Temporal and Spatial Variability of Hydrogeomorphological Attributes in Coastal Wetlands—Lagoa do Peixe National Park, Brazil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
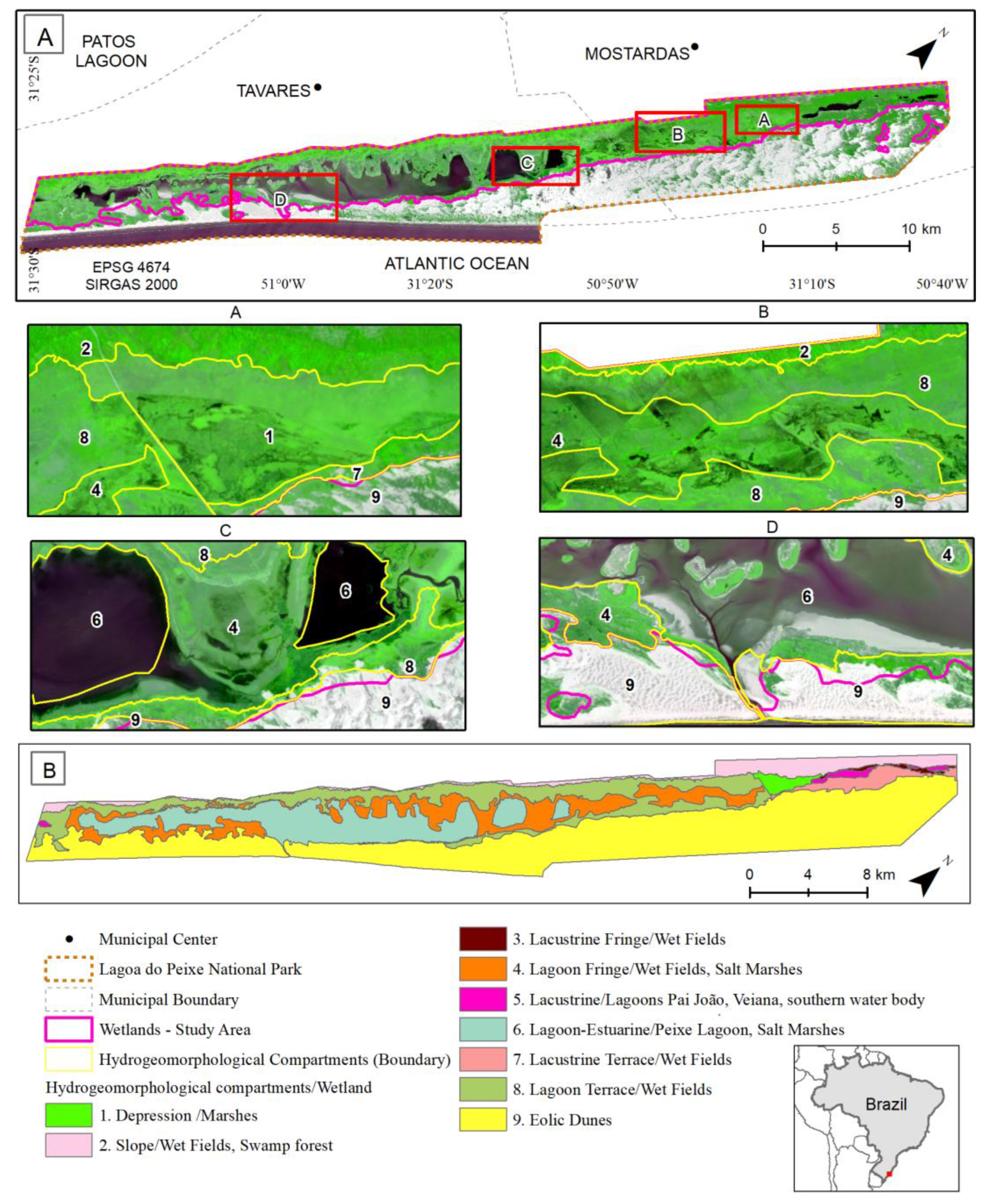
2.1. Study Area
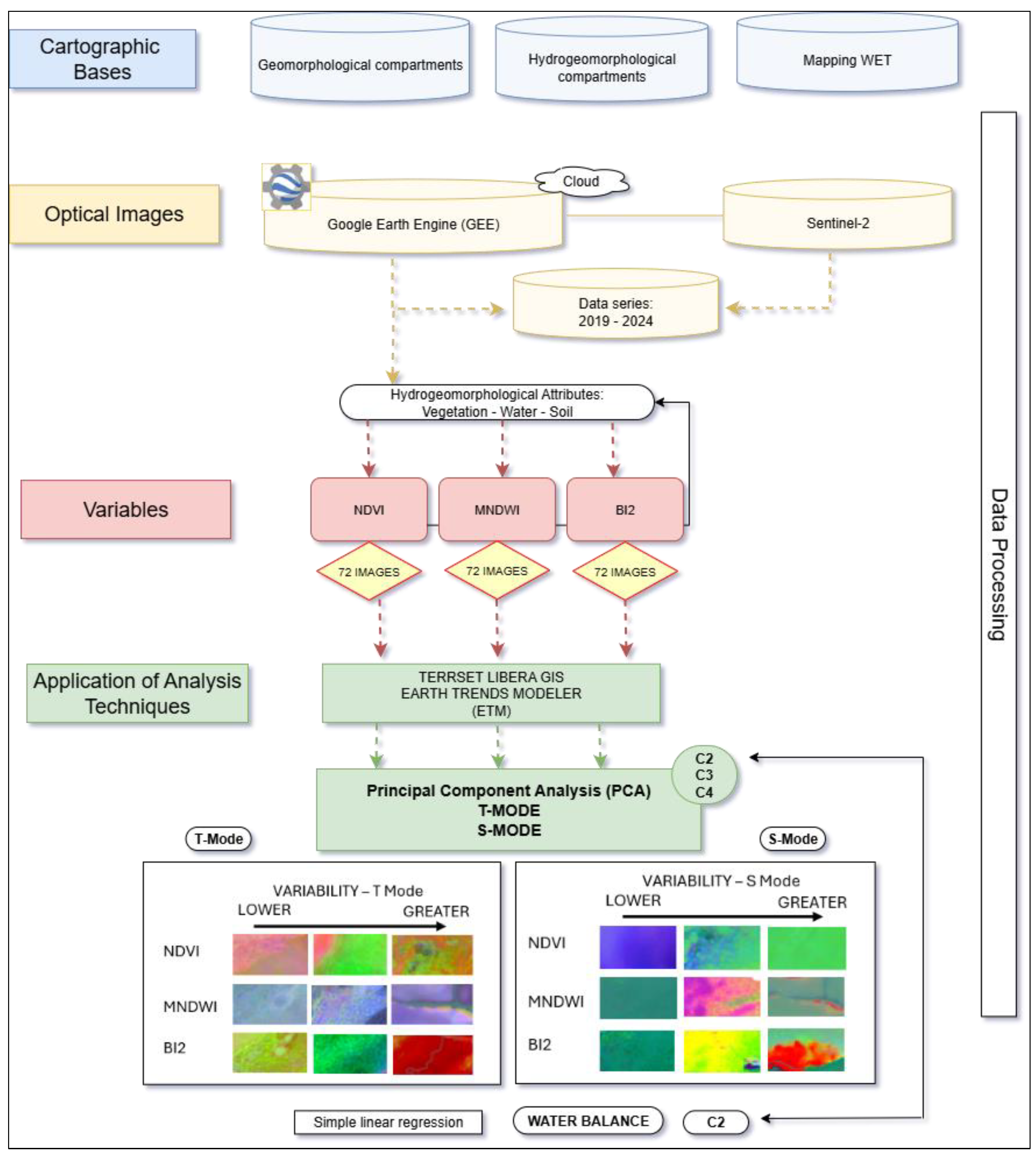
2.2. Data and Procedures
2.3. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
3. Results
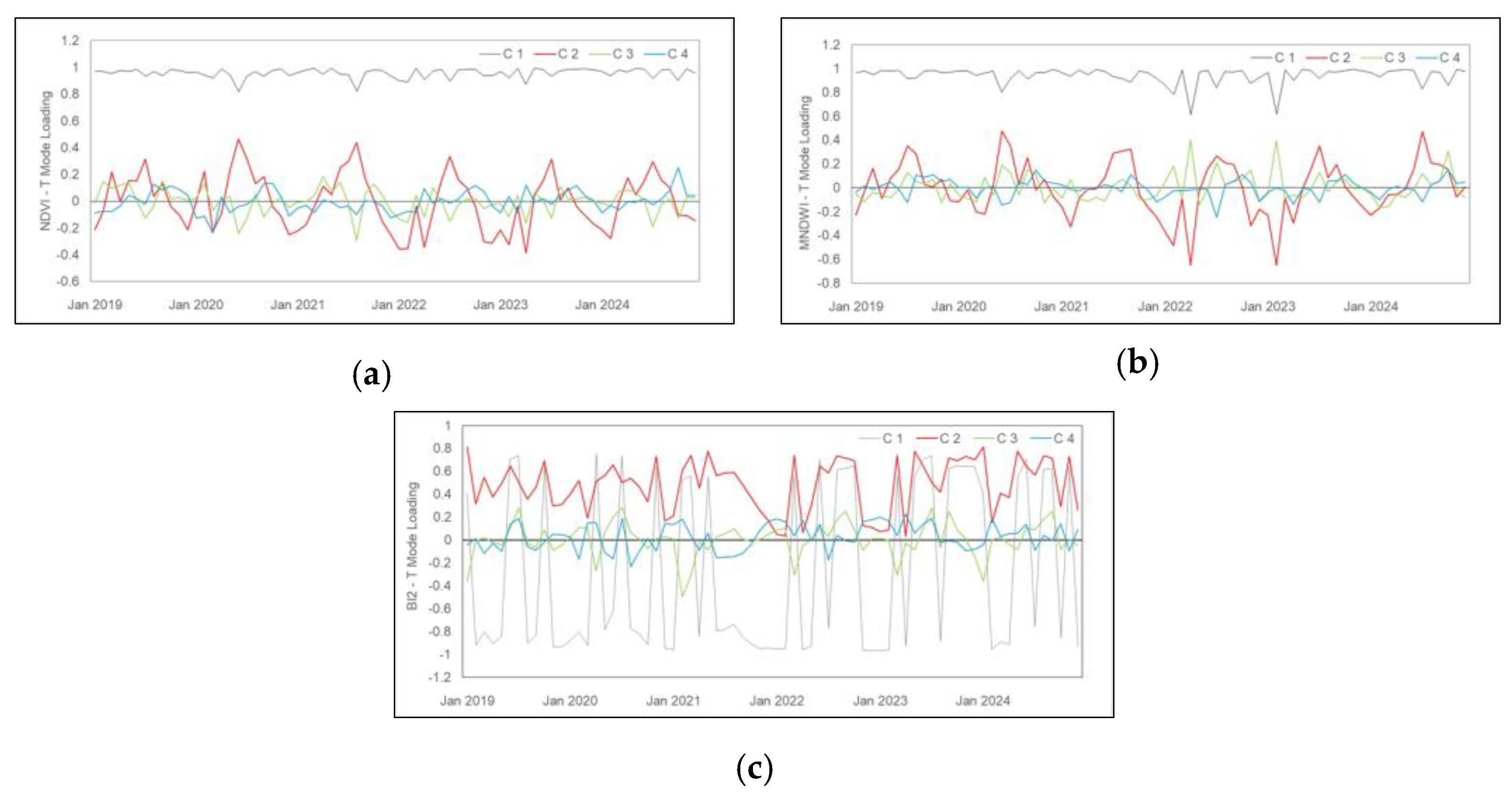
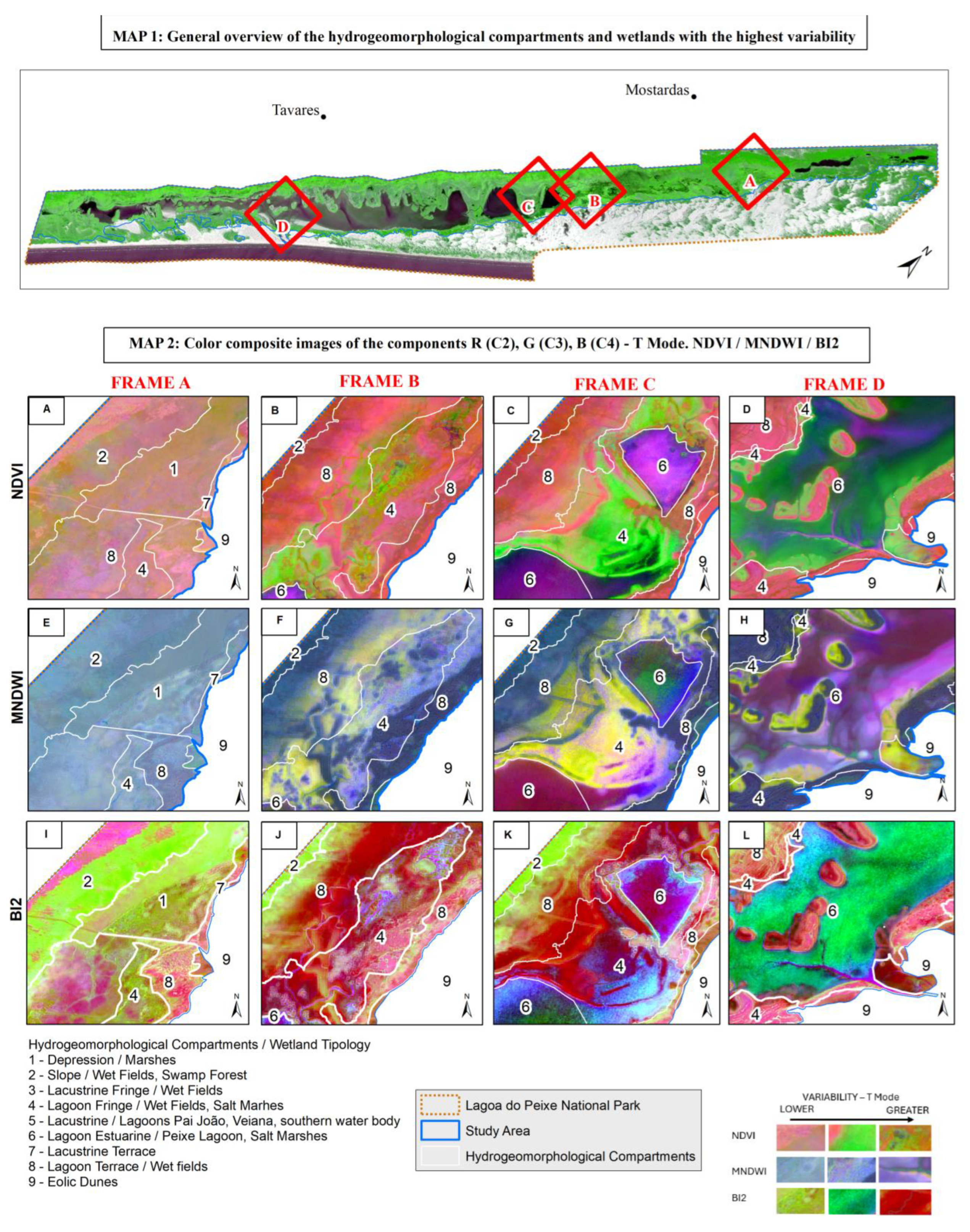
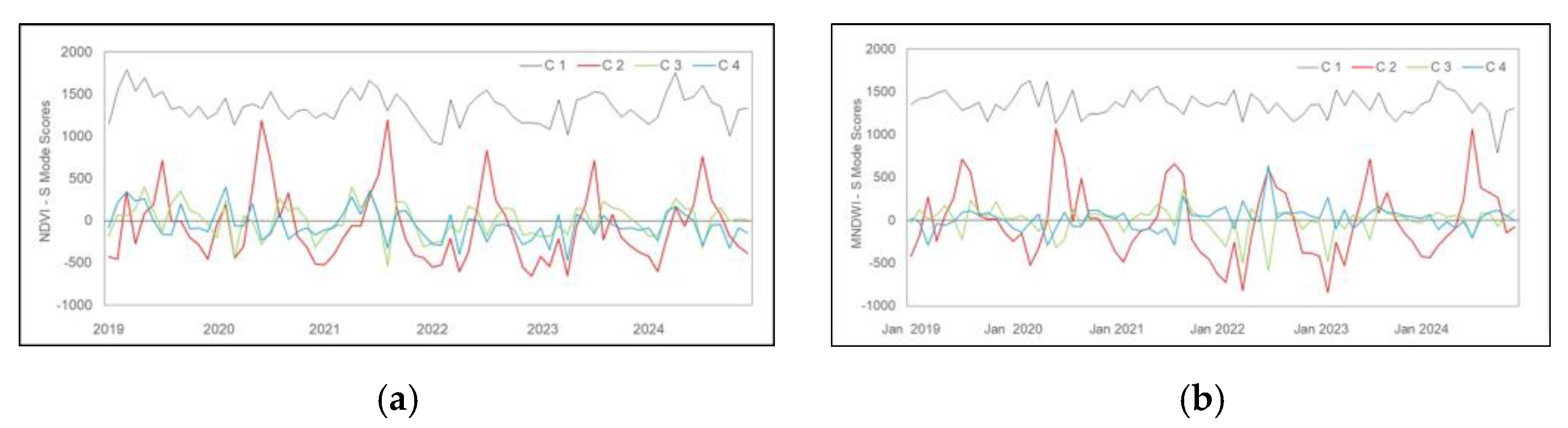
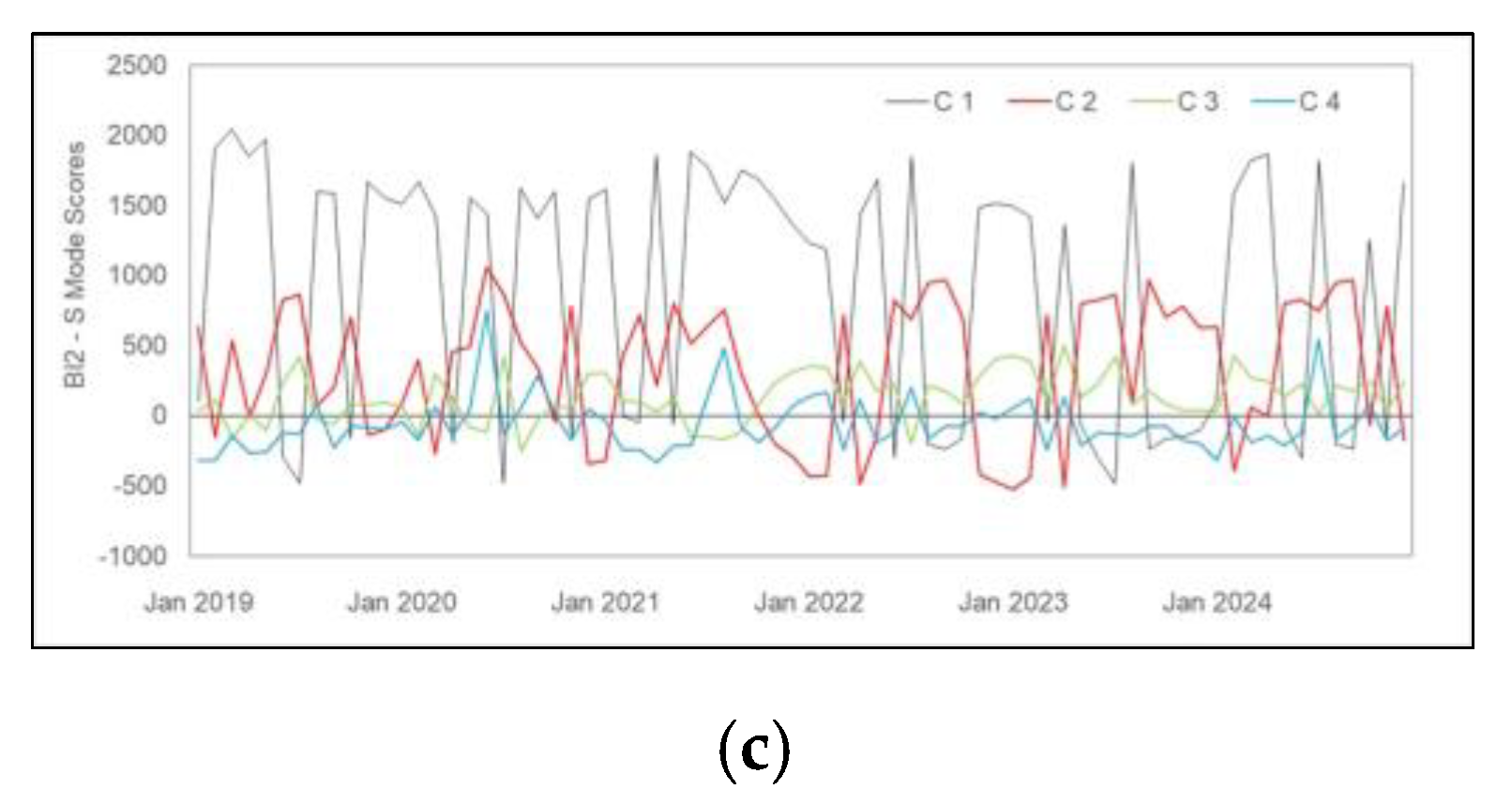
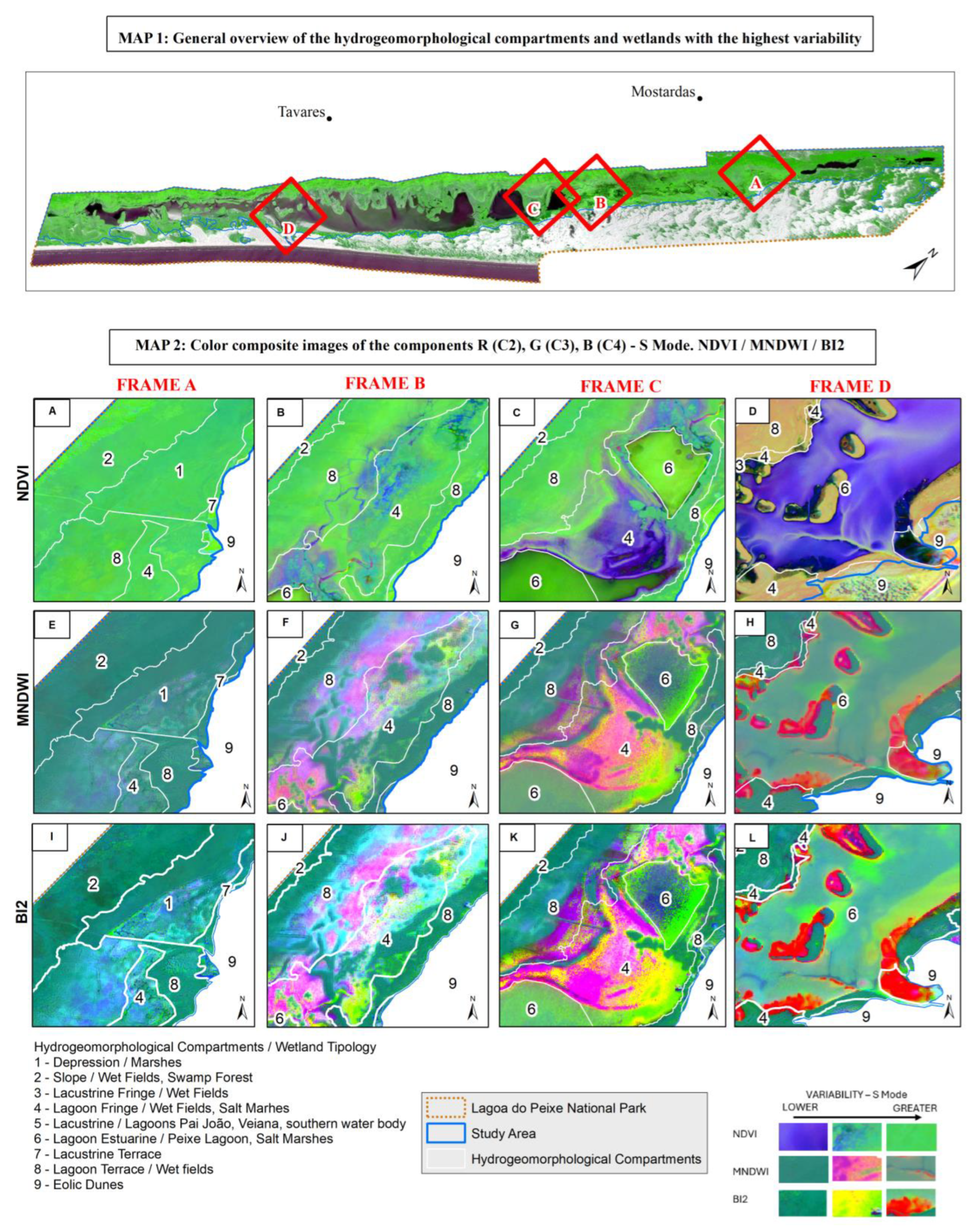
3.1. Temporal and Spatial Variability
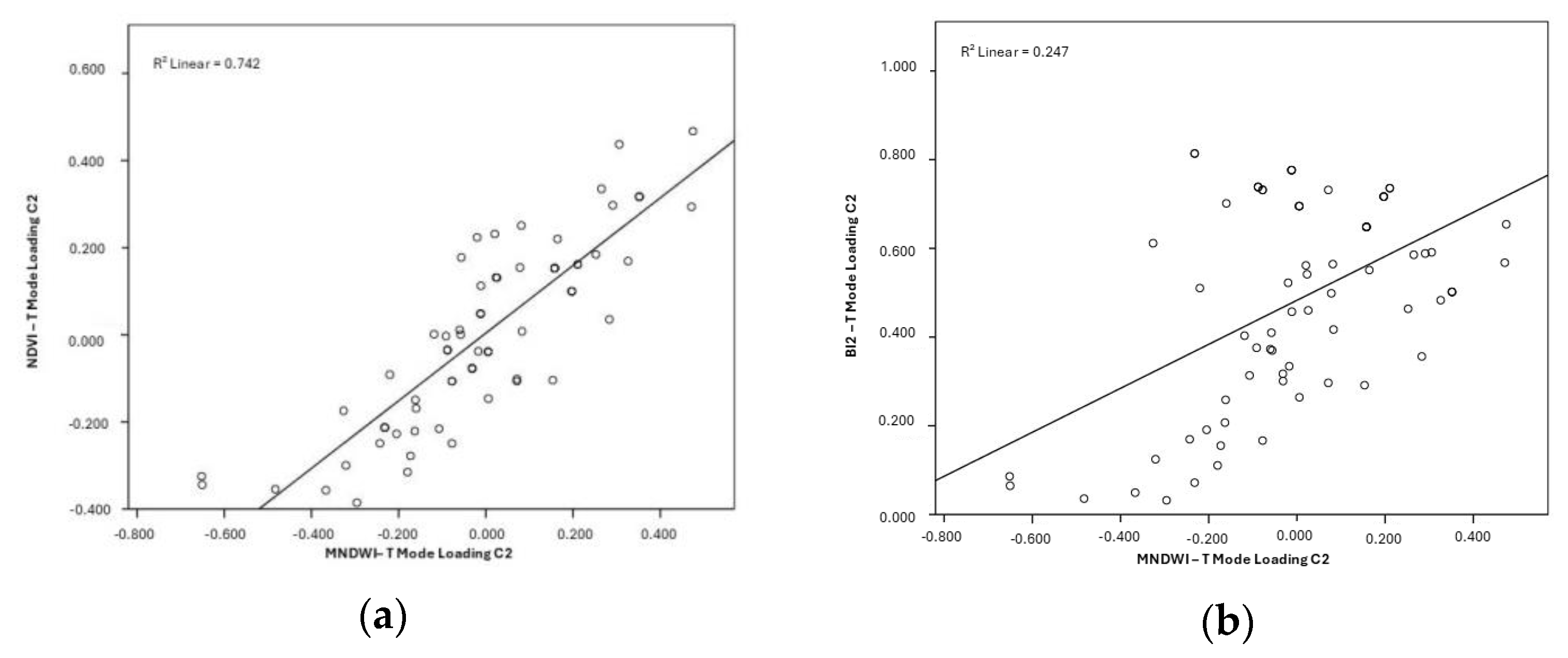
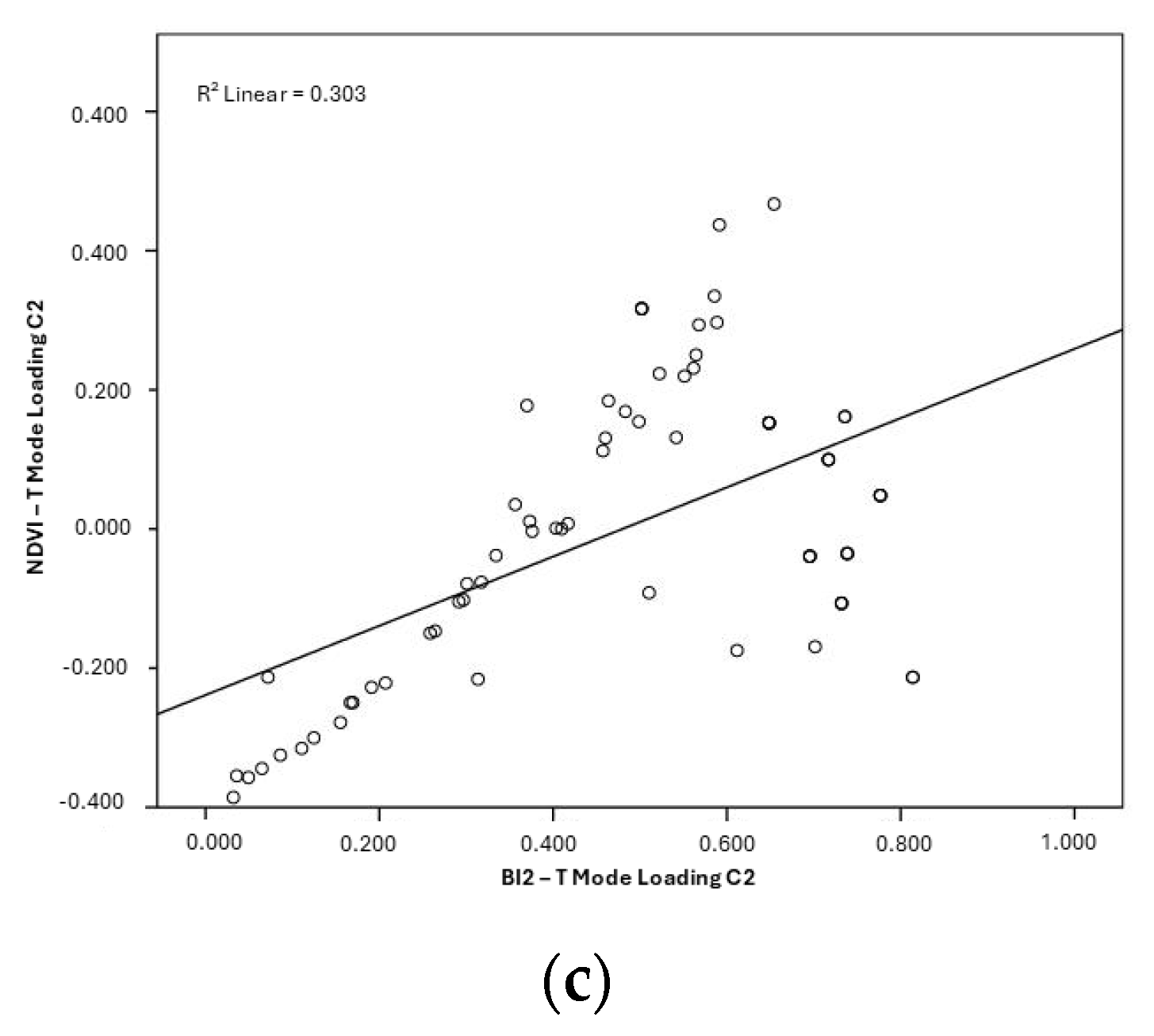
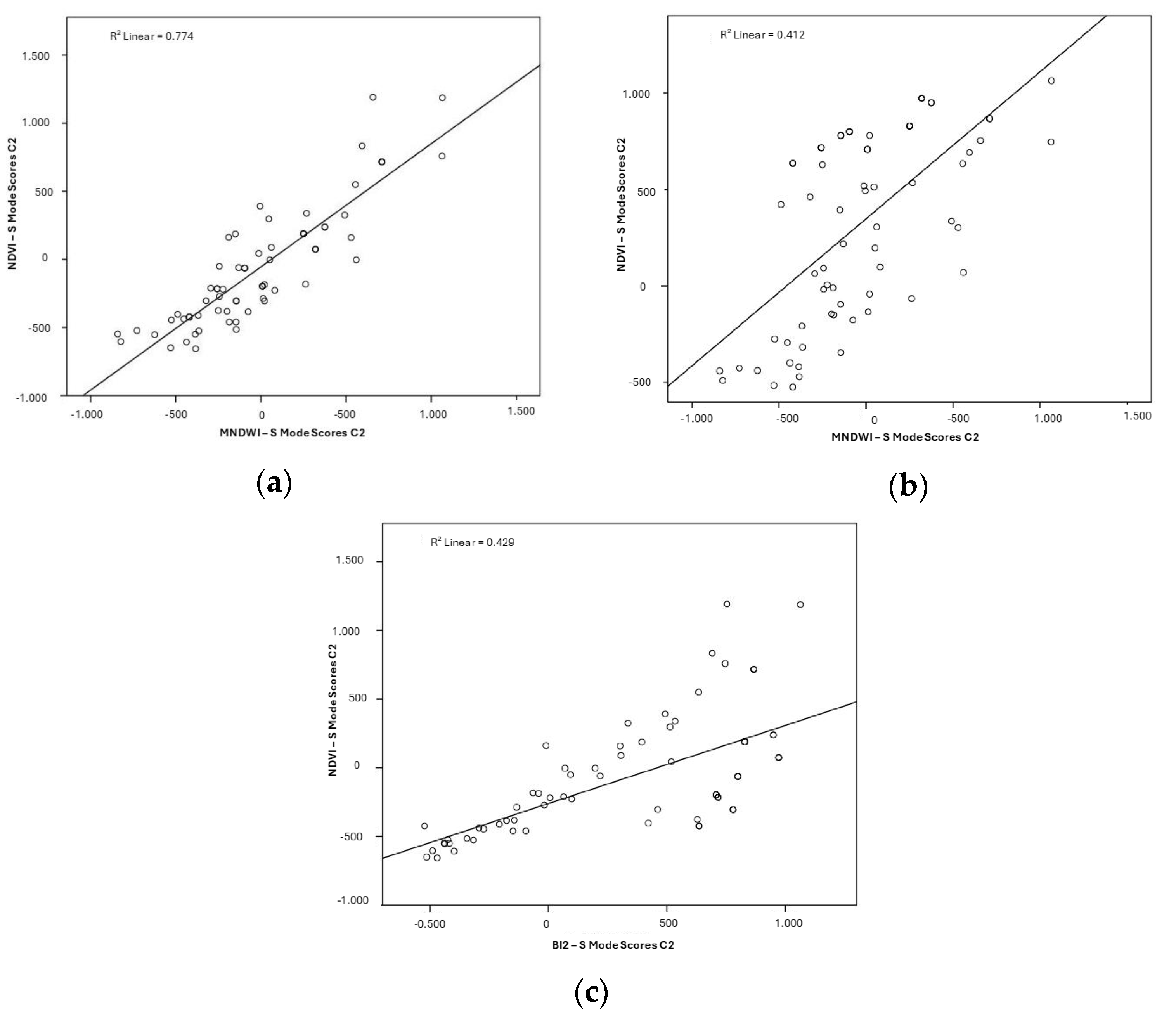
3.2. Relationship Between Hydrogeomorphological Attributes
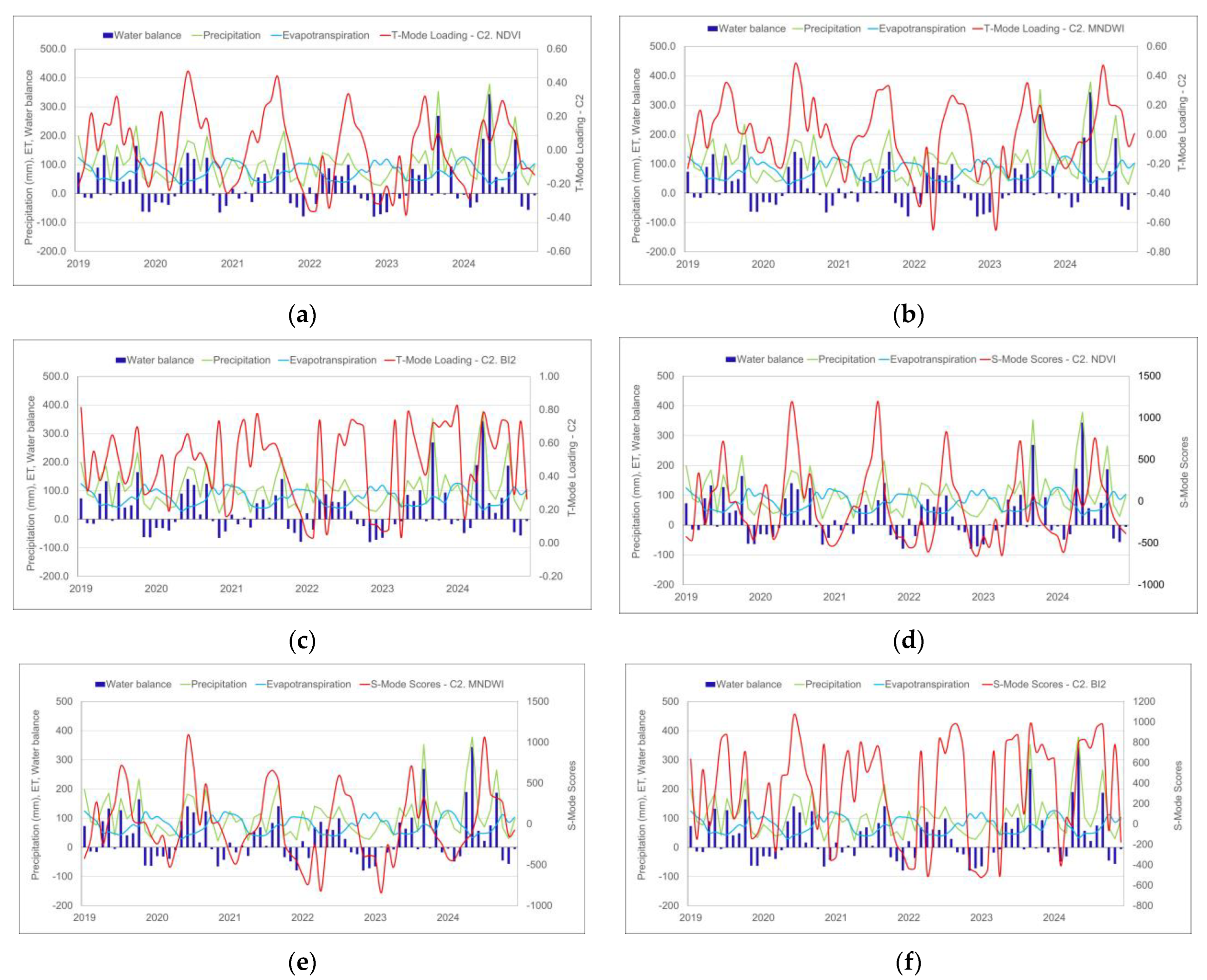
3.3. Hydrogeomorphological Attributes and Water Balance
4. Discussion
4.1. Temporal and Spatial Variability
4.2. Hydrogeomorphological Interactions
5. Conclusions
Implications for Conservation and Future Research
- Continuous monitoring of coastal wetlands, integrating remote sensing and hydrological data to anticipate responses to climate change;
- Differentiated protection by compartment, considering the higher sensitivity of areas such as the Lagoon Fringe to hydrological variations;
- Investigation of subsurface processes, such as water storage and exchanges with the water table, to better understand soil and vegetation resilience.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mitsch, W.J.; Bernal, B.; Nahlik, A.M.; Mander, Ü.; Zhang, L.; Anderson, C.J.; Jørgensen, S.E.; Brix, H. Wetlands, Carbon, and Climate Change. Landsc. Ecol. 2013, 28, 583–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simioni, J.P.D. Métodos de Classificação de Imagens de Satélite Para Delineamento de Banhados. Tese de Doutorado, Programa de Pós-Graduação em Sensoriamento Remoto, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul: Porto Alegre. 