Abstract
Streams play vital roles in surrounding communities and provide essential ecosystem services. The protection of streams is important, they are legally protected under the Clean Water Act, and they can be monitored through the continuous analyses of biological data, such as algal or other aquatic communities. The goals of this study were to analyze the long-term recovery of Tobler Creek, a recovering agricultural stream on the site of a National Historic Landmark, and yield comparisons to a local low-impact stream, Murder Creek, located within the Oconee National Forest. In 2011, Tobler Creek exceeded reference criteria values for total phosphorus (TP) but met the nitrate nitrogen criteria. With an 11-year recovery period, Tobler Creek met both nutrient reference criteria. In 2022, periphyton samples were collected according to standard protocols, confirming that diatoms are the dominant algal group in the community. With recovery, Tobler Creek showed an increase in diatom species richness (χ2 = 116.11, df = 5, p < 0.01) but this was significantly lower than the values documented in Murder Creek. The multi-metric index (MMI), calculated using diatom community analysis to estimate ecological health, indicated that Tobler Creek experienced degradation from 2011 to 2022 (χ2 = 55.97, df = 5, p < 0.05) and is below the regional 25th percentile. The percentage of sediment-tolerant taxa (surirelloid, naviculoid, and nitzschoid) was significantly higher in Tobler Creek in 2022 (χ2 = 500.96, df = 5, p < 0.01) compared to Murder Creek in 2022 (t = −4.67, df = 10, p < 0.01). Despite a reduction in nutrients given the 42-year recovery period, the diatom community in Tobler Creek was significantly different than other regional protected streams. Ecological degradation of the habitat was likely driven by sedimentation due to run-off in the recovering agriculture stream. These findings highlight the importance of protecting water quality, as the recovery of nutrients can be a decades-long process overlayed with many potentially new stressors influencing aquatic organisms.
1. Introduction
Assessing the ecological health of lotic systems can be difficult to quantify, with many different abiotic and biotic features reflecting ecosystem integrity on different spatial and temporal scales [1]. A stream’s ecology can be informed by biomonitoring, driving decisions as to whether action must be taken to either protect or restore stream health. Currently, a general guideline is set for abiotic properties’ streams, which streams must meet in order to be considered suitable for good ecological standing and to support biodiverse communities (nutrient criteria, dissolved oxygen, pH, and temperature standards), with the understanding that habitat protection is vital to preserving biodiversity [2]. As abiotic properties can serve as surrogates for water quality, biological communities must be assessed to capture the entirety of “good ecological health” [3]. Furthermore, understanding the biology of aquatic organisms provides a deeper understanding of the ecological integrity of aquatic systems.
1.1. Nutrients and the Clean Water Act
According to the USDA, 52% of land use in the United States is dedicated to agricultural production [4]. Nutrient run-off from agricultural sites can promote algal growth and degrade aquatic habitats [5]. Algal communities serve as the base trophic level in aquatic systems, meaning that they influence the entire aquatic ecosystem and regulate bottom-up processes. Diatoms are a group of algae characterized by a hydrated silica cell wall, and they are typically found dominating stream environments. Additionally, their cell walls are well preserved; therefore, diatoms serve as great candidates for historical research. Diatom community analyses can incorporate these effects with meaningful interpretations such as lower species richness and the increasing dominance of tolerant species, serving as a warning of increased nutrients [6,7]. Nitrate-nitrogen is a major source of pollution from agricultural processes and is a major problem globally [7]. Phosphorus-based fertilizers have been of less concern than nitrogen-based fertilizers in the past due to the misconception that phosphorus will not leech from the soils [5,8]. However, run-off and the over-application of phosphorus can oversaturate the soils and end up in waterways, with this having detrimental effects on biotic communities [8]. These effects have led to a number of regulatory programs and regulations being implemented to negate these effects. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) established reference criteria for nitrate-nitrogen and total phosphates for monitored streams’ water quality for comparison to “ecologically healthy” streams within the region. Reference stream criteria vary among US regions, with middle Georgia falling into EPA Region IV, ecoregion IX. The reference stream criteria set for this ecoregion are based on 25th percentiles of an aggregation of nutrient data collected; the reference stream criteria set for total phosphorus (TP) and total nitrogen (TN) are set as 0.037 mg/L and 0.69 mg/L, respectively [3,9].
There is no lack of documentation of the impacts that anthropogenic processes have on aquatic systems (invasive species, harmful algal blooms, the loss of biodiversity, etc.) [10,11]; however, the recovery processes in terms of timing and aquatic community composition are less understood and documented. Anthropogenic problems are often followed by man-made solutions, which can have positive effects but also bring about novel consequences as well [12,13]. The other option is to protect sites and allow recovery to take place naturally. Tobler Creek, a recovering agricultural stream, can be compared with a reference stream that has no documented urban or agricultural influences.
