Abstract
Ralstonia spp. are low-virulent environmental Gram-negative bacteria that can cause serious nosocomial infections in immunocompromised patients. We report the characteristics of a cluster of R. insidiosa bacteremia cases occurring in our oncology day ward in Milan, Italy, between January and March 2022. A case was defined as a cancer patient attending our day ward and whose blood culture (performed because of bacteremia symptoms) led to the isolation of Ralstonia insidiosa. An epidemiological investigation was conducted in order to seek the possible source of infection. Seven adult patients received curative or palliative treatment via infusion through a Port-a-Cath (PAC). All developed symptoms within 24 h of the infusion (three during the infusion itself). Ralstonia insidiosa was isolated in the blood drawn from the PAC in all patients. All of the isolates were susceptible to carbapenems, fluoroquinolones, and piperacillin/tazobactam but resistant to aminoglycosides and cephalosporins. Systemic and/or lock antibiotic therapy led to stable symptom resolution and negative blood cultures in five patients, whereas bacteremia recurred in two patients. An epidemiological investigation suggested that extrinsic contamination of antiseptic solutions was the possible cause of the R. insidiosa infections. Although R. insidiosa is not considered a virulent pathogen, clinicians, microbiologists, and infection control teams should be aware about its potential to cause outbreaks of nosocomial bloodstream infections, especially in immunocompromised patients bearing central venous catheters.
1. Introduction
Non-fermenting, Gram-negative bacilli (NFGNB) represent an increasing healthcare problem since they can cause serious opportunistic infections in immunocompromised patients [1]. This subtype of bacteria is ubiquitous, but they preferably live in soil and water; however, the contamination of in-hospital environments poses a serious risk of healthcare-related infections. Their inherent antibiotic resistance and capability to persist after routine environmental sanitization due to their biofilm production might hamper the clinical management of NFGNB infections. These characteristics further contribute to their success as nosocomial pathogens [1].
The NFGNB most frequently involved in severe nosocomial infections are Pseudomonas spp., Acinetobacter spp., and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, but other NFGNB, generally considered of limited clinical significance, have been emerging as opportunistic pathogens in recent years. In particular, a series of recent reports raised concerns about the pathogenic potential of Ralstonia, a genus of NFGNB that was first described in 1995 [1]. Determined genus members (R. pickettii, R. mannitolilytica and R. insidiosa, previously attributed to the Burkholderia genus) were recently identified as a cause of opportunistic infection in immunocompromised patients, including patients with cancer [1]. In addition, different hospital outbreaks of Ralstonia spp. infections (mainly R. pickettii and R. mannitolilytica) were caused by contaminated infusion-grade water, saline solutions, or pharmaceutical preparations for intravenous infusion [2,3,4,5].
Previous studies reported that Ralstonia spp. can survive under a wide range of conditions and can pass through the 0.2 μm filters that are commonly used to sterilize medical products during their production [1].
We here describe the clinical and epidemiological characteristics of a cluster of R. insidiosa bacteremia cases identified in patients attending an oncology day ward in Milan, Italy, between January and March 2022.
