Micro- and Nanoplastics in the Atmosphere: Methodology for Microplastics Size-Fractionation Sampling
Abstract
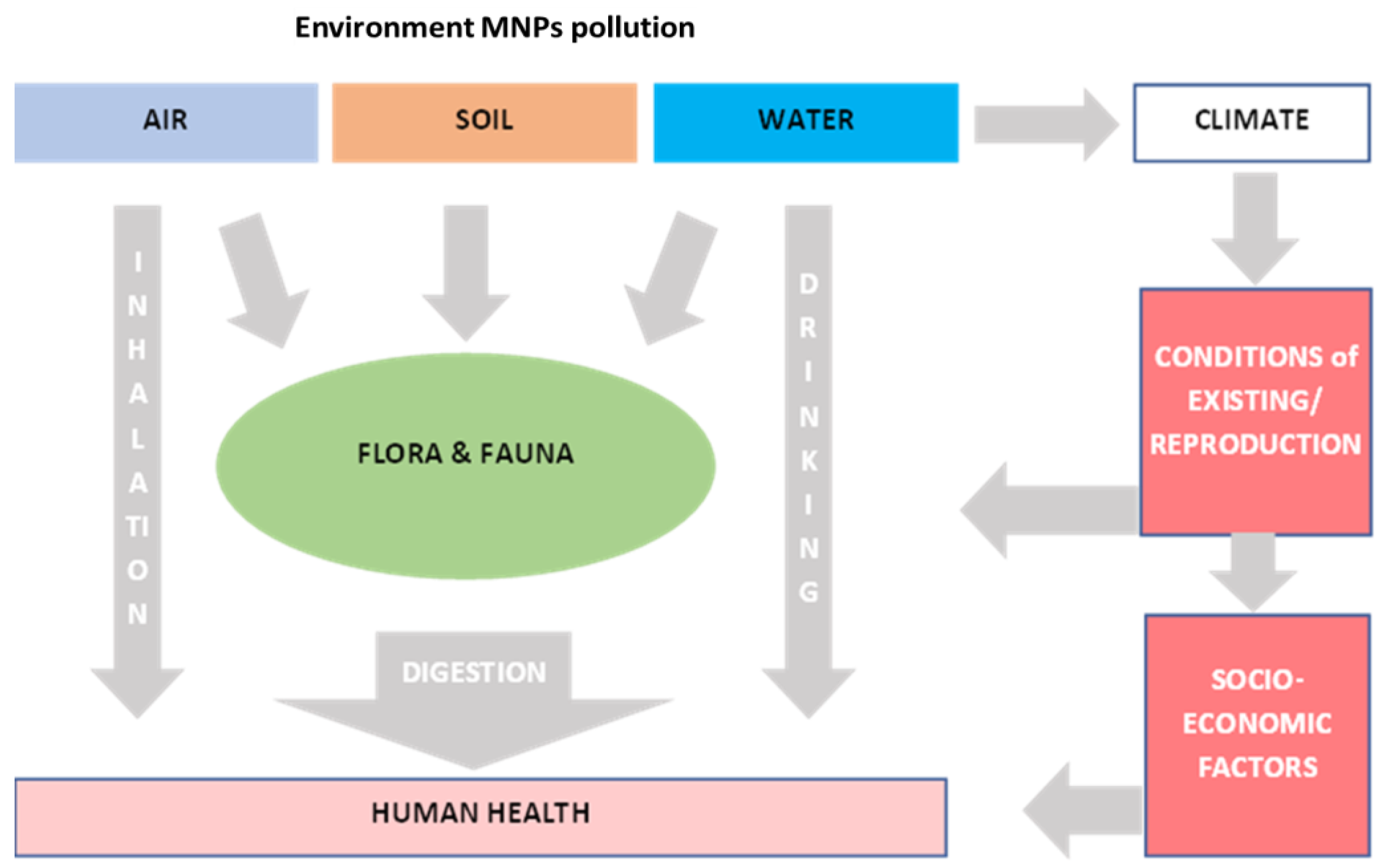
1. Introduction
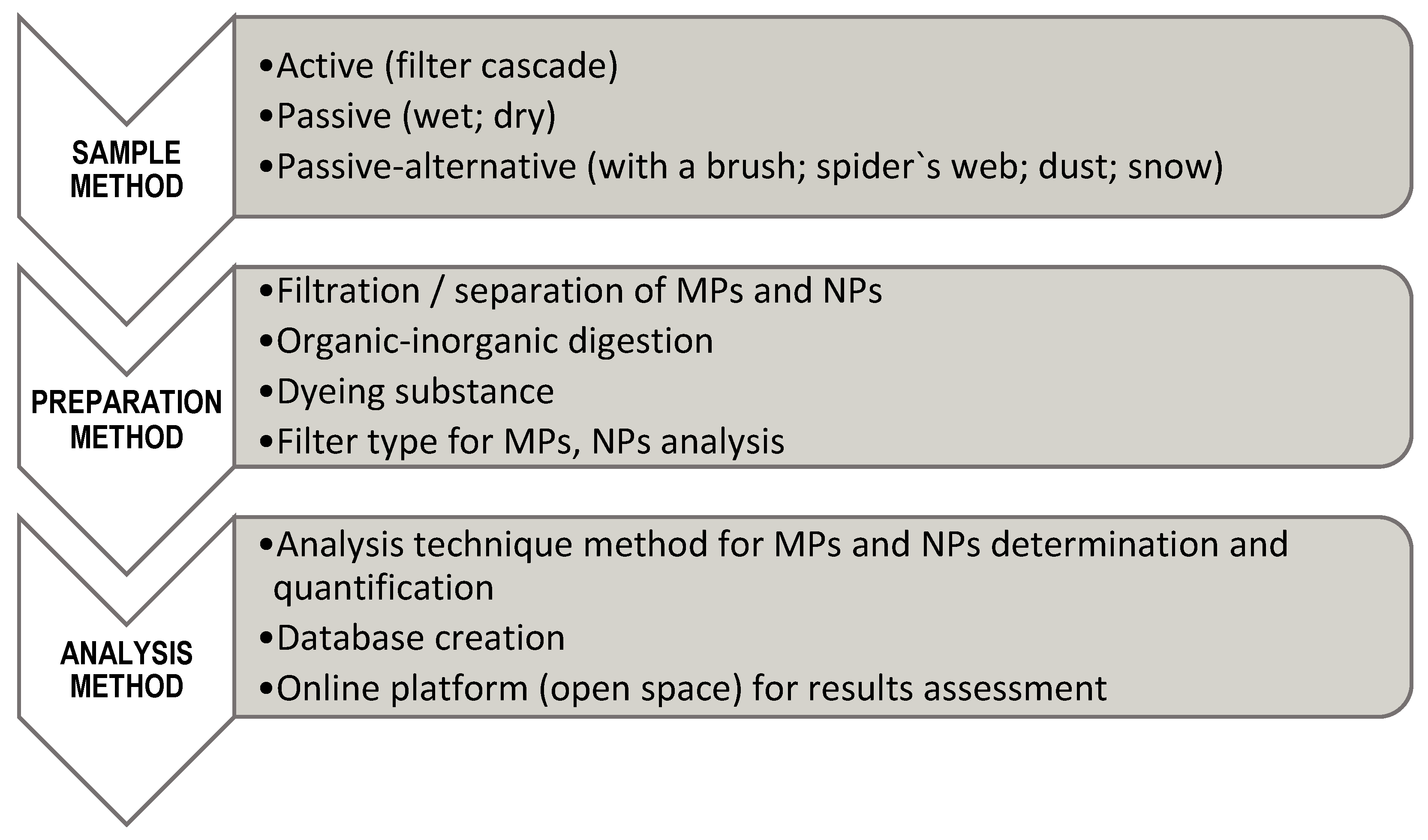
2. Sampling and Treatment of Plastic Aerosol
2.1. Revised Sampling Methods
2.2. Revised Sample Preparation
3. Size Fractionation Protocol Proposed for Atmospheric MPs
- (i)
- The dry or wet deposition, collected using no-plastic passive samplers such as the Norwegian Institute of Air Research (NILU) collector, undergoes thorough washing with pure water and then transfers to a dark glass vial.
- (ii)
- A cascade of metallic sieves, including those with mesh sizes of 125 μm, 63 μm, and 25 μm, is utilized for the size fractionation of MPs, facilitating the removal of larger non-organic/organic particles and reducing the risk of clogging.
- (iii)
- After sieving, MPs are separated into various size fractions, using suitable membrane filters with properties that lead to consideration of analysis techniques, with pore sizes of 12 and 1.2 μm. These specific pore sizes were chosen to assess the respirable fraction of microplastics, which partially fall within the size intervals defined for respirable matter PM10 and PM2.5.
- (iv)
- After sieving, the sieves and their content are placed in beakers with 200 mL of H2O2 (15%) for 12 h (overnight) at 50 °C. The matter retained on the sieve in step “ii” is detached via sonication. After organic matter digestion and eventually dispersing agglomerated particles, the sample is dispersed via ultra-sounds. It will go again through steps “ii” and “iii,” i.e., the cascade of sieves and filters.
4. Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lombardi, G.; Russo, M.D.; Zjalic, V.; Lanza, V.; Simmons, M.; Moscato, U.; Ricciardi, W.; Chiara, C. Microplastics inhalation and their effects on human health: A systematic review. Eur. J. Public Health 2022, 32, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Zuo, C.; Shi, H. An Overview of Chemical Additives on (Micro)Plastic Fibers: Occurrence, Release, and Health Risks. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 260, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamichhane, G.; Acharya, A.; Marahatha, R.; Modi, B.; Paudel, R.; Adhikari, A.; Raut, B.K.; Aryal, S.; Parajuli, N. Microplastics in Environment: Global Concern, Challenges, and Controlling Measures. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 20, 4673–4694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrady, A.L.; Neal, M.A. Applications and Societal Benefits of Plastics. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1977–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, R.; Jambeck, J.R.; Law, K.L. Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesinger, H.; Wang, Z.; Hellweg, S. Deep Dive into Plastic Monomers, Additives, and Processing Aids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 9339–9351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uurasjärvi, E.; Hartikainen, S.; Setälä, O.; Lehtiniemi, M.; Koistinen, A. Microplastic concentrations, size distribution, and polymer types in the surface waters of a northern European lake. Water Environ. Res. 2020, 92, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, L.; Bartosova, Z.; Braun, K.; Oehlmann, J.; Völker, C.; Wagner, M. Plastic Products Leach Chemicals That Induce In Vitro Toxicity under Realistic Use Conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 11814–11823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardo, M.; Qiu, X.; Zimmermann, R.; Rudich, Y. Particulate Matter Toxicity Is Nrf2 and Mitochondria Dependent: The Roles of Metals and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2020, 33, 1110–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, M.A. Sources and Pathways of Microplastics to Habitats. In Marine Anthropogenic Litter; Bergmann, M., Gutow, L., Klages, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 229–244. ISBN 978-3-319-16510-3. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Wang, J. The chemical behaviors of microplastics in marine environment: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 142, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, R.C.; Olsen, Y.; Mitchell, R.P.; Davis, A.; Rowland, S.J.; John, A.W.G.; McGonigle, D.; Russell, A.E. Supporting Material: Lost at Sea: Where Is All the Plastic? Science 2004, 304, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, D.K.A.; Galgani, F.; Thompson, R.C.; Barlaz, M. Accumulation and Fragmentation of Plastic Debris in Global Environments. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1985–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrady, A.L. Microplastics in the Marine Environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auta, H.S.; Emenike, C.U.; Fauziah, S.H. Distribution and Importance of Microplastics in the Marine Environment. A Review of the Sources, Fate, Effects, and Potential Solutions. Environ. Int. 2017, 102, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.; Guilhermino, L. Transgenerational Effects and Recovery of Microplastics Exposure in Model Populations of the Freshwater Cladoceran Daphnia Magna Straus. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michishita, S.; Gibble, C.; Tubbs, C.; Felton, R.; Gjeltema, J.; Lang, J.; Finkelstein, M. Microplastic in Northern Anchovies (Engraulis Mordax) and Common Murres (Uria Aalge) from the Monterey Bay, California USA—Insights into Prevalence, Composition, and Estrogenic Activity. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 316, 120548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, B.M.; Jantunen, L.; Bergmann, M.; Vorkamp, K.; Aherne, J.; Magnusson, K.; Herzke, D.; Granberg, M.; Hallanger, I.G.; Gomiero, A.; et al. Monitoring Microplastics in the Atmosphere and Cryosphere in the Circumpolar North: A Case for Multi-Compartment Monitoring. Arct. Sci. 2022, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dris, R.; Gasperi, J.; Rocher, V.; Saad, M.; Renault, N.; Tassin, B. Microplastic Contamination in an Urban Area: A Case Study in Greater Paris. Environ. Chem. 2015, 12, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Wang, J.; Peng, J.; Tan, Z.; Zhan, Z.; Tan, X.; Chen, Q. Characteristic of Microplastics in the Atmospheric Fallout from Dongguan City, China: Preliminary Research and First Evidence. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 24928–24935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pironti, C.; Notarstefano, V.; Ricciardi, M.; Motta, O.; Giorgini, E.; Montano, L. First Evidence of Microplastics in Human Urine, a Preliminary Study of Intake in the Human Body. Toxics 2023, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pengfei Wu, P.; Lin, S.; Cao, G.; Wu, J.; Jin, H.; Wang, C.; Wonge, M.H.; Yanga, Z.; Cai, Z. Absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion and toxicity of microplastics in the human body and health implications. J. Hazard Mater. 2022, 437, 129361. [Google Scholar]
- Jenner, L.C.; Rotchell, J.M.; Bennett, R.T.; Cowen, M.; Tentzeris, V.; Sadofsky, L.R. Detection of Microplastics in Human Lung Tissue Using $μ$FTIR Spectroscopy. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragusa, A.; Notarstefano, V.; Svelato, A.; Belloni, A.; Gioacchini, G.; Blondeel, C.; Zucchelli, E.; De Luca, C.; D’Avino, S.; Gulotta, A.; et al. Raman Microspectroscopy Detection and Characterisation of Microplastics in Human Breastmilk. Polymers 2022, 14, 2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Guo, J.; Liu, X.; Yang, R.; Wang, H.; Sun, Y.; Chen, B.; Dong, R. Detection of Various Microplastics in Placentas, Meconium, Infant Feces, Breastmilk and Infant Formula: A Pilot Prospective Study. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 854, 158699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, H.A.; van Velzen, M.J.M.; Brandsma, S.H.; Vethaak, A.D.; Garcia-Vallejo, J.J.; Lamoree, M.H. Discovery and Quantification of Plastic Particle Pollution in Human Blood. Environ. Int. 2022, 163, 107199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.-J.; Huang, X.-P.; Xiang, L.; Wang, Y.-Z.; Li, Y.-W.; Li, H.; Cai, Q.-Y.; Mo, C.-H.; Wong, M.-H. Source, Migration and Toxicology of Microplastics in Soil. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffin, S. The emergence of microplastics: Charting the path from research to regulations. Environ. Sci. Adv. 2023, 2, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/commission/presscorner/detail/en/ip_23_4581 (accessed on 20 October 2023).
