The Individual and Combined Effects of Microplastics and Heavy Metals on Marine Organisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Effects of Microplastics on Marine Organisms
3. Effects of Heavy Metals on Marine Organisms
| Heavy Metal | Concentration | Species Name | Effects | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper oxide nanoparticles | 30, 60, 90 and 120 mg/L | Paramecium sp. | Inhibition in the growth of paramecium, especially for 120 mg/L concentration | [67] |
| Selenium nanoparticles | 0.5 mg/kg, 1 mg/kg, 2 mg/kg | Cyprinus carpio | 1 mg/kg concentration of Se can improve fish growth and antioxidant defense system. | [68] |
| Titanium dioxide | 0.1, 0.5, 1, 5, 10, 50 and 100 mg/L | Daphnia magna | Abnormal food intake, which considerably affected growth and reproduction | [69] |
| Cadmium | 2.5 mg/kg | Oreochromis niloticus | Kidney, gill, and other organs were badly affected | [61] |
| Manganese | 4 mg/L, 8 mg/L | Carassius auratus | Enhancement in antioxidant enzyme activity, modification in differential blood cell count. | [52] |
| Copper | 0.84 μM, 0.34 Μm | Carassius auratus | Increment in kidney activities at high concentration | [70] |
| Copper sulfate and zinc chloride | 1, 2, 5 and 10 mg/L | Paramecium aurelia | The average swimming speed dropped to almost half in both media | [71] |
| Copper oxide nanoparticles | 0, 30, 60, 90 and 120 mg/L | Paramecium sp. | Dose-dependent inhibition on cell growth | [67] |
| Chromium | 0, 30, 60, 120, 200 mg/L | Sebastes schlegelii | Significant alteration in antioxidant enzymes | [58] |
| Copper | 100 mg/L | Tetrahyrnena | Intense stimulation found in food vacuoles | [72] |
4. Combined Effect of Microplastic and Heavy Metals on Microorganisms
5. Adsorption Mechanism of Heavy Metals on Microplastics
6. Potential Risk to Human Health
| Metals | Main Sources | Toxic Effects | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arsenic | Arsenical pesticides, natural mineral deposits, ground water and soil, improperly disposed arsenical chemicals, sewage fertilizers, and mining | Weakness and anemia, skin and lung cancer, diabetic problems, neuropathy, gastrointestinal problems, cardiovascular failure, hematopoietic effects, and sometimes acute illness leading to death | [129] |
| Lead | Storage batteries; petrol additives, paint, cable sheathing and cosmetics, mining, pottery, and ceramic dishes | Anemia, high risk of kidney damage, B.P problem, fertility and reproduction problems, nervous/brain system damage. | [132] |
| Mercury | Medical waste, toothpaste, skin cream, vaccines, batteries, volcanoes and oceans, and contaminated fish | Muscle weakness, blindness, mental retardation, impairment of hearing, speech or/and walking, swollen gums, kidneys, and liver, immune system damage, and loss of memory and concentration | [133] |
| Cadmium | Industrial waste, nickel–cadmium batteries, plastic and paint industries, cadmium alloy, welding, and smelting | Bone fracture, diarrhea, nausea, problems in reproduction, stomach aches, shortness of breath, severe kidney, liver, and lung disease | [134] |
| Copper | Mining, smelting, water pipes, copper wires, combustion of fossil fuels and copper sheet metals | Nausea, headache, damage to red blood results, anemia, liver and kidney injury, and sometimes death | [135] |
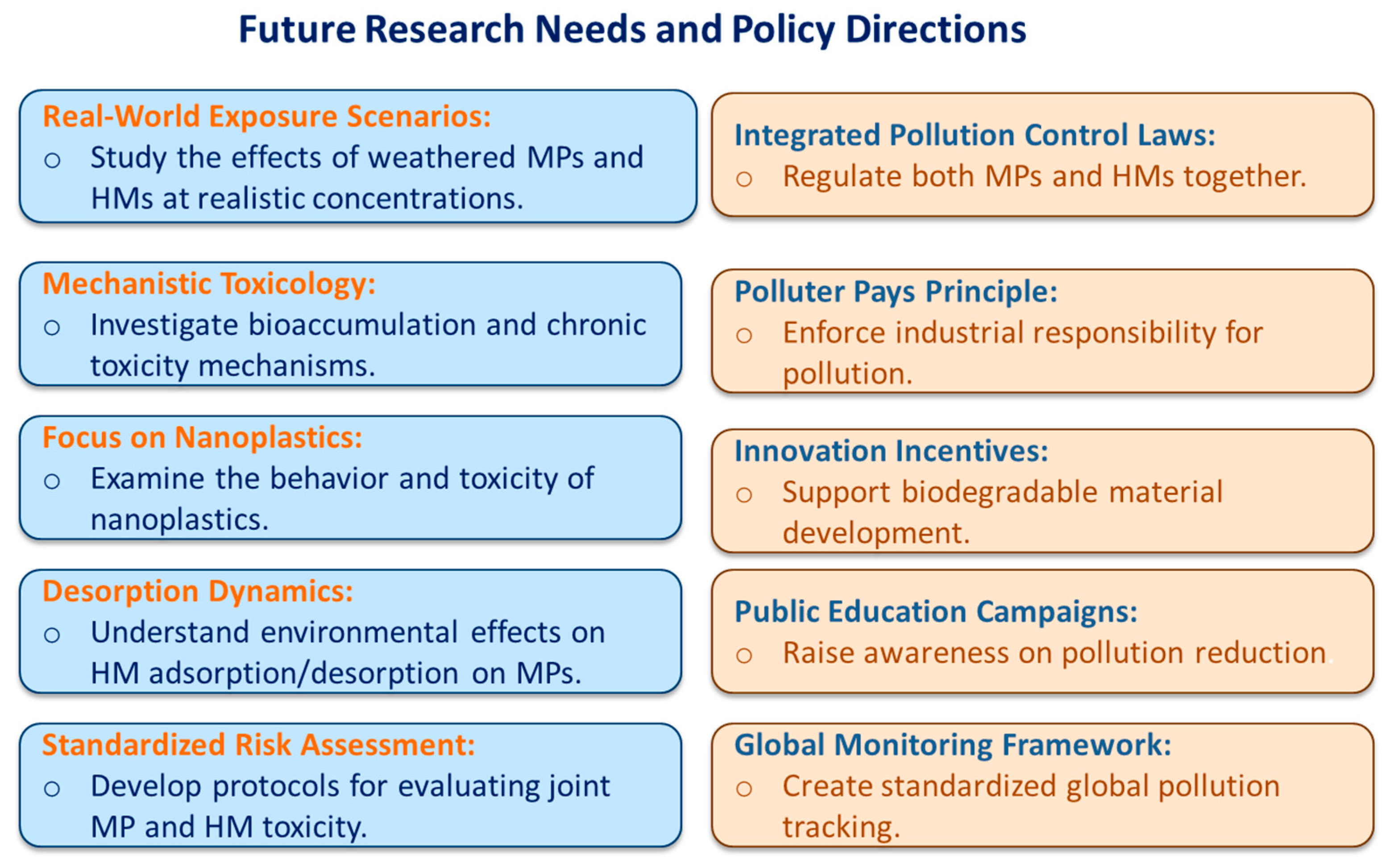
Critical Insights and Research Needs
7. Conclusions and Future Perspective
- Stricter control of industrial effluents.
