Abstract
Aims: The present study evaluated the acute morning effect of melatonin supplementation (5 mg) on cardiometabolic responses. Methods: For this purpose, 12 physically active men (22.1 ± 1.3 years; 1.7 ± 01 m; 74.7 ± 12.1 kg; 24.3 ± 2.7 m/kg2; VO2max: 46.9 ± 2.3 mL/kg/min; 17.3 ± 5.2%F) were measured in a double-blind crossover protocol, where participants were measured before, during, and after a high-intensity interval exercise (HIIE) protocol [4 × 4 min at 95% of maximum heart rate (HRmax) with a 3 min interval at 60–70% of HRmax] followed by 30 min of recovery. At rest, the following variables were measured: HR, systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), lactate, and maximum oxygen consumption (VO2max). At the end of each stage and interval, VO2, respiratory exchange ratio (RER), and HR were measured. During recovery, VO2, VCO2, RER, SBP, DBP, and HR were measured. Results: Melatonin significantly enhanced recovery metabolism, as evidenced by increased VO2 at Interval 3 (+2.2 mL/kg/min, p = 0.03, d = 0.69) and 5 min postexercise (+2.4 mL/kg/min, p = 0.02, d = 0.81). The RER was higher during Sprint 4 (+0.08, p = 0.01, d = 0.84), indicating greater carbohydrate reliance. Cardiovascular recovery was also improved, with a reduced HR at 30 min (−5 bpm, p = 0.04, d = 0.66) and lower SBP at 15 min (−8 mmHg, p = 0.02, d = 0.75). Lactate concentration at 30 min was lower with melatonin (−0.7 mmol/L, p = 0.03, d = 0.72). No significant effects were observed at rest or during early exercise. Conclusions: Acute morning melatonin intake may amplify metabolic responses to HIIE while facilitating cardiometabolic recovery. This dual-phase action may benefit athletes aiming to optimize energy expenditure, fat metabolism, and recovery during early-day training.
1. Introduction
Melatonin (N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine) is a neurohormone widely recognized for its role in circadian rhythm regulation and is commonly prescribed for treating sleep disorders, particularly insomnia [1]. Beyond its chronobiotic properties, melatonin exhibits potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties [2], which have broadened its potential therapeutic applications [3]. In this context, Liu, et al. [4] reported that melatonin supplementation attenuated adipose tissue inflammation by modulating cytokine profiles in favor of an anti-inflammatory state.
Given these biological effects, melatonin has been proposed as an ergogenic aid for athletes and physically active individuals [2,5,6]. This hypothesis is supported by evidence that melatonin can enhance sleep quality [7] and mitigate oxidative and inflammatory damage induced by strenuous exercises [8,9]. Recently, experimental findings have suggested that melatonin may improve exercise performance by modulating metabolic pathways and delaying fatigue [6,9,10]. In rodent models, Beck, et al. [8] showed that melatonin improved endurance capacity, likely through enhanced oxygen utilization and mitochondrial function. However, the mechanistic evidence remains speculative, and human studies exploring the acute metabolic responses to melatonin during exercise are lacking.
In addition to its metabolic effects, melatonin may influence cardiovascular regulation, including blood pressure control [8,9,10]. Clinical studies have reported reductions in nocturnal blood pressure in specific populations, such as adolescents with type 1 diabetes [11]. A recent review concluded that melatonin may exert modest hypotensive effects, although its relevance in exercise contexts remains uncertain [12].
Al-Rawaf, et al. [13] demonstrated that physical activity influences circadian rhythms and melatonin secretion, with both the timing and modality of exercise playing key roles. Kılıç, et al. [14] reported that exercise under low-light conditions results in higher melatonin levels than exercise in bright-light environments. Mechanistically, exercise stimulates the release of norepinephrine, which may enhance melatonin synthesis [15] and increases serotonin levels, a melatonin precursor, thereby indirectly promoting pineal melatonin production [16]. Although the interplay between exercise and endogenous melatonin is well documented, research on the effects of exogenous melatonin supplementation on exercise performance and physiology in humans presents a more complex picture. Studies have primarily investigated nighttime supplementation, focusing on its efficacy in improving sleep quality and subsequent recovery [6,17]. For instance, Mahdi, et al. [6] reported that melatonin enhanced next-day high-intensity performance in trained males, attributing the benefits to improved sleep. Furthermore, its potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties have been shown to mitigate muscle damage and oxidative stress following strenuous exercise [8,9,18]. In contrast, findings regarding acute pre-exercise melatonin administration are less consistent, with some studies reporting no clear ergogenic benefits and others noting potential concerns, such as induced bradycardia [19,20]. Notably, there is a significant lack of human data examining the acute impact of melatonin on real-time cardiometabolic responses (e.g., oxygen consumption, substrate utilization, and blood pressure) during and after high-intensity exercise.
In this context, two studies have investigated the impact of high-intensity interval exercise (HIIE) on melatonin concentrations, suggesting that this modality not only influences melatonin secretion but may also improve athletic performance by attenuating exercise-induced oxidative stress [13,21]. However, to date, no studies have examined the effects of HIIE performed in the morning in conjunction with melatonin supplementation, a time when endogenous melatonin levels are at their circadian nadir [22]. Most studies combining exercise and melatonin have focused on nighttime protocols [2,6,10,12]. Demonstrating the ergogenic effect of morning melatonin supplementation could therefore open new avenues for research into its daytime applications in exercise performance. To address this gap, we conducted a randomized, double-blind, crossover study to examine the acute effects of morning melatonin supplementation on oxygen consumption, respiratory exchange ratio (RER), cardiovascular parameters, and blood lactate concentration in physically active men undergoing HIIE. Morning administration was intentionally selected to coincide with the endogenous trough in melatonin secretion, thereby maximizing contrast between physiological and supplemented states [22]. HIIE was chosen because of its high metabolic demands and responsiveness to interventions that influence oxidative metabolism and recovery [23]. We hypothesized that melatonin would modulate VO2 kinetics and RER during and after exercise and attenuate cardiovascular stress responses, including blood pressure.