2021. Available online: https://lume.ufrgs.br/bitstream/handle/10183/222604/001127156.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- Aitali, R.; Snoussi, M.; Kolker, A.S.; Oujidi, B.; Mhammdi, N. Effects of Land Use/Land Cover Changes on Carbon Storage in North African Coastal Wetlands. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erwin, K.L. Wetlands and Global Climate Change: The Role of Wetland Restoration in a Changing World. Wetl. Ecol Manag. 2009, 17, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, S.; Xu, X.; Jia, G.; Zhang, A. Interannual Variability of Global Wetlands in Response to El Niño Southern Oscillations (ENSO) and Land-Use. Front. Earth Sci. 2019, 7, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jiang, W.; Peng, K.; Wu, Z.; Ling, Z.; Li, Z. Assessment of the Impact of Wetland Changes on Carbon Storage in Coastal Urban Agglomerations from 1990 to 2035 in Support of SDG15.1. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 877, 162824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunois, M.; Jackson, R.B.; Bousquet, P.; Poulter, B.; Canadell, J.G. The Growing Role of Methane in Anthropogenic Climate Change. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 120207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPBE. The IPBES Regional Assessment Report on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services for the Americas; Zenodo: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kuenzer, C.; Bluemel, A.; Gebhardt, S.; Quoc, T.V.; Dech, S. Remote Sensing of Mangrove Ecosystems: A Review. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 878–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcleod, E.; Chmura, G.L.; Bouillon, S.; Salm, R.; Björk, M.; Duarte, C.M.; Lovelock, C.E.; Schlesinger, W.H.; Silliman, B.R. A Blueprint for Blue Carbon: Toward an Improved Understanding of the Role of Vegetated Coastal Habitats in Sequestering CO2. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2011, 9, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirwan, M.L.; Megonigal, J.P. Tidal Wetland Stability in the Face of Human Impacts and Sea-Level Rise. Nature 2013, 504, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fluet-Chouinard, E.; Stocker, B.D.; Zhang, Z.; Malhotra, A.; Melton, J.R.; Poulter, B.; Kaplan, J.O.; Goldewijk, K.K.; Siebert, S.; Minayeva, T.; et al. Extensive Global Wetland Loss over the Past Three Centuries. Nature 2023, 614, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Peng, S.; Ciais, P.; Chen, Y. Future impacts of climate change on inland Ramsar wetlands. Nat. Clim. Change 2021, 11, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Niu, Z.; Chen, Y. Global Wetland Datasets: A Review. Wetlands 2017, 37, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Li, S.; Liang, Z.; Xu, S.; Yang, X.; Li, X. Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data for Wetland Information Extraction: A Case Study of the Nanweng River National Wetland Reserve. Sensors 2024, 24, 6664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doughty, C.L.; Ambrose, R.F.; Okin, G.S.; Cavanaugh, K.C. Characterizing Spatial Variability in Coastal Wetland Biomass across Multiple Scales Using UAV and Satellite Imagery. Remote Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 7, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korb, C.C.; Guasselli, L.A.; Belloli, T.F.; Cunha, C.S.; Bauer, A.L.; dos Santos Brückmann, C. Hydrogeomorphological compartmentalization in coastal wetlands—Lagoa do Peixe National Park, Brazil. Rev. Bras. Geomorfol. 