Alkalinema pantanalense and Roholtiella edaphica (Cyanobacteria): Two New Species Records for Egypt
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
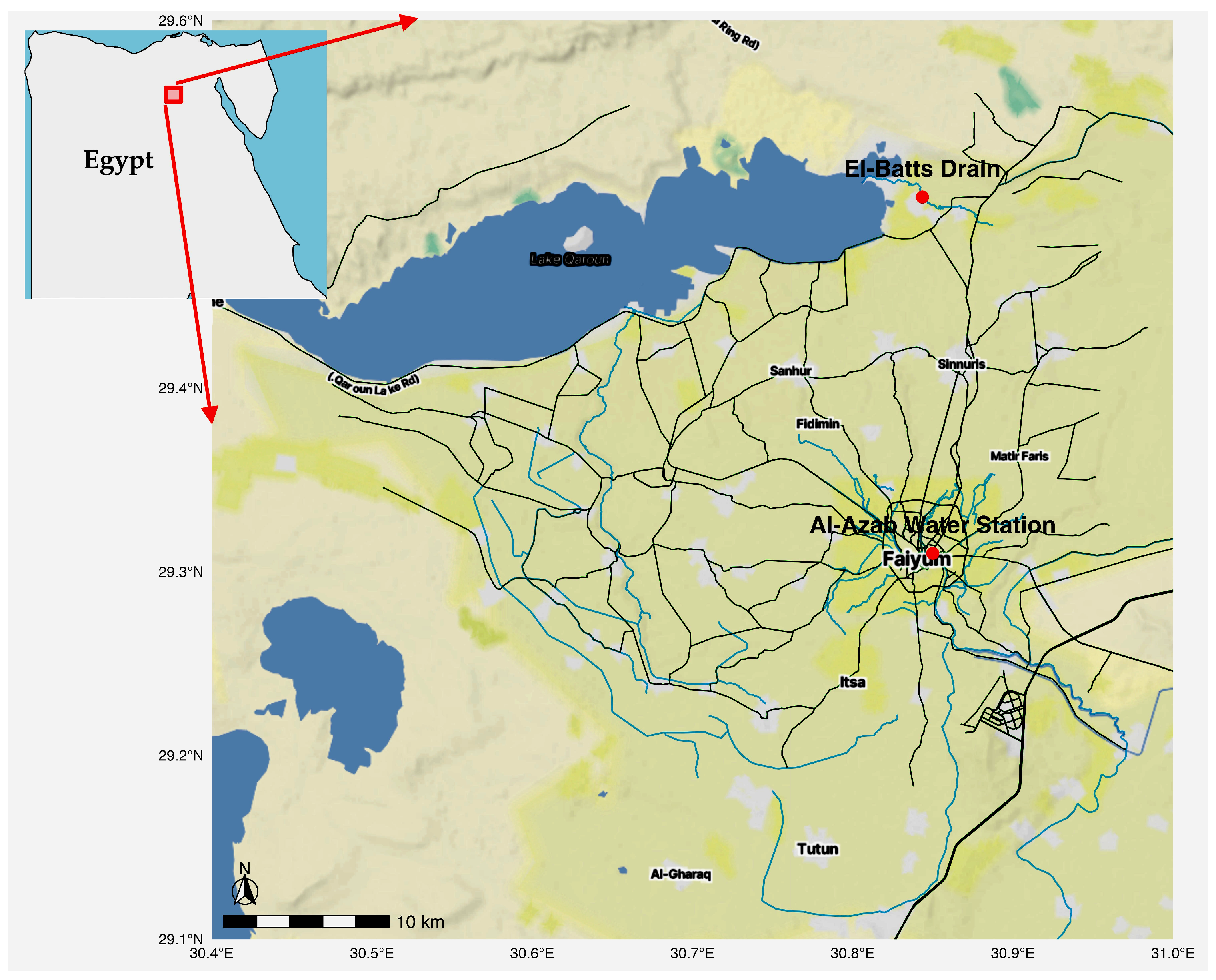
2.1. Sampling and Isolation of Cyanobacterial Strains
2.2. Hydrochemical Analyses
2.3. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, Sequencing, and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.4. Morphological Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Hydrochemical Characterization
3.2. Taxonomic Descriptions
3.2.1. Alkalinema Pantanalense Vieira Vaz et al. [13] (Figure 3a–h)

3.2.2. Roholtiella edaphica Bohunická & Lukesová [14] (Figure 4a–s)

3.3. Phylogenetic Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saber, A.A.; El-Refaey, A.A.; Saber, H.; Singh, P.; van Vuuren, S.J.; Cantonati, M. Cyanoprokaryotes and algae: Classification and habitats. In Handbook of Algal Biofuels: Aspects of Cultivation, Conversion and Biorefinery; El-Sheekh, M., Abomohra, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 2022; pp. 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Komárek, J.; Anagnostidis, K. Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa. Cyanoprokaryota. Oscillatoriales; Elsevier Spektrum Akademischer Verlag: München, Germany, 2005; Volume 19, p. 759. [Google Scholar]
- Komárek, J.; Kaštovský, J.; Ventura, S.; Turicchia, S.Š. The cyanobacterial genus Phormidesmis. Algol. Stud. 2009, 129, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitton, B.A. Cyanobacteria (Cyanophyta). In The Freshwater Algal Flora of the British Isles: An Identification Guide to Freshwater and Terrestrial Algae, 2nd ed.; John, D.M., Whitton, B.A., Brook, A.J., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011; pp. 31–158. [Google Scholar]
- Andreote, A.P.D.; Vieira Vaz, M.G.; Genuário, D.B.; Barbiero, L.; Rezende-Filho, A.T.; Fiore, M.F. Nonheterocytous cyanobacteria from Brazilian saline-alkaline lakes. J. Phycol. 2014, 50, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komárek, J. A polyphasic approach for the taxonomy of cyanobacteria: Principles and applications. Eur. J. Phycol. 2016, 51, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komárek, J. Taxonomic review of cyanobacteria 2021/2022 according to polyphasic evaluation. Fottea 2023, 23, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaštovský, J. Welcome to the jungle!: An overview of modern taxonomy of cyanobacteria. Hydrobiologia 2024, 851, 1063–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, J.R.; Kovacik, L.; Casamatta, D.A.; Fučíková, K.; Kaštovský, J. Utility of 16S-23S ITS sequence and secondary structure for recognition of intrageneric and intergeneric limits within cyanobacterial taxa: Leptolyngbya corticola sp. nov. (Pseudanabaenaceae, Cyanobacteria). Nova Hedwig. 2011, 92, 283–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strunecký, O.; Ivanova, A.P.; Mareš, J. An updated classification of cyanobacterial orders and families based on phylogenomic and polyphasic analysis. J. Phycol. 