Links Between the Coastal Climate, Landscape Hydrology, and Beach Dynamics near Cape Vidal, South Africa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data Sources and Attributes
2.2. Statistical Methods and Analysis
3. Results
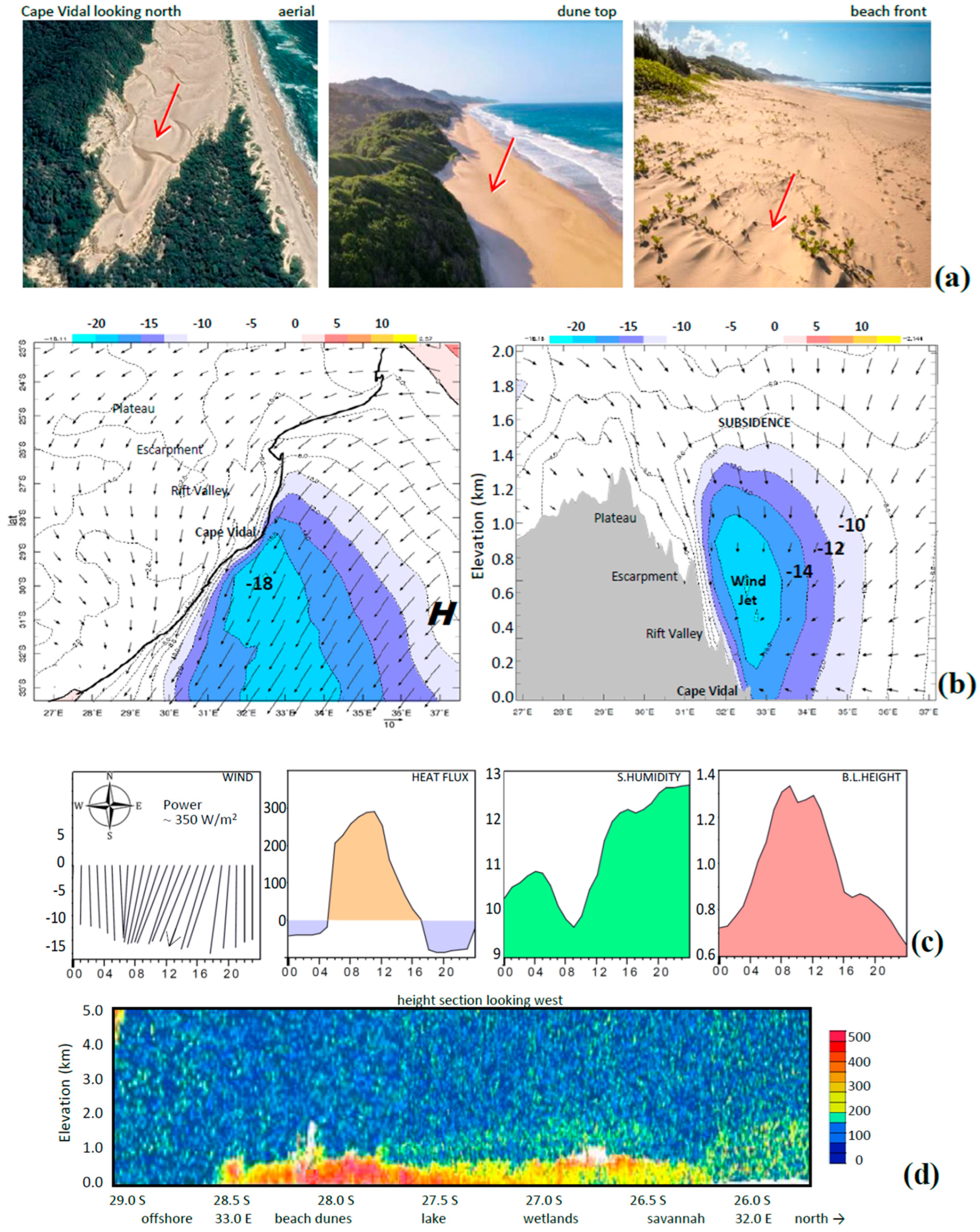
3.1. Coastal Hydrology and Landscape
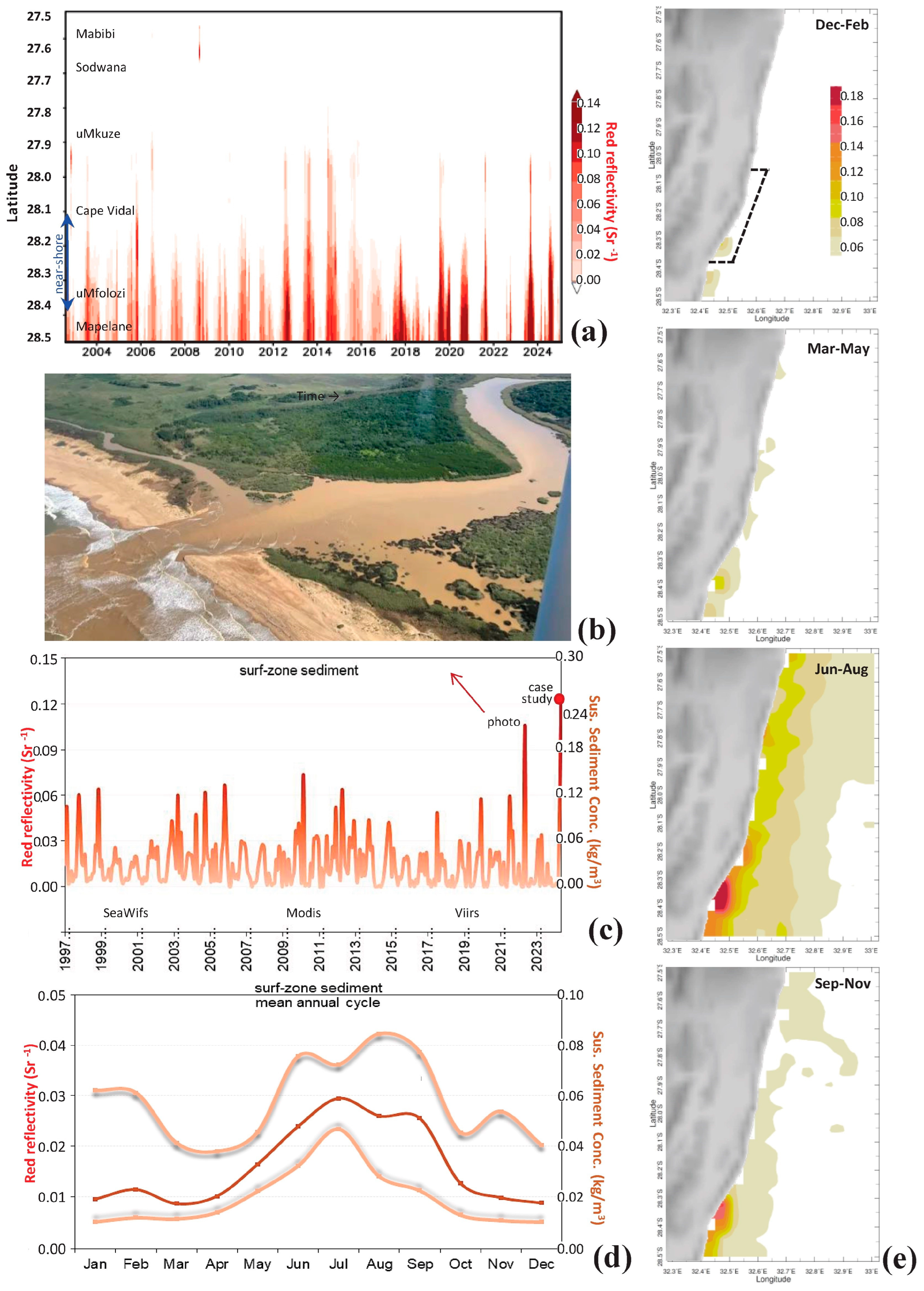
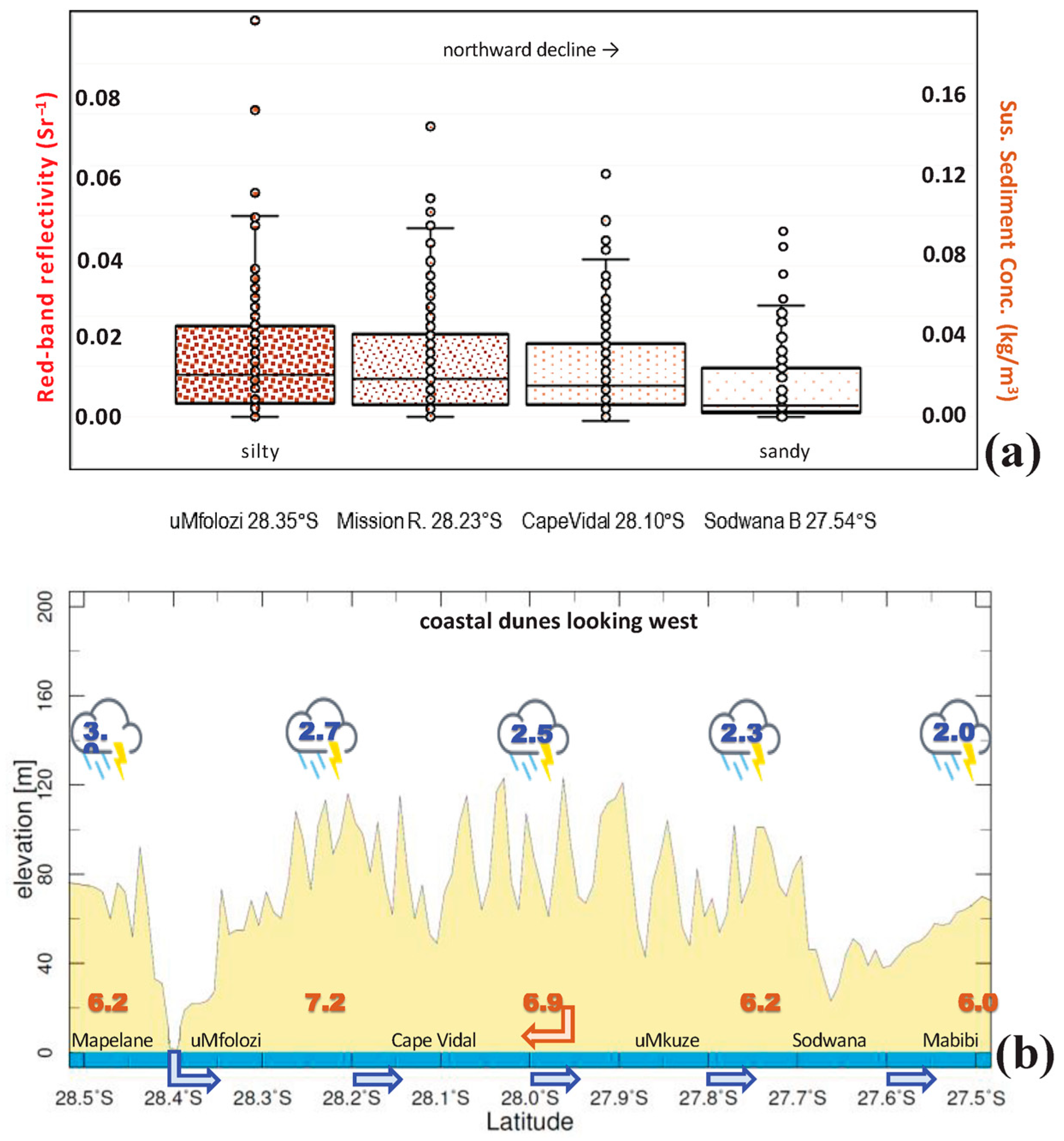
3.2. Red-Band Reflectivity
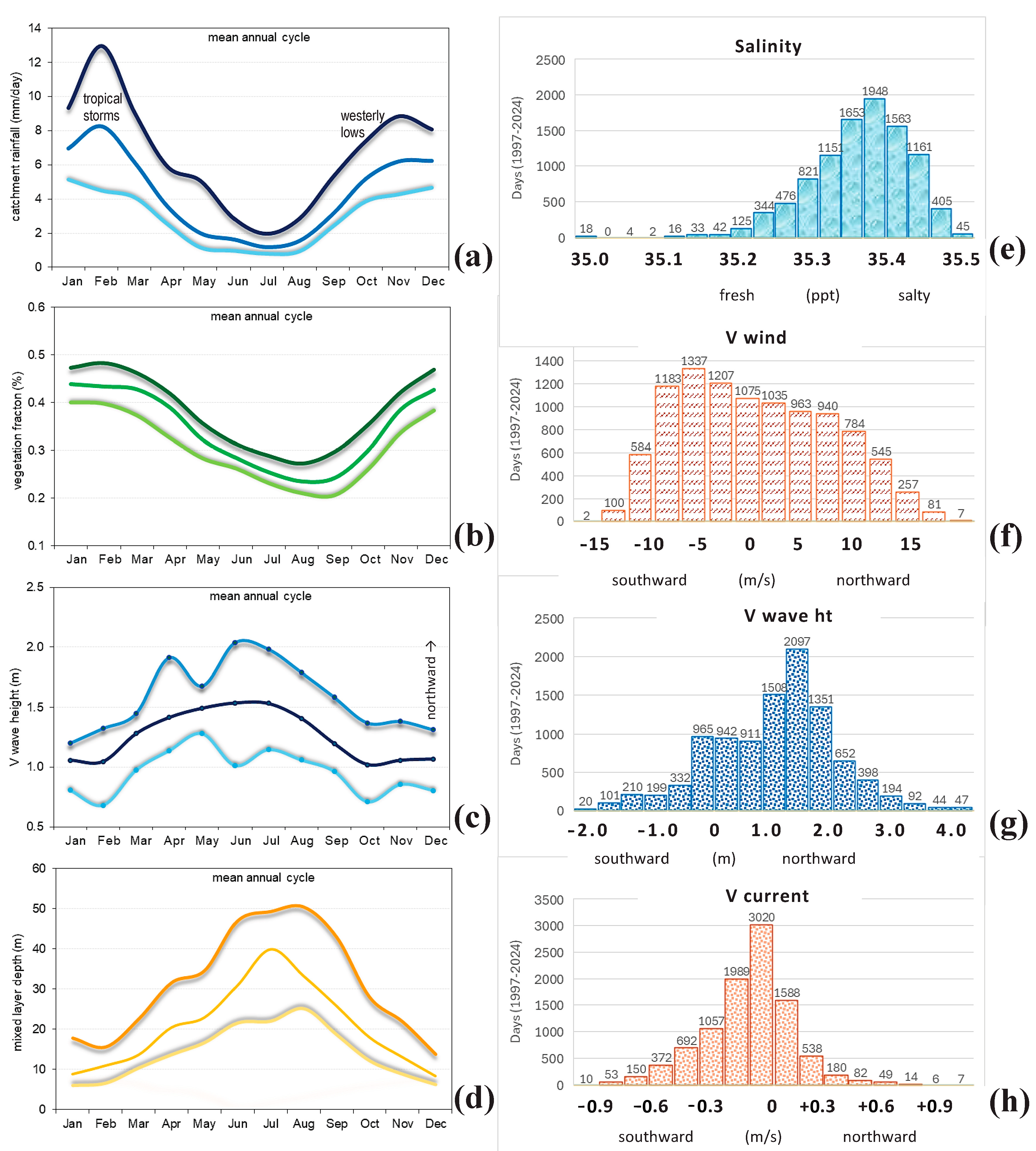
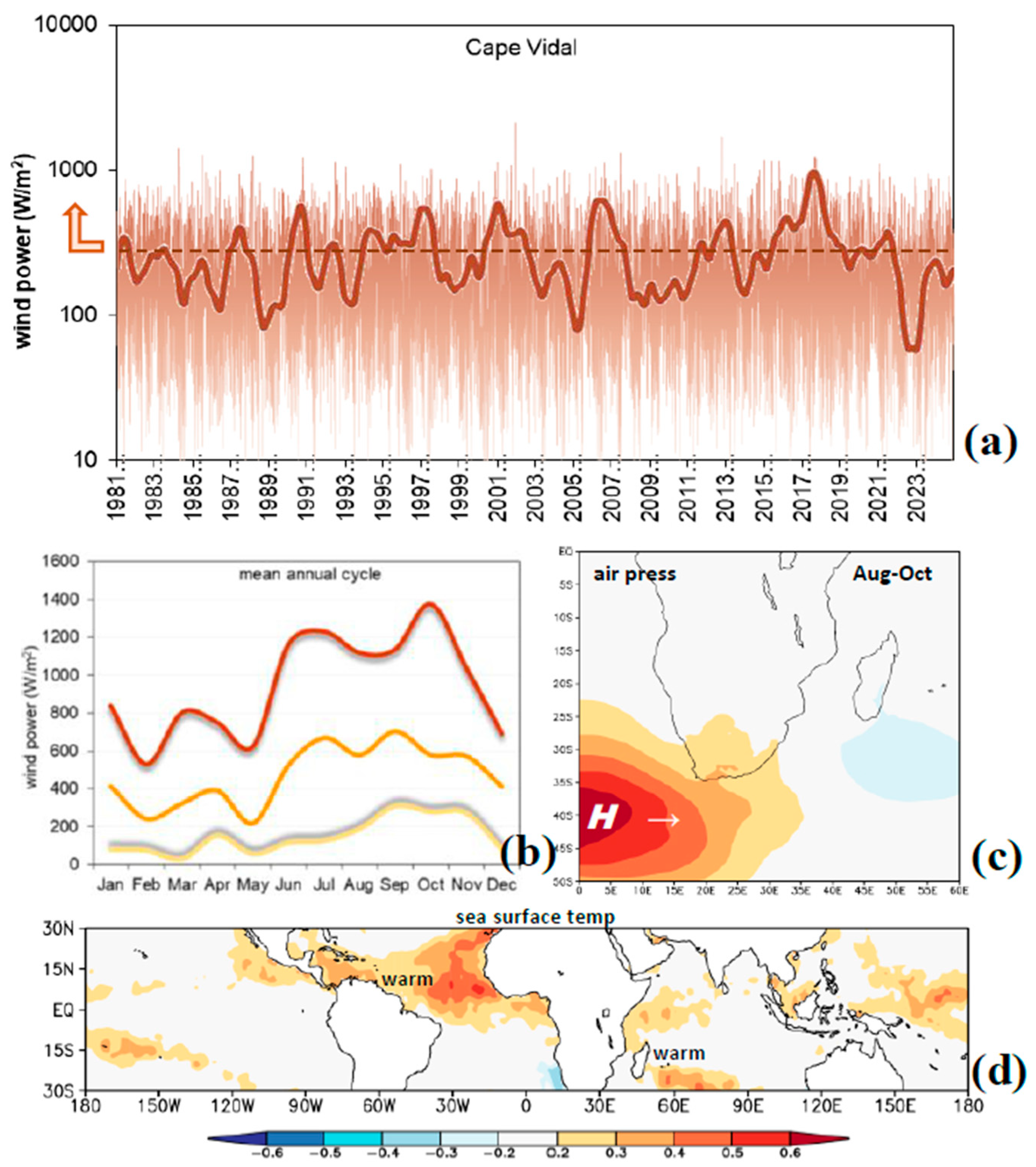
3.3. Mean Annual Cycle and Frequency Distributions
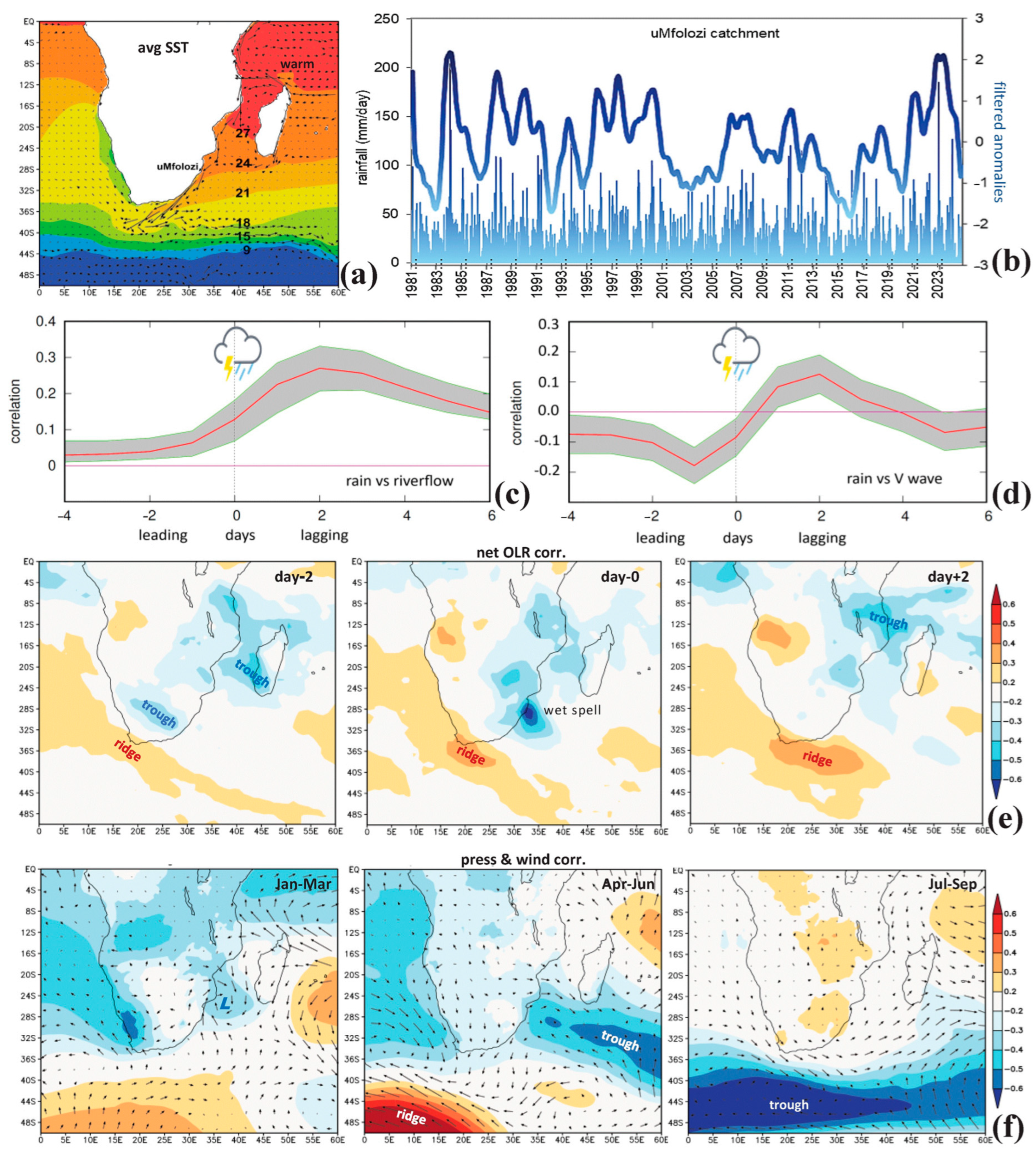
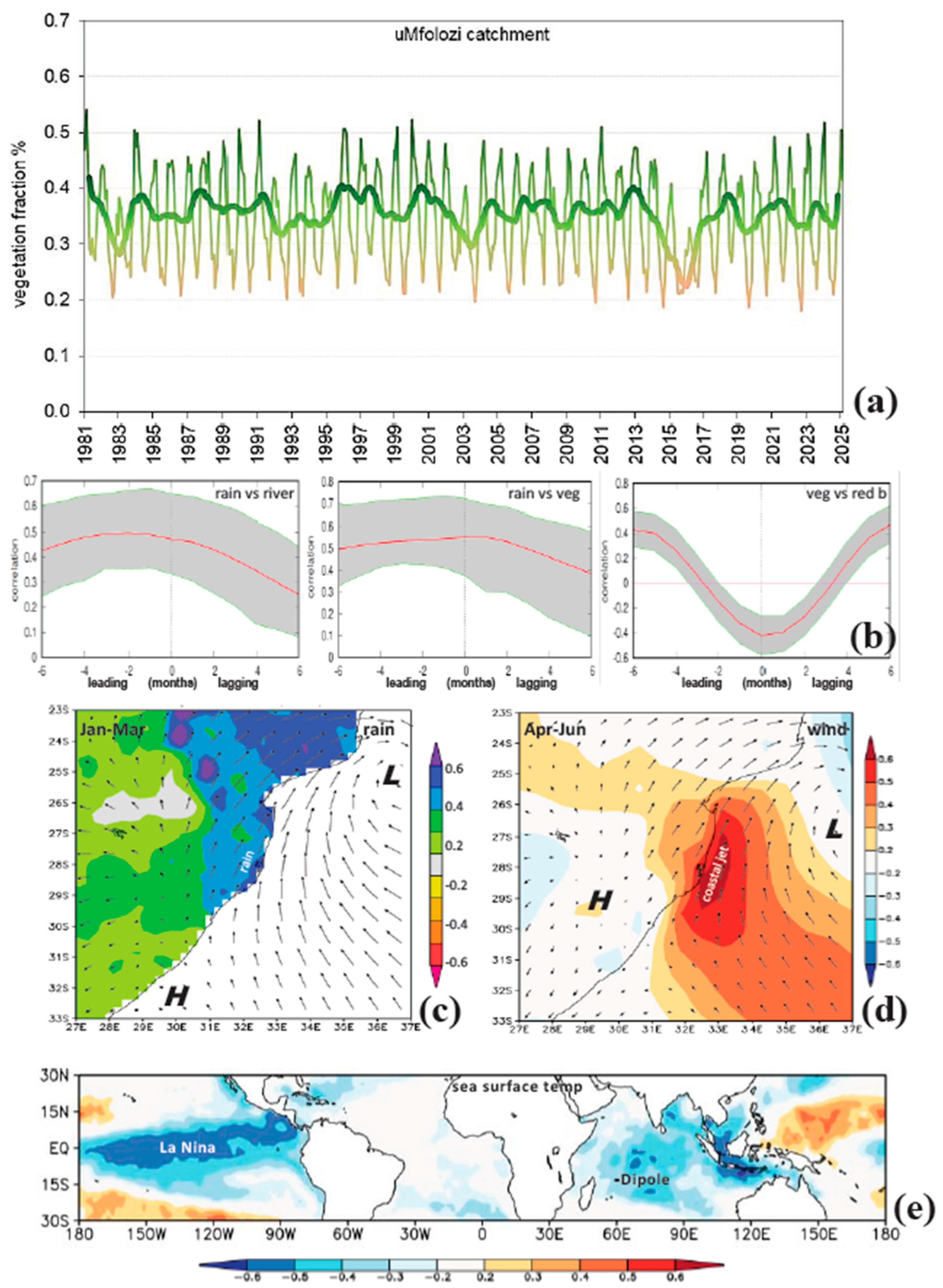
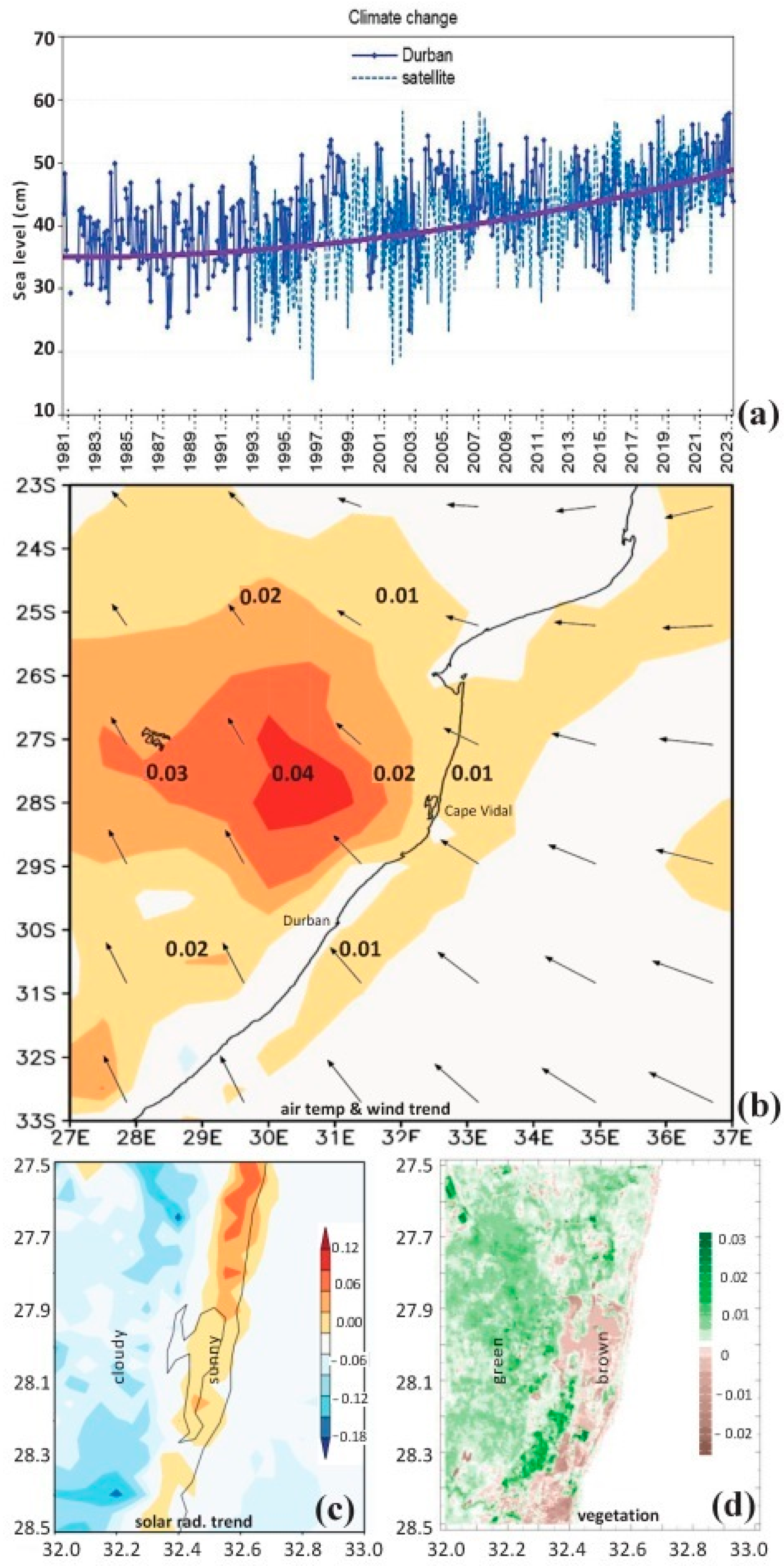
3.4. Drivers of Catchment Hydrology
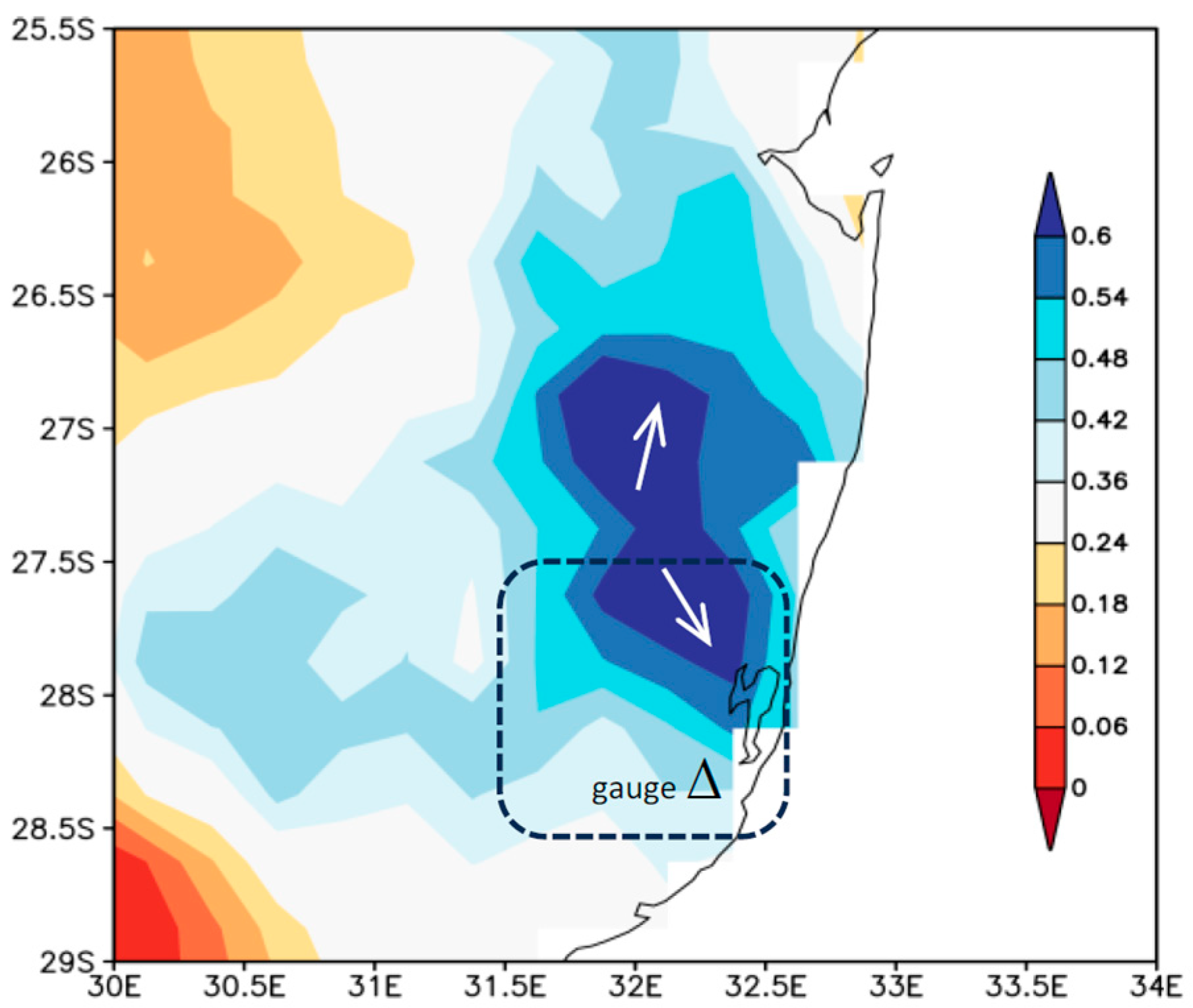
3.5. Wind Power, Spectral Analysis, and Contrasting Climates
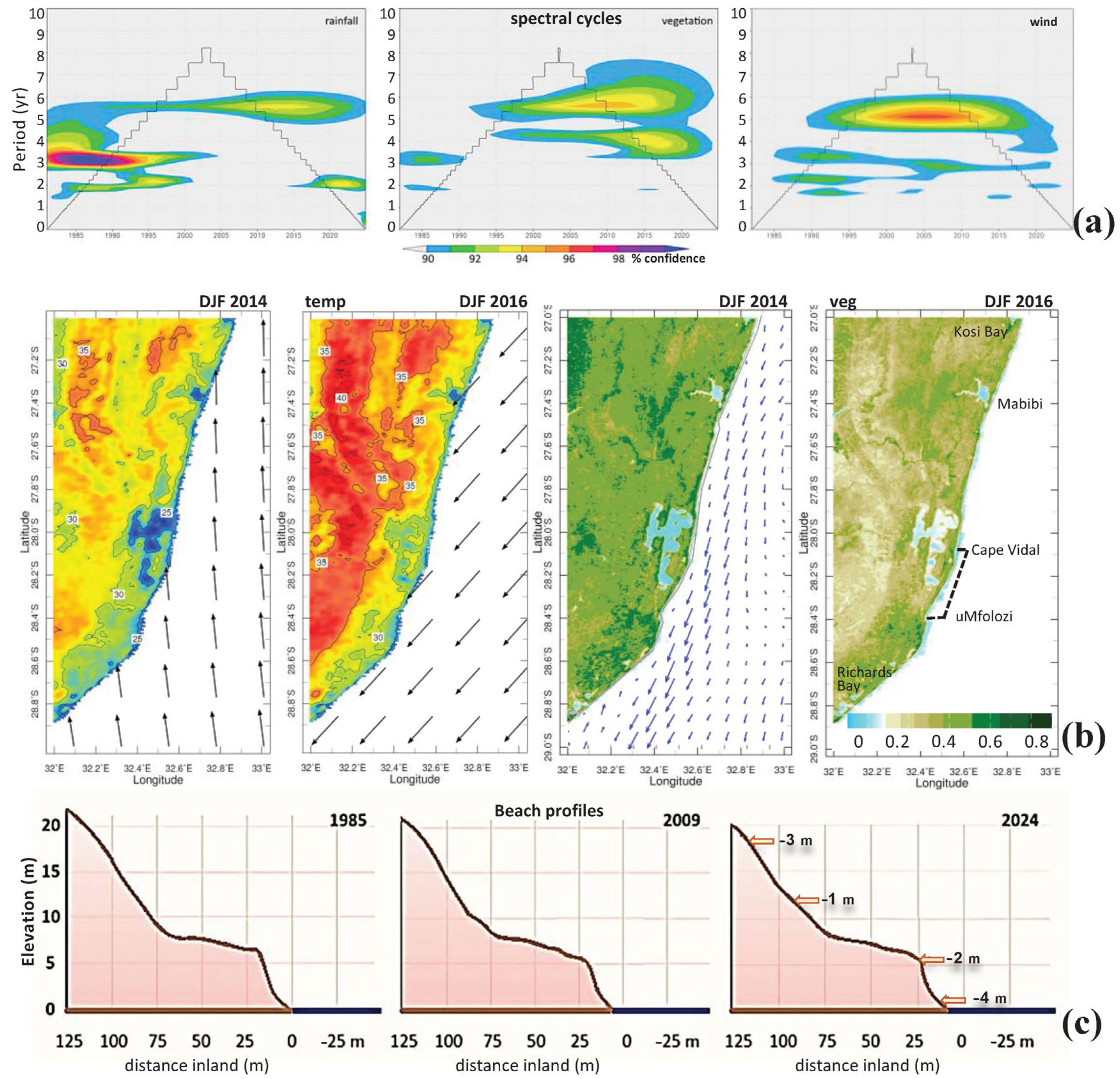
3.6. Outcome of Field Surveys

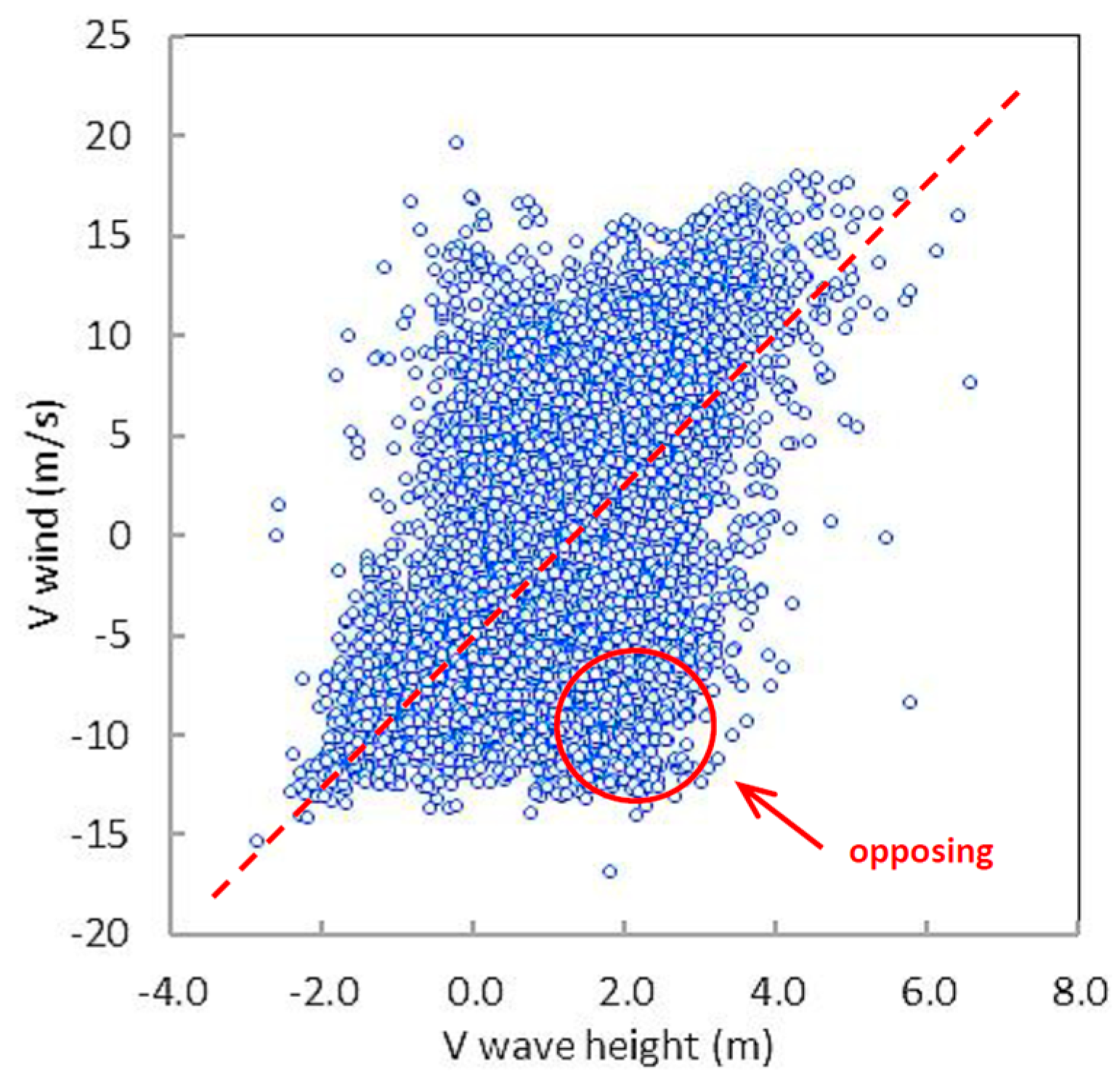
3.7. Case Study Wind and Flood Events
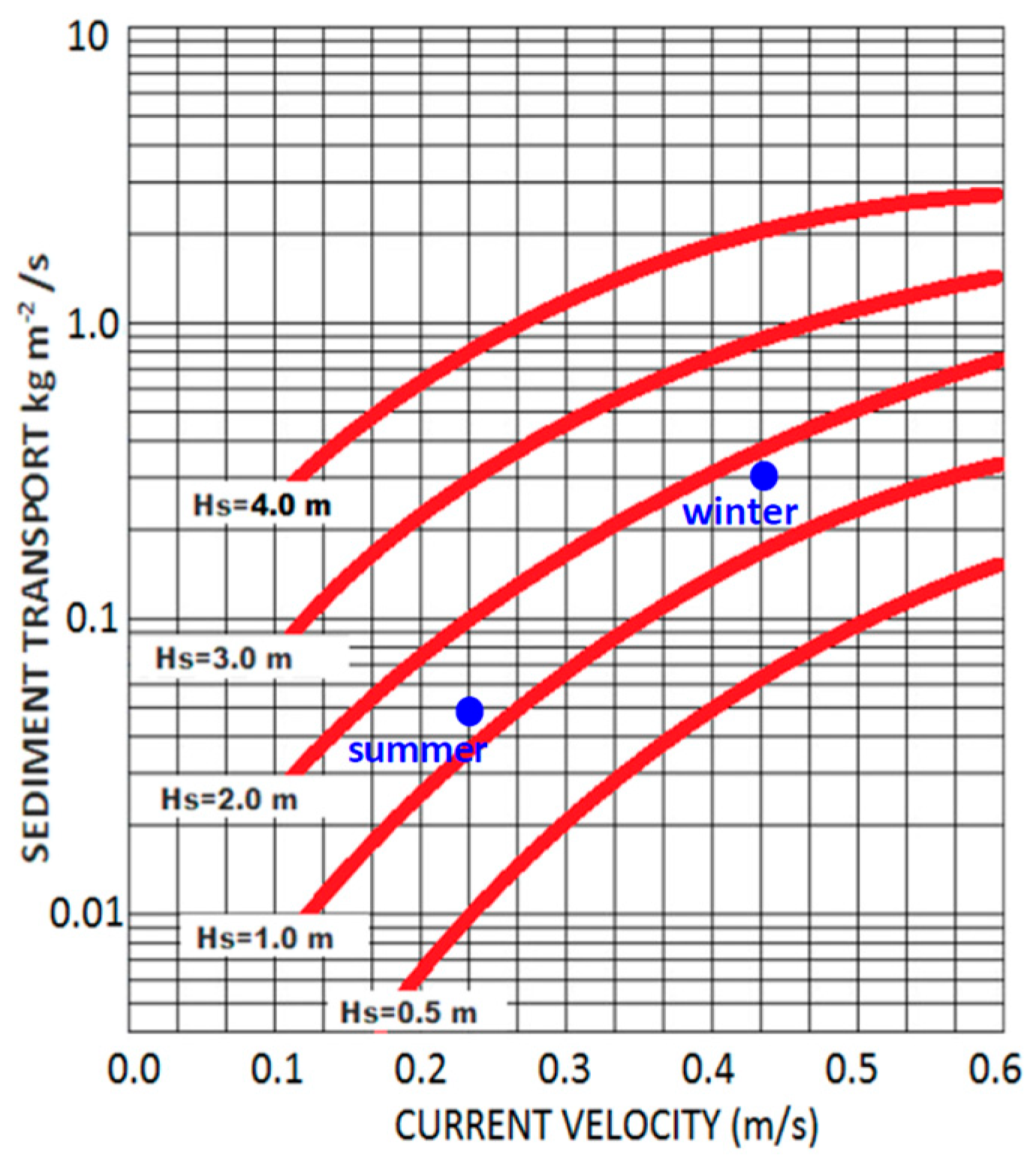
3.8. Contributions to Sediment Transport
4. Concluding Discussion
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A



References
