Intervention of Natural Microalgal Bioactives on Type 2 Diabetes: Integrated Scientometric Mapping and Cellular Efficacy Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Instruments and Equipment
2.3. Extraction, Purification, and Physicochemical Properties of EPS-P
2.4. Literature Collection and Analysis
2.5. Cell Experiment
2.5.1. Cell Culture and Establishment of an IR-HepG2 Cell Model
2.5.2. Assessment of Cell Viability Effects of Astaxanthin, β-Carotene, and Porphyridium Polysaccharides on HepG2 Cells Using the CCK-8 Assay
2.5.3. Effects of Astaxanthin, β-Carotene, and Porphyridium Polysaccharides on Glucose Consumption in IR-HepG2 Cells
2.5.4. Effects of Astaxanthin, β-Carotene, and Porphyridium Polysaccharides on Glycogen Content and Pyruvate Kinase (PK) Activity in IR-HepG2 Cells
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Bibliometric Analysis
3.1.1. Annual Trend of Publications
3.1.2. National Distribution and Collaboration Networks
3.1.3. Research Institutions
3.1.4. Authors and Co-Authorship Networks
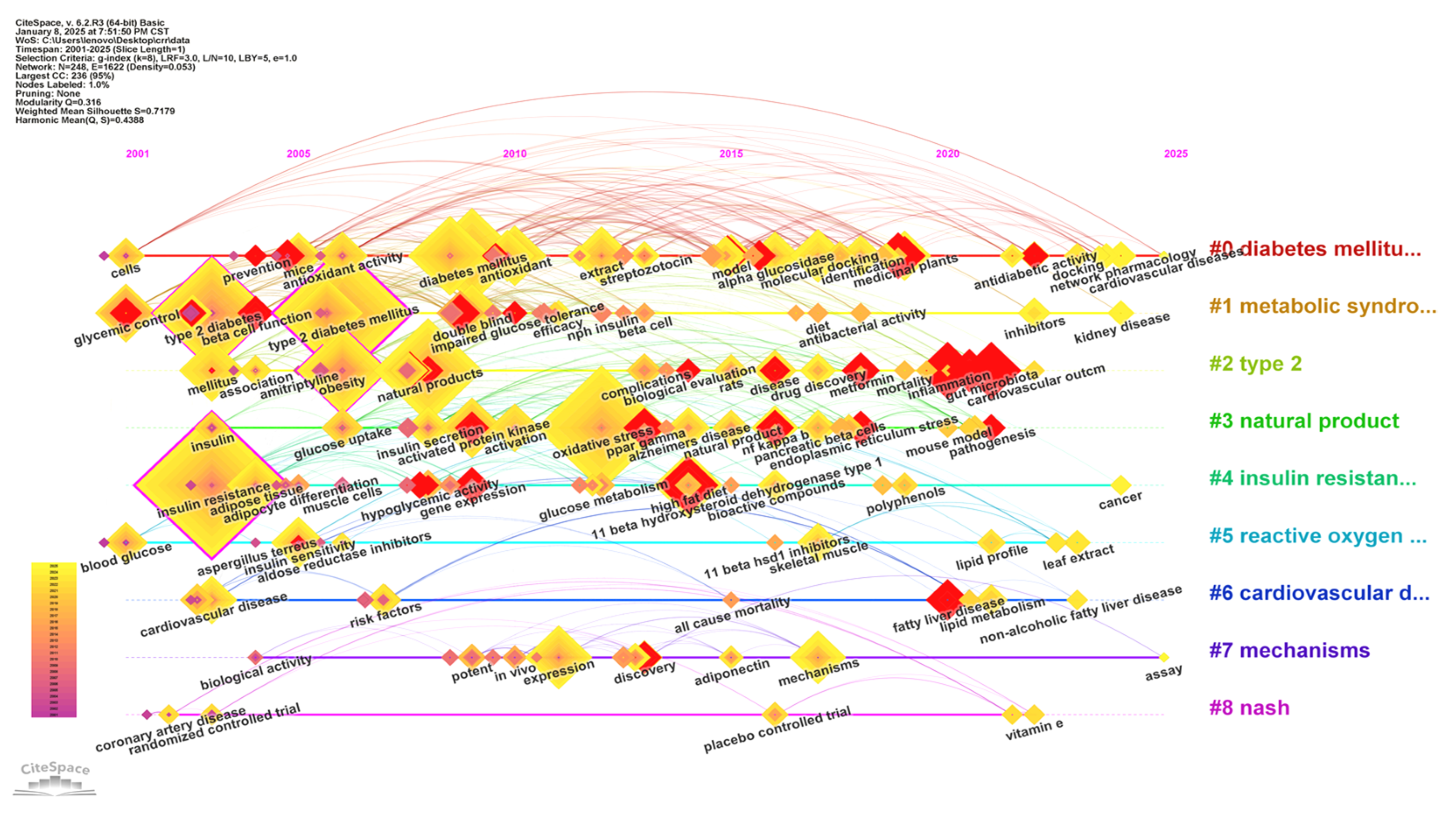
3.1.5. Keyword Co-Occurrence Analysis
3.1.6. Keyword Clustering Analysis
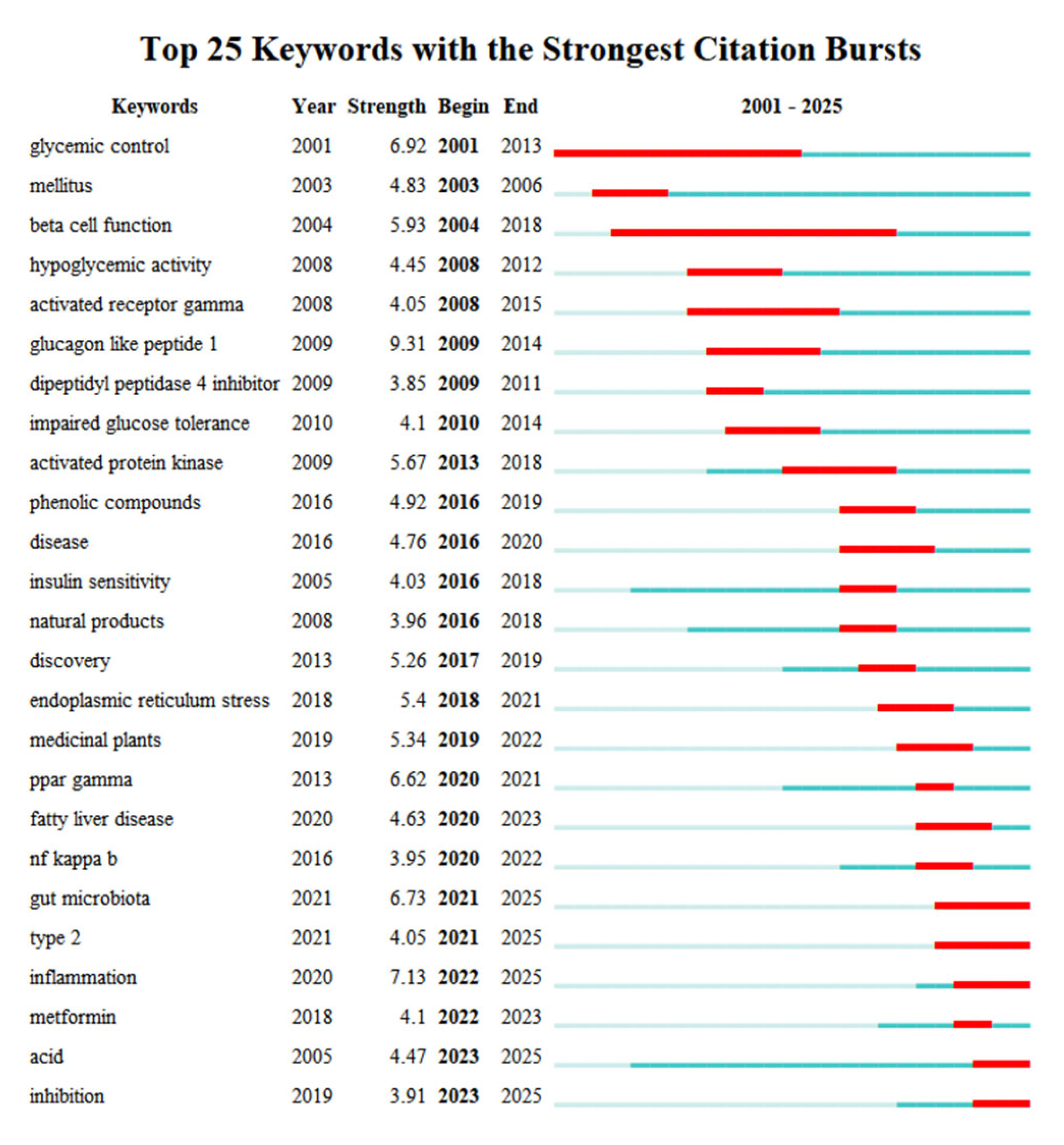
3.1.7. Keyword Burst Analysis
3.1.8. Timeline Visualization of Keyword Co-Occurrence and Burst Analysis
3.2. In Vitro Experiments
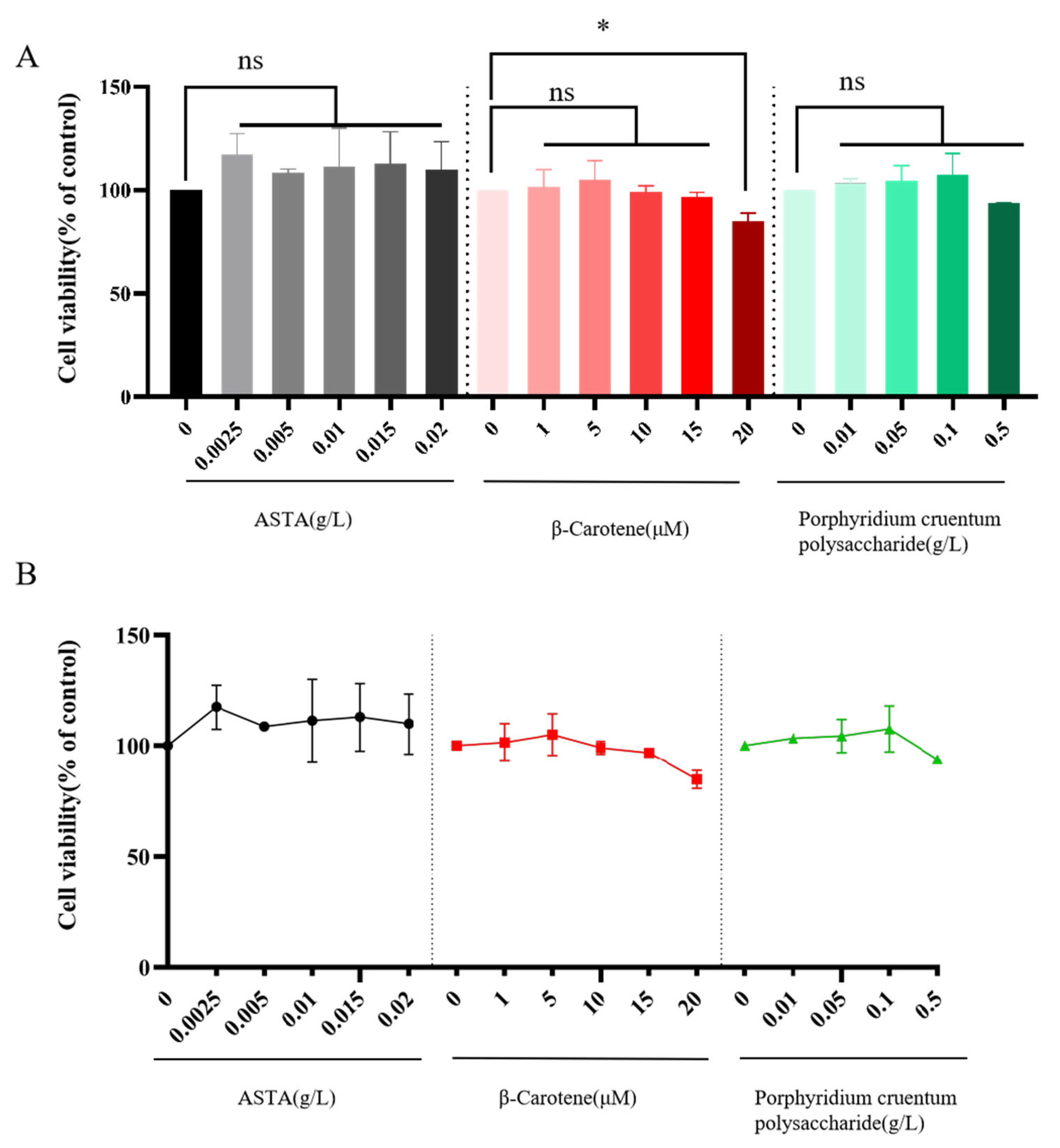
3.2.1. Effects of Three Natural Algal Active Substances on HepG2 Cell Viability
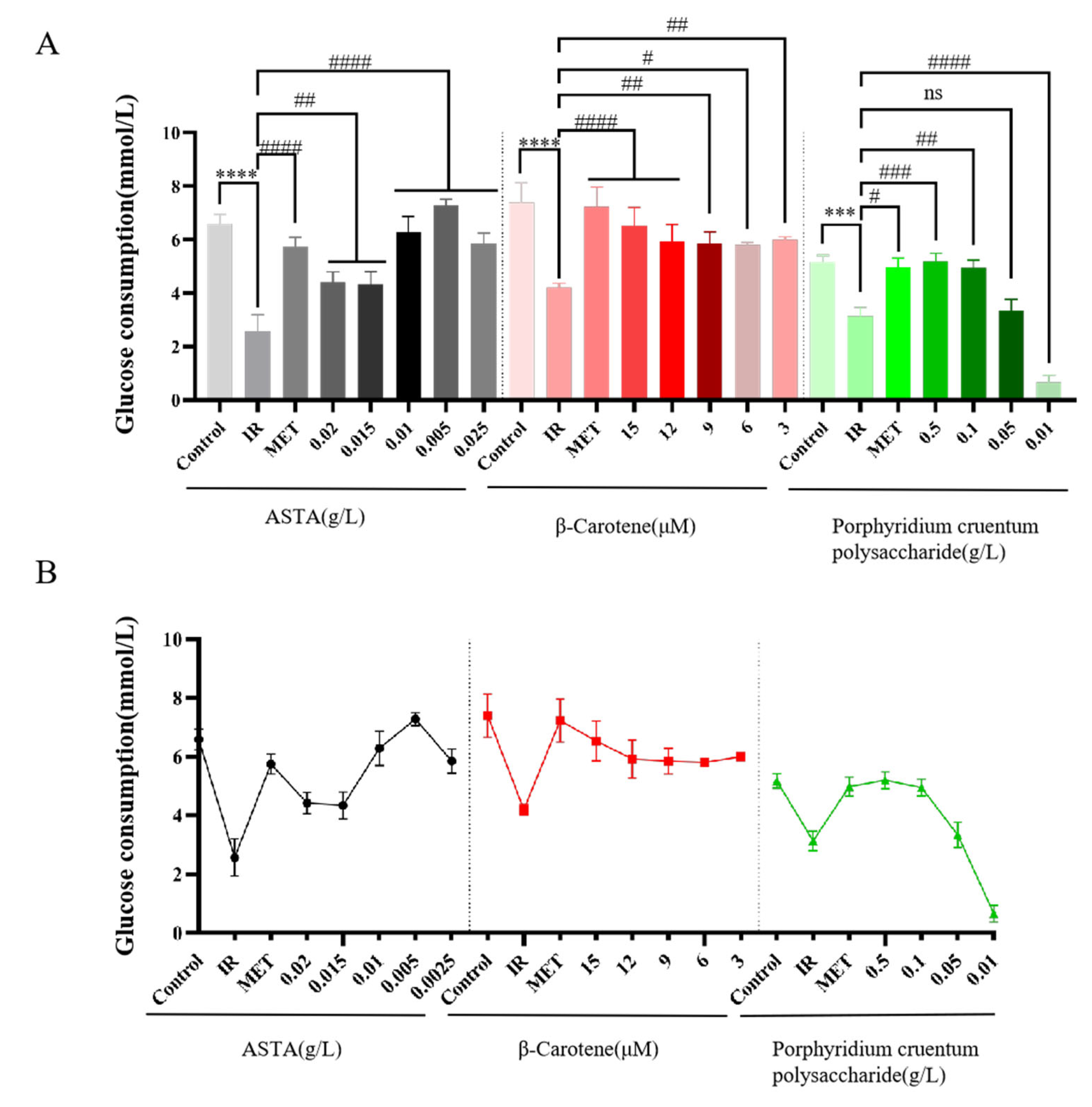
3.2.2. Effects of Three Natural Algal Active Substances on Glucose Consumption in IR-HepG2 Cells
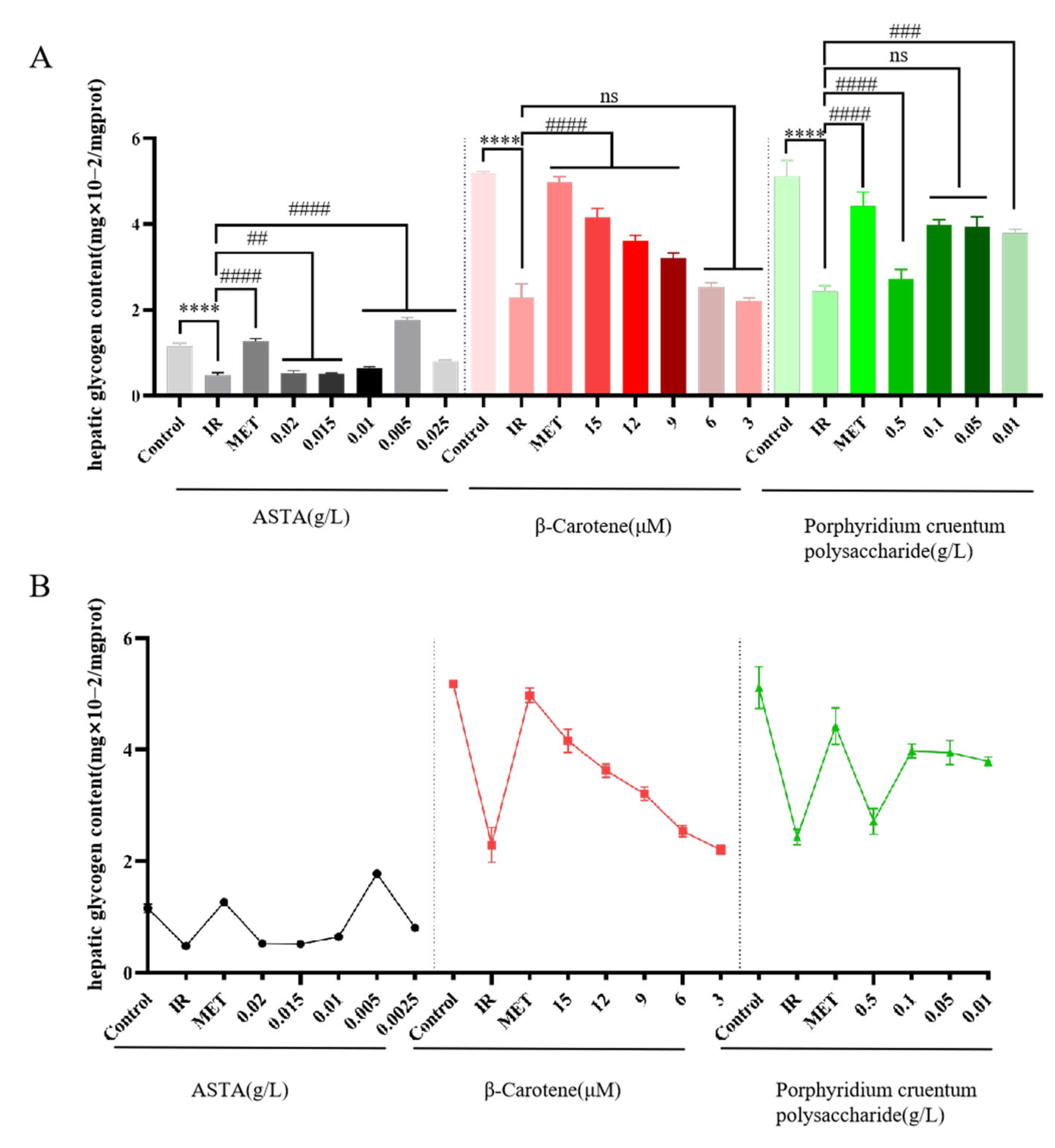
3.2.3. Effects of Three Natural Algal Active Substances on Glycogen Content in IR-HepG2 Cells
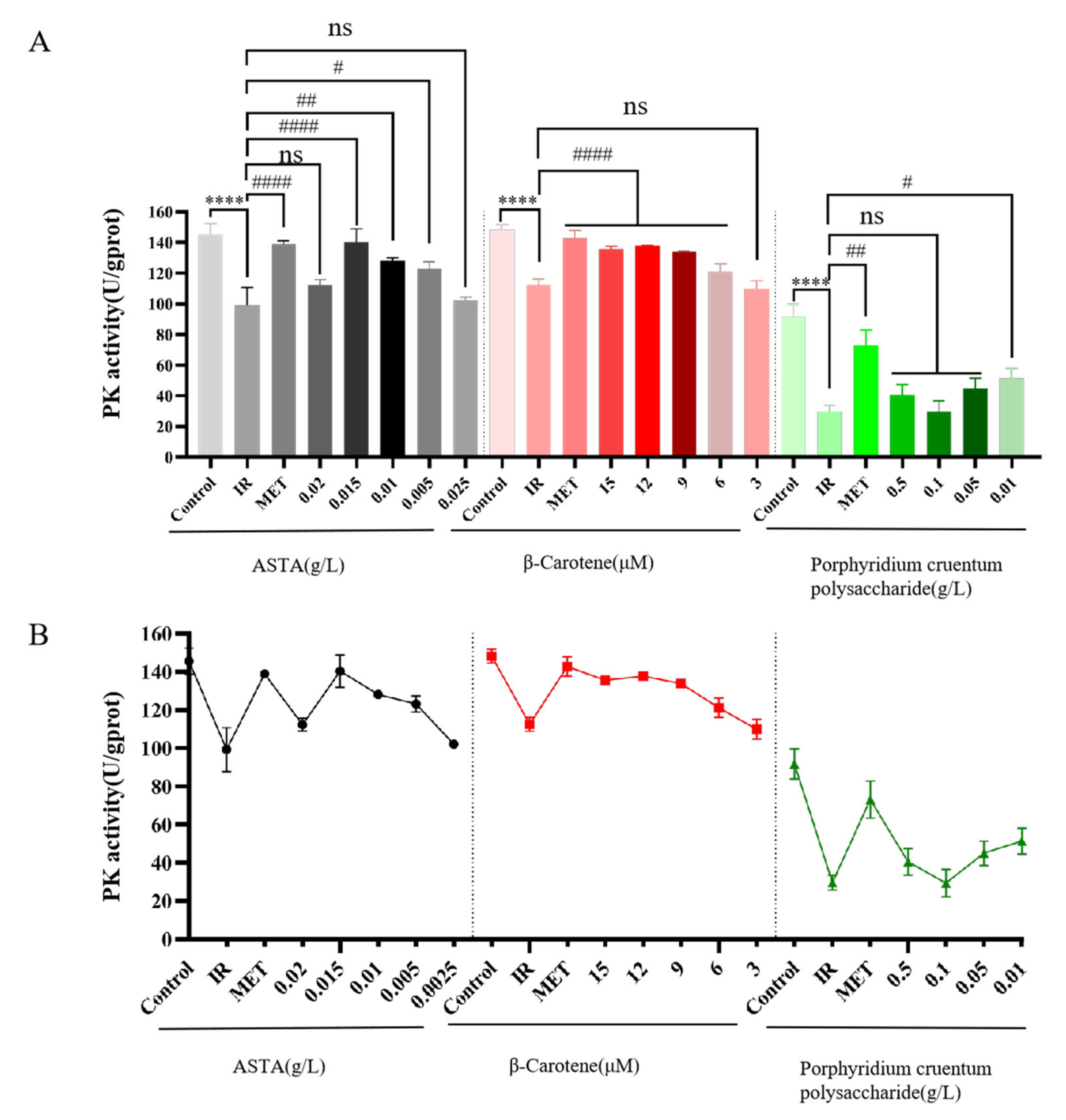
3.2.4. Effects of Three Natural Algal Active Substances on Pyruvate Kinase Activity in IR-HepG2 Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, S.; Zhu, Y.; Schultz, R.D.; Li, N.; He, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Caron, A.; Zhu, Q.; Sun, K.; Xiong, W.; et al. Partial Leptin Reduction as an Insulin Sensitization and Weight Loss Strategy. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 706–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landon, R.; Gueguen, V.; Petite, H.; Letourneur, D.; Pavon-Djavid, G.; Anagnostou, F. Impact of astaxanthin on diabetes pathogenesis and chronic complications. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsholme, P.; Cruzat, V.F.; Keane, K.N.; Carlessi, R.; de Bittencourt, P.I.H. Molecular mechanisms of ROS production and oxidative stress in diabetes. Biochem. J. 2016, 473, 4527–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, K.; Akash, M.S.H. Mechanism of Generation of Oxidative Stress and Pathophysiology of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: How Are They Interlinked? Oxidative Stress and diabetes mellitus. Cell Biochem. 2017, 118, 3577–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.Y.; Che, J.Y.; Yarla, N.S.; Wu, H.Y.; Lu, T.R.; Xu, B.; Zhu, H. Type 2 diabetes treatment and drug development study. Open Diabetes J. 2018, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladkova, T.; Georgieva, N.; Staneva, A.; Gospodinova, D. Recent progress in antioxidant active substances from marine biota. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambati, R.R.; Moi, P.S.; Ravi, S.; Aswathanarayana, R.G. Astaxanthin: Sources, extraction, stability, biological activities and its commercial applications—A review. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 128–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routray, W.; Dave, D.; Cheema, S.K.; Ramakrishnan, V.V.; Pohling, J. Biorefinery approach and environment-friendly extraction for sustainable production of astaxanthin from marine wastes. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2019, 39, 469–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashhadi, N.S.; Zakerkish, M.; Mohammadiasl, J.; Zarei, M.; Mohammadshahi, M.; Haghighizadeh, M.H. Astaxanthin improves glucose metabolism and reduces blood pressure in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 27, 341–346. [Google Scholar]