2024, 25, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinson, M.M. A Hydrogeomorphic Classification for Wetlands; U.S. Army Corps of Engineers: Washington, DC, USA, 1993; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Simioni, J.P.D.; Guasselli, L.A.; Etchelar, C.B. Connectivity among Wetlands of EPA of Banhado Grande, RS. RBRH 2017, 22, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, I.; Abell, R.; Darwall, W.; Thieme, M.L.; Thickner, D.; Timboe, I. The Freshwater Biodiversity Crisis. Science 2018, 362, 1369. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Sun, W.; Chen, H.; Xue, B.; Yu, J.; Tian, Z. Interannual and Seasonal Variations of Hydrological Connectivity in a Large Shallow Wetland of North China Estimated from Landsat 8 Images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliani, C.R.; Hartmann, C.; Calliari, L.J.; Griep, G.H. Geologia e Geomorfologia da Porção Sul do Parque Nacional da Lagoa do Peixe, RS, Brasil. In Congresso Brasileiro de Geologia, 37; Anais: São Paulo, Brazil, 1992; pp. 292–294. Available online: https://www.sbgeo.org.br/home/pages/44 (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Xu, T.; Liu, R.; Shi, K.; Huang, C. Super-Resolution Mapping of Wetland Inundation from Remote Sensing Imagery Based on Integration of Back-Propagation Neural Network and Genetic Algorithm. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 164, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapinel, S.; Mony, C.; Lecoq, L.; Clément, B.; Thomas, A.; Hubert-Moy, L. Evaluation of Sentinel-2 Time-Series for Mapping Floodplain Grassland Plant Communities. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 223, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandus, P.; Minotti, P.G.; Morandeira, N.S.; Grimson, R.; González Trilla, G.; González, E.B.; San Martín, L.; Gayol, M.P. Remote Sensing of Wetlands in South America: Status and Challenges. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 993–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simioni, J.P.D.; Guasselli, L.A. Dual-Season Comparison of OBIA and Pixel-Based Approaches for Coastal Wetland Classification. RBRH 2024, 29, e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, X.; Chang, J. Changes in Wetland Landscape and Inundation Patterns in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River Basin from 1990 to 2020. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 161, 111992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pronk, M.; Hooijer, A.; Eilander, D.; Haag, A.; de Jong, T.; Vousdoukas, M.; Vernimmen, R.; Ledoux, H.; Eleveld, M. DeltaDTM: A Global Coastal Digital Terrain Model. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastman, J.R. TerrSet Libera GIS. Eospatial Monitoring and Modeling System; Tutorial; Version 2024; Clark University: Worcester, MA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Neeti, N.; Ronald Eastman, J. Novel Approaches in Extended Principal Component Analysis to Compare Spatio-Temporal Patterns among Multiple Image Time Series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 148, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, T.I.R.; Penatti, N.C.; Ferreira, L.G.; Arantes, A.E.; do Amaral, C.H. Principal Component Analysis Applied to a Time Series of MODIS Images: The Spatio-Temporal Variability of the Pantanal Wetland, Brazil. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2015, 23, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.E.; Noveli, R.A.P.; Filho, A.C.P. Uso de Análise de Componentes Principais (PCA) para Caracterização das Sub-Regiões do Megaleque do Taquari—Pantanal. Rev. GeoPantanal. 