- Mofijur, M.; Ahmed, S.F.; Rahman, S.M.A.; Arafat Siddiki, S.K.Y.; Islam, A.B.M.S.; Shahabuddin, M.; Ong, H.C.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Djavanroodi, F.; Show, P.L. Source, Distribution and Emerging Threat of Micro- and Nanoplastics to Marine Organism and Human Health: Socio-Economic Impact and Management Strategies. Environ. Res. 2021, 195, 110857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Meulen, M.D.; De Vriese, L.; Lee, J.; Maes, T.; Van Dalfsen, J.A.; Huvet, A.; Soudant, P.; Robbens, J.; Vethaak, A.D. Socio-economic impact of microplastics in the 2 Seas, Channel and France Manche Region: An initial risk assessment. MICRO Interreg Proj. Iva. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aeschlimann, M.; Li, G.; Kanji, Z.A.; Mitrano, D.N. Potential impacts of atmospheric microplastics and nanoplastics on cloud formation processes. Nat. Geosci. 2022, 15, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revell, L.E.; Kuma, P.; Le Ru, E.C.; Somerville, W.R.C.; Gaw, S. Direct radiative effects of airborne microplastics. Nature 2021, 598, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, J.M.; Ferreiro, B.; López-Mahía, P.; Muniategui-Lorenzo, S. Standardization of the Minimum Information for Publication of Infrared-Related Data When Microplastics are Characterized. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 154, 111035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logvina, Y.; Ribeiro, H.; Pinto da Silva, L.; Esteves da Silva, J. Monitoring and Size Fractionation of Micro-Nanoplastics in Porto’s Atmosphere: Quantification over a Five-Month Period. In Proceedings of the 6th International Electronic Conference on Atmospheric Sciences, Online, 15–30 October 2023; MDPI: Basel, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Li, C.; Liu, K.; Zhu, L.; Song, Z.; Li, D. Atmospheric Microplastic over the South China Sea and East Indian Ocean: Abundance, Distribution and Source. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 121846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Wu, T.; Wang, X.; Song, Z.; Zong, C.; Wei, N.; Li, D. Consistent transport of terrestrial microplastics to the ocean through atmosphere. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 10612–10619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kernchen, S.; Löder, M.G.J.; Fischer, F.; Fischer, D.; Moses, S.R.; Georgi, C.; Nölscher, A.C.; Held, A.; Laforsch, C. Airborne Microplastic Concentrations and Deposition across the Weser River Catchment. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 818, 151812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, S.; Fowler, S.W.; Habibi, N.; Sajid, S.; Dupont, S.; Behbehani, M. Indoor Aerosol—Kuwait’s Baseline. Toxics 2022, 2–17. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, L.; Mallach, G.; Kulka, R.; Halappanavar, S. Microplastics and Nanoplastics Science: Collecting and Characterizing Airborne Microplastics in Fine Particulate Matter. Nanotoxicology 2021, 15, 1253–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.; Allen, D.; Phoenix, V.R.; Le Roux, G.; Durántez Jiménez, P.; Simonneau, A.; Binet, S.; Galop, D. Atmospheric Transport and Deposition of Microplastics in a Remote Mountain Catchment. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, L.; Scibetta, L.; Markuszewski, P.; Mazurkiewicz, M.; Drozdowska, V.; Makuch, P.; Jutrzenka-Trzebiatowska, P.; Zaleska-Medynska, A.; Andò, S.; Saliu, F.; et al. Airborne and Marine Microplastics from an Oceanographic Survey at the Baltic Sea: An Emerging Role of Air-Sea Interaction? Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 824, 153709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, B.; Aherne, J.; Paterson, A.M.; Yao, H.; McConnell, C. Atmospheric Deposition of Anthropogenic Particles and Microplastics in South-Central Ontario, Canada. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 835, 155426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aves, A.R.; Revell, L.E.; Gaw, S.; Ruffell, H.; Schuddeboom, A.; Wotherspoon, N.E.; Larue, M.; Mcdonald, A.J. First Evidence of Microplastics in Antarctic Snow. Cryosphere 2022, 16, 2127–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarosz, K.; Janus, R.; Wądrzyk, M.; Wilczyńska-Michalik, W.; Natkański, P.; Michalik, M. Characteristic of Airborne Microplastic in the Atmospheric Deposition in Krakow (Southern Poland): A New Semi-Quantitative Approach by Means of the Py-Gc-Ms Technique. SSRN Electron. J. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Sun, C.; He, C.; Zheng, L.; Dai, D.; Li, F. Atmospheric Microplastics in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean: Distribution, Source, and Deposition. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 829, 154337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napper, I.; Parker-Jurda, N.; Wright, S.; Thompson, R. Examining the Release of Synthetic Microfibres to the Environment via Two Major Pathways: Atmospheric Deposition and Treated Wastewater Effluent. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 857, 154166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amato-Lourenço, L.F.; dos Santos Galvão, L.; Wiebeck, H.; Carvalho-Oliveira, R.; Mauad, T. Atmospheric Microplastic Fallout in Outdoor and Indoor Environments in São Paulo Megacity. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 821, 153450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, W.; Wang, R.; He, D. Air Conditioner Filters Become Sinks and Sources of Indoor Microplastics Fibers. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292, 118465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Lee, I.; Kim, H.; Park, J.; Cho, S.; Oh, S.; Lee, M.; Kim, H. Comparison of Microplastic Characteristics in the Indoor and Outdoor Air of Urban Areas of South Korea. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2022, 233, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Chen, C.; Gan, Q.; Wang, T.; Li, W.; Zeng, W.; Xu, X.; Chen, G.; Wang, L.; Lu, Z.; et al. Indoor Microplastics and Bacteria in the Atmospheric Fallout in Urban Homes. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 852, 158233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangeliou, N.; Tichý, O.; Eckhardt, S.; Zwaaftink, C.G.; Brahney, J. Sources and Fate of Atmospheric Microplastics Revealed from Inverse and Dispersion Modelling: From Global Emissions to Deposition. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 432, 128585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Liao, Z.; Ji, X.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Z.; Lu, C.; Shi, C.; Chen, Z.; Ge, L.; Zhang, M.; et al. Microplastic Ingestion from Atmospheric Deposition during Dining/Drinking Activities. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 432, 128674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goßmann, I.; Süßmuth, R.; Scholz-Böttcher, B.M. Plastic in the Air?!—Spider Webs as Spatial and Temporal Mirror for Microplastics Including Tire Wear Particles in Urban Air. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 832, 155008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Duan, Y.; Han, X.; Munyaneza, J.; Ma, J.; Xiu, G. Atmospheric Deposition of Microplastics in the Megalopolis (Shanghai) during Rainy Season: Characteristics, Influence Factors, and Source. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 847, 149501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, X.; Zhu, L.; Liu, K.; Zong, C.; Wei, N.; Li, D. Enhanced Impacts Evaluation of Typhoon Sinlaku (2020) on Atmospheric Microplastics in South China Sea during the East Asian Summer Monsoon. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Shao, L.; Li, Y.; Jones, T.; Cao, Y.; Yang, C.-X.; Zhang, M.; Santosh, M.; Feng, X.; BéruBé, K. Microplastic Atmospheric Dustfall Pollution in Urban Environment: Evidence from the Types, Distribution, and Probable Sources in Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 155989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nematollahi, M.J.; Zarei, F.; Keshavarzi, B.; Zarei, M.; Moore, F.; Busquets, R.; Kelly, F.J. Microplastic Occurrence in Settled Indoor Dust in Schools. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, Z.; Mao, R.; Hu, E.; Xiao, C.; Yang, C.; Guo, X. The Indoor Exposure of Microplastics in Different Environments. Gondwana Res. 2022, 108, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, D.; Banerjee, T.; Badola, N.; Chauhan, J.S. Evidences of Microplastics in Aerosols and Street Dust: A Case Study of Varanasi City, India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 82006–82013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purwiyanto, A.I.S.; Prartono, T.; Riani, E.; Naulita, Y.; Cordova, M.R.; Koropitan, A.F. The Deposition of Atmospheric Microplastics in Jakarta-Indonesia: The Coastal Urban Area. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 174, 113195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shruti, V.C.; Kutralam-muniasamy, G.; Pérez-guevara, F.; Roy, P.D.; Martínez, I.E. Science of the Total Environment Occurrence and Characteristics of Atmospheric Microplastics in Mexico City. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 847, 157601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syafina, P.R.; Yudison, A.P.; Sembiring, E.; Irsyad, M.; Tomo, H.S. Identification of Fibrous Suspended Atmospheric Microplastics in Bandung Metropolitan Area, Indonesia. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 100310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Li, Y.; Feng, Y.; Cheng, W.; Wang, Y. Inhalable Microplastics Prevails in Air: Exploring the Size Detection Limit. Environ. Int. 2022, 162, 107151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Glamoclija, M.; Murphy, A.; Gao, Y. Characterization of Microplastics in Indoor and Ambient Air in Northern New. Environ. Res. 2022, 207, 112142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Lai, Z.; Peng, G.; Luo, L.; Liu, K.; Huang, X.; Xu, Y.; Shen, Q.; Li, D. Microplastic Abundance and Distribution in a Central Asian Desert. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 800, 149529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zou, X.; Wang, C.; Feng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Q.; Chen, H. The Abundance and Characteristics of Atmospheric Microplastic Deposition in the Northwestern South China Sea in the Fall. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 253, 118389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; He, T.; Yan, M.; Yang, L.; Gong, H.; Wang, W.; Qing, X.; Wang, J. Atmospheric Transport and Deposition of Microplastics in a Subtropical Urban Environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 126168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenner, L.C.; Sadofsky, L.R.; Danopoulos, E.; Rotchell, J.M. Household Indoor Microplastics within the Humber Region (United Kingdom): Quantification and Chemical Characterisation of Particles Present. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 259, 118512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knobloch, E.; Ruffell, H.; Aves, A.; Pantos, O.; Gaw, S.; Revell, L.E. Comparison of Deposition Sampling Methods to Collect Airborne Microplastics in Christchurch, New Zealand. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Ji, X.; Ma, Y.; Lv, B.; Huang, W.; Zhu, X.; Fang, M.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Dahlgren, R.; et al. Airborne Microplastics in Indoor and Outdoor Environments of a Coastal City in Eastern China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 126007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narmadha, V.V.; Jose, J.; Patil, S.; Farooqui, M.O.; Srimuruganandam, B.; Saravanadevi, S.; Krishnamurthi, K. Assessment of Microplastics in Roadside Suspended Dust from Urban and Rural Environment of Nagpur, India. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2020, 14, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, S.; Okoffo, E.D.; Rauert, C.; O’Brien, J.W.; Ribeiro, F.; Burrows, S.D.; Toapanta, T.; Wang, X.; Thomas, K.V. Quantification of Selected Microplastics in Australian Urban Road Dust. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peñalver, R.; Costa-Gómez, I.; Arroyo-Manzanares, N.; Moreno, J.M.; López-García, I.; Moreno-Grau, S.; Córdoba, M.H. Assessing the Level of Airborne Polystyrene Microplastics Using Thermogravimetry-Mass Spectrometry: Results for an Agricultural Area. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 787, 147656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, N.S.; Taylor, M.P.; Wilson, S.P. Quantification and Exposure Assessment of Microplastics in Australian Indoor House Dust. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 283, 117064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szewc, K.; Graca, B.; Dołęga, A. Atmospheric Deposition of Microplastics in the Coastal Zone: Characteristics and Relationship with Meteorological Factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 143272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, T.N.S.; Strady, E.; Kieu-Le, T.C.; Tran, Q.V.; Le, T.M.T.; Thuong, Q.T. Microplastic in Atmospheric Fallouts of a Developing Southeast Asian Megacity under Tropical Climate. Chemosphere 2021, 272, 129874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xumiao, L.; Prata, J.C.; Alves, J.R.