2023, 59, 12–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrada, N.A.; McGovern, C.A.; Thomas, A.L.; Hurley, A.C.; Mooney, M.R.; Casamatta, D.A. The CIMS (Cyanobacterial ITS motif slicer) for molecular systematics. Fottea 2024, 24, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginn, B.L.; Lau, C.Y.; Asma, N.A.; Serri, N.A.; Broady, P.; Convey, P.; Muangmai, N.; Merican, F. Desmonostoc cockrellii sp. nov. (Nostocales, Cyanobacteria): A new record of a subaerophytic species from the Habitat Penang Hill, Malaysia. Fottea 2025, 25, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira Vaz, M.G.; Genuário, D.B.; Andreote, A.P.; Malone, C.F.; Sant’Anna, C.L.; Barbiero, L.; Fiore, M.F. Pantanalinema gen. nov. and Alkalinema gen. nov.: Novel pseudanabaenacean genera (Cyanobacteria) isolated from saline-alkaline lakes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 298–308. [Google Scholar]
- Bohunická, M.; Pietrasiak, N.; Johansen, J.R.; Gómez, E.B.; Hauer, T.; Gaysina, L.A.; Lukesova, A. Roholtiella, gen. nov. (Nostocales, Cyanobacteria)—A tapering and branching cyanobacteria of the family Nostocaceae. Phytotaxa 2015, 197, 84–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiry, M.D.; Guiry, G.M.; AlgaeBase. World-Wide Electronic Publication;National University of Ireland, Galway. 2025. Available online: http://www.algaebase.org (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Abdullin, S.R.; Nikulin, V.Y.; Nikulin, A.Y.; Manyakhin, A.Y.; Bagmet, V.B.; Suprun, A.R.; Gontcharov, A.A. Roholtiella mixta sp. nov. (Nostocales, Cyanobacteria): Morphology, molecular phylogeny, and carotenoid content. Phycologia 2021, 60, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaysina, L.A.; Johansen, J.R.; Saraf, A.; Allaguvatova, R.Z.; Pal, S.; Singh, P. Roholtiella volcanica sp. nov., a new species of cyanobacteria from Kamchatkan Volcanic Soils. Diversity 2022, 14, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaaban, A.S. Freshwater Algae of Egypt. In Biological Diversity of Egypt; Egyptian Environmental Affairs Agency: Cairo, Egypt, 1994; p. 150. [Google Scholar]
- Hamed, A.F. Survey of distribution and diversity of blue-green algae (Cyanobacteria) in Egypt. Acta Bot. Hung. 2005, 47, 117–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, A.F. Biodiversity and distribution of blue-green algae/cyanobacteria and diatoms in some of the Egyptian water habitats in relation to conductivity. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2008, 2, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Saber, A.A.; Cantonati, M.; Mareš, J.; Anesi, A.; Guella, G. Polyphasic characterization of Westiellopsis prolifica (Cyanobacteria) from the El-Farafra Oasis (Western Desert, Egypt). Phycologia 2017, 56, 697–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saber, A.A.; El-Sheekh, M.; Nikulin, A.Y.; Cantonati, M.; Saber, H. Taxonomic and ecological observations on some algal and cyanobacterial morphospecies new for or rarely recorded in either Egypt or Africa. Egypt. J. Bot. 2021, 61, 283–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentschke, G.S.; Ciancas Jiménez, J.C.; Hoepfner, C.; Guzmán, D.; Mesquita, M.J.; Vasconcelos, V. The extremophile Eurychoronema bolivianum gen. et sp. nov. (Nodosilineales, Cyanobacteria) and Leptolyngbya aquatica comb. nov. Phycologia 2024, 63, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasem, W.M.; El-Gamal, A.D.; Mahfouz, A.Y.; Saber, A.A.; Salah El Din, R.A. Desikacharya aegyptiaca sp. nov. (Nostocaceae, Cyanobacteria) PQ309038, a novel species isolated from Egyptian soil. Egypt. J. Bot. 2025, 65, 509–517. [Google Scholar]