2023, 18, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munyati, C. Use of Principal Component Analysis (PCA) of Remote Sensing Images in Wetland Change Detection on the Kafue Flats, Zambia. Geocarto Int. 2004, 19, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, M.; Sousa, D.; Quandt, A.; Ganster, P.; Biggs, T. Mapping Multi-Decadal Wetland Loss: Comparative Analysis of Linear and Nonlinear Spatiotemporal Characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 302, 113969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlanga-Robles, C.A. Trends in Mangrove Canopy and Cover in the Teacapan-Agua Brava Lagoon System (Marismas Nacionales) in Mexico: An Approach Using Open-Access Geospatial Data. Wetlands 2024, 45, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepita-Villanueva, M.R.; Berlanga-Robles, C.A.; Ruiz-Luna, A.; Morales Barcenas, J.H. Spatio-Temporal Mangrove Canopy Variation (2001–2016) Assessed Using the MODIS Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI). J. Coast Conserv. 2019, 23, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, G.; Xue, B.; Zhang, M.; Tan, Z. Dynamic Landscapes and the Driving Forces in the Yellow River Delta Wetland Region in the Past Four Decades. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 787, 147644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolon, A.S. Diversidade de Macrófitas Aquáticas Em Áreas Úmidas Do Parque Nacional Da Lagoa Do Peixe, Rio Grande Do Sul. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Federal de São Carlos, Sao Carlos, Brazil, 2011. Available online: https://repositorio.ufscar.br/handle/20.500.14289/1740 (accessed on 27 December 2024).
