Abstract
Zeolites with the LTL framework topology are attractive materials for use in optoelectronics, gas adsorption and as chemical reactors. This is due to their unique, one-dimensional (1D) channel systems which are large enough to act as hosts for organic dye molecules and other guest materials. Here, we use high-resolution X-ray diffraction to show the effect of cation exchange on the pore geometry of LTL-type zeolites. The nature of the exchanging cation is shown to influence the free access diameter, volume and water content of the 12-ring (12R) channel systems. As such, cation exchange can be used to tune the molecular sieving and adsorption properties of LTL-type zeolites. This offers new possibilities for these materials in technologically relevant applications.
1. Introduction
Zeolites are crystalline, microporous materials renowned for their molecular sieving and catalytic applications [1,2]. The aluminosilicate framework is assembled from silica and alumina tetrahedra linked through apical oxygen atoms. Charge-compensating cations reside in the zeolite pores to render an overall neutral framework. Existing zeolite materials are often modified to optimise their performance in many applications. For example, cation exchange can be used to tailor the pore architecture of a zeolite to significantly improve its selectivity, adsorption and diffusion properties. We have previously shown that changing the nature of the extra-framework cations in zeolites A (LTA) and Y (FAU) can cause structural modifications, such as altering the size of the unit-cell and pore windows and changing the local environment of aluminium atoms in the framework [3,4]. In this work, we explore the effect of cation exchange on the pore dimensions, cation locations and water distribution within the 12-ring (12R) channel systems of LTL-type zeolites. Zeolites with the LTL topology have attracted particular attention because of their unique, quasi-1D, 12R channel systems, with free access diameters of 7 Å [5,6,7]. The geometric constraints imparted by the LTL framework, and the electrostatic fields generated by non-framework cations, create an ideal host environment for a variety of polar guest materials. For example, donor and acceptor chromophores are readily ordered into supramolecular arrays within the 12R channels, allowing efficient resonance energy transfer to occur. These host–guest materials are of particular interest as artificial antenna systems for light harvesting, with applications in photochemical and optoelectronic devices [8,9,10,11,12]. The cylindrical shape of the 1D channels not only suppresses the aggregation of adsorbed dye molecules, but can further enhance their photochemical properties. An example can be given for encapsulated proflavine dye molecules which align within the 1D channels and are forced to adopt a bent configuration due to the confinement effects of the framework. This alters the fluorescent properties of the material in comparison to the isolated dye [13]. The importance of non-framework cations in generating composite materials that are stable and water-resistant has also been shown. The stability of fluoroenone-KL materials has been attributed to strong interactions between non-framework potassium cations in the 12R channels and the carbonyl oxygen atoms of the organic dye molecules [14]. The applications currently being investigated for LTL composite materials, ranging from catalysis and optoelectronics, to drug delivery, all make use of the available void space and host–guest interactions within the channel systems [9,15,16]. Tuning the zeolite pore dimensions and electrostatic fields via cation-exchange is one way to alter the physical and chemical properties of the material. It has previously been shown that the catalytic activity of platinum-L zeolites can be improved by increasing the size of non-framework cations. Selectivity for the dehydrocyclisation of n-hexane and hydrogenation of benzene increases from Li to Cs exchanged Pt/L zeolites [17]. On the other hand, exchange with smaller Mg cations leads to a greater ethanol adsorption capacity. The small ionic radius and high charge density of non-framework Mg cations in the pores allows them to bind more strongly to ethanol molecules which restricts their motion [18]. Here, we explore the effect of cation exchange on the pore geometry of zeolite L. Non-framework K cations are exchanged with larger Cs and smaller Li ions to physically alter pore apertures, cation locations and water distribution within the 12R channels. Advanced structural characterisation provides insight into the locations of these extra-framework cations and water molecules. This is fundamental in understanding and exploiting the characteristics of these materials. This work is a step towards tuning LTL-zeolites for better use as functional materials.
The 12R, 1D channel of the LTL framework is orientated along the crystallographic c-axis, enclosed by vertical stacks of alternating cancrinite cages (can) and double-6 ring units (d6rs), with smaller, elliptical 8R channels alternating between these columns, Figure 1. K cations have previously been shown to reside at four distinct cation sites, labelled A–D in Figure 2 [6,7,19]. Site A is located at the centre of the d6r units (z = 0), site B at the centre of the can cages (z = 1/2), site C in the window between the elliptical 8R channels and walls of the 12R channel (z = 1/2) and site D at the periphery of the 12R channel (z = 0).