1.2. Study Goals
In this study, we are interested in the recovery of an agricultural stream and a comparison of it with a regional stream placed within a protected forest. Ecological health can be quantified as abiotic factors that meet regional reference criteria as well as biotic factors, such as diatom communities, which display valued ecological indicators, such as high community richness, diversity, and evenness. Diatom-specific indices, such as the trophic diatom index (TDI) and the multi-metric index (MMI) were assessed as well. TDI assesses organic pollution within a site based off a range of sensitivity and tolerance values, as well as the abundance of species within a community [6]. MMI’s assess total ecological health given species-level identification of diatom species within a given region, and it was developed in the United States [14]. Diatoms, a common algal group in streams, were chosen because microbial communities are often under-studied although they provide the basis for energetics at a macro-scale. Additionally, studies have shown diatoms to be the sensitive bioindicators and the quickest to respond, with them having short generation times equaling to days [15]. Tobler Creek is decades-long into the recovery process, with no additional best management practices being put into restoring the stream. The goals of this research were to (1) assess the rates of nutrient recovery in Tobler Creek over 10 years, (2) assess the community dynamics of diatoms in response to lowering nutrients and compare them to a local low-impact stream, (3) assess seasonal variation in diatom communities in middle Georgia low-impact streams, and (4) produce a diatom voucher flora of specimens found within this region.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites
Site 1: Tobler Creek in Milledgeville, Georgia (lat. 33.121218, long. −83.267738), is a rural, low-disturbance stream on the site of Andalusia Farms in Milledgeville, Georgia (Figure 1 and Figure 2).). Andalusia Farms is the home of Flannery O’Connor, a well-renowned literary author, and is now a decommissioned agricultural space. Prior to the 1980s, Andalusia served as a 100-acre cotton plantation, then as a dairy and cattle farm, and finally as a hay farm (Figure 2a). Due to the historical significance of Flannery O’Conner’s literary prowess, Andalusia Farm was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1980 and was designated as a National Historic Landmark by the National Park Service in 2022 [16]. All agricultural processes ceased after 1980 and aerial images provide evidence that the vegetative landscape has recovered (Figure 2b). In 2011, base-line nutrients and diatom samples were taken and analyzed [17]. Despite the area within the watershed being designated as museum land no longer practicing agricultural processes, TP was found to exceed the reference criteria. At the time of collection in 2022, Tobler creek was wadable and had a stream width of 2 m and a stream depth at the collection site of 15 cm.
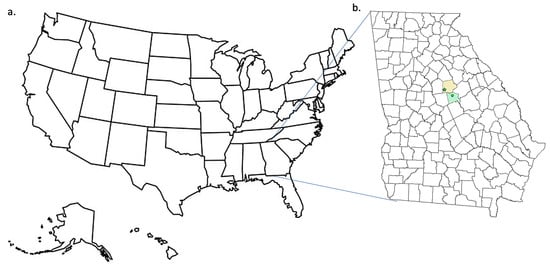
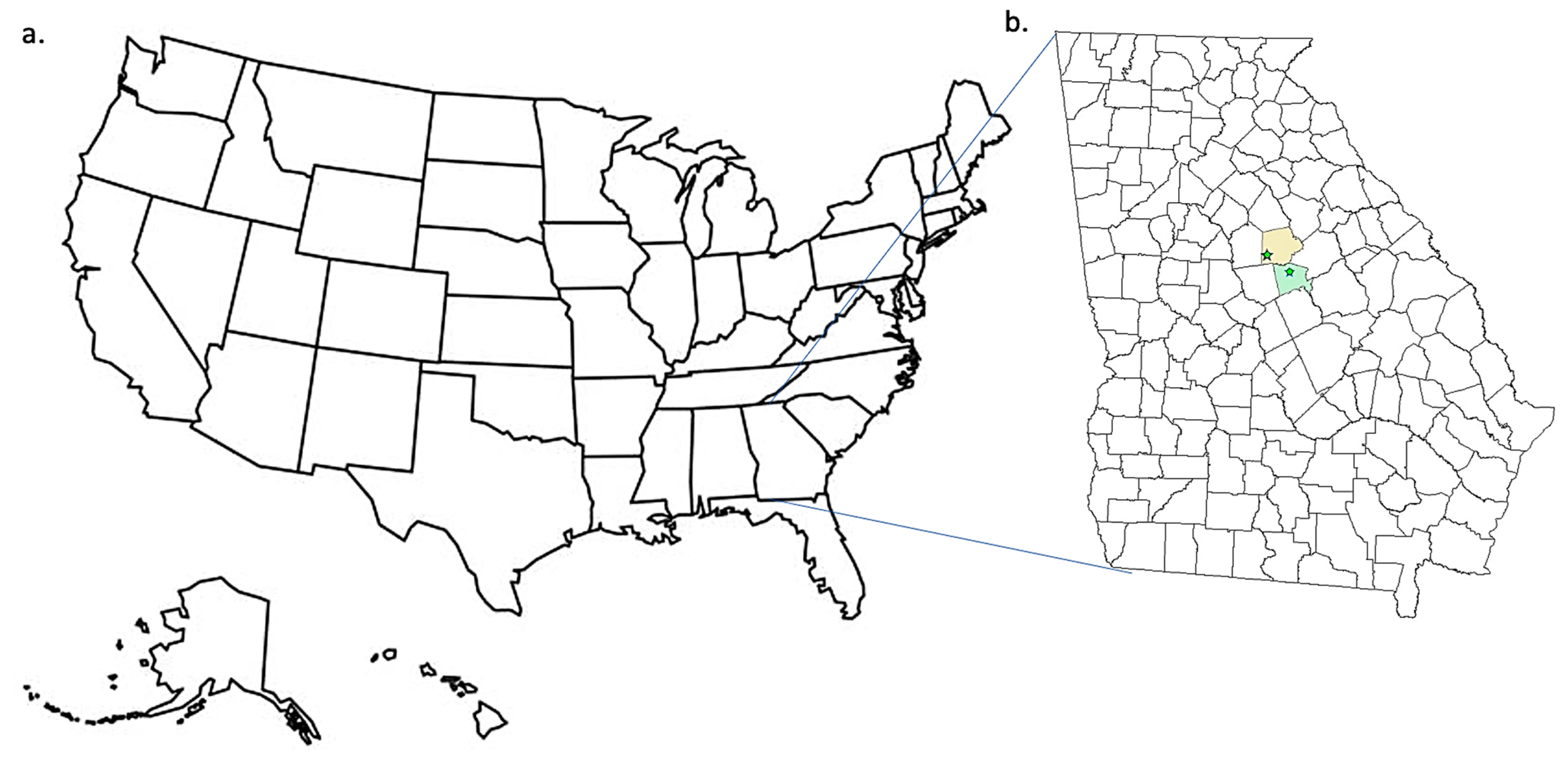
Figure 1.