- Incentives for biodegradable material innovation.
- Improved waste management and recycling systems.
- Public awareness campaigns promoting responsible plastic use.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chae, Y.; An, Y.-J. Current research trends on plastic pollution and ecological impacts on the soil ecosystem: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 240, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enyoh, C.E.; Devi, A.; Kadono, H.; Wang, Q.; Rabin, M.H. The plastic within: Microplastics invading human organs and bodily fluids systems. Environments 2023, 10, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enyoh, C.E.; Devi, A.; Maduka, T.O.; Tyagi, L.; Rana, S.; Akuwudike, I.S.; Wang, Q. A Review of Materials for the Removal of Micro- and Nanoplastics from Different Environments. Micro 2025, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, K.L. Plastics in the marine environment. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2017, 9, 205–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Silva, Y.; Rajagopalan, U.; Kadono, H. Microplastics on the growth of plants and seed germination in aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems. Glob. J. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2021, 7, 347–368. [Google Scholar]
- do Sul, J.A.I.; Costa, M.F. The present and future of microplastic pollution in the marine environment. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 185, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, C.B.; Quinn, B. Microplastic Pollutants; Elsevier Limited: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.J.; Shin, S.R.; Park, J.J.; Lee, J.S. Feeding, excretion, survival, and histological alterations in zebrafish Danio rerio from single and combined exposure to microplastics and copper. Korean J. Environ. Biol. 2024, 42, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mance, G. Pollution Threat of Heavy Metals in Aquatic Environments; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bhupander, K.; Mukherjee, D. Assessment of human health risk for arsenic, copper, nickel, mercury and zinc in fish collected from tropical wetlands in India. Adv. Life Sci. Technol. 2011, 2, 13–24. [Google Scholar]
- Łuczyńska, J.; Paszczyk, B.; Łuczyński, M.J. Fish as a bioindicator of heavy metals pollution in aquatic ecosystem of Pluszne Lake, Poland, and risk assessment for consumer’s health. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 153, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Naggar, Y.; Khalil, M.S.; Ghorab, M.A. Environmental pollution by heavy metals in the aquatic ecosystems of Egypt. Open Acc. J. Toxicol 2018, 3, 555603. [Google Scholar]
- Hylander, L.D.; Goodsite, M.E. Environmental costs of mercury pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 368, 352–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besseling, E.; Wegner, A.; Foekema, E.M.; Van Den Heuvel-Greve, M.J.; Koelmans, A.A. Effects of microplastic on fitness and PCB bioaccumulation by the lugworm Arenicola marina (L.). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-W.; Shim, W.J.; Kwon, O.Y.; Kang, J.-H. Size-dependent effects of micro polystyrene particles in the marine copepod Tigriopus japonicus. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 11278–11283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Moos, N.; Burkhardt-Holm, P.; Köhler, A. Uptake and effects of microplastics on cells and tissue of the blue mussel Mytilus edulis L. after an experimental exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11327–11335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, M.; Ribeiro, A.; Hylland, K.; Guilhermino, L. Single and combined effects of microplastics and pyrene on juveniles (0+ group) of the common goby Pomatoschistus microps (Teleostei, Gobiidae). Ecol. Indic. 2013, 34, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sá, L.C.; Luís, L.G.; Guilhermino, L. Effects of microplastics on juveniles of the common goby (Pomatoschistus microps): Confusion with prey, reduction of the predatory performance and efficiency, and possible influence of developmental conditions. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 196, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.L.; Thompson, R.C.; Galloway, T.S. The physical impacts of microplastics on marine organisms: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 178, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulannga, R.B.; Schmidt, S. Uptake and accumulation of microplastic particles by two freshwater ciliates isolated from a local river in South Africa. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, F.; Quinn, B. The effects of microplastic on freshwater Hydra attenuata feeding, morphology & reproduction. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 487–494. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.; Fileman, E.; Halsband, C.; Goodhead, R.; Moger, J.; Galloway, T.S. Microplastic ingestion by zooplankton. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 6646–6655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setälä, O.; Fleming-Lehtinen, V.; Lehtiniemi, M. Ingestion and transfer of microplastics in the planktonic food web. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 185, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Luo, X.; Zheng, H. Short-term toxicity of polystryrene microplastics on mysid shrimps Neomysis japonica. