Application of Remote Sensing for the Detection and Monitoring of Microplastics in the Coastal Zone of the Colombian Caribbean
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
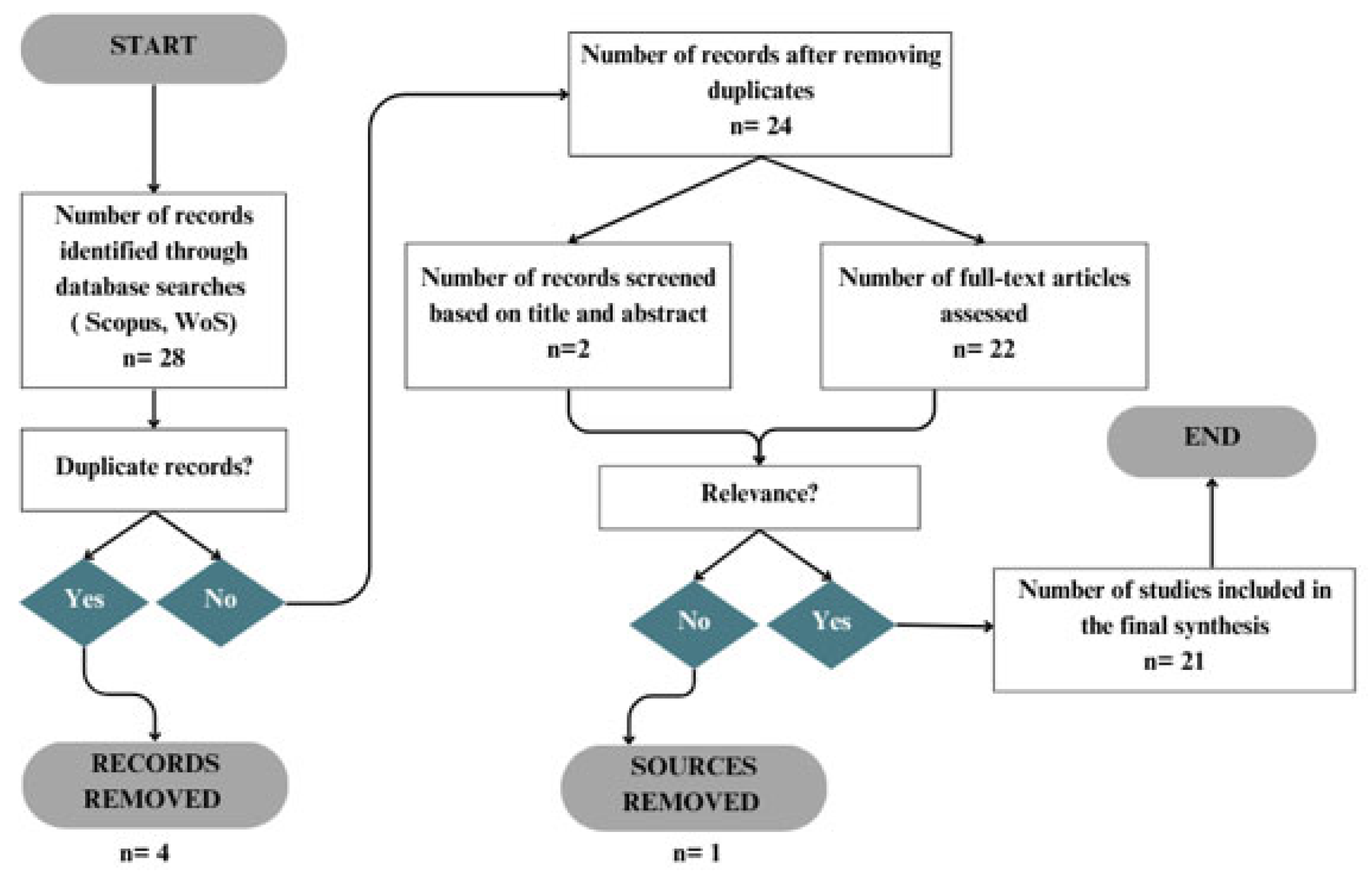
2.1. Literature Review
2.2. Microplastic Field Data Collection, Quantification, and Characterization
2.3. Sentinel-2 Satellite Image Processing
2.4. Environmental Impact Assessment of Microplastic Pollution
3. Results
3.1. Literature Review
Microplastic Detection Techniques
3.2. Field Data
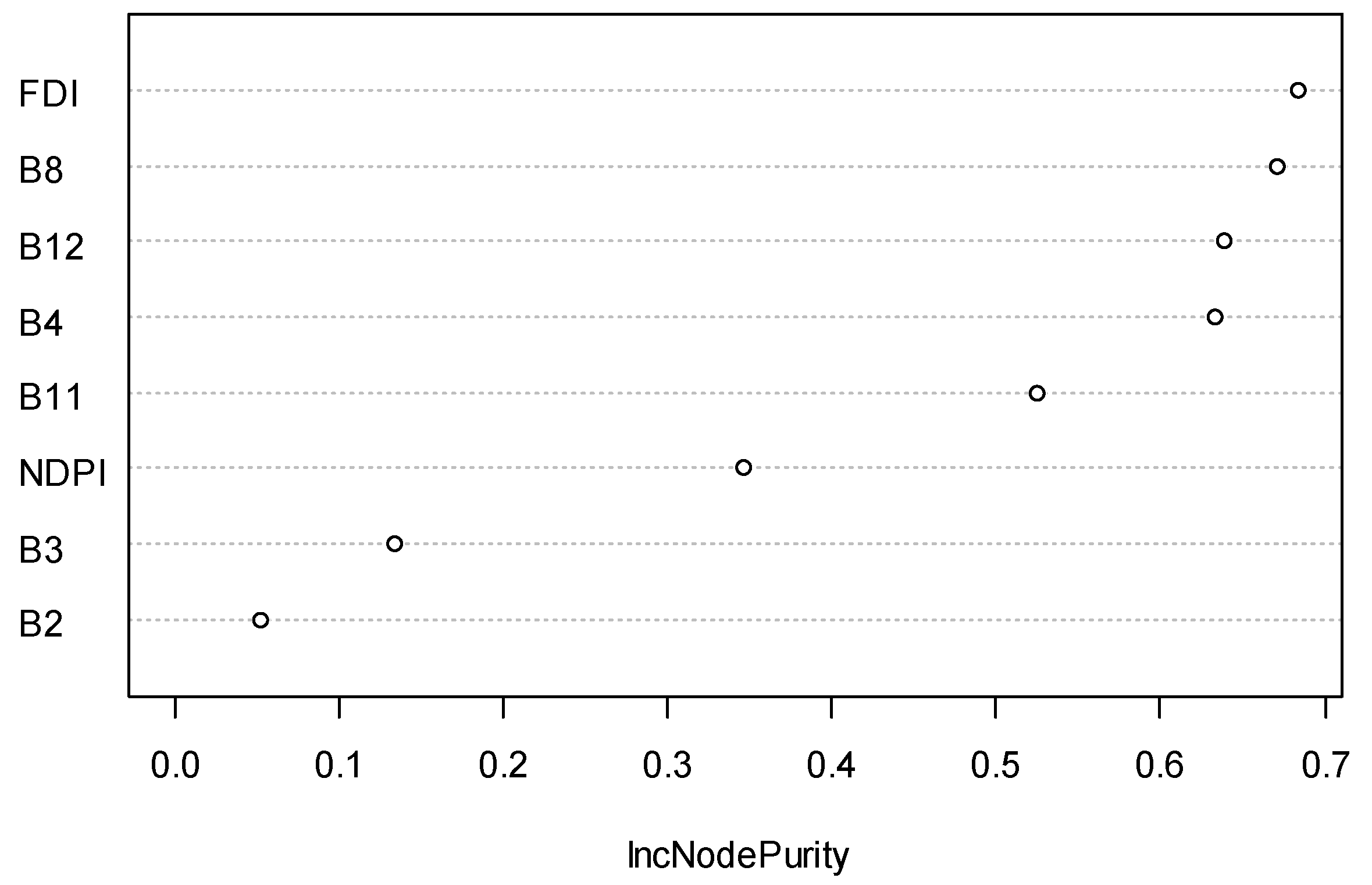
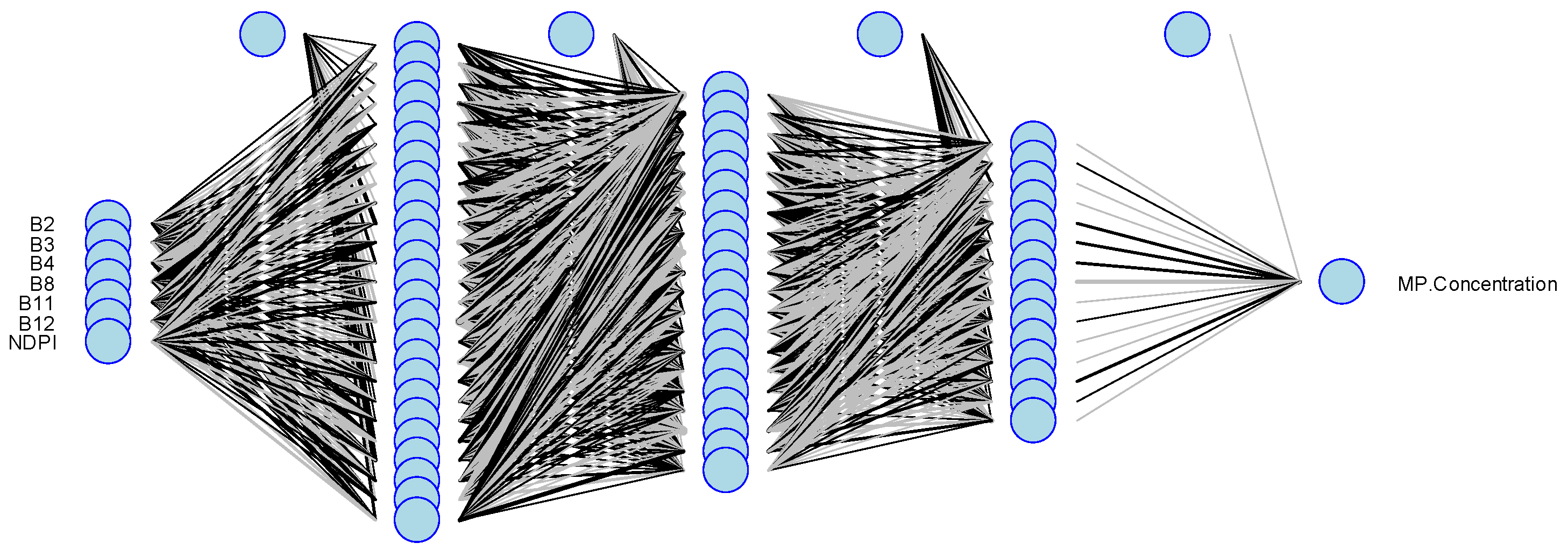
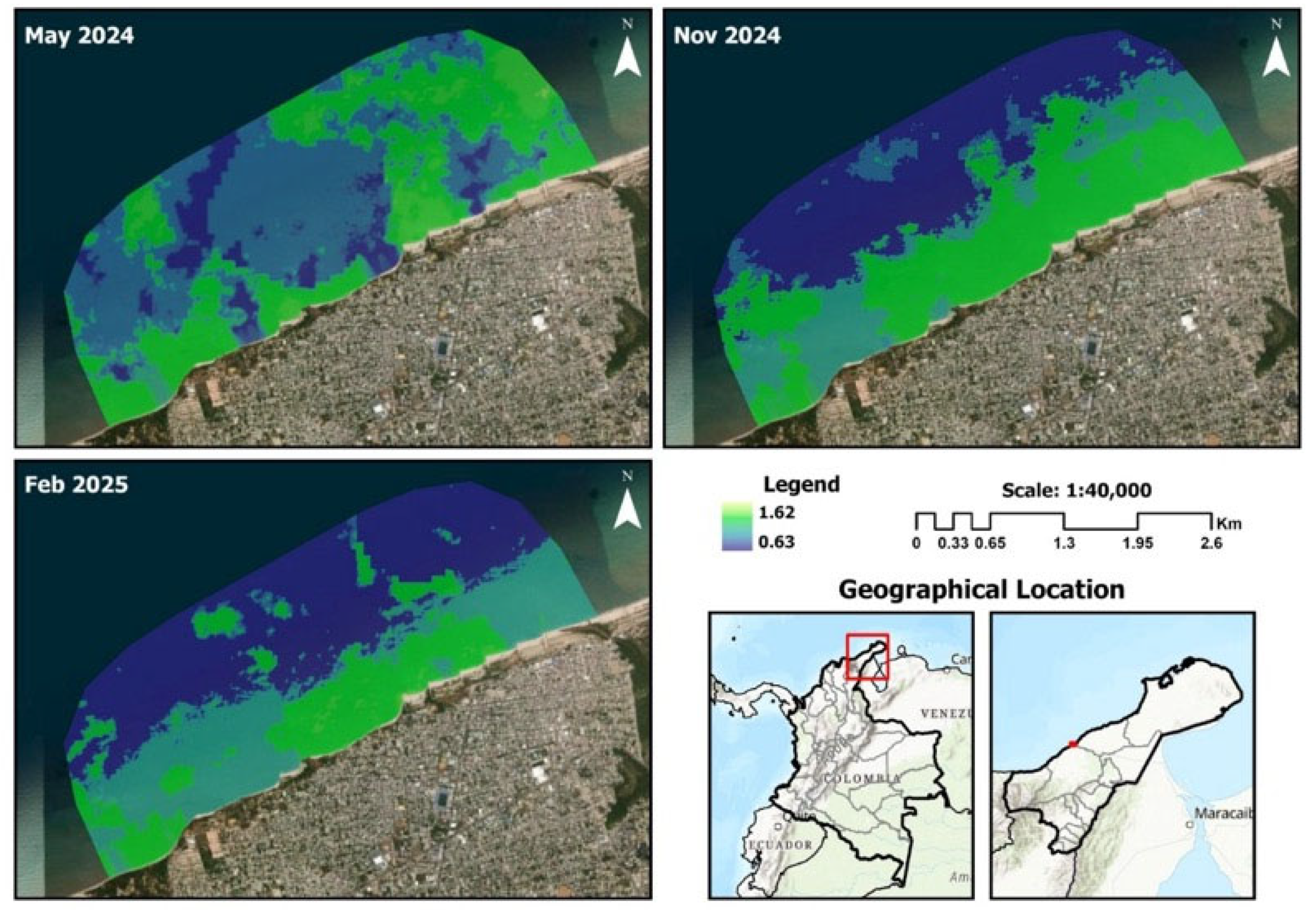
3.3. Satellite Image Processing
3.4. Environmental Risk Maps
4. Discussion
4.1. Literature Review
4.2. Field Data
4.3. Satellite Image Processing
4.4. Environmental Risk Maps
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiao, S.; Cui, Y.; Brahney, J.; Mahowald, N.M.; Li, Q. Long distance atmospheric transport of microplastic fibres influenced by their shapes. Nat. Geosci. 2023, 16, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarahmadi, A.; Heidari, S.; Sepahvand, P.; Afkhami, H.; Kheradjoo, H. Microplastics and environmental effects: Investigating the effects of microplastics on aquatic habitats and their impact on human health. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1411389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro-Núñez, A.; Astorga, D.; Cáceres-Farías, L.; Bastidas, L.; Soto Villegas, C.; Macay, K.; Christensen, J.H. Microplastic pollution in seawater and marine organisms across the Tropical Eastern Pacific and Galápagos. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo Montero, A.A.; Costa-Redondo, L.C.; Vasco-Echeverri, O.; Arana, V.A. Microplastic pollution in coastal areas of Colombia: Review. Mar. Environ. Res. 2023, 190, 106027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, P.; Xiao, J.; Liu, H.; Niu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Ma, Y. An inversion model of microplastics abundance based on satellite remote sensing: A case study in the Bohai Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 909, 168537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biermann, L.; Clewley, D.; Martinez-Vicente, V.; Topouzelis, K. Finding plastic patches in coastal waters using optical satellite data. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, P.; Shi, Y.; Sheerin, E.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, L.; Xiao, L.; Hill, C.; Gordon, C.; Ruether, M.; et al. Stress-induced phase separation in plastics drives the release of amorphous polymer micropollutants into water. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.T.d.S.; Oliveira, R.C.d.; Siegle, E.; Ribeiro, M.C.H.; Esteves, L.S.; Kuznetsova, M.; Dipold, J.; Freitas, A.Z.d.; Wetter, N.U. Microplastic Deposits Prediction on Urban Sandy Beaches: Integrating Remote Sensing, GNSS Positioning, µ-Raman Spectroscopy, and Machine Learning Models. Microplastics 2025, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Curbelo, M.Á.; Cruz-Pérez, A.; Gutiérrez-Bouzán, C.; López-Mesas, M. Assessing microplastic pollution along the Caribbean coast of La Guajira, Colombia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 212, 117511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcés-Ordóñez, O.; Espinosa, L.F.; Costa Muniz, M.; Salles Pereira, L.B.; Meigikos Dos Anjos, R. Abundance, distribution, and characteristics of microplastics in coastal surface waters of the Colombian Caribbean and Pacific. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 43431–43442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- INVEMAR. Informe del Estado de los Ambientes y Recursos Marinos y Costeros en Colombia, 2023; Serie Public. Periód. No. 3; INVEMAR: Santa Marta, Colombia; 242p.
- Gutiérrez Álvarez, N.; Arroyo De La Ossa, M.; Carrasco Aquino, R.J. Effects of climate change: An analysis in the Wayúu territory north of La Guajira, Colombia. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Agríc. 2022, 13, 893–904. [Google Scholar]
