Optimising Galdieria sulphuraria ACUF 427 Biomass for Enhanced Urban Wastewater Treatment: Evaluating Pollutant Removal Efficiency, Algal Growth, and Phycocyanin Production
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Allen Medium Preparation
2.2. Cultivation of Stock Solution
2.3. The Urban Wastewater
2.4. Sampling and Data Collection
2.5. Chemical Analysis
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
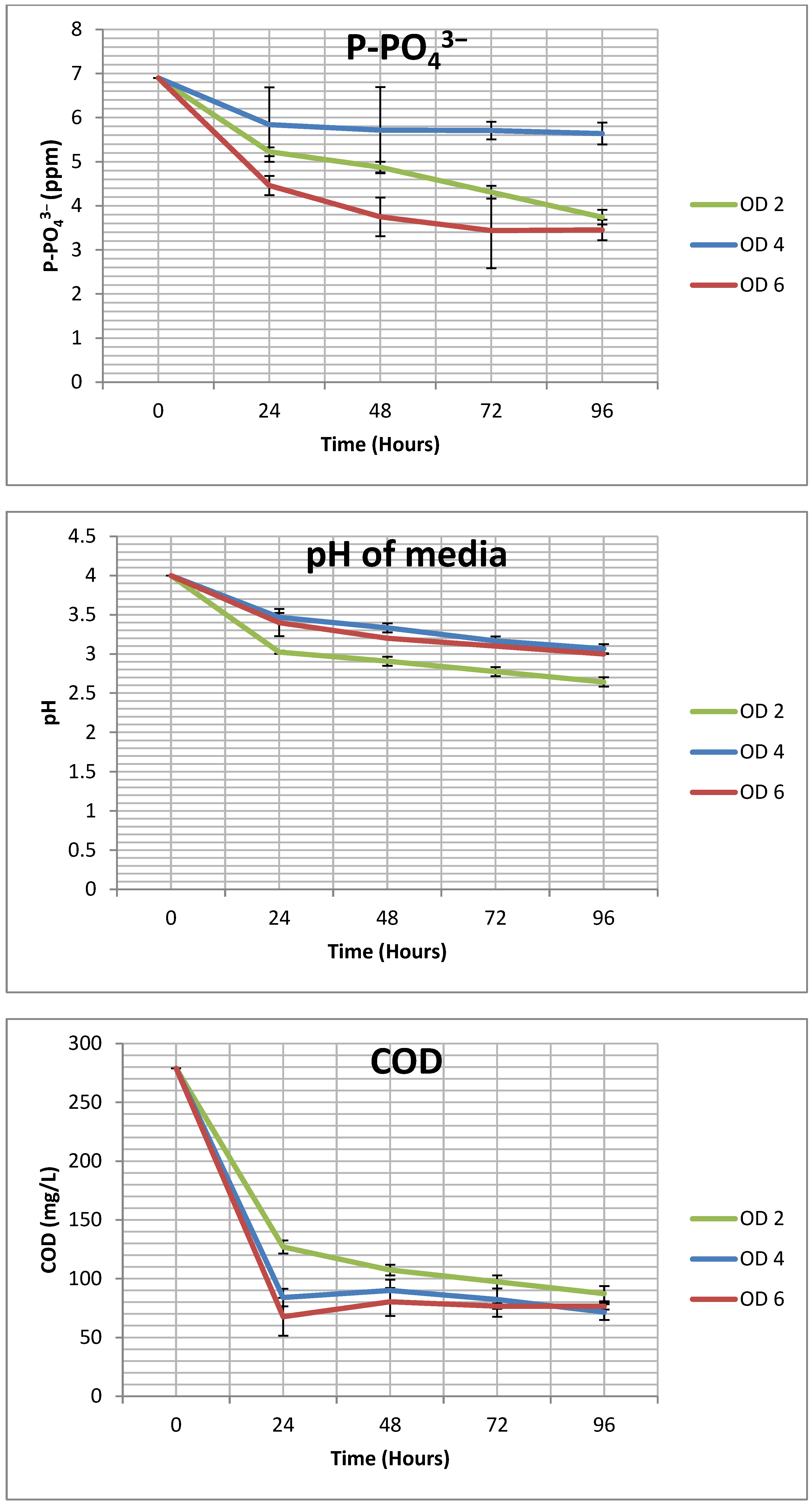
3.1. G. sulphuraria’s Contaminant Removal Rate and Efficiency
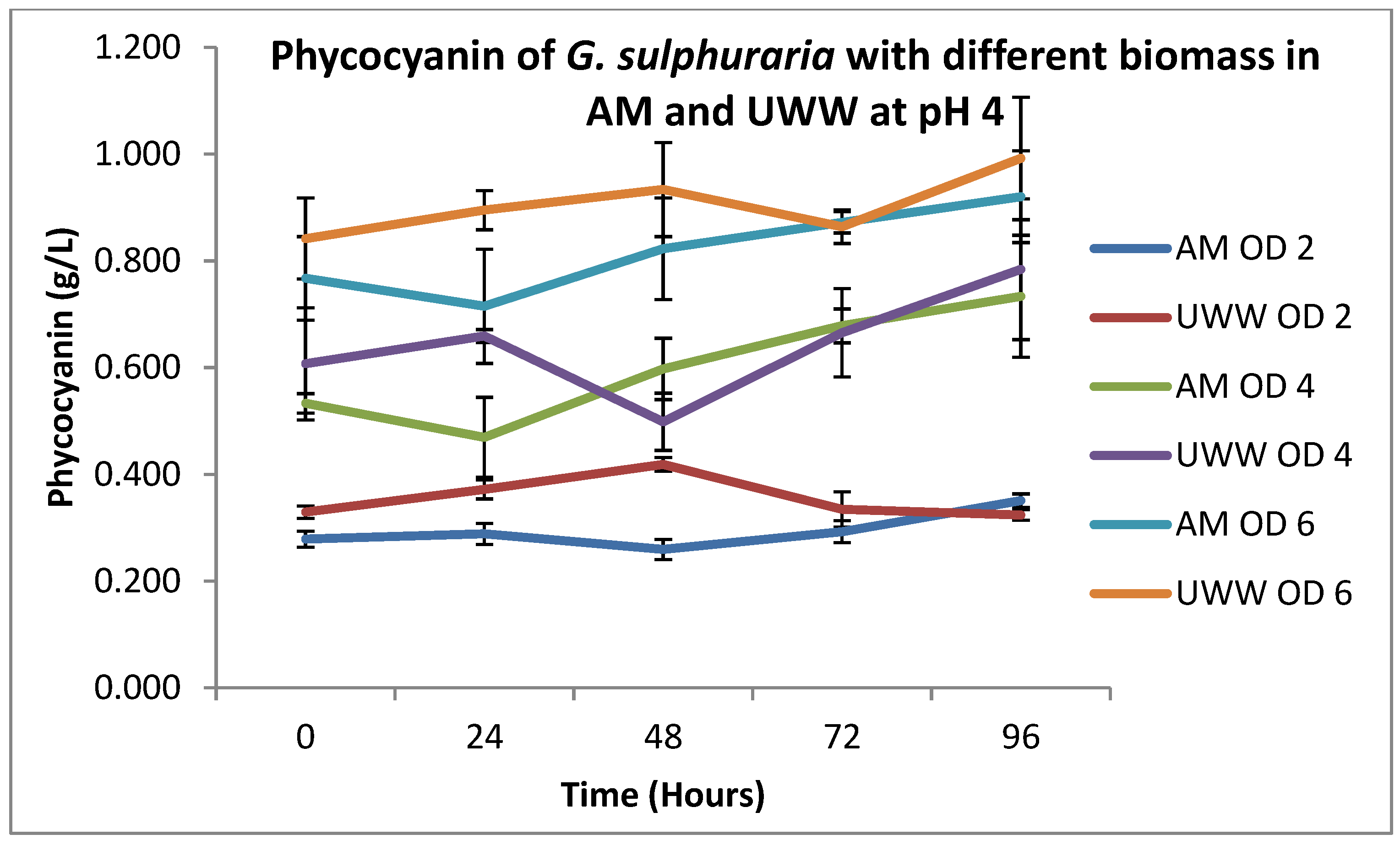
3.2. Growth and Phycocyanin Production:
3.3. The Maximum Growth Rate
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liyanage, C.P.; Yamada, K. Impact of Population Growth on the Water Quality of Natural Water Bodies. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Puijenbroek, P.J.T.M.; Beusen, A.H.W.; Bouwman, A.F. Global nitrogen and phosphorus in urban waste water based on the Shared Socio-economic pathways. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 231, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Sonne, C.; Chen, X.; Yue, X.; Gu, H.; Lam, S.S.; Peng, W. Phytosphere purification of urban domestic wastewater. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 336, 122417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Wu, J.; Coin, L.; O’Brien, J.; Hai, F.; Jiang, G. Molecular Methods for Pathogenic Bacteria Detection and Recent Advances in Wastewater Analysis. Water 2021, 13, 