- Mehda, S.; Muñoz-Martín, M.Á.; Oustani, M.; Hamdi-Aïssa, B.; Perona, E.; Mateo, P. Microenvironmental conditions drive the differential cyanobacterial community composition of biocrusts from the Sahara Desert. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehda, S.; Muñoz-Martín, M.A.; Oustani, M.; Hamdi-Aïssa, B.; Perona, E.; Mateo, P. Lithic cyanobacterial communities in the polyextreme Sahara Desert: Implications for the search for the limits of life. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 24, 451–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyneva-Gartner, M.P.; Gartner, G.; Uzunov, B.; Descy, J.-P.; Okello, W. Cyanocystopsis kitagatae gen. et sp. nov. (Cyanoprokaryota/Cyanobacteria) from the tropical lake Kitagata (Uganda, Africa). Wulfenia 2021, 28, 51–65. [Google Scholar]
- Komárek, J. Areas of distribution in Cyanobacteria; specificity of the cyanoprokaryotic microflora in the Mediterranean region. Bocconea 2003, 16, 341–354. [Google Scholar]
- Nichols, H.W. MBL medium-CSIRO modification adapted for freshwater algae. In Handbook of Phycological Methods; Guillard, R.R.L., Stein, J.R., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Rippka, R.; Deruelles, J.; Waterbury, J.B.; Herdman, M.; Stanier, R.Y. Generic assignments, strain histories and properties of pure cultures of cyanobacteria. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1979, 111, 1–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, H.D.; Pratt, P.F. Methods of Analysis for Soil, Plants and Water; Division of Agricultural Sciences, University of California: Oakland, CA, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Bremner, J.M.; Shaw, K. Determination of ammonia and nitrate in soil. J. Agric. Sci. 1955, 46, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, H.; Folkard, A.R. The determination of nitrites: A comparison of existing techniques. Analyst 1951, 76, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullin, J.B.; Riley, J.P. The spectrophotometric determination of nitrate in natural waters, with particular reference to sea-water. Anal. Chim. Acta. 1955, 12, 464–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krausse, G.L.; Schelske, C.L.; Davis, C.O. Comparison of three wet-alkaline methods of digestion of biogenic silica in water. Freshw. Biol. 1983, 13, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casamatta, D.A.; Johansen, J.R.; Vis, M.L.; Broadwater, S.T. Molecular and morphological characterization of ten polar and near-polar strains within the Oscillatoriales (Cyanobacteria). J. Phycol. 2005, 41, 421–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony Methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dela Cerna, V.A.M.V.; Geraldino, P.J.L. First record of Alkalinema sp. (Cyanobacteria) thermophilic strains in Negros Oriental, Philippines. Philipp. J. Sci. 2024, 153, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genuário, D.B.; Vieira Vaz, M.G.M.; de Melo, I.S. Phylogenetic insights into the diversity of homocytous cyanobacteria from Amazonian rivers. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2017, 116, 120–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.Y.; Teng, W.K.; Zhao, L.; Han, B.P.; Song, L.R.; Shu, W.S. Comparative genomics reveals insights into cyanobacterial evolution and habitat adaptation. ISME J. 2021, 15, 211–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.F.; Bowange, R.W.T.M.R.; Kumara, K.L.W.; Magana-Arachchi, D.N.; Ratnayake, R.R. First record of cyanobacteria species: Cephalothrix komarekiana, from Tropical Asia. Environ. Eng. Res. 2021, 26, 200040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, O.M. Newly recorded genera and species, Pantanalinema rosaneae and Alkalinema pantanalense (Leptolyngbyaceae, Cyanobacteria) isolated in Korea. J. Species Res. 2022, 11, 10–21. [Google Scholar]