2. Materials and Methods
Luigi Sacco Hospital is a university teaching hospital in Milan that admits an average of 20,000 patients per year. It has nearly 500 licensed beds in 27 wards, including an oncology ward for in- and outpatients. The oncology day ward is equipped with four two-bedded treatment rooms and a room with six reclining armchairs for chemotherapy infusions and is attended by an average of 35 patients per day. Between January and March 2022, it was attended by nearly 400 patients for 2150 visits and, during this period, a series of cases of R. insidiosa bacteremia occurred and were the subject of a subsequent epidemiological investigation. The latter was conducted through the multidisciplinary collaboration of oncologists, infectious disease specialists, microbiologists, and members of our infection prevention and control team. A case was defined as a cancer patient attending our day ward whose blood culture (performed because of the onset of fever and/or chills) led to the isolation of Ralstonia insidiosa, and the clinical records of these cases and their common medical procedures were reviewed in order to seek the possible source of the infection. Verbal informed consent from patients was required. Blood samples obtained from a central venous catheter (CVC) and/or a peripheral vein at the time of the onset of symptoms were cultured by means of incubation in a BACT/ALERT® VIRTUO® system (bioMérieux, Marcy-l’Étoile, France). All positive blood cultures were routinely subjected to subculture on different solid media (blood agar, chocolate agar, CNA agar, MacConkey agar, and Sabouraud dextrose agar) and Gram staining. Matrix-assisted laser desorption–ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS, BioMérieux, Marcy-l’Étoile, France) was used to identify bacterial isolates. According to the manufacturer’s guidelines, a confidence value of 60% or more was considered acceptable to determine the identification of an organism at the species level. For isolates with multiple identifications with low discrimination, identification at the genus level was accepted if all the identifications were from the same genus. Otherwise, the isolate was considered unidentifiable. The susceptibility profiles of the isolates were tested using a Vitek2 system (BioMèrieux, Marcy-l’Étoile, France). Antimicrobial susceptibility was evaluated according to the breakpoint profile of similar species, including Pseudomonas spp. and Acinetobacter spp., since the breakpoints of Ralstonia spp. were not specified in the latest European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) guidelines [6].
3. Results
Between 14 January and 9 March 2022, seven patients attending our day ward developed R. insidiosa bacteremia (attack rate 1.75%). In the same period, no other R. insidiosa bacteremia cases were recorded in the rest of our hospital. Table 1 summarizes the clinical characteristics of the cases: six females with breast cancer and one male with urothelial cell carcinoma whose median age was 60 years (min–max 50–76). One woman was being treated with intravenous (i.v.) paclitaxel alone, two with i.v. paclitaxel plus trastuzumab, one with i.v. trastuzumab alone, and two with iv trastuzumab plus pertuzumab; the man was being treated with i.v. pembrolizumab. All of these drugs were diluted in a saline solution, under aseptic conditions, and administered immediately after being prepared.

Table 1.
Clinical characteristics of patients with R. insidiosa bacteremia.
Therapies were infused through an implanted CVC (Port-a-Cath, PAC), placed a median of 17 months (min–max 3–24) before. According to our standard protocols, the skin over the port was disinfected using a multi-dose bottle of commercial chlorhexidine 2% that was applied for a time ranging from 10 to 15 seconds. Then, the catheters were routinely flushed with a single-use isotonic sodium chloride solution before and after use.
All developed symptoms of bacteremia (fever, shaking chills, malaise and/or arthralgia) within 24 h from PAC flushing or usage for chemotherapy infusion (three during the course of the infusion itself). None of the patients presented signs of infection of the skin above the PAC or evidence of any other source of infection. The symptoms spontaneously subsided within 24 h in all of the patients, except one, whose symptoms persisted for three consecutive days.
Blood samples for microbiological examination were drawn from both a peripheral vein and the PAC in five cases, in the remaining two, peripheral veins were unobtainable. Blood cultures grew Gram-negative bacteria and subcultures showed the growth of the pathogen on blood agar, chocolate agar, and MacConkey agar (Figure 1).
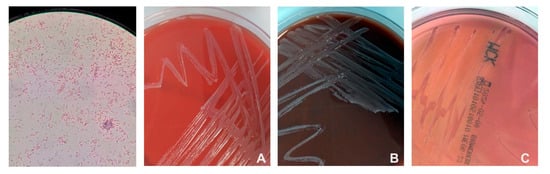
Figure 1.
Ralstonia insidiosa in Gram stain (first on the left) and its growth on blood agar (A), chocolate agar (B) and MacConkey agar (C).
Isolates were identified through MALDI-TOF MS as R. insidiosa, with a confidence value of 99.9% in all of the cases. All of the isolates had the same antibiotic susceptibility profile: they were susceptible to cefepime, ciprofloxacin, imipenem, meropenem, and piperacillin/tazobactam, and resistant to amikacin, gentamicin, cefotaxime, and ceftazidime.