- Arunkumar, E.; Bhuvaneswari, S.; Anuradha, C.V. An intervention study in obese mice with astaxanthin, a marine carotenoid—Effects on insulin signaling and pro-inflammatory cytokines. Food Funct. 2012, 3, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, I.; Adin, S.N.; Panda, B.P.; Mujeeb, M. β-Carotene—Production methods, biosynthesis from Phaffia rhodozyma, factors affecting its production during fermentation, pharmacological properties: A review. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2022, 69, 2517–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounien, L.; Tourniaire, F.; Landrier, J.F. Anti-obesity effect of carotenoid: Direct impact on adipose tissue and adipose tissue-driven indirect effects. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Concepcion, M.; Avalos, J.; Bonet, M.L. A global perspective on carotenoids: Metabolism, biotechnology, and benefits for nutrition and health. Progress. Lipid Res. 2018, 70, 62–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, C.R.; Yen, G.M. Functional properties of carotenoids in human health. Int. J. Food Prop. 2007, 10, 201–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, A.C.; Amaro, H.M.; Malcata, F.X. Microalgae as sources of carotenoids. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 625–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohn, T. Determinants and determination of carotenoid bioavailability from infant food formulas and adult nutritionals including liquid dairy products. J. AOAC Int. 2019, 102, 1044–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Hong, P.; Zheng, X. β-carotene attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation via inhibition of the nf-κb, jak2/stat3 and jnk/p38 mapk signaling pathways in macrophages. Anim. Sci. J. 2018, 90, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Xie, Y.; Wu, Z.; Li, Y.; Jiang, M.; Yu, H. β-carotene protects mice against lipopolysaccharide and d-galactosamine induced acute liver injury via regulation of nf-κb, mapk, and nrf2 signaling. J. Oleo Sci. 2023, 72, 