Sampling locations. (a) USA map and the state of Georgia and (b). County locations in the state of Georgia: yellow—Putnam County for Murder Creek and green—Baldwin County for the location of Tobler Creek.

Figure 2.
Aerial images of Tobler Creek within Andalusia Farm, Milledgeville, GA. (a). October 1937 and (b). October 2019 captured via the Google Earth application, sampling location showed with an arrow.
Site 2: Reference streams serve as comparisons to streams with questionable ecological status. Murder Creek below Eatonton, Georgia (lat. 33.252200, long. −83.481400), is a stream previously surveyed by the USGS NAWQA program from 1990 to 2000 (USGS #02221525). Murder Creek is a low nutrient impacted stream with a watershed within the Oconee National Forest south of highway I20. This was also a wadable stream with a stream width at the collection site of 3 m and a stream depth at the collection site of 15 cm.
2.2. Sampling Methods
Tobler Creek and Murder Creek were sampled, both for algal samples and nutrient samples, in February 2022 and April 2022. During both sampling events, physicochemical data were collected in triplicate in the same localities in which the algal samples were taken, using the YSI 556 MPI (Multi-probe System), measuring the following: water temperature (°C), DO (%, mg/L), pH, and conductivity (µS/cm). Triplicate composite algal samples were taken following standard protocols [18]. Composite sampling included sampling microhabitats typically inhabited by algae (including water, periphyton, woody debris, and submerged vegetation) to yield the most representative communities and the samples were brought to 250 mL. The samples were analyzed as replicates, with triplicates taken in differing reaches in relatively close proximity to each other (Figure 1). Triplicate 125 mL samples of surface water were also collected, to serve as replicates for analysis, and shipped off to the University of Georgia—Agricultural and Environmental Services Laboratories, (Baldwin County Extension 320 Linda Drive NE, Milledgeville, GA 31061) to analyze the total nitrogen content in the sampled stream. An additional triplicate of 125 mL samples of surface water was collected and shipped to the UGA extension for measurement of the following chemicals/nutrients using EPA Method 200.7 and Water Analysis: W1 and W32: hardness, Al, B, Ca, Cr, Cu, Fe, K, Mg, Mn, Mo, Na, Ni, P, Si, and Zn [19].
2.3. Processing
From the total 250 mL sample, 20 mL of the sample was subsampled and shaken to yield the most representative samples and preserved with 37% formaldehyde to reach a total 2% concentration. This serves the purpose of conducting live counts to ensure that diatoms are dominating the community. The remaining 230 mL was acid-cleaned with 70% nitric acid and potassium dichromate. Varying concentrations (yielding single layer spread of diatom valves) of the sample were mounted onto 22 × 22 mm coverslips and mounted into permanent slides using Naphrax® (Brunel Microscopes Ltd., Chippenham, Wiltshire, UK).
2.4. Enumeration
For preserved replicate samples, 100 natural algal units were enumerated due to the low density of algae and high density of silt, to assess algal group proportions and estimate a dominant algal group. Live diatoms, as defined by possessing physiologically active chloroplast at the time of collection, were required to be dominating at 60% and higher to warrant diatom counts of cleaned material to be conducted and interpreted in the diatom analyses.
For the diatom samples, a minimum of 600 valves were enumerated per replicate, as per the standard protocol set by the EPA periphyton protocol [16]. Identification was conducted to the lowest taxonomic level, under 1000× oil immersion on the LeicaCTR5000 equipped with differential interference contrast (DIC). Images were taken with a Leica DFC450C digital camera, which served for the creation of a flora voucher. Species descriptions from previous research were evaluated with the newest taxonomic concepts and compared with the current research. Populations were delimited by creating a working voucher flora of morphological operational taxonomic units, gathering a range of measurements of population morphological features, and comparing them to species descriptions in the taxonomic literature as well as voucher floras developed within the Manoylov Phycology lab [20,21,22,23,24,25,26]. Data from the archived samples were collected from enumerating an archived permanent slide within the Georgia College & State University Museum of Natural History and used as historical references for collections from Tobler Creek from 2011. Slides and materials from this research are deposited in the publicly available algal collection at the Georgia College & State University Museum of Natural History.
2.5. Ecological Indices and Analyses
To analyze the community structure, the following ecological indices were calculated: species richness (SR), species relative abundances (RA), Shannon–Wiener diversity index (H’), maximum diversity (H’max), Simpson’s diversity (D), inverse Simpson’s (1/D), and species evenness (J). The data were recorded using Microsoft Excel and calculations for SR, H’max, RA, and J were calculated using Microsoft Excel, as was the chi-squared analysis. Diversity indices (H’, D, and 1/D) were calculated using the vegan: Community Ecology Package [27]. Additionally, two diatom matrices were applied: the trophic diatom index (TDI) and the multi-metric index (MMI) described by Kelly and Whitton 1995 and Carlisle et al., 2022, respectively [6,14]. The TDI calculations were completed via Microsoft Excel whilst the MMI calculations were completed via the R Shiny Application [14]. To analyze statistical differences between Tobler Creek in 2011 and 2022, chi-squared analyses were conducted, as one representative sample from 2011 (expected value) was compared to the triplicate values of the February and April 2022 values collected (observed values). In order to detect significant differences between low-impact streams in 2022 (Tobler Creek and Murder Creek), unpaired t-tests were calculated (between-stream variation). Seasonal analysis within-stream differences were detected using paired t-tests (February 2022 versus April 2022 triplicates). Both paired and unpaired t-tests were conducted using the rstatix package in R: A language and environment for statistical computing [28]. Graphs were generated using the ggplot2 and ggpubr packages [29,30].
