Comparison of Sensitivity and Specificity of Commercial Amphetamine Tests
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Validation of a Chromatographic Method for the Determination of Amphetamine in Synthetic Urine Diluent
3.1.1. Specificity
3.1.2. Linearity
3.1.3. Accuracy
3.1.4. Repeatability and Intermediate Precision
3.1.5. Limit of Detection and Limit of Quantification
3.1.6. Measurement Range
3.1.7. Quantitative Analysis of Amphetamine in Samples to Evaluate the Sensitivity of Cassette Test
3.1.8. Evaluation of Sensitivity and Specificity of Cassette Tests
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction European Drug Report 2022: Trends and Developments; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2022; ISBN 9789294977694.
- Carvalho, M.; Carmo, H.; Costa, V.M.; Capela, J.P.; Pontes, H.; Remião, F.; Carvalho, F.; de Bastos, M.L. Toxicity of Amphetamines: An Update. Arch. Toxicol. 2012, 86, 1167–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heal, D.J.; Smith, S.L.; Gosden, J.; Nutt, D.J. Amphetamine, Past and Present—A Pharmacological and Clinical Perspective. J. Psychopharmacol. 2013, 27, 479–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleemeier, L.B.; Kleemeier, R.W. Effects of Benzedrine Sulfate (Amphetamine) on Psychomotor Performance. Am. J. Psychol. 1947, 60, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, N. Amphetamine-Type Stimulants: The Early History of Their Medical and Non-Medical Uses. In International Review of Neurobiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 120, pp. 9–25. ISBN 9780128029787. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen, N. Medical Science and the Military: The Allies’ Use of Amphetamine during World War II. J. Interdiscip. Hist. 2011, 42, 205–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomolka, E.; Morawska, A. Advantages and Disadvantages of Rapid Tests, How to Determine Drugs of Abuse in Medical Laboratory. Diagn. Lab. 2011, 47, 197–203. [Google Scholar]
- Moeller, K.E.; Lee, K.C.; Kissack, J.C. Urine Drug Screening: Practical Guide for Clinicians. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, S. Position of Immunological Techniques in Screening in Clinical Toxicology. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2004, 42, 1288–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghipour, F.; Giroud, C.; Rivier, L.; Veuthey, J.L. Rapid Determination of Amphetamines by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with UV Detection. J. Chromatogr. A 1997, 761, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use: Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology Q2(R1). ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guideline. 2014. Available online: https://database.ich.org/sites/default/files/Q2%28R1%29%20Guideline.pdf (accessed on 2 December 2022).
- Willard, H.H.; Merritt, L.L.; Dean, J.A. Instrumental Methods of Analysis; Wadsworth Pub Co.: Belmont, CA, USA, 1952; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. Association of Official Agricultural Chemists Appendix F: Guidelines for Standard Method Performance Requirements; AOAC INTERNATIONAL: Rockville, MD, USA, 2016; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Center, N.; Statistics, D.A. Drug Related Crime Statistics. Available online: https://drugabusestatistics.org/drug-related-crime-statistics/ (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- Osterloh, J.D.; Becker, C.E. Cheimical Dependency and Drug Testing in the Workplace. J. Psychoact. Drugs 1990, 22, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drug Testing in Rehab Centers—Accurate and Quick Results Needed to Meet Treatment Goals. Available online: https://www.blockscientific.com/drug-testing-in-rehab-centers-accurate-quick-results-needed-to-meet-treatment-goals (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- Moeller, K.E.; Kissack, J.C.; Atayee, R.S.; Lee, K.C. Clinical Interpretation of Urine Drug Tests. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2017, 92, 774–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitman, A.; Park, H.-D.; Fitzgerald, R.L. False-Positive Interferences of Common Urine Drug Screen Immunoassays: A Review. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2014, 38, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertholf, R.L.; Johannsen, L.M.; Reisfield, G.M. Sensitivity of an Opiate Immunoassay for Detecting Hydrocodone and Hydromorphone in Urine from a Clinical Population: Analysis of Subthreshold Results. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2015, 39, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reisfield, G.M.; Goldberger, B.A.; Bertholf, R.L. ‘False-Positive’ and ‘False-Negative’ Test Results in Clinical Urine Drug Testing. Bioanalysis 2009, 1, 937–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fucci, N. False Positive Results for Amphetamine in Urine of a Patient with Diabetes Mellitus. Forensic Sci. Int. 2012, 223, e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthier, M.; Bonneau, D.; Mura, P.; Piriou, A.; Oriot, D. Benzathine as a Cause for a False-Positive Test Result for Amphetamines. J. Pediatr. 