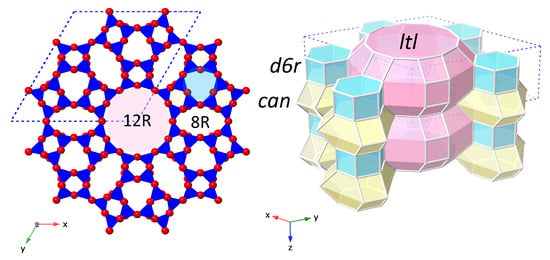
Figure 1.
The LTL framework structure shown in polyhedral view (left) and in stereo view (right). One hexagonal unit-cell is marked with a blue dotted line. Left: polyhedral view of the LTL framework viewed along the z-direction (parallel to the crystallographic c-axis and 12R channel). TO units are shaded blue, with oxygen atoms shown in red at the vertices. Right: stereo view of the LTL framework, where the vertices represent T-atoms and the edges represent oxygen links between them. The composite building units (CBUs) that build the LTL framework are shaded: double 6-ring units (d6rs) in blue, cancrinite cages (can) in yellow and ltl cavities in pink. Stacks of can-d6r-can units are oriented around a 3-fold axis to form the 1D, 12R channels with smaller, elliptical 8-ring (8R) channels running between them.
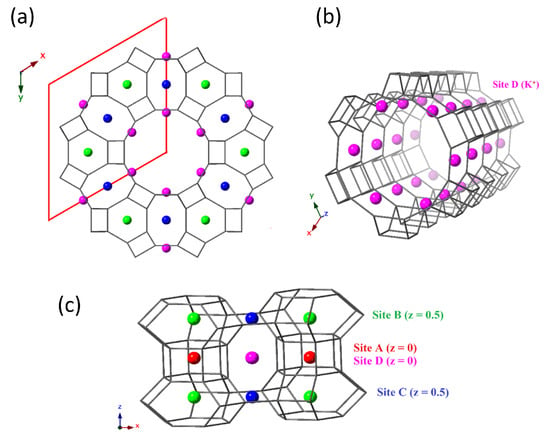
Figure 2.
Cation sites A–D in the LTL framework. Going clockwise from (a–c): (a) The hexagonal unit-cell is shown in red with a view down the 12R channel running parallel to the crystallographic c-axis. (b) Site D is at the periphery of the 12R channels (z = 0). (c) Sites A–C are located in the stacks of can cages and d6r units surrounding the 12R channels; site A (z = 0) is at the centre of the d6rs, site B (z = 0.5) is at the centre of the can cages and site C (z = 0) in the windows of the elliptical 8R channels.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis and Ion Exchange of K-L
Zeolite K-L (LTL) was synthesised via hydrothermal methods with a batch composition of 4KO:10 SiO:AlO:100HO, following the method described by Bhat et al. [20]. Solution 1 was prepared by adding 2.267 g NaOH pellets (100% NaOH, Fisher, Burlington, MA, USA) to 4.034 g of deionised water and stirred at room temperature until homogeneous. An amount of 1.572 g Al(OH) (100%, Fisher) was added and the weight noted, prior to heating the solution at 110 C until homogeneous. Any mass loss during heating was compensated for by re-adding the appropriate amount of deionised water. Solution 2 was prepared by adding 12.273 g of a colloidal solution of silica (Ludox, 40 wt% SiO, Aldrich, Waltham, MA, USA) to 7.018 g deionised water and stirred until homogeneous. Solution 2 was slowly added to solution 1 and left to stir for 30 min at room temperature, to allow the formation of a viscous gel. This gel was then transferred to an autoclave and heated in an oven at 160 C for 3 days. The powder was recovered via Buchner filtration and washed with deionised water until the filtrate was neutral pH 7–8. Partial cation exchange of K for Li and Cs was achieved by adding 2 g of K-L to 0.25 M and 0.5 M solutions of LiCl (Fisher 99.9%) and CsCl (Fisher 99.9%), respectively. The exchange process was performed 3 times at 95 C whilst stirring for 5 h. The final sample was filtered, washed with deionised water and oven dried in an oven at 80 C overnight.
2.2. Powder X-ray Diffraction (PXRD)
K-L and partially exchanged Li-L and Cs-L zeolites were characterised at ambient conditions by performing high-resolution X-ray diffraction measurements. To optimise the resolution, overnight scans (scan speed 0.1 min with step size 0.02 across a 2 range from 1 to 40) were performed on a Rigaku Smartlab diffractometer with a high flux rotating copper anode X-ray source (monochromator, = 1.544414 Å) at the materials characterisation lab, ISIS Neutron and Muon Source.
