Taxonomic Structure and Diversity of Benthic Diatoms (Bacillariophyta) in the Northern Shelf of the Black Sea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Efforts
2.2. Biomaterial Analysis
2.3. Microscopy
2.4. Deposited Material
2.5. Bacillariophyta Database
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mann, D.G.; Crawford, R.M.; Round, F.E. Bacillariophyta. In Handbook of the Protists; Archibald, J.M., Simpson, A.G.B., Slamovits, C., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 205–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seckbach, J.; Kociolek, J.P. (Eds.) The Diatom World; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2011; 533p. [Google Scholar]
- Blanco, S.; Cejudo-Figueiras, C.; Tudesque, L.; Bécares, E.; Hoffmann, L.; Ector, L. Are diatom diversity indices reliable monitoring metrics? Hydrobiologia 2012, 695, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borja, A.; Elliott, M.; Andersen, J.H.; Cardoso, A.C.; Carstensen, J.; Ferreira, J.G.; Heiskanen, A.-S.; Marques, J.C.; Neto, J.M.; Teixeira, H.; et al. Good Environmental Status of marine ecosystems: What is it and how do we know when we have attained it? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 76, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keck, F.; Rimet, F.; Franc, A. Phylogenetic signal in diatom ecology: Perspectives for aquatic ecosystems biomonitoring. Ecol. Appl. 2016, 26, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Winter, M.; Devictor, V.; Schweiger, O. Phylogenetic diversity and nature conservation: Where are we? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2013, 28, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoie, I.; Hamilton, P.B.; Morin, S.; Tiam, S.K.; Kahlert, M.; Gonçalves, S.; Falasco, E.; Fortin, C.; Gontero, B.; Heudre, D.; et al. Diatom teratologies as biomarkers of contamination: Are all deformities ecologically meaningful? Ecol. Indic. 2017, 82, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimet, F.; Bouchez, A. Biomonitoring river diatoms: Implications of taxonomic resolution. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 15, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenger-Kovács, C.; Tóth, L.; Tóth, F.; Hajnal, E.; Padisák, J. Stream order-dependent diversity metrics of epilithic diatom assemblages. Hydrobiologia 2014, 721, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsarenko, P.M.; Wasser, S.P.; Nevo, E. (Eds.) Algae of Ukraine: Diversity, Nomenclature, Taxonomy, Ecology and Geography. 2. Bacillariophyta; A.R.G. Gantner Verlag K.G.: Ruggell, Liechtenstein, 2009; 413p. [Google Scholar]
- Ryabushko, L. Microalgae of the Black Sea Benthos; Kovalevsky Institute of Biology of the Southern Seas, NAS of Ukraine. EKOSI-Gidrophizica: Sevastopol, Russia, 2006; 143p, (In Russian, Abstract in English). [Google Scholar]
- Nevrova, E.L.; Snigireva, A.A.; Petrov, A.N.; Kovaleva, G.V. Guidelines for Quality Control of the Black Sea. Microphytobenthos; Gaevskaya, A.V., Ed.; N. Orianda: Sevastopol, Russia, 2015; 176p, (In Russian, Abstract in English). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nevrova, E.L. Diversity and Structure of Benthic Diatom Taxocenes (Bacillariophyta) of the Black Sea; Gaevskaya, A.V., Ed.; A. O. Kovalevsky Institute of Biology of the Southern Seas RAS: Sevastopol, Russia, 2022; 329p, (In Russian, Abstract in English). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konsulov, A. Black Sea Biological Diversity: Bulgaria; GEF Black Sea Environmental Series; Institute of Oceanology BAS, United Nations Publications: New York, NY, USA, 1998; Volume 5, 131p. [Google Scholar]
