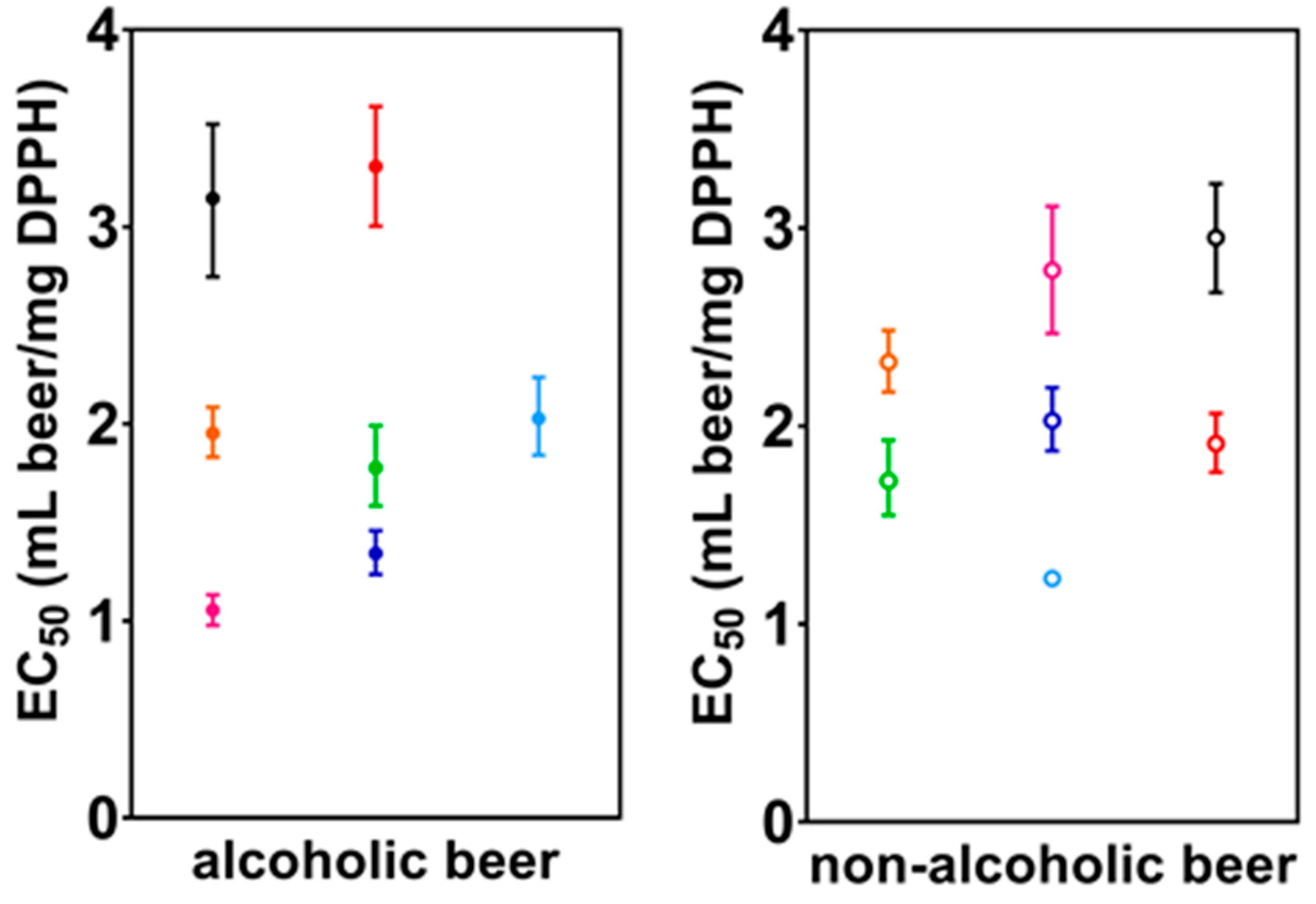
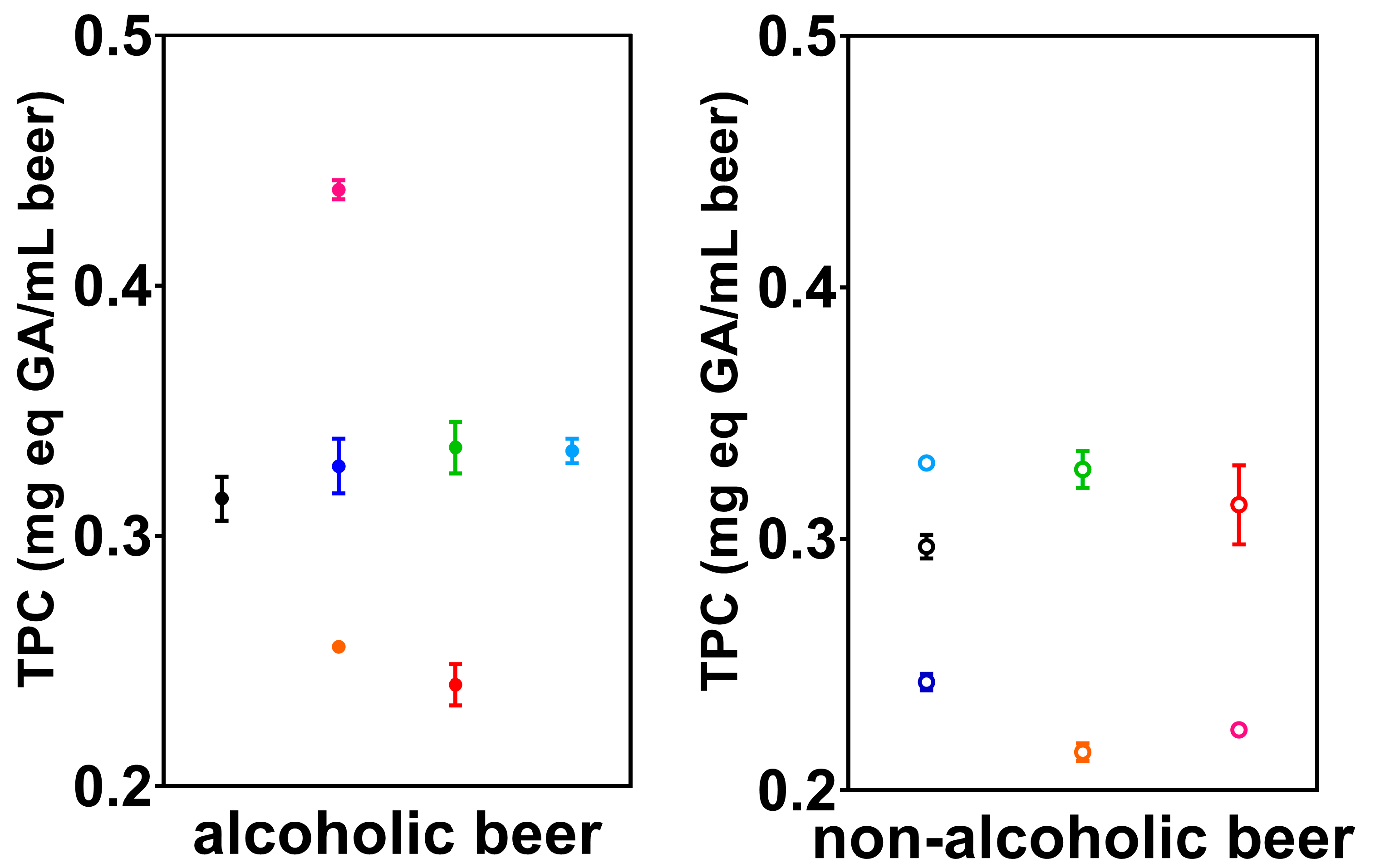



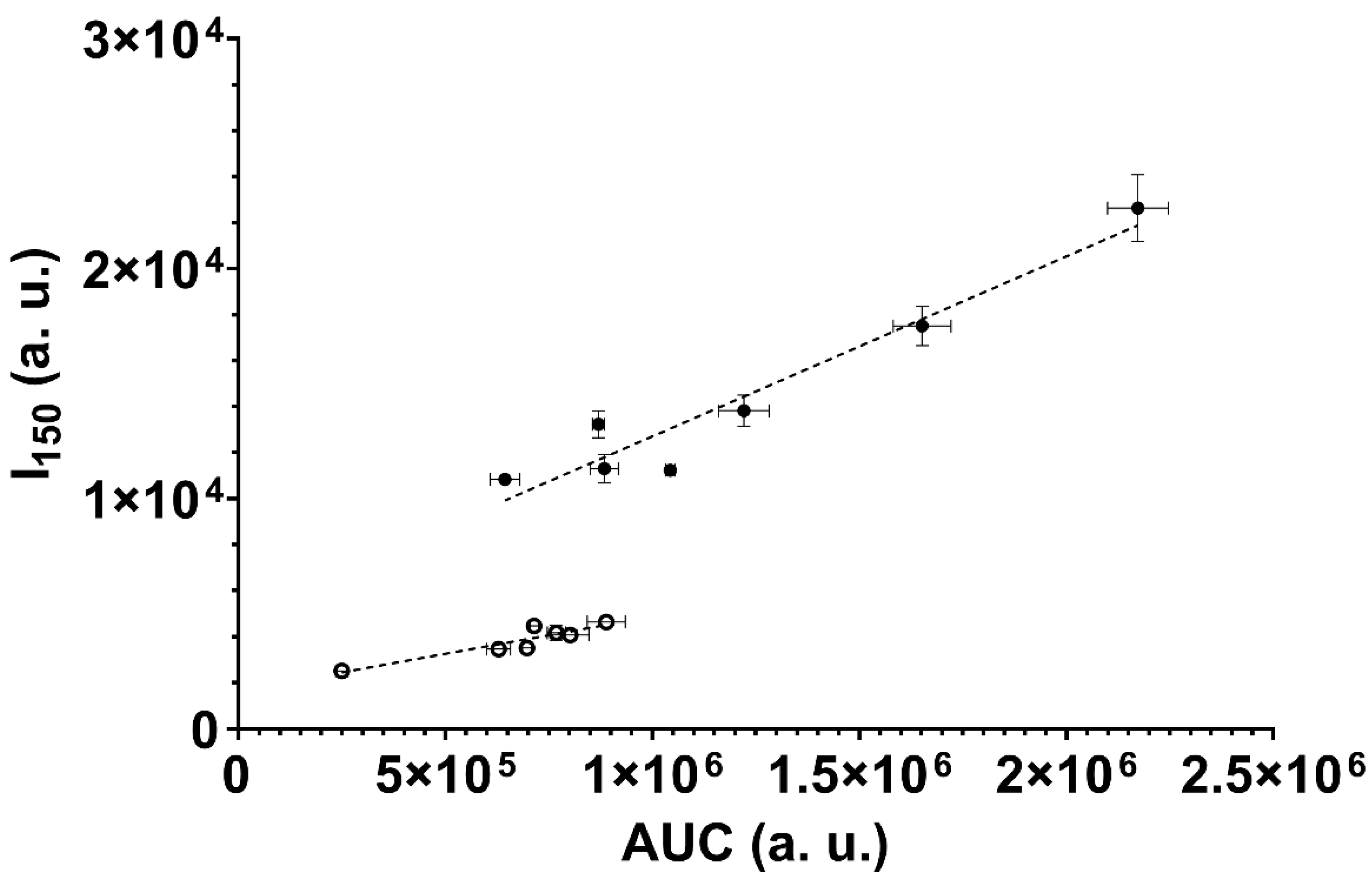


| Beer | AUC (a. u.) | I150 (a. u.) | EC50 (mL Beer/ mg DPPH) | TPC (mg eq GA/ mL Beer) | TBI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 2.17 × 106 ± 7.30 × 104 | 2.26 × 104 ± 1.45 × 103 | 1.343 (1.236–1.458) | 0.328 ± 0.011 | 0.366 ± 0.001 |
| W | 8.84 × 105 ± 3.44 × 104 | 1.13 × 104 ± 6.19 × 102 | 1.777 (1.584–1.991) | 0.335 ± 0.010 | 0.298 ± 0.007 |
| B | 6.44 × 105 ± 3.54 × 104 | 1.08 × 104 ± 2.63 × 102 | 1.953 (1.831–2.085) | 0.256 ± 0.001 | 0.253 ± 0.001 |
| P | 1.65 × 106 ± 6.98 × 104 | 1.75 × 104 ± 8.57 × 102 | 1.055 (0.978–1.133) | 0.438 ± 0.004 | 0.321 ± 0.020 |