3. Results
3.1. Nutrient Data
A reduction in nitrate-nitrogen was documented from 0.36 ppm to less than or equal to 0.06 and 0.19 ppm for February and April 2022, respectively, thus meeting the reference criteria for the region. The total phosphorus in 2011 exceeded the reference criteria of 0.04 ppm, but phosphorus conformed to the regional criteria for both sampling periods in 2022. Murder Creek met the reference criteria during both sampling periods in 2022 (Table 1).

Table 1.
Historic and current sampling site locations and nutrient data; values = mean ± standard error; n = 3 for all nutrient analyses.
Tobler Creek had a silty benthos and Murder Creek had a rocky bottom substrate. The physicochemical parameters showed slightly acidic pH at both sites, high levels of dissolved oxygen, and varying levels of water temperature based on the season (Table 2). Low levels of mineral/chemical contents were detected within all samples (Supplemental Table S1).

Table 2.
Historical * and current physicochemical data for low-impact streams. The values are the mean ± standard error; x means no data available for that year.
3.2. Community Metrics
Live whole community enumerations from the preserved samples showed that live diatoms with physiologically active chloroplasts were dominating the communities (69–97% relative abundance) followed by Chlorophyta and Euglenophyta representatives. The diatom community voucher images are given in Plates S1–S7 (Supplemental files). Recounting the archived slide from 2011, Tobler Creek is dominated by Gomphonema parvulum (Kützing) Kützing 1849 (29.00%, Plate S4, Figures S16–S19) and Meridion constrictum Ralfs 1843 (16.83%, Plate S1, Figures S19–S21). Looking at the replicate values (n = 3), in 2022, the community shifts and Tobler Creek is dominated by Pinnularia mesogongyla Ehrenberg 1843 (8.94% ± 2.68%, Plate S3, Figure S11), Gomphonema sp. 1 (7.83% ± 1.48%, Plate S5, Figures S3 and S4) in February and Fragilaroid taxa Staurosirella pinnata (Ehrenberg) D.M. Williams and Round 1988 (8.33% ± 4.17%) and Staurosira construens Ehrenberg 1843 (7.06% ± 2.64%, Plate S1, Figures S22 and S23). The Murder Creek replicates (n = 3), a regional low nutrient impacted stream, were dominated by Navicula cryptocephala Kützing 1844 (6.39% ± 3.69%, Plate S2, Figures S22 and S23) in February. The community shifted in April, with Gomphonema kobayasii Kociolek and Kingston 1999 (8.22% ± 4.02%, Plate S4, Figures S20–S22) and Melosira varians Agardh 1827 (7.94% ± 4.37%, Plate S1, Figures S1 and S2) dominating.
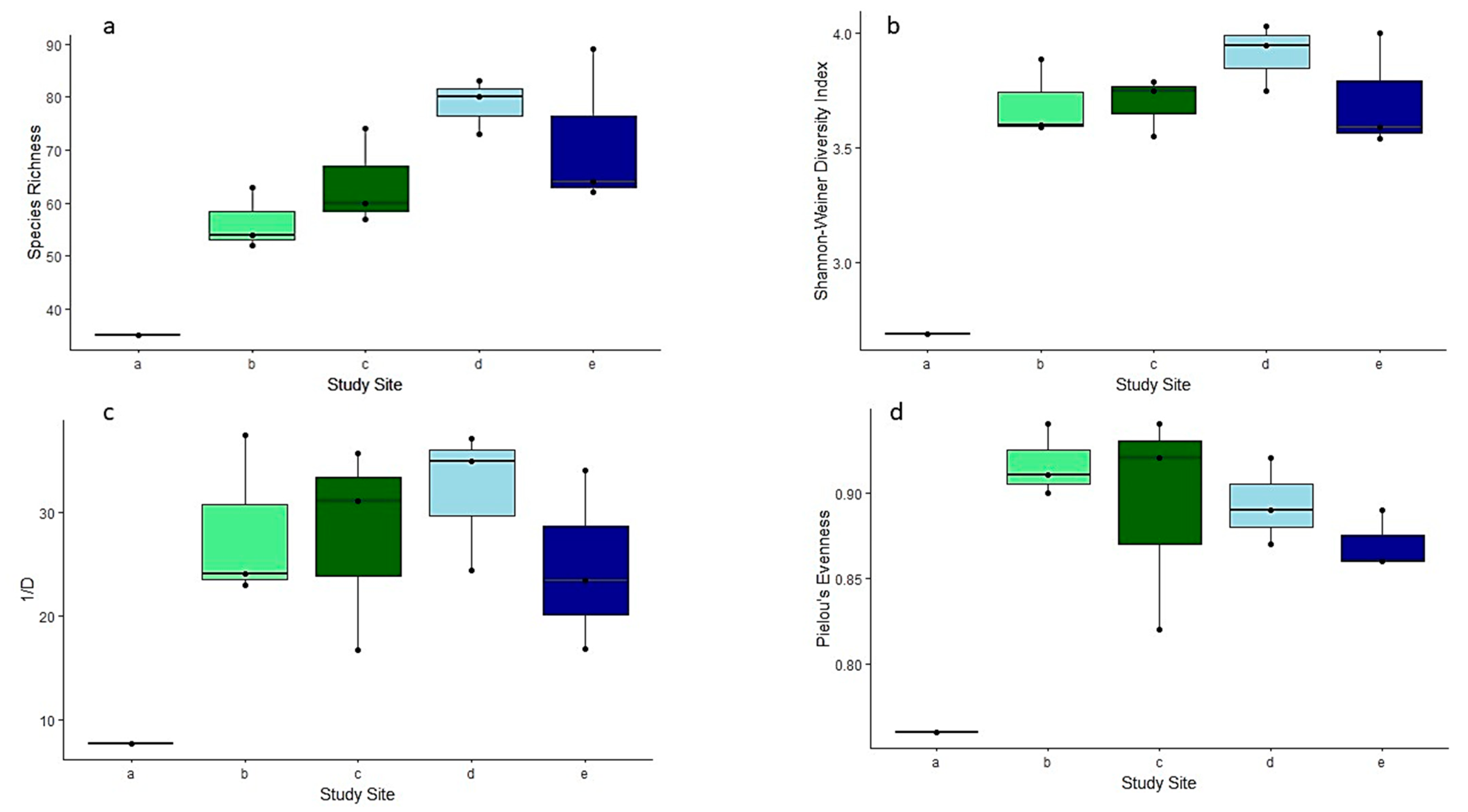
Species richness significantly increased from 2011 to 2022 in Tobler Creek (χ2 = 116.11, df = 5, p < 0.01) as well as Simpson’s inverse diversity (1/D) (χ2 = 364.17, df = 5, p < 0.01) while there was no significant increase in Shannon–Wiener diversity (H’) or evenness (J) (Figure 3).