Two of the patients were treated with oral ciprofloxacin for 10 days, and five underwent lock therapy with piperacillin–tazobactam because of suspected PAC colonization. Treatment led to stable symptom resolution and negative blood culture in five patients. In the remaining two, symptomatic bacteremia recurred after PAC usage, but both resolved immediately after PAC removal. Cultures of the CVC tips were negative in both cases.
The samples of disinfectants and solutions used to prepare and administer chemotherapy in this series were no longer available at the time of the study, and further epidemiological or microbiological investigations were no longer performable. On the other hand, all of the hygiene and infection control procedures (particularly those regarding the preparation of therapeutic infusions and PAC management) were reviewed and actively monitored, and all antiseptic dispensers were changed to touch-free dispensers in order to prevent manual contamination of the bottles.
There have since been no other cases of R. insidiosa infection in the day ward after the application of the recommended preventive measures.
4. Discussion
We here describe a cluster of seven cases of R. insidiosa bacteremia in cancer patients being treated at an Italian oncology day ward. Similar outbreaks of Ralstonia spp. bacteremia have been described in other oncology healthcare settings. Lucarelli et al. reported a cluster of R. mannitolityca infections involving 22 patients attending an oncology ward in Rome, Italy [7], and although the authors could not identify the origin of the infections, the flushing of CVCs with extrinsically contaminated saline solutions contained in multi-use vials was considered the most likely source. Similarly, Ramani et al. have described an outbreak of R. mannitolilytica infection involving 17 patients admitted to an oncology care center in southern India that was also possibly due to contaminated bottles of saline solution [2]. Environmental contamination has also been hypothesized as the possible cause of an outbreak of R. pickettii bacteremia reported in an Italian hematopoietic stem cell transplant unit by Mikulska et al. [8].
Contaminated saline solutions or antiseptics may have caused PAC colonization and consequent bacteremia in our patients. We could not confirm this hypothesis for the late identification of the cluster, since R. insidiosa was not among the alert agents routinely sought by our laboratory-based infection control system. Nonetheless, Gram-negative and biofilm-producing bacteria are capable of surviving on the surface of the chlorhexidine bottles used for routine antisepsis, as previously reported [9,10,11].
Notably, three patients developed symptoms of bacteremia (including fever and shaking chills) during the chemotherapy administration itself. Similar situations can mimic drug hypersensitivity reactions. Therefore, clinicians should consider and promptly investigate potential bacteremia correlated to PAC colonization in these cases to avoid inappropriate chemotherapy discontinuation.
In all cases, R. insidiosa was identified via MALDI-TOF MS with a confidence value of 99.9%. While polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is the gold standard, previous studies have shown that MALDI-TOF has a similar predictive power to identify Ralstonia at the species level in a more cost-effective manner [12,13,14].
Ralstonia spp. can produce various enzymes that confer resistance to a wide range of antibiotics, but previous studies showed a considerable heterogeneity in the prevalence of resistance [1]. Our antibiotic susceptibility tests revealed resistance to amikacin, gentamicin, cefotaxime, and ceftazidime and no resistance to cefepime, ciprofloxacin, imipenem, meropenem, or piperacillin/tazobactam. The patients were subsequently treated with ciprofoxacin and/or lock therapy with piperacillin/tazobactam.
As reported in previous studies of Ralstonia spp. outbreaks conducted in hemato-oncology units [2,4,5,7,8], the final outcomes of our cases of R. insidiosa bacteremia were favorable, although two patients required the removal of their PAC because of symptoms and positive blood culture recurrence, despite previous treatment with systemic antibiotics and/or lock therapy, suggesting a microbial PAC colonization.
Removing a CVC could be detrimental and distressing in patients with cancer, since this can lead to treatment delays and an impaired dose intensity. Moreover, CVC removal can be complicated by bleeding and air embolisms [15,16].