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, L.; Xiang-Dong, W.; Bronson, R.T.; Smith, D.E.; Krinsky, N.I.; Russell, R.M. Effects of physiological versus pharmacological β-carotene supplementation on cell proliferation and histopathological changes in the lungs of cigarette smoke-exposed ferrets. Carcinogenesis 2000, 21, 2245–2253. [Google Scholar]
- Beydoun, M.A.; Chen, X.; Jha, K.; Beydoun, H.A.; Zonderman, A.B.; Canas, J.A. Carotenoids, vitamin A, and their association with the metabolic syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Rev. 2019, 77, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.K.; Laroche, C.; Marcati, A.; Ursu, A.V.; Jubeau, S.; Marchal, L.; Michaud, P. Separation and fractionation of exopolysaccharides from Porphyridium cruentum. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 145, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvir, I.; Chayoth, R.; Sod-Moriah, U. Soluble polysaccharide and biomass of red microalga Porphyridium sp. alter intestinal morphology and reduce serum cholesterol in rats. Br. J. Nutr. 2000, 84, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setyaningsih, I.; Prasetyo, H.; Agungpriyono, D.R.; Tarman, K. Antihyperglycemic activity of Porphyridium cruentum biomass and extra-cellular polysaccharide in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 156, 1381–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, N.; Li, K.; Zhang, Z. The preservation effect of purple algae polysaccharide coating treatment on Nanhu Ling. Food Fer Ind. 2024, 50, 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, N. Isolation, Purification, and Application Research of Extracellular Polysaccharides from Porphyridium. Master’s Thesis, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L. Preparation and Biological Activity Study of Purple Algae Polysaccharides. Ph.D. Thesis, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, S.P.; Li, J.; Huang, C. Study on the Effect and Mechanism of Tanshinone Ⅰ on Insulin Resistance in HepG2 Cells. Acta Univ. Med. Anhui 2016, 51, 974–977. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Miao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Q.; Liu, X.; Shen, T.; Guo, G. A bibliometric analysis of the trends and evolution on inhalation injury research. J. Burn Care Res. 2024, 45, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Yan, F.; Du, C. A comprehensive analysis of energy management strategies for hybrid electric vehicles based on bibliometrics. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 48, 88–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Chen, Y.; Hu, N.; Long, D.; Cao, Y. The uses of zebrafish (Danio rerio) as an in vivo model for toxicological studies: A review based on bibliometrics. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 272, 116023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Min, T.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, C.; Yin, H.; Yue, J. The developments and trends of electrospinning active food packaging: A review and bibliometrics analysis. Food Control 2024, 160, 110291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Z.; Chen, S.; Ding, L.; Liu, J.; Cui, X.; Li, F.; Qiu, F. Current perspectives and trend of nanomedicine in cancer: A review and bibliometric analysis. J. Control. Release 2022, 352, 211–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yin, Y.; Liu, W.; Dunford, M. Visualizing the intellectual structure and evolution of innovation systems research: A bibliometric analysis. Scientometrics 2015, 103, 135–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chai, L. Three new bibliometric indicators/approaches derived from keyword analysis. Scientometrics 2018, 116, 721–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ye, X.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Z.; Chen, W.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, B.; Wang, H.; Yao, J. Combination of Evidence from Bibliometrics and Bioinformatics Analysis Identifies miR-21 as a Potential Therapeutical Target for Diabetes. Metabolites 2024, 14, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, L. Trends in exercise therapy research for neurological diseases: A bibliometric and visualization approach from 2000 to 2024. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1479731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Xie, F. Global research hotspots and trends of iodinated contrast agents in medical imaging: A bibliometric and visualization analysis. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1506634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Xu, Z.; Hong, N.; Hussain, A. A bibliometric study and science mapping research of intelligent decision. Cogn. Comput. 2022, 14, 989–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Pan, H.X.; Tang, G.L. Research progress on biosynthesis of natural product drugs in the past decade. Synth. Biol. J. 2024, 5, 408–446. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.J.; Shuai, Z.R.; Gong, P. Study on the Extraction of Urticaceae Polysaccharides and Their Hypoglycemic Effect on HepG2 Cells. Food Fer Ind. 2024, 50, 23–33. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, J.; Bain, S.; Kanamarlapudi, V. A review of current trends with type 2 diabetes epidemiology, aetiology, pathogenesis, treatments and future perspectives. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2021, 14, 3567–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Bao, Y.; Bai, B. An update on the economic burden of type 2 diabetes mellitus in China. Expert. Rev. Pharmacoecon. Outcomes Res. 2022, 22, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, C.P.; Lai, F.Y.; Nath, M.; Ye, S.; Webb, T.R.; Schunkert, H.; Samani, N.J. Genetic assessment of potential long-term on-target side effects of PCSK9 (Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9) inhibitors. Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2019, 12, e002196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Lai, J.; Fan, X. Extraction of polysaccharides from Polygonum cuspidatum with activity against Type 2 Diabetes via alterations in gut microbiota. Food Chem. 2025, 470, 140047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.T.; He, Y.T.; Du, Z.C. Research on the Source and Hypoglycemic Activity of Polysaccharides from Hypoglycemic Plants. Chin. Arch. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2017, 35, 358–360. [Google Scholar]