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 61, 012136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugroho, F.A.; Fyda, J. Uptake of plastic microbeads by ciliate Paramecium aurelia. Sci. Technol. Innov. 2020, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, Q.; Zhu, M.; Liang, J.; Zheng, S.; Zhao, Y. Ingestion of microplastics by natural zooplankton groups in the northern South China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 115, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vroom, R.J.E.; Koelmans, A.A.; Besseling, E.; Halsband, C. Aging of microplastics promotes their ingestion by marine zooplankton. Env. Pollut 2017, 231, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, H.K.A.; Chan, K.Y.K. Negative effects of microplastic exposure on growth and development of Crepidula onyx. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 233, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messinetti, S.; Mercurio, S.; Parolini, M.; Sugni, M.; Pennati, R. Effects of polystyrene microplastics on early stages of two marine invertebrates with different feeding strategies. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 1080–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.S.; Jung, Y.-J.; Hong, N.-H.; Hong, S.H.; Park, J.-W. Toxicological effects of irregularly shaped and spherical microplastics in a marine teleost, the sheepshead minnow (Cyprinodon variegatus). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 129, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desforges, J.-P.W.; Galbraith, M.; Ross, P.S. Ingestion of microplastics by zooplankton in the Northeast Pacific Ocean. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 69, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amélineau, F.; Bonnet, D.; Heitz, O.; Mortreux, V.; Harding, A.M.; Karnovsky, N.; Walkusz, W.; Fort, J.; Grémillet, D. Microplastic pollution in the Greenland Sea: Background levels and selective contamination of planktivorous diving seabirds. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebolledo, E.L.B.; Van Franeker, J.A.; Jansen, O.E.; Brasseur, S.M. Plastic ingestion by harbour seals (Phoca vitulina) in The Netherlands. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 67, 200–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besseling, E.; Foekema, E.; Van Franeker, J.; Leopold, M.; Kühn, S.; Rebolledo, E.B.; Heße, E.; Mielke, L.; IJzer, J.; Kamminga, P. Microplastic in a macro filter feeder: Humpback whale Megaptera novaeangliae. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 95, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusher, A.L.; Hernandez-Milian, G.; O’Brien, J.; Berrow, S.; O’Connor, I.; Officer, R. Microplastic and macroplastic ingestion by a deep diving, oceanic cetacean: The True’s beaked whale Mesoplodon mirus. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 199, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadal, M.; Alomar, C.; Deudero, S. High levels of microplastic ingestion by the semipelagic fish bogue Boops boops (L.) around the Balearic Islands. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 214, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, M.A.; Dissanayake, A.; Galloway, T.S.; Lowe, D.M.; Thompson, R.C. Ingested microscopic plastic translocates to the circulatory system of the mussel, Mytilus edulis (L.). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5026–5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, E.R.; Thompson, J.T. Deposit-and suspension-feeding sea cucumbers (Echinodermata) ingest plastic fragments. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2009, 368, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühn, S.; van Franeker, J.A. Plastic ingestion by the northern fulmar (Fulmarus glacialis) in Iceland. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 1252–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, N.; Berry, K.; Rintoul, L.; Hoogenboom, M. Microplastic ingestion by scleractinian corals. Mar. Biol. 2015, 162, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.; Fileman, E.; Halsband, C.; Galloway, T.S. The impact of polystyrene microplastics on feeding, function and fecundity in the marine copepod Calanus helgolandicus. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1130–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobre, C.; Santana, M.; Maluf, A.; Cortez, F.; Cesar, A.; Pereira, C.; Turra, A. Assessment of microplastic toxicity to embryonic development of the sea urchin Lytechinus variegatus (Echinodermata: Echinoidea). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 92, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaposi, K.L.; Mos, B.; Kelaher, B.P.; Dworjanyn, S.A. Ingestion of microplastic has limited impact on a marine larva. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 1638–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, M. Microplastic Swallowing Zooplankton Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 6646–6655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, P.; Nelson, K. Trophic level transfer of microplastic: Mytilus edulis (L.) to Carcinus maenas (L.). Environ. Pollut. 