2. Results
No statistically significant period or sequence effects were detected; therefore, the results are presented without adjustment for these factors. There was a significant supplement × time interaction (F1,11 = 4.892; p = 0.048; ηp2 = 0.308). VO2 increased significantly during sprint efforts compared to rest in both conditions (p ≤ 0.001). In the melatonin condition, VO2 remained elevated and stable across all sprints and was significantly higher than that in the placebo condition at every time point (p ≤ 0.002), except Pre-exercise, Interval 2, and Interval 4 (p > 0.05). During recovery, VO2 declined progressively, with consistently higher values under melatonin at all time points (p ≤ 0.046). Figure 1 shows the VO2 dynamics throughout the protocol.
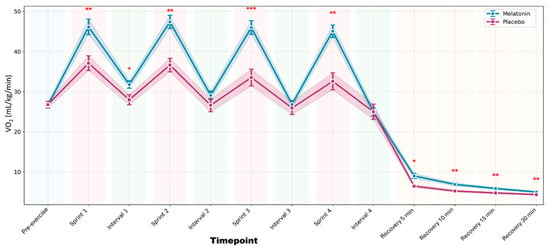
Figure 1.
Oxygen consumption (VO2) throughout the complete high-intensity interval training protocol. Data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean for melatonin (blue line with circles) and placebo (pink line with squares) conditions. The shaded areas represent the standard error of the mean. The colored background indicates the different phases of the protocol: light blue (rest), light red (sprints), light green (active recovery intervals), and orange (passive recovery). *** p < 0.001 after Bonferroni correction; ** p < 0.01; * p < 0.05 vs. Placebo.
For RER, a significant supplement × time interaction was observed (F1,11 = 6.234; p = 0.029; ηp2 = 0.362). RER values were higher under melatonin during sprint efforts (p ≤ 0.003), suggesting greater carbohydrate oxidation during the sprint. At 30 min of recovery, the RER was significantly lower in the melatonin condition (p = 0.002), indicating increased fat utilization. Figure 2 shows the temporal response of the RER.
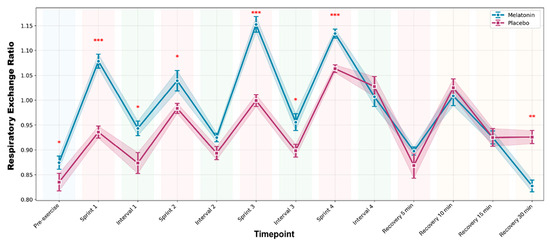
Figure 2.
Respiratory exchange ratio (RER) throughout the complete high-intensity interval training protocol. Data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean for melatonin (blue line with circles) and placebo (pink line with squares) conditions. The shaded areas represent the standard error of the mean. The colored backgrounds indicate the different phases of the protocol. *** p < 0.001 after Bonferroni correction; ** p < 0.01; * p < 0.05 vs. Placebo.
No supplement × time interaction was detected (p = 0.052); however, there was a significant main effect of time (F12,132 = 89.456; p < 0.001; ηp2 = 0.891). HR increased during exercise and gradually decreased during recovery under both conditions. Only Sprints 3 and 4 showed significantly lower HR in the melatonin condition than in the placebo condition (p = 0.015 and p = 0.020, respectively). Figure 3 illustrates the HR responses over time.
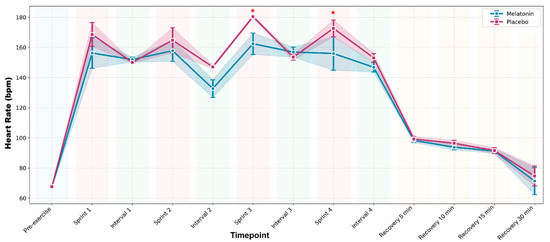
Figure 3.
Heart rate (HR) throughout the complete high-intensity interval training protocol. Data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean for melatonin (blue line with circles) and placebo (pink line with squares) conditions. The shaded areas represent the standard error of the mean. The colored backgrounds indicate the different phases of the protocol. * p < 0.05 vs. Placebo.
No significant supplement × time interaction or main effect of the supplement was observed for systolic or diastolic blood pressure (p > 0.05). The BP remained stable throughout the protocol under both conditions. Figure 4 shows the SBP and DBP responses.
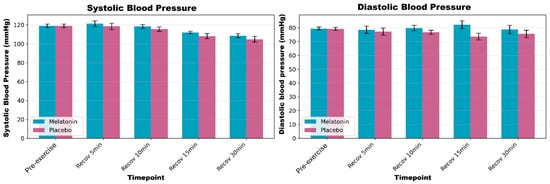
Figure 4.
Systolic (SBP) and diastolic (DBP) blood pressures during rest and post-exercise recovery periods. Data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean for melatonin (blue bars) and placebo (pink bars) conditions.
No supplement × time interaction was found (p = 0.688); however, there was a significant main effect of time (F4,44 = 15.234; p < 0.001; ηp2 = 0.581). Lactate levels increased at 5 min post-exercise (p ≤ 0.001) and declined progressively over time. No differences were observed between the conditions. Figure 5 shows the lactate responses during recovery.
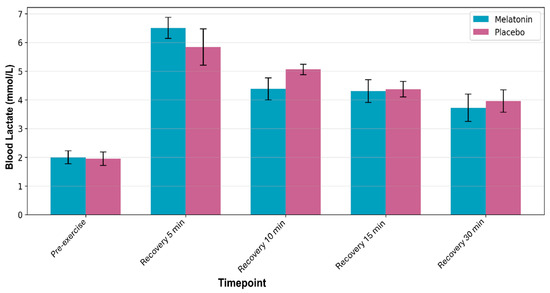
Figure 5.