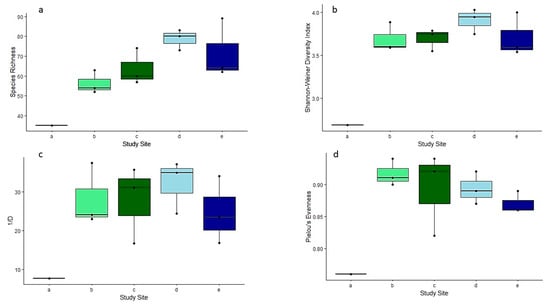
Figure 3.
Boxplots for different community metrics per sample. Values calculated for sampling events. (a) Species richness (SR). (b) Shannon-Weiner diversity index. (c) Simpson’s inverse diversity (1/D). (d) Pielou’s evenness (J). Site IDs provided in Table 1.
Seasonal variation in Tobler Creek in 2022 was not significantly different between February 2022 and April 2022 for SR (t = −0.97, df = 2, p > 0.05). The same held true for Murder Creek (t = 1.00, df = 2, p > 0.05). There was a significant difference in SR between the two study sites in 2022 (t = −2.78, df = 10, p < 0.05). No other community matrices (H’, D, or J) significantly differed in terms of between-stream or within-stream seasonal variation in 2022.
3.3. Diatom Metrics
3.3.1. Multi-Metric Index (MMI)
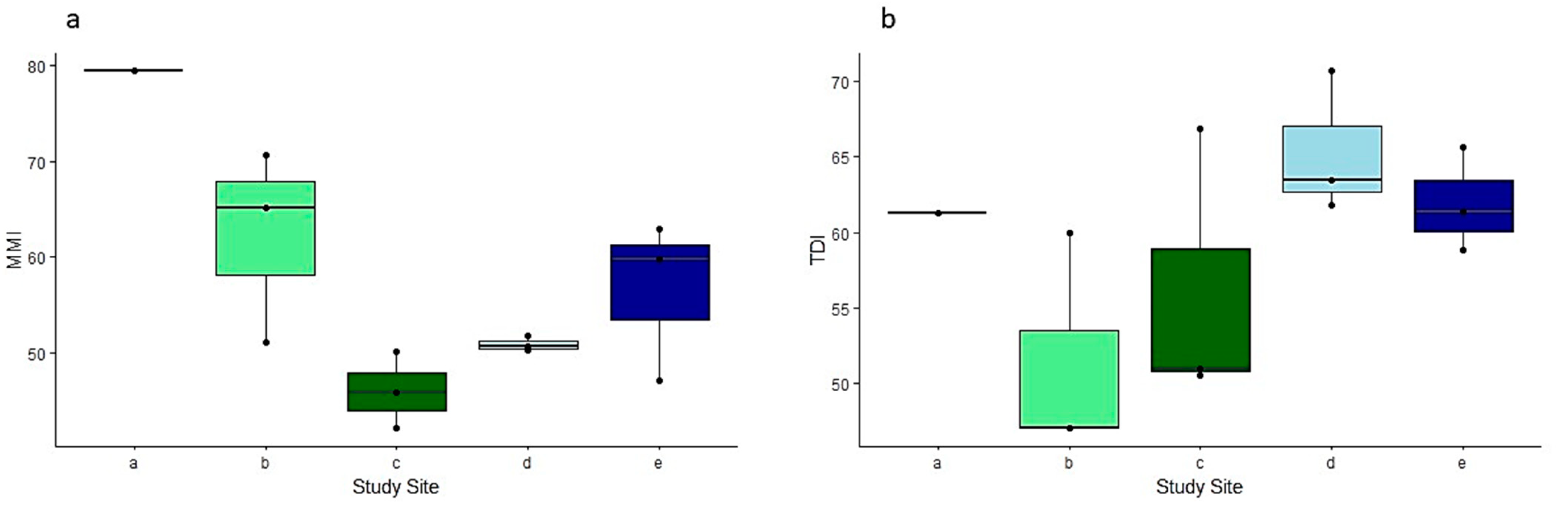
The multi-metric index (MMI) value calculated for Tobler Creek in 2011 is significantly higher than the MMI values calculated for Tobler Creek in 2022, (χ2 = 55.97, df = 5, p < 0.05) (Figure 4a).
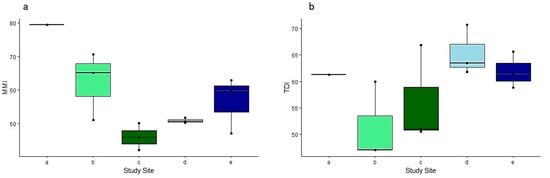
Figure 4.
Boxplots for different diatom metrics per sample. (a) Multi-metric index (MMI). (b) Trophic Diatom Index (TDI). Site IDs provided in Table 1.