Although R. insidiosa is not considered as a major pathogen, clinicians, microbiologists, and infection control teams should be aware of the possibility of outbreaks of bloodstream infections, especially in immunocompromised patients bearing central venous catheters [17,18,19,20]. Our findings suggest that, in the absence of an evident source of infection during an R. insidiosa outbreak, reinforcement and monitoring of all the hygiene and infection control practices are mandatory, and extrinsic contamination of antiseptics needs particular attention.
In conclusion, in patients with solid cancer, CVC hygiene is fundamental to prevent bloodstream infections, even for low-virulent environmental bacteria such as Ralstonia spp. This becomes even more critical for patients treated for curable diseases, as bloodstream infections could impair the dose intensity of anti-cancer treatment and could lead to symptoms mistaken for a drug hypersensitivity reaction.
Author Contributions
The corresponding author is responsible for ensuring that the descriptions are accurate and agreed by all authors and that all authors have reviewed the proofread versions of the manuscript. Conceptualization: L.R., A.L.R., S.G.R. and N.L.V.; Methodology: A.L.R., S.G.R., P.O., G.R., S.A. and N.L.V.; Validation: P.O., G.R., S.A. and N.L.V.; Investigation: L.R., S.G.R., M.S.C., D.D., A.G., S.F., C.F., M.A., C.G.R. and N.L.V.; Resources: S.G.R. and P.O.; Data curation: L.R., A.L.R., S.G.R. and N.L.V.; Writing—Original Draft: L.R., S.G.R. and N.L.V.; Writing—Review and Editing: A.L.R.; Visualization: L.R. and A.L.R.; Supervision: G.R., S.A. and N.L.V.; Project Administration: L.R. and N.L.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The Milano Area A Ethics Committee has confirmed that no ethical approval is required for retrospective observational studies without drug intervention. This study was performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments.
Informed Consent Statement
All patients involved in this retrospective study gave their informed consent for the publication of data regarding the study itself only.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request to the corresponding author for ethical reasons.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all of the members of the RSS di Epidemiologia e Controllo Infezioni Ospedaliere of Luigi Sacco Hospital who contributed to this epidemiological investigation, as well as Ilaria Pedroli and all of the nurses and physicians of the Oncology Unit for their collaboration.
Conflicts of Interest
La Verde reports receiving a grant as consulting or advisory role for Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, MSD and Astrazeneca; speaker bureau from GSK, Pfizer, Roche, Gentili, Lilly; travel expenses from Pfizer and Roche; and research funding from EISAI. Dalu reports receiving grants from Gentili and travel expenses from Roche, Gentili, and Eisai. Rizzardini received fees as speaker, teacher, and advisory board member for AbbVie, Gilead, MSD, Viiv, GSK, Angelini, and Janssen. The other authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
References
- Ryan, M.P.; Adley, C.C. Ralstonia spp.: Emerging global opportunistic pathogens. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 33, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eucast: Clinical Breakpoints and Dosing of Antibiotics. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/clinical_breakpoints (accessed on 26 November 2022).
- Ramani, V.K.; Ganesha Dv Sarathy, V.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Ganeshan, S.; Naik, R. Outbreak of Ralstonia mannitolilytica Infection at a Tertiary Care Oncology Center in South India: A Case Series. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Biol. 2021, 6, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosocomial Ralstonia pickettii Colonization Associated with Intrinsically Contaminated Saline Solution—Los Angeles, California, 1998. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/00052013.htm (accessed on 26 November 2022).