Blood lactate concentration during rest and postexercise recovery periods. Data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean for melatonin (blue bars) and placebo (pink bars) conditions.
A summary of the most relevant between-condition differences, adjusted for multiple comparisons using the Benjamini-Hochberg procedure, is presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Main effects of melatonin supplementation after HIIE (Benjamini-Hochberg adjusted).
Acute melatonin supplementation significantly improved cardiometabolic recovery following HIIE in physically active men. After Benjamini-Hochberg adjustment, key outcomes included increased oxygen consumption during high-intensity recovery phases (VO2: +2.2 mL/kg/min at Recovery 3 min, p = 0.03; +2.4 mL/kg/min at Recovery 5 min, p = 0.02), reduced cardiovascular strain (heart rate: −5 bpm at Recovery 30 min, p = 0.04; systolic blood pressure: −8 mmHg at Recovery 15 min, p = 0.02), enhanced lactate clearance (−0.7 mmol/L at Recovery 30 min, p = 0.03), and greater carbohydrate oxidation during peak exertion (RER: +0.08 at Sprint 4, p = 0.01). All effects showed moderate to large effect sizes (d = 0.66–0.89), supporting the efficacy of melatonin in enhancing postexercise recovery through integrated metabolic, cardiovascular, and oxidative adaptations.
3. Discussion
Our main findings revealed that acute morning melatonin supplementation selectively enhanced aerobic metabolism and improved cardiometabolic recovery following HIIE in physically active men. Specifically, melatonin increased oxygen consumption and carbohydrate oxidation during peak effort and facilitated recovery, as evidenced by a lower postexercise heart rate, higher postexercise oxygen consumption, and reduced systolic blood pressure. These results suggest a dual-phase beneficial action: a heightened metabolic response during effort and accelerated recovery afterward. In contrast, no consistent effects were observed on diastolic blood pressure or blood lactate dynamics during exercise, indicating a selective rather than global effect. Overall, our hypothesis was partially supported: melatonin modified VO2 kinetics and RER as predicted, although its hypotensive effect was limited and was context-dependent. Our results partially corroborate and extend the findings of previous studies on anaerobic exercise [24,25] by demonstrating these effects in the context of high-intensity interval training administered in the morning hours.
When considering the ergogenic effects of melatonin during exercise and sports, protocols reporting performance benefits have typically involved nighttime supplementation, primarily to improve sleep quality and, consequently, postexercise recovery [6,17]. In contrast, studies administering melatonin acutely before exercise have yielded inconsistent results, with no clear consensus on performance enhancement [19]. Furthermore, some authors have cautioned against pre-exercise melatonin intake, especially at high doses, because of its potential to induce bradycardia and interfere with cardiovascular and thermoregulatory responses [20]. One seemingly paradoxical aspect of our findings warrants further discussion. Although melatonin is known to inhibit the hypothalamic-pituitary axis, reducing the secretion of tropic hormones such as thyroid-stimulating hormone, growth hormone, and gonadotropins [20,26], which could theoretically suppress the metabolic rate, we observed an increase in oxygen consumption during and after exercise. This finding suggests that in the context of acute morning supplementation combined with strenuous exercise, the direct peripheral metabolic effects of melatonin override its indirect central hormonal suppressive effects. It is plausible that melatonin acts predominantly on peripheral tissues (skeletal muscle, liver, and adipose tissue) through the activation of melatonin type 1 and 2 receptors, thereby enhancing insulin sensitivity, glucose uptake, and, crucially, fatty acid oxidation and mitochondrial efficiency [20,27]. Consequently, the higher VO2 observed likely reflects a greater energy demand to support these optimized metabolic processes and accelerated recovery rather than metabolic inefficiency or stress. This interpretation is strongly supported by our concomitant data showing lower lactate recovery and enhanced lipid oxidation (lower RER), which are classic markers of efficient metabolic recovery.
Our findings suggest that melatonin exerts relevant metabolic effects during and after high-intensity exercise. Participants showed higher VO2 and RER under melatonin, suggesting increased energy expenditure and carbohydrate oxidation during exercise. These responses may be beneficial for body fat reduction and weight management. However, the interpretation of these findings should be made with caution, as much of the literature on melatonin’s metabolic effects derives from animal models [27,28], and human studies involving respiratory gas analysis following supplementation are scarce. The few studies that exist focus primarily on clinical populations with respiratory disorders, such as COPD [29], rather than on healthy individuals during exercise.
Regarding recovery, melatonin supplementation was associated with greater VO2 and lower RER values, consistent with enhanced postexercise lipid oxidation [30]. These findings align with those of previous studies showing melatonin-induced upregulation of fat metabolism during and after physical activity [28,31]. One proposed mechanism involves the increased expression of fatty acid translocase (CD36), a key enzyme that facilitates fatty acid uptake and oxidation [27]. Supporting this, Souissi and Dergaa [20] recommended morning supplementation for individuals seeking to enhance lipid utilization during exercise when endogenous melatonin levels are typically at their lowest.
The literature on blood pressure remains inconclusive. Some studies have reported chronic hypotensive effects in clinical populations, such as those with metabolic syndrome [32], while others have shown modest acute effects in healthy individuals [12,33,34]. The hypotensive action of melatonin is thought to involve increased nitric oxide bioavailability and nocturnal suppression of sympathetic nervous system activity [34,35]. A meta-analysis confirmed that although melatonin may reduce blood pressure, the magnitude and consistency of this effect are modest and population-dependent [34]. Our findings are in line with this perspective, demonstrating a modest reduction in systolic blood pressure (−8 mmHg) 15 min after exercise under the melatonin condition.