| M | 1.04 × 106 ± 1.17 × 104 | 1.12 × 104 ± 9.03 × 101 | 3.306 (3.004–3.611) | 0.240 ± 0.008 | 0.212 ± 0.004 |
| C | 8.70 × 105 ± 1.48 × 104 | 1.32 × 104 ± 5.87 × 102 | 3.145 (2.746–3.522) | 0.315 ± 0.009 | 0.425 ± 0.008 |
| H | 1.22 × 106 ± 6.10 × 104 | 1.38 × 104 ± 6.81 × 102 | 2.028 (1.841–2.237) | 0.334 ± 0.005 | 0.380 ± 0.006 |
| N0 | 8.01 × 105 ± 4.48 × 104 | 4.07 × 103 ± 1.31 × 102 | 2.028 (1.875–2.194) | 0.243 ± 0.003 | 0.318 ± 0.010 |
| W0 | 8.89 × 105 ± 4.59 × 104 | 4.64 × 103 ± 2.42 × 102 | 1.724 (1.550–1.929) | 0.328 ± 0.007 | 0.328 ± 0.007 |
| B0 | 2.50 × 105 ± 1.42 × 104 | 2.52 × 103 ± 9.21 × 101 | 2.323 (2.172–2.483) | 0.215 ± 0.003 | 0.268 ± 0.012 |
