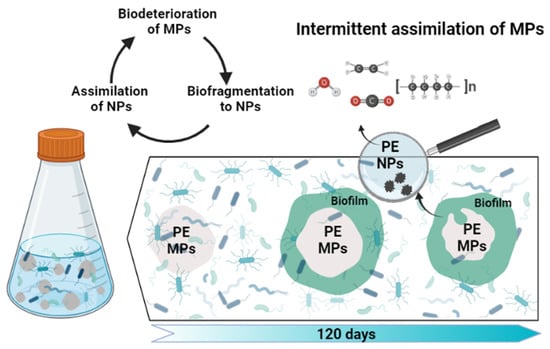
Nanoplastic Generation from Secondary PE Microplastics: Microorganism-Induced Fragmentation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials/ Generation of Secondary MPs
2.2. Biodegradation Assays
2.2.1. Marine Communities
2.2.2. Experimental Design
2.2.3. Viable Cell Concentration and Extracellular Polymeric Substances
2.3. FTIR
2.4. Nanoparticle Detection–Light Scattering
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
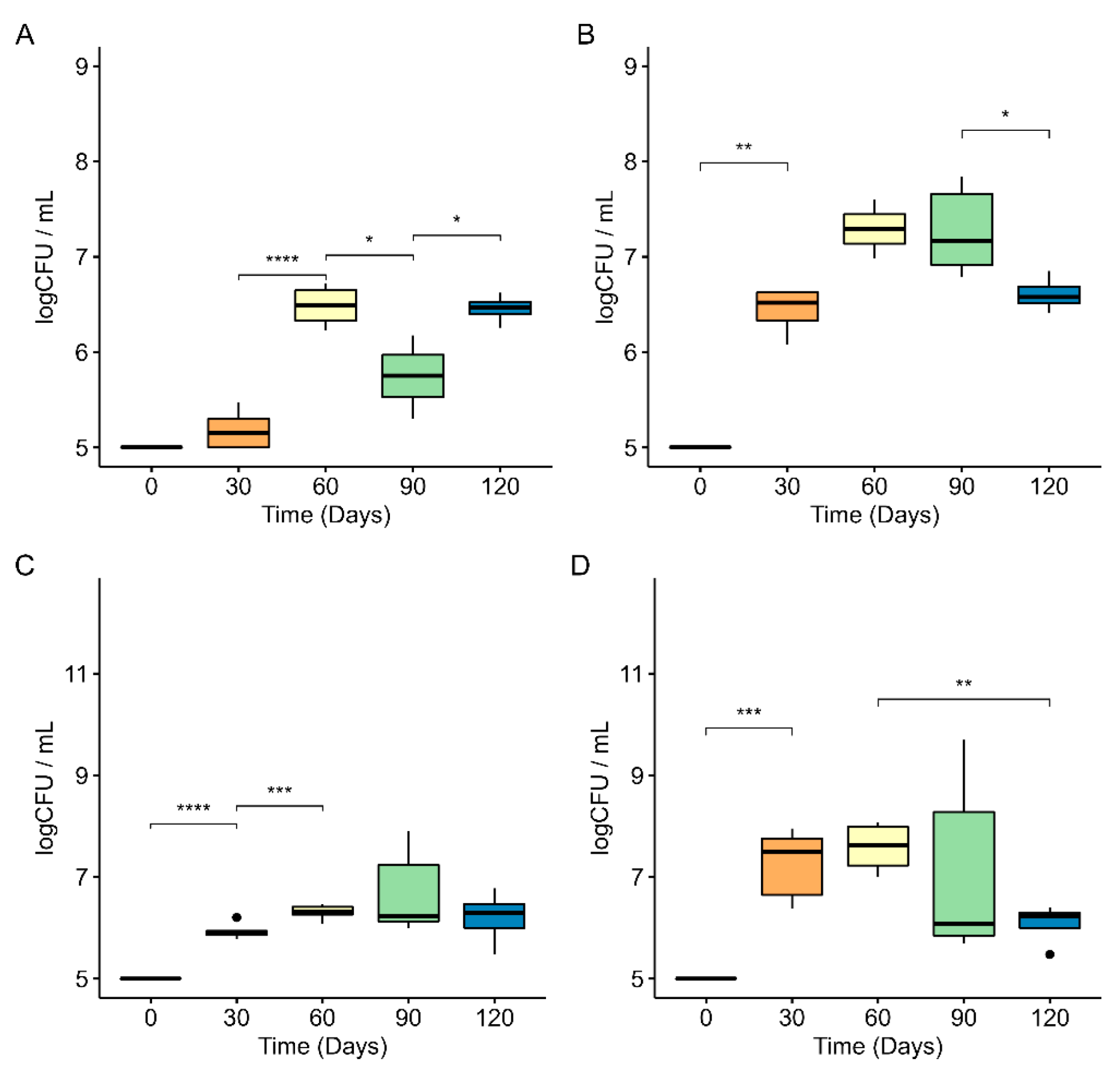
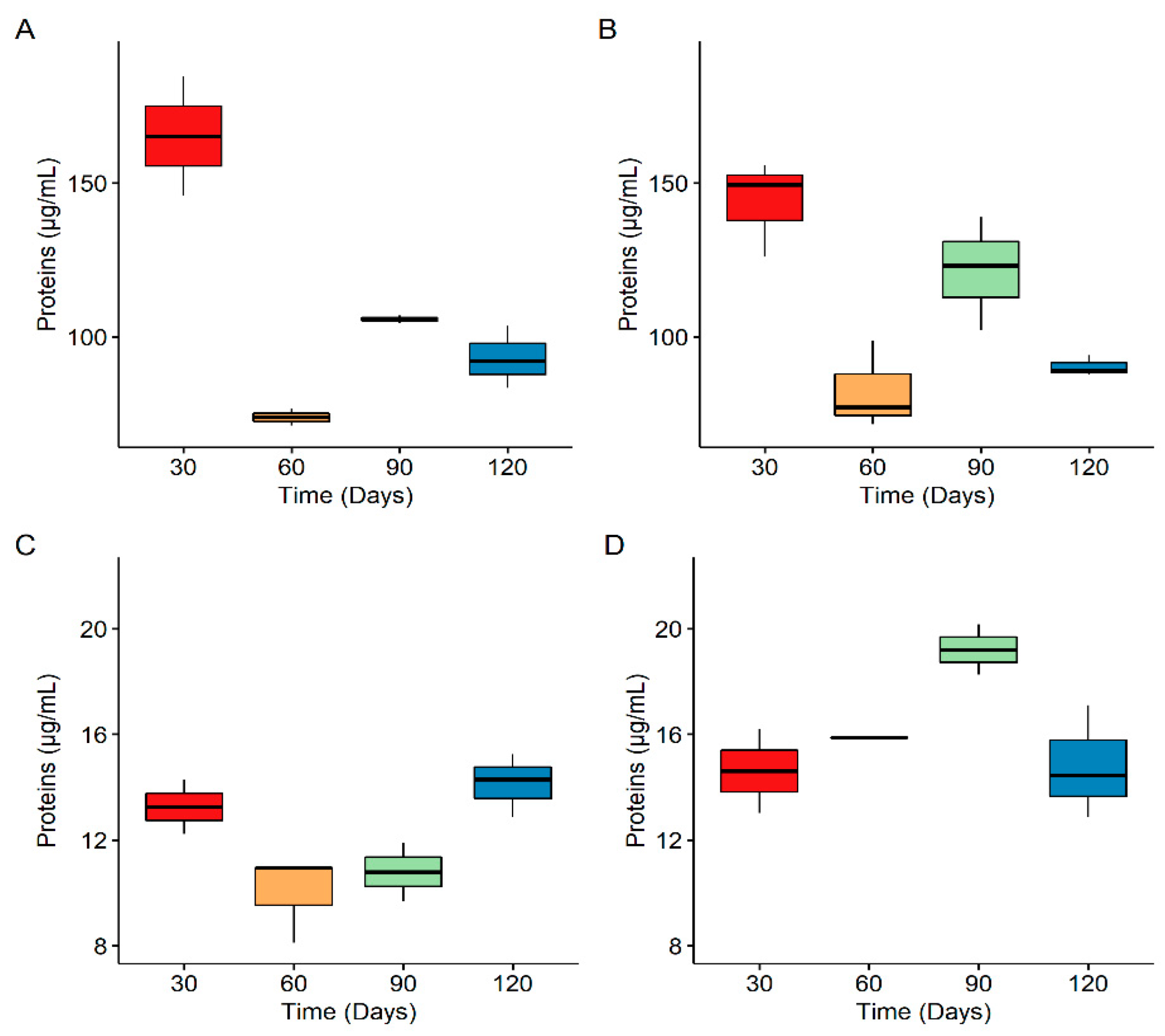
3.1. Biofilm Populations on PE Secondary Microplastics
3.2. FTIR
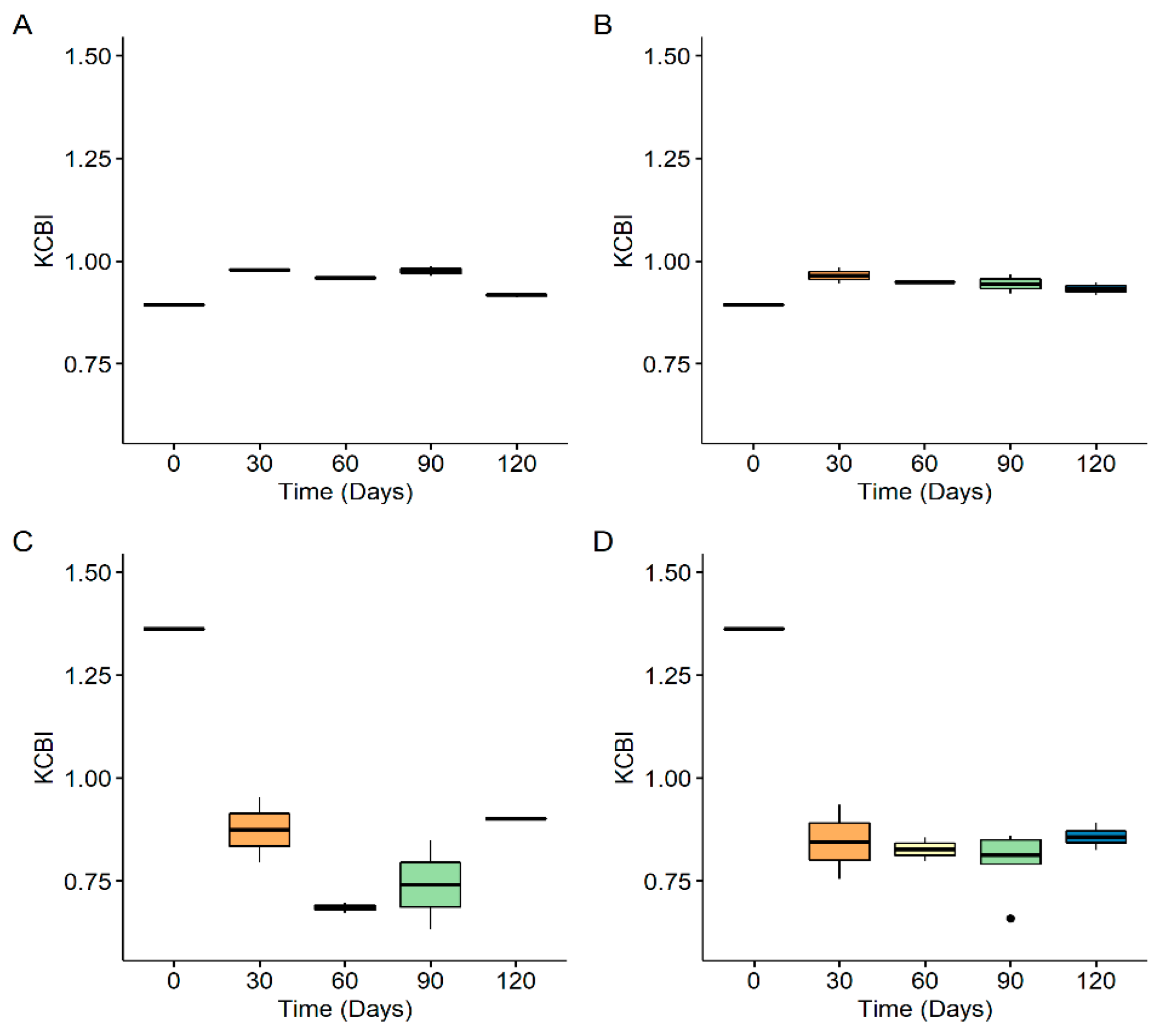
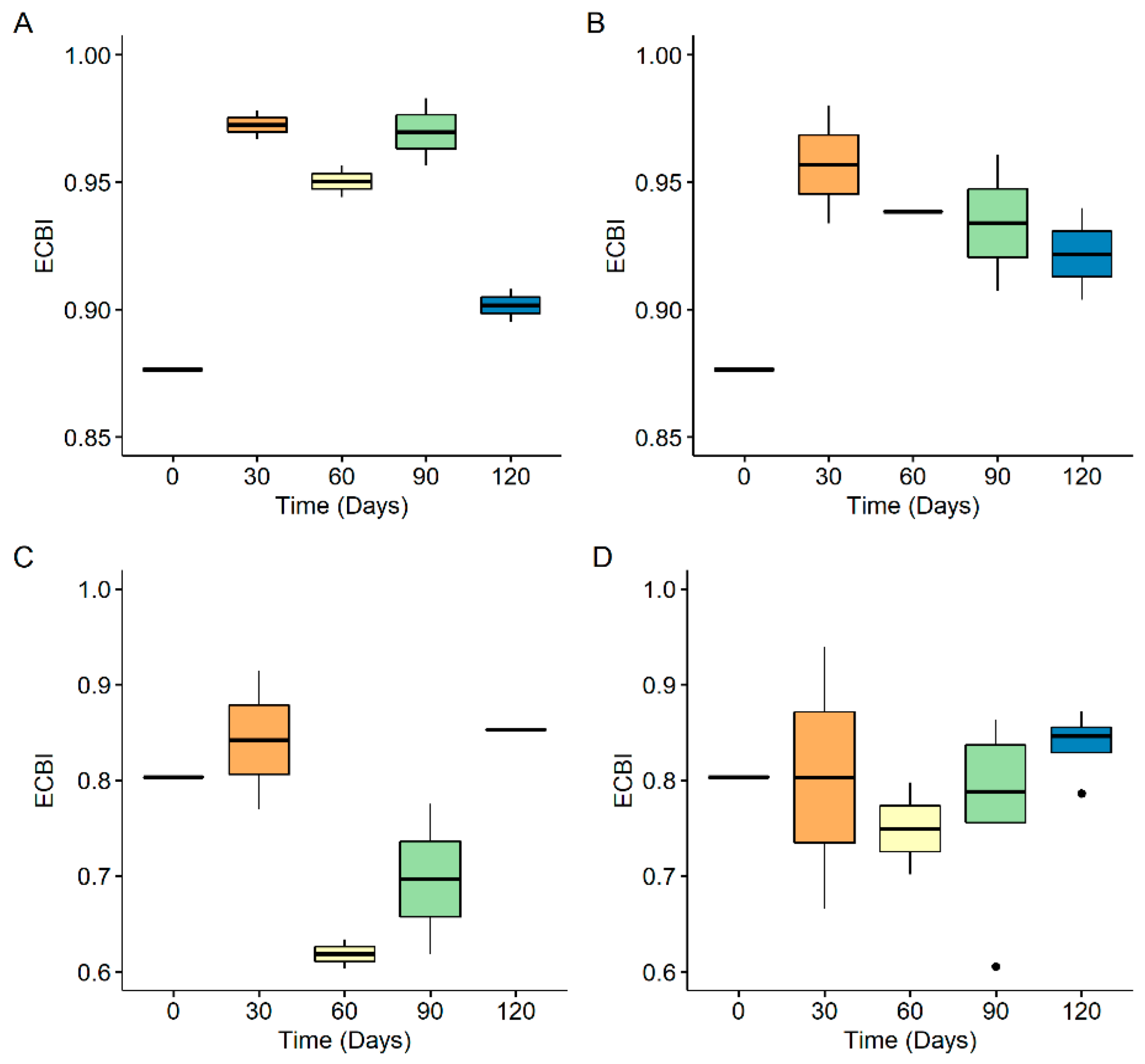
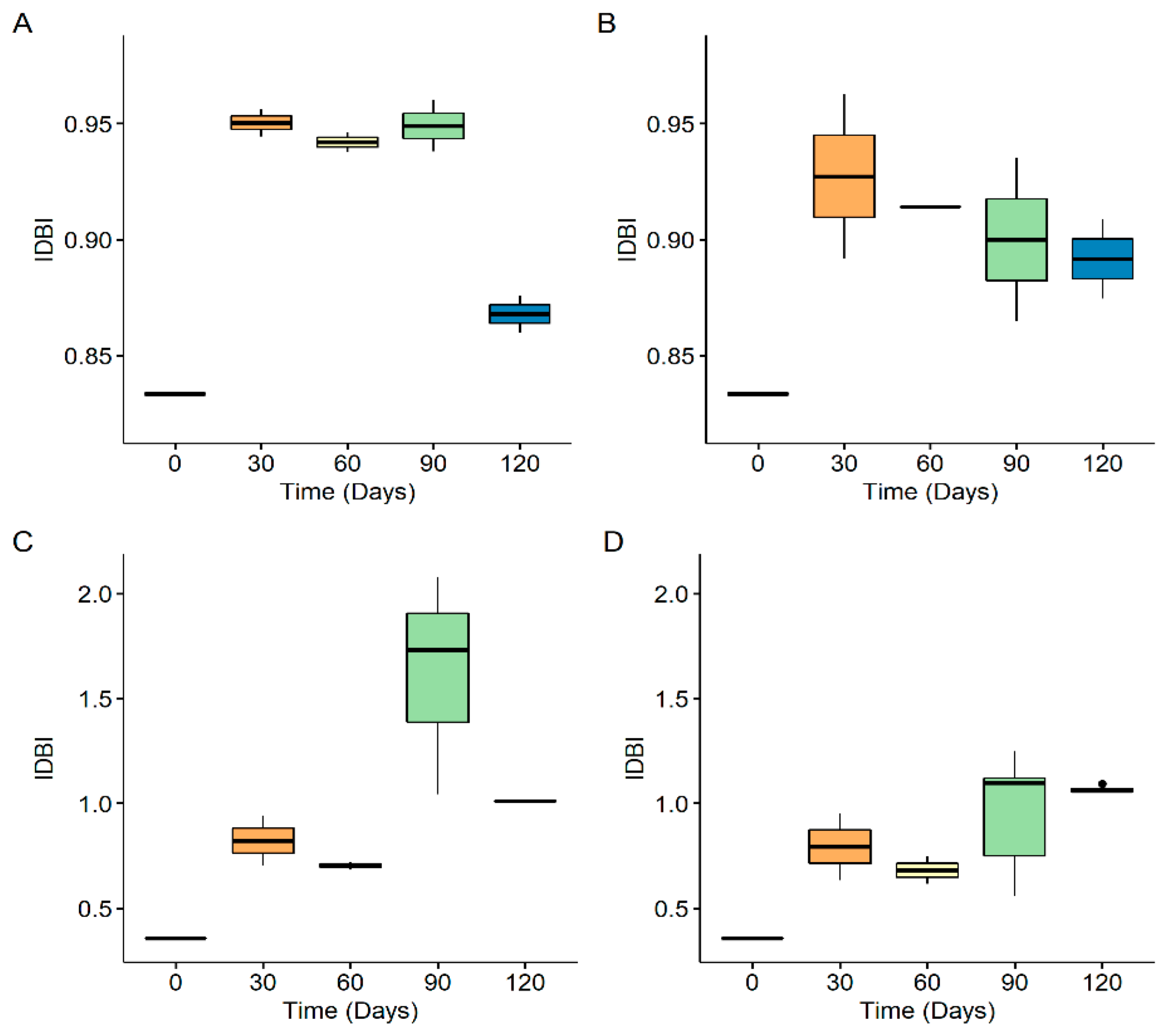
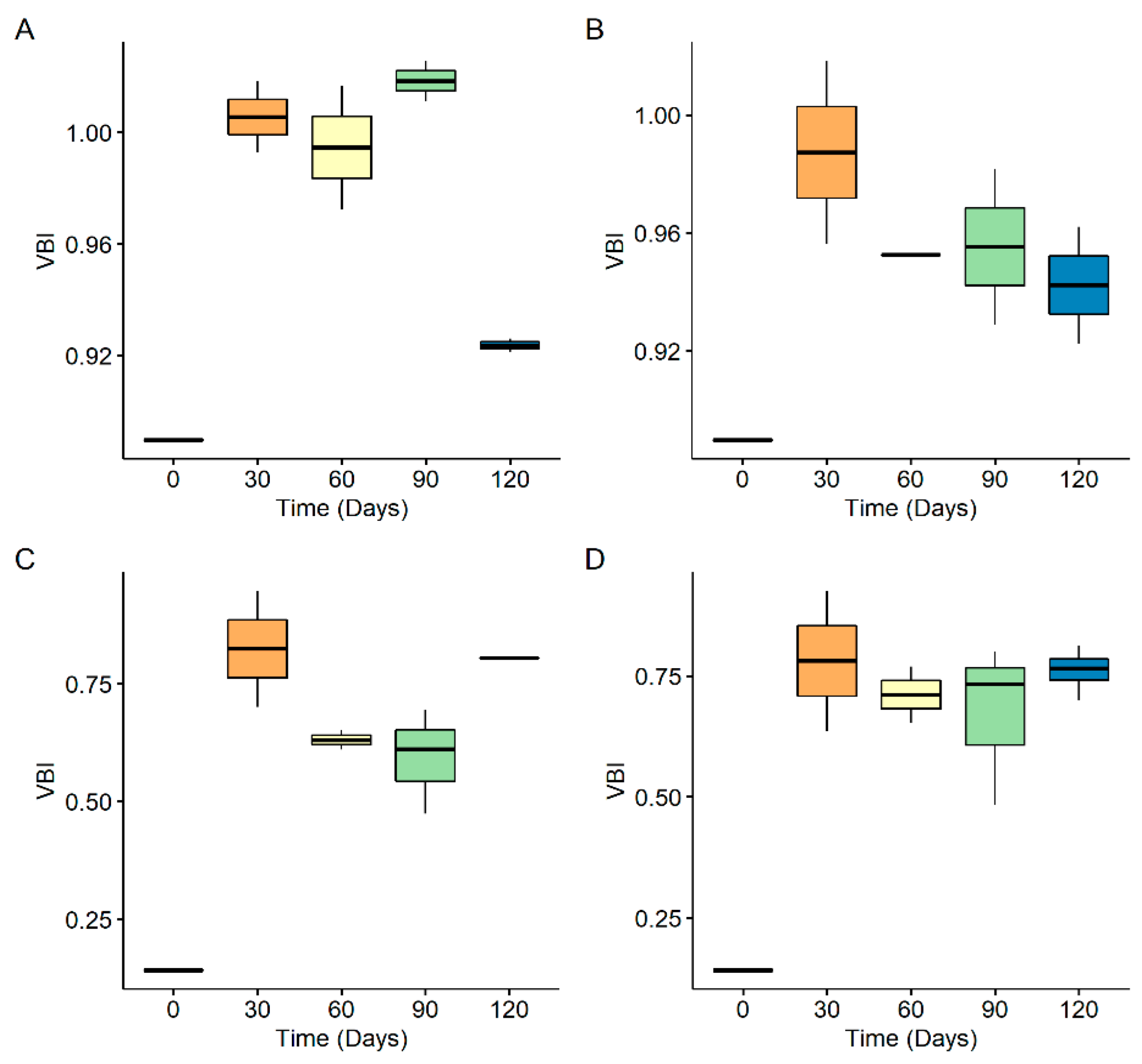
3.3. Size Distribution of Generated Nanoplastics
4. Discussion
4.1. Changes of Incubated Secondary Microplastics
4.2. Nanoplastics Generation and Fate
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gong, J.; Xie, P. Research progress in sources, analytical methods, eco-environmental effects, and control measures of microplastics. Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Costa, J.P.; Santos, P.S.M.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. (Nano)plastics in the environment—Sources, fates and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566–567, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksen, M.; Lebreton, L.C.M.; Carson, H.S.; Thiel, M.; Moore, C.J.; Borerro, J.C.; Galgani, F.; Ryan, P.G.; Reisser, J. Plastic Pollution in the World’s Oceans: More than 5 Trillion Plastic Pieces Weighing over 250,000 Tons Afloat at Sea. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Auta, H.S.; Emenike, C.U.; Fauziah, S.H. Distribution and importance of microplastics in the marine environmentA review of the sources, fate, effects, and potential solutions. Environ. Int. 2017, 102, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cózar, A.; Echevarría, F.; González-gordillo, J.I.; Irigoien, X.; Úbeda, B. Plastic debris in the open ocean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 10239–10244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaandorp, M.L.A.; Dijkstra, H.A.; van Sebille, E. Modelling size distributions of marine plastics under the influence of continuous cascading fragmentation. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 054075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malankowska, M.; Echaide-Gorriz, C.; Coronas, J. Microplastics in marine environment: A review on sources, classification, and potential remediation by membrane technology. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2021, 7, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.K.; Hong, S.H.; Jang, M.; Han, G.M.; Jung, S.W.; Shim, W.J. Combined Effects of UV Exposure Duration and Mechanical Abrasion on Microplastic Fragmentation by Polymer Type. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4368–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rummel, C.D.; Jahnke, A.; Gorokhova, E.; Kühnel, D.; Schmitt-Jansen, M. The Impacts of Biofilm Formation on the Fate and Potential Effects of Microplastic in the Aquatic Environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, B.; Sharma, N. Mechanistic implications of plastic degradation. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2008, 93, 561–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.G.; Anjana, K.; Hinduja, M.; Sujitha, K.; Dharani, G. Review on plastic wastes in marine environment—Biodegradation and biotechnological solutions. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 150, 110733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Cheng, Q.; Ding, T.; Yiguang, Q.; Yuechao, Z.; Sun, H.; Peng, C.; Naz, I.; Li, J.; Liu, J. Micro- and nanoplastics in the environment: Occurrence, detection, characterization and toxicity—A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 313, 127863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigault, J.; Pedrono, B.; Maxit, B.; Ter Halle, A. Marine plastic litter: The unanalyzed nano-fraction. Environ. Sci. Nano 2016, 3, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorasan, C.; Edo, C.; González-Pleiter, M.; Fernández-Piñas, F.; Leganés, F.; Rodríguez, A.; Rosal, R. Generation of nanoplastics during the photoageing of low-density polyethylene. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 289, 117919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Xu, M.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, B. On the degradation of (micro)plastics: Degradation methods, influencing factors, environmental impacts. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 806, 151312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raddadi, N.; Fava, F. Biodegradation of oil-based plastics in the environment: Existing knowledge and needs of research and innovation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 679, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auta, H.S.; Emenike, C.U.; Jayanthi, B.; Fauziah, S.H. Growth kinetics and biodeterioration of polypropylene microplastics by Bacillus sp. and Rhodococcus sp. isolated from mangrove sediment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 127, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syranidou, E.; Karkanorachaki, K.; Amorotti, F.; Avgeropoulos, A.; Kolvenbach, B.; Zhou, N.Y.; Fava, F.; Corvini, P.F.X.; Kalogerakis, N. Biodegradation of mixture of plastic films by tailored marine consortia. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 375, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalogerakis, N.; Karkanorachaki, K.; Kalogerakis, G.C.; Triantafyllidi, E.I.; Gotsis, A.D.; Partsinevelos, P.; Fava, F. Microplastics Generation: Onset of Fragmentation of Polyethylene Films in Marine Environment Mesocosms. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syranidou, E.; Karkanorachaki, K.; Amorotti, F.; Repouskou, E.; Kroll, K.; Kolvenbach, B.; Corvini, P.F.X.; Fava, F.; Kalogerakis, N. Development of tailored indigenous marine consortia for the degradation of naturally weathered polyethylene films. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e183984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrady, A.L. The plastic in microplastics: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 119, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, N.; Pradhan, N.; Singh, S.; Barla, A.; Shrivastava, A.; Khatua, P.; Rai, V.; Bose, S. Evaluation of HDPE and LDPE degradation by fungus, implemented by statistical optimization. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 39515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerritse, J.; Leslie, H.A.; de Tender, C.A.; Devriese, L.I.; Vethaak, A.D. Fragmentation of plastic objects in a laboratory seawater microcosm. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre, D.Y.Z.D.; Santos, L.A.D.; Reyes, M.L.C.; Baculi, R.Q. Biodegradation of low-density polyethylene by bacteria isolated from serpentinization-driven alkaline spring. Philipp. Sci. Lett. 2018, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Balasubramanian, V.; Natarajan, K.; Hemambika, B.; Ramesh, N.; Sumathi, C.S.; Kottaimuthu, R.; Rajesh Kannan, V. High-density polyethylene (HDPE)-degrading potential bacteria from marine ecosystem of Gulf of Mannar, India. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 51, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilan (Orr), I.; Hadar, Y.; Sivan, A. Colonization, biofilm formation and biodegradation of polyethylene by a strain of Rhodococcus ruber. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 65, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Depraect, O.; Lebrero, R.; Rodriguez-Vega, S.; Bordel, S.; Santos-Beneit, F.; Martínez-Mendoza, L.J.; Aragão Börner, R.; Börner, T.; Muñoz, R. Biodegradation of bioplastics under aerobic and anaerobic aqueous conditions: Kinetics, carbon fate and particle size effect. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 344, 126265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangeetha Devi, R.; Rajesh Kannan, V.; Nivas, D.; Kannan, K.; Chandru, S.; Robert Antony, A. Biodegradation of HDPE by Aspergillus spp. from marine ecosystem of Gulf of Mannar, India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 96, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudhakar, M.; Doble, M.; Murthy, P.S.; Venkatesan, R. Marine microbe-mediated biodegradation of low- and high-density polyethylenes. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2008, 61, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzur, A.; Limón-González, M.; Favela-Torres, E. Biodegradation of Physicochemically Treated LDPE by a Consortium of Filamentous Fungi. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 92, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamas, A.; Moon, H.; Zheng, J.; Qiu, Y.; Tabassum, T.; Jang, J.H.; Abu-Omar, M.M.; Scott, S.L.; Suh, S. Degradation Rates of Plastics in the Environment. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 3494–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez-Romo, A.; González-Mota, R.; Soto-Bernal, J.J.; Rosales-Candelas, I. Investigating the Degradability of HDPE, LDPE, PE-BIO, and PE-OXO Films under UV-B Radiation. J. Spectrosc. 2015, 2015, 586514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eyheraguibel, B.; Traikia, M.; Fontanella, S.; Sancelme, M.; Bonhomme, S.; Fromageot, D.; Lemaire, J.; Lauranson, G.; Lacoste, J.; Delort, A.M. Characterization of oxidized oligomers from polyethylene films by mass spectrometry and NMR spectroscopy before and after biodegradation by a Rhodococcus rhodochrous strain. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harshvardhan, K.; Jha, B. Biodegradation of low-density polyethylene by marine bacteria from pelagic waters, Arabian Sea, India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 77, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syranidou, E.; Karkanorachaki, K.; Amorotti, F.; Franchini, M.; Repouskou, E.; Kaliva, M.; Vamvakaki, M.; Kolvenbach, B.; Fava, F.; Corvini, P.F.-X.; et al. Biodegradation of weathered polystyrene films in seawater microcosms. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delacuvellerie, A.; Cyriaque, V.; Gobert, S.; Benali, S.; Wattiez, R. The plastisphere in marine ecosystem hosts potential specific microbial degraders including Alcanivorax borkumensis as a key player for the low-density polyethylene degradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 380, 120899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amobonye, A.; Bhagwat, P.; Singh, S.; Pillai, S. Plastic biodegradation: Frontline microbes and their enzymes. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montazer, Z.; Habibi-Najafi, M.B.; Mohebbi, M.; Oromiehei, A. Microbial Degradation of UV-Pretreated Low-Density Polyethylene Films by Novel Polyethylene-Degrading Bacteria Isolated from Plastic-Dump Soil. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 3613–3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gewert, B.; Plassmann, M.M.; MacLeod, M. Pathways for degradation of plastic polymers floating in the marine environment. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2015, 17, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bardají, D.K.R.; Moretto, J.A.S.; Furlan, J.P.R.; Stehling, E.G. A mini-review: Current advances in polyethylene biodegradation. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 36, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeenat; Elahi, A.; Bukhari, D.A.; Shamim, S.; Rehman, A. Plastics degradation by microbes: A sustainable approach. J. King Saud Univ.—Sci. 2021, 33, 101538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, S.; Kim, Y.; Won, Y.; Myung, J. Bridging Three Gaps in Biodegradable Plastics: Misconceptions and Truths about Biodegradation. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 671750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M.; Galloway, T.S. Ingestion of Nanoplastics and Microplastics by Pacific Oyster Larvae. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 14625–14632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alimi, O.S.; Farner Budarz, J.; Hernandez, L.M.; Tufenkji, N. Microplastics and Nanoplastics in Aquatic Environments: Aggregation, Deposition, and Enhanced Contaminant Transport. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1704–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, Y.; An, Y.J. Effects of micro- and nanoplastics on aquatic ecosystems: Current research trends and perspectives. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 124, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattsson, K.; Jocic, S.; Doverbratt, I.; Hansson, L.A. Nanoplastics in the Aquatic Environment. Microplastic Contamination in Aquatic Environments: An Emerging Matter of Environmental Urgency; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Chapter 13; pp. 379–399. ISBN 9780128137475. [Google Scholar]
- Alprol, A.E.; Gaballah, M.S.; Hassaan, M.A. Micro and Nanoplastics analysis: Focus on their classification, sources, and impacts in marine environment. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 42, 101625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karkanorachaki, K.; Tsiota, P.; Dasenakis, G.; Syranidou, E.; Kalogerakis, N. Nanoplastic Generation from Secondary PE Microplastics: Microorganism-Induced Fragmentation. Microplastics 2022, 1, 85-101. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics1010006
Karkanorachaki K, Tsiota P, Dasenakis G, Syranidou E, Kalogerakis N. Nanoplastic Generation from Secondary PE Microplastics: Microorganism-Induced Fragmentation. Microplastics. 2022; 1(1):85-101. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics1010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarkanorachaki, Katerina, Panagiota Tsiota, Giorgos Dasenakis, Evdokia Syranidou, and Nicolas Kalogerakis. 2022. "Nanoplastic Generation from Secondary PE Microplastics: Microorganism-Induced Fragmentation" Microplastics 1, no. 1: 85-101. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics1010006
APA StyleKarkanorachaki, K., Tsiota, P., Dasenakis, G., Syranidou, E., & Kalogerakis, N. (2022). Nanoplastic Generation from Secondary PE Microplastics: Microorganism-Induced Fragmentation. Microplastics, 1(1), 85-101. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics1010006