- Gröbner, S.; Heeg, P.; Autenrieth, I.B.; Schulte, B. Monoclonal outbreak of catheter-related bacteraemia by Ralstonia mannitolilytica on two haemato-oncology wards. J. Infect. 2007, 55, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marroni, M.; Pasticci, M.B.; Pantosti, A.; Colozza, M.A.; Stagni, G.; Tonato, M. Outbreak of Infusion-Related Septicemia by Ralstonia pickettii in the Oncology Department. Tumori 2003, 89, 575–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucarelli, C.; Di Domenico, E.G.; Toma, L.; Bracco, D.; Prignano, G.; Fortunati, M.; Pelagalli, L.; Ensoli, F.; Pezzotti, P.; García-Fernández, A.; et al. Ralstonia mannitolilytica infections in an oncologic day ward: Description of a cluster among high-risk patients. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2017, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikulska, M.; Durando, P.; Pia Molinari, M.; Alberti, M.; Del Bono, V.; Dominietto, A.; Raiola, A.M.; van Lint, M.T.; Bregante, S.; Orengo, G.; et al. Outbreak of Ralstonia pickettii bacteraemia in patients with haematological malignancies and haematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. J. Hosp. Infect. 2009, 72, 187–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der beek, D.; Magerman, K.; Bries, G.; Mewis, A.; Declercq, P.E.; Peeters, V.; Rummens, J.L.; Raymaekers, M.; Cartuyvels, R. Infection with Ralstonia insidiosa in two patients. Clin. Microbiol. Newsl. 2005, 27, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Feng, Y.; Feng, P.; Wang, X.; Zong, Z. Nosocomial bloodstream infection and the emerging carbapenem-resistant pathogen Ralstonia insidiosa. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akduman Alaşehir, E.; Öngen İpek, B.; Thomas, D.T.; Sitar, M.E.; Erener Ercan, T. Ralstonia insidiosa neonatal sepsis: A case report and review of the literature. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2020, 15, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranas, D.R.; Demot, B.A.; Cajulao, T.P.T. Outbreak of Ralstonia bacteraemia among chronic kidney disease patients in a haemodialysis unit in the Philippines. West. Pac. Surveill. Response J. 2022, 13, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tüzemen, N.Ü.; Önal, U.; Kazak, E.; Tezgeç, N.; Eren, H.; Şimşek, H.; Bakkaloğlu, Z.; Ünaldı, Ö.; Çelebi, S.; Yılmaz, E.; et al. An outbreak of Ralstonia insidiosa bloodstream infections caused by contaminated heparinized syringes. J. Infect. Chemother. 2022, 28, 1387–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrie, T.J.; Costerton, J.W. Prolonged Survival of Serratia Marcescens in Chlorhexidine. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1981, 42, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, S.E.; Walczak, M.A.; Hameed, R.; Coonan, P. Chlorhexidine Resistance in Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria Isolated from the Surfaces of Dispensers of Soap Containing Chlorhexidine. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2002, 23, 692–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellmann, A.; Cloud, J.; Maier, T.; Keckevoet, U.; Ramminger, I.; Iwen, P.; Dunn, J.; Hall, G.; Wilson, D.; LaSala, P.; et al. Evaluation of matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time-of-flight mass spectrometry in comparison to 16S rRNA gene sequencing for species identification of nonfermenting bacteria. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 1946–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degand, N.; Carbonnelle, E.; Dauphin, B.; Beretti, J.L.; Le Bourgeois, M.; Sermet-Gaudelus, I.; Segonds, C.; Berche, P.; Nassif, X.; Ferroni, A.; et al. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry for identification of nonfermenting gram-negative bacilli isolated from cystic fibrosis patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 3361–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurjadi, D.; Boutin, S.; Schmidt, K.; Ahmels, M.; Hasche, D. Identification and elimination of the clinically relevant multi-resistant environmental bacteria Ralstonia insidiosa in Primary Cell Culture. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mennim, P.; Coyle, C.F.; Taylor, J.D. Venous air embolism associated with removal of central venous catheter. BMJ 1992, 305, 171–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinson, D.R.; Ballard, D.W.; Hance, L.G.; Hung, Y.; Rauchwerger, A.S.; Reed, M.E.; Kene, M.V.; Chettipally, U.K.; Elms, A.R.; Mark, D.G.; et al. Bleeding complications of central venous catheterization in septic patients with abnormal hemostasis. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2014, 32, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).