There were no significant differences calculated between the MMI values in terms of the between-streams and within-streams in 2022. The lowest MMI was documented for the April 2022 sampling period (Figure 4a).
3.3.2. Trophic Diatom Index (TDI)
There was no significant difference between the TDI values from 2011 to 2022 in Tobler Creek. Additionally, there was no seasonal within-stream variation in 2022 for Tobler Creek or Murder Creek. There was a significant difference in the TDI values between Tobler Creek and Murder Creek (t = −2.69, df = 10, p < 0.05). The TDI values for Tobler Creek were lower for both seasons compared to Murder Creek (Figure 4b).
3.3.3. Sensitive Versus Tolerant Taxa
Surirelloid, naviculoid, and nitzschoid taxa are sediment-tolerant and representatives of those genera that fall within the motile diatom guild [31,32]. The percentage of sediment-tolerant taxa significantly rose in Tobler Creek from 2011 to 2022 (χ2 = 500.96, df = 5, p < 0.01). In terms of within-stream variance in 2022, there was no significant difference between the percentage of sediment-tolerant diatoms, meaning no seasonal variation. However, in 2022, Murder Creek had a significantly higher percentage of sediment-tolerant diatoms within its community than Tobler Creek did (t = −4.67, df = 10, p = 0.0009).
4. Discussion
A major goal of this study is to find the implications of the impact of nutrient recovery on stream ecosystems. In the 1900s, Tobler Creek’s watershed comprised heavy agricultural land with nearly no natural land coverage. No baseline nutrients nor algal samples were taken during this time period. Tobler Creek was impacted by nutrient run-off based on eye-witnesses’ documented accounts in Milledgeville claiming that algal blooms would frequently occur in the pond (hydrologically related to Tobler Creek [17]) within the watershed [11].
Baseline nutrients were recorded in 2011, 31 years after the termination of agricultural use. Given the 31-year recovery, the nutrient criteria for Tobler Creek were not met. While not quantified, the land use has additionally shifted into open natural meadows and forests harvested for wood as indicated by the landscapes surrounding the stream during and after 2011. In 2022, the nutrient criteria were met. It took more than 40 years for a significant decrease in nitrogen.
Low algal community similarity between Tobler Creek in 2011 and 2022 implied that the community significantly shifted toward an improvement in the water quality conditions. In 2011, Tobler Creek was dominated by a few taxa, for example Meridion constrictum, an early-colonizer, and Gomphonema parvulum, a high-nutrient taxon [6,26]. Gomphonema parvulum likely outcompeted the other species due to it being more tolerant to trophic pollution [6]. Simpson’s inverse diversity between Tobler Creek was significantly higher in 2022, which is indicative of there no longer being high dominance of a few taxa. In comparison to Murder Creek, Tobler Creek in 2022 did have significantly fewer species; however, there was no significant difference in diversity between the two sites. Higher species richness may be driven by slightly higher nutrient concentrations in Murder Creek or by stream order [33].
The diatom-specific metrics provide more robust information about the health of the stream ecosystems. Tobler Creek provided interesting outcomes which were not detected by basic ecological indices alone. The multi-metric indices showed that Tobler Creek had lower water quality in 2022 compared to 2011, which is the opposite of what is expected by long-term recovery. Additionally, most of the replicate values still fall below the 25th percentile of regional MMI values, indicating that the stream is still biologically impaired. The trophic diatom index was slightly higher in Tobler Creek in 2011, although not enough to detect a significant difference, which could be attributed to the nitrate-nitrogen but not the phosphorus meeting the reference criteria. In comparison to Murder Creek, Tobler Creek in 2022 had similar MMI values but significantly lower TDI values, which reflects the higher nutrient levels measured in Murder Creek. Again, Murder Creek had an even higher proportion of sediment-tolerant diatoms than Tobler Creek did. Preliminary analyses of these streams found the same trends [34]. With a higher number of taxa identified and confirmed at the species level, these conclusions are confirmed here. Sedimentation rates were not analyzed within the context of this study, but their obvious negative impact (such as decreased light availability) on the diatom communities is reflected.
Moving forward, the findings from this study have implications for the EPA’s goal of protecting and restoring ecosystems [2]. First, this research informs us that recovery is a long-term process, which could take decades to complete if no additional restoration efforts are made. Additional restoration efforts may speed up the recovery process but can be extremely costly depending on the scale of the effort [35]. In this study, a 42-year recovery period was required to recover the base trophic microbial community. Recovery could possibly be longer for organisms with longer generation times [36]. One likely explanation can be the propensity of phosphorus to bind to clays, the main substrate of Tobler Creek benthos, leading to long-term retention of higher-than-accepted phosphorus levels [8]. Nitrate-nitrogen does not readily bind to clays in the same way [7]. Additionally, re-establishing biodiversity once it is decreased or lost will be happening under new conditions. Fossil records suggest that recovery from the total catastrophe of ecosystems can require millions to tens of millions of years, and one of the suggestions for protecting biodiversity is to protect key habitats or biodiverse “hotspots” [37]. However, this study shows that it still comes at a cost, as the study sites chosen were low-impact sites and yet faced the consequences of anthropogenic effects degrading the habitat and altering the diatom community composition. We suggest that more research on diatom communities in the context of recovery be conducted because of the important bottom-up processes they regulate. Additionally, more research needs to be carried out on entire food web energetics, seeing that 1. macroinvertebrate recovery has never been documented in macroinvertebrates in streams with decades-long recovery and 2. macroinvertebrates play a significant role in top-down control in algal communities [38].