- Bodeanu, N. Structure et dynamique de l’algoflore unicellulaire dans les eaux du littoral Roumain de la mer Noire. Cercet. Mar. 1987, 20, 19–250. [Google Scholar]
- Petranu, A. Black Sea Biological Diversity: Romania; GEF Black Sea Environmental Series; Romanian Marine Research Institute, United Nations Publications: New York, NY, USA, 1997; Volume 4, 314p. [Google Scholar]
- Guslyakov, N.; Zakordonez, O.; Gerasimuk, V. Atlas of Diatom Algae of Benthos of the Black Sea North-West Part and Adjacent Aquatories; Naukova Dumka: Kiev, Ukraine, 1992; (In Russian, Abstract in English). [Google Scholar]
- Zaitsev, Y.; Alexandrov, B.G. Black Sea Biological Diversity: Ukraine; GEF Black Sea Environmental Series; NASU Odessa Branch Institute of Biology of the Southern Seas, United Nations Publications: New York, NY, USA, 1998; Volume 7, 351p. [Google Scholar]
- Proshkina-Lavrenko, A.I. Planctonic Diatoms of the Black Sea; AS USSR: Moscow, Russia, 1955; 222p, [Proshkina-Lavrenko, A.I. Diatomovyie Vodorosli Planktona Chernogo Morya; AN SSSR: Moskva, Russia, 1955; 222s]. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Proshkina-Lavrenko, A.I. Benthic Diatoms of the Black Sea; AS USSR: Moscow-Leningrad, Russia, 1963; 243p. [Proshkina-Lavrenko A. I. Diatomovyie Vodorosli Bentosa Chernogo Morya; AN SSSR: Moskva, Russia, 1963; 243s]. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Komahidze, A.; Mazmanidi, N. Black Sea Biological Diversity: Georgia; GEF Black Sea Environmental Series; United Nations Publications: New York, NY, USA, 1998; Volume 8, 167p. [Google Scholar]
- Öztürk, B. Black Sea Biological Diversity: Turkey; GEF Black Sea Environmental Series; United Nations Publications: New York, NY, USA, 1998; Volume 9, 114p. [Google Scholar]
- Microplankton Species of Turkish Seas. Ege University Faculty of Fisheries Department of Hydrobiology. Available online: http://plankweb.ege.edu.tr/ (accessed on 5 March 2022).
- Baytut, Ö.; Gönülol, A.; Koray, T. New records for marine phytoplankton of Turkish Seas from Southern Black Sea coasts. Ege J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2005, 22, 229–231. [Google Scholar]
- Baytut, Ö.; Moestrup, Ø.; Lundholm, N.; Gönülol, A. Contributions to the Diatom flora of the Black Sea from ultrastructural and molecular studies: New records of Skeletonema marinoi, Pseudo-nitzschia pungens var. aveirensis and Chaetoceros tenuissimus for the marine flora of Turkey. Nova Hedwig. 2013, 96, 427–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirican, S.; Kaleli, A.; Yilmaz, E.; Özer, A.; Dayioglu, H. New records of diatoms (Bacillariales, Rhopalodiales & Surirellales) with ultrastructure details from the Black Sea coast of Turkey. Aquat. Sci. Eng. 2022, 37, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaleli, A.; Akçaalan, R. Checklist of marine diatoms from Turkish coastal waters with updated nomenclature. Aquat. Res. 2021, 4, 88–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zidarova, R.; Ivanov, P.; Hristova, O.; Dzhurova, B.; Hineva, E. The unexpected diversity in Amphora sensu lato (Bacillariophyta) at Sozopol Bay, the western Black Sea. Phytotaxa 2022, 544, 103–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protasov, A.A. Biodiversity and its assessment. Conceptual Diversicology; Institute of Hydrobiology of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, Acadeperiodica of NAS of Ukraine: Kyiv, Ukraine, 2002; 106p, [Protasov, A.A. Bioraznoobrazie i Ego Otsenka. Kontseptualnaya Diversikologiya; In-t Gidrobiologii NAN Ukrainyi, Akademperiodika NAN Ukrainyi: Kyiv, Ukraine, 2002; 106s]. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Warwick, R.M.; Clarke, K.R. Taxonomic distinctness and environmental assessment. J. Appl. Ecol. 1998, 35, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warwick, R.M.; Clarke, K.R. Practical measures of marine biodiversity based on relatedness of species. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 2001, 39, 207–231. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, K.R.; Warwick, R.M. A taxonomic distinctness index and its statistical properties. J. Appl. Ecol. 1998, 35, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Warwick, R.M. The taxonomic distinctness measure of biodiversity weighting of step lengths between hierarchical levels. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1999, 184, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke KR Warwick, R.M. A further biodiversity index applicable to species list: Variation in taxonomic distinctness. Mar. Biol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 216, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Warwick, R.M. Change in Marine Communities: An Approach to Statistical Analysis and Interpretation, 2nd ed.; PRIMER-E Ltd.: Plymouth, UK, 2001; 154p. [Google Scholar]
- Round, F.E.; Crawford, R.M.; Mann, D.G. The Diatoms: Biology and Morphology of the Genera; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1990; 747p. [Google Scholar]
- Levkov, Z. Amphora Sensu Lato, Diatoms of Europe; A.R.G. Gantner Verlag: Ruggell, Liechtenstein, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Reid, G. A revision of the family Pleurosigmataceae. In Diatom Monographs; Witkowski, A., Ed.; A.R.G. Gantner Verlag K.G.: Ruggell, Liechtenstein, 2012; Volume 14, pp. 1–163. [Google Scholar]
- Witkowski, A.; Lange-Bertalot, H.; Metzeltin, D. Diatom Flora of Marine Coast 1. Iconographia Diatomologica. VII; A.R.G. Gantner Verlag K.G.: Ruggell, Liechtenstein, 2000; 926p. [Google Scholar]
- Witkowski, A.; Kulikovskiy, M.; Nevrova, E.; Lange-Bertalot, H.; Gogorev, R. The genus Navicula in ancient basins. I. Two novelties from the Black Sea. Plant Ecol. Evol. 2010, 143, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowski, A.; Nevrova, E.; Lange-Bertalot, H.; Kociolek, J. Navicula petrovii sp. nov. (Bacillariophyceae), a naviculoid diatom with amphoroid symmetry and its relationship to Navicula sensu stricto and other naviculoid genera. Nova Hedwig. 2014, 143, 469–484. [Google Scholar]
- Guiry, M.D.; Guiry, G.M. AlgaeBase; World-Wide Electronic Publication; National University of Ireland: Galway, Ireland, 2023; Available online: http://www.algaebase.org (accessed on 5 March 2022).
- Fourtanier, E.; Kociolek, J. Catalogue of Diatom Names; California Academy of Sciences: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2011; Available online: http://researcharchive.calacademy.org/research/diatoms/names/index.asp (accessed on 5 March 2022).
- Dendroscope3 (An Interactive Viewer for Rooted Phylogenetic Trees and Networks). 2015. Available online: https://software-ab.informatik.uni-tuebingen.de/download/dendroscope3/welcome.html (accessed on 5 March 2022).