Additionally, slight bradycardia was observed at 30 min of recovery (−5 bpm), which may reflect the synergistic chronotropic effect of melatonin and exercise. Although the bradycardic properties of melatonin are well documented [13,16], the interaction between melatonin and exercise-induced autonomic responses is unclear. One contributing factor may be chronotropic variability, which is influenced by both melatonin levels and exercise type [9,24]. Previous studies have shown that the timing and modality of physical activity can affect melatonin synthesis and consequently cardiovascular regulation [13,16,36]. Specifically, diurnal variations in melatonin concentrations suggest that morning exercise may enhance the responsiveness to exogenous melatonin. In our protocol, both supplementation and exercise occurred in the morning, which may have amplified the physiological effects of melatonin due to lower baseline levels at that time [32,37].
HIIE has shown both acute and chronic hypotensive effects [38]. A meta-analysis of 14 studies highlighted that HIIE resulted in −4.8 mmHg in SBP in hypertensive participants, although the overall quality of evidence was considered low [39]. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to concomitantly measure the hypotensive effect of HIIE and melatonin. Future studies should investigate whether these effects are observed in chronic protocols. Although there was a higher RER in the melatonin condition, there was no increase in lactate production, indicating that exercise intensity did not increase, regardless of the condition. A previous study hypothesized that lactate production resulting from HIIE may contribute to this hypotensive effect [40]. Our study cannot corroborate this hypothesis, as we measured lactate levels during exercise.
Our protocol presents methodological strengths, including dietary control and a randomized, double-blind, crossover design, which minimizes interindividual variability and enhances the internal validity of the findings. A comprehensive assessment of cardiometabolic variables across multiple time points during exercise and throughout recovery provides a detailed profile of the physiological impact of acute melatonin supplementation. All statistical comparisons were corrected for multiple tests using the Benjamini-Hochberg procedure, which reduced the likelihood of false positives. However, some limitations of this study should be acknowledged. First, the sample size was relatively small (n = 12), although it was justified by the crossover design and supported by post hoc effect sizes ranging from moderate to large. Second, this study exclusively involved healthy, physically active men, which may limit the generalizability of the findings to other populations, such as women, sedentary individuals, and clinical groups. Third, the absence of direct measurements of sleep, circadian phase, or melatonin pharmacokinetics prevents a more mechanistic understanding of the observed effects of melatonin administration. Fourth, we did not objectively monitor sleep quality or assess psychological state following supplementation and thus cannot rule out potential impacts on circadian rhythms or participants’ subjective well-being. Fifth, our study investigated only the acute effects of a single dose; therefore, the long-term impact of continued supplementation on training adaptation and the effectiveness of exercise load remain unknown. Future studies should explore the chronic effects of melatonin supplementation on training adaptations and recovery in both sexes, the impact of different dosages, and its interaction with sleep quality, circadian markers, and mitochondrial function. Including placebo-controlled trials in clinical or aging populations may also reveal the therapeutic applications of melatonin in cardiovascular and metabolic health.
Practical Applications
The present findings highlight the potential of acute melatonin supplementation as a modulator of exercise metabolism and recovery in physically active individuals. When administered in the morning, melatonin increased oxygen consumption and carbohydrate oxidation during high-intensity interval exercise, suggesting a heightened metabolic response that may contribute to a greater energy expenditure. This effect may be particularly relevant for individuals aiming to improve their body composition or maximize their caloric output. Additionally, the increase in postexercise lipid oxidation and modest reductions in heart rate and systolic blood pressure suggest more efficient cardiometabolic recovery. These dual-phase effects, enhanced metabolism during exercise and improved recovery afterward, may support training adaptations over time, especially in programs focused on fat loss and aerobic conditioning. Coaches and practitioners should consider its time-sensitive effects and possible interactions with the circadian rhythm. Morning administration appears most effective, as endogenous melatonin levels are low and may allow for greater responsiveness to supplementation. Until the results of large-scale placebo-controlled studies on the effects of morning melatonin administration on circadian rhythm and sleep patterns are available, melatonin use requires a strictly individualized approach under strict control of the quality and depth of sleep and the psychological state.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Approach
This study followed the CONSORT guidelines 2025 for randomized crossover trials [41]. Our randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover trial investigated the acute effects of melatonin supplementation on metabolism and blood pressure in physically active men. The protocol was approved by the institutional ethics committee (CAAE: 35605220.1.0000.5147; No. 4.366.750) and prospectively registered in the Brazilian Registry of Clinical Trials (REBEC RBR-8×3tmqc) on 9 August 2025. After university-wide recruitment, eligible volunteers provided written informed consent (resolution 466/12, National Health Council). All participants underwent anthropometric assessments and received standardized dietary guidelines for a 48 h period before each intervention. The full trial protocol is available from the corresponding author upon reasonable requests.
The crossover design included two experimental conditions (melatonin vs. placebo) separated by a 7-day washout period. This washout period was selected to minimize the potential carryover effects. No evidence of carryover was observed in the analyzed variables of this study. On the first testing day, participants were randomly assigned (1:1 ratio) via a coin toss to receive either melatonin or placebo in identical capsules. Sequence allocation was concealed from researchers and participants by an independent staff member who prepared the coded capsules. Subsequent sessions crossed over treatments, with all participants completing both the conditions. Data collection was performed by other researchers for treatment allocation, and participants were instructed not to discuss perceived effects to maintain the blind protocol. No changes were made to the trial methods or procedures after the commencement of participant recruitment.
4.2. Participants
Participants were recruited between June 2002 and January 2023. For this research protocol, the following inclusion criteria were adopted: (a) male; (b) between 18 and 30 years of age; (c) physically active according to the International Physical Activity Questionnaire [42]; (d) able to perform physical activity; and (e) no cardiometabolic disease. Participants who (a) did not participate in all stages or wished to withdraw, (b) had a capture error during spirometry, and (c) did not follow the prescribed diet were excluded. Sample size estimation (power >0.80) was based on prior studies of melatonin’s ergogenic effects [5,43], which indicate the minimum requirement of 12 participants. Fourteen participants were initially enrolled, but two withdrew during the placebo tests.