2.3. Rietveld Refinements
Structural characterisation was performed by Rietveld refinements using the GSAS suite of programs [21]. A multiphase refinement was performed to address the 2.5% merlinoite impurity from the hydrothermal synthesis of K-L. The background curve was fitted using a shifted Chebyschev polynomial with 15 coefficients. To reduce the number of refinement parameters, isotropic displacement factors were constrained to be equal for T-atoms (silicon and aluminium), framework oxygens, extra-framework water oxygens and K cations. The refinement of the parent K-L zeolite was modelled on the structure of K/Na-L with space group P6/mmm first reported by Barrer (ICSD 18099) [19]. The refined structure of K-L was then used as a starting model for refinements of the partially exchanged Li-L and Cs-L zeolites. K was replaced by Cs or Li at each site and their fractional occupancies and crystallographic coordinates were refined. Fourier maps were used to help refine partial occupancies of sites populated with both K and either Li or Cs ions. Extra Li or Cs ions were added to the phase structure and tested at these sites by refining their fractional occupancies. This process was repeated until the fit to the data was optimised. Atoms at each of the sites for Cs-L were tested in light of Cs-gallosilicate L reported by Gigli and Lee and Li positions in light of DFT calculations reported by Meeprasert et al. [13,22,23].
3. Results and Discussion
Figure 3 shows powder X-ray diffraction data and associated Rietveld refinement profiles for K-L and partially exchanged Li-L and Cs-L at ambient pressure. Crystal structures and cell parameters for all refined samples are given in the Appendix A Table A1, Table A2, Table A3, Table A4, Table A5, Table A6.
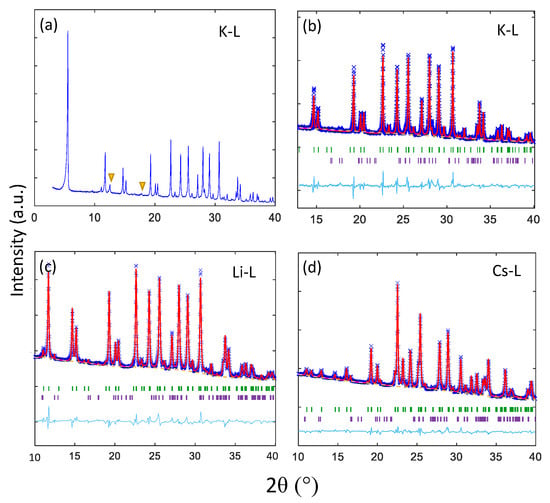
Figure 3.
Diffraction data for K-L and partially exchanged Li and Cs-L samples collected at ambient pressure. (a) Shows powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) data for characterisation of as-synthesised K-L. Minor peaks from a merlinoite impurity are marked with an orange triangle. (b–d) Show X-ray diffraction data and associated Rietveld refinement profiles for K-L, Li-L and Cs-L, respectively. Observed and calculated profiles are shown as blue crosses and red lines, respectively. Backgrounds are plotted with orange dotted lines. The residual (observed minus calculated intensity) plot is shown below as a cyan line and Bragg reflections for K-L and merlinoite are marked with vertical green and purple bars, respectively.
Rietveld refinement of high-resolution, powder X-ray diffraction data for our LTL zeolites reveal that extra-framework cations are located at sites B-D. Site B is at the centre of the can cages, site C is at the windows of the elliptical 8R channels and site D is at the periphery of the 12R channels, as shown in Figure 4.
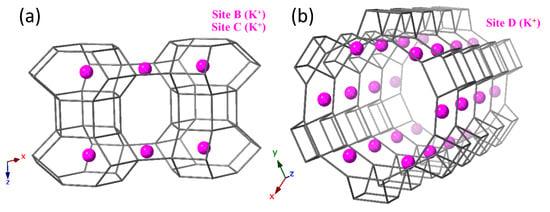
Figure 4.
Refined K positions in K-L. (a) Site B is at the centre of the can cages and site C is in the windows of the elliptical 8R channel. (b) site D is located at the periphery of the 12R channel.