5. Conclusions
This study provides evidence that recovering impacted streams is a process that can take decades, or longer, to complete and is very nuanced. Despite a 31-year recovery period, Tobler Creek did not meet the reference criteria for nutrients. The diatom community reflects this outcome by being dominated by a high-nutrient taxon. With an additional 11-year recovery period, we see nutrients finally meeting the EPA’s reference criteria for the ecoregion. However, degradation shifts from being nutrient-driven to sedimentation-driven. This is likely due to logging taking place in the area, as documented through historical aerial images [39]. Despite Tobler Creek being on the site of a historical national landmark and receiving little anthropogenic influence, the recovery process has been long, and algae have been exposed to other negative impacts.
When compared to Murder Creek, another low-impact site, high sedimentation rates affected the diatom community as well. Murder Creek meets the reference criteria but was not classified as a reference stream for the State of Georgia due to it exceeding fecal coliform measurements [40]. This study shows that a more holistic approach, beyond just monitoring nutrients-loading, is needed for the protection of sensitive species and conserving stream microbial biodiversity.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/phycology3020019/s1. Plates S1–S7: Voucher flora images; Table S1: Chemical values detected in the samples. Values = mean ± standard error. N = 3 for all. * represents samples below detectable limits.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.B. and K.M.M.; methodology, S.B. and K.M.M.; software, K.M.M.; validation, K.M.M.; formal analysis, S.B.; investigation, S.B.; resources, K.M.M.; data curation, K.M.M.; writing—original draft preparation, S.B.; writing—review and editing, S.B., K.M.M.; visualization, S.B.; supervision, K.M.M.; project administration, K.M.M.; funding acquisition, K.M.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by a Georgia Power Endowed Professorship and Watershed Protection Branch, Environmental Protection Division, Georgia Department of Natural Resources, Grant Number 58 6002054 to KMM as well as the Paul C. Silva grant provided by the International Phycological Society.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the editor for the invitation to submit the manuscript and the three anonymous reviewers for their helpful suggestions. We would like to thank Anna Agi for helping with the field collections and Katie Johnson for her valuable suggestions and collaboration. We are thankful to Mary Skopec and the Friends of Lakeside at Iowa Lakeside Laboratory for awarding a visiting research scholarship to S.B. We would also like to thank Matt Davis, the Director of Historic Museums at GC&SU, for providing historical information and images of Andalusia Farms. This work was part of the first author’s master’s graduate research at the Department of Biological and Environmental Sciences and the Graduate School at Georgia College & State University.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Davies, S.; Jackson, S. The biological condition gradient: A descriptive model for interpreting change in aquatic ecosystems. Freshw. Bioassess. 2006, 16, 1251–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summary of the Clean Water Act. Available online: https://19january2021snapshot.epa.gov/laws-regulations/summary-clean-water-act_.html#:~:text=33%20U.S.C.%20%C2%A71251%20et%20seq.%20%281972%29%20The%20Clean,States%20and%20regulating%20quality%20standards%20for%20surface%20waters (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Karr, J.; Dudley, D. Ecological perspective on water quality goals. Environ. Manag. 1981, 5, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land Use, Land Value, & Tenure. Available online: https://www.ers.usda.gov/topics/farm-economy/land-use-land-value-tenure/ (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Paerl, H.; Xu, H. Protecting global aquatic resources from the mountains to the sea: Growing need for dual nutrient (N and P) input controls along the freshwater-to-marine continuum. Sci. Bull. 2023, 68, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, M.G.; Whitton, B.A. The Trophic Diatom Index: A new index for monitoring eutrophication in rivers. J. Appl. Phycol. 1995, 7, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatch, D.; Goulding, K.; Murphy, D. Nitrogen. In Agriculture, Hydrology, and Water Quality; Haygarth, P.M., Jarvis, S.C., Eds.; CABI Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 7–28. [Google Scholar]
- Lienweber, P.; Turner, B.; Meissner, R. Phosphorus. In Agriculture, Hydrology, and Water Quality; Haygarth, P.M., Jarvis, S.C., Eds.; CABI Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 29–56. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Rivers and Streams in Nutrient Ecoregion IX. In Ambient Water Quality Criteria Recommendations; EPA 822-B-00-019; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- USDA. Federal Noxious Weed List; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. Available online: https://www.aphis.usda.gov/plant_health/plant_pest_info/weeds/downloads/weedlist.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- USEPA. Monitoring and Responding to Cyanobacteria and Cyanotoxins in Recreational Waters; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, 2022.
- Haram, B.; Wilde, S.; Chamberlain, M.; Boyd, K. Vacuolar myelinopathy: Waterbird risk on a southeastern impoundment co-infested with Hydrilla verticillata and Aetokthonos hydrillicola. Biol. Invasions 2020, 22, 2651–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brienliner, S.; Phillips, T.; Haram, B.; Mares, J.; Yerena, J.; Hrouzek, P.; Sobotka, R.; Henderson, W.M.; Schmieder, P.; Williams, S.; et al. Hunting the eagle killer: A cyanobacterial neurotoxin causes vacuolar myelinopathy. Science 2021, 371, 1335. [Google Scholar]
- Carlisle, D.; Spaulding, S.; Tyree, M.; Schulte, N.; Lee, S.; Mitchell, R.; Pollard, A. A web-based tool for assessing the condition of benthic diatom assemblages in streams and rivers in conterminous United States. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 135, 108513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, J.; Pan, Y. Assessing environmental conditions in rivers and streams with diatoms. In The Diatoms: Applications for the Environmental and Earth Sciences, 2nd ed.; Smol, J., Stoermer, E., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010; pp. 57–85. [Google Scholar]
- Andalusia Farm, Home to Flannery O’Connor, Designated as a National Historic Landmark. Office of Communications. Available online: https://www.nps.gov/orgs/1207/andalusia-farm-nhl-designation.htm (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Moseley, R.; Manoylov, K. Diatom community composition from low human impact areas in southeast U.S. Ga. J. Sci. 2012, 70, 123–143. [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson, J.; Bahls, L. Periphyton Protocols. In Rapid Bioassessment Protocols for Use in Wadeable Streams and Rivers: Periphyton, Benthic Macroinvertebrates, and Fish, 2nd ed.; EPA 841-B-99-002; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. EPA. Method 200.7: Determination of Metals and Trace Elements in Water and Wastes by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Atomic Emission Spectrometry, Revision 4.4; U.S. EPA: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1994.