2013, 177, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, E.; Piazza, V.; Lavorano, S.; Faimali, M.; Garaventa, F.; Gambardella, C. Trophic transfer of microplastics from copepods to jellyfish in the marine environment. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 571732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Jiang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Geng, J.; Ding, L.; Ren, H. Uptake and accumulation of polystyrene microplastics in zebrafish (Danio rerio) and toxic effects in liver. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4054–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, A.J.; Urbina, M.A.; Goodhead, R.; Moger, J.; Lewis, C.; Galloway, T.S. Effect of microplastic on the gills of the shore crab Carcinus maenas. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5364–5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, G.; Madhuri, S. Heavy metals causing toxicity in animals and fishes. Res. J. Anim. Vet. Fish. Sci. 2014, 2, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Vieira, L.R.; Gravato, C.; Soares, A.; Morgado, F.; Guilhermino, L. Acute effects of copper and mercury on the estuarine fish Pomatoschistus microps: Linking biomarkers to behaviour. Chemosphere 2009, 76, 1416–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Tang, X. Acute and chronic toxic effects of Pb2+ on polychaete Perinereis aibuhitensis: Morphological changes and responses of the antioxidant system. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 1681–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliko, V.; Qirjo, M.; Sula, E.; Morina, V.; Faggio, C. Antioxidant defense system, immune response and erythron profile modulation in gold fish, Carassius auratus, after acute manganese treatment. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 76, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaniappan, P.R.; Karthikeyan, S. Bioaccumulation and depuration of chromium in the selected organs and whole body tissues of freshwater fish Cirrhinus mrigala individually and in binary solutions with nickel. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ay, Ö.; Kalay, M.; Tamer, L.; Canli, M. Copper and lead accumulation in tissues of a freshwater fish Tilapia zillii and its effects on the branchial Na, K-ATPase activity. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1999, 62, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firat, Ö.; Kargın, F. Biochemical alterations induced by Zn and Cd individually or in combination in the serum of Oreochromis niloticus. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 36, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Jiang, H.; Wang, S.; Wu, X.; Fei, W.; Li, L.; Nie, G.; Li, X. Effects of copper exposure on the hatching status and antioxidant defense at different developmental stages of embryos and larvae of goldfish Carassius auratus. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 1458–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atli, G.; Canli, M. Metals (Ag+, Cd2+, Cr6+) affect ATPase activity in the gill, kidney, and muscle of freshwater fish Oreochromis niloticus following acute and chronic exposures. Environ. Toxicol. 2013, 28, 707–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Kang, J.-C. Oxidative stress, neurotoxicity, and metallothionein (MT) gene expression in juvenile rock fish Sebastes schlegelii under the different levels of dietary chromium (Cr6+) exposure. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 125, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaryashree; Kumar Choudhary, A.; Devi, A.; Tyagi, L.; Maheshawari Rajagopalan, U.; Kadono, H. Non-invasive detection of arsenic-induced changes in lentil seed activity using biospeckle optical coherence tomography. Opt. Contin. 2025, 4, 968–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Kang, J.-C. The arsenic accumulation and its effect on oxidative stress responses in juvenile rockfish, Sebastes schlegelii, exposed to waterborne arsenic (As3+). Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 39, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Santos, S.; Monteiro, S.; Malakpour-Kolbadinezhad, S.; Fontaínhas-Fernandes, A.; Wilson, J. Effects of Cd injection on osmoregulation and stress indicators in freshwater Nile tilapia. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 167, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, P.; Samal, A.C.; Majumdar, J.; Santra, S.C. Uptake of arsenic in rice plant varieties cultivated with arsenic rich groundwater. Environ. Asia 2010, 3, 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Gundlach, M.; Yang, S.; Jiang, J.; Velki, M.; Yin, D.; Hollert, H. Quantitative investigation of the mechanisms of microplastics and nanoplastics toward zebrafish larvae locomotor activity. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584, 1022–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, A.; Kadono, H.; Rajagopalan, U.M. Fast Assessment of Quality of Water Containing Inorganic Pollutants Using Laser Biospeckles in Microbioassay. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, A.; Kadono, H.; Rajagopalan, U.M. Laser biospeckle method for a fast and reliable microbioassay. Appl. Opt. 2024, 63, 5721–5727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, A.; Kadono, H.; Rajagopalan, U.M. Fast and reliable micro bioassay techniques based on biospeckle for swift water assessment using plankton. Biophotonics Point-Care III 2024, 13008, 1300804. [Google Scholar]