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T.; Cerqueira, M. Airborne Microplastics and Fibers in Indoor Residential Environments in Aveiro, Portugal. Environ. Adv. 2021, 6, 100134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Huang, W.; Fang, M.; Liao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xu, L.; Mu, Q.; Shi, C.; Lu, C.; Deng, H.; et al. Airborne Microplastic Concentrations in Five Megacities of Northern and Southeast China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 12871–12881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.; Allen, D.; Moss, K.; Le Roux, G.; Phoenix, V.R.; Sonke, J.E. Examination of the Ocean as a Source for Atmospheric Microplastics. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato-Lourenço, L.F.; dos Santos Galvão, L.; de Weger, L.A.; Hiemstra, P.S.; Vijver, M.G.; Mauad, T. An Emerging Class of Air Pollutants: Potential Effects of Microplastics to Respiratory Human Health? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 141676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahney, J.; Hallerud, M.; Heim, E.; Hahnenberger, M.; Sukumaran, S. Plastic Rain in Protected Areas of the United States. Science 2020, 368, 1257–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaston, E.; Woo, M.; Steele, C.; Sukumaran, S.; Anderson, S. Microplastics Differ Between Indoor and Outdoor Air Masses: Insights from Multiple Microscopy Methodologies. Appl. Spectrosc. 2020, 74, 1079–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Pleiter, M.; Edo, C.; Aguilera, Á.; Viúdez-Moreiras, D.; Pulido-Reyes, G.; González-Toril, E.; Osuna, S.; de Diego-Castilla, G.; Leganés, F.; Fernández-Piñas, F.; et al. Occurrence and Transport of Microplastics Sampled within and above the Planetary Boundary Layer. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 761, 143213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levermore, J.M.; Smith, T.E.L.; Kelly, F.J.; Wright, S.L. Detection of Microplastics in Ambient Particulate Matter Using Raman Spectral Imaging and Chemometric Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 8732–8740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Tang, C. A Review of Possible Pathways of Marine Microplastics Transport in the Ocean. Anthr. Coasts 2020, 3, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Wang, X.; Song, Z.; Wei, N.; Li, D. Terrestrial plants as a potential temporary sink of atmospheric microplastics during transport. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 742, 140523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Wang, X.; Song, Z.; Wei, N.; Ye, H.; Cong, X.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; Qu, L.; Zhu, L.; et al. Global inventory of atmospheric fibrous microplastics input into the ocean: An implication from the indoor origin. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Materić, D.; Kasper-Giebl, A.; Kau, D.; Anten, M.; Greilinger, M.; Ludewig, E.; Van Sebille, E.; Röckmann, T.; Holzinger, R. Micro-and Nanoplastics in Alpine Snow: A New Method for Chemical Identification and (Semi)Quantification in the Nanogram Range. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 2353–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roblin, B.; Ryan, M.; Vreugdenhil, A.; Aherne, J. Ambient Atmospheric Deposition of Anthropogenic Microfibers and Microplastics on the Western Periphery of Europe (Ireland). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 11100–11108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trainic, M.; Flores, J.M.; Pinkas, I.; Pedrotti, M.L.; Lombard, F.; Bourdin, G.; Gorsky, G.; Boss, E.; Rudich, Y.; Vardi, A.; et al. Airborne Microplastic Particles Detected in the Remote Marine Atmosphere. Commun. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.L.; Ulke, J.; Font, A.; Chan, K.L.A.; Kelly, F.J. Atmospheric Microplastic Deposition in an Urban Environment and an Evaluation of Transport. Environ. Int. 2020, 136, 105411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yukioka, S.; Tanaka, S.; Nabetani, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Ushijima, T.; Fujii, S.; Takada, H.; Van Tran, Q.; Singh, S. Occurrence and Characteristics of Microplastics in Surface Road Dust in Kusatsu (Japan), Da Nang (Vietnam), and Kathmandu (Nepal). Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Kannan, K. Microplastics in House Dust from 12 Countries and Associated Human Exposure. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Du, F.; Cai, H.; Wang, G.; Shi, H. Microplastic Fallout in Different Indoor Environments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6530–6539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Deng, J.; Gao, Y.; Yu, L.; Zhang, J.; Sun, H. Widespread distribution of PET and PC microplastics in dust in urban China and their estimated hμman exposure. Environ. Int. 2019, 128, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Wang, X.; Fang, T.; Xu, P.; Zhu, L.; Li, D. Source and potential risk assessment of suspended atmospheric microplastics in Shanghai. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 675, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Wang, X.; Wei, N.; Song, Z.; Li, D. Accurate Quantification and Transport Estimation of Suspended Atmospheric Microplastics in Megacities: For Human Health. Environ. Int. 2019, 132, 105127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prata, J.C.; da Costa, J.P.; Girão, A.V.; Lopes, I.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. Identifying a Quick and Efficient Method of Removing Organic Matter without Damaging Microplastic Samples. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurley, R.R.; Lusher, A.L.; Olsen, M.; Nizzetto, L. Validation of a Method for Extracting Microplastics from Complex, Organic-Rich, Environmental Matrices. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 7409–7417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, N.; Uddin, S.; Fowler, S.W.; Behbehani, M. Microplastics in the Atmosphere: A Review. J. Environ. Expo. Assess. 2022, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Li, Y.; Jones, T.; Santosh, M.; Liu, P.; Zhang, M.; Xu, L.; Li, W.; Lu, J.; Yang, C.X.; et al. Airborne Microplastics: A Review of Current Perspectives and Environmental Implications. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 347, 131048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, P.; Ji, B.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, T. How Can We Trace Microplastics in Wastewater Treatment Plants: A Review of the Current Knowledge on Their Analysis Approaches. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 745, 140943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutroneo, L.; Reboa, A.; Geneselli, I.; Capello, M. Considerations on Salts Used for Density Separation in the Extraction of Microplastics from Sediments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 166, 112216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
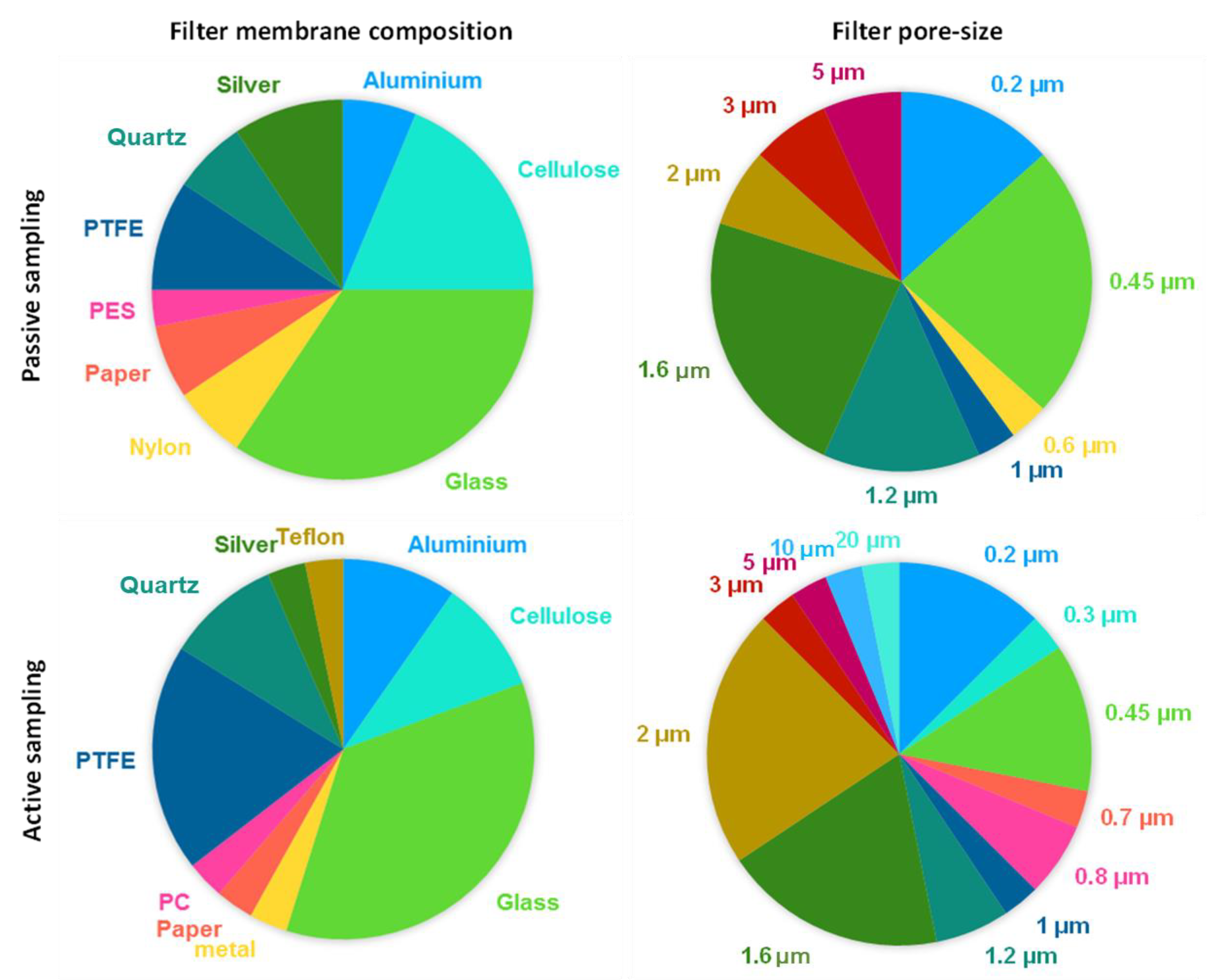

| Ref. | Sampling Method | Filter Type | Filter Pore Size μm | Sampling Collect Time | Digestion | Temperature/Time | Sieving |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [41] | Passive | PTFE | 0.45 | 2018; 1 month | H2O2; 30% | RT/7 days | --- |
| [42] | Active/Passive | --- | --- | 2019; --- | --- | --- | --- |
| [43] | Passive | Glass fiber | 1.6 | 2019–2020; 3–48 days | --- | --- | --- |
| [44] | Passive/Snow | CN; glass fiber | 0.45; 1.2 | 2019; 1 time | Fenton’s reagent | 45 °C/2–3 h | --- |
| [45] | Passive | --- | --- | 2019–2020; 1 month | HF | --- | --- |
| [46] | Active | Glass fiber | 1.60 | 2017; 24 h | --- | --- | --- |
| [47] | Passive | CN; glass fiber | 12; 1.6 | 2018–2019; 24 h | --- | --- | 30 |
| [48] | Passive | Quartz fiber | 1.6 | 2019–2020; --- | --- | --- | --- |
| [49] | Passive | CN | 3 | --- | TWEEN | 20 (0.1%) | --- |
| [50] | Active | CN | 5 | 2020; 48 h | H2O2; 30% | 40 °C/2 h | 20 μm |
| [51] | Passive | Silver fiber | 0.45 | 2021; 24 h | Washing with ethanol | --- | |
| [52] | Passive | PTFE | 0.45 | 2017–2019; 1 week–1 month | --- | --- | |
| [53] | Passive | PTFE | 0.45 | 2019; 30 min | H2O2; 30% | 55 °C/24 h | --- |
| [54] | Passive | Glass fiber | 1 | 2020; --- | Fenton’s reagent (FeSO4 + H2O2) | --- | --- |
| [55] | Passive | Nylon fiber | 0.22 | 2021; 24 h | --- | --- | --- |
| [38] | Active/Passive | Aluminum oxide | 0.2 | 2018; 3 h; 1 month | Fenton’s reagent (FeSO4 + H2O2); +enzymatic digestion | 40 °C/2 h | 500 μm |
| [56] | Active/Passive | Glass fiber | 1.6 | 2020; 12 h | --- | --- | --- |
| [57] | Passive/Dust | Silver fiber | 0.45 | --- | H2O2; 30% | 24 h | --- |
| [58] | Passive/Dust | Paper | 2 | 2019; --- | H2O2; 30% | RT/10 days | 5 mm |
| [59] | Passive | --- | --- | 2020; 1 week | --- | --- | --- |
| [60] | Active/Dust | Paper | --- | 2019; each 7 days | H2O2; 30% | RT/8 days | 5 mm |
| [61] | Passive | CN | 0.45 | 2018–2019; 96 h | H2O2; 30% | 60 °C/48 h | 0.2–5 mm |
| [62] | Active | PTFE | 2 | 2020; 24 h | --- | --- | --- |
| [63] | Active | Glass fiber | 0.3 | 2019; 24 h | --- | --- | --- |
