Real-Time Electroencephalography-Guided Binaural Beat Audio Enhances Relaxation and Cognitive Performance: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Sham-Controlled Repeated-Measures Crossover Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Participant Characteristics
2.2. Primary Relaxation EEG Indices
2.3. Exploratory EEG Indices
2.4. Cognitive Outcomes
2.4.1. Stop Signal Task
2.4.2. Novelty Encoding Task
2.5. Subjective Ratings
2.6. Sensitivity Analyses
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
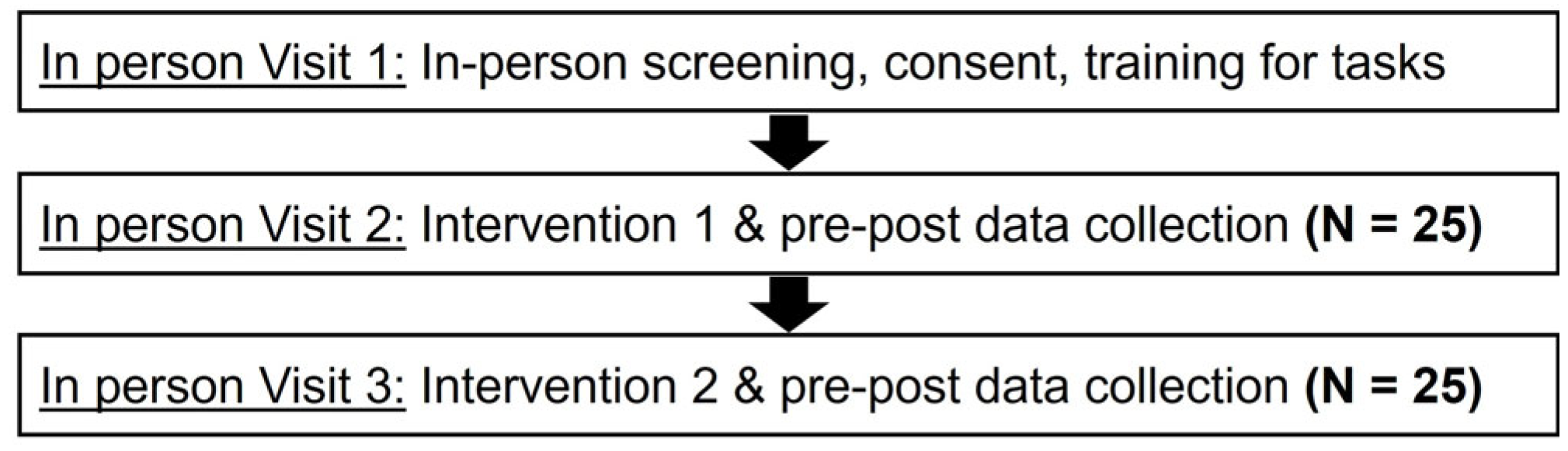
4.1. Study Design and Participants
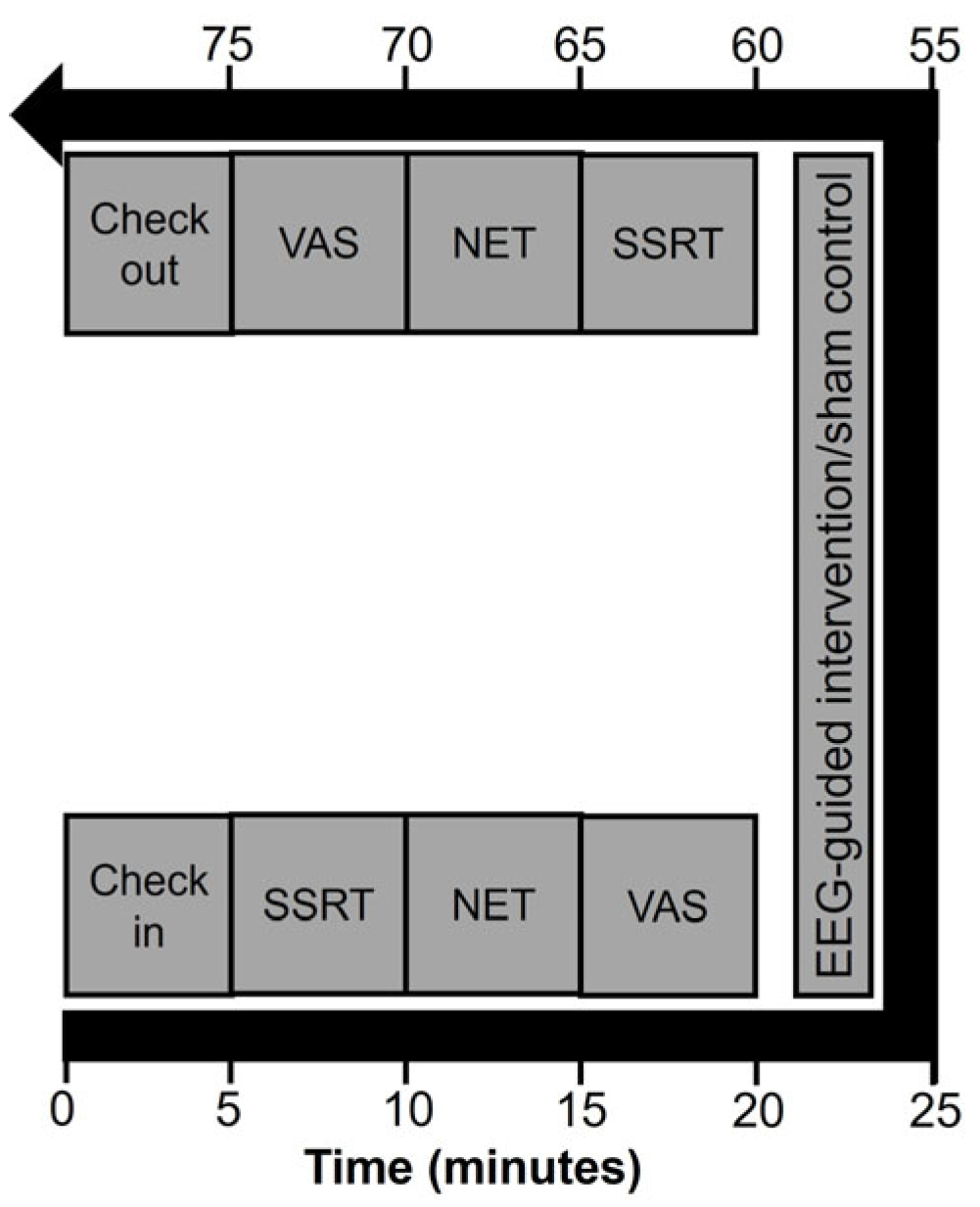
4.2. Procedure
4.3. EEG Acquisition and Preprocessing
4.4. EEG-Guided Binaural Beat Intervention
4.5. Outcome Measures
4.5.1. EEG Outcomes
4.5.2. Subjective Measures
4.5.3. Stop Signal Task
4.5.4. Novelty Encoding Task
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garcia-Argibay, M.; Santed, M.A.; Reales, J.M. Binaural auditory beats affect long-term memory. Psychol. Res. 2019, 83, 1124–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oster, G. Auditory beats in the brain. Sci. Am. 1973, 229, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, J.T.; Worden, F.G. Sound evoked frequency-following responses in the central auditory pathway. Laryngoscope 1968, 78, 1149–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becher, A.K.; Höhne, M.; Axmacher, N.; Chaieb, L.; Elger, C.E.; Fell, J. Intracranial electroencephalography power and phase synchronization changes during monaural and binaural beat stimulation. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2015, 41, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jirakittayakorn, N.; Wongsawat, Y. Brain responses to a 6-Hz binaural beat: Effects on general theta rhythm and frontal midline theta activity. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernon, D.; Peryer, G.; Louch, J.; Shaw, M. Tracking EEG changes in response to alpha and beta binaural beats. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2014, 93, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, H.D.O.; Dumas, G.; Lehmann, A. Binaural beats through the auditory pathway: From brainstem to connectivity patterns. eNeuro 2020, 7, ENEURO.0232-19.2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelbregt, H.; Barmentlo, M.; Keeser, D.; Pogarell, O.; Deijen, J.B. Effects of binaural and monaural beat stimulation on attention and EEG. Exp. Brain Res. 2021, 239, 2781–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Caballero, F.; Escera, C. Binaural beat: A failure to enhance EEG power and emotional arousal. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Argibay, M.; Santed, M.A.; Reales, J.M. Efficacy of binaural auditory beats in cognition, anxiety, and pain perception: A meta-analysis. Psychol. Res. 2019, 83, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingendoh, R.M.; Posny, E.S.; Heine, A. Binaural beats to entrain the brain? A systematic review of the effects of binaural beat stimulation on brain oscillatory activity, and the implications for psychological research and intervention. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0286023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Liu, H. Efficacy of acoustic stimulation for insomnia: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Neurosci. 2025, 19, 1345678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chockboondee, M.; Jatupornpoonsub, T.; Lertsukprasert, K.; Wongsawat, Y. Effects of daily listening to 6 Hz binaural beats over one month: An event-related potentials study. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 18059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huwiler, S.; Ferster, M.L.; Brogli, L.; Huber, R.; Karlen, W.; Lustenberger, C. Sleep and cardiac autonomic modulation in older adults: Insights from an at-home study with auditory deep sleep stimulation. J Sleep Res. 2025, 34, e14328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Anjos, T.; Altimari, L.R.; Bortolotti, H.; Braz, T.V.; Melo, E.S.; Coimbra, D.R.; Fontes, E.B. Brain wave modulation and EEG power changes during auditory beats stimulation. Neuroscience 2024, 545, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaieb, L.; Wilpert, E.C.; Reber, T.P.; Fell, J. Auditory beat stimulation and its effects on cognition and mood states. Front. Psychiatry 2015, 6, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodin, P.; Ciorciari, J.; Baker, K.; Carrey, A.M.; Harper, M.; Kaufman, J. A high-density EEG investigation into steady state binaural beat stimulation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Cao, H.; Ming, D.; Qi, H.; Wang, X.; Chen, R.; Zhou, P. Analysis of EEG activity in response to binaural beats with different frequencies. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2014, 94, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, W.M.F.W.M.; Zaini, N.; Norhazman, H.; Latip, M.F.A. Dynamic encoding of binaural beats for brainwave entrainment. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Control System, Computing and Engineering, Penang, Malaysia, 29 November–1 December 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, K.; Sliney, A.; Pitt, I.; Murphy, D. Evaluating a brain-computer interface to categorise human emotional response. In Proceedings of the 2010 10th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies, Sousse, Tunisia, 5–7 July 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, N.; Acharya, J.; Benickzy, S.; Caboclo, L.; Finnigan, S.; Kaplan, P.W.; Shibasaki, H.; Pressler, R.; van Putten, M. A revised glossary of terms most commonly used by clinical electroencephalographers and updated proposal for the report format of the EEG findings. Revision 2017. Clin. Neurophysiol. Pract. 2017, 2, 170–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeln, V.; Kleinert, J.; Strüder, H.K.; Schneider, S. Brainwave entrainment for better sleep and post-sleep state of young elite soccer players—A pilot study. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2014, 14, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevrier, A.D.; Noseworthy, M.D.; Schachar, R. Dissociation of response inhibition and performance monitoring in the stop signal task using event-related fMRI. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2007, 28, 1347–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, J.L.; Hughes, J.R. Early history of electroencephalography and establishment of the American Clinical Neurophysiology Society. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2013, 30, 28–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enkavi, A.Z.; Eisenberg, I.W.; Bissett, P.G.; Mazza, G.L.; MacKinnon, D.P.; Marsch, L.A.; Poldrack, R.A. Large-scale analysis of test-retest reliabilities of self-regulation measures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 5472–5477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleiss, J.L. Design and Analysis of Clinical Experiments; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A guideline of selecting and reporting intraclass correlation coefficients for reliability research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Band, G.P.; Van Der Molen, M.W.; Logan, G.D. Horse-race model simulations of the stop-signal procedure. Acta Psychol. 2003, 112, 105–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratcliff, R. A theory of memory retrieval. Psychol. Rev. 1978, 85, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang-Pollock, C.; Ratcliff, R.; McKoon, G.; Shapiro, Z.; Weigard, A.; Galloway-Long, H. Using the diffusion model to explain cognitive deficits in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 2017, 45, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichardt, R.; Polner, B.; Simor, P. The graded novelty encoding task: Novelty gradually improves recognition of visual stimuli under incidental learning conditions. Behav. Res. Methods 2023, 55, 1587–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaRocco, J.; Le, M.D.; Paeng, D.G. A systemic review of available low-cost EEG headsets used for drowsiness detection. Front. Neuroinform. 2020, 14, 553352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieiro, H.; Diaz-Piedra, C.; Morales, J.M.; Catena, A.; Romero, S.; Roca-Gonzalez, J.; Fuentes, L.J.; Di Stasi, L.L. Validation of electroencephalographic recordings obtained with a consumer-grade, single dry electrode, low-cost device: A comparative study. Sensors 2019, 19, 2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawangjai, P.; Hompoonsup, S.; Leelaarporn, P.; Kongwudhikunakorn, S.; Wilaiprasitporn, T. Consumer grade EEG measuring sensors as research tools: A review. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 20, 3996–4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabio, J.; Williams, N.S.; McArthur, G.M.; Badcock, N.A. A scoping review on the use of consumer-grade EEG devices for research. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0291186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogino, M.; Kanoga, S.; Muto, M.; Mitsukura, Y. Analysis of prefrontal single-channel EEG data for portable auditory ERP-based brain–computer interfaces. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, S.J.; Blackman, R.; Bruggemann, J.M. EEG from a single-channel dry-sensor recording device. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 2012, 43, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, J.M.; Johnstone, S.J.; Aminov, A. Test–retest reliability of a single-channel, wireless EEG system. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2016, 106, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.D.; Cha, H.S.; Kim, K.; Im, C.H. Detection of eye blink artifacts from single prefrontal channel electroencephalogram. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2016, 124, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plöchl, M.; Ossandón, J.P.; König, P. Combining EEG and eye tracking: Identification, characterization, and correction of eye movement artifacts in electroencephalographic data. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. EEGLAB: An open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2004, 134, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widmann, A.; Schröger, E.; Maess, B. Digital filter design for electrophysiological data—A practical approach. J. Neurosci. Methods 2015, 250, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, T.; Kothe, C.; Chi, Y.M.; Ojeda, A.; Kerth, T.; Makeig, S.; Cauwenberghs, G.; Jung, T.P. Real-time modeling and 3D visualization of source dynamics and connectivity using wearable EEG. In Proceedings of the 2013 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 2184–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, V.; Shukla, S. Automatic removal of artifacts from EEG signal based on spatially constrained ICA using Daubechies wavelet. Int. J. Mod. Educ. Comput. Sci. 2014, 6, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Krishnaveni, V.; Jayaraman, S.; Anitha, L.; Ramadoss, K. Removal of ocular artifacts from EEG using adaptive thresholding of wavelet coefficients. J. Neural Eng. 2006, 3, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mammone, N.; La Foresta, F.; Morabito, F.C. Automatic artifact rejection from multichannel scalp EEG by wavelet ICA. IEEE Sens. J. 2012, 12, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.E.; James, C.J. Source separation using single channel ICA. Signal Process. 2007, 87, 1819–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmaprani, D.; Nguyen, H.K.; Lewis, T.W.; DeLosAngeles, D.; Willoughby, J.O.; Pope, K.J. A comparison of independent component analysis algorithms and measures to discriminate between EEG and artifact components. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2017, 128, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noorbasha, S.K.; Sudha, G.F. Removal of EOG artifacts and separation of different cerebral activity components from single channel EEG—An efficient approach combining SSA–ICA with wavelet thresholding for BCI applications. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2020, 63, 102201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richman, J.S.; Moorman, J.R. Physiological time-series analysis using approximate entropy and sample entropy. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2000, 278, H2039–H2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, S.; Borges, A.F.; Henriques, T.; Goldberger, A.L.; Costa, M.D. Use of multiscale entropy to facilitate artifact detection in electroencephalographic signals. In Proceedings of the 2015 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; pp. 7869–7872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Kim, M.; Hwang, W.J.; Kim, T.; Kwak, Y.B.; Kwon, J.S. Relationship between resting-state theta phase-gamma amplitude coupling and neurocognitive functioning in patients with first-episode psychosis. Schizophr. Res. 2022, 239, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enriquez-Geppert, S.; Huster, R.J.; Herrmann, C.S. EEG-neurofeedback as a tool to modulate cognition and behavior: A review tutorial. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, W.P., Jr.; Swets, J.A. A decision-making theory of visual detection. Psychol. Rev. 1954, 61, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
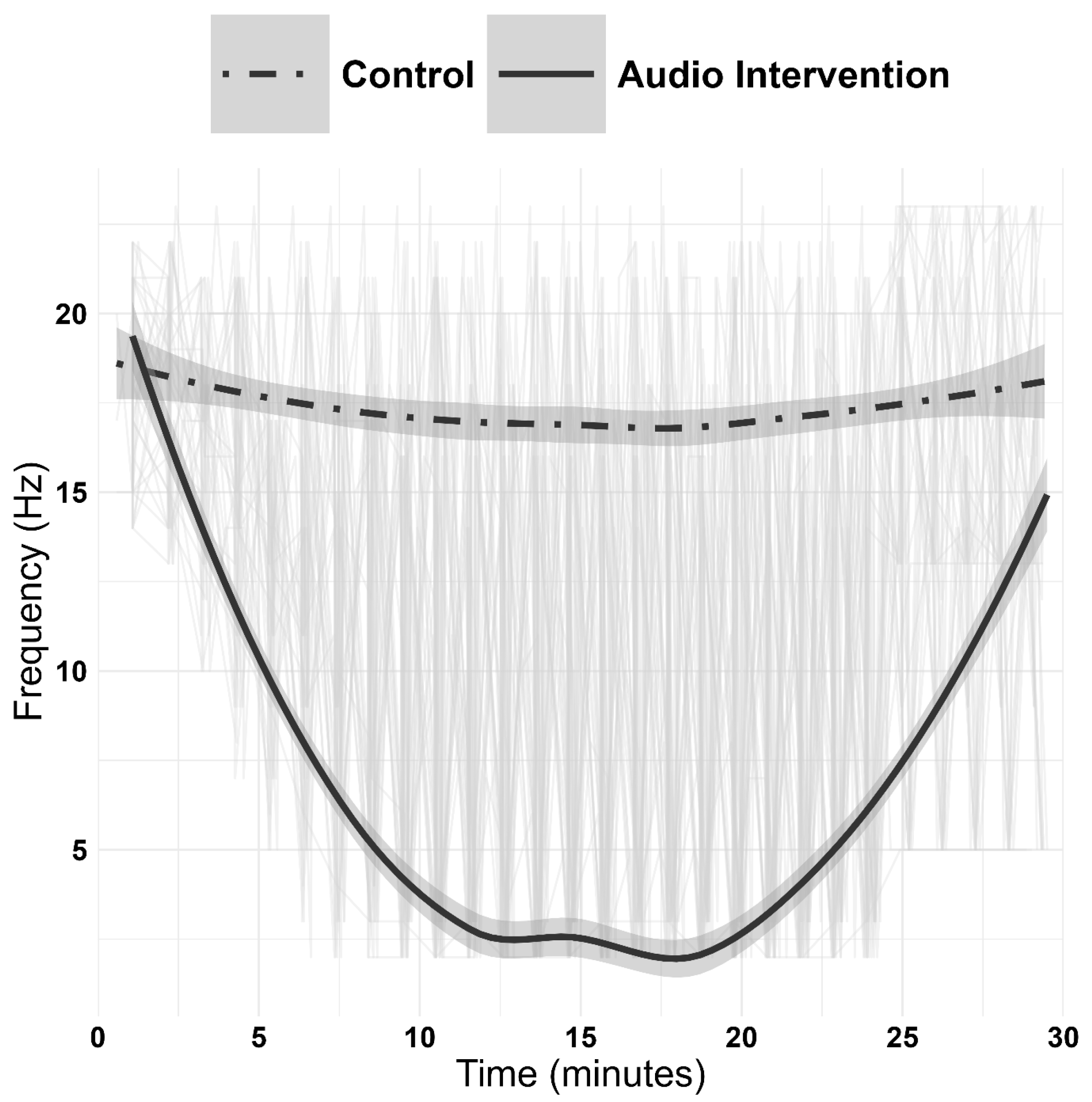
| Sham-Control ± SD) | Intervention ± SD) | t-Statistic | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 17.92 ± 2.74 | 18.44 ± 2.60 | −0.653 | 0.520 |
| 5 min | 17.63 ± 2.75 | 10.00 ± 2.86 | −8.495 | <0.001 |
| 10 min | 17.50 ± 4.10 | 3.08 ± 1.75 | −15.358 | <0.001 |
| 15 min | 17.79 ± 4.23 | 2.84 ± 0.80 | −16.749 | <0.001 |
| 20 min | 17.71 ± 4.08 | 2.52 ± 0.71 | −17.52 | <0.001 |
| Pre-awakening | 17.52 ± 3.40 | 2.72 ± 0.84 | −21.288 | <0.001 |
| Awakening | 16.92 ± 3.03 | 12.16 ± 7.05 | −3.297 | 0.003 |
| Time Point | Sham-Control | Intervention | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δ | Θ | Low α | High α | β | δ | θ | Low α | High α | β | |
| Baseline | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 25 |
| (0) | (0) | (0) | (0) | (100) | (0) | (0) | (0) | (0) | (100) | |
| 5 min | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 24 | 0 | 7 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| (0) | (0) | (0) | (4) | (96) | (0) | (28) | (20) | (24) | (28) | |
| 10 min | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 23 | 20 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| (0) | (4) | (0) | (4) | (92) | (80) | (16) | (0) | (4) | (0) | |
| 15 min | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 23 | 23 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| (0) | (4) | (0) | (4) | (92) | (92) | (8) | (0) | (0) | (0) | |