3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Qin, Y.; Han, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zou, Y. Effects of wastewater treatment plant effluent on microbial risks of pathogens and their antibiotic resistance in the receiving river. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 345, 123461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avio, C.G.; Gorbi, S.; Regoli, F. Plastics and microplastics in the oceans: From emerging pollutants to emerged threat. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 128, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamond, J.; Altenburger, R.; Coors, A.; Dyer, S.D.; Focazio, M.; Kidd, K.; Koelmans, A.A.; Leung, K.M.Y.; Servos, M.R.; Snape, J.; et al. Use of prospective and retrospective risk assessment methods that simplify chemical mixtures associated with treated domestic wastewater discharges. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 690–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Cheng, H.; Tao, S. Environmental and human health challenges of industrial livestock and poultry farming in China and their mitigation. Environ. Int. 2017, 107, 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Amin, M.; Kamal, I.; Shahid, A.; Xu, J.; Alam, M.A.; Mehmood, M.A.; Ashraf, G.A.; Boopathy, R. Algae-Mediated Resource Recovery from Urban Wastewater. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2023, 9, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Y. Circular economy is game-changing municipal wastewater treatment technology towards energy and carbon neutrality. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molazadeh, M.; Ahmadzadeh, H.; Pourianfar, H.R.; Lyon, S.; Rampelotto, P.H. The Use of Microalgae for Coupling Wastewater Treatment With CO2 Biofixation. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Thaher, M.; Abdulquadir, M.; Faisal, M.; Mehariya, S.; Al-Najjar, M.A.A.; Al-Jabri, H.; Das, P. Utilization of Microalgae for Urban Wastewater Treatment and Valorization of Treated Wastewater and Biomass for Biofertilizer Applications. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.I.; Cho, C.H.; Ciniglia, C.; Huang, T.; Liu, S.; Bustamante, D.E.; Calderon, M.S.; Mansilla, A.; McDermott, T.; Andersen, R.A.; et al. Revised classification of the Cyanidiophyceae based on plastid genome data with descriptions of the Cavernulicolales ord. nov. and Galdieriales ord. nov. (Rhodophyta). J. Phycol. 2023, 59, 444–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, H.M. Microbial genomes as cheat sheets. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeb, V.; Bhattacharya, D. The Thermo-Acidophilic Cyanidiophyceae (Cyanidiales). In Red Algae in the Genomic Age; Seckbach, J., Chapman, D.J., Eds.; Cellular Origin, Life in Extreme Habitats and Astrobiology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; Volume 13, pp. 409–426. ISBN 978-90-481-3794-7. Available online: http://link.springer.com/10.1007/978-90-481-3795-4_22 (accessed on 21 July 2023).