1995, 127, 669–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
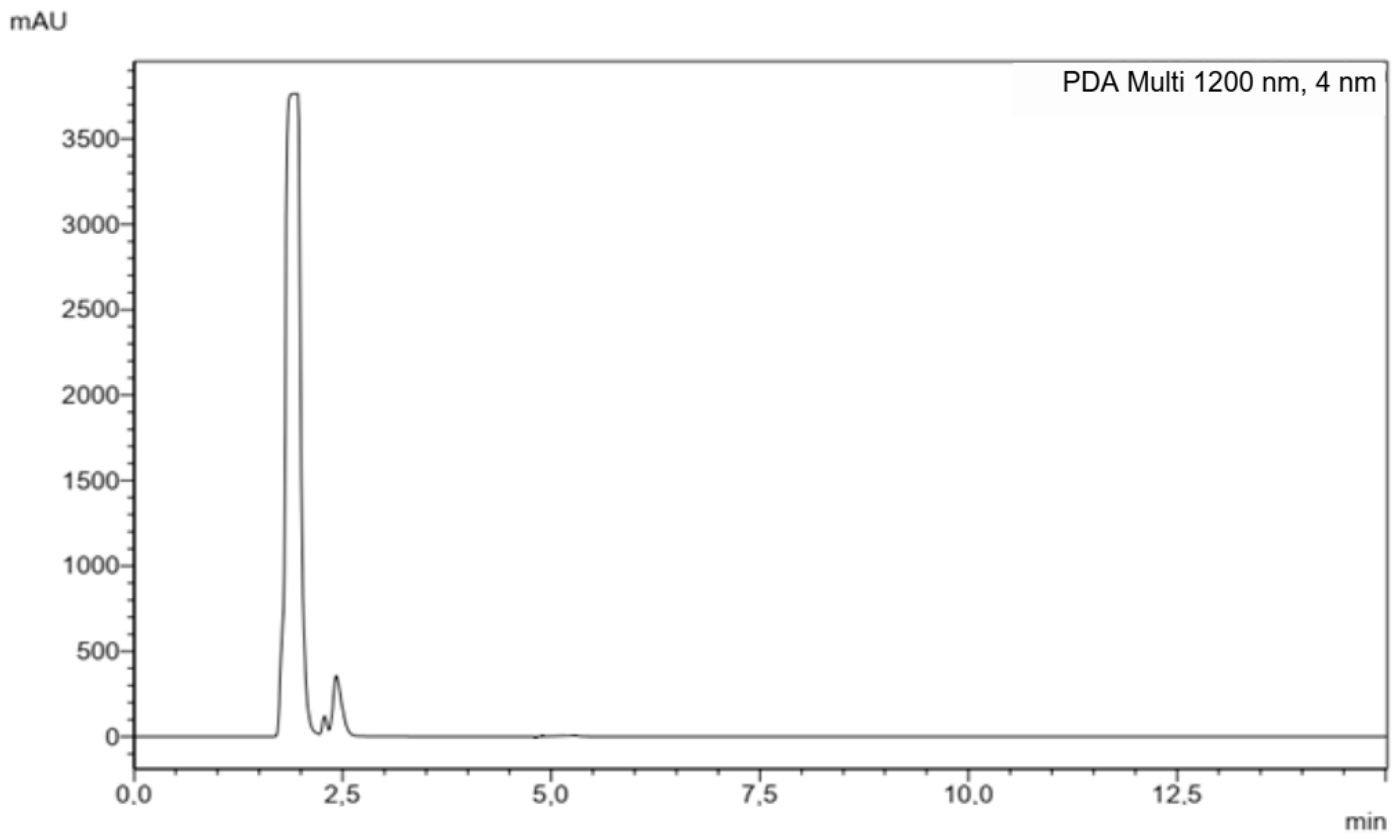
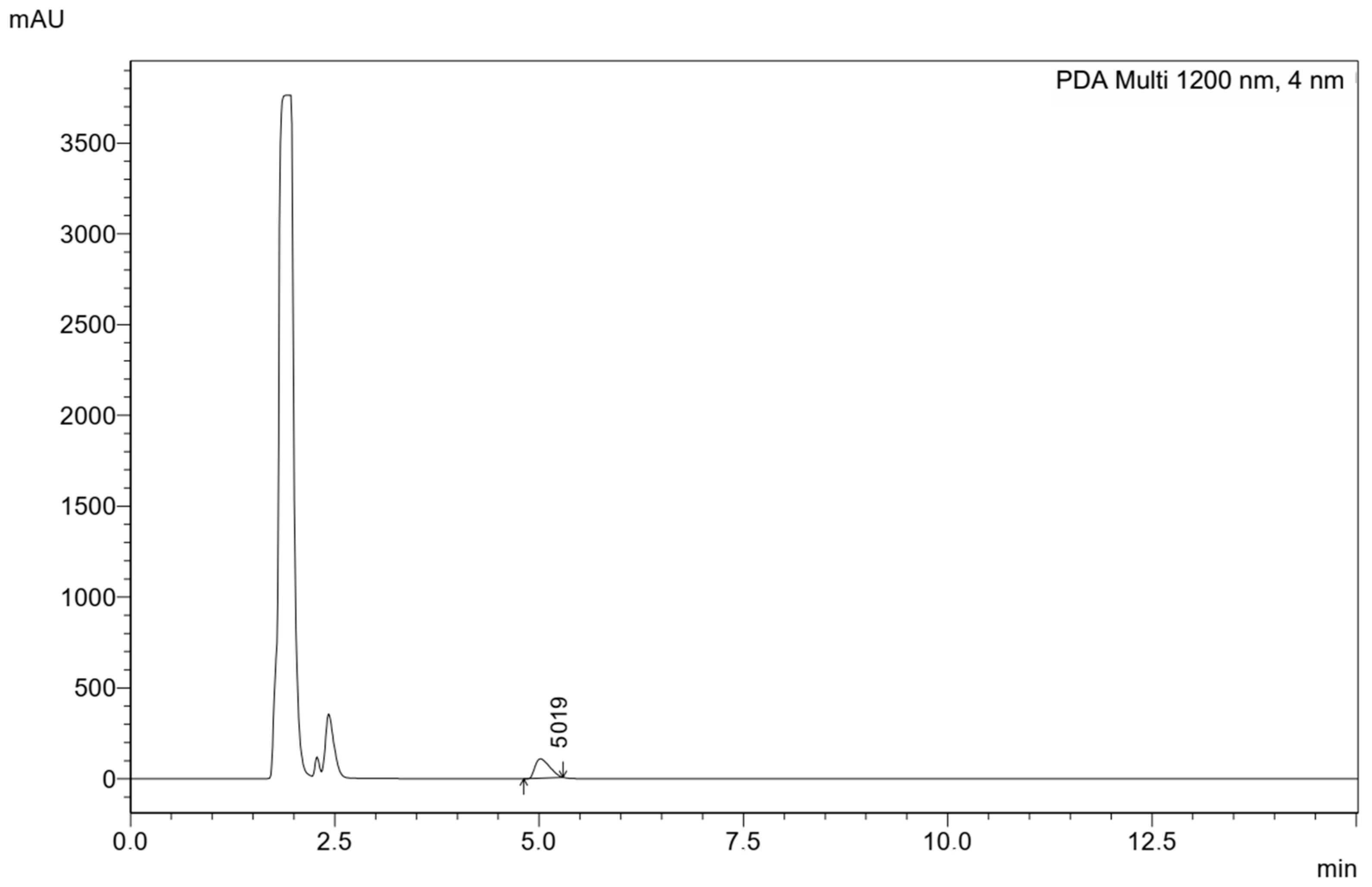
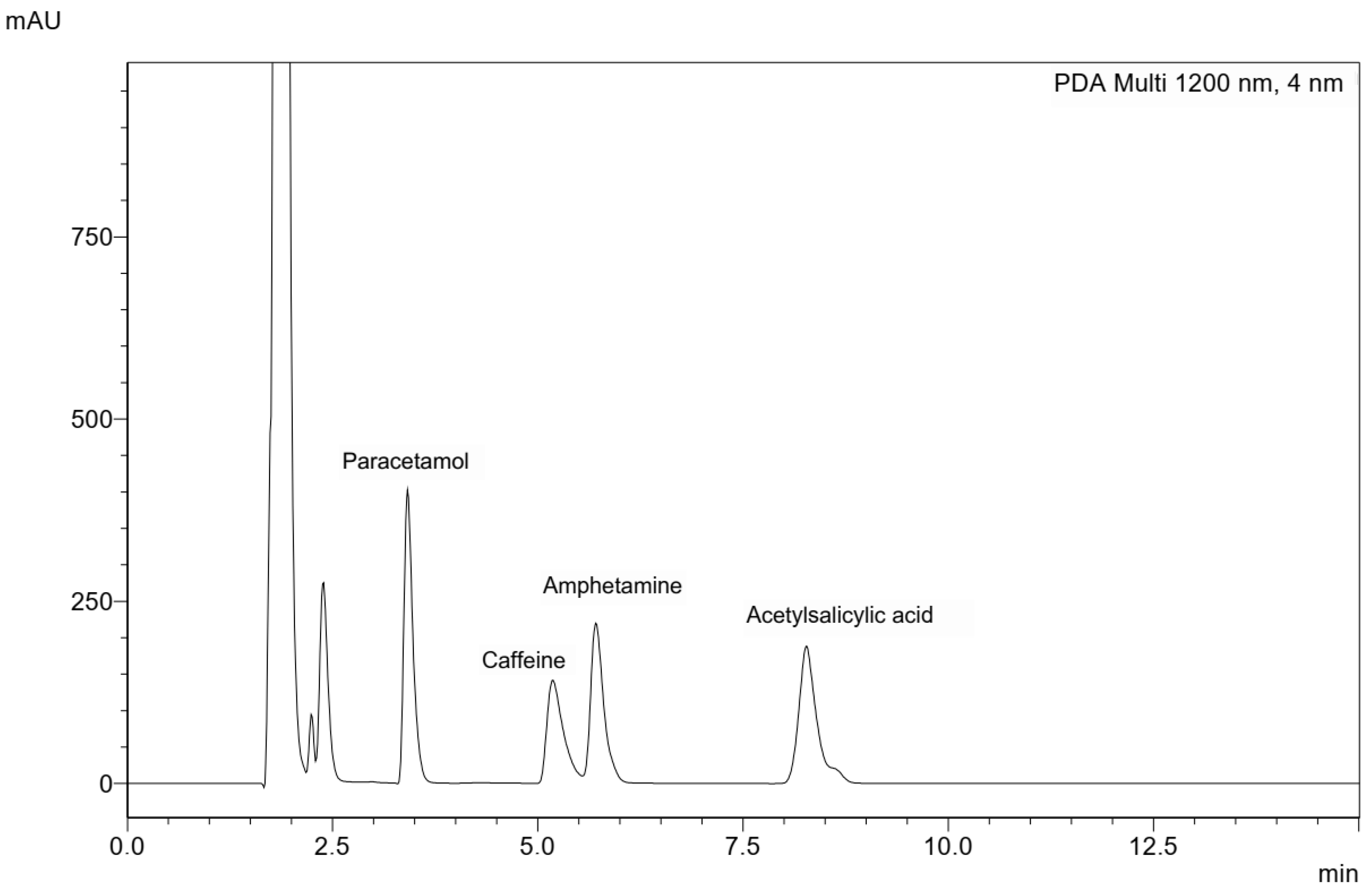
| Y = ax + b | Accuracy | Repeatability | Intermediate Precision | Limit of Detection (LOD) (µg/mL) | Limit of Quantification (LOQ) (µg/mL) | Measurement Range | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | |||||||
| 0.9999 | 148,495.7251 | 5852.5099 | 100.12 ± 0.15% | 0.13% | 0.36% | 0.13 | 0.40 | 0.5 to 20 μg/mL |
| Determination of Amphetamine in Synthetic Urine Diluent Samples | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Declared Contents (μg/mL) | Tagged Content (μg/mL) | Recovery (%) | Mean Recovery (%) | CV (%) |
| 0.5 | 0.46 | 91.29 | 90.32 | 1.26 |
| 0.45 | 90.59 | |||
| 0.45 | 89.07 | |||
| 1.0 | 0.92 | 92.26 | 92.00 | 0.90 |
| 0.93 | 92.66 | |||
| 0.91 | 91.08 | |||
| 5.0 | 4.95 | 99.04 | 99.10 | 0.25 |
| 4.94 | 98.88 | |||
| 4.97 | 99.37 | |||
| 10.0 | 9.94 | 99.36 | 99.16 | 0.28 |
| 9.93 | 99.28 | |||
| 9.88 | 98.84 | |||
| Substance | Type of Test | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Amphetamine 10 µg/mL | Test a | Test b | Test c |
| Concentration/HPLC result: 9.92 µg/mL |  |  |  |
| Precision: 0.28% | |||
| Result: | Result: | Result: | |
| Positive | Positive | Positive | |
| Chromatogram | 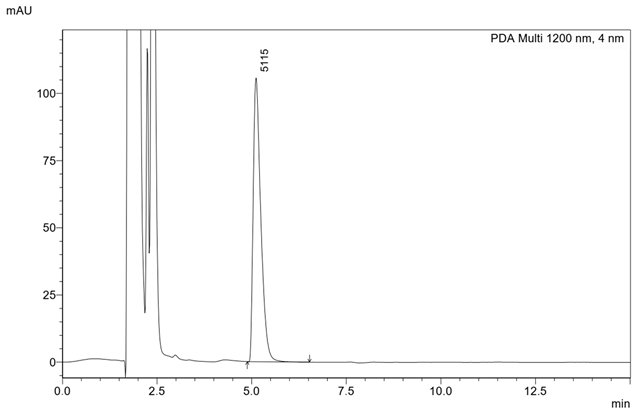 | ||
| Substance | Type of Test | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Amphetamine 0.5 g/mL | Test a | Test b | Test c |