| 20 min | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 23 | 24 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| (0) | (4) | (0) | (8) | (88) | (96) | (4) | (0) | (0) | (0) | |
| Pre- awakening | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 24 | 23 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| (0) | (0) | (4) | (0) | (96) | (92) | (8) | (0) | (0) | (0 | |
| Awakening | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 24 | 0 | 9 | 2 | 1 | 13 |
| (0) | (0) | (4) | (0) | (96) | (0) | (36) | (8) | (4) | (52) | |
| Variable | Control | Intervention | Main Effects | Interaction F(df1, df2) p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre ± SD | Post ± SD | Pre ± SD | Post ± SD | Condition
F(df1, df2) p | Time
F(df1, df2) p | ||
| SSRT (s) | 0.089 ± 0.040 | 0.102 ± 0.059 | 0.109 ± 0.060 | 0.093 ± 0.045 | 2.82(1,68.2) 0.097 | 1.11(1,68.5) 0.295 | 2.82(1,68.8) 0.098 † |
| a2 | 1.91 ± 0.119 | 1.85 ± 0.219 | 1.86 ± 0.161 | 1.92 ± 0.122 | 0.97(1,67.0) 0.328 | 2.19(1,67.6) 0.143 | 3.52(1,68.0) 0.065 † |
| v2 | −4.75 ± 1.21 | −5.43 ± 0.916 | −5.11 ± 1.04 | −4.99 ± 1.08 | 1.41(1,68.7) 0.240 | 4.80(1,69.5) 0.032 * | 3.40(1,69.8) 0.070 † |
| NET-RT (s) | 1.13 ± 0.209 | 1.16 ± 0.229 | 1.23 ± 0.259 | 1.10 ± 0.217 | 2.45(1,54.6) 0.124 | 0.00(1,54.6) 0.974 | 4.50(1,54.4) 0.039 * |
| Cognitive Performance | 69.3 ± 13.8 | 62.2 ± 20.1 | 66.9 ± 16.3 | 67.3 ± 19.6 | 0.57(1,72) 0.454 | 4.99(1,72) 0.029 * | 2.79(1,72) 0.099 † |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kahathuduwa, C.N.; Blume, J.; Mani, C.; Dhanasekara, C.S. Real-Time Electroencephalography-Guided Binaural Beat Audio Enhances Relaxation and Cognitive Performance: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Sham-Controlled Repeated-Measures Crossover Trial. Physiologia 2025, 5, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/physiologia5040044
Kahathuduwa CN, Blume J, Mani C, Dhanasekara CS. Real-Time Electroencephalography-Guided Binaural Beat Audio Enhances Relaxation and Cognitive Performance: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Sham-Controlled Repeated-Measures Crossover Trial. Physiologia. 2025; 5(4):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/physiologia5040044
Chicago/Turabian StyleKahathuduwa, Chanaka N., Jessica Blume, Chinnadurai Mani, and Chathurika S. Dhanasekara. 2025. "Real-Time Electroencephalography-Guided Binaural Beat Audio Enhances Relaxation and Cognitive Performance: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Sham-Controlled Repeated-Measures Crossover Trial" Physiologia 5, no. 4: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/physiologia5040044
APA StyleKahathuduwa, C. N., Blume, J., Mani, C., & Dhanasekara, C. S. (2025). Real-Time Electroencephalography-Guided Binaural Beat Audio Enhances Relaxation and Cognitive Performance: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Sham-Controlled Repeated-Measures Crossover Trial. Physiologia, 5(4), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/physiologia5040044