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.N. PRIMER v6: User Manual/Tutorial; PRIMER-E: Plymouth, UK, 2006; 126p. [Google Scholar]
- Nevrova, E.; Witkowski, A.; Kulikovskiy, M.; Lange-Bertalot, H.; Kociolek, J.-P. A revision of the diatom genus Lyrella Karayeva (Bacillariophyta: Lyrellaceae) from the Black Sea, with descriptions of five new species. Phytotaxa 2013, 83, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevrova, E.L. Benthic diatoms of the Black Sea: Rare, invasive, extinct species and assessment of taxonomic exclusivity. Vopr. Sovrem. Algol. 2022, 2, 46–56, (In Russian, Abstract in English). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevrova, E.; Petrov, A. Taxonomic diversity of benthic diatoms of the Black Sea. In Microalgae of the Black Sea: Problems of Biodiversity, Preservation and Biotechnology; Tokarev, U., Gaevskaya, A., Eds.; NAS Ukraine, IBSS. Ekosi-Gidrophyzika: Sevastopol, Russia, 2008; pp. 60–84, (In Russian, Abstract in English). [Google Scholar]
- Leonard, D.; Clarke, K.; Somerfield, P.; Warwick, R. The application of an indicator based on taxonomic distinctness for UK marine biodiversity assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2006, 78, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouliott, D.; Gaillard, S.; Aliaume, C.; Veriaque, M.; Belsher, T.; Troussellier, M.; Chi, T. Ability of taxonomic diversity indices to discriminate coastal lagoon environmental based on macrophyte communities. Ecol. Indic. 2005, 5, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warwick, R.M.; Ashman, C.M.; Brown, A.R.; Clarke, K.R.; Dowell, B.; Hart, B.; Lewis, R.E.; Shillabeer, N.; Somerfield, P.J.; Tapp, J.F. Inter-annual changes in the biodiversity and commuity structure of the macrobenthos in Tees Bay and the Tees estuary, UK, associated with local and regional environmental events. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 234, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urbach, V.Y. Biometric Methods; High School: Moscow, Russia, 1964; 416p, [Urbah, V.Yu. Biometricheskie Metodyi; Vysshaya Shkola: Moscow, Russia, 1964; 416s]. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Petrov, A.N.; Nevrova, E.L. Evaluation of reproducibility and reliability of benthic diatoms species composition at coastal location of SW Crimea. Mar. Ecol. J. 2012, 11, 79–88, (In Russian, Abstract in English). [Google Scholar]
- Petrov, A.N.; Nevrova, E.L. Prognostic Estimation of Species Richness of Benthic Bacillariophyta. Int. J. Algae 2013, 15, 5–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, A.N.; Nevrova, E.L. Numerical analysis of the structure of benthic diatom assemblages in replicate samples (Crimea, the Black Sea). Nova Hedwig. 2014, 143, 245–253. [Google Scholar]