| Concentration/HPLC result: 0.45 µg/mL |  |  | 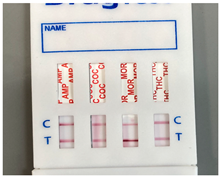 |
| Precision: 1.26% | |||
| Result: | Result: | Result: | |
| Negative | Positive | Negative | |
| Chromatogram | 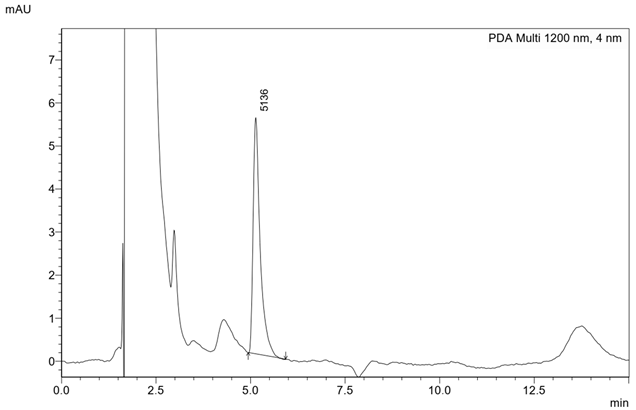 | ||
| Substance | Type of Test | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Paracetamol 150 µg/mL | Test a | Test b | Test c |
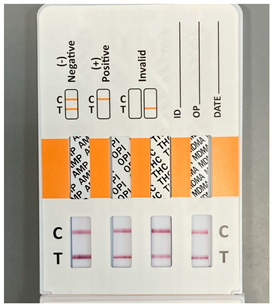 |  |  | |
| Result: | Result: | Result: | |
| Negative | Negative | Negative | |
| Chromatogram |  | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miłos, A.; Gackowski, M.; Przybylska, A.; Kośliński, P.; Koba, M. Comparison of Sensitivity and Specificity of Commercial Amphetamine Tests. AppliedChem 2023, 3, 141-152. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem3010010
Miłos A, Gackowski M, Przybylska A, Kośliński P, Koba M. Comparison of Sensitivity and Specificity of Commercial Amphetamine Tests. AppliedChem. 2023; 3(1):141-152. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem3010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiłos, Aleksandra, Marcin Gackowski, Anna Przybylska, Piotr Kośliński, and Marcin Koba. 2023. "Comparison of Sensitivity and Specificity of Commercial Amphetamine Tests" AppliedChem 3, no. 1: 141-152. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem3010010
APA StyleMiłos, A., Gackowski, M., Przybylska, A., Kośliński, P., & Koba, M. (2023). Comparison of Sensitivity and Specificity of Commercial Amphetamine Tests. AppliedChem, 3(1), 141-152. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem3010010