- Barcytė, D.; Nedbalová, L.; Culka, A.; Košek, F.; Jehlička, J. Burning coal spoil heaps as a new habitat for the extremophilic red alga Galdieria sulphuraria. Fottea 2018, 18, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vítová, M.; Goecke, F.; Sigler, K.; Řezanka, T. Lipidomic analysis of the extremophilic red alga Galdieria sulphuraria in response to changes in pH. Algal Res. 2016, 13, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiusi, F.; Trompetter, E.; Hoenink, H.; Wijffels, R.H.; Janssen, M. Autotrophic and mixotrophic biomass production of the acidophilic Galdieria sulphuraria ACUF 64. Algal Res. 2021, 60, 102513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchinda, D.; Henkanatte-Gedera, S.M.; Abeysiriwardana-Arachchige, I.S.A.; Delanka-Pedige, H.M.K.; Munasinghe-Arachchige, S.P.; Zhang, Y.; Nirmalakhandan, N. Single-step treatment of primary effluent by Galdieria sulphuraria: Removal of biochemical oxygen demand, nutrients, and pathogens. Algal Res. 2019, 42, 101578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaratnam, T.; Pegallapati, A.K.; Montelya, F.; Rodriguez, G.; Nirmalakhandan, N.; Van Voorhies, W.; Lammers, P.J. Evaluation of a thermo-tolerant acidophilic alga, Galdieria sulphuraria, for nutrient removal from urban wastewaters. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 156, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaratnam, T.; Pegallapati, A.; Montelya, F.; Rodriguez, G.; Nirmalakhandan, N.; Lammers, P.J.; van Voorhies, W. Feasibility of algal systems for sustainable wastewater treatment. Renew. Energy 2015, 82, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henkanatte-Gedera, S.M.; Selvaratnam, T.; Karbakhshravari, M.; Myint, M.; Nirmalakhandan, N.; Van Voorhies, W.; Lammers, P.J. Removal of dissolved organic carbon and nutrients from urban wastewaters by Galdieria sulphuraria: Laboratory to field scale demonstration. Algal Res. 2017, 24, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Microsoft Corporation. Microsoft Excel Professional Plus 2010; Microsoft Corporation: Redmond, WA, USA, 2010; Available online: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/excel (accessed on 15 June 2025).
- Posit Team. RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R; Posit Software, PBC: Boston, MA, USA, 2024; Available online: http://www.posit.co/ (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Sirakov, M.; Palmieri, M.; Iovinella, M.; Davis, S.J.; Petriccione, M.; di Cicco, M.R.; De Stefano, M.; Ciniglia, C. Cyanidiophyceae (Rhodophyta) Tolerance to Precious Metals: Metabolic Response to Palladium and Gold. Plants 2021, 10, 2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, A.; Bogorad, L. Complementary chromatic adaptation in a filamentous blue-green alga. J. Cell Biol. 1973, 58, 419–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doekhi-Bennani, Y.; Leilabady, N.M.; Fu, M.; Rietveld, L.C.; van der Hoek, J.P.; Heijman, S.G.J. Simultaneous removal of ammonium ions and sulfamethoxazole by ozone regenerated high silica zeolites. Water Res. 2021, 188, 116472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Wei, D.; Pohnert, G. The thermoacidophilic red alga Galdieria sulphuraria is a highly efficient cell factory for ammonium recovery from ultrahigh-NH4+ industrial effluent with co-production of high-protein biomass by photo-fermentation. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 438, 135598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeysiriwardana-Arachchige, I.S.A.; Nirmalakhandan, N. Predicting removal kinetics of biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) and nutrients in a pilot scale fed-batch algal wastewater treatment system. Algal Res. 2019, 43, 101643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oesterhelt, C.; Schmälzlin, E.; Schmitt, J.M.; Lokstein, H. Regulation of photosynthesis in the unicellular acidophilic red alga Galdieria sulphuraria†: Regulation of photosynthesis in Galdieria. Plant J. 2007, 51, 500–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Dixon, K.L.; Nawaz, T.; Rahman, A.; Selvaratnam, T. Evaluation of Galdieria sulphuraria for nitrogen removal and biomass production from raw landfill leachate. Algal Res. 2021, 54, 102183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.