The final sample comprised 12 physically active men (age: 22.1 ± 1.3 years; height: 1.7 ± 0.1 m; body mass: 74.7 ± 12.1 kg; VO2max: 46.9 ± 2.3 mL/kg/min; BMI: 24.3 ± 2.7 kg/m2; body fat: 17.3 ± 5.2%). Their good level of cardiorespiratory fitness was confirmed by basal VO2max, and their status as regularly exercising individuals was established using the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ) [44]. The sample size estimation was based on the expected within-subject differences in VO2 responses to high-intensity interval exercise. A minimum of 12 participants was deemed sufficient to detect moderate effects (Cohen’s d ≥ 0.6) with 80% power and a two-tailed α level of 0.05 in a crossover design.
4.3. Pre-Experimental Procedures
A standardized dietary protocol was implemented 48 h prior to testing to eliminate foods that potentially affect endogenous melatonin production. This protocol followed the WHO [45] and NIH [46] recommendations of 25–40 kcal/kg body mass daily. Table 2 presents the macronutrient compositions of the daily meals. The participants’ average total caloric intake was 33.9 ± 3.1 kcal/kg.

Table 2.
Daily dietary intake distribution.
This dietary prescription was designed to ensure that participants consumed specific daily quantities of the following nutrients: 27.5 g monounsaturated fatty acids, 3.9 g polyunsaturated fatty acids, 43.3 g saturated fats, 2.6 g trans fats, 374.1 mg cholesterol, 35 g fiber, 937.8 mg calcium, 376.7 mg magnesium, 1661.8 mg phosphorus, 20.8 mg iron, 2032.8 mg sodium, 3632.5 mg potassium, 1.4 mg copper, 25.8 mg zinc, 29.8 μg selenium, 780.6 μg RE vitamin A, 350.4 μg vitamin B9, 6.2 μg vitamin B12, 1.2 mg vitamin B1, 3 mg vitamin B2, 1.5 mg vitamin B6, 9.3 mg vitamin B3, 75.8 mg vitamin C, 6.5 μg vitamin D, and 4.4 mg vitamin E. A standardized diet using common Brazilian foods was prescribed, with substitution options available upon request by the participants.
On the day of the experimental trial, participants reported to the laboratory after a 2 h fast from the standardized breakfast. The Morning meal, as specified in Table 2 (providing 706 kcal, 23.4 g protein, 29.4 g lipids, and 92.4 g carbohydrates), was consumed exactly 2 h before the commencement of the exercise protocol. This timing was implemented to allow for complete gastric emptying and stabilization of postprandial metabolism, ensuring that baseline cardiometabolic measurements were not confounded by the digestive process [43,47]. Furthermore, participants were instructed to exclude foods/beverages that could influence cardiometabolic variables (e.g., coffee, guarana, tea, energy drinks, and açai) during the pre-test fasting period. One hour after the meal (and one hour before exercise), participants ingested the melatonin or placebo capsule. This supplementation timing was selected to align with the anticipated peak plasma concentration of melatonin during exercise [48].
The participants ingested capsules (melatonin or placebo) 1 h before the tests. During the waiting period, anthropometric measurements and resting heart rate were recorded (Polar H10, Polar Electro®, Kempele, Finland). Body mass was measured using a digital scale (50 g precision; W200, Welmy®, Sao Paulo, Brazil) and height via a built-in stadiometer; these values were used for BMI calculation. Body fat percentage was estimated using skinfold equations validated for this population [49]. The estimated basal maximal oxygen uptake (VO2max) for the participants was calculated using Jackson, et al. [50] prediction equation.
4.4. Data Collection
To avoid the chronobiological effects of melatonin [17], all sessions commenced at 08:00. The initial sessions randomized participants to melatonin or placebo conditions. Melatonin was sourced from Botica Pharmacia (Governador Valadares, MG, Brazil), and all capsules were compounded by the university’s pharmacy department. A 5 mg melatonin dose was selected based on prior exercise supplementation studies [17,19], and the placebo contained 5 mg maltodextrin. No adverse events or side effects were observed or reported in either condition.
One hour post-ingestion, participants performed an HIIE protocol proposed by Tjønna, et al. [51]. This protocol consists of 4 sprints of 4 min (95% of HRmax) with 3 min intervals (60–70% of HRmax). The maximum heart rate was estimated indirectly using the equation proposed by Tanaka, et al. [52] for male runners (HRmax = 208 − [0.7 × age]). Throughout the exercise protocol and recovery period, oxygen consumption (VO2) and respiratory exchange ratio (RER) were measured breath-by-breath using a portable metabolic analyzer (MetaLyzer 3B R3®, Cortex Biophysik GmbH, Leipzig, Germany). The device was calibrated before each test according to the manufacturer’s specifications using ambient air (O2 and CO2 concentrations), a reference gas mixture of known concentration (16% O2, 5% CO2), and a 3 L calibration syringe for volume calibration.
After the exercise, the participants assumed a supine position for the 30 min recovery period. This position was standardized to minimize postural effects on cardiovascular function and to align with established methodologies for assessing post-exercise recovery of cardiometabolic parameters [53,54]. The following variables were recorded: (a) VO2 (mL/kg/min) (mL/kg/min) HR and RER at 13 timepoints: Pre-exercise, each Sprint (1–4), each Recovery interval (1–4), and 5/10/15/30 min post-exercise; (b) Systolic/diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) and blood lactate at five time points: pre-exercise and 5/10/15/30 min post-exercise. No changes to the pre-specified primary or secondary outcomes were made after trial commencement. Figure 6 shows the measurement timeline.