- Vylkanov, A.; Danov, X.; Marinov, X.; Vladev, P. Black Sea; Gidrometeoizdat: Leningrad, Russia, 1983; 408p, [Vylkanov, A.; Danov, X.; Marinov, X.; Vladev, P. Chornoe more: Sbornik; Gidrometeoizdat: Leningrad, Russia, 1983; 408s]. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Alimov, A.F. Elements of the Theory of Ecosystem Functioning; ZIN RAN: St-Petersburg, Russia, 2000; 147p, [Alimov, A.F. Elementyi Teorii Funktsionirovaniya Ekosistem; ZIN RAN: St-Petersburg, Russia, 2000; 147s]. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Petrova-Karadjova, V.I. Diatom algae of marine fouling. Izvestiya na Institut po Ribni Resursi 1977, 15, 55–65. [Petrova-Karadzhova V. I. Diatomovye vodorosli morskih obrastanij. Izvestiya na Instituta po Ribni Resursi 1977, 15, 55–65](In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Cărăus, I. The Algae of Romania: A Distributional Checklist of Actual Algae [Version 2.3]; Studii si Cercetari Biologie, Universitatea Bacau: Bacau, Romania, 2012; 809p. [Google Scholar]
- Nevrova, E.L. Benthic diatoms (Bacillariophyta) at Zernov Phyllophora Field (Northern-Western part of the Black Sea): Taxonomic diversity and structure of taxocene. Mar. Ecol. J. 2014, 13, 47–58, (In Russian, Abstract in English). [Google Scholar]
- Ryabushko, L.I. Microphytobenthos of the Zernov Phyllophora Field; Academy of Sciences Ukrainian SSR, Kovalevsky Institute of Biology of the Southern Seas: Sevastopol, Russia, 1991; 28p, [Ryabushko, L.I. Mikrofitobentos Fillofornogo Polya Zernova; AN USSR, InBUM im. A. O. Kovalevskogo: Sevastopol, Russia, 1991; 28s]. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Guslyakov, N.E.; Nevrova, E.L. Composition of Diatom Algae on Solid Substrates in the Sevastopol Bay Area; Ukrainian Academy of Sciences, A.O. Kovalevsky Institute of Biology of Southern Seas: Sevastopol, Russia, 1987; 14p, [Guslyakov, N.E.; Nevrova, E.L. Sostav Diatomovyh Vodoroslej na Tverdyh Substratah v Rajone Sevastopol’skoj Buhty; AN USSR, Institut biologii yuzhnyh morej im. A.O. Kovalevskogo: Sevastopol, Russia, 1987; 14s]. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kovalchuk, Y.L.; Nevrova, E.L.; Shalaeva, E.A. Diatom Fouling of Solid Substrates; Russian Academy of Sciences, A.N. Severtsov Institute for Ecology and Evolution, KMK: Moscow, Russia, 2008; 174p, [Kovalchuk, Yu.L.; Nevrova, E.L.; Shalaeva, E.A. Diatomovye Obrastaniya Tverdyh Substratov; Rossijskaya Akademiya Nauk, Institut Problem Ekologii i evolyucii im. A.N. Severcova; KMK: Moskva, Russia, 2008; 174s]. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kucherova, Z.S. Diatom Algae and Their Role in the Fouling Cenosis of the Black Sea. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Biology of Southern Seas, Sevastopol, Russia, 1973; 145p. [Kucherova, Z.S. Diatomovye Vodorosli i ih rol’ v Cenoze Obrastaniya Chornogo Morya. Dissertaciya na soiskanie uchenoj stepeni kandidata biologicheskih nauk, Institute of Biology of Southern Seas, Sevastopol, Russia, 1973; 145s](In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Nevrova, E.L. Diatom algae of stony substrates of the Black Sea near Karadag (Crimea). Biol. Sci. 1991, 5, 79–86. [Nevrova, E.L. Diatomovye vodorosli kamenistyh gruntov Chornogo morya u Karadaga (Krym). Biol. Nauk. 1991, 5, 79–86].(In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Nevrova, E.L. Benthic diatom algae in shallow water near Sevastopol (Black Sea). Algologia 1998, 8, 278–285. [Nevrova, E L. Donnye diatomovye vodorosli na melkovodye u Sevastopolya (Chornoe more). Algologia 1998, 8, 278–285](In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Nevrova, E.L. Benthic diatom algae on soft bottom in the deep-water part of the mouth of Sevastopol Bay. Algologia 1999, 9, 43–54. [Nevrova, E.L. Donnye diatomovye vodorosli ryhlyh gruntov v glubokovodnoj chasti ustyia Sevastopolskoj buhty. Algologia 1999, 9, 43–54](In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Nevrova, E.L. Structure and taxonomical diversity of benthic diatom at estuarines of Rivers Belbek and Chernaya (South-West Crimea, Ukraine). Algologia 2013, 23, 471–492, (In Russian, Abstract in English). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevrova, E.L. Taxonomic diversity and structure of benthic diatom taxocene (Bacillariophyta) at Sevastopol Bay (the Black Sea). Mar. Ecol. J. 2013, 12, 55–67, (In Russian, Abstract in English). [Google Scholar]
- Nevrova, E.L. Taxonomic diversity and environmental assessment of benthic diatoms at Balaklava Bay (South-Western Crimea, the Black Sea, Ukraine). Algologia 2014, 24, 47–66, (In Russian, Abstract in English). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bukhtiyarova, L.N. Diatoms of Ukraine. Inland Waters; National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, N.G. Kholodny Institute of Botany: Kyiv, Ukraine, 1999; 132p. [Google Scholar]
- Davidovich, N.A.; Gastineau, R.; Gaudin, P.; Davidovich, O.I.; Mouget, J.-L. Sexual reproduction in the newly-described blue diatom. Haslea Karadagensis Fottea 2012, 12, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


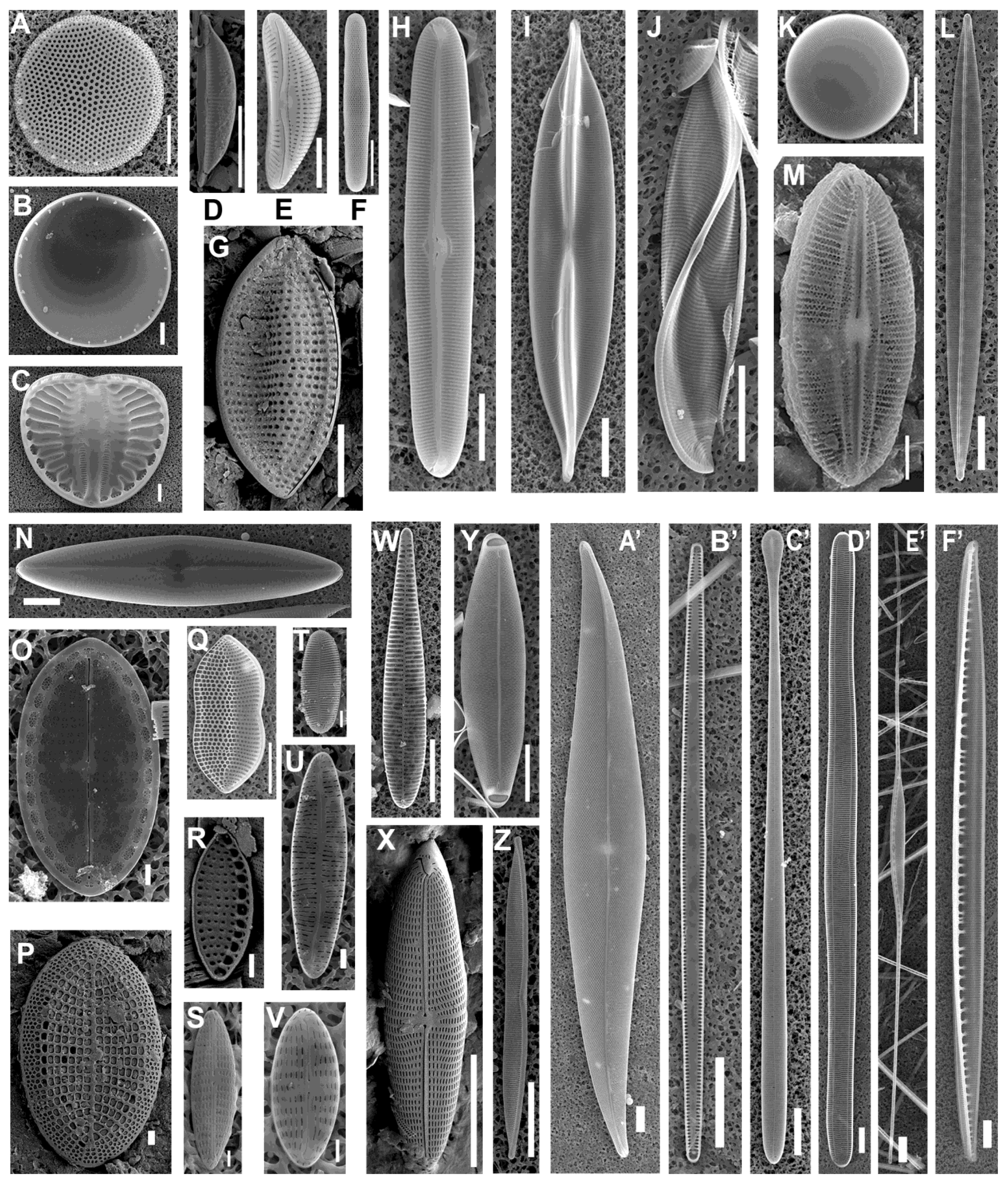


| Studied Area | Date | Coordinates | Depth, m | Number of Samples | Substrates | Number of Species and ISTs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northwestern part of the Black Sea | |||||||
| Zernov Phyllophora field | 5 November 2010 | 45°50′38″ N, 30°44′32″ E | 19–52 | 10 | Silty-sandy | 160 | |
| Black Sea Crimean coast | |||||||
| Karkinitsky Bay | 10 July 2008 | 45°34′31″ N, 32°48′22″ E | 0.5–1 | 4 | Silty-sandy | 22 | |