- Bouraiou, C.; Berrebbah, H.; Djekoun, M.; Bouarroudj, T.; Yahyaoui, A.; Khene, L.; Kahli, H.; Djebar, M.R. Growth inhibition and oxidative stress in the freshwater Ciliate paramecium sp. exposed to copper oxide nanoparticles. Stud. Univ. “ Vasile Goldis” Arad. Ser. Stiintele Vietii (Life Sci. Ser.) 2019, 29, 82–90. [Google Scholar]
- Ashouri, S.; Keyvanshokooh, S.; Salati, A.P.; Johari, S.A.; Pasha-Zanoosi, H. Effects of different levels of dietary selenium nanoparticles on growth performance, muscle composition, blood biochemical profiles and antioxidant status of common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Aquaculture 2015, 446, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Chang, Y.; Chen, Y. Toxicity and bioaccumulation of TiO2 nanoparticle aggregates in Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyson, S.; Liew, H.J.; Fazio, A.; Van Dooren, N.; Delcroix, A.; Faggio, C.; Blust, R.; De Boeck, G. Kidney activity increases in copper exposed goldfish (Carassius auratus auratus). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 190, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shunmugam, A.P.; Subramanian, G.; Fernandez, J.G. Measurements of the swimming speeds of motile microorganisms using object tracking and their correlation with water pollution and rheology levels. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, J.R. Effects of copper on phagocytosis inTetrahymena. Protoplasma 1981, 109, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steer, M.; Cole, M.; Thompson, R.C.; Lindeque, P.K. Microplastic ingestion in fish larvae in the western English Channel. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 226, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGoran, A.R.; Clark, P.F.; Morritt, D. Presence of microplastic in the digestive tracts of European flounder, Platichthys flesus, and European smelt, Osmerus eperlanus, from the River Thames. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrady, A.L. Microplastics in the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Song, B.; Zeng, G.; Hu, D.; Wen, X.; Ren, X. Recent advances in toxicological research of nanoplastics in the environment: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maršić-Lučić, J.; Lušić, J.; Tutman, P.; Varezić, D.B.; Šiljić, J.; Pribudić, J. Levels of trace metals on microplastic particles in beach sediments of the island of Vis, Adriatic Sea, Croatia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 137, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, L.A.; Turner, A.; Thompson, R.C. Interactions between trace metals and plastic production pellets under estuarine conditions. Mar. Chem. 2014, 167, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochman, C.M.; Hoh, E.; Kurobe, T.; Teh, S.J. Ingested plastic transfers hazardous chemicals to fish and induces hepatic stress. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, M.; Soliman, H.A.; Osman, A.G.; Sayed, A.E.-D.H. Antioxidants and molecular damage in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) after exposure to microplastics. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 14581–14588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banaee, M.; Soltanian, S.; Sureda, A.; Gholamhosseini, A.; Haghi, B.N.; Akhlaghi, M.; Derikvandy, A. Evaluation of single and combined effects of cadmium and micro-plastic particles on biochemical and immunological parameters of common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Peng, L.-B.; Wang, D.; Zhu, Q.-L.; Zheng, J.-L. Combined effects of polystyrene microplastics and cadmium on oxidative stress, apoptosis, and GH/IGF axis in zebrafish early life stages. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 813, 152514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinhui, S.; Sudong, X.; Yan, N.; Xia, P.; Jiahao, Q.; Yongjian, X. Effects of microplastics and attached heavy metals on growth, immunity, and heavy metal accumulation in the yellow seahorse, Hippocampus kuda Bleeker. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 149, 110510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Hamid, N.; Deng, S.; Jia, P.-P.; Pei, D.-S. Individual and combined toxicogenetic effects of microplastics and heavy metals (Cd, Pb, and Zn) perturb gut microbiota homeostasis and gonadal development in marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma). J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 397, 122795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davarpanah, E.; Guilhermino, L. Single and combined effects of microplastics and copper on the population growth of the marine microalgae Tetraselmis chuii. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 167, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barboza, L.G.A.; Vieira, L.R.; Guilhermino, L. Single and combined effects of microplastics and mercury on juveniles of the European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax): Changes in behavioural responses and reduction of swimming velocity and resistance time. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 1014–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Jin, S.-R.; Chen, Z.-Z.; Gao, J.-Z.; Liu, Y.-N.; Liu, J.-H.; Feng, X.