Site A, reported by Barrer at the centre of the d6rs is vacant in our as-synthesised K-L and cation exchanged Li and Cs-L zeolites [19]. The occupancy at site A depends on the synthesis conditions, particularly the Si/Al ratio, where additional cations may be required to render an overall neutral structure. Analysis by energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) gave an average Si/Al ratio of 3.4(2) for the parent K-L sample. Refinement of cation occupancies for the parent K-L zeolite reveal that sites B and C are fully occupied by K cations, whereas site D is statistically occupied by 0.63 K ions per unit-cell. This is consistent with a Si/Al of 3.1, which is in close agreement to the average value obtained from EDX data. Cation exchange at these sites occur in variable degrees to produce partially exchanged Cs and Li-L zeolites. Site B remains fully occupied by K ions in both cases, as the small windows of the can cages restrict the exchange pathway. Site B can, therefore, be regarded as a locked site and is inert to cation exchange with both Li and Cs ions. Cations are preferentially exchanged at sites D and C, decreasing in the order D > C > B.
Figure 5 shows the refined, partially exchanged Cs-L structure. Site D undergoes a complete exchange of 0.63 K ions per unit-cell and is repopulated by 0.72 Cs ions per unit-cell. In comparison to the parent K-L structure (Figure 4), Cs ions located at site D are inset further into the 12R channels so that stability is achieved by accommodating their higher steric demands. Cs ions can, therefore, be considered stable at site D and a 100% exchange rate proves that this is an open site. Refined occupancies reveal that site C is partially occupied by 0.45 and 0.38 K or Cs ions, respectively. Refinement models with K solely populating site C result in occupancies > 1 and this excess electron density indicates the presence of Cs. Site C is, in fact, not a closed site, as previously suggested by Newell and Rees, and can exchange K ions with Cs ions [24]. Our refinement models show that site C is susceptible to exchange with Cs ions and is similarly populated to its gallosilicate analogue, reported by Seoung et al., to have a 50:50 fractional occupancy at this same site [25]. It is also important to note that the overall occupancy at site C by K and Cs ions combined is 0.83 per unit cell compared to the full occupancy by K ions in the parent K-L zeolite. To render an overall neutral structure, this is compensated for by the increased overall occupancy at site D which is 0.72 Cs per unit-cell compared to the 0.63 K in the parent K-L zeolite. This emphasises that Cs ions preferentially occupy site D over site C as the free volume available is greater here to accommodate larger Cs cations. Exchange of the parent K-L zeolite with Li ions leads to a partially exchanged Li-L zeolite. Again, site B is inert to exchange and remains fully occupied by K ions. Interestingly, unlike with Cs ion exchange, site C is also locked and remains fully populated by K ions. Only site D is shown to be susceptible to Li exchange and our refinement models show it to be partially occupied by 0.11 and 0.57 Li and K ions, respectively. Refinement models with only K ions at site D again show excess electron density, separate to that associated with the K ions, and this identifies as Li ions that sit further towards the periphery of the 12R channel.
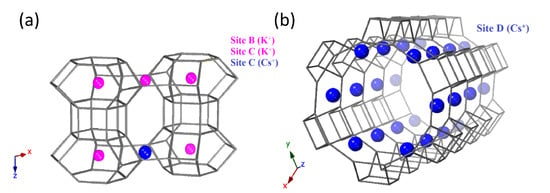
Figure 5.
Refined K and Cs positions in partially exchanged Cs-L. (a) Site B is at the centre of the can cages (left), site C is in the windows of the elliptical 8R channel, showing partial occupancy by K and Cs ions (left) and (b) site D is at the periphery of the 12R channel (right).
Figure 6 illustrates the positions of Li and K ions at site D which vary in their y coordinates, sitting at y = 0.36 and y = 0.29, respectively. Partial exchange of K ions for Li ions at site D implies that Li ions are less stable here than larger K or Cs ions. Because of their small ionic radii, Li ions must sit much closer to the zeolite framework in order to achieve stability through electrostatic interactions with AlO tetrahedra. However, even when sitting at the very periphery of the channel walls, Li ions still struggle to fully exploit the free volume available and cannot maximise their interactions with the framework at this site. K and Cs ions have larger ionic radii and are much better matched to the volume of this site. They benefit from stabilising interactions from the surrounding framework. Similarly, at site C, the windows of the elliptical 8R channels are large in comparison to the small Li ions. Larger K ions are more stable at this site and it would be unfavourable for K ions to exchange with Li ions here. The partial occupancy of Cs and K ions at site C indicates that Cs ions are somewhat stable here, but K ions are still preferable. Cs ions are too large to achieve 100% occupancy at site C. The topology of the site also plays a role. For example, site D is more versatile, and cations can be displaced along the a/b-axis, either into the channel centre or towards the wall periphery. This is not possible at site C because it is a symmetric site. AlO tetrahedra may be randomly distributed surrounding the cation and electrostatic interactions can occur in multiple directions. Such detailed information of site occupancies is not attainable from semi-qualitative analysis, such as EDX. Refining site occupancies is, therefore, important in order to identify low exchange rates which could compromise the efficacy of the 1D chemical reactor for applications in catalysis or gas adsorption. Table 1 shows how cation exchange at site D affects the 12R channel apertures (measured from O1-O1 and O2-O2). This can be used to control diffusion into and out of the channel.