- Costa, J.C.; Pereira, G.; Siqueira, M.E.; Cardozo, F.d.S.; da Silva, V.V. Validação dos Dados de Precipitação Estimados pelo CHIRPS para o Brasil. Rev. Bras. Climatol. 2019, 24, 228–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.; Winemiller, K.; Hoeinghaus, D.; Claudino, M.; Bastos, R.; Correa, F.; Huckembeck, S.; Vieira, J.; Loebmann, D.; Abreu, P.; et al. Hydrologic Pulsing Promotes Spatial Connectivity and Food Web Subsidies in a Subtropical Coastal Ecosystem. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2017, 567, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arejano, T.B. Geologia e Evolução Holocênica do Sistema Lagunar da Lagoa do Peixe, Litoral Médio do Rio Grande Do Sul, Brasil. Ph.D. Thesis, Programa de Pós-Graduação em Geociências, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2006. Available online: https://lume.ufrgs.br/handle/10183/8527 (accessed on 26 December 2024).
- Sbruzzi, J.B. Análise da Dinâmica da Embocadura da Lagoa do Peixe—RS Utilizando Dados de Sensoriamento Remoto Orbital. Master’s Thesis, Programa de Pós-Graduação em Sensoriamento Remoto, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2015. Available online: https://lume.ufrgs.br/bitstream/handle/10183/130851/000979924.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 21 December 2024).
- Schossler, V. Morfodinâmica da Embocadura da Lagoa do Peixe e da Linha de Praia Adjacente. Master’s Thesis, Programa de Pós-Graduação em Geociências, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2011. Available online: https://lume.ufrgs.br/bitstream/handle/10183/32663/000786858.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 27 December 2024).
- Schossler, V. Influência das Mudanças Climáticas em Geoindicadores na Costa Sul do Brasil. Ph.D. Thesis, Programa de Pós-Graduação em Geociências, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, Porto Alegre, 2016. Available online: https://lume.ufrgs.br/bitstream/handle/10183/149450/001006590.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 28 December 2024).
- Manzolli, R.P.; Portz, L.C.; Fontán-Bouzas, A.; Bitencourt, V.J.B.; Alcántara-Carrió, J. Contribution of Reverse Dune Migration to Stabilization of a Transgressive Coastal Dune Field at Lagoa do Peixe National Park Dune Field (South of Brazil). Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korb, C.C.; Guasselli, L.A.; Belloli, T.F.; Cunha, C.S. Dinâmica espaço-temporal de pulsos de inundações nas Áreas Úmidas do Parque Nacional da Lagoa do Peixe, sul do Brasil. Investig. Geogr. Una Mirada Desde El Sur 2023, 1, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junk, W.J. Definição, Delineamento e Classificação Brasileira das Áreas Úmidas. In Inventário das Áreas Úmidas Brasileiras: Distribuição, Ecologia, Manejo, Ameaças e Lacunas de Conhecimento; Carlini & Caniato Editorial: Cuiabá, Brazil, 2024; pp. 29–42. ISBN 978-85-8009-353-7. Available online: https://inau.org.br/site/images/e-book/c_c_inventario_das_areas_umidas_brasileiras_inau_e-book.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Villwock, J.A.; Tomazelli, L.J.; Loss, E.L.; Dehnhardt, E.A.; Bachi, F.A.; Dehnhardt, B.A. Quaternary of South America and Antarctic Peninsula. Geol. Rio Gd. Do Sul Coast. Prov. 1986, 4, 79–97. [Google Scholar]
- Tomazelli, L.J.; Villwock, J.A. O Cenozóico do Rio Grande do Sul: Geologia da Planície Costeira. In Geologia do Rio Grande do Sul; Holz, F., DeRos, L.F., Eds.; UFRGS: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2000; p. 444. [Google Scholar]
- Schäffer, A.; Lanzer, R.; Scur, L. Atlas Socioambiental Dos Municípios de Cidreira, Balneário Pinhal, Palmares Do Sul; Editora da Universidade de Caxias do Sul: Caxias do Sul, Brazil, 2013; Available online: https://www.ucs.br/educs/livro/atlas-socioambiental-dos-municipios-de-cideira-balneario-pinhal-e-palmares-do-sul-projeto-lagoas-costeiras-ii/ (accessed on 26 December 2024).
- Ramos, R.A.; Pasqualeto, A.I.; Balbueno, R.A.; Das Neves, D.D.; De Quadros, E.L.L. Mapeamento e Diagnóstico de Áreas Úmidas No Rio Grande Do Sul, Com o Uso de Ferramentas de Geoprocessamento. In Proceedings of the Anais, Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2014; pp. 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Belloli, T.F.; Guasselli, L.A.; Cunha, C.S.; Korb, C.C. Mudanças e Transição da Cobertura e Uso da Terra nas Áreas Úmidas da Região Geomorfológica Planície Costeira—RS. Geo UERJ 2024, 1, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, V.L. Uso do Solo e Conservação Ambiental no Parque Nacional da Lagoa do Peixe e Entorno (RS). Master’s Thesis, Programa de Pós-Graduação em Geografia, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2009. Available online: https://lume.ufrgs.br/bitstream/handle/10183/23706/000738097.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 19 December 2024).
- Portz, L.C.; Guasselli, L.A.; Corrêa, I.C.S. Variação Espacial e Temporal de NDVI na Lagoa do Peixe, RS. Rev. Bras. Geogr. Física 2011, 5, 897–908. [Google Scholar]
- IBGE. Banco de Dados e Informações Ambientais (BDIA). Mapeamento de Recursos Naturais (MRN), Escala 1:250 000. 2023. Available online: https://www.ibge.gov.br/pt/inicio.html (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- ICMBio. Limites Oficiais de Unidades de Conservação Federais. 2024. Available online: https://www.gov.br/icmbio/pt-br/assuntos/dados_geoespaciais/mapa-tematico-e-dados-geoestatisticos-das-unidades-de-conservacao-federais. (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Streck, E.V.; Kämpf, N.; Dalmolin, R.S.D.; Klamt, E.; Nascimento, P.C.; Scheneider, P.; Giasson, E.; Pinto, L.F.S. Solos Do Rio Grande Do Sul, 2nd ed.; Emater-Ascar: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Signori, L.M. Mapeamento espaço temporal da exótica invasora Pinus spp. na área norte do Parque Nacional da Lagoa do Peixe. Master’s Thesis, Programa de Pós-Graduação em Sensoriamento Remoto, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2018. Available online: https://lume.ufrgs.br/bitstream/handle/10183/179643/001069723.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Portz, L.; Manzolli, R.P.; Alcántara-Carrió, J.; Rockett, G.C.; Barboza, E.G. Degradation of a Transgressive Coastal Dunefield by Pines Plantation and Strategies for Recuperation (Lagoa Do Peixe National Park, Southern Brazil). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 259, 107483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reboita, M.S.; Ambrizzi, T.; da Rocha, R.P. Relationship between the Southern Annular Mode and Southern Hemisphere Atmospheric Systems Relação Entre o Modo Anular Sul e os Sistemas Atmosféricos no Hemisfério Sul. Rev. Bras. Meteorol. 2009, 24, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, D.C.; Berlato, M.A. Influência do El Niño Oscilação Sul sobre a precipitação do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul. Rev. Bras. Agrometeorol. 1997, 5, 127–132. Available online: https://revistas.ufpr.br/revistaabclima/article/view/25408 (accessed on 2 January 2025).