-S. Single and combined effects of microplastics and cadmium on the cadmium accumulation, antioxidant defence and innate immunity of the discus fish (Symphysodon aequifasciatus). Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fu, D.; Gao, L.; Qi, H.; Su, Y.; Peng, L. Aged microplastics decrease the bioavailability of coexisting heavy metals to microalga Chlorella vulgaris. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 217, 112199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Qiao, R.; An, H.; Zhang, Y. Influence of microplastics on the accumulation and chronic toxic effects of cadmium in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere 2018, 202, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, J. Toxicological effects of microplastics and heavy metals on the Daphnia magna. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 746, 141254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Dong, H.; Wang, Y.; Ren, R.; Qin, X.; Wang, S. Effects of microplastics and their adsorption of cadmium as vectors on the cladoceran Moina monogolica Daday: Implications for plastic-ingesting organisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, J. Ecotoxicological effects of microplastics and cadmium on the earthworm Eisenia foetida. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 392, 122273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.; Félix, L.; Luzio, A.; Parra, S.; Bellas, J.; Monteiro, S.M. Single and combined acute and subchronic toxic effects of microplastics and copper in zebrafish (Danio rerio) early life stages. Chemosphere 2021, 277, 130262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Shi, J.; Wang, J.; Dai, Y.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, P. Interactions between microplastics and heavy metals in aquatic environments: A review. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zheng, M.; Wang, L.; Lou, Y.; Shi, L.; Jiang, S. Sorption of three synthetic musks by microplastics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 126, 606–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zon, N.F.; Iskendar, A.; Azman, S.; Sarijan, S.; Ismail, R. Sorptive behaviour of chromium on polyethylene microbeads in artificial seawater. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 250, 06001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nethaji, S.; Sivasamy, A.; Mandal, A. Adsorption isotherms, kinetics and mechanism for the adsorption of cationic and anionic dyes onto carbonaceous particles prepared from Juglans regia shell biomass. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 10, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öz, N.; Kadizade, G.; Yurtsever, M. Investigation of heavy metal adsorption on microplastics. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019, 17, 7301–7310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, T.R.; Prelot, B. Adsorption processes for the removal of contaminants from wastewater: The perspective role of nanomaterials and nanotechnology. In Nanomaterials for the Detection and Removal of Wastewater Pollutants; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 161–222. [Google Scholar]
- Ford, R.G.; Sparks, D.L. Frontiers in metal sorption/precipitation mechanisms on soil mineral surfaces. Adv. Agron. 2001, 74, 41–62. [Google Scholar]
- Abdurahman, A.; Cui, K.; Wu, J.; Li, S.; Gao, R.; Dai, J.; Liang, W.; Zeng, F. Adsorption of dissolved organic matter (DOM) on polystyrene microplastics in aquatic environments: Kinetic, isotherm and site energy distribution analysis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 198, 110658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Hu, G.; Fan, X.; Jia, H. Sorption properties of cadmium on microplastics: The common practice experiment and a two-dimensional correlation spectroscopic study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 190, 110118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Tan, Z.; Qi, Y.; Ouyang, C. Sorption of tri-n-butyl phosphate and tris (2-chloroethyl) phosphate on polyethylene and polyvinyl chloride microplastics in seawater. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 149, 110490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezzati, R.; Ezzati, S.; Azizi, M. Exact solution of the Langmuir rate equation: New Insights into pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order kinetics models for adsorption. Vacuum 2024, 220, 112790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyam, S.; Patra, S. Innovations and challenges in adsorption-based wastewater remediation: A comprehensive review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagalakshmi, M.; Devi, S.G.; Ananthi, P.; Pius, A. Adsorption isotherms and kinetic models. In Carbon Nanomaterials and Their Composites as Adsorbents; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 135–154. [Google Scholar]
- Tenea, A.-G.; Dinu, C.; Rus, P.A.; Ionescu, I.A.; Gheorghe, S.; Iancu, V.I.; Vasile, G.G.; Pascu, L.F.; Chiriac, F.L. Exploring adsorption dynamics of heavy metals onto varied commercial microplastic substrates: Isothermal models and kinetics analysis. Heliyon 2024, 10, e35364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, R.; Karthik, R.; Purvaja, R.; Ganguly, D.; Anandavelu, I.; Mugilarasan, M.; Ramesh, R. Holistic assessment of microplastics in various coastal environmental matrices, southwest coast of India. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayebi, L.; Sobhanardakani, S. Analysis of heavy metal contents and non-carcinogenic health risk assessment through consumption of Tilapia Fish (Oreochromis niloticus). Pollution 2020, 6, 59–67. [Google Scholar]