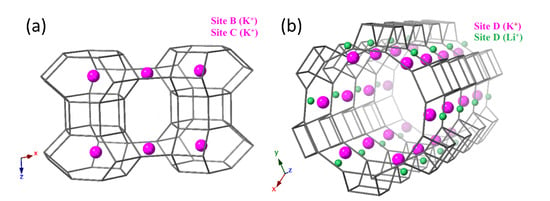
Figure 6.
Refined K and Li positions in partially exchanged Li-L. (a) Site B is at the centre of the can cages (left), site C is in the windows of the elliptical 8R channel (left) and (b) site D is at the periphery of the 12R channel, showing partial occupancy by Li and K ions, with Li ions sitting at the very periphery of the channel walls (right).

Table 1.
Water content and 12R aperture diameters (O-O distances Å) of the parent K-L and partially exchanged Cs-L and Li-L zeolites.
Steric and electronic effects at site D cause smaller Li cations to retreat along the a/b direction towards the periphery of the channel and larger Cs cations are displaced further into the centre of the channel. The free-access diameter is, therefore, smaller for the Cs-exchanged sample. This could be envisaged as a tool to control the entrance and exit of reactant and product molecules to the ‘1D reactor’ during catalytic reactions. Water molecules are exclusively confined within the 1D channels of LTL zeolites.
Figure 7 illustrates the refined water sites in K-L that are fractionally occupied. The O-O distances suggest that water molecules form discrete, hydrogen-bonded layers and cation-stabilised water clusters, in agreement with those nanostructures in the analogous gallosilicate reported by Lee et al. [23]. Cation exchange can be utilised as a tool to manipulate the geometries of the water nanostructures within the 1-D channel system of LTL-type zeolites. Water content fluctuates with the nature of the cation at site D. This could be particularly useful for host–guest systems which depend on variable degrees of hydrogen bonding for stabilisation. Table 1 shows that the overall water content of the channel decreases upon exchange of K ions with both Li and Cs ions. For Cs-L, this can be rationalised by the decrease in free volume available to accommodate water molecules. Large Cs ions are further displaced into the centre of channel and there is a drastic reduction in the number of water molecules per unit-cell that can be supported in a cation-stabilised cluster. Water content also decreases when K is partially exchanged for Li. Again, the decrease in water content can be accounted for by the position of the cations at site D. Smaller Li ions are displaced towards the channel walls and cannot interact as efficiently with water molecules to form cation clusters. Furthermore, the reduced K occupancy at site D means that there is also a reduction in stabilising interactions from K ions with water in the cation-stabilised water cluster.
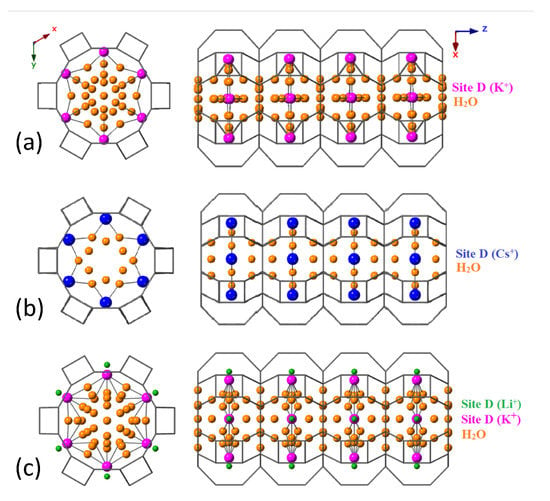
Figure 7.
Water sites (orange) are confined exclusively in the 12R channel, the occupancies and positions of which are influenced by the cation identity at site D. (a) The parent zeolite K-L (b) partially exchanged Cs-L and (c) partially exchanged Li-L.