- Ulloa, A. The rights of the Wayúu people and water in the context of mining in La Guajira, Colombia: Demands of relational water justice. Hum. Geogr. 2020, 13, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pabortsava, K.; Lampitt, R.S. High concentrations of plastic hidden beneath the surface of the Atlantic Ocean. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandt, J.; Bittrich, L.; Fischer, F.; Kanaki, E.; Tagg, A.; Lenz, R.; Labrenz, M.; Brandes, E.; Fischer, D.; Eichhorn, K.J. High-throughput analyses of microplastic samples using Fourier transform infrared and Raman spectrometry. Appl. Spectrosc. 2020, 74, 1185–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannigrahi, S.; Basu, B.; Basu, A.S.; Pilla, F. Detection of marine floating plastic using Sentinel-2 imagery and machine learning models. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.03694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqas, M.; Wong, M.S.; Stocchino, A.; Abbas, S.; Hafeez, S.; Zhu, R. Marine plastic pollution detection and identification by using remote sensing-meta analysis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 197, 115746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutler, A.; Cutler, D.R.; Stevens, J.R. Random forests. In Ensemble Machine Learning: Methods and Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2012; pp. 157–175. [Google Scholar]
- Palczewska, A.; Palczewski, J.; Marchese Robinson, R.; Neagu, D. Interpreting random forest classification models using a feature contribution method. In Integration of Reusable Systems; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 193–218. [Google Scholar]
- Speiser, J.L.; Miller, M.E.; Tooze, J.; Ip, E. A comparison of random forest variable selection methods for classification prediction modeling. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 134, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsch, S.; Guenther, F.; Guenther, M.F. Package ‘neuralnet.’ Training of Neural Networks. R Package 2019, 2, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Krogh, A. What are artificial neural networks? Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 195–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambeck, J.R.; Geyer, R.; Wilcox, C.; Siegler, T.R.; Perryman, M.; Andrady, A.; Narayan, R.; Law, K.L. Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean. Science 2015, 347, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Dai, Y.; Zhou, H.; Sun, Y.; Yu, H.; Dai, Y.; Wang, M.; Ergu, D.; Zhou, P. Using artificial intelligence to rapidly identify microplastics pollution and predict microplastics environmental behaviors. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 474, 134865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Zhang, F.; Yu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Jiang, H. Machine learning: Next promising trend for microplastics study. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 344, 118756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacace, T.; del Coco, M.; Cocca, M.; da Silva Junior, A.G.; Gonçalves, L.M.G.; Carcagnì, P.; Paturzo, M.; Distante, C. Compact holographic imaging and machine learning for microfiber quantification in laundry wastewater. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Microplastic Pollution in the Mediterranean Sea, Naples, Italy, 25–28 September 2022; pp. 157–163. [Google Scholar]
- Molnár, A.D.; Málnás, K.; Bőhm, S.; Gyalai-Korpos, M.; Cserép, M.; Kiss, T. Comparative Analysis of Riverine Plastic Pollution Combining Citizen Science, Remote Sensing and Water Quality Monitoring Techniques. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Yang, C.; Peng, Y.; Yang, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yan, F.; Xing, B.; Ji, R. Lensless shadow microscopy-based shortcut analysis strategy for fast quantification of microplastic fibers released to water. Water Res. 2024, 258, 121758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alboody, A.; Vandenbroucke, N.; Porebski, A.; Sawan, R.; Viudes, F.; Doyen, P.; Amara, R. A new remote hyperspectral imaging system is embedded on an unmanned aquatic drone to detect and identify floating plastic litter using machine learning. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekman, M.B.; Walther, B.; Peter, C.; Gutow, L.; Bergmann, M. Impacts of plastic pollution in the oceans on marine species, biodiversity and ecosystems. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 197, 115746. [Google Scholar]