- Milatou, N.; Dassenakis, M.; Megalofonou, P. Mercury concentrations in reared Atlantic bluefin tuna and risk assessment for the consumers: To eat or not to eat? Food Chem. 2020, 331, 127267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, A.; Golieskardi, A.; Ho, Y.B.; Larat, V.; Salamatinia, B. Microplastics in eviscerated flesh and excised organs of dried fish. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simionov, I.-A.; Cristea, V.; Petrea, Ş.-M.; Coadă, M.T.; Cristea, D.S. The presence of heavy metals in fish meat from Danube River: An overview. Aquac. Aquar. Conserv. Legis. 2016, 9, 1388–1399. [Google Scholar]
- Ture, M.; Kilic, M.B.; Altinok, I. Relationship between heavy metal accumulation in fish muscle and heavy metal resistance genes in bacteria isolated from fish. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 1595–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wootton, N.; Reis-Santos, P.; Gillanders, B.M. Microplastic in fish–A global synthesis. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2021, 31, 753–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, Y.S.K.; Rajagopalan, U.M.; Kadono, H.; Li, D. Positive and negative phenotyping of increasing Zn concentrations by Biospeckle Optical Coherence Tomography in speedy monitoring on lentil (Lens culinaris) seed germination and seedling growth. Plant Stress 2021, 2, 100041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwabl, P.; Köppel, S.; Königshofer, P.; Bucsics, T.; Trauner, M.; Reiberger, T.; Liebmann, B. Detection of various microplastics in human stool: A prospective case series. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 171, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragusa, A.; Notarstefano, V.; Svelato, A.; Belloni, A.; Gioacchini, G.; Blondeel, C.; Zucchelli, E.; De Luca, C.; D’Avino, S.; Gulotta, A. Raman Microspectroscopy Detection and Characterisation of Microplastics in Human Breastmilk. Polymers 2022, 14, 2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montano, L.; Raimondo, S.; Piscopo, M.; Ricciardi, M.; Guglielmino, A.; Chamayou, S.; Gentile, R.; Gentile, M.; Rapisarda, P.; Conti, G.O. First evidence of microplastics in human ovarian follicular fluid: An emerging threat to female fertility. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 291, 117868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhu, L.; Weng, J.; Jin, Z.; Cao, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, Z. Detection and characterization of microplastics in the human testis and semen. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 877, 162713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Li, D.; Wang, H.; Xu, H.; Liu, Y.; Kang, R.; Chen, Q.; Zheng, L. Discovery and analysis of microplastics in human bone marrow. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 477, 135266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, A.; Rodríguez-Viso, P.; Domene, A.; Orozco, H.; Vélez, D.; Devesa, V. Dietary microplastics: Occurrence, exposure and health implications. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato-Lourenço, L.F.; Dantas, K.C.; Júnior, G.R.; Paes, V.R.; Ando, R.A.; de Oliveira Freitas, R.; da Costa, O.M.M.M.; Rabelo, R.S.; Bispo, K.C.S.; Carvalho-Oliveira, R. Microplastics in the olfactory bulb of the human brain. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2440018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaji, M. Role of experts and public participation in pollution control: The case of Itai-itai disease in Japan1. Ethics Sci. Environ. Politics 2012, 12, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.; Shukla, G.S.; Srimal, R. Cadmium-induced alterations in blood-brain barrier permeability and its possible correlation with decreased microvessel antioxidant potential in rat. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 1996, 15, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.; Xi, S. The effects of heavy metals on human metabolism. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2020, 30, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Waalkes, M.P. Liver is a target of arsenic carcinogenesis. Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 105, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Marshall, G.; Ferreccio, C.; Steinmaus, C.; Liaw, J.; Bates, M.; Smith, A.H. Kidney cancer mortality: Fifty-year latency patterns related to arsenic exposure. Epidemiology 2010, 21, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.H.; Marshall, G.; Yuan, Y.; Ferreccio, C.; Liaw, J.; Von Ehrenstein, O.; Steinmaus, C.; Bates, M.N.; Selvin, S. Increased mortality from lung cancer and bronchiectasis in young adults after exposure to arsenic in utero and in early childhood. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 1293–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, D.G. Chronic arsenic toxicity & human health. Indian J. Med. Res. 2008, 128, 436–447. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.-S.; Liao, W.-T.; Chai, C.