| [39] | Active | --- | 7.0; 4.7; 3.3; 2.1; 0.65 | 2021; 6 h | --- | --- | --- |
| [64] | Active | Aluminum oxide | 0.22 | 2020–2021; 4 h | HCl; pH3 | 24 h | --- |
| [65] | Active/Passive | Quartz fiber | 2.2 | - | H2O2; 30% | RT/24 h | --- |
| [66] | Active | Glass fiber | 1.6 | 2019–2020; 24 h | --- | --- | --- |
| [67] | Active/Passive | Glass fiber | 3 | 2019; 12–24 h | --- | --- | --- |
| [68] | Passive | CN | 0.45 | ---; 22–40 days | H2O2; 30% | RT/24 h | --- |
| [69] | Passive | MCE | 5 | 2019; 7 days | H2O2; 30% | 55 °C/3 days | --- |
| [70] | Passive | Glass fiber | 1.2 | 2020; 6 days | --- | --- | --- |
| [71] | Active | Glass fiber; PTFE | 0.7; 0.45 | 2019; 2–3 days | H2O2; 30% | 70 °C/1 h | --- |
| [72] | Active | PTFE | 2 | ---; 24 h | H2O2; 30% | RT/1 day | --- |
| [73] | Passive/Dust | --- | --- | 2020; --- | --- | --- | 5–1 mm |
| [74] | Active | Glass fiber | 1.6 | 2017; 24 h | --- | --- | --- |
| [40] | Active | Teflon; silver fiber | 0.2; 1.2 | ---; 24 h | --- | --- | --- |
| [75] | Passive/Dust | Glass fiber | 0.6 | 30 days | --- | --- | --- |
| [76] | Passive | Glass fiber | 1.6 | 2017–2018; 1–8 days | --- | --- | --- |
| [77] | Passive | Glass fiber | 1.6 | 2018–2019; 1 year; 3–4 days | Bioenzym SE/F + H2O2 | 40 °C/48 h | 1 mm |
| [36] | Passive/Dust | CN | 1.2 | ---; 1 day | H2O2; 30% | --- | --- |
| [78] | Active | Quartz fiber; glass fiber | 2.2; 1.2 | 2020; 24 h | H2O2; 15% | RT/8 days | --- |
| [79] | Active | PTFE | --- | 2019; --- | H2O2; 30% | --- | --- |
| [80] | Active | Quartz fiber; PTFE; aluminum oxide | 10; 0.45; 0.2 | 2018; 8 days | H2O2; 30% | 55 °C/7 days | --- |
| [81] | Active | Glass fiber | 1 | 2020; 24 h | --- | --- | --- |
| [82] | Passive | PES | 0.45 | 2017–2019; 1–2 month | --- | --- | --- |
| [83] | Active | Glass fiber | 1.6 | 2019; 8 h | --- | --- | --- |
| [84] | Active | --- | --- | ---; 4 h | --- | --- | 25 μm |
| [85] | Active | PTFE | 2.0 | 2017; 24 h | --- | --- | --- |
| [86] | Active/Dust | MCE | 0.8 | 2018; 6–8 h | --- | --- | --- |
| [87] | Passive | Glass fiber | --- | 2018; --- | --- | --- | --- |
| [88] | Active/Passive | Glass fiber | 1.6 | 2018–2019; --- | H2O2; 30% + FeSO4 (0.05 M) | --- | --- |
| [89] | Passive/Snow | PTFE | 0.2 | 2017; --- | --- | --- | --- |
| [90] | Passive | Glass fiber | 1.6 | 2017–2018; 1 month | --- | --- | --- |
| [91] | Active | PC | 0.8 | 2016; 12–24 h | --- | --- | --- |
| [36] | Active | Glass fiber | 1.6 | 20219; 10–48 h | --- | --- | --- |
| [92] | Passive | Aluminum oxide; silver fiber | 0.2; 1.2 | 2018; 3–4 days | --- | --- | --- |
| [93] | Passive | Nylon fiber | 100 | 2017; 1 min | H2O2; 30% | RT/1 week | 75 μm |
| [94] | Passive | --- | --- | 2010–2014; --- | --- | --- | 150 μm |
| [95] | Passive | Cellulose | 5 | 2019; 24 h | --- | --- | --- |
| [96] | Passive | Glass fiber | 1.2 | 2017–2018; --- | --- | --- | 2 mm |
| [97] | Active | Glass fiber | 1.6 | 2018; 1 h | --- | --- | --- |
| [98] | Active | Glass fiber | 1.6 | 2019; 1 h | --- | --- | --- |
| [37] | Active | Glass fiber | 1.6 | 2018–2019; 4–24 h | --- | --- | --- |
| [99] | Active | Glass fiber | 1.2 | 2019; 48 h | H2O2; 15% | RT/8 days | --- |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Logvina, Y.; Matas, I.M.; Ribeiro, H.; Pinto da Silva, L.; Rodrigues, P.; Leitão, J.; da Silva, J.E. Micro- and Nanoplastics in the Atmosphere: Methodology for Microplastics Size-Fractionation Sampling. Microplastics 2024, 3, 82-97. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics3010006
Logvina Y, Matas IM, Ribeiro H, Pinto da Silva L, Rodrigues P, Leitão J, da Silva JE. Micro- and Nanoplastics in the Atmosphere: Methodology for Microplastics Size-Fractionation Sampling. Microplastics. 2024; 3(1):82-97. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics3010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleLogvina, Yuliya, Isabel M. Matas, Helena Ribeiro, Luís Pinto da Silva, Pedro Rodrigues, João Leitão, and Joaquim Esteves da Silva. 2024. "Micro- and Nanoplastics in the Atmosphere: Methodology for Microplastics Size-Fractionation Sampling" Microplastics 3, no. 1: 82-97. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics3010006
APA StyleLogvina, Y., Matas, I. M., Ribeiro, H., Pinto da Silva, L., Rodrigues, P., Leitão, J., & da Silva, J. E. (2024). Micro- and Nanoplastics in the Atmosphere: Methodology for Microplastics Size-Fractionation Sampling. Microplastics, 3(1), 82-97. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics3010006