- Godasiaei, S.H. Predictive modeling of microplastic adsorption in aquatic environments using advanced machine learning models. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 958, 178015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latwal, M.; Arora, S.; Murthy, K.S.R. Data driven AI (artificial intelligence) detection furnish economic pathways for microplastics. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2024, 264, 104365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munagala, N.S.; Kumar, V.; Srividhya, S.; Usha, G.; Jeyalakshmi, R. Micro-Objects Classification for Microplastic Pollution Detection using Holographic Images. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communication and Applied Informatics (ACCAI), Chennai, India, 9–10 May 2024; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Tirkey, A.; Upadhyay, L.S.B. Discrete sensors to detect microplastics in environment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 21, 2357–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, M.; Crump, P.; Niven, S.; Teuten, E.; Tonkin, A.; Galloway, T.; Thompson, R. Accumulation of Microplastic on Shorelines Worldwide: Sources and Sinks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9175–9179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, B.K.; Jeong, H.H.; Ju, M.J.; Ko, U.; Dae, K.H.; Kim, H.J.; Cho, C.R.; Soh, H.Y.; Ishibashi, Y.; Cho, H.S. Baseline study on microplastic distribution in the open surface waters of the Korean Southwest Sea. Water 2023, 15, 2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, G.; Poveda, G.; Roldán, P.; Andrade, C. Patrones de variabilidad de las temperaturas superficiales del mar en la costa Caribe colombiana. Rev. Acad. Colomb. Cienc. Exact. Fís. Nat. 2006, 30, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueda-Roa, D.; Muller-Karger, F.E. The southern Caribbean upwelling system: Sea surface temperature, wind forcing and chlorophyll concentration patterns. Deep-Sea Res. Part I 2013, 78, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez Leones, G.A.; Correa Ramírez, M.A.; Hormazabal Fritz, S.E. Análisis de la variabilidad espacio-temporal del sistema de surgencia de La Guajira en el dominio espacio-frecuencia, empleando el MTM-SVD. Bol. Cient. CIOH 2015, 33, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, M.; Hormazabal, S. MultiTaper Method–Singular Value Decomposition (MTM-SVD): Variabilidad espacio-frecuencia de las fluctuaciones del nivel del mar en el Pacífico suroriental. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2012, 40, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Lavers, J.L.; Bond, A.L. Exceptional and rapid accumulation of anthropogenic debris on one of the world’s most remote and pristine islands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 6052–6055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Technique | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Satellite imagery (Sentinel-2, MODIS) | Use of multispectral imaging to identify areas of microplastic accumulation | Wide coverage, free data access | Low spatial resolution | [25,33] |
| Hyperspectral spectroscopy | Differentiation of microplastics by detailed spectral analysis | High identification accuracy | High cost, limited access | [32] |
| UAV sensors (drones) | Capture of high-resolution aerial images to analyze the presence of microplastics in surface waters | High image resolution, flexibility in hard-to-reach areas | Lower spatial coverage | [34] |
| AI (neural networks, machine learning) | Automated classification of microplastic particles from satellite or spectroscopic imagery | Adaptability to different data sources, improvements in accuracy | Reliance on large volumes of training data | [25] |
| Method | Average Accuracy | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Satellite imagery + IA | 92% | Wide coverage, automated processing | Limited spatial resolution |
| Hyperspectral spectroscopy | 88% | High identification accuracy | High costs, limited access |
| UAV sensors | 85% | High-resolution images | Low spatial coverage |
| Machine learning algorithms | 90% | Adaptability to different data sources | High-volume data requirements |
| Sampling Point | Average (particles/m3) | Max (particles/m3) | Min (particles/m3) | Average Total Particles | Max Total Particles | Min Total Particles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 (11.55, −72.91) | 1.74 | 1.95 | 1.53 | 224.80 | 252 | 198 |
| P2 (11.56, −72.93) | 0.67 | 0.70 | 0.60 | 76.60 | 81 | 69 |