4. Conclusions
Non-framework cations in LTL-type zeolites can be exchanged to tune the chemical and physical properties of these materials for applications in catalysis and photo-electronics. Using high-resolution X-ray diffraction and Rietveld refinement, the locations of Li, K and Cs cations and water molecules in the pores have been identified. As-synthesised K-L and partially exchanged Li and Cs-L zeolites show three distinct cation sites. With regards to cation exchange at 95 C, site B can be considered as locked and is inert to exchange with both Li and Cs ions, site D is deemed open and K ions here are freely exchangeable and site C is selectively open to exchange with Cs but not Li. The occupancy of site C seems to be favoured by larger cations such as Cs, where the instability of Li is likely a result of its small cationic radius, long bond lengths and a low interaction energy with the framework. Refinement of water positions shows that water molecules are partitioned into two distinct layers—a cation-stabilised cluster and a hydrogen-bonded layer. This is in agreement with the analogous gallosilicate reported by Lee [23]. Exchange of K for Cs or Li induces the re-distribution of water among these layers, suggesting that their arrangement is dictated by the stabilising effect and steric requirements of the extra-framework cation. The free access diameter of the 12R channel, cation locations and water distribution in LTL-type zeolites can be tuned by altering the size of the exchanging cations. In addition to steric effects, cations with different ionic radii have different charge densities which alters the electric field within the pore systems. This not only has important implications for the selective adsorption of guest molecules, but will also affect their diffusion and stability within the channels. By selecting the appropriate non-framework cation, the LTL-framework can be finely tuned to enhance selectivity and host–guest interactions for applications in catalysis, molecular sieving, and zeolite-dye optoelectronic materials.
Author Contributions
Syntheses and refinements were carried out by Z.J. PXRD data were collected by Z.J., G.S. and D.N. Writing and editing of the manuscript was carried out by L.A.P., Z.J. and A.N., L.A.P. and Z.J. prepared all figures. Supervision from A.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by The Royal Society University Research Fellowship.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The dataset generated during the current study is available in the University of Bath Research Data Archive at https://doi.org/10.15125/BATH-00648 (accessed on 6 July 2022).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| 1D | One-dimensional |
| 12R | 12-ring |
| 8R | 8-ring |
| can | cancrinite cage |
| d6r | double 6-ring |
Appendix A. Rietveld Refinement Data

Table A1.
Refined cell-parameter data for K-L.
Table A1.
Refined cell-parameter data for K-L.
| a/b (Å) | c (Å) | () | () |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18.388(3) | 7.529(2) | 90 | 120 |

Table A2.
Crystal Structure of K-L.
Table A2.
Crystal Structure of K-L.
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso | Occ. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K (Site D) | 0 | 0.2918 | 0 | 0.051273 | 0.63 |
| K (Site B) | 0.3333 | 0.6667 | 0.5 | 0.051273 | 1 |
| K (Site C) | 0 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.051273 | 1 |
| Si (1) | 0.0946 | 0.3595 | 0.5 | 0.012316 | 0.75 |
| Si (2) | 0.1662 | 0.4989 | 0.2137 | 0.012316 | 0.75 |
| Al (1) | 0.0946 | 0.3595 | 0.5 | 0.012316 | 0.25 |
| Al (2) | 0.1662 | 0.4989 | 0.2137 | 0.012318 | 0.25 |
| O (1) | 0 | 0.267247 | 0.5 | 0.029498 | 1 |
| O (2) | 0.164702 | 0.329401 | 0.5 | 0.029498 | 1 |
| O (3) | 0.272687 | 0.545376 | 0.261401 | 0.029498 | 1 |
| O (4) | 0.096766 | 0.412575 | 0.323641 | 0.029498 | 1 |
| O (5) | 0.433088 | 0.866174 | 0.269393 | 0.029498 | 1 |
| O (6) | 0.126437 | 0.453851 | 0 | 0.029498 | 1 |
| H2O (1) | 0.069974 | 0.13995 | 0.5 | 0.237862 | 0.39518 |
| H2O (2) | 0 | 0.117857 | 0.5 | 0.237862 | 0.26205 |
| H2O (3) | 0 | 0.151173 | 0.222767 | 0.237862 | 0.500229 |
| H2O (4) | 0 | 0 | 0.078289 | 0.23786 | 0.681591 |
| H2O (5) | 135078 | 0.270158 | 0 | 0.237862 | 0.691272 |
| H2O (6) | 0 | 0.187275 | 0 | 0.237862 | 0.325574 |

Table A3.
Refined cell parameter data for Cs-L.
Table A3.
Refined cell parameter data for Cs-L.
| a/b (Å) | c (Å) | () | () |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18.453(5) | 7.558(3) | 90 | 120 |

Table A4.
Rietveld refinement data for Cs-L.
Table A4.
Rietveld refinement data for Cs-L.