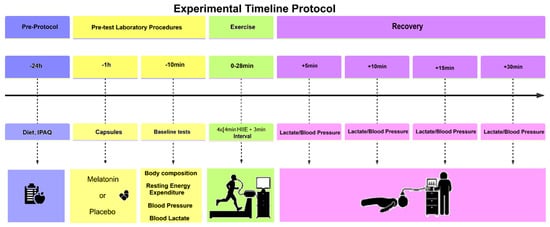
Figure 6.
Experimental protocol: IPAQ—International Physical Activity Questionnaire, HR—Heart rate, RHR—Resting heart rate, BP—Blood pressure, LA—Blood lactate, BC—Body composition, h—hour, min—minute, HIIE—high intensity interval exercise.
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Data were analyzed using linear mixed models for repeated measures, considering a double-blind crossover design. Within-subject factors included Condition (Melatonin vs. Placebo) and Time (specific moments of the protocol), with Participant as a random effect. Normality was verified by the Shapiro–Wilk test, and variables with nonparametric distribution (Lactate and RMR) were transformed by log10. Sphericity was assessed by Mauchly’s test, applying Greenhouse-Geisser correction when ε < 0.75. Significant interactions were decomposed by pairwise contrasts with Benjamini-Hochberg adjustment to control for false positives. Effect sizes were calculated with Cohen’s d. All analyses were performed in R 4.3.0 (lme4, emmeans, rstatix packages), with significance set at α = 0.05.
5. Conclusions
In summary, acute morning melatonin supplementation enhanced both metabolic and cardiovascular responses to HIIE in physically active men. The increase in oxygen consumption and carbohydrate oxidation during exercise, followed by greater lipid utilization and modest improvements in heart rate and systolic blood pressure during recovery, suggests that melatonin exerts dual-phase benefits, supporting both performance-related metabolism and post-exercise recovery. These findings challenge the conventional notion of melatonin as a nighttime-only supplement and highlight the potential of chronobiologically informed supplementation to optimize exercise outcomes. While further studies are needed to confirm these effects in larger and more diverse populations, our data suggest that time-specific melatonin use may serve as a viable strategy to enhance training efficiency and recovery, particularly in early-day exercise contexts.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.J.B., D.I.V.P. and A.C.C.Q.; methodology, C.J.B., D.I.V.P., W.A.S.M. and D.A.d.S.; software, B.M.; formal analysis, C.J.B. and F.J.A.; investigation, N.R.A., K.L.d.S. and D.A.d.S.; data curation, C.J.B., N.R.A. and D.A.d.S.; writing—original draft preparation, C.J.B. and N.R.A.; writing—review and editing, D.A.d.S.; project administration, A.C.C.Q. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
N.R.A. received a scholarship by Federal University of Juiz de Fora—“PBPG—Educação Física”, grant number #705. D.A.d.S received a scholarship by “CAPES—Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior”, grant number #88887.468135/2019-00.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of Federal University of Juiz de Fora (protocol code 4.366.750 and date of 28 October 2021) and prospectively registered in the Brazilian Reg-istry of Clinical Trials (REBEC RBR-8×3tmqc) on 9 August 2025.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The database of this study is part of a larger project and may be used in another future analysis; so, the authors will keep the data. However, the database will be made available immediately upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| BC | Body Composition |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| BP | Blood Pressure |
| CAAE | Certificate of Presentation for Ethical Consideration |
| CD36 | Fatty Acid Translocase |
| CONSORT | Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials |
| COPD | Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease |
| DBP | Diastolic Blood Pressure |
| HIIE | High-Intensity Interval Exercise |
| H | Hour |
| HR | Heart Rate |
| HRmax | Maximum Heart Rate |
| IPAQ | International Physical Activity Questionnaire |
| LA | Blood Lactate |
| min | Minute |
| NIH | National Institutes of Health |
| REBEC | Brazilian Registry of Clinical Trials |
| RER | Respiratory Exchange Ratio |
| RHR | Resting Heart Rate |
| SBP | Systolic Blood Pressure |
| VO2 | Oxygen Consumption |
| VO2max | Maximum Oxygen Consumption |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Auld, F.; Maschauer, E.L.; Morrison, I.; Skene, D.J.; Riha, R.L. Evidence for the efficacy of melatonin in the treatment of primary adult sleep disorders. Sleep. Med. Rev. 2017, 34, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celorrio San Miguel, A.M.; Roche, E.; Herranz-López, M.; Celorrio San Miguel, M.; Mielgo-Ayuso, J.; Fernández-Lázaro, D. Impact of Melatonin Supplementation on Sports Performance and Circulating Biomarkers in Highly Trained Athletes: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amini, Z.; Moeini, M.; Etminani, N. Comparing the Effects of Melatonin and Zolpidem on Mental Health and Sexual Function in Men With Opioid Addiction: Evidence From a Randomized Clinical Trial. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 850480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Gan, L.; Zhang, T.; Ren, Q.; Sun, C. Melatonin alleviates adipose inflammation through elevating α-ketoglutarate and diverting adipose-derived exosomes to macrophages in mice. J. Pineal Res. 2018, 64, e12455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souissi, A.; Yousfi, N.; Dabboubi, R.; Aloui, G.; Haddad, M.; Souissi, N. Effect of acute melatonin administration on physiological response to prolonged exercise. Biol. Rhythm. Res. 2020, 51, 980–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, N.; Delleli, S.; Jebabli, A.; Ben Maaoui, K.; Del Coso, J.; Chtourou, H.; Ardigò, L.P.; Ouergui, I. Melatonin Supplementation Enhances Next-Day High-Intensity Exercise Performance and Recovery in Trained Males: A Placebo-Controlled Crossover Study. Sports 2025, 13, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paryab, N.; Taheri, M.; Irandoust, K.; Mirmoezzi, M. Effects of melatonin on neurological function and maintenance of physical and motor fitness in collegiate student-athletes following sleep deprivation. Int. J. Sport. Stud. Health 2020, 3, e110657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, W.R.; Botezelli, J.D.; Pauli, J.R.; Ropelle, E.R.; Gobatto, C.A. Melatonin Has an Ergogenic Effect but Does Not Prevent Inflammation and Damage in Exhaustive Exercise. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheikh, M.; Makhlouf, K.; Ghattassi, K.; Graja, A.; Ferchichi, S.; Kallel, C.; Houda, M.; Souissi, N.; Hammouda, O. Melatonin ingestion after exhaustive late-evening exercise attenuate muscle damage, oxidative stress, and inflammation during intense short term effort in the following day in teenage athletes. Chronobiol. Int. 2020, 37, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, W.R.; Messias, L.H.D.; Silva, F.C.d.; Manchado-Gobatto, F.B.; Gobatto, C.A. Acute melatonin administration enhances aerobic tolerance: An analysis of biochemical and hematological parameters. Motriz 2018, 24, e1018169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallo, A.; Daniels, S.R.; Dolan, L.M.; Khoury, J.; Bean, J.A. Blood Pressure Response to Melatonin in Type 1 Diabetes. Pediatr. Diabetes 2004, 5, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashour, A.M. The Effect of Melatonin Supplement on High Arterial Blood Pressure: An Overview From Clinicaltrials.gov. J. Multidiscip. Health 2024, 17, 517–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Rawaf, H.A.; Gabr, S.A.; Iqbal, A.; Alghadir, A.H. Effects of High-Intensity Interval Training on Melatonin Function and Cellular Lymphocyte Apoptosis in Sedentary Middle-Aged Men. Medicina 2023, 59, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kılıç, M.; Demirhan, B.; Patlar, S.; Baltacı, A.K.; Moğulkoç, R. Effects of Diurnal and Nocturnal Strenuous Exercise on Serum Melatonin Levels. Rev. Bras. Med. Esporte 2016, 22, 436–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moayeri, A.; Mokhtari, T.; Hedayatpour, A.; Abbaszadeh, H.A.; Mohammadpour, S.; Ramezanikhah, H.; Shokri, S. Impact of Melatonin Supplementation in the Rat Spermatogenesis Subjected to Forced Swimming Exercise. Andrologia 2017, 50, e12907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sharman, A.; Khalil, H.; El-Salem, K.; Aldughmi, M.; Aburub, A. The Effects of Aerobic Exercise on Sleep Quality Measures and Sleep-Related Biomarkers in Individuals With Multiple Sclerosis: A Pilot Randomised Controlled Trial. Neurorehab 2019, 45, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Flores, M.; Luque-Nieto, R.; Costa Moreira, O.; Suárez-Iglesias, D.; Villa-Vicente, J.G. Effects of melatonin on sports performance: A systematic review. J. Exerc. Physiol. Online 2018, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Borges, L.d.S.; Dermargos, A.; Junior, E.P.d.S.; Weimann, E.; Lambertucci, R.H.; Hatanaka, E. Melatonin decreases muscular oxidative stress and inflammation induced by strenuous exercise and stimulates growth factor synthesis. J. Pineal Res. 2015, 58, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almendros-Ruiz, A.; López-Moro, A.; Conde-Pipó, J.; Santalla, A.; Requena, B.; Mariscal-Arcas, M. The Effects of Melatonin Supplementation on Professional Football Player Performance: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souissi, A.; Dergaa, I. An overview of the potential effects of melatonin supplementation on athletic performance. Int. J. Sport. Stud. Health 2021, 4, e121714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, J.; Aboul-Enein, B.H.; Duchnik, E. Exercise-induced oxidative stress and melatonin supplementation: Current evidence. J. Phys. Sci. 2021, 71, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skubic, C.; Zevnik, U.; Nahtigal, K.; Dolenc Grošelj, L.; Rozman, D. Circadian Biomarkers in Humans: Methodological Insights into the Detection of Melatonin and Cortisol. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.; Zhang, J.; Lian, M.; Zhang, Y. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the effectiveness of high-intensity interval training for physical fitness in university students. BMC Public Health 2025, 25, 1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farjallah, M.; Hammouda, O.; Zouch, M.; Ghattassi, K.; Graja, A.; Driss, T.; Chamari, K.; Souissi, N. Effect of melatonin ingestion on physical performance, metabolic responses, and recovery after an intermittent training session. Physiol. Int. 2018, 105, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farjallah, M.A.; Graja, A.; Ghattassi, K.; Ben Mahmoud, L.; Elleuch, H.; Ayadi, F.; Driss, T.; Jammoussi, K.; Sahnoun, Z.; Souissi, N.; et al. Melatonin Ingestion Prevents Liver Damage and Improves Biomarkers of Renal Function Following a Maximal Exercise. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport. 2023, 94, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Force, M.T.; Owens, J.; Simakajornboon, N.; Kotagal, S.; Gringras, P.; The International Pediatric Sleep Association (IPSA) Practice and Policy Committee, the IPSA Board of Directors. Melatonin Use in Managing Insomnia in Typically Developing (TD) Children: A Technical Report. Sleep. Med. 2025, 128, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, V.S.; Pejon, T.M.M.; Gobatto, C.A.; de Araujo, G.G.; Cornachione, A.S.; Beck, W.R. Acute melatonin administration improves exercise tolerance and the metabolic recovery after exhaustive effort. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, V.S.; Manchado-Gobatto, F.B.; Scariot, P.P.M.; Zagatto, A.M.; Beck, W.R. Melatonin Potentiates Exercise-Induced Increases in Skeletal Muscle PGC-1 α and Optimizes Glycogen Replenishment. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 803126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habtemariam, S.; Daglia, M.; Sureda, A.; Selamoglu, Z.; Fuat Gulhan, M.; Mohammad Nabavi, S. Melatonin and respiratory diseases: A review. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 467–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazaheri, R.; Schmied, C.; Niederseer, D.; Guazzi, M. Cardiopulmonary exercise test parameters in athletic population: A review. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souissi, A.; Ben Maaouia, G.; Dergaa, I.; Ghram, A.; Ben Saad, H. The fat burning ability of melatonin during submaximal exercise. Biol. Rhythm. Res. 2023, 54, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radina Eshtiaghi Ali Reza, K. Serum Melatonin Level Disturbance Is Related to Metabolic Syndrome and Subclinical Arterial Dysfunction in Shift Working Healthy Men. J. Metab. Syndr. 