- Krammer, K.; Lange-Bertalot, H. Bacillariophyceae. 1. Teil: Naviculaceae. In Süsswasserflora von Mitteleuropa; Band 2/1; Ettl, H., Gerloff, J., Heynig, H., Mollenhauer, D., Eds.; Gustav Fisher Verlag: Jena, Germany, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Krammer, K.; Lange-Bertalot, H. Bacillariophyceae. 2. Teil: Bacillariaceae, Epithemiaceae, Surirellaceae. In Süsswasserflora von Mitteleuropa; Ettl, H., Gerloff, J., Heynig, H., Mollenhauer, D., Eds.; Gustav Fisher Verlag: Jena, Germany, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Krammer, K.; Lange-Bertalot, H. Bacillariophyceae. 3. Teil: Centrales, Fragilariaceae, Eunotiaceae. In Süsswasserflora von Mitteleuropa; Ettl, H., Gerloff, J., Heynig, H., Mollenhauer, D., Eds.; Gustav Fisher Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Krammer, K.; Lange-Bertalot, H. Bacillariophyceae 4. Teil: Achnanthaceae, Kritische Erganzungen zu Navicula (Lineolatae), Gomphonema Gesamtliteraturverzeichnis Teil 1-4. In Süsswasserflora von Mitteleuropa; Ettl, H., Gerloff, J., Heynig, H., Mollenhauer, D., Eds.; Spektrum Akademischer Verlad Heidelberg: Heidelberg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, I.W.; Esposito, R.M.; Tyree, M.; Spaulding, S. A diatom voucher flora from selected southeast rivers (USA). Phytotaxa 2017, 332, 101–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.M. Diatom Voucher Flora and Comparison of Collection Methods for Biodiversity Hotspot Upper Three Runs Creek. Master’s Thesis, Georgia College & State University, Milledgeville, GA, USA, 2020; p. 7. Available online: https://kb.gcsu.edu/biology/7 (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Lange-Bertalot, H.; Hoffman, G.; Werum, M.; Cantonati, M. Freshwater Benthic Diatoms of Central Europe over 800 Common Species Used in Ecological Assessment; Cantonati, M., Kelly, M., Lange-Bertalot, H., Eds.; Koeltz Botanical Books: Oberreifenberg, Germany, 2017; p. 942. [Google Scholar]
- Okansen, J.; Simpson, J.; Blanchet, F.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.; O’Hara, R.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.; Szoecs, E.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package Version 2.6-4. 2022. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 17 March 2023).
- Kassambara, A. Rstatix: Pipe-Friendly Framework for Basic Statistical Tests. R Package Version 0.7.2. 2023. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=rstatix (accessed on 19 March 2023).
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis. 2016. Available online: https://ggplot2.tidyverse.org (accessed on 17 February 2023).
- Kassambara, A. Ggpubr: ‘Ggplot2’ Based Publication Ready Plots. R Package Version 0.6.0. 2023. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=ggpubr (accessed on 17 February 2023).
- Bahls, L. Periphyton Bioassessment Method for Montana Streams; Water Quality Bureau: Helena, MT, USA, 1993; p. 23. [Google Scholar]
- Poulíčková, A.; Manoylov, K. Ecology of freshwater diatoms—Current trends and applications. In Diatoms: Fundamentals and Applications; Seckbach, J., Gordon, R., Eds.; Scrivener Publishing LLC: Beverly, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 289–309. [Google Scholar]
- Vannote, R.; Minshall, G.W.; Cummins, K.W.; Sedell, J.R.; Cushing, C.E. The river continuum concept. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci 1980, 37, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.; Manoylov, K. Comparison of diatom communities in low-impact streams in middle Georgia. Ga. J. Sci. 2023, 81, 41. [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman, G.J. The cost of Clean Water in the Delaware River Basin (USA). Water 2018, 10, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, J.S.; Benfield, E.F.; Bolstad, P.V.; Helfman, G.S.; Jones, E.B.D., III. Stream biodiversity: The ghost of land use past. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 14843–14847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novecek, M.; Cleland, E. The current biodiversity extinction event: Scenarios for mitigation and recovery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 5466–5470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colón-Gaud, C.; Whiles, M.R.; Brenes, R.; Kilham, S.S.; Lips, K.R.; Pringle, C.M.; Connelly, S.; Peterson, S.D. Potential functional redundancy and resource facilitation between tadpoles and insect grazers in tropical headwater streams. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 2077–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Google Earth Pro Version 7.3.6. 33°07′16.38″ N 83°16′03.86″ W elev 378 ft. Available online: https://earth.google.com/web/search/33.121218,+-83.267738/@33.121218,-83.267738,115.33991566a,867.63508117d,35y,0h,45t,0r/data=ClkaLxIpGeDXSBKEj0BAIV95kJ4i0VTAKhUzMy4xMjEyMTgsIC04My4yNjc3MzgYAiABIiYKJAkoDn_YuK43QBElDn_YuK43wBlmwBWh57NFQCEzn_asen1PwCgC (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- GAEPD. 2008 Integrated 305(b)/303(d) List. Streams—Supporting Designated Uses. Georgia Environmental Protection Division. Available online: https://epd.georgia.gov/https%3A/epd.georgia.gov/assessment/water-quality-georgia (accessed on 20 February 2023).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).