Fluorinated-Polyether-Grafted Graphene-Oxide Magnetic Composite Material for Oil–Water Separation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
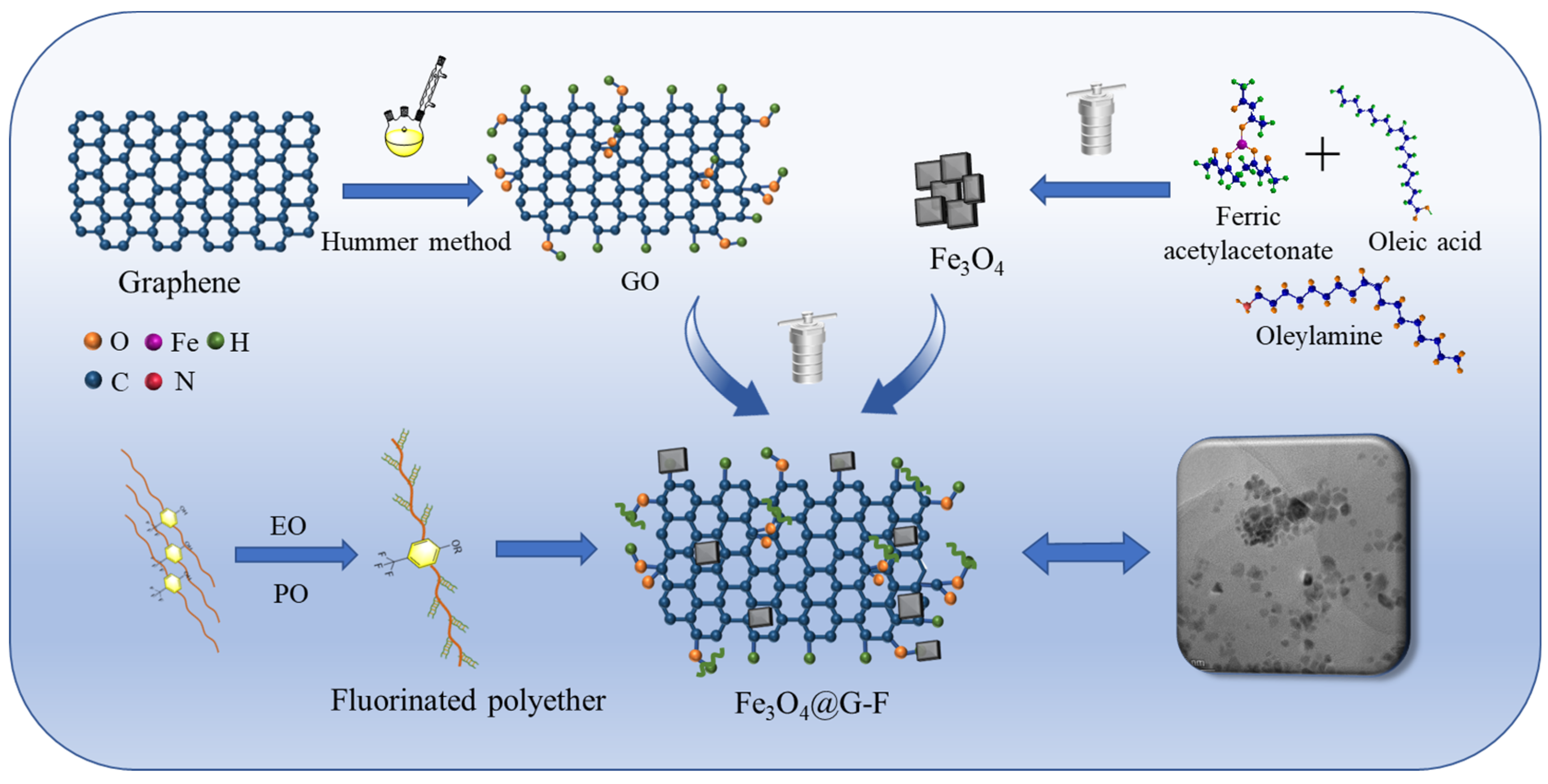
2.2. One-Pot Preparation of Magnetic Demulsifiers
2.3. Preparation of Crude Oil Emulsion
2.4. Demulsification Performance Test
2.5. Demulsification Recovery Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Modified Fluoropolyether
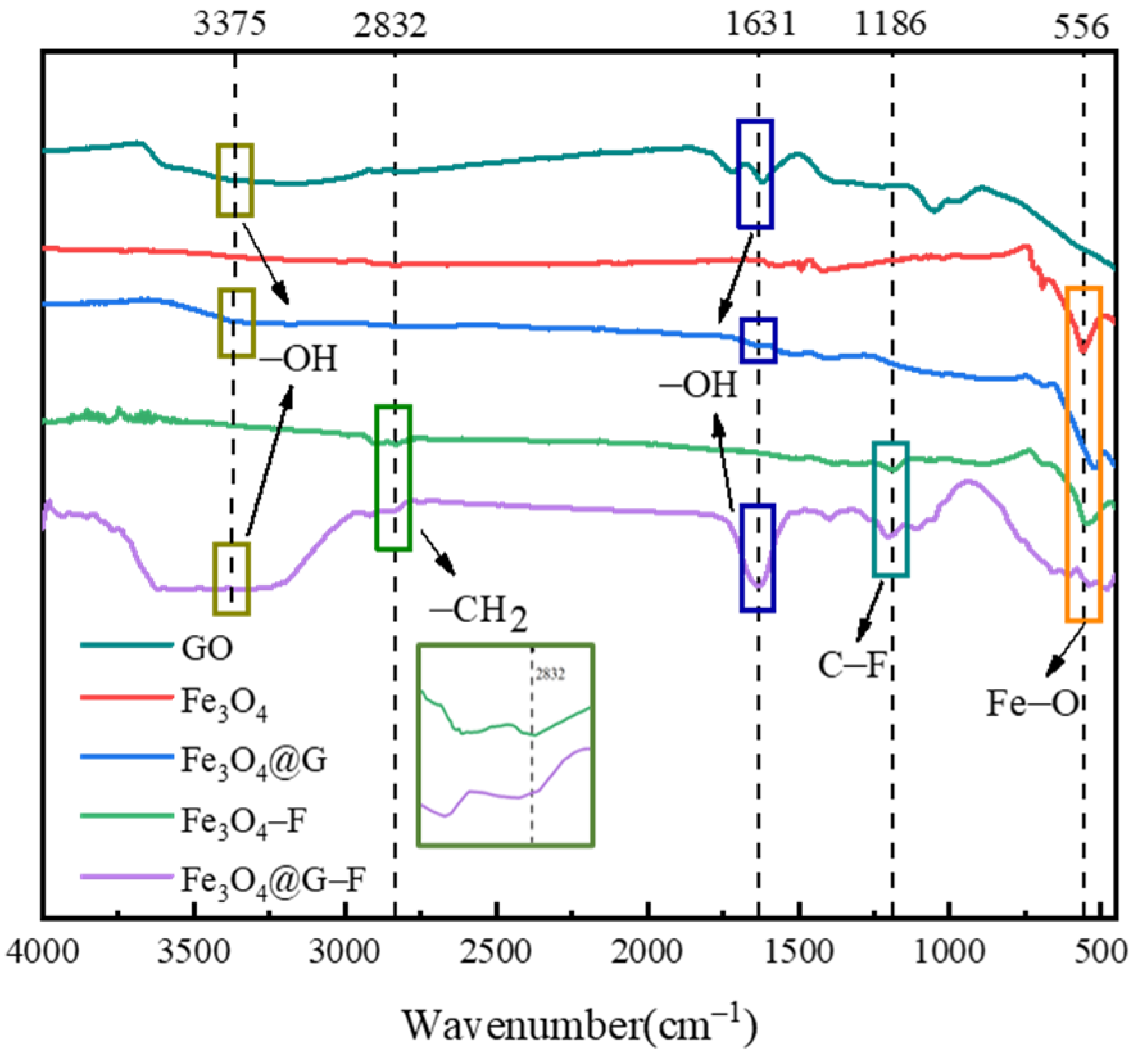
3.1.1. Infrared Spectra of Different Materials
3.1.2. XPS of Modified Fluorinated Polyether
3.1.3. TEM and SEM of Composite Materials
3.1.4. TGA of Modified Fluoropolyether
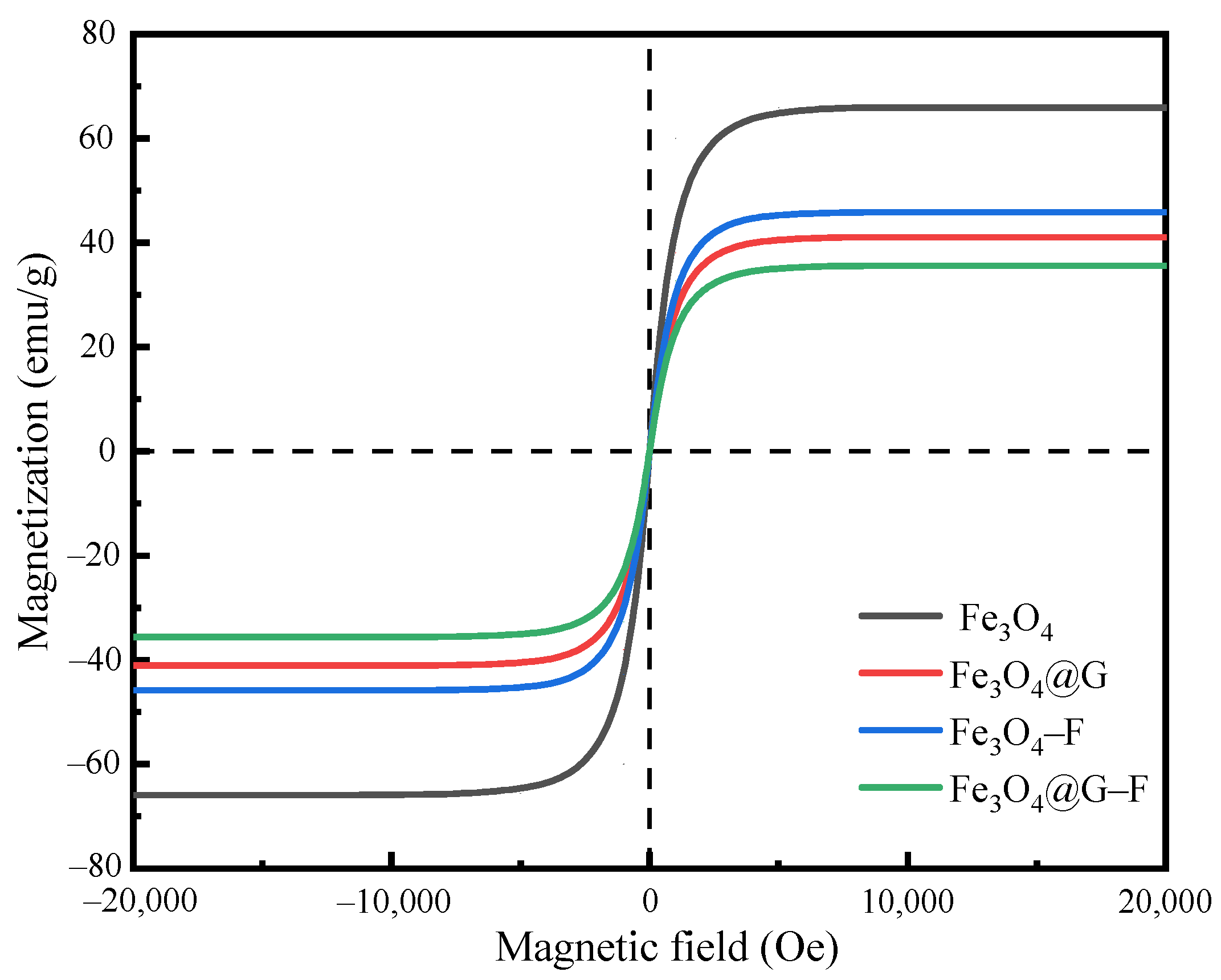
3.1.5. VSM of Modified Fluorinated
3.2. The Demulsification Performance of Modified Fluorinated Polyether
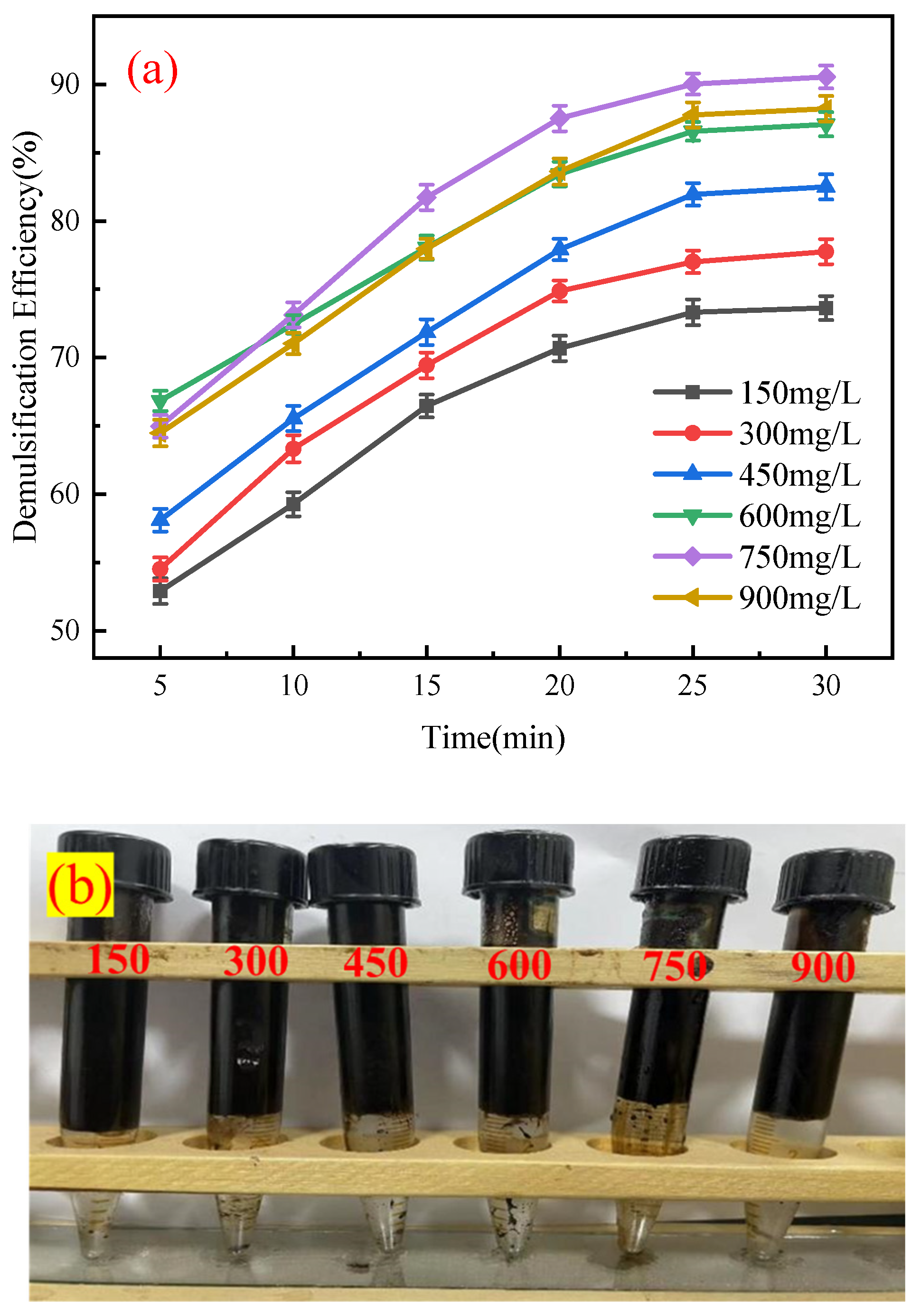
3.2.1. Effect of Demulsifier Dosage on Demulsification Performance
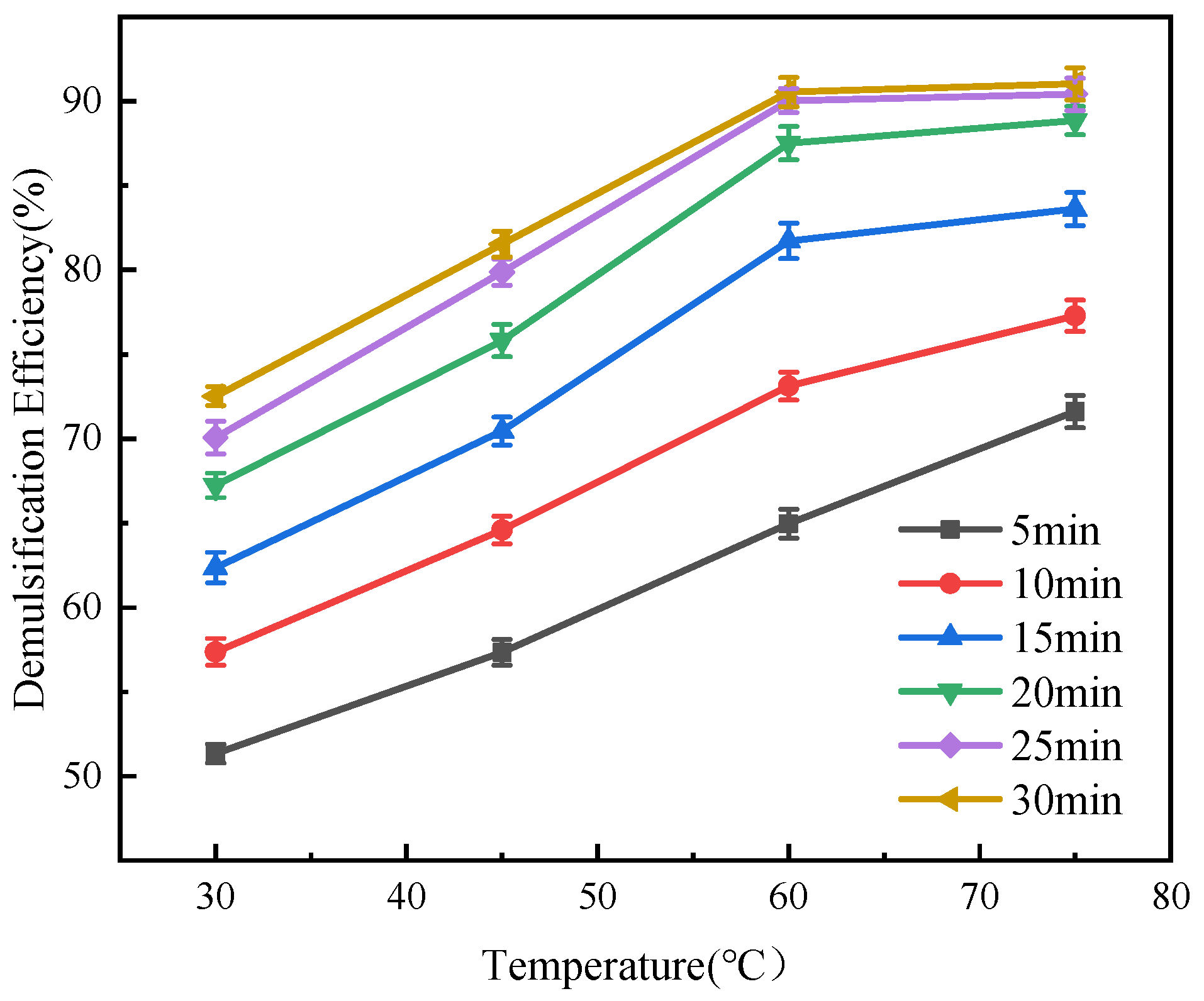
3.2.2. Effects of Time and Temperature on Demulsification Performance
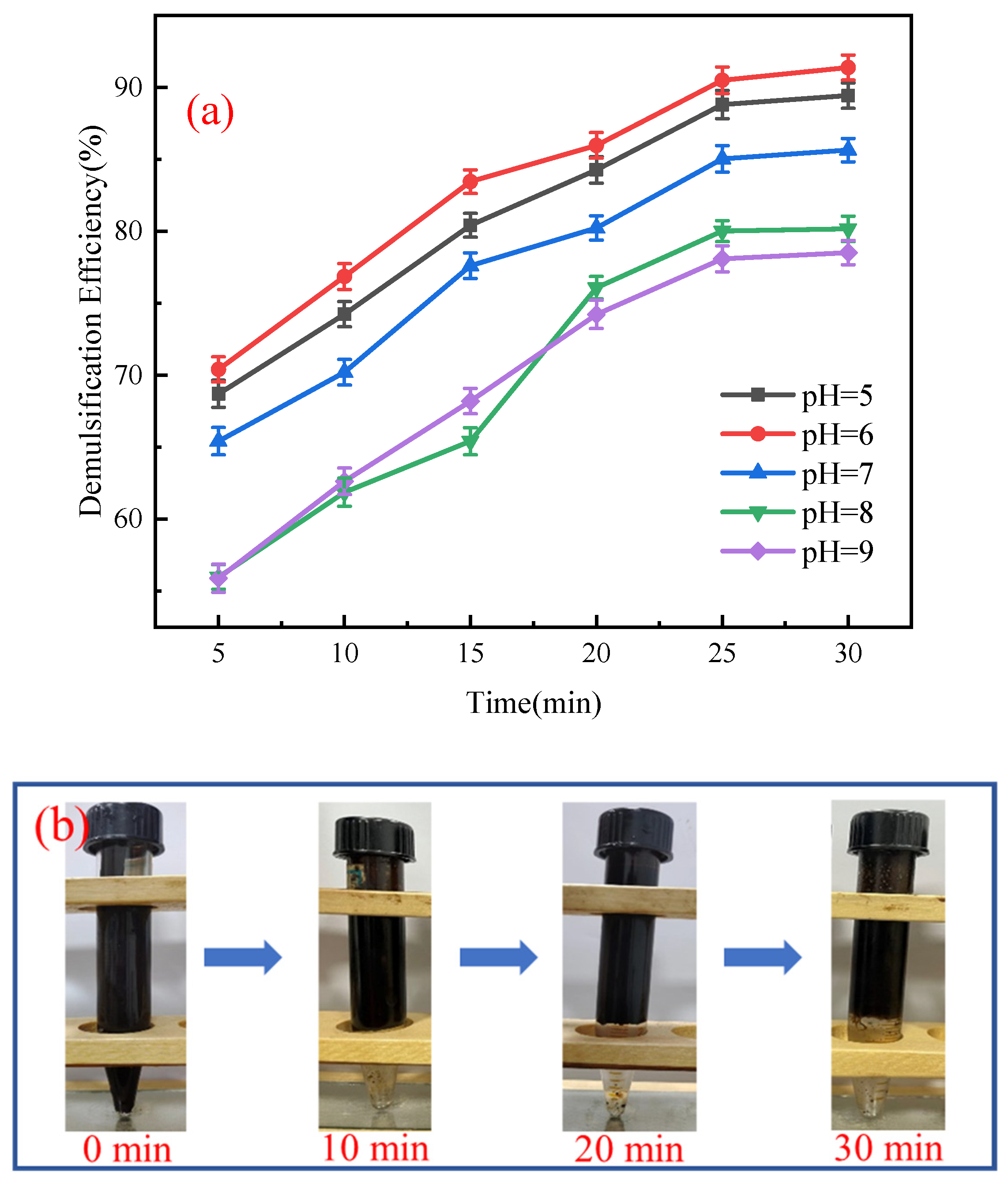
3.2.3. Effect of pH on Demulsification Performance
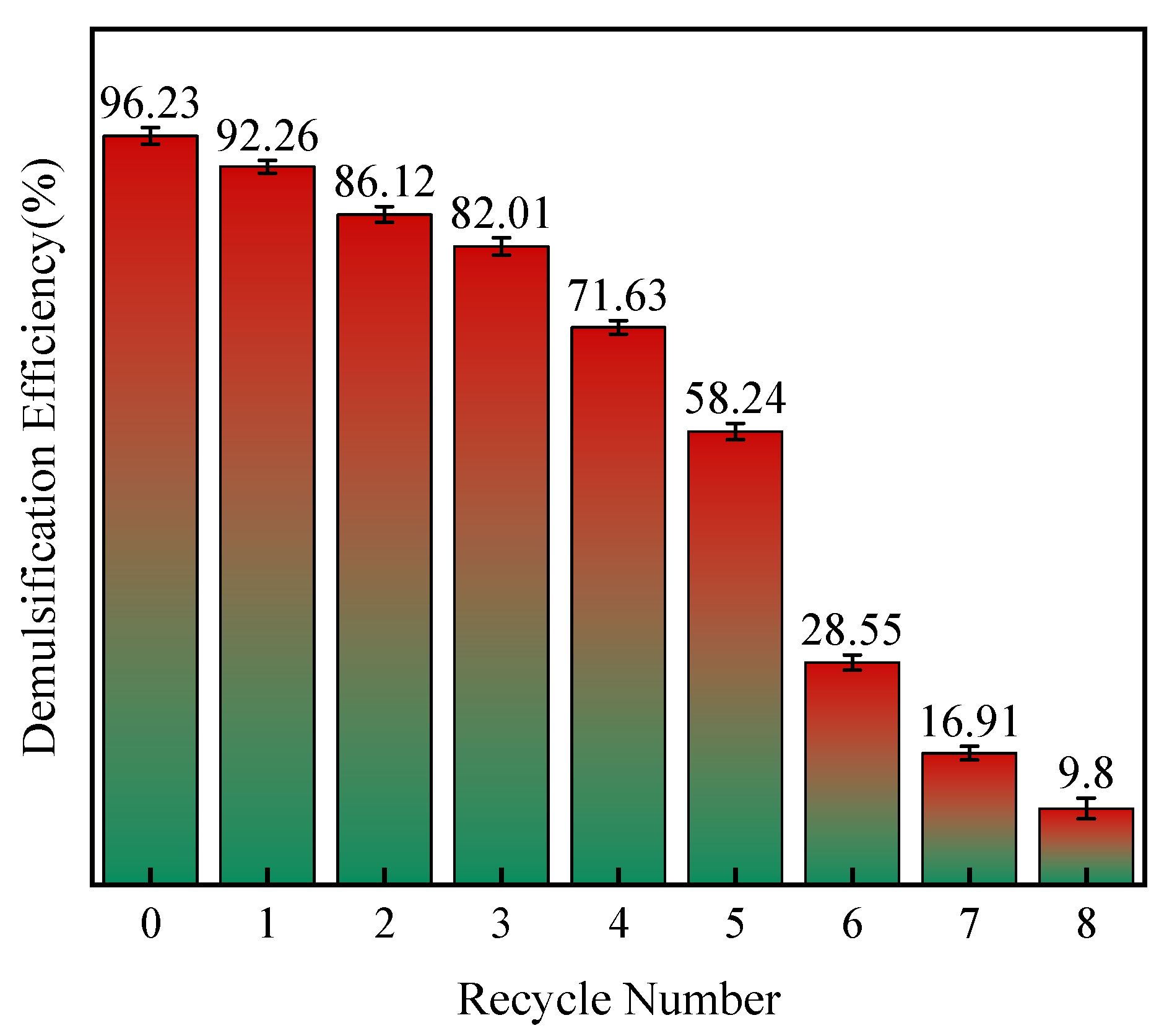
3.2.4. Recovery Performance Test
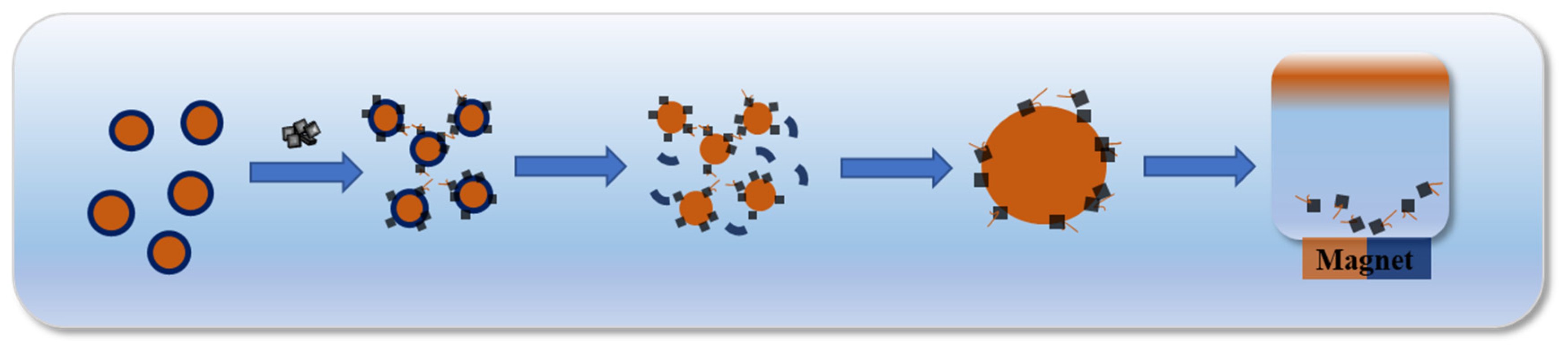
3.3. The Demulsification Mechanism of Fe3O4@G-F
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdulredha, M.M.; Hussain, S.A.; Abdullah, L.C.; Hong, T.L. Water-in-oil emulsion stability and demulsification via surface-active compounds: A review. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 209, 109848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Qi, Y.; Han, H.; Luo, X.; Guan, J.; Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Gong, X. Resin transfer in oil-water interface intensified by H2O2 and demulsifier for efficient water separation in tight oil. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 301, 121994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meza, L.; Alvarado, J.G.; Márquez, R.; Forgiarini, A. Performance Evaluation of Demulsifier Using the Optimum Formulation HLD Concept: A Practical Case Using Heavy Crude Oil Diluted in Naphtha or in Synthetic Aromatic Oil. SPE J. 2022, 27, 1856–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhou, J.; He, C.; He, L.; Li, X.; Sui, H. The formation, stabilization and separation of oil–water emulsions: A Review. Processes 2022, 10, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahú, J.O.; Miranda, N.T.; Khouri, N.G.; Batistella, C.B.; Concha, V.O.C.; Maciel, M.R.W.; Schiavon, M.I.R.B.; Filho, R.M. Crude oil emulsion breaking: An investigation about gravitational and rheological stability under demulsifiers action. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 210, 110089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, L.D.; Rivera-Gonzalez, N.; Cool, N.; Bajpayee, A.; Udayakantha, M.; Liu, G.-W.; Anita; Banerjee, S. A Materials Science Perspective of Midstream Challenges in the Utilization of Heavy Crude Oil. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 1547–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husain, A.; Al-Harthi, M.A. Chemical treatment of oilfield wastewater and the effect of temperature on treatment efficiency: A review. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2023, 220, 111089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanshahi, N.; Hu, G.; Li, J. Investigation of Dioctyl Sodium Sulfosuccinate in Demulsifying Crude Oil-in-Water Emulsions. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 33397–33407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamedi, H.; Rezaei, N.; Zendehboudi, S. A comprehensive review on demulsification using functionalized magnetic nanoparticles. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 380, 134868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Jiang, H.; Su, R.; Zhang, L.; Shen, L.; Sun, H. Experimental Study on Synergistic Demulsification of Microwave-Magnetic Nanoparticles. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 35523–35531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Chang, X.; Sun, H.; Shen, L.; Su, R. Study on the Coupling Effect of Microwave and Magnetic Nanoparticles on Oil Droplet Coalescence. SPE J. 2022, 27, 3051–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, N.; Bashipour, F. Demulsification of water-in-oil emulsions applying Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles for demulsifier modification: Experimental optimization via response surface methodology. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 216, 110806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Jia, W.; Hou, K.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, S.; Wang, J. Similar chemical composition with different tribological properties: Influences of CF bond strength carbon-skeleton structure on fluorinated graphene, P.T.F.E. Tribol. Int. 2022, 165, 107250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, A.M.; Dullinger, P.; Biswas, A.; Jandl, C.; Horinek, D.; Gulder, T. Enzyme-like polyene cyclizations catalyzed by dynamic, self-assembled, supramolecular fluoro alcohol-amine clusters. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad, M.A.; Kamil, M.; Abdurahman, N.H.; Yunus, R.M.; Awad, O.I. An Overview of Recent Advances in State-of-the-Art Techniques in the Demulsification of Crude Oil Emulsions. Processes 2019, 7, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernikova, I.B.; Yunusov, M.S. Synthesis and properties of fluorinated uracils as promising drugs for medicine. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2022, 71, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogapriya, R.; Kasibhatta, K.R.D. Hydrophobic-Superoleophilic Fluorinated Graphene Nanosheet Composites with Metal–Organic Framework HKUST-1 for Oil–Water Separation. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 5816–5825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, L.; Guo, H.; Shan, C.; Jia, X.; Wei, L.; Cai, Y.; Han, L. Screening and Demulsification Mechanism of Fluorinated Demulsifier Based on Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Molecules 2022, 27, 1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xue, D.D.; Li, Y.F.; Zhao, M.; Bai, X.L.; Zhang, J.; Hao, J.S.; Zhao, Y.X. Synthesis of fluorinated silicon-containing amphiphilic copolymer and its demulsification performance. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 558, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Zhang, L.; Guo, S.; Jia, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, C.; Dai, X. Synthesis and Study of a New Type of Fluorinated Polyether Demulsifier for Heavy Oil Emulsion Demulsification. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 25518–25528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewunmi, A.A.; Kamal, M.S.; Solling, T.I. Application of magnetic nanoparticles in demulsification: A review on synthesis, performance, recyclability, and challenges. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 196, 107680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, C.; Qi, D.; Lü, T.; Zhang, D. One-Step Synthesis of Polyethylenimine-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles and its Demulsification Performance in Surfactant-Stabilized Oil-in-Water Emulsion. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2019, 40, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yu, B.; Wang, S.; Shen, Y.; Cong, H. Preparation, surface functionalization and application of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 281, 102165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, N.; Zhao, X.; Han, Z.; Jiang, X.; Fang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, D. Dodecenylsuccinic anhydride-modified oxalate decarboxylase loaded with magnetic nano-Fe3O4@SiO2 for demulsification of oil-in-water emulsions. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Bian, J. Preparation of a recyclable demulsifier for the treatment of emulsified oil wastewater by chitosan modification and sodium oleate grafting Fe3O4. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, B.; Sarma, D.; Jain, S.; Sarma, T.K. One-Pot Magnetic Iron Oxide–Carbon Nanodot Composite-Catalyzed Cyclooxidative Aqueous Tandem Synthesis of Quinazolinones in the Presence of tert-Butyl Hydroperoxide. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 13711–13719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.-J.; He, X.; Lai, L.; Lu, Q.; Cheng, L.; Wu, J. Polydopamine-anchored polyether on Fe3O4 as magnetic recyclable nanoparticle-demulsifiers. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 617, 126142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Niu, J.; Lu, M.; Liu, X.; Cai, Z. Analysis of flavors and fragrances by HPLC with Fe3O4@ GO magnetic nanocomposite as the adsorbent. Talanta 2017, 166, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, B.; Sarma, D.; Bhattacharya, T.; Sarma, T.K. Graphene Oxide as Metal-Free Catalyst in Oxidative Dehydrogenative C–N Coupling Leading to α-Ketoamides: Importance of Dual Catalytic Activity. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 9286–9294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Ning, L. Magnetically Recyclable Graphene Oxide Demulsifier Adapting Wide pH Conditions on Detachment of Oil in the Crude Oil-in-Water Emulsion. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 6748–6757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Jia, W.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, S. Recyclable magnetic graphene oxide for rapid and efficient demulsification of crude oil-in-water emulsion. Fuel 2017, 189, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tian, G.; Liang, H.; Liang, Y. Synthesis of magnetically responsive hyperbranched polyamidoamine based on the graphene oxide: Application as demulsifier for oil-in-water emulsions. Int. J. Energy Res. 2019, 43, 4756–4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, K.K.; Tan, I.S.; Foo, H.C.Y.; Lam, M.K.; Tiong, A.C.Y.; Lim, S. Optimization and evaluation of reduced graphene oxide hydrogel composite as a demulsifier for heavy crude oil-in-water emulsion. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 33, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wei, L.; Shi, L.; Dai, X.; Guo, S.; Jia, X.; Liu, C. Synthesis and characterization of a novel reticulated multi-branched fluorinated polyether demulsifier for w/o emulsion demulsification. J. Polym. Res. 2022, 29, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohzadi, H.; Soleiman-Beigi, M. XPS and structural studies of Fe3O4-PTMS-NAS@Cu as a novel magnetic natural asphalt base network and recoverable nanocatalyst for the synthesis of biaryl compounds. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Liu, Y.; Ren, W. Structure switch between α-Fe2O3, γ-Fe2O3 and Fe3O4 during the large scale and low temperature sol–gel synthesis of nearly monodispersed iron oxide nanoparticles. Adv. Powder Technol. 2013, 24, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahil, H.; Faramawy, A.; El-Sayed, H.; Abdel-Sattar, A. Magnetic Properties and SAR for Gadolinium-Doped Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Prepared by Hydrothermal Method. Crystals 2021, 11, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Wei, L.; Jia, X.; Gu, Y.; Guo, H.; Geng, X. Fluorinated-Polyether-Grafted Graphene-Oxide Magnetic Composite Material for Oil–Water Separation. AppliedChem 2023, 3, 400-413. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem3030025
Liu C, Wei L, Jia X, Gu Y, Guo H, Geng X. Fluorinated-Polyether-Grafted Graphene-Oxide Magnetic Composite Material for Oil–Water Separation. AppliedChem. 2023; 3(3):400-413. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem3030025
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Chao, Lixin Wei, Xinlei Jia, Yuxin Gu, Haiying Guo, and Xiaoheng Geng. 2023. "Fluorinated-Polyether-Grafted Graphene-Oxide Magnetic Composite Material for Oil–Water Separation" AppliedChem 3, no. 3: 400-413. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem3030025
APA StyleLiu, C., Wei, L., Jia, X., Gu, Y., Guo, H., & Geng, X. (2023). Fluorinated-Polyether-Grafted Graphene-Oxide Magnetic Composite Material for Oil–Water Separation. AppliedChem, 3(3), 400-413. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem3030025