- Wright, L.D.; Short, A.D. Morphodynamic variability of surf-zones and beaches: A synthesis. Mar. Geol. 1984, 50, 93–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rijn, L.C. Prediction of dune erosion due to storms. Coast. Eng. 2009, 56, 441–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.; Guastella, L.; Botes, Z.; Bundy, S.; Mather, A. Forecasting cyclic coastal erosion on a multi-annual to multi-decadal scale: Southeast African coast. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2014, 150, 12010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, R.W.G.; Jennings, S.C.; Orford, J.D. Headland erosion by waves. J. Coast. Res. 1990, 6, 517–529. [Google Scholar]
- Silvester, R.; Hsu, J.R.C. Coastal Stabilization; Prentice Hall: Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1993; 578p. [Google Scholar]
- van Rijn, L.C. Unified view of sediment transport by currents and waves II: Suspended transport. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2007, 133, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphries, M.S.; Kindness, A.; Ellery, W.N.; Hughes, J.C.; Bond, J.K.; Barnes, K.B. Vegetation influences on groundwater salinity and chemical heterogeneity in a freshwater recharge floodplain wetland in South Africa. J. Hydrol. 2011, 411, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenfell, S.E.; Ellery, W.N. Hydrology, sediment transport dynamics and geomorphology of a variable flow river: The Mfolozi River South Africa. Water SA 2009, 35, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bjerner, M.; Johansson, J. Economic and Environmental Impacts of Nature-Based Tourism: A Case Study of Ponta do Ouro, Mozambique; Technical Report; Göteborg University: Gothenburg, Sweden, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Tinley, K.L. Coastal Dunes of South Africa; National Scientific Programmes Unit (CSIR): New Delhi, India, 1985; Volume 109, p. 300. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, R.W.G. Coastal Environments: An Introduction to the Physical, Ecological and Cultural Systems of Coastlines; Academic Press: London, UK, 1988; 611p. [Google Scholar]
- Jury, M.R. Coastal climate and beach dynamics at Ponta do Ouro, Mozambique. Sci. Res. Essays 2015, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaliraj, S.; Chandrasekar, N.; Magesh, N.S. Impacts of wave energy and littoral currents on shoreline erosion/accretion along the south-west coast of Tamil Nadu. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 71, 4523–4542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Chen, X.; Tian, L.; Zhang, W. Numerical simulation-aided Modis capture of sediment transport for the Bohai Sea. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 4225–4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouillon, S.; Douillet, P.; Petrenko, A.; Neveux, J.; Dupouy, C.; Froidefond, J.-M.; Andréfouët, S.; Muñoz-Caravaca, A. Optical algorithms at satellite wavelengths for total suspended matter in tropical coastal waters. Sensors 2008, 8, 4165–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrigan, S.; Zsoter, E.; Alfieri, L.; Prudhomme, C.; Salamon, P.; Wetterhall, F.; Barnard, C.; Cloke, H.; Pappenberger, F. Glofas-ERA5 operational global river discharge reanalysis 1979–present. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2020, 12, 2043–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelaro, R.; McCarty, W.; Suárez, M.J.; Todling, R.; Molod, A.; Takacs, L.; Randles, C.A.; Darmenov, A.; Bosilovich, M.G.; Reichle, R.; et al. The modern-era retrospective analysis for research and applications v2 (Merra2). J. Clim. 2017, 30, 5419–5454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Rijn, L.C.; Strypsteen, G. A fully predictive model for aeolian sand transport. Coast. Eng. 2020, 156, 103600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, C.; Peterson, P.; Landsfeld, M.; Pedreros, D.; Verdin, J.; Shukla, S.; Husak, G.; Rowland, J.; Harrison, L.; Hoell, A.; et al. The climate hazards infrared precipitation with stations, a new environmental record for monitoring extremes. Sci. Data 2015, 2, 150066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinzon, J.E.; Tucker, C.J. A non-stationary 1981–2012 AVHRR NDVI time series. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 6929–6960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chassignet, E.P.; Hurlburt, H.E.; Metzger, E.J.; Smedstad, O.M.; Cummings, J.A.; Halliwell, G.R.; Bleck, R.; Baraille, R.; Wallcraft, A.J.; Lozano, C.; et al. US GODAE: Global ocean prediction with the Hybrid coordinate ocean model (Hycom). Oceanography 2009, 22, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolman, H.L. User manual and system documentation of Wavewatch3. In NCEP Technical Note; US Department of Commerce, NOAA, NWS, NCEP: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; 139p. [Google Scholar]
- Jury, M.R. Meteorological controls on big waves south of Africa. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2019, 27, 100538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-T. Climate algorithm theoretical basis document: Outgoing longwave radiation (OLR). NOAA’s climate data record program. Tech. Rep. 2014, 111, 2804–2822. [Google Scholar]
- Copernicus Marine. Global Ocean Gridded Sea Surface Height L4 Product, European Union Data Store; Copernicus Marine: Toulouse, France, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezemvelo Wildlife. Annual Reports to KZN Provincial Government by the Conservation Service, Durban; Ezemvelo Wildlife: Pietermaritzburg, South Africa, 2019–2023; pp. 110–144. [Google Scholar]
- Govender, Y.; Jury, M.R. The local environmental gradient and species richness in a coastal nature reserve in Maputaland South Africa. S. Afr. Geogr. J. 2005, 87, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jury, M.R. Modulation of the marine environment in the Natal Bight. Remote Sens. 2023, 14, 3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbello, S.; Stretch, D.D. Decadal trends in beach morphology on the east coast of South Africa and likely causative factors. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 12, 2515–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psuty, N. Spatial variation in coastal foredune development. In Coastal Dunes: Geomorphology, Ecology and Management for Conservation; Carter, R.W.G., Curtis, T.G.F., Sheehy-Skeffington, M.J., Eds.; Balkema: Hague, The Netherlands, 1992; pp. 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, H.C. Field measurements of longshore sediment transport during storms. Coast. Eng. 1999, 36, 301–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wellen, E.; Chadwick, A.J.; Mason, T. A review and assessment of longshore sediment transport equations for coarse-grained beaches. Coast. Eng. 2000, 40, 243–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteves, L.S.; Williams, J.J.; Lisniowski, M.A. Measuring and modelling longshore sediment transport. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 83, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.; Adam, E.; Woodborne, S.; Miller, D.; Xulu, S.; Evans, M. Monitoring shoreline changes along the SW coast of South Africa from 1937 to 2020 using varied data approaches. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Acronym | Name and Variables | Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| CHIRPS2 | Climate Hazards Group InfraRed Precipitation v2 Interpolated from gauge + satellite | 25 km monthly |
| EC | European Community Hydrology reanalysis streamflow | 25 km daily |
| G. EARTH | Google Earth digital archive | Locale ~monthly |
| IN-SITU | Field surveys at Mabibi Sand sampling, surf-zone drifters, biodiversity | Point bi-annual |
| HYCOM3 | Hybrid coupled ocean model v3 Sea temp, current, salinity, mixed layer depth | 10 km daily |
| MERRA2 | NASA Meteorology reanalysis v2 Wind, air temp, pressure, humidity, evaporation | 50 km daily |
| MODIS | Moderate Imaging Sensor (satellite) Land and ocean color: visible reflectivity | 1 km monthly |
| NOAA | National Oceanic & Atmospheric Admin. Satellite sea temp, net outgoing IR radiation | 25 km weekly |
| SA HYDRO | South African Hydrology Dept Gauged streamflow (Umfolozi) | Point daily |
| TIDE | Gauged sea level (Durban) Satellite altimetry reanalysis | Point monthly |
| VIIRS | Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite satellite ocean color: red-band reflectivity | 1 km daily, monthly |
| W3 | Wavewatch ocean reanalysis v3 wave height, period, direction | 25 km daily |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jury, M.R. Links Between the Coastal Climate, Landscape Hydrology, and Beach Dynamics near Cape Vidal, South Africa. Coasts 2025, 5, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/coasts5030025
Jury MR. Links Between the Coastal Climate, Landscape Hydrology, and Beach Dynamics near Cape Vidal, South Africa. Coasts. 2025; 5(3):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/coasts5030025
Chicago/Turabian StyleJury, Mark R. 2025. "Links Between the Coastal Climate, Landscape Hydrology, and Beach Dynamics near Cape Vidal, South Africa" Coasts 5, no. 3: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/coasts5030025
APA StyleJury, M. R. (2025). Links Between the Coastal Climate, Landscape Hydrology, and Beach Dynamics near Cape Vidal, South Africa. Coasts, 5(3), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/coasts5030025