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso | Occ. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K (Site B) | 0.3333 | 0.6667 | 0.5 | 0.0298 | 1 |
| K (Site C) | 0 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.0298 | 0.3751 |
| Cs (Site C) | 0 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.0298 | 0.446 |
| Cs (Site D) | 0 | 0.275554 | 0 | 0.0298 | 0.7238 |
| Si (1) | 0.104606 | 0.364589 | 0.5 | 0.0152 | 0.75 |
| Si (2) | 0.170499 | 0.500876 | 0.207083 | 0.0152 | 0.75 |
| Al (1) | 0.0946 | 0.3595 | 0.5 | 0.0152 | 0.25 |
| Al (2) | 0.1662 | 0.4989 | 0.2137 | 0.0152 | 0.25 |
| O (1) | 0 | 0.289743 | 0.5 | 0.0341 | 1 |
| O (2) | 0.161538 | 0.32308 | 0.5 | 0.0341 | 1 |
| O (3) | 0.274509 | 0.549017 | 0.276285 | 0.0341 | 1 |
| O (4) | 0.11304 | 0.433529 | 0.309766 | 0.0341 | 1 |
| O (5) | 0.427542 | 0.855089 | 0.255541 | 0.0341 | 1 |
| O (6) | 0.114231 | 0.437655 | 0 | 0.0341 | 1 |
| H2O (1) | 0 | 0.127013 | 0.334108 | 0.2514 | 0.6092 |
| H2O (2) | 0.101592 | 0.203184 | 0 | 0.2514 | 0.3631 |

Table A5.
Refined cell parameter data for Li-L.
Table A5.
Refined cell parameter data for Li-L.
| a/b (Å) | c (Å) | () | () |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18.386(5) | 7.529(3) | 90 | 120 |

Table A6.
Rietveld refinement data for Li-L.
Table A6.
Rietveld refinement data for Li-L.
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso | Occ. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K (Site B) | 0.3333 | 0.6667 | 0.5 | 0.0848 | 1 |
| K (Site C) | 0 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.0848 | 1 |
| K (Site D) | 0 | 0.293855 | 0 | 0.0848 | 0.5696 |
| Li (Site D) | 0 | 0.357731 | 0 | 0.0848 | 0.1119 |
| Si (1) | 0.0946 | 0.3595 | 0.5 | 0.0152 | 0.75 |
| Si (2) | 0.1662 | 0.4989 | 0.2137 | 0.0152 | 0.75 |
| Al (1) | 0.0946 | 0.3595 | 0.5 | 0.0152 | 0.25 |
| Al (2) | 0.1662 | 0.4989 | 0.2137 | 0.0152 | 0.25 |
| O (1) | 0 | 0.264863 | 0.5 | 0.0431 | 1 |
| O (2) | 0.165997 | 0.331993 | 0.5 | 0.0431 | 1 |
| O (3) | 0.272915 | 0.545829 | 0.258433 | 0.0431 | 1 |
| O (4) | 0.099272 | 0.419473 | 0.320544 | 0.0431 | 1 |
| O (5) | 0.430069 | 0.860139 | 0.270699 | 0.0431 | 1 |
| O (6) | 0.131235 | 0.459158 | 0 | 0.0431 | 1 |
| H2O (1) | 0.108684 | 0.217367 | 0.5 | 0.2196 | 0.2751 |
| H2O (2) | 0 | 0.145016 | 0.275609 | 0.2196 | 0.4133 |
| H2O (3) | 0.142988 | 0.28598 | 0 | 0.2196 | 0.5295 |
| H2O (4) | 0 | 0.178042 | 0 | 0.2196 | 0.3054 |
References
- Barrer, R.M. Hydrothermal Chemistry of Zeolites. In Department of Chemistry Imperial College of Science and Technology London; Academic Press Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1982; p. 360. [Google Scholar]
- Abdo, F.S.; Wilson, T.S. Zeolites in Industrial Catalysis. In Zeolites in Catalysis: Properties and Applications; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2017; Section 9; pp. 310–350. [Google Scholar]
- Sartbaeva, A.; Rees, N.H.; Edwards, P.P.; Ramirez-Cuesta, A.J.; Barney, E. Local probes show that framework modification in zeolites occurs on ammonium exchange without calcination. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 7415–7421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, L.; Leung, M.K.; Sartbaeva, A. Local and Average Structural Changes in Zeolite A upon Ion Exchange. Magnetochemistry 2017, 3, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baerlocher, C.; McCusker, L. Database of Zeolite Structures. Available online: http://www.iza-structure.org/databases/ (accessed on 20 April 2022).