| vil. Marjino area | 20 July 2010 | 45°20′15″ N, 32°42′12″ E | 6 | 4 | Sandy | 140 | |
| r. Belbek area | 5 November 2009 | 44°39′45″ N, 33°32′31″ E | 6–19 | 20 | Sandy-silty | 243 | 279 |
| Reference site R3 | 5 November 2009 | 44°38′25″ N, 33°31′45″ E | 10–12 | 4 | Sandy | 119 | |
| Karantinnaya Bay | 25 August 1994 | 44°37′05″ N, 33°30′10″ E | 0.5–32 | 44 | Silty-sandy, rocky | 136 | |
| Sevastopol Bay | 11 July 2001 | 44°37′19″ N, 33°31′27″ E | 4–17 | 62 | Silty-sandy | 186 | |
| Inkerman Bay | 6 November 2009 | 44°36′20″ N, 33°35′50″ E | 3–10 | 12 | Silty-sandy | 116 | |
| Omega Bay | 28 July 2004 | 44°35′55″ N, 33°26′56″ E | 1.5–16 | 8 | Sandy-silty | 260 | |
| Golubaya Bay | 15 August 2009 | 44°35′03″ N, 33°22′48″ E | 1.5–6 | 6 | Sandy | 124 | |
| Cape Fiolent | 12 August 2009 | 44°30′53″ N, 33°28′18″ E | 1.5–12 | 16 | Sandy, macrophytes | 290 | |
| Balaklava Bay | 14 October 2006 | 44°29′12″ N, 33°36′53″ E | 6–20 | 34 | Silty-sandy | 191 | 342 |
| Reference site R6 | 14 October 2006 | 44°28′37″ N, 33°37′30″ E | 17–23 | 4 | Sandy | 233 | |
| Laspi Bay | 27 June 1996 | 44°25′10″ N, 33°42′27″ E | 0.5–52 | 74 | Silty-sandy, macrophytes | 217 | |
| Cape Sarych | 20 August 2007 | 44°23′14″ N, 33°44′17″ E | 3–5 | 4 | Sandy, pebbles | 82 | |
| vil. Novyi Svet | 14 August 2009 | 44°49′27″ N, 34°54′25″ E | 0.5–3 | 4 | Sandy | 93 | |
| Karadag Natural Reserve | 10 August 2010 | 44°54′53″ N, 35°13′51″ E | 5–8 | 6 | Sandy, pebbles | 300 | |
| Dvujakornaya Bay | 11 August 2008 | 44°59′28″ N, 35°22′04″ E | 2–9 | 22 | Sandy | 304 | |
| Northeastern part of the Black Sea | |||||||
| Anapa area and Novorossiysk area | 14 October 1999 | 44°52′08″ N, 37°17′44″ E | 0.5–75 | 190 | Silty-sandy, macrophytes | 225 | |
| Tuapse area | 20 August 1990 | 44°04′59″ N, 39°03′04″ E | 25–52 | 6 | Silty | 49 | |
| Total | 534 | ||||||
| Class | Order | Family | Genera | Species | ISTs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coscinodiscophyceae | 12 | 18 | 30 | 91 | 105 |
| Fragilariophyceae | 9 | 10 | 31 | 88 | 101 |
| Bacillariophyceae | 10 | 33 | 88 | 774 | 894 |
| In total | 31 | 61 | 149 | 953 | 1100 |
| Species | Genus | Family | Order | Class | Region of the Black Sea’s Northern Shelf |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actinoptychus senarius | 1 | 1 | 1 | Coscinodisco- phyceae | BC, NWBS, CC |
| Aulacoseira distans | 1 | 1 | 1 | RC | |
| Aulacoseira granulata | RC, NWBS, CC | ||||
| Aulacoseira islandica | RC | ||||
| Aulacoseira italica | RC, NWBS | ||||
| Asteromphalus flabellatus | 1 | 1 | 1 | RC, NEBS | |
| Asteromphalus robustus | RC, CC | ||||
| Anaulus minutus | 1 | 1 | 1 | BC, NWBS, CC | |
| Auliscus sculptus | 1 | 1 | 1 | NWBS, CC | |
| Cerataulus smithii | 1 | NWBS, NEBS, CC | |||
| Cerataulus turgidus | RC, CC | ||||