| P3 (11.57, −72.95) | 0.42 | 0.51 | 0.32 | 59.20 | 72 | 45 |
| P4 (11.58, −72.97) | 0.44 | 0.48 | 0.42 | 52.40 | 57 | 49 |
| Sample | B2 | B3 | B4 | B8 | B11 | B12 | FDI | NDPI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1, Dec 2024 | 1808 | 1782.5 | 2184 | 2241 | 2925 | 2289 | 162.015 | 0.132 |
| P1, Jan 2025 | 1760.5 | 1725.5 | 1986 | 2249 | 2770 | 2194 | 252.446 | 0.105 |
| P1, Feb 2025 | 1847.5 | 1773.5 | 2137.5 | 2235.5 | 2917 | 2405 | 165.255 | 0.133 |
| P1, Mar 2025 | 2027.75 | 2017.5 | 2418 | 2534.75 | 3285.5 | 2729 | 188.197 | 0.129 |
| P1, Ap 2025 | 1774.5 | 1510 | 1345.5 | 1492 | 1478 | 987 | −9.696 | −0.004 |
| P2, Dec 2024 | 1640.5 | 1355 | 867.5 | 860 | 515 | 349.5 | −277.015 | −0.251 |
| P2, Jan 2025 | 1684 | 1546 | 861 | 391.5 | 249 | 183 | −817.921 | −0.222 |
| P2, Feb 2025 | 1676 | 1525 | 814 | 390.5 | 294.5 | 241.5 | −815.178 | −0.14 |
| P2, Mar 2025 | 1928.833 | 1772.833 | 1186.5 | 793.667 | 690.667 | 535 | −698.338 | −0.069 |
| P2, Ap 2025 | 1730.5 | 1452.5 | 943.5 | 705.5 | 618 | 457 | −530.442 | −0.066 |
| P3, Dec 2024 | 1283 | 1059 | 584 | 344 | 729 | 861 | −629.363 | 0.359 |
| P3, Jan 2025 | 1708 | 1448 | 664 | 329 | 220 | 164 | −800.327 | −0.199 |
| P3, Feb 2025 | 1699 | 1447 | 738 | 415 | 338 | 279 | −744.208 | −0.102 |
| P3, Mar 2025 | 1877.5 | 1619.5 | 1013.5 | 742.5 | 624.5 | 478 | −618.792 | −0.086 |
| P3, Ap 2025 | 1686 | 1400 | 851 | 656 | 582 | 440 | −531.724 | −0.06 |
| P4, Dec 2024 | 1245 | 916.5 | 399.5 | 241 | 124 | 85 | −469.842 | −0.32 |
| P4, Jan 2025 | 1724 | 1480.5 | 668.5 | 298.5 | 211 | 161.5 | −852.558 | −0.17 |
| P4, Feb 2025 | 1519 | 1171 | 621 | 404.5 | 272.5 | 185 | −533.334 | −0.195 |
| P4, Mar 2025 | 1785.75 | 1468.25 | 915.75 | 678.5 | 580.5 | 443.25 | −559.374 | −0.078 |
| P4, Ap 2025 | 1735.5 | 1426 | 897 | 721.5 | 629 | 468 | −497.674 | −0.068 |
| Regression Coefficients | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Estimate | Std. Error | t-Value | p-Value |
| B2 | −0.0015354 | 0.0018339 | −0.837 | 0.4301 |
| B3 | 0.0037555 | 0.0032171 | 1.167 | 0.2813 |
| B4 | −0.0041328 | 0.0029710 | −1.391 | 0.2068 |
| B8 | 0.0005345 | 0.0014114 | 0.379 | 0.7162 |