- Britto, F.P.; Barletta, R.; Mendonça, M. Variabilidade Espacial e Temporal da Precipitação Pluvial no Rio Grande Do Sul: Influência do fenômeno El Niño Oscilação Sul. Rev. Bras. Climatol. 2008, 3, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, B.D. Comportamento Dos Sistemas Frontais No Estado Do Rio Grande Do Sul Durante Os Episódios ENOS. Master’s Thesis, Programa de Pós-Graduação em Sensoriamento Remoto, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2015. Available online: https://lume.ufrgs.br/bitstream/handle/10183/139305/000989919.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 2 January 2025).
- Rouse, J.W.; Haas, R.H.; Schell, J.A.; Deering, D.W. Monitoring Vegetation Systems in the Great Plains with ERTS (Earth Resources Technology Satellite); Greenbelt: Austin, TX, USA, 1973; pp. 309–317. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H. Modification of Normalised Difference Water Index (NDWI) to Enhance Open Water Features in Remotely Sensed Imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escadafal, R. Remote Sensing of Arid Soil Surface Color with Landsat Thematic Mapper. Adv. Space Res. 1989, 9, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado-Machado, E.A.; Neeti, N.; Eastman, J.R.; Chen, H. Implications of Space-Time Orientation for Principal Components Analysis of Earth Observation Image Time Series. Earth Sci. Inf. 2011, 4, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsar Convention Secretariat. Wetland Inventory: A Ramsar Framework for Wetland Inventory and Ecological Character Description, 4th ed.; Ramsar Convention Secretariat: Gland, Switzerland, 2010; Volume 15. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, J.R. Sensoriamenro Remoto Do Ambiente: Uma Perspectiva Em Recursos Terrestre; Parêntese: Sao Jose dos Campos, Brazil, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuária. Sistema Brasileiro de Classificação de Solos, 2nd ed.; Embrapa Solos: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Giardina, F.; Gentine, P.; Konings, A.G.; Seneviratne, S.I.; Stocker, B.D. Diagnosing Evapotranspiration Responses to Water Deficit across Biomes Using Deep Learning. New Phytol. 2023, 240, 968–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stocker, B.D.; Tumber-Dávila, S.J.; Konings, A.G.; Anderson, M.C.; Hain, C.; Jackson, R.B. Global Patterns of Water Storage in the Rooting Zones of Vegetation. Nat. Geosci. 2023, 16, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Guo, H.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.; van der Tol, C.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, J. Meteorological Controls on Evapotranspiration over a Coastal Salt Marsh Ecosystem under Tidal Influence. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 279, 107755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dronova, I.; Gong, P.; Wang, L.; Zhong, L. Mapping Dynamic Cover Types in a Large Seasonally Flooded Wetland Using Extended Principal Component Analysis and Object-Based Classification. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 158, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rioja-Nieto, R.; Barrera-Falcón, E.; Torres-Irineo, E.; Mendoza-González, G.; Cuervo-Robayo, A.P. Environmental Drivers of Decadal Change of a Mangrove Forest in the North Coast of the Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico. J. Coast Conserv. 2017, 21, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penatti, N.C.; de Almeida, T.I.R.; Ferreira, L.G.; Arantes, A.E.; Coe, M.T. Satellite-Based Hydrological Dynamics of the World’s Largest Continuous Wetland. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 170, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junk, W.J.; Bayley, P.B.; Sparks, R.E. Flood Pulse Concept in River—Floodplain-Systems. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1989, 106, 110–127. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, S.; Han, G.; Chu, X.; Sun, B.; Song, W.; He, W.; Wang, X.; Li, P.; Yu, D. Prolonged Impacts of Extreme Precipitation Events Weakened Annual Ecosystem CO2 Sink Strength in a Coastal Wetland. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 310, 108655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ablat, X.; Liu, G.; Liu, Q.; Huang, C. Using MODIS-NDVI Time Series to Quantify the Vegetation Responses to River Hydro-Geomorphology in the Wandering River Floodplain in an Arid Region. Water 2021, 13, 2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, E.; Porporato, A. Impact of Hydroclimatic Fluctuations on the Soil Water Balance. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42, W06401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Sinha, R. Hydrogeomorphic Indicators of Wetland Health Inferred from Multi-Temporal Remote Sensing Data for a New Ramsar Site (Kaabar Tal), India. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 127, 107739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, O.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, S. Hydrological Simple Water Balance Modeling for Increasing Geographically Isolated Doline Wetland Functions and Its Application to Climate Change. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 149, 105812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penatti, N.C.; de Almeida, T.I.R. Subdvision of Pantanal Quaternary Wetlands: MODIS NDVI Time Series in the Indirect Detection of Sediments Granulometry. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2012, 39, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narváez-Salcedo, S.; Hoyos, N.; Aldana-Domínguez, J. Spatial and Temporal Trend of EVI in Mangrove Forests of Coastal Lagoons in the Colombian Caribbean; Universidad del Norte: Barranquilla, Colombia, 2022. [Google Scholar]



| Hydrogeomorphological Attribute/Variable | Formula | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) | [64] | |
| Modified Normalized Difference Water Index (MNDWI) | [65] | |
| Second Brightness Index (BI2) | [66] |
| NDVI | MNDWI | BI2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NDVI | Pearson Correlation | - | - | - |
| p value | - | - | - | |
| MNDWI | Pearson Correlation | 0.862 | - | - |
| p value | p < 0.001 | - | - | |
| BI2 | Pearson Correlation | 0.550 | 0.497 | - |
| p value | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | - | |
| NDVI | MNDWI | BI2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NDVI | Pearson Correlation | - | - | - |
| p value | - | - | - | |
| MNDWI | Pearson Correlation | 0.880 | - | - |
| p value | p < 0.001 | - | - | |
| BI2 | Pearson Correlation | 0.655 | 0.642 | - |
| p value | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | - | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Korb, C.C.; Guasselli, L.A.; Hasenack, H.; Belloli, T.F.; Cunha, C.S. Temporal and Spatial Variability of Hydrogeomorphological Attributes in Coastal Wetlands—Lagoa do Peixe National Park, Brazil. Coasts 2025, 5, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/coasts5030023
Korb CC, Guasselli LA, Hasenack H, Belloli TF, Cunha CS. Temporal and Spatial Variability of Hydrogeomorphological Attributes in Coastal Wetlands—Lagoa do Peixe National Park, Brazil. Coasts. 2025; 5(3):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/coasts5030023
Chicago/Turabian StyleKorb, Carina Cristiane, Laurindo Antonio Guasselli, Heinrich Hasenack, Tássia Fraga Belloli, and Christhian Santana Cunha. 2025. "Temporal and Spatial Variability of Hydrogeomorphological Attributes in Coastal Wetlands—Lagoa do Peixe National Park, Brazil" Coasts 5, no. 3: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/coasts5030023
APA StyleKorb, C. C., Guasselli, L. A., Hasenack, H., Belloli, T. F., & Cunha, C. S. (2025). Temporal and Spatial Variability of Hydrogeomorphological Attributes in Coastal Wetlands—Lagoa do Peixe National Park, Brazil. Coasts, 5(3), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/coasts5030023