-Y. Arsenic carcinogenesis in the skin. J. Biomed. Sci. 2006, 13, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, G.; Ferreccio, C.; Yuan, Y.; Bates, M.N.; Steinmaus, C.; Selvin, S.; Liaw, J.; Smith, A.H. Fifty-year study of lung and bladder cancer mortality in Chile related to arsenic in drinking water. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2007, 99, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellinger, D.C. Lead contamination in Flint—An abject failure to protect public health. N. Eng. J. Med. 2016, 374, 1101–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, K.M.; Walker Jr, E.M.; Wu, M.; Gillette, C.; Blough, E.R. Environmental mercury and its toxic effects. J. Prev. Med. Public Health 2014, 47, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.; Bannigan, J. Cadmium: Toxic effects on the reproductive system and the embryo. Reprod. Toxicol. 2008, 25, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahurpawar, M. Effects of heavy metals on human health. Int. J. Reseacrh-Granthaalayah 2015, 530, 2394–3629. [Google Scholar]
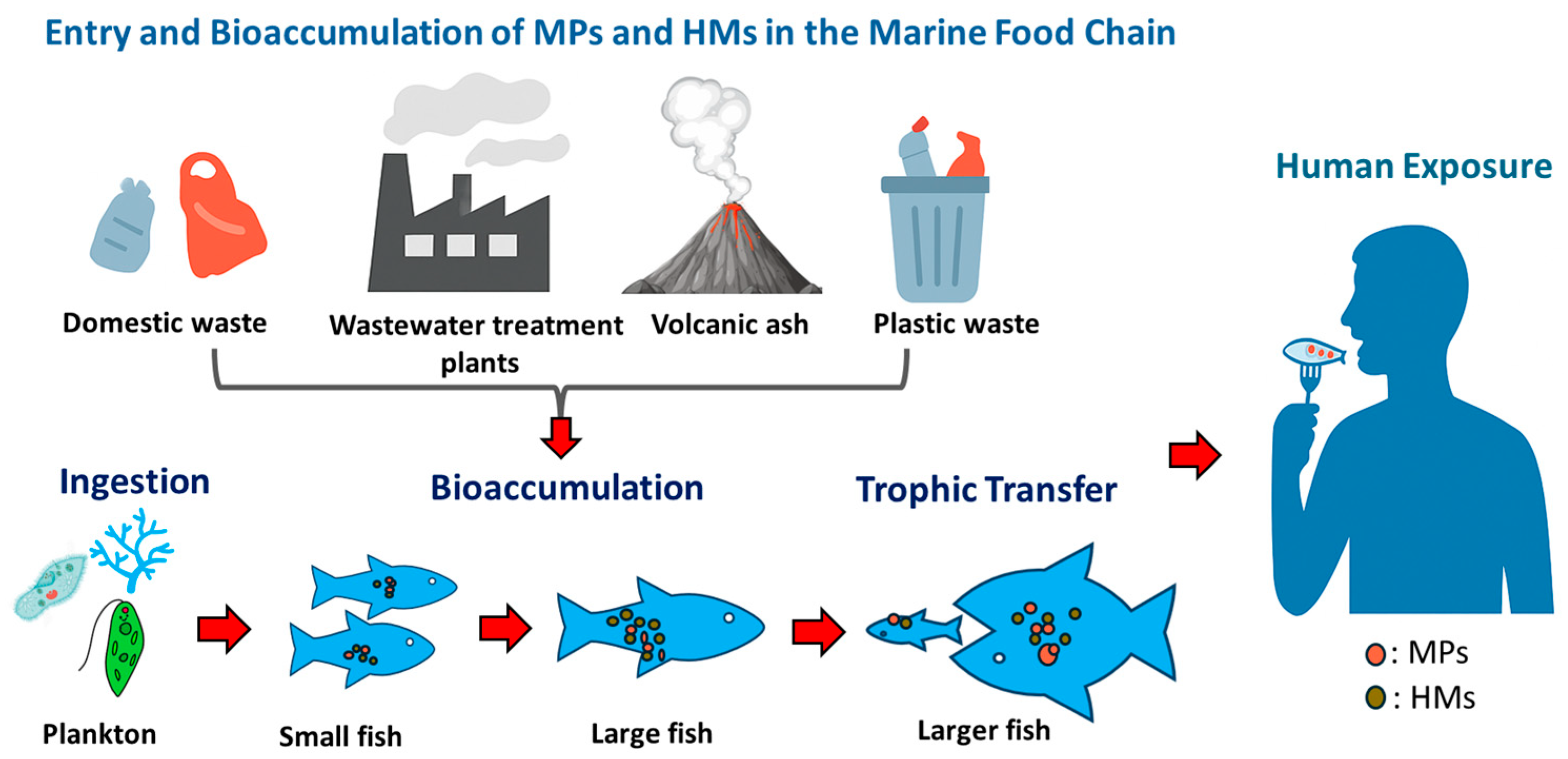

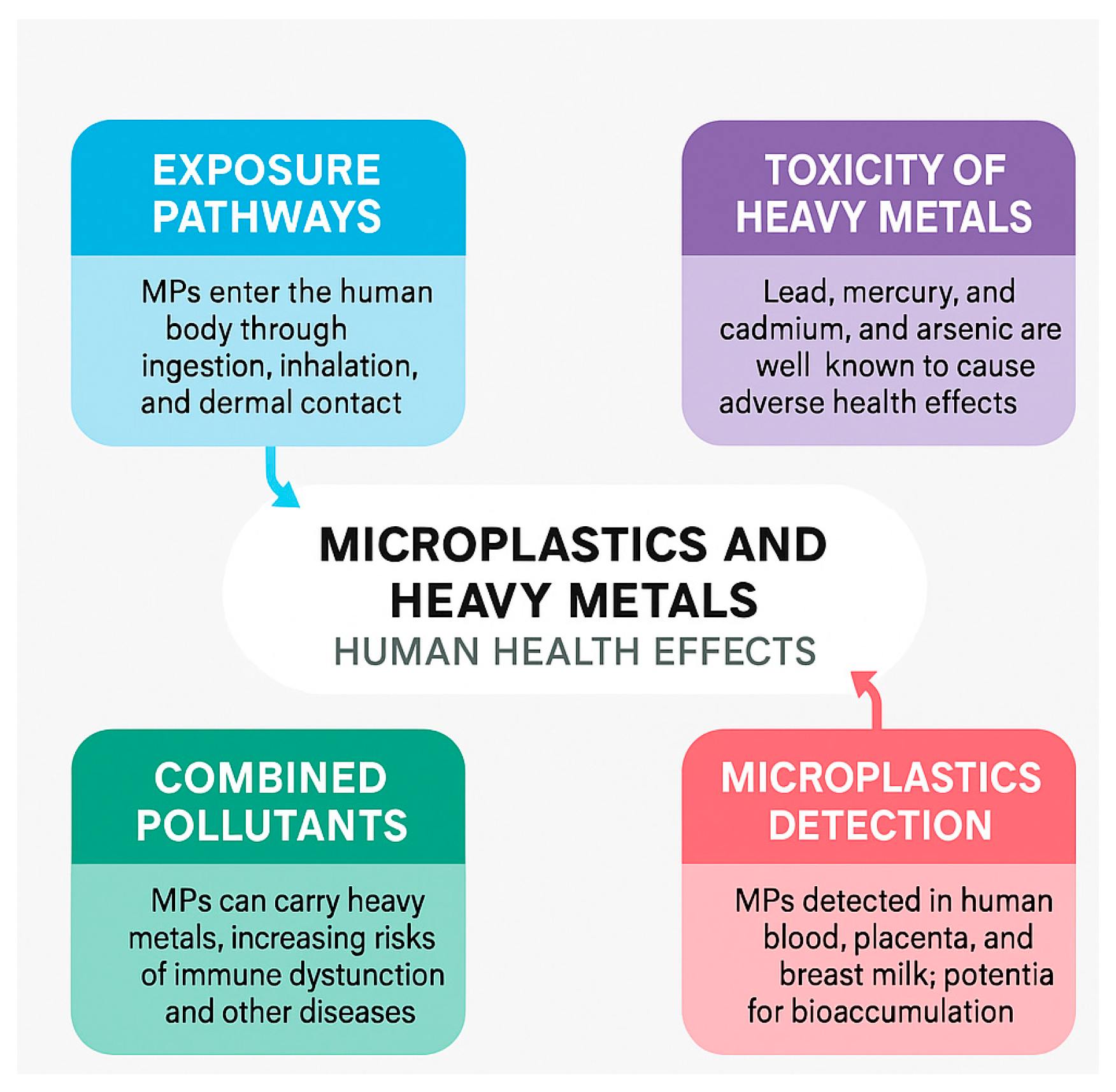
| Name of MPs/Shape | Size | Species | Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene (Beads) | 7.3–30.3 μm | Holo, mero, microplankton | Zooplanktons easily ingest MPs | [44] |
| Polystyrene (Sphere) | 2 µm | Mytilus edulis, | Ingested microscopic plastic translocates to the circulatory system | [37] |
| Polystyrene (Sphere) | 0.5 μm | Mytilus edulis prey, Carcinus maenas predator | Trophic level transfer of microplastic from Mytilus edulis to Carcinus maenas | [45] |
| Polystyrene (Beads) | 2, 5, and 10 μm | Paramecium sp. strain RB1 and tetrahymena sp. strain RB2 | Paramecium sp. strain RB1 ingested all three sizes of microspheres, while tetrahymena sp. strain RB2 only ingested 2 and 5 μm | [20] |
| Polyethylene (Beads) | 1–5 μm | Tigriopus fulvus, and Aurelia sp. | Trophic level transfer of MPs from Tigriopus fulvus as prey to Aurelia sp. as a predator | [46] |
| Polystyrene (Beads) | 2 μm | Paramecium Aurelia | Ingestion and accumulation of microbeads in P. Aurelia | [25] |
| Polyethylene (Flakes) | <400 μm | Hydra attenuata | Non-lethal morphological changes | [21] |
| Polystyrene (Beads) | 2–5 μm | Crepidula onyx | Relatively slower growth rate and faster settlement | [28] |
| Polystyrene (Beads) | 70 nm, 5 and 20 μm | Danio rerio | Inflammation and lipid accumulation in the fish liver caused by 5 μm and 70 nm | [47] |
| Polystyrene (sphere) | 8 μm | C. maenas | Significant dose-dependent effect on oxygen consumption | [48] |
| Organisms | Heavy Metals/Concentration | Microplastic/Concentration | Exposure Time | Toxic Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zebrafish (Danio rerio) | Cadmium (100 mg/L) | Polystyrene beads (20, 200 µg/L) | 3 weeks | The toxicity of Cd enhanced by the MPs caused oxidative damage and tissue inflammation | [89] |
| Daphnia magna | Pb (0.836 mg/L), Cu (0.085 mg/L), Cd (0.108 mg/L), Ni (1.846 mg/L) | Polystyrene (50 mg/L) | 72 Hrs. | Size-dependent toxicity observed | [90] |
| Cladoceran (Moina monogolica Daday) | Cd (5, 10 μg/L) | Polyethylene (300 μg/L) | 21-days | Impaired development, fecundity, and reproductive output across treatment groups lead to parental mortality and poor nutritional status in progeny | [91] |
| Earthworm (Eisenia foetida) | Cd (8 mg/kg) | PP (300, 3000, 6000 and 9000 mg/kg soil) | 14, 28, and 42 days | Combined exposure to MPs and Cd posed higher adverse effects | [92] |
| Zebrafish (Danio rerio) | Cu (60 and 125 μg/L) | MPs (2 mg/L), | 14-days | Induced oxidative stress and inhibited antioxidant enzymes | [93] |
| Model | Type | Main Assumption | Environmental Relevance | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-First Order (PFO) | Kinetic | Adsorption rate depends on unoccupied sites (initial stages) | Limited to early-stage adsorption | [104] |
| Pseudo-Second Order (PSO) | Kinetic | Adsorption occurs via chemisorption (electron sharing/exchange) | Frequently fits experimental data; widely used | [105] |
| Elovich | Kinetic | Adsorption rate decreases exponentially with time | Useful for heterogeneous surfaces | [106] |
| Langmuir | Isotherm | Monolayer adsorption on homogeneous surface | Best for uniform materials, less realistic | [100] |
| Freundlich | Isotherm | Multilayer adsorption on heterogeneous surfaces | Most applicable in environmental studies | [107] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Devi, A.; De Silva, Y.S.K.; Tyagi, L.; Aaryashree. The Individual and Combined Effects of Microplastics and Heavy Metals on Marine Organisms. Microplastics 2025, 4, 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4030038
Devi A, De Silva YSK, Tyagi L, Aaryashree. The Individual and Combined Effects of Microplastics and Heavy Metals on Marine Organisms. Microplastics. 2025; 4(3):38. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4030038
Chicago/Turabian StyleDevi, Arti, Y. Sanath K. De Silva, Lavista Tyagi, and Aaryashree. 2025. "The Individual and Combined Effects of Microplastics and Heavy Metals on Marine Organisms" Microplastics 4, no. 3: 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4030038
APA StyleDevi, A., De Silva, Y. S. K., Tyagi, L., & Aaryashree. (2025). The Individual and Combined Effects of Microplastics and Heavy Metals on Marine Organisms. Microplastics, 4(3), 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4030038