- Segawa, T.; Yonezawa, T.; Edwards, A.; Akiyoshi, A.; Tanaka, S.; Uetake, J.; Irvine-Fynn, T.; Fukui, K.; Li, Z.; Takeuchi, N. Biogeography of cryoconite forming cyanobacteria on polar and Asian glaciers. J. Biogeogr. 2017, 44, 2849–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaysina, L.A.; Bohunická, M.; Hazuková, V.; Johansen, J.R. Biodiversity of terrestrial cyanobacteria of the South Ural region. Cryptogam. Algol. 2018, 39, 167–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, J.R.; Jusko, B.M.; Mesfin, M.; Lunkis, M.A.; Wain, A.; Hoyer, W.F.; Hasenstab-lehman, K.E. Pseudoacaryochloris (Acaryochloridaceae, Cyanobacteria) species from Africa and North America: A disjunct distribution suggesting transatlantic wind dispersal. West. North Am. Nat. 2025, 85, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, W.A.; Chalmersh, M.O. Airborne dispersal of Antarctic terrestrial algae and cyanobacteria. Ecography 1997, 20, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Després, V.R.; Huffman, J.A.; Burrows, S.M.; Hoose, C.; Safatov, A.S.; Buryak, G.; Fröhlich-Nowoisky, J.; Elbert, W.; Andreae, M.O.; Pöschl, U.; et al. Primary biological aerosol particles in the atmosphere: A review. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2012, 64, 15598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelstaedter, S.; Tegen, I.; Washington, R. North African dust emissions and transport. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2006, 79, 73–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prospero, J.M.; Delany, A.C.; Carlson, T.N. The discovery of African dust transport to the Western Hemisphere and the Saharan air layer: A history. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2021, 102, e1239–e1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahmoud, R.M.; El-Sheekh, M.M.; Adawy, A.A.; Saber, A.A. Alkalinema pantanalense and Roholtiella edaphica (Cyanobacteria): Two New Species Records for Egypt. Phycology 2025, 5, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology5030046
Mahmoud RM, El-Sheekh MM, Adawy AA, Saber AA. Alkalinema pantanalense and Roholtiella edaphica (Cyanobacteria): Two New Species Records for Egypt. Phycology. 2025; 5(3):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology5030046
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahmoud, Rania M., Mostafa M. El-Sheekh, Asmaa A. Adawy, and Abdullah A. Saber. 2025. "Alkalinema pantanalense and Roholtiella edaphica (Cyanobacteria): Two New Species Records for Egypt" Phycology 5, no. 3: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology5030046
APA StyleMahmoud, R. M., El-Sheekh, M. M., Adawy, A. A., & Saber, A. A. (2025). Alkalinema pantanalense and Roholtiella edaphica (Cyanobacteria): Two New Species Records for Egypt. Phycology, 5(3), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology5030046