-K.; Min, K.; Park, W.-K. Use of an extremophile red microalga (Galdieria sulphuraria) to produce phycocyanin from tangerine peel waste. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2023, 22, 101446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- di Cicco, M.R.; Palmieri, M.; Altieri, S.; Ciniglia, C.; Lubritto, C. Cultivation of the Acidophilic Microalgae Galdieria phlegrea with Wastewater: Process Yields. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, G.L.; Langellotti, A.L.; Oliviero, M.; Baselice, M.; Sacchi, R.; Masi, P. Valorization of second cheese whey through cultivation of extremophile microalga Galdieria sulphuraria. AIMS Environ. Sci. 2021, 8, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| UWW Composition | Values (ppm) |
|---|---|
| Ammonium nitrogen (N-NH4+) | 31.93 |
| Nitrogen dioxide (N-NO2) | 0.1 |
| Nitrous oxide (N-N2O) | 0.1 |
| Ammonia nitrogen (N-NH3) | 24.8 |
| Phosphate phosphorus P-PO43− | 7.2 |
| COD (mg/L) | 279 |
| pH | 7.5 |
| Parameters | OD 2 | OD 4 | OD 6 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RR (mg/L/d) | RE (%) | RR (mg/L/d) | RE (%) | RR (mg/L/d) | RE (%) | |
| N-NH4+ | 5.17 ± 0.36 | 62.73 ± 4.35 | 5.8 ± 0.69 | 70.61 ± 8.41 | 7.49 ± 0.19 | 90.74 ± 2.26 |
| N-NH3 | 4.64 ± 0.28 | 66.01 ± 3.96 | 5.14 ± 0.54 | 73.20 ± 7.67 | 6.43 ± 0.14 | 91.55 ± 2.05 |
| P-PO43− | 0.79 ± 0.04 | 45.75 ± 0.59 | 0.32 ± 0.06 | 18.28 ± 3.59 | 0.86 ± 0.06 | 49.97 ± 3.34 |
| COD | 47.92 ± 1.6 | 68.70 ± 2.33 | 51.83 ± 1.66 | 74.31 ± 2.38 | 50.58 ± 0.72 | 72.52 ± 1.03 |
| Parameters (ppm) | Biomass (OD 2) | Biomass (OD 4) | Biomass (OD 6) |
|---|---|---|---|
| N-NH4 | 21.949 ± 7.418 a | 18.582 ± 6.986 b | 12.433 ± 7.903 c |
| N-NH3 | 17.045 ± 5.760 a | 14.679 ± 5.562 b | 9.654 ± 6.137 c |
| P-PO43− | 4.539 ± 0.599 a | 5.726 ± 0.573 b | 3.775 ± 0.610 c |
| pH | 2.837 ± 0.153 a | 3.258 ± 0.168 b | 3.175 ± 0.171 b |
| COD (mg/L) | 104.750 ± 15.882 a | 82 ± 10.954 b | 75.333 ± 9.948 b |
| DW (g/L) | 1.524 ± 0.094 a | 2.421 ± 0.407 b | 3.419 ± 0.292 c |
| PC (mg/mL) | 0.356 ± 0.040 a | 0.643 ± 0.121 b | 0.905 ± 0.085 c |
| Variables | Values | OD 2 | OD 4 | OD 6 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AM | UWW | p-Values | AM | UWW | p-Values | AM | UWW | p-Values | ||
| DW (g/L) | Mean | 1.308 | 1.524 | 5.34 × 10−6 | 2.242 | 2.421 | 0.216 | 3.093 | 3.419 | 0.005 |
| SD | 0.114 | 0.094 | 0.368 | 0.407 | 0.306 | 0.292 | ||||
| PC (g/L) | Mean | 0.294 | 0.356 | 0.0001 | 0.603 | 0.643 | 0.353 | 0.819 | 0.905 | 0.019 |
| SD | 0.035 | 0.040 | 0.114 | 0.121 | 0.103 | 0.085 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Retta, B.; Iovinella, M.; Ciniglia, C. Optimising Galdieria sulphuraria ACUF 427 Biomass for Enhanced Urban Wastewater Treatment: Evaluating Pollutant Removal Efficiency, Algal Growth, and Phycocyanin Production. Phycology 2025, 5, 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology5030040
Retta B, Iovinella M, Ciniglia C. Optimising Galdieria sulphuraria ACUF 427 Biomass for Enhanced Urban Wastewater Treatment: Evaluating Pollutant Removal Efficiency, Algal Growth, and Phycocyanin Production. Phycology. 2025; 5(3):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology5030040
Chicago/Turabian StyleRetta, Berhan, Manuela Iovinella, and Claudia Ciniglia. 2025. "Optimising Galdieria sulphuraria ACUF 427 Biomass for Enhanced Urban Wastewater Treatment: Evaluating Pollutant Removal Efficiency, Algal Growth, and Phycocyanin Production" Phycology 5, no. 3: 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology5030040
APA StyleRetta, B., Iovinella, M., & Ciniglia, C. (2025). Optimising Galdieria sulphuraria ACUF 427 Biomass for Enhanced Urban Wastewater Treatment: Evaluating Pollutant Removal Efficiency, Algal Growth, and Phycocyanin Production. Phycology, 5(3), 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology5030040