| P0 | 6.97 × 105 ± 1.07 × 104 | 3.51 × 103 ± 1.91 × 102 | 2.787 (2.468–3.110) | 0.224 ± 0.001 | 0.324 ± 0.012 |
| M0 | 7.68 × 105 ± 2.19 × 104 | 4.16 × 103 ± 3.22 × 102 | 1.911 (1.767–2.064) | 0.313 ± 0.016 | 0.323 ± 0.002 |
| C0 | 7.15 × 105 ± 9.75 × 103 | 4.47 × 103 ± 1.70 × 102 | 2.952 (2.675–3.224) | 0.297 ± 0.005 | 0.412 ± 0.010 |
| H0 | 6.29 × 105 ± 2.87 × 104 | 3.47 × 103 ± 6.04 × 101 | 1.230 (1.206–1.254) | 0.330 ± 0.002 | 0.315 ± 0.019 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Porcu, M.C.; Sanna, D. Electron Spin Resonance Spectroscopy Suitability for Investigating the Oxidative Stability of Non-Alcoholic Beers. Oxygen 2025, 5, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/oxygen5030014
Porcu MC, Sanna D. Electron Spin Resonance Spectroscopy Suitability for Investigating the Oxidative Stability of Non-Alcoholic Beers. Oxygen. 2025; 5(3):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/oxygen5030014
Chicago/Turabian StylePorcu, Maria Cristina, and Daniele Sanna. 2025. "Electron Spin Resonance Spectroscopy Suitability for Investigating the Oxidative Stability of Non-Alcoholic Beers" Oxygen 5, no. 3: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/oxygen5030014
APA StylePorcu, M. C., & Sanna, D. (2025). Electron Spin Resonance Spectroscopy Suitability for Investigating the Oxidative Stability of Non-Alcoholic Beers. Oxygen, 5(3), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/oxygen5030014