- Newsam, J.M. Structures of dehydrated potassium zeolite L at 298 and 78 K and at 78 K containing sorbed perdeuteriobenzene. J. Phys. Chem. 1989, 93, 7689–7694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsam, J.M. Structural characterization of dehydrated gallium zeolite L. Mater. Res. Bull. 1986, 21, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzaferri, G.; Huber, S.; Maas, H.; Minkowski, C. Host–guest antenna materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 3732–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vohra, V.; Bolognesi, A.; Calzaferri, G.; Botta, C. Multilevel organization in hybrid thin films for optoelectronic applications. Langmuir 2009, 25, 12019–12023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzaferri, G.; Meallet-Renault, R.; Bruhwiler, D.; Pansu, R.; Dolamic, I.; Dienel, T.; Adler, P.; Li, H.R.; Kunzmann, A. Designing Dye-Nanochannel Antenna Hybrid Materials for Light Harvesting, Transport and Trapping. ChemPhysChem 2011, 12, 580–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insuwan, W.; Jungsuttiwong, S.; Rangsriwatananon, K. Host–guest composite materials of dyes loaded zeolite LTL for antenna applications. J. Lumin. 2015, 161, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insuwan, W.; Rangsriwatananon, K.; Meeprasert, J.; Namuangruk, S.; Surakhot, Y.; Kungwan, N.; Jungsuttiwong, S. Combined experimental and theoretical investigation on fluorescence resonance energy transfer of dye loaded on LTL zeolite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 241, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeprasert, J.; Kungwan, N.; Jungsuttiwong, S.; Namuangruk, S. Location and reactivity of extra-framework cation in the alkali exchanged LTL zeolites: A periodic density functional study. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 195, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fois, E.; Tabacchi, G.; Calzaferri, G. Interactions, Behavior, And Stability of Fluorenone inside Zeolite Nanochannels. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 10572–10579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jentoft, R.E.; Tsapatsis, M.; Davis, M.E.; Gates, B.C. Platinum Clusters Supported in Zeolite LTL: Influence of Catalyst Morphology on Performance in n-Hexane Reforming. J. Catal. 1998, 179, 565–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertucci, A.; Lülf, H.; Septiadi, D.; Manicardi, A.; Corradini, R.; De Cola, L. Intracellular Delivery of Peptide Nucleic Acid and Organic Molecules Using Zeolite-L Nanocrystals. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2014, 3, 1812–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besoukhanova, C.; Guidot, J.; Barthomeuf, D.; Breysse, M.; Bernard, J.R. Platinum–zeolite interactions in alkaline L zeolites. Correlations between catalytic activity and platinum state. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. Phys. Chem. Condens. Phases 1981, 77, 1595–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani Shabolaghi, K.; Irani, M. Ethanol adsorption in cation-exchanged linde type L zeolite, studied by molecular simulations. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2022, 1207, 113498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrer, R.M.; Villiger, H. The crystal structure of the synthetic zeolite L. Z. Kristallogr. Cryst. Mater. 1969, 128, 352–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, S.D.; Niphadkar, P.S.; Gaydhankar, T.R.; Awate, S.V.; Belhekar, A.A.; Joshi, P.N. High temperature hydrothermal crystallization, morphology and yield control of zeolite type K-LTL. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2004, 76, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, A.C.; VonDreele, R.B. GSAS General Structure Analysis System Operation Manual; Los Alamos National Laboratory: Santa Fe, NM, USA, 2000; Volume 86, pp. 1–179. [Google Scholar]
- Gigli, L.; Arletti, R.; Fois, E.; Tabacchi, G.; Quartieri, S.; Dmitriev, V.; Vezzalini, G. Unravelling the high-pressure behaviour of dye-zeolite L hybrid materials. Crystals 2018, 8, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.; Kao, C.C.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, H.-H.; Lee, D.R.; Shin, T.J.; Choi, J.-Y. Water nanostructures confined inside the quasi-one-dimensional channels of ltl zeolite. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 6252–6257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, P.A.; Rees, L.V.C. Ion-exchange and cation site locations in zeolite L. Zeolites 1983, 3, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seoung, D.; Lee, Y.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, H.-H.; Ahn, D.; Shin, N.-S.; Vogt, T.; Lee, Y. Pressure-induced hydration and cation migration in a Cs+ exchanged gallosilicate zeolite LTL: Synchrotron X-ray powder diffraction study at ambient and high pressures. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2010, 136, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).