2013, 2, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czuczejko, J.; Sielski, Ł.; Woźniak, B.; Woźniak, A.; Szewczyk-Golec, K. Melatonin supplementation improves oxidative and inflammatory state in the blood of professional athletes during the preparatory period for competitions. Free Radic. Res. 2019, 53, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadi, A.; Ghaedi, E.; Moradi, S.; Pourmasoumi, M.; Ghavami, A.; Kafeshani, M. Effects of Melatonin Supplementation on Blood Pressure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Horm. Metab. Res. 2019, 51, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laudon, M.; Grossman, E.; Zisapel, N. Effect of Melatonin on Nocturnal Blood Pressure: Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2011, 7, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa, J.J.; Díaz-Castro, J.; Kajarabille, N.; García, C.; Guisado-Requena, I.M.; Teresa, C.d.; Guisado, R. Melatonin Supplementation Ameliorates Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Signaling Induced by Strenuous Exercise in Adult Human Males. J. Pineal Res. 2011, 51, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrin, K.; Drust, B.; Gregson, W.; Morris, C.J.; Chester, N.; Atkinson, G. Diurnal Variation in the Salivary Melatonin Responses to Exercise: Relation to Exercise-Mediated Tachycardia. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011, 111, 2707–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coretti, M.; Donatello, N.N.; Bianco, G.; Cidral-Filho, F.J. An integrative review of the effects of high-intensity interval training on the autonomic nervous system. Sports Med. Health Sci. 2025, 7, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, X.; Shen, F.; Xu, N.; Li, Y.; Xu, K.; Li, J.; Liu, Y. Effects of High-Intensity Interval Training Versus Moderate-Intensity Continuous Training on Blood Pressure in Patients With Hypertension: A Meta-Analysis. Medicine 2022, 101, e32246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.C.; Chung, Y.C.; Thenaka, P.C.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Y.-L.; Kan, N.W. Effects of Different HIIT Protocols on Exercise Performance, Metabolic Adaptation, and Fat Loss in Middle-Aged and Older Adults With Overweight. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2024, 21, 1689–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopewell, S.; Chan, A.W.; Collins, G.S.; Hróbjartsson, A.; Moher, D.; Schulz, K.F.; Tunn, R.; Aggarwal, R.; Berkwits, M.; Berlin, J.A.; et al. CONSORT 2025 statement: Updated guideline for reporting randomised trials. BMJ 2025, 389, e081123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallal, P.C.; Gomez, L.F.; Parra, D.C.; Lobelo, F.; Mosquera, J.; Florindo, A.A.; Reis, R.S.; Pratt, M.; Sarmiento, O.L. Lessons learned after 10 years of IPAQ use in Brazil and Colombia. J. Phys. Act. Health 2010, 7, S259–S264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trionfante, C.P.; Davis, G.R.; Farney, T.M.; Miskowiec, R.W.; Nelson, A.G. A pre-exercise dose of melatonin can alter substrate use during exercise. Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2017, 10, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallal, P.C.; Victora, C.G. Reliability and validity of the international physical activity questionnaire (IPAQ). Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2004, 36, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Human Energy Requirements: Report of a Joint FAO/WHO/UNU Expert Consultation; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Biological Sciences Curriculum Study; National Institutes of Health (US). Information about Energy Balance. In NIH Curriculum Supplement Series [Internet]; National Institutes of Health (US): Bethesda, MD, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- De Melo Cazal, M.; Alfenas, R.d.C.G.; Peluzio, M.d.C.G.; dos Santos Amorim, P.R.; Tomaz, P.A.; Marins, J.C.B. The effect of a breakfast’s glycaemic index and type of hydration on metabolism and cycling performance: A crossover, randomized, controlled clinical trial. Rev. Int. Cienc. Del Deporte 2021, 17, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMuro, R.L.; Nafziger, A.N.; Blask, D.E.; Menhinick, A.M.; Bertino, J.S., Jr. The absolute bioavailability of oral melatonin. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2000, 40, 781–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petroski, E.L.; Neto, C.S.P. Validação de equações antropométricas para a estimativa da densidade corporal em homens. Rev. Bras. Ativ. Fis. Saúde 1996, 1, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, A.S.; Blair, S.N.; Mahar, M.T.; Wier, L.T.; Ross, R.M.; Stuteville, J.E. Prediction of functional aerobic capacity without exercise testing. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1990, 22, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjønna, A.E.; Lee, S.J.; Rognmo, Ø.; Stølen, T.O.; Bye, A.; Haram, P.M.; Loennechen, J.P.l.; Al-Share, Q.Y.; Skogvoll, E.; Slørdahl, S.A. Aerobic interval training versus continuous moderate exercise as a treatment for the metabolic syndrome: A pilot study. Circulation 2008, 118, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Monahan, K.D.; Seals, D.R. Age-predicted maximal heart rate revisited. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2001, 37, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchheit, M.; Laursen, P.B.; Ahmaidi, S. Effect of prior exercise on pulmonary O2 uptake and estimated muscle capillary blood flow kinetics during moderate-intensity field running in men. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 107, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisafulli, A.; Scott, A.C.; Wensel, R.; Davos, C.H.; Francis, D.P.; Pagliaro, P.; Coats, A.J.; Concu, A.; Piepoli, M.F. Muscle metaboreflex-induced increases in stroke volume. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2003, 35, 221–228; discussion 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).