| B11 | 0.0047245 | 0.0022687 | 2.083 | 0.0758 |
| B12 | −0.0035553 | 0.0016744 | −2.123 | 0.0714 |
| NDPI | 0.2002734 | 0.8566249 | 0.234 | 0.8218 |
| ANOVA and Adjusted R2 | ||||
| F Statistic | Degrees of Freedom | p-value | Adjusted R2 | |
| 18.74 | 7 | 7 | 0.0004931 | 0.8987 |
| Model | MAE (particles/m3) | RMSE (particles/m3) | Number of Trees | Number of Neurons per (Hidden) Layer | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear regression | Fitting | 0.217 | 0.320 | NA | NA |
| Prediction | 0.189 | 0.235 | |||
| Random forest | Fitting | 0.122 | 0.166 | 300 | NA |
| Prediction | 0.106 | 0.123 | |||
| ANN | Fitting | 0.041 | 0.068 | NA | (25, 20, 25) |
| Prediction | 0.040 | 0.071 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Torregroza-Espinosa, A.C.; Portnoy, I.; Correa-Solano, R.; Blanco-Álvarez, D.A.; Echeverría-González, A.M.; González-Márquez, L.C. Application of Remote Sensing for the Detection and Monitoring of Microplastics in the Coastal Zone of the Colombian Caribbean. Microplastics 2025, 4, 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4040077
Torregroza-Espinosa AC, Portnoy I, Correa-Solano R, Blanco-Álvarez DA, Echeverría-González AM, González-Márquez LC. Application of Remote Sensing for the Detection and Monitoring of Microplastics in the Coastal Zone of the Colombian Caribbean. Microplastics. 2025; 4(4):77. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4040077
Chicago/Turabian StyleTorregroza-Espinosa, Ana Carolina, Iván Portnoy, Rodney Correa-Solano, David Alejandro Blanco-Álvarez, Ana María Echeverría-González, and Luis Carlos González-Márquez. 2025. "Application of Remote Sensing for the Detection and Monitoring of Microplastics in the Coastal Zone of the Colombian Caribbean" Microplastics 4, no. 4: 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4040077
APA StyleTorregroza-Espinosa, A. C., Portnoy, I., Correa-Solano, R., Blanco-Álvarez, D. A., Echeverría-González, A. M., & González-Márquez, L. C. (2025). Application of Remote Sensing for the Detection and Monitoring of Microplastics in the Coastal Zone of the Colombian Caribbean. Microplastics, 4(4), 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4040077