- Fassett, R.G.; Coombes, J.S. Astaxanthin: A potential therapeutic agent in cardiovascular disease. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 447–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; He, X.; Chen, A.; Zhong, J.; Lin, S.; Guo, Y. Astaxanthin attenuates glucose-induced liver injury in largemouth bass: Role of p38mapk and pi3k/akt signaling pathways. Cell Biosci. 2024, 14, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.S.; Lee, K.S.; Jang, J.H.; Quan, Z.; Yang, K.M.; Burri, B.J. The effect of dietary supplementation of β-carotene on lipid metabolism in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Nutr. Res. 2004, 24, 1011–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, N.; Gao, Z. β-Carotene regulates glucose transport and insulin resistance in gestational diabetes mellitus by increasing the expression of SHBG. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2022, 49, 1307–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannin-Spitz, T.; Bergman, M.; Van-Moppes, D.; Grossman, S.; Arad, S. Antioxidant activity of the polysaccharide of the red microalga Porphyridium sp. J. Appl. Phycol. 2005, 17, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Gao, X.; Chen, R.; Lu, S.; Wan, X.; Farag, M.A.; Zhao, C. Metabolomics and Biochemical Insights on the Regulation of Aging-Related Diabetes by a Low-Molecular-Weight Polysaccharide from Green Microalga Chlorella Pyrenoidosa. Food Chem. X 2022, 14, 100316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurkolis, F.; Harbuwono, D.S.; Taslim, N.A.; Soegondo, S.; Suastika, K.; Sparringa, R.A.; Tjandrawinata, R.R. New insight on dietary strategies to increase insulin sensitivity and reduce diabetes prevalence: An expert perspective and recommendation. Discov. Food 2025, 5, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mularczyk, M.; Michalak, I.; Marycz, K. Astaxanthin and other nutrients from Haematococcus pluvialis—Multifunctional applications. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathasivam, R.; Ki, J.S. A review of the biological activities of microalgal carotenoids and their potential use in healthcare and cosmetic industries. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


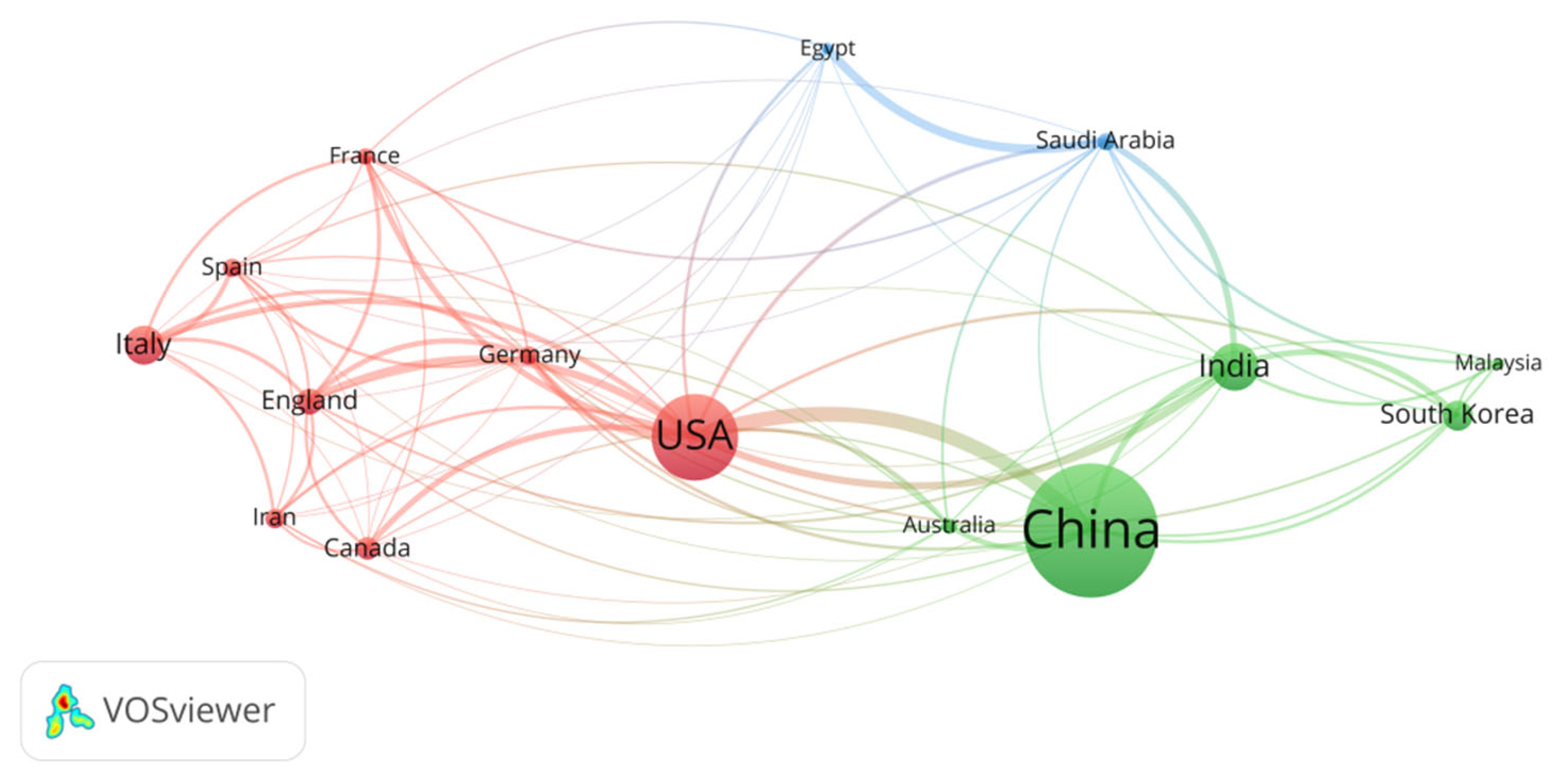

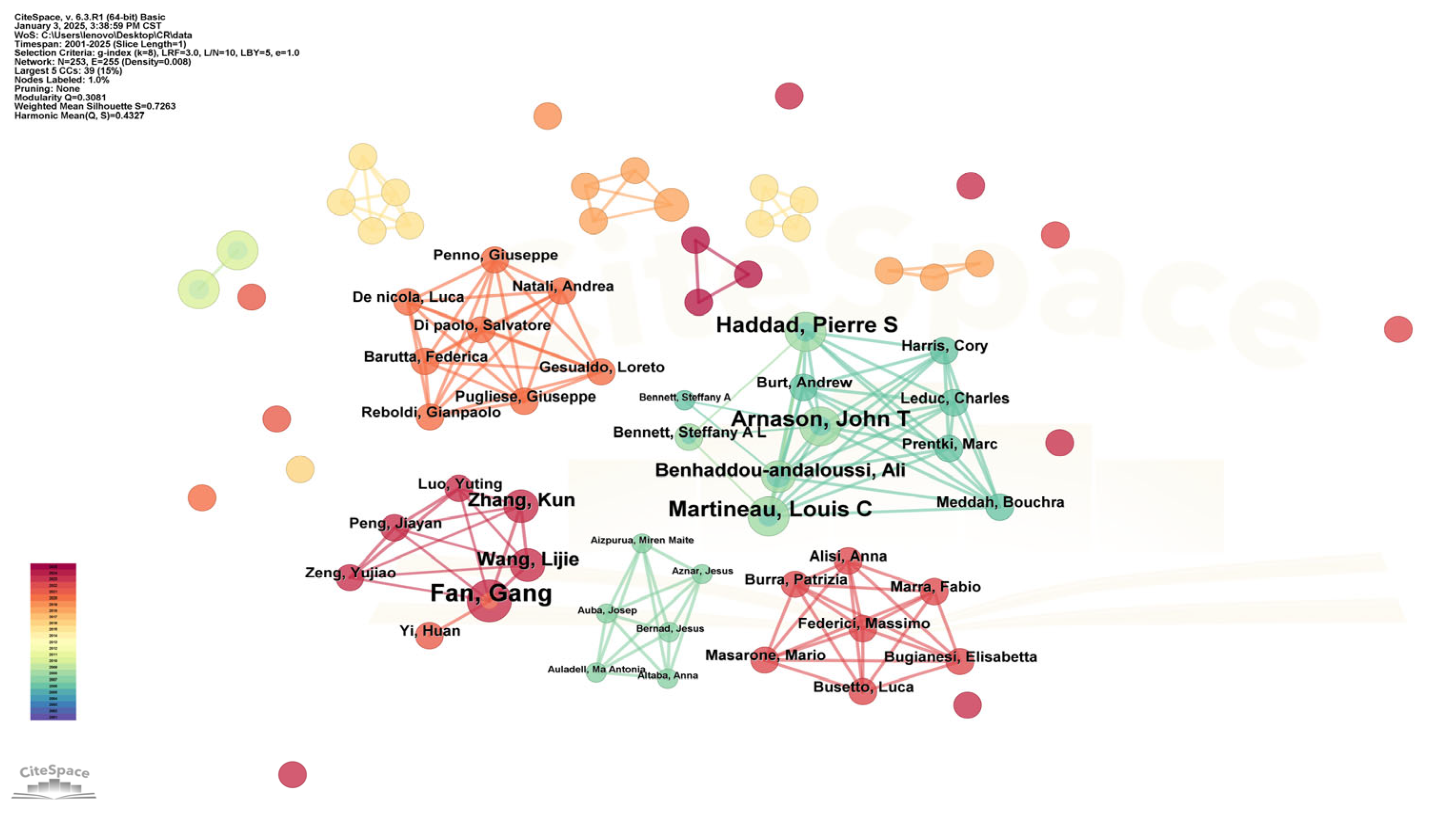
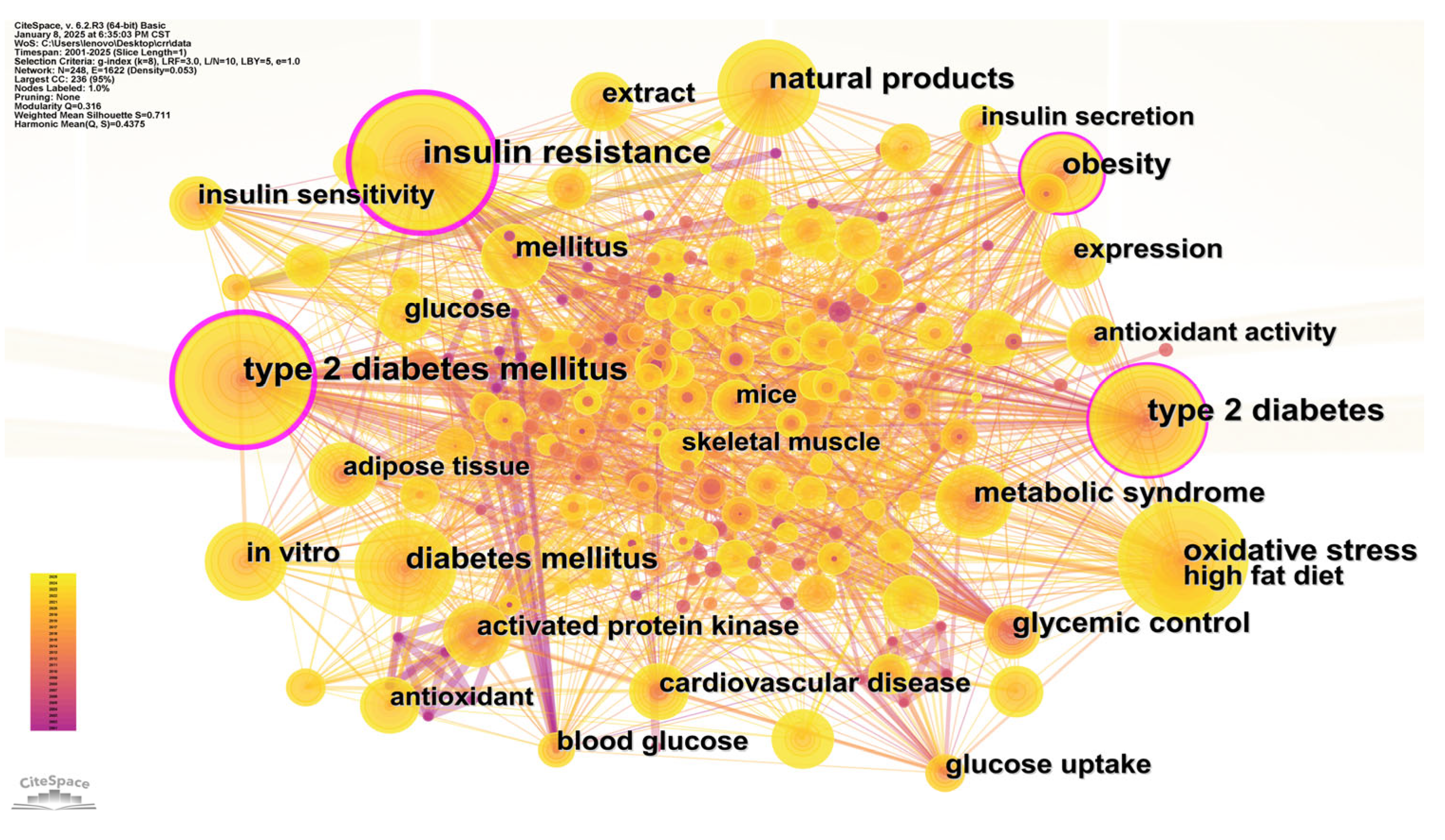
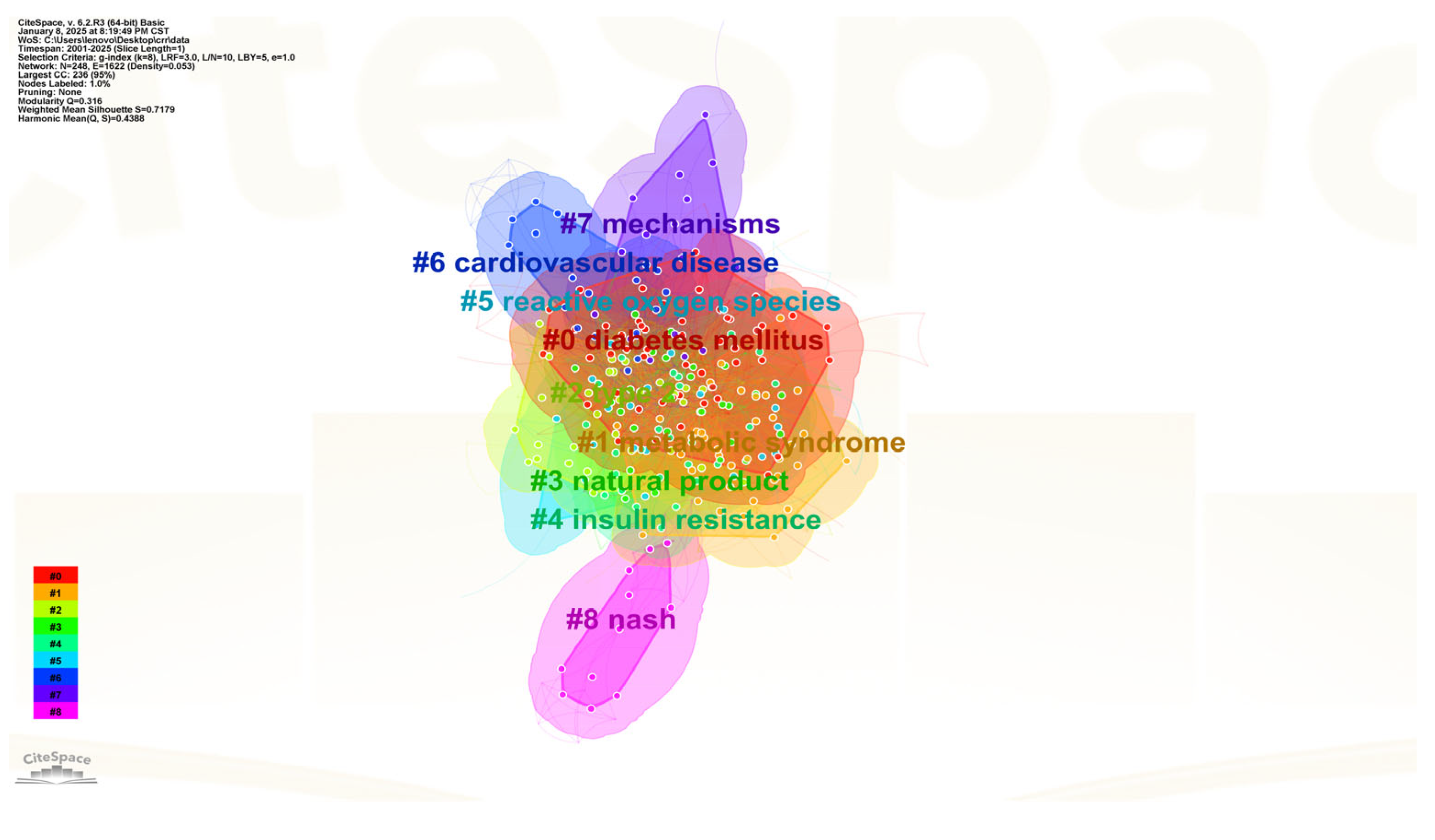
| Ranking | Country | Total Link Strength |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | USA | 112 |
| 2 | China | 66 |
| 3 | India | 58 |
| 4 | England | 56 |
| 5 | Germany | 49 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, R.; Zhao, H.; Wu, S.; Yang, N.; Zhang, Z.; Li, K.; Chen, J.; Wang, P.; Liu, X.; Zhang, R. Intervention of Natural Microalgal Bioactives on Type 2 Diabetes: Integrated Scientometric Mapping and Cellular Efficacy Studies. Phycology 2025, 5, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology5030036
Chen R, Zhao H, Wu S, Yang N, Zhang Z, Li K, Chen J, Wang P, Liu X, Zhang R. Intervention of Natural Microalgal Bioactives on Type 2 Diabetes: Integrated Scientometric Mapping and Cellular Efficacy Studies. Phycology. 2025; 5(3):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology5030036
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Ran, Hongxiang Zhao, Shilin Wu, Ning Yang, Zhen Zhang, Kun Li, Jingyun Chen, Pei Wang, Xiaojun Liu, and Rongqing Zhang. 2025. "Intervention of Natural Microalgal Bioactives on Type 2 Diabetes: Integrated Scientometric Mapping and Cellular Efficacy Studies" Phycology 5, no. 3: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology5030036
APA StyleChen, R., Zhao, H., Wu, S., Yang, N., Zhang, Z., Li, K., Chen, J., Wang, P., Liu, X., & Zhang, R. (2025). Intervention of Natural Microalgal Bioactives on Type 2 Diabetes: Integrated Scientometric Mapping and Cellular Efficacy Studies. Phycology, 5(3), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology5030036