| Pleurosira laevis | 1 | RC, NWBS, CC | |||
| Triceratium antediluvianum | 1 | All five regions | |||
| Bacteriastrum hyalinum | 1 | 1 | 1 | NWBS, CC | |
| Paralia sulcata | 1 | 1 | 1 | All five regions | |
| Glyphodesmis distans | 1 | 1 | 1 | All five regions | |
| Cymatosira belgica | 1 | 1 | 1 | CC, NWBS, NEBS | |
| Plagiogrammopsis sp. | 1 | CC | |||
| Endictya oceanica | 1 | 1 | 1 | RC, NWBS, CC, NEBS | |
| Biddulphia rostrata | 1 | 1 | 1 | NWBS, CC, NEBS | |
| Biddulphia vesiculosa | RC | ||||
| Ardissonea crystallina | 1 | 1 | 1 | Fragilario- phyceae | All five regions |
| Ardissonea baculus | All five regions | ||||
| Ardissonea robusta | CC | ||||
| Climacosphenia moniligera | 1 | 1 | 1 | NWBS, BC | |
| Delphineis minutissima | 1 | 1 | 1 | NWBS, CC | |
| Delphineis surirella | NWBS, CC, NEBS | ||||
| Rhaphoneis amphiceros | 1 | CC, NEBS | |||
| Psammodiscus nitidus | 1 | 1 | 1 | All five regions | |
| Thalassionema nitzschioides | 1 | 1 | 1 | All five regions | |
| Toxarium undulatum | 1 | 1 | 1 | All five regions | |
| Anomoeoneis spaerophora | 1 | 1 | 1 | Bacillario- phyceae | NWBS, CC |
| Proschkinia complanatoides | 1 | 1 | 1 | NWBS, CC |
| Species | Genus | Family | Order | Class | Region of the Black Sea’s Northern Shelf |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brachysira aponina | 1 | 1 | 1 | Bacillariophyceae | NWBS |
| Proschkinia complanatula | 1 | 1 | NWBS | ||
| Cavinula lacustris | 1 | 1 | RC | ||
| Neidium binodis | 1 | 1 | CC | ||
| Amicula specululum | 1 | 1 | |||
| Astartiella bahusiensis | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Astartiella producta | |||||
| Astartiella sp.1DV | 1 | ||||
| Pauliella taeniata | 1 | ||||
| Orthoseira roeseana | 1 | 1 | 1 | Coscinodiscophyceae | RC |
| Hannaea arcus | 1 | 1 | 1 | Fragilariophyceae |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nevrova, E. Taxonomic Structure and Diversity of Benthic Diatoms (Bacillariophyta) in the Northern Shelf of the Black Sea. Phycology 2023, 3, 337-355. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology3030022
Nevrova E. Taxonomic Structure and Diversity of Benthic Diatoms (Bacillariophyta) in the Northern Shelf of the Black Sea. Phycology. 2023; 3(3):337-355. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology3030022
Chicago/Turabian StyleNevrova, Elena. 2023. "Taxonomic Structure and Diversity of Benthic Diatoms (Bacillariophyta) in the Northern Shelf of the Black Sea" Phycology 3, no. 3: 337-355. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology3030022
APA StyleNevrova, E. (2023). Taxonomic Structure and Diversity of Benthic Diatoms (Bacillariophyta) in the Northern Shelf of the Black Sea. Phycology, 3